Improvement of the Fluidity of Heavy Oil Using a Composite Viscosity Reducer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Properties of the Heavy Oil Sample
2.3. Reduction of the Heavy Oil Viscosity Using Oil-Soluble Viscosity Reducers
2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Analysis (DSC)
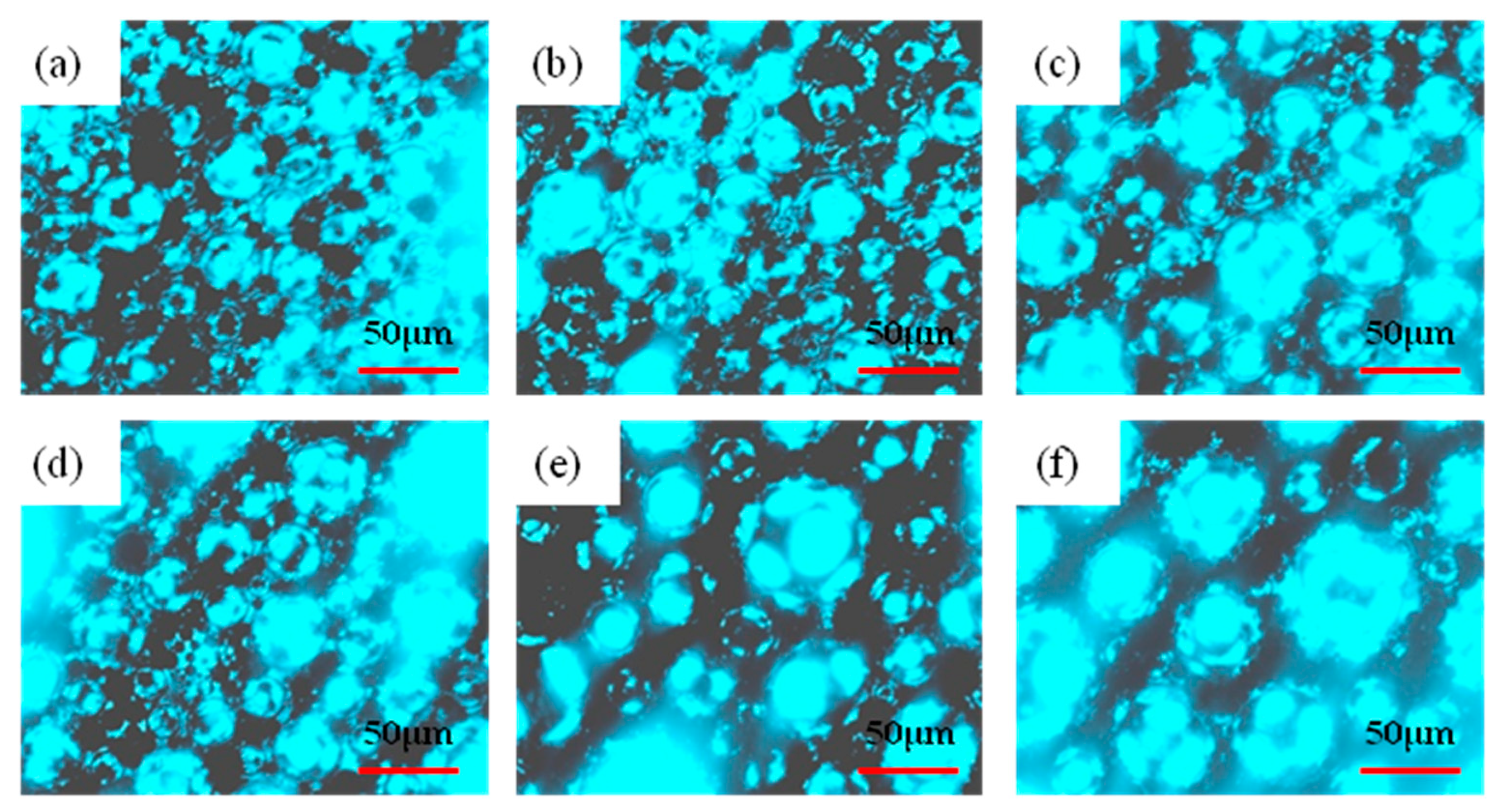
2.5. Wax Crystal Morphology Analysis
2.6. Heavy Oil Emulsion Preparation Using a Water-Soluble Emulsifier
2.7. Emulsifier Performance Evaluation
2.8. Analysis of the Combined Effect of the Oil-Soluble Viscosity Reducer and Water-Soluble Emulsifier
2.9. Analysis of the Microstructure of O/W Emulsions
3. Results and Discussion
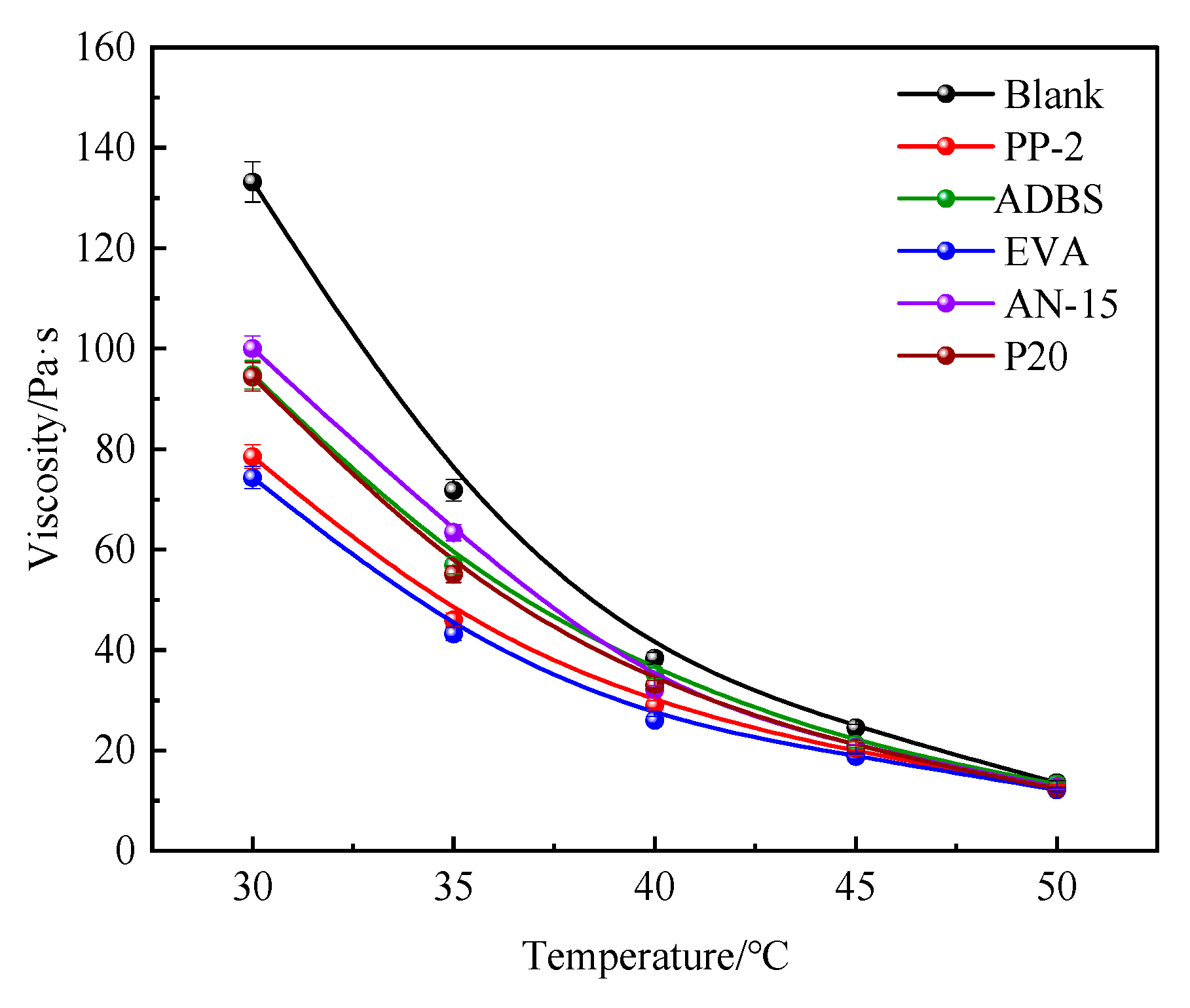
3.1. Effect of the Oil-Soluble Viscosity Reducers on the Heavy Oil Viscosity
3.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.3. Morphological Analysis of Wax Crystals
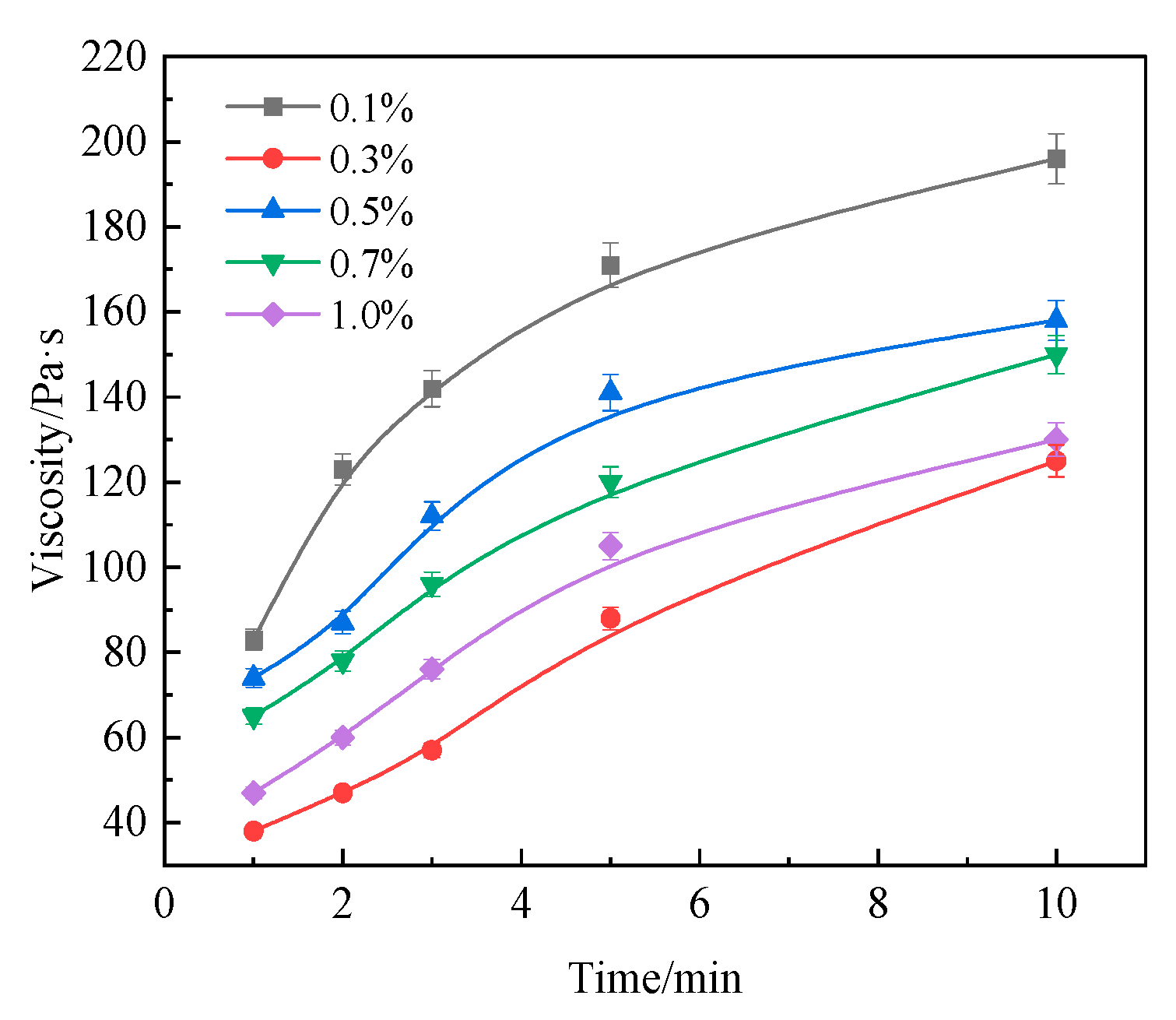
3.4. Effect of a Water-Soluble Emulsifier Addition on the Viscosity of Heavy Oil
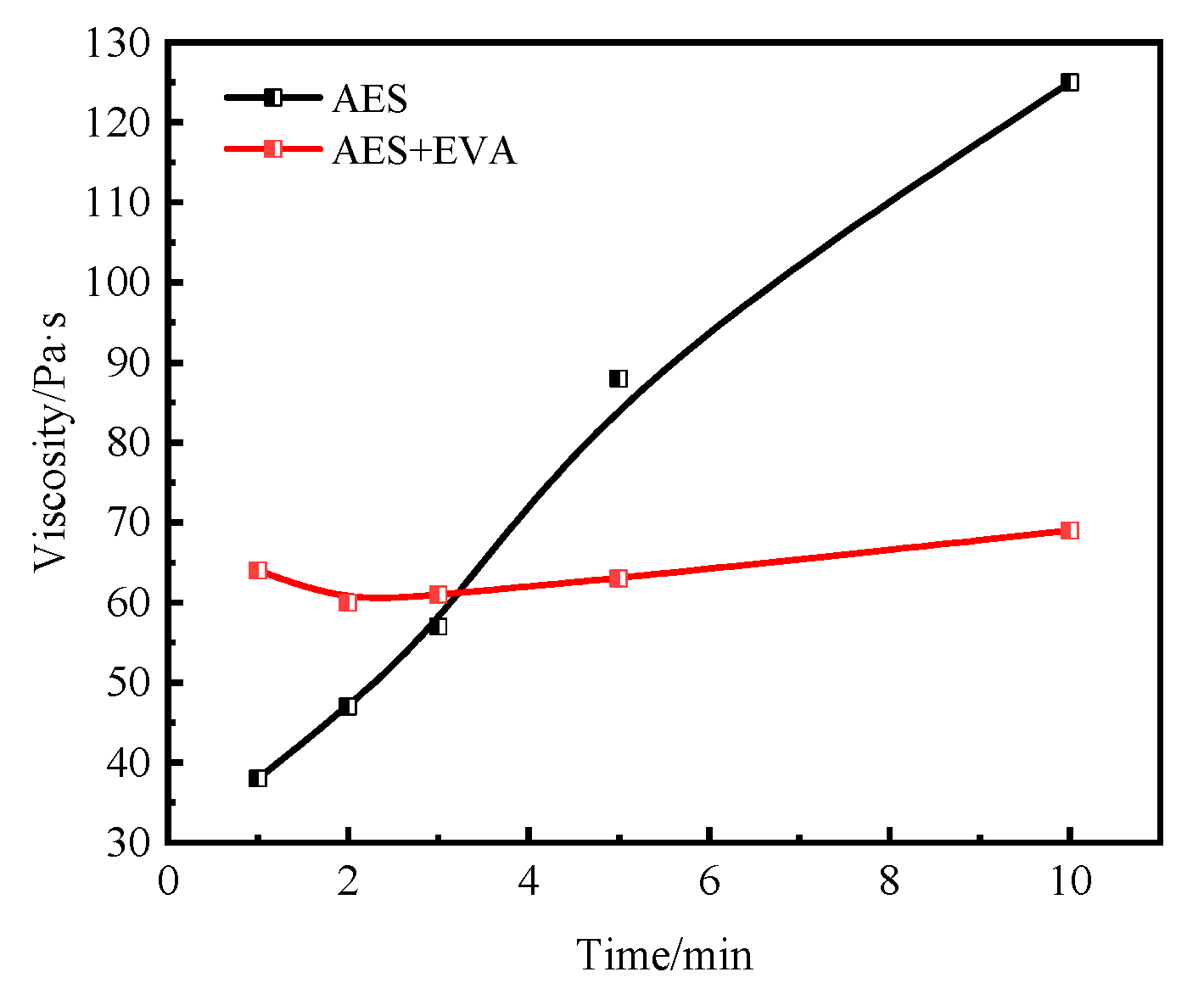
3.5. Combined Effect of the Oil-Soluble Viscosity Reducer and Water-Soluble Emulsifier
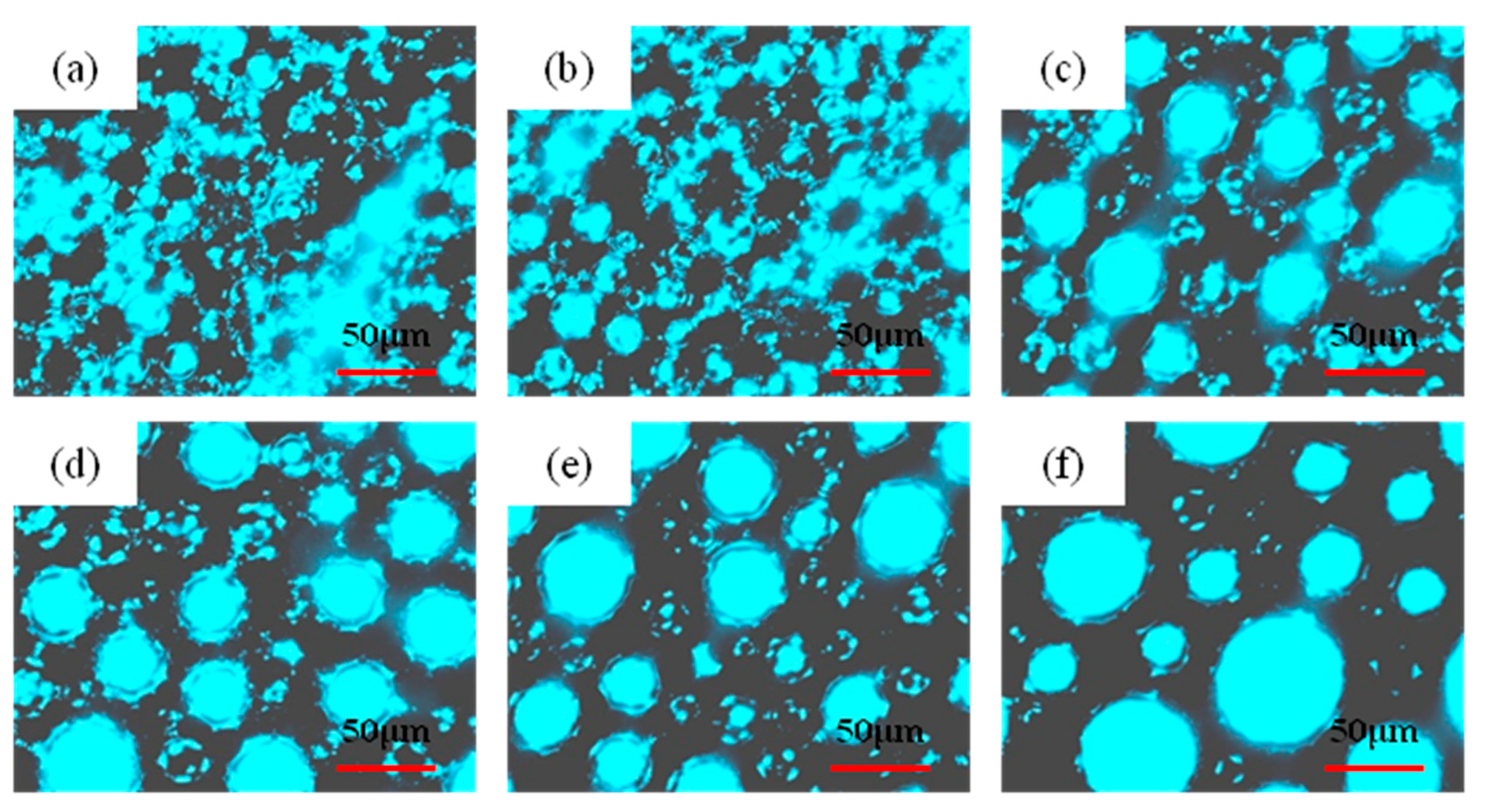
3.6. Microstructure of O/W Emulsions
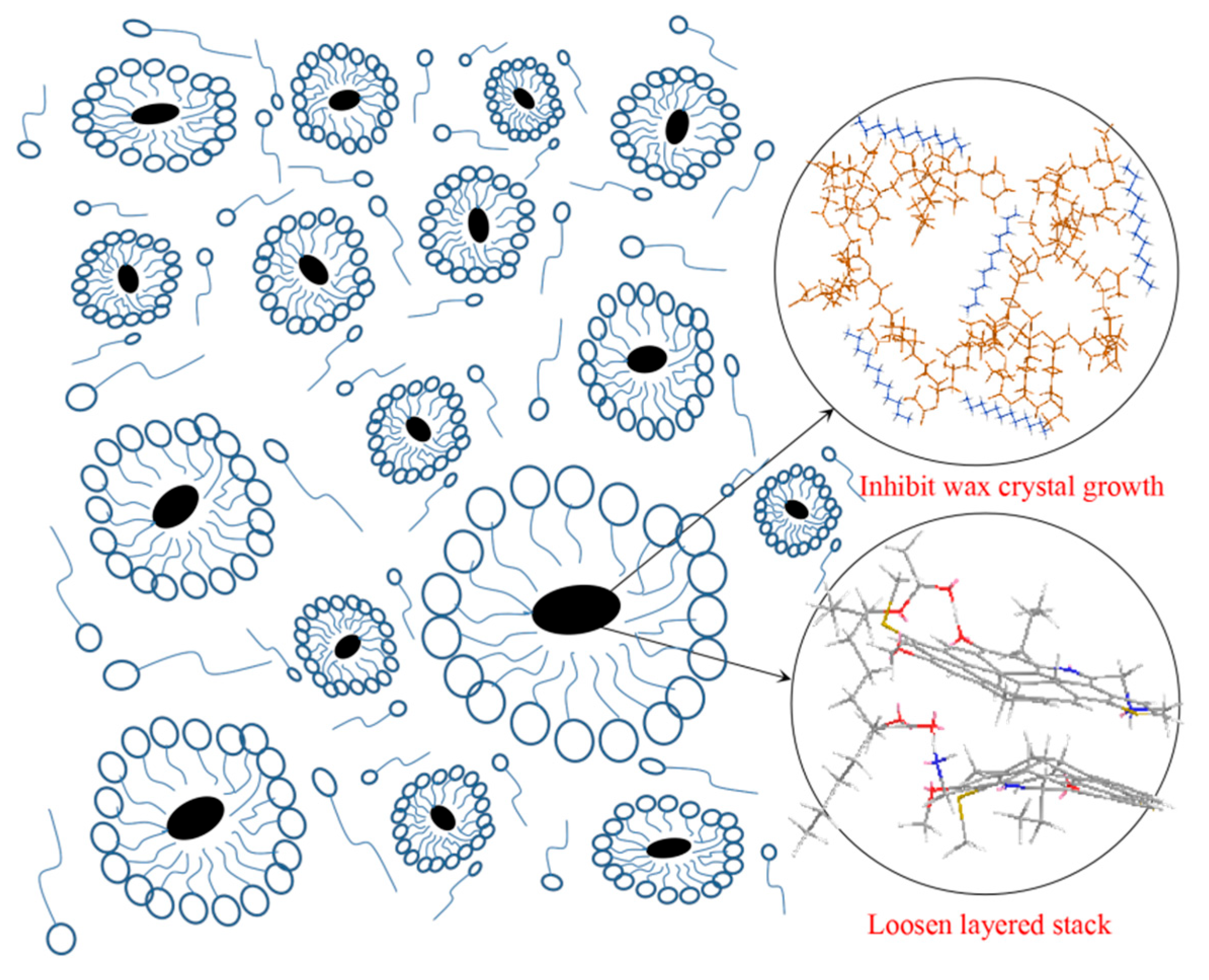
3.7. Proposed Mechanism of the Observed Phenomenon
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Okolie, J.A.; Patra, B.R.; Mukherjee, A.; Nanda, S.; Dalai, A.K.; Kozinski, J.A. Futuristic applications of hydrogen in energy, biorefining, aerospace, pharmaceuticals and metallurgy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 8885–8905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, H. Experimental Studies on Viscosity Reduction of Heavy Crude Oil by Ultrasonic Irradiation. Acoust. Phys. 2020, 66, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.C.; Kang, Z.; Yang, X.J.; Lin, C.; Zheng, L.; Zuo, M.; Mao, J.H.; Dai, S.K.; Xue, J.X.; Ouyang, D. Synthesis and Performance Evaluation of a Nanocomposite Pour-Point Depressant and Viscosity Reducer for High-Pour-Point Heavy Oil. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 7965–7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.F.; Gao, L.; Li, Y.F.; Dong, K.; Zhang, J.; Du, W.C.; Qu, C.T.; Chen, G. Performance and mechanism of span surfactants as clean flow improvers for crude oil. Pet. Chem. 2020, 60, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souas, F.; Safri, A.; Benmounah, A. A review on the rheology of heavy crude oil for pipeline transportation. Pet. Res. 2021, 6, 116–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afra, S.; Nasr-El-Din, H.A.; Socci, D.; Cui, Z. Green phenolic amphiphile as a viscosity modifier and asphaltenes dispersant for heavy and extra-heavy oil. Fuel 2018, 220, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherratt, J.; Sharifi Haddad, A.; Rafati, R. Hot Solvent-Assisted Gravity Drainage in Naturally Fractured Heavy Oil Reservoirs: A New Model and Approach to Determine Optimal Solvent Injection Temperature. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 3043–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, W.H.; Song, H.; Jeje, A. Synthesis of new flow improvers from canola oil and application to waxy crude oil. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, M.; Ren, G.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Sun, D. Viscosity reduction of extra-heavy oil using toluene in water emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 560, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, D.; Poteau, S.; Hénaut, I.; Argillier, J.F. Crude Oil Emulsion Properties and Their Application to Heavy Oil Transportation. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 2004, 59, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Babadagli, T. Comprehensive review on heavy-oil emulsions: Colloid science and practical applications. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 228, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, N.; Xia, S. Research progress and development trend of heavy oil emulsifying viscosity reducer: A review. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2021, 39, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, J.X.; Cheng, Z.F.; Wu, W.M.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, J.W.; Yang, Z.G.; Zhang, D.S. New Composite Viscosity Reducer with Both Asphaltene Dispersion and Emulsifying Capability for Heavy and Ultraheavy Crude Oils. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shen, X.; Yu, J.; Yang, S. A New Composite Viscosity Reducer for Abnormal Low Temperature Extra-Heavy Oil Reservoir with High Acid Value. Pet. Chem. 2020, 60, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gu, X.; Xue, M.; Li, Y.; Dong, S.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J. Resource utilization of medical waste under COVID-19: Waste mask used as crude oil fluidity improver. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 358, 131903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SY/T 0541-2009; Test Method for Gel Point of Crude Oils. National Petroleum Corporation: Beijing, China, 2009.
- SY/T 0520-2008; Viscosity Determination of Crude Petroleum-Equilibrium Method by a Rotational Viscometer. National Petroleum Corporation: Beijing, China, 2008.
- SY/T 5119-2008; Analysis Method for Fractions of Rock Extract and Crude Oil. National Petroleum Corporation: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Liu, J.; Li, L.; Xu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhao, M.; Dai, C. CO2-responsive zwitterionic copolymer for effective emulsification and facile demulsification of crude heavy oil. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 325, 115166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Q/SHCG 65-2013; Technical Requirements of Viscosity Reducer for Heavy Oil. Sinopec: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Gu, X.; Li, Y.F.; Yan, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.X.; Zhao, J.S.; Chen, G. Synthesis and Investigation of a Spiro Diborate as a Clean Viscosity-Reducer and Pour Point Depressor for Crude Oil. Pet. Chem. 2019, 59, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhou, Z.C.; Shi, X.D.; Zhang, X.L.; Dong, S.B.; Zhang, J. Synthesis of alkylbenzenesulfonate and its behavior as flow improver in crude oil. Fuel 2021, 288, 119644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, A.Y. Oil as an Object of Rheology (Review). Pet. Chem. 2019, 59, 1092–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elganidi, I.; Elarbe, B.; Ridzuan, N.; Norhayati, A. Synthesis, characterisation and pre-evaluation of a novel terpolymer as pour point depressants to improve the Malaysian crude oil flowability. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2022, 12, 2067–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, A.Y.; Zuev, K.V.; Arinina, M.P.; Kulichikhin, V.G. Modifying the Viscosity of Heavy Crude Oil Using Surfactants and Polymer Additives. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 11991–11999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, G.; Wu, D.; Wang, S. Aggregation of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide with hydrolyzed polyacrylamide at the paraffin oil/water interface: Interfacial rheological behavior study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 317, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Du, H.; Zhang, Y.; Han, G.; Wang, H.; Yuan, D.; Wang, B.; Wang, X. Towards efficient solar demulsification (I): A solar electrical role on interfacial film of emulsions. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2021, 30, e00344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, T.N.; Pugh, R.J.; Franks, G.V.; Jameson, G.J. The role of particles in stabilising foams and emulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 137, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arinina, M.P.; Zuev, K.V.; Kulichikhin, V.G.; Malkin, A.Y. Effect of Composition and Interfacial Tension on the Rheology and Morphology of Heavy Oil-In-Water Emulsions. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 16460–16469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umar, A.A.; Saaid, I.B.M.; Sulaimon, A.A.; Pilus, R.B.M. A review of petroleum emulsions and recent progress on water-in-crude oil emulsions stabilized by natural surfactants and solids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 165, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.C.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhang, F.T.; Zhang, X.; Dong, S.B.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G. Synthesis of barium alkylbenzene sulfonate and its behavior as a flow improver for crude oil. C. R. Chim. 2021, 24, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Gao, L.Y.; Liu, M.H.; Nian, Y.; Shu, Q.L.; Xia, S.Q.; Han, Y. Viscosity reduction mechanism of surface-functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles in different types of heavy oil. Fuel 2024, 360, 130535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Han, T.K.; Li, J.W.; Zhu, B.J.; Yan, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Pathway of Oil-Soluble Additives to Reduce Heavy Crude Oil Viscosity Depends on the Molecular Characteristics of Asphaltene. Energy Fuel 2024, 38, 4990–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Guo, J.X.; Fei, D.T.; Wang, L.; Peng, Z.Y.; Li, J.M.; Dong, J.F. Polymer surfactants as viscosity reducers for ultra-heavy oil: Synthesis and viscosity reduction mechanism. Fuel 2024, 357, 129871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, G.L.; Ye, P.; Zhang, Y.L. The action mechanism of wax inhibitors (WI) on pour point and viscosity of mixed waxy oil. Pet. Chem. 2017, 57, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yu, P.F.; Ni, W.Q.; Peng, H.P.; Liu, Y.; Lv, X.F.; Zhao, H.J. Study on the Kinetic Process of Asphaltene Precipitation during Crude Oil Mixing and Its Effect on the Wax Behavior of Crude Oil. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Density, g/mL, at 25 °C | 0.94 |
| Specific gravity, at 25 °C | 1.06 |
| Pour point, °C | 17.20 |
| Viscosity, Pa·s, at 30 °C | 133.20 |
| Saturates, wt % | 38.23 |
| Aromatics, wt % | 27.57 |
| Resins, wt % | 18.46 |
| Asphaltenes, wt % | 15.74 |
| Wax content, wt % | 20.49 |
| Emulsifier | Emulsion Type | Dehydration Rate, % | Viscosity Reduction Rate, %, 30 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 min | 60 min | |||
| CTAB | O/W | 0 | 0 | 99.9 |
| Span-60 | W/O | 10.5 | 39.5 | – |
| AES | O/W | 14.4 | 95.6 | 99.9 |
| SDBS | O/W | 42.5 | 69.2 | 85.1 |
| AEO | O/W | 95.8 | 95.8 | 98.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, P.; Gu, X.; Chen, G. Improvement of the Fluidity of Heavy Oil Using a Composite Viscosity Reducer. Processes 2025, 13, 3547. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113547
Hu J, Yang J, Wang P, Gu X, Chen G. Improvement of the Fluidity of Heavy Oil Using a Composite Viscosity Reducer. Processes. 2025; 13(11):3547. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113547
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jiale, Jingwen Yang, Peng Wang, Xuefan Gu, and Gang Chen. 2025. "Improvement of the Fluidity of Heavy Oil Using a Composite Viscosity Reducer" Processes 13, no. 11: 3547. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113547
APA StyleHu, J., Yang, J., Wang, P., Gu, X., & Chen, G. (2025). Improvement of the Fluidity of Heavy Oil Using a Composite Viscosity Reducer. Processes, 13(11), 3547. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113547






