Abstract
To investigate the impact of periodic water-level fluctuations on soil microbial community structure in the riparian zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, this study focused on the riparian zone at Zhangjiawan near the dam. Surface soil samples (0–20 cm) were collected in spring, summer, and autumn from three elevation gradients: below 160 m, 160–170 m, and above 170 m. Phospholipid fatty acid (PLFA) was employed to characterize the microbial community structure. The results indicated that microbial community distribution was significantly influenced by both elevation and season, with bacteria dominating community variations. In terms of elevation, the total microbial biomass and bacterial abundance were highest at the 160–170 m gradient, followed by the area above 170 m, and lowest below 160 m. Season and elevation exhibited a significant interactive effect on fungi. Seasonal patterns showed that total microbial biomass and bacterial abundance peaked in summer, whereas fungal abundance and the fungi-to-bacteria ratio were higher in autumn. In contrast, actinobacterial abundance remained stable across seasons. Soil organic carbon (SOC; 60.3%) was identified as the predominant environmental factor influencing microbial community structure, followed by total nitrogen (TN; 13.9%) and pH (2.4%). SOC was identified as the key driver of microbial community dynamics. These findings clarify the respective roles of water level fluctuation, seasonal variation, and environmental factors in shaping riparian microbial communities, providing critical baseline data and theoretical support for ecological protection and scientific management of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area.
1. Introduction
The Three Gorges Dam is the world’s largest hydropower project. Its impoundment led to the formation of a riparian zone—a specific area with frequent water-level fluctuations—along the reservoir banks. This zone experiences a water-level amplitude of approximately 30 m and covers an area of about 349 km2 [1]. As a transitional and connecting region between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, the riparian zone plays a critical role in bank stabilization, biodiversity conservation, runoff regulation, pollutant interception, and climate regulation. It forms a unique wetland ecosystem that is crucial for maintaining regional ecological balance, water purification, and providing habitats [2,3,4]. However, due to periodic hydraulic scouring and gravitational erosion, the physicochemical properties of the soil, vegetation biomass, and diversity within the riparian zone are altered, consequently affecting the structure and distribution of soil microbial communities [5,6]. Soil microorganisms, as vital components of ecosystems, participate in key ecological processes such as nutrient cycling, energy transformation, and organic matter decomposition, playing an essential role in soil fertility, plant growth, and ecosystem stability [7]. Investigating the distribution of soil microbial communities in the riparian zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, particularly exploring potential temporal patterns across different flooding gradients, will contribute to a deeper understanding of the environmental adaptability of microbial taxa to seasonal inundation and the interaction mechanisms between the riparian zone ecosystem and its microbial communities.
Currently, studies on microbial communities in the riparian zone remain relatively limited, with most focusing on isolated analyses of either seasonal variations [8] or elevation gradients [9,10]. In fact, seasonal variations also lead to changes in environmental factors such as temperature and moisture, which in turn regulate microbial activity and enzyme function [11,12]. Furthermore, soil physicochemical properties differ markedly across elevation gradients within the riparian zone, affecting habitat connectivity and substrate availability for microorganisms [13,14]. These spatial and temporal factors act together to shape the structure and distribution of microbial communities. Studying the impact of either elevation or season in isolation may limit the accurate assessment of microbial dynamics under their interactive effects. Therefore, this study simultaneously investigates the distribution and variation patterns of microbial communities in the riparian zone from both temporal and spatial perspectives, under the unique anti-seasonal water-level fluctuation condition. The objective is to clarify the ecological relationships between water level regulation, temporal changes, and microbial communities, as well as the interaction mechanisms between soil physicochemical properties and microbial communities under flooding stress.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Location
This study selected the Zhangjiawan riparian zone near (about 30 km) the dam section of the Three Gorges Reservoir as the research site (Figure 1), which is located in the Tongzhuang River basin of Guojiaba Town, Zigui County, Yichang City, Hubei Province (110°44′ E, 30°57′ N). The study area experiences a subtropical monsoon climate, with a multi-year average precipitation of 900–1300 mm and a multi-year average temperature ranging between 15 °C and 18 °C.
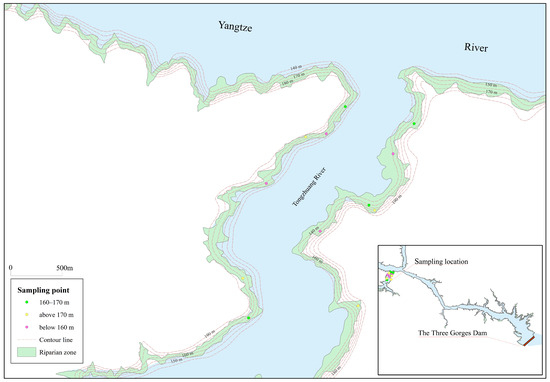
Figure 1.
Location of the study area and distribution of sampling points.
The riparian zone along the riverbanks predominantly consists of steep slopes and gorges. The area below 160 m is mainly covered by herbaceous plants such as Cynodon dactylon (L.) Persoon, Abutilon theophrasti Medicus, and Xanthium sibiricum Patrin ex Widder. The 160–170 m zone supports shrub-grass vegetation, including Melilotus officinalis (L.) Pall., Xanthium sibiricum Patrin ex Widder, and Setaria viridis (L.) Beauv. The area above 170 m is primarily forested, dominated by Pinus massoniana Lamb., Quercus variabilis Blume, and Citrus reticulata Blanco, with understory shrubs and grasses. The soil type is predominantly Purplish soil. The physicochemical properties of different elevation intervals are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Physical and chemical properties of soil at different elevation intervals.
2.2. Measurement
Soil samples were collected in May (spring), July (summer), and September (autumn) of 2022 from plots at different elevations: below 160 m, 160–170 m, and above 170 m. Four 2 m × 2 m quadrats (N = 4) were established at each elevation, and within each quadrat, two adjacent sub-samples were collected and combined to form one composite sample, therefore, a total of 12 sampling points were established and 36 sample data were collected over three seasons. Samples were transported to the laboratory on the same day. Visible plant and animal residues were removed, and the soil was sieved through a 2 mm sieve. One portion was air-dried and stored at 4 °C for the analysis of soil physicochemical properties (e.g., SOC, pH). The other portion was stored in sterile sealed bags at −80 °C for Phospholipid Fatty Acid (PLFA) analysis.
Microbial community composition was investigated using PLFA analysis. This method is based on the principle that phospholipids are essential and relatively stable components of cell membranes [15,16]. Samples were analyzed using gas chromatography (Agilent 7890A, Santa Clara, CA, USA) coupled with a fully automated microbial identification system to quantify the percentages of various biomarkers and the total microbial biomass. Different microbial groups can be identified based on group-specific PLFA signatures [17]. Fungal biomarkers primarily included 18:2ω6 and 18:1ω9c. Bacterial abundance was indicated by biomarkers such as i15:0, a15:0, 15:0, i16:0, i16:1ω9, 16:1ω7t, i17:0, a17:0, 17:0, 18:1ω7, and cy19:0. Actinobacterial biomarkers mainly included 10Me17:0 and 10Me18:0 [18]. Total microbial biomass was calculated as the sum of the absolute contents of all detected PLFA biomarkers. This marker set accounts for over 90% of microbial groups, with the remainder primarily consisting of protozoa biomarkers (e.g., 20:2ω6, 20:3ω6, 20:4ω6).
2.3. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
Data analysis was performed using SPSS 26.0. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to assess differences among data groups from different locations, elevations, and seasons (p < 0.05). Two-way ANOVA was employed to analyze the effects of elevation, season, and their interaction on microbial community distribution. Redundancy Analysis (RDA) was conducted using Canoco 5 to identify key driving factors influencing changes in community structure. Multiple stepwise regression analysis in SPSS was used to further identify the primary driving factors of SOC. Tables and figures were prepared using Excel and Origin 9.0.
3. Results
3.1. Altitudinal Distribution Characteristics of Microbial Communities
Significant spatial differences were observed in fungal abundance, bacterial abundance, and the fungi-to-bacteria ratio (F/B) among the elevation gradients (below 160 m, 160–170 m, and above 170 m) (p < 0.05; Table 2), with no significant interaction effect between season and elevation. Total microbial biomass and bacterial abundance followed the trend: 160–170 m > above 170 m > below 160 m. Fungal abundance and the F/B ratio showed the trend: below 160 m > 160–170 m = above 170 m. No significant differences were detected in actinobacterial abundance across elevation gradients (p > 0.05).

Table 2.
Variation values of microbial communities in different elevation intervals.
3.2. Seasonal Distribution Characteristics of Microbial Communities
The distribution of various microbial groups exhibited significant temporal heterogeneity (p < 0.01; Figure 2). Total microbial biomass overall displayed a “unimodal” distribution pattern over time, peaking in summer, followed by autumn, and being lowest in spring. Furthermore, two-way ANOVA revealed a significant interactive effect of season and elevation on microbial biomass (p < 0.01). Microbial biomass in spring showed the trend: 160–170 m > above 170 m = below 160 m. In both summer and autumn, the trend was 160–170 m > above 170 m > below 160 m, with the highest values in summer, intermediate in autumn, and lowest in spring. The maximum value (7.88 nmol/g) occurred in the 160–170 m interval during summer. Bacterial abundance was lowest in spring and autumn, peaking in summer, with the maximum value (89.2%) also observed in the 160–170 m interval during summer. Fungal abundance and the F/B ratio were significantly higher in autumn than in summer, with no significant difference between spring and the other two seasons. Their maximum values occurred in the below 160 m interval during spring (19.0% and 0.25, respectively). Actinobacteria showed no significant seasonal variation.
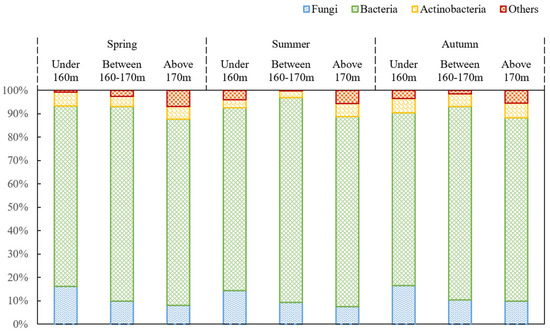
Figure 2.
Abundance of fungi, bacteria, actinomycetes, and the ratio of fungi to bacteria in different seasons.
The correlation results indicated that bacteria and season were the dominant factors influencing the variation of microbial community. Multiple stepwise regression results showed that bacteria and season explained 65.8% and 13.3% of the variation in microbial biomass, respectively. Bacterial abundance was negatively correlated with fungal abundance (p < 0.001), actinobacterial abundance (p < 0.01), and the F/B ratio (p < 0.001). Fungal abundance was significantly positively correlated with the F/B ratio (p < 0.001). According to the results of Redundancy Analysis (RDA) (Figure 3), the first two axes explained 63.3% and 13.2% of the variation in the microbial community, respectively. The environmental factors contributing to the microbial community structure were SOC (60.3%), TN (13.9%), and pH (2.4%). SOC was identified as the key driver of microbial community structure. The results of the multi-stage experiment further confirm that bacteria dominate the changes in microbial communities within the riparian zone.
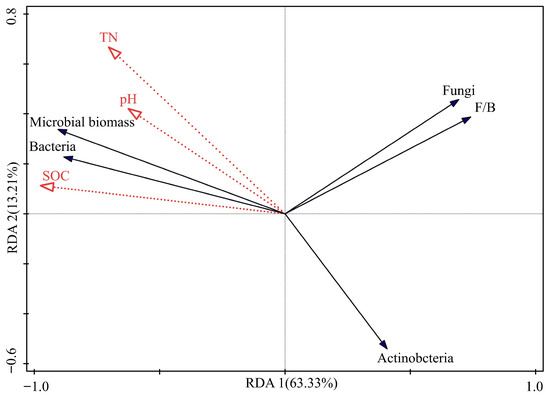
Figure 3.
Redundancy analysis (RDA) of microbial communities and environmental factors.
4. Discussion
4.1. Altitudinal Distribution of Microbial Communities
This study reveals that both the total microbial biomass and bacterial abundance were highest under moderate flooding stress conditions (160–170 m). This pattern may be attributed to the intermediate elevation zone experiencing a balanced frequency of wet–dry cycles, resulting in more optimal aeration and moisture conditions. Such an environment is likely more conducive to the accumulation of organic carbon during inundation periods. The higher elevation soil is affected by rainfall and runoff erosion, which can transport surface fine particles to middle and lower areas [19,20]. Conversely, prolonged flooding and erosion in the below 160 m interval resulted in the lowest microbial biomass [20]. Although previous studies in this area have found no differences in soil moisture content across elevation zones during sampling [21], soil organic carbon and nitrogen content were also highest under moderate flooding stress conditions [22], which promotes the most intense soil respiration [19] and the highest species diversity [23]. These findings align with those of Yang Wenhang et al. [24], who also reported higher soil microbial biomass under moderate flooding compared to other elevation ranges. The dominant bacterial community prefers relatively moist environments (160–170 m elevation) for reproduction and growth, and is noticeably affected by soil moisture or drought stress [25]. Thus, the riparian zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir demonstrates distinct environmental resource patterns across elevation gradients, with moderate flooding proving particularly favorable for microbial community survival.
In contrast, fungal abundance and the F/B ratio did not follow the same pattern as total microbial biomass and bacterial abundance; instead, they were higher in the severely flooded zone below 160 m compared to the less flooded areas above 160 m. This discrepancy may be explained by two key factors: the generally lower abundance of fungi relative to bacteria, and their greater resilience to harsh environmental conditions [26,27]. Additionally, previous studies have shown that flood stress can lead to significant shifts in rhizosphere microbial composition [28], and species such as mycorrhizal or Dark Septate Endophytes can mitigate the negative effects of flooding stress [29]. This study found no significant difference in actinobacterial abundance across elevation gradients. Other studies suggest that microbial communities exhibit significant variations in abundance across waterlogged zones, with waterlogging significantly reducing actinomycete abundance [30]. Furthermore, actinomycetes show a positive correlation with soil moisture gradients [21]. Therefore, the impact of waterlogging on actinomycetes requires further investigation.
4.2. Seasonal Distribution of Microbial Communities
Both total soil microbial biomass and bacterial abundance peak in summer and decline in spring. This seasonal pattern primarily stems from higher water temperatures, which enhance the ability of bacteria and other microorganisms to rapidly utilize periodic nutrient inputs in the riparian zone (e.g., organic matter from sediments during inundation) and root exudates from rapidly growing vegetation. Soil enzyme activity also increases with rising temperatures [31], and most bacteria exhibit higher growth rates under the relatively high temperatures of summer (e.g., above 35 °C) [32]. Furthermore, in spring, the soil has just been exposed, temperatures are lower, plant growth is slow, root exudate turnover is low, and organic matter has not fully decomposed, which limits microbial activity and soil nutrient cycling [33].
Actinobacteria showed no seasonal variation, whereas fungal abundance and the F/B ratio were higher in autumn than in summer. Combined with the observed peak in bacterial abundance during summer, these findings strongly suggest the temporal ecological niche differentiation within the microbial community [34]. On one hand, the relative abundance of soil organic matter in summer favors an increase in bacterial abundance, allowing them to dominate and potentially competitively exclude fungi. On the other hand, fungi are more efficient at utilizing recalcitrant compounds like cellulose and lignin. In autumn, the microbial community adjusts its structure, increasing fungal abundance and proportion to fully decompose and utilize the abundant substrates accumulated during the growing season [35].
5. Conclusions
This study investigated the spatiotemporal distribution patterns of soil microbial communities in the riparian zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. The results indicate that the degree of waterlogging is a key limiting factor affecting the composition of the soil microbial community. Both the total microbial biomass and bacterial abundance reached their highest levels under moderate waterlogging conditions. In contrast, severe waterlogging favored fungal growth and community dominance, which may be influenced by multiple factors such as SOC, TN, and pH. The total microbial biomass and bacterial abundance were highest in summer, which can be attributed to the high temperature and humidity promoting vigorous vegetation growth and enhanced microbial activity. In autumn, substrate accumulation provided more favorable conditions for fungal populations to dominate. This study provides a critical scientific theoretical foundation for analyzing microbial community structures in the riparian zone, and is also significant for studies on carbon cycling and carbon sink capacity assessment in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Moreover, it contributes to understanding the effects of long-term flooding on soil physicochemical properties and microbial communities during the process of primary vegetation succession or plant community reassembly in the hydro-fluctuation zone.
Author Contributions
Methodology, B.J.; Software, H.Z. and S.H.; Formal analysis, P.X.; Resources, S.C.; Data curation, J.Z.; Writing—original draft, Z.L.; Writing—review & editing, Z.G.; Supervision, Z.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Hubei Province Key Research and Development Program Project (No. 2023EHA007), the Fundamental Research Fund for Central Public Welfare Research Institutes (No. CKSF20241025/TG8 and CKSF2025533/TG8), research Project of the Three Gorges Follow-up Work of the Ministry of Water Resources (No. 12621400000021J001) and research fund from Mid-route Source of South-to-North Water Transfer Corp. Ltd. (No. ZSY/YG-ZX(2024)045), National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2022YFE0117000).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Zheng Li, Baojie Jia, Ping Xie Shufang He, Haiqin Zhu, Jinlong Zhang were employed by the company Wuhan Changjiang Kechuang Technology Development Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The company had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Qin, P.; Xu, H.; Liu, M.; Du, L.; Xiao, C.; Liu, L. Climate change impacts on Three Gorges reservoir impoundment and hydropower generation. J. Hydrol. 2020, 580, 123922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidon, P.G.; Welsh, M.K.; Hassanzadeh, Y.T. Twenty years of riparian zone research (1997–2017): Where to next? J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wantzen, K.M.; Machado, F.A.; Voss, M.; Boriss, H.; Junk, W.J. Floodpulse-induced isotopic changes in fish of the Pantanal wetland, Brazil. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 64, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wantzen, M.K.; Rothhaupt, K.; Mörtl, M.; Cantonati, M.; Tóth, L.G.; Fischer, P. Ecological effects of water-level fluctuations in lakes: An urgent issue. Hydrobiologia 2008, 613, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.J.; O’Connor, P.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ye, X.X. Linking soil nutrient cycling and microbial community with vegetation cover in riparian zone. Geoderma 2021, 384, 114801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleston, E.M.; Lee, D.Y.; Owens, M.S.; Cornwell, J.C.; Crump, B.C.; Hewson, I. Key respiratory genes elucidate bacterial community respiration in a seasonally anoxic estuary. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 2306–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C. Microbial decomposition and soil health: Mechanisms and ecological implications. Mol. Soil Biol. 2024, 15, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, L.M.; Yuan, Z.X.; Li, C.X. Seasonal dynamics and functional prediction of bacterial community in the rhizosphere of two suitable herbaceous species in the riparian zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 9699–9709. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mei, Y.; Huang, P.; Wang, P.; Zhu, K. Effects of Water Level Fluctuations and Vegetation Restoration on Soil Prokaryotic Microbial Community Structure in the Riparian Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 2715–2726. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Sun, Y.J.; Yu, J.S.; Xia, X.F.; Ding, A.Z.; Zhang, D.Y. Impacts of groundwater level fluctuation on soil microbial community, alkane degradation efficiency and alkane-degrading gene diversity in the critical zone: Evidence from an accelerated water table fluctuation simulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 83060–83070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, J.; Yihong, Z.; Qayum, M.; Afzal, U.; Aslam, M. Effects of dam on temperature, humidity and precipitation of surrounding area: A case study of Gomal Zam Dam in Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 14592–14603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.M.; Supronienė, S.; Žvirdauskienė, R.; Aleinikovienė, J. Climate, Soil, and Microbes: Interactions Shaping Organic Matter Decomposition in Croplands. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, L. Bacterial and Fungal Community Composition and Functional Activity Associated with Lake Wetland Water Level Gradients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Yuan, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, S.; Zhou, L. Water Level Has Higher Influence on Soil Organic Carbon and Microbial Community in Poyang Lake Wetland Than Vegetation Type. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, K.; Zhao, Y.; Kang, Z.; Ma, R.; Wright, A.L.; Jiang, X.J. Pyrolysis-assisted transesterification for accurate quantification of phospholipid fatty acids: Application to microbial community analysis in 1000-years paddy soil chronosequence. Geoderma 2022, 406, 115504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najdegerami, H.E.; Manaffar, R. Using a combination of phospholipid fatty acids profiles and DNA-based sequencing analyses to detect shifts in the biofloc microbial community in different carbon sources and carbon/nitrogen ratios. Vet. Res. Forum Int. Q. J. 2024, 15, 425–434. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.J.; Xue, Y.W.; Wu, D.H.; Xu, M.C.; Li, A.D.; Zhang, X.; Mo, J.M.; Zheng, M.H. Long-term nitrogen and phosphorus addition have stronger negative effects on microbial residual carbon in subsoils than topsoils in subtropical forests. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Y.; Felice, M.L.; Scow, K.M. Impacts and interactions of biochar and biosolids on agricultural soil microbial communities during dry and wet-dry cycles. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 152, 103570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cao, S.L.; Zhu, H.Q.; Xie, P.; Jia, B.J. Study on CO2 Emissions in the Subsidence Area of the Three Gorges Reservoir near the Dam Section under Water Level Change. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2025. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=2t0iREynv6l37J8bvNk1CcZ13llbOc8Ib0TG7B1325DdbIU534g_K0rVswMrzqzox8RU8-bhD8PnUJsEDL2LJoRoQKWcAwZFUvJmVt_x23a5LJd5opaAxpNTGs_mqdmoy_D59a8DElbtKfJrc5o832Dl8F-3lpszaRvXyjRenxzo6q3pub-yzQ==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 1 April 2025). (In Chinese).
- Zhang, S. The Effect of Alternating Wet and Dry Conditions on Soil Organic Carbon Decomposition. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing Three Gorges University, Chongqing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.Y. Characterization of Soil Microbial Community Structure and Function Diversity Along the Water-Level Fluctuation in Tongzhuang River Riparian Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Master’s Thesis, China Three Gorges University, Yichang, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.H.; Wang, X.G.; Liu, X.L. Progress of Research of the Effect of Impounding on Soil and Vegetation in Water-Level Fluctuation Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Hydroecol. 2024. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Q.; Zhang, G.H.; Luo, Y.F.; Zhou, H.; Wang, K.W.; Wang, C.S. Soil erodibility indicators as affected by water level fluctuations in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Catena 2021, 207, 105692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.H.; Qing, H.; Ren, Q.S.; He, Y.Y.; Li, X.X.; Li, C.X. Characteristics of soil microbial biomass C and N under revegetation in the hydro-fluctuation belt of the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 7947–7955. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, X. The Effects of Plant Decomposition on Soil Carbon Pool in Poyang Lake Wetlands Driven by Water Conditions and the Soil Bacterial Response. Master’s Thesis, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo-Ortiz, M.A.; Gabaldón, T. Fungal evolution: Major ecological adaptations and evolutionary transitions. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 1443–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleine, C.; Stajich, J.E.; Selbmann, L. Fungi are key players in extreme ecosystems. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2022, 37, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francioli, D.; Cid, G.; Kanukollu, S.; Ulrich, A.; Hajirezaei, M.R.; Kolb, S. Flooding causes dramatic compositional shifts and depletion of putative beneficial bacteria on the spring wheat microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 773116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Arias, C.; Witzell, J.; Solla, A.; Martin, A.J.; Rodríguez-Calcerrada, J. Beneficial and pathogenic plant-microbe interactions during flooding stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2022, 45, 2875–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.N.; Ge, Z.M.; Li, Y.L.; Li, S.H.; Tan, L.S.; Li, X.Z. Effects of waterlogging and increased salinity on microbial communities and extracellular enzyme activity in native and exotic marsh vegetation soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.M.; Li, J.; Lin, Z.A.; Li, Y.T.; Yang, X.D.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhao, B.Q. Temperature effects on soil organic carbon, soil labile organic carbon fractions, and soil enzyme activities under long-term fertilization regimes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 102, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, L.; Arif, M.; Ding, D.; Hu, X.; Zheng, J.; Yuan, Z.; Li, C. Artificial plantation responses to periodic submergence in massive dam and reservoir riparian zones: Changes in soil properties and bacterial community characteristics. Biology 2021, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrova, K. Assessing microbial activity in soil samples collected during the transition period between seasons using the Biolog EcoPlate method. Ecol. Balk. 2024, 16, 187–204. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, Q.W.; Yakov, K. Mechanisms and implications of bacterial-fungal competition for soil resources. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, K.; Kohlstedt, M.; Erven, G.; Klostermann, C.E.; America, A.H.P.; Bakx, E.; Baars, J.J.P.; Gorissen, A.; Visser, R.; Vries, R.P.; et al. From 13C-lignin to 13C-mycelium: Agaricus bisporus uses polymeric lignin as a carbon source. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadl3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).