Peer-to-Peer Energy Storage Capacity Sharing for Renewables: A Marginal Pricing-Based Flexibility Market for Distribution Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
- An energy storage flexibility market that allows multiple vendors and customers to bid and be awarded for utilizing the capacity of shared energy storage is innovated.
- On the basis of the proposed energy storage flexibility market, a marginal pricing approach is developed to rationalize pricing and settle the market.
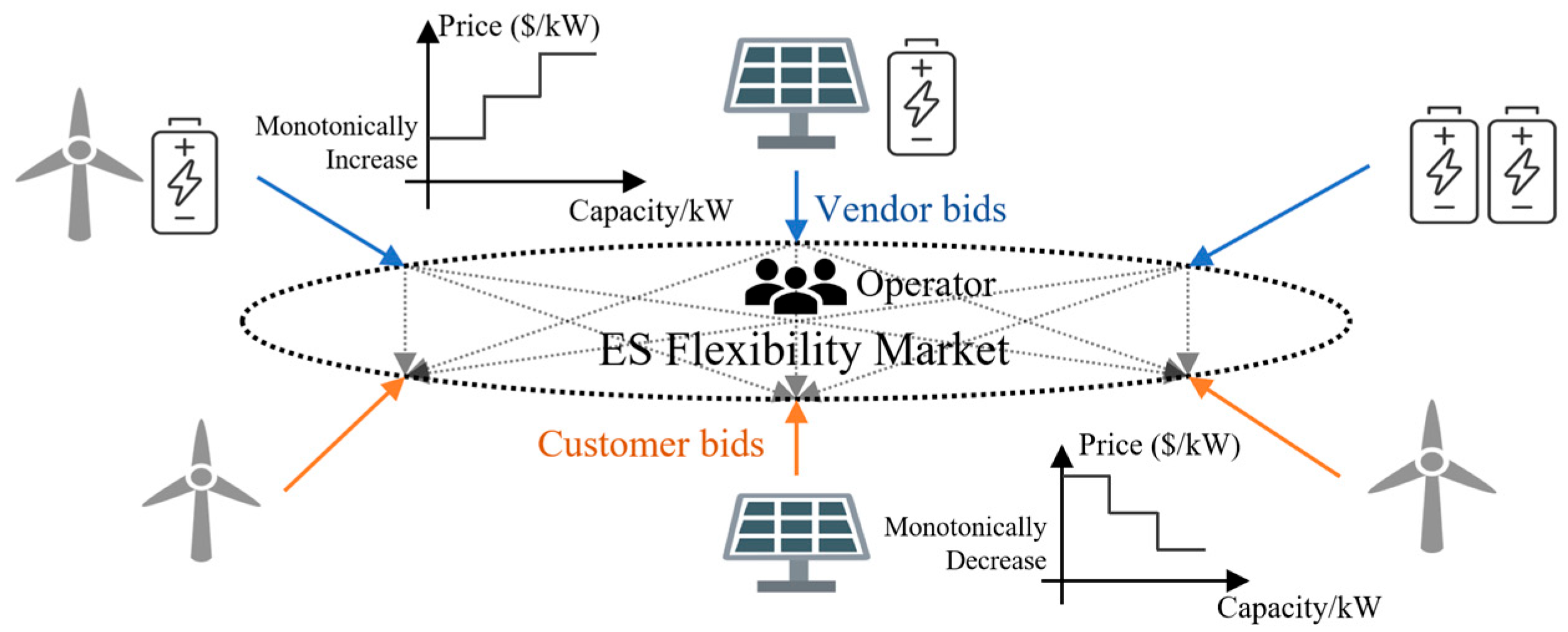
2. The Flexibility Market of Shared Energy Storage
2.1. The Energy Storage Flexibility Market Design
2.2. The Energy Storage Flexibility Market Model
3. The Carryover Energy and the Marginal Pricing Mechanism
3.1. The Carryover Energy
3.2. The Marginal Pricing Mechanism
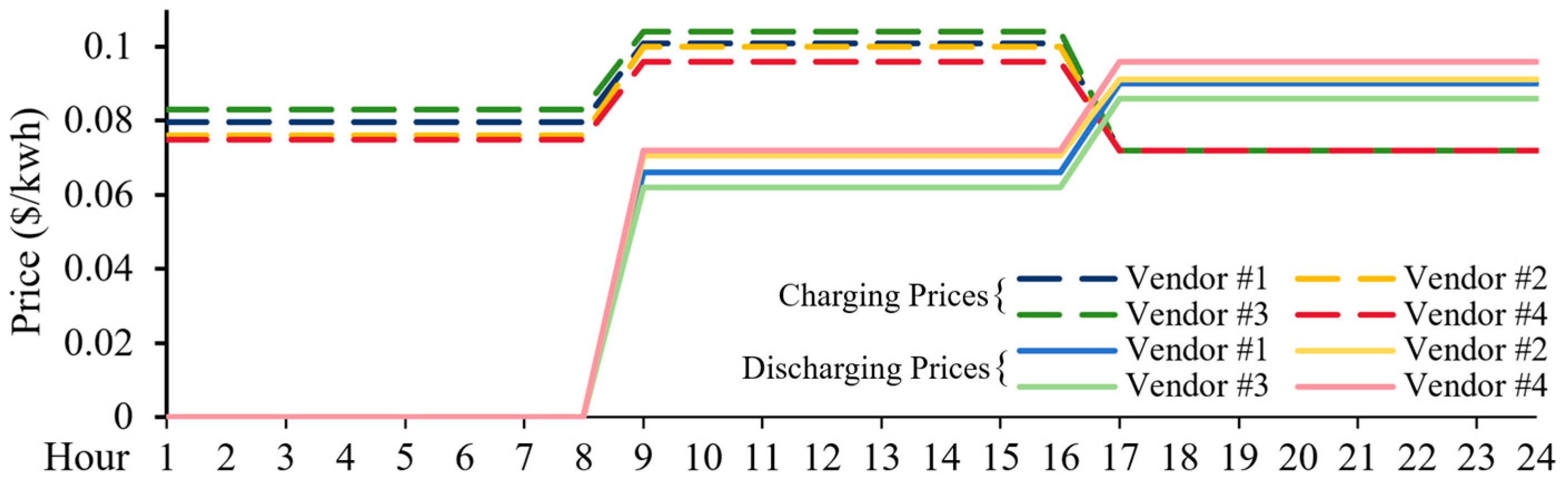
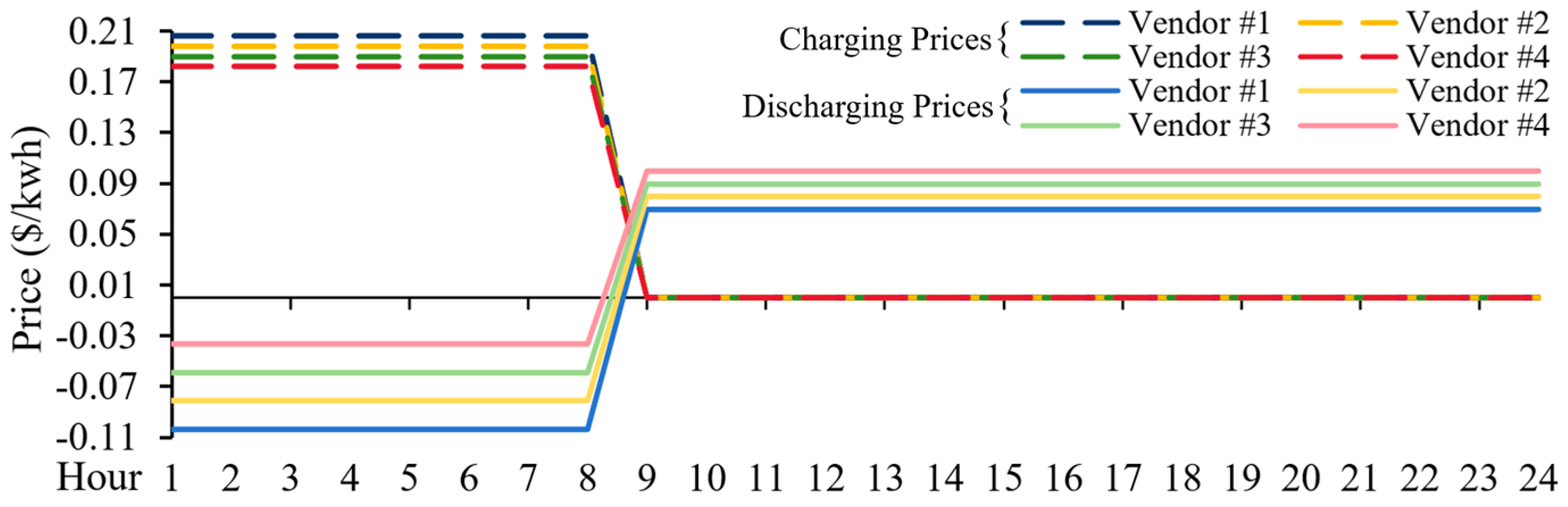
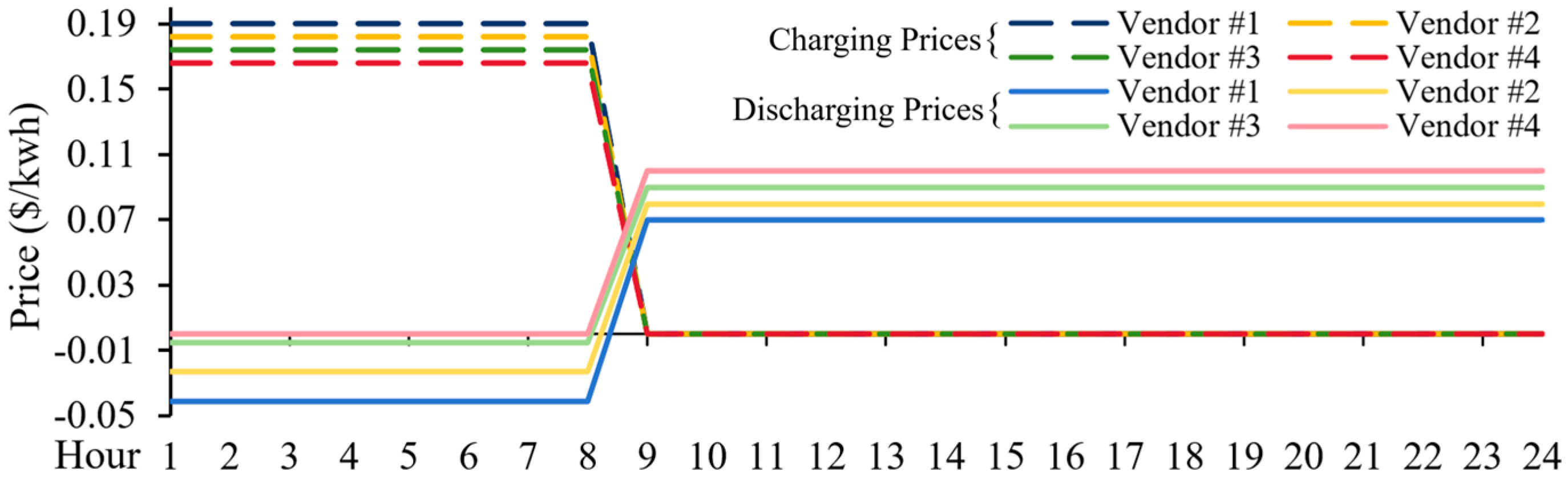
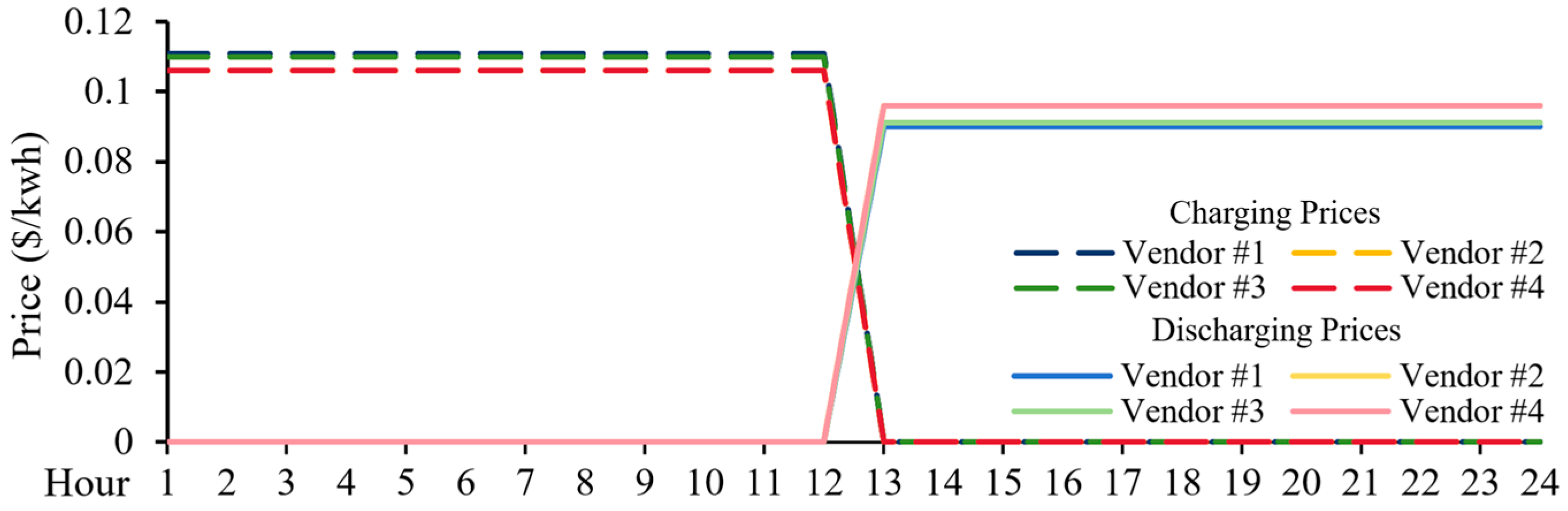
4. Case Study
4.1. The Markets Without Power and Energy Capacity Deficit
4.2. The Markets with Power and Energy Capacity Deficit
4.3. The Markets with the Carryover Energy Constraints
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IRENA. Innovation Landscape Brief: Peer-to-Peer Electricity Trading; International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Majumder, B.P.; Faqiry, M.N.; Das, S.; Pahwa, A. An efficient iterative double auction for energy trading in microgrids. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence Applications in Smart Grid, Orlando, FL, USA, 9–12 December 2014; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, S.; Hayes, B.P.; Breslin, J.G. Distributed double auction for peer to peer energy trade using blockchains. In Proceedings of the 2018 5th International Symposium on Environment-Friendly Energies and Applications, Rome, Italy, 24–26 September 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Feng, C.; Liu, A.L. Comparisons of auction designs through multiagent learning in peer-to-peer energy trading. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 14, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Xu, S.; Hu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, J.; Wang, J. A Consortium Blockchain-Enabled Double Auction Mechanism for Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading among Prosumers. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2024, 9, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.; Morstyn, T.; Han, L.; McCulloch, M. Flexible cooperative game theory tool for peer-to-peer energy trading analysis. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Portland, OR, USA, 5–10 August 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tushar, W.; Saha, T.K.; Yuen, C.; Liddell, P.; Bean, R.; Poor, H.V. Peer-to-peer energy trading with sustainable user participation: A game theoretic approach. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 62932–62943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tushar, W.; Saha, T.K.; Yuen, C.; Azim, M.I.; Morstyn, T.; Poor, H.V.; Niyato, D.; Bean, R. A coalition formation game framework for peer-to-peer energy trading. Appl. Energy 2020, 261, 114436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, M.I.; Tushar, W.; Saha, T.K. Coalition graph game-based P2P energy trading with local voltage management. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 4389–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, A.; Chaudhari, K.; Long, C.; Gooi, H.B. Peer-to-peer energy trading in a prosumer-based community microgrid: A game-theoretic model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 6087–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anoh, K.; Maharjan, S.; Ikpehai, A.; Zhang, Y.; Adebisi, B. Energy peer-to-peer trading in virtual microgrids in smart grids: A game-theoretic approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Xiang, Y.; Gu, C.; Liu, J. Peer-to-peer coupled trading of energy and carbon emission allowance: A stochastic game-theoretic approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 24364–24375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, R.; Na Xie, M.; Wang, F.X.; Chen, L.X. Fair P2P energy trading between residential and commercial multi-energy systems enabling integrated demand-side management. Appl. Energy 2020, 262, 114551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.H.; Bose, A.; Singh, C.; Chow, J.H.; Mu, G.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y. Control and stability of large-scale power system with highly distributed renewable energy generation: Viewpoints from six aspects. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 9, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.N. A review of peer-to-peer energy trading markets: Enabling models and technologies. Energies 2024, 17, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xue, Y.; Tian, L.; Yuan, X. Research on optimal configuration strategy of energy storage capacity in grid-connected microgrid. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2017, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero, F.; Cañizares, C.A.; Bhattacharya, K.; Anierobi, C.; Calero, I.; de Souza, M.F.Z.; Farrokhabadi, M.; Guzman, N.S.; Mendieta, W.; Peralta, D.; et al. A review of modeling and applications of energy storage systems in power grids. Proc. IEEE 2023, 111, 806–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Santacruz, C.; Gomez, P.J.; Carrasco, J.M.; Galvan, E. Multi P2P energy trading market, integrating energy storage systems and used for optimal scheduling. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 64302–64315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Morstyn, T.; McCulloch, M. Incentivizing prosumer coalitions with energy management using cooperative game theory. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Saad, W.; Han, Z.; Poor, H.V.; Basar, T. A game-theoretic approach to energy trading in the smart grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Liu, X.; Wu, C.; Tang, Y. Game-theoretic energy management with storage capacity optimization in the smart grids. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2018, 6, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediwaththe, C.P.; Shaw, M.; Halgamuge, S.; Smith, D.B.; Scott, P. An incentive-compatible energy trading framework for neighborhood area networks with shared energy storage. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2020, 11, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, M.-H.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Chai, S.; He, Y. Data-driven game-based pricing for sharing rooftop photovoltaic generation and energy storage in the residential building cluster under uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 4480–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Qiu, W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lin, Z.; Yang, L. Cooperative-game-based day-ahead scheduling of local integrated energy systems with shared energy storage. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2022, 13, 1994–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, S.; Gu, W.; Zhu, C.; Chen, X.G. Optimal operation of micro-energy grids considering shared energy storage systems and balanced profit allocations. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 9, 254–271. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, H.; Li, Z.; Zhu, X. Research on the optimal configuration method of shared energy storage basing on cooperative game in wind farms. Energy Rep. 2024, 12, 3700–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brijs, T.; Huppmann, D.; Siddiqui, S.; Belmans, R. Auction-based allocation of shared electricity storage resources through physical storage rights. J. Energy Storage 2016, 7, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tushar, W.; Chai, B.; Yuen, C.; Huang, S.; Smith, D.B.; Poor, H.V.; Yang, Z. Energy storage sharing in smart grid: A modified auction-based approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 1462–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Xie, K.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Xie, S. Multi-resource allocation of shared energy storage: A distributed combinatorial auction approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 4105–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, W.; Liu, G. Research on the future development of electricity retail market based on the wholesale retail market convergence mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 6th Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, Chongqing, China, 24–26 May 2024; pp. 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Fang, J.; Ai, X.; Cui, S.; Yao, W.; Chen, Z.; Wen, J. Storage right-based hybrid discrete-time and continuous-time flexibility trading between energy storage station and renewable power plants. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2023, 14, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Li, Z. Different models and properties on LMP calculations. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting, Montreal, QC, Canada, 18–22 June 2006. [Google Scholar]


| Focused System | References | Based Theory | Model and Pricing Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microgrid | [2,3,4,5] | Double auction | The auction platform clears the bids according to certain rules |
| [6,7,8,9] | Cooperative game | Form coalition, revenue is allocated based on member contributions | |
| [10,11,12,13] | Non-cooperative game | Nash equilibrium price formed based on game-theoretic strategies | |
| Independent energy storage | [18] | Double auction | Bilateral pairing method, prices are determined by participant bids |
| [19] | Cooperative game | Nucleolus-based benefit allocation | |
| [20,21] | Non-cooperative game | Users optimize independently and reach the Nash equilibrium | |
| Shared energy storage | [22,23] | Stackelberg game | The energy storage acts as the leader, and the market is settled at the Nash equilibrium |
| [24,25,26] | Cooperative game | Cost allocation is based on the principles of the Shapley value or Nash bargaining | |
| [27,28,29] | Auction | Buyers bid and auctioneer matches supply/ demand to determine prices | |
| [30,31] | Package | Fixed-rate package |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y. Peer-to-Peer Energy Storage Capacity Sharing for Renewables: A Marginal Pricing-Based Flexibility Market for Distribution Networks. Processes 2025, 13, 3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103143
Li X, Liu T, Liu Y. Peer-to-Peer Energy Storage Capacity Sharing for Renewables: A Marginal Pricing-Based Flexibility Market for Distribution Networks. Processes. 2025; 13(10):3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103143
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiang, Tianqi Liu, and Yikui Liu. 2025. "Peer-to-Peer Energy Storage Capacity Sharing for Renewables: A Marginal Pricing-Based Flexibility Market for Distribution Networks" Processes 13, no. 10: 3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103143
APA StyleLi, X., Liu, T., & Liu, Y. (2025). Peer-to-Peer Energy Storage Capacity Sharing for Renewables: A Marginal Pricing-Based Flexibility Market for Distribution Networks. Processes, 13(10), 3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103143







