In Situ Combustion Characteristics of Heavy Oil in the Liaohe Oilfield at Different Temperatures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Oxidation Process of the Crude Oil
2.2. Characterization of Oil Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Composition Characteristics of Crude Oil in Block D
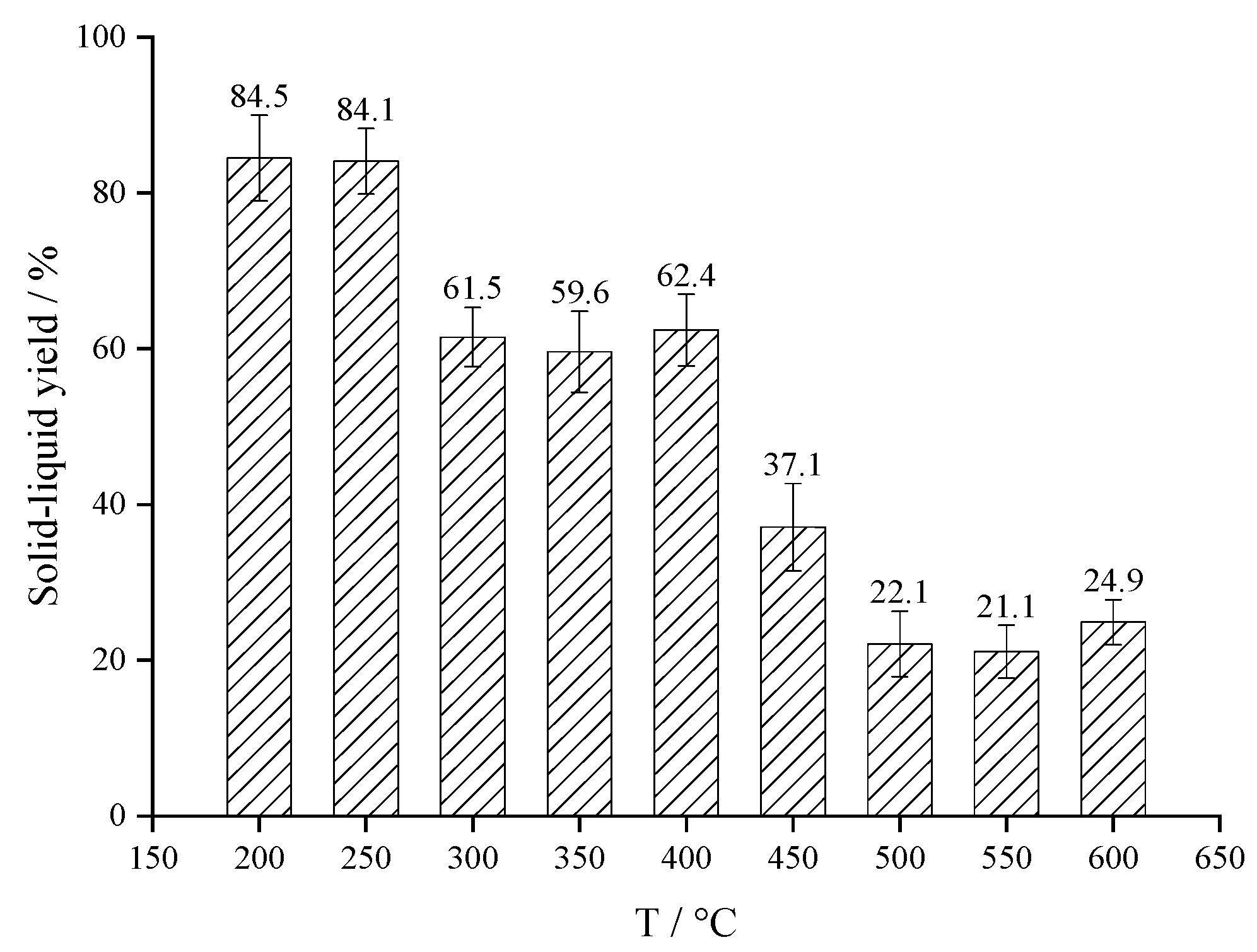
3.2. Effect of Reaction Temperature on the Yield of Thermal Reaction Products
3.3. Effect of Thermal Reaction Products on SARA Components
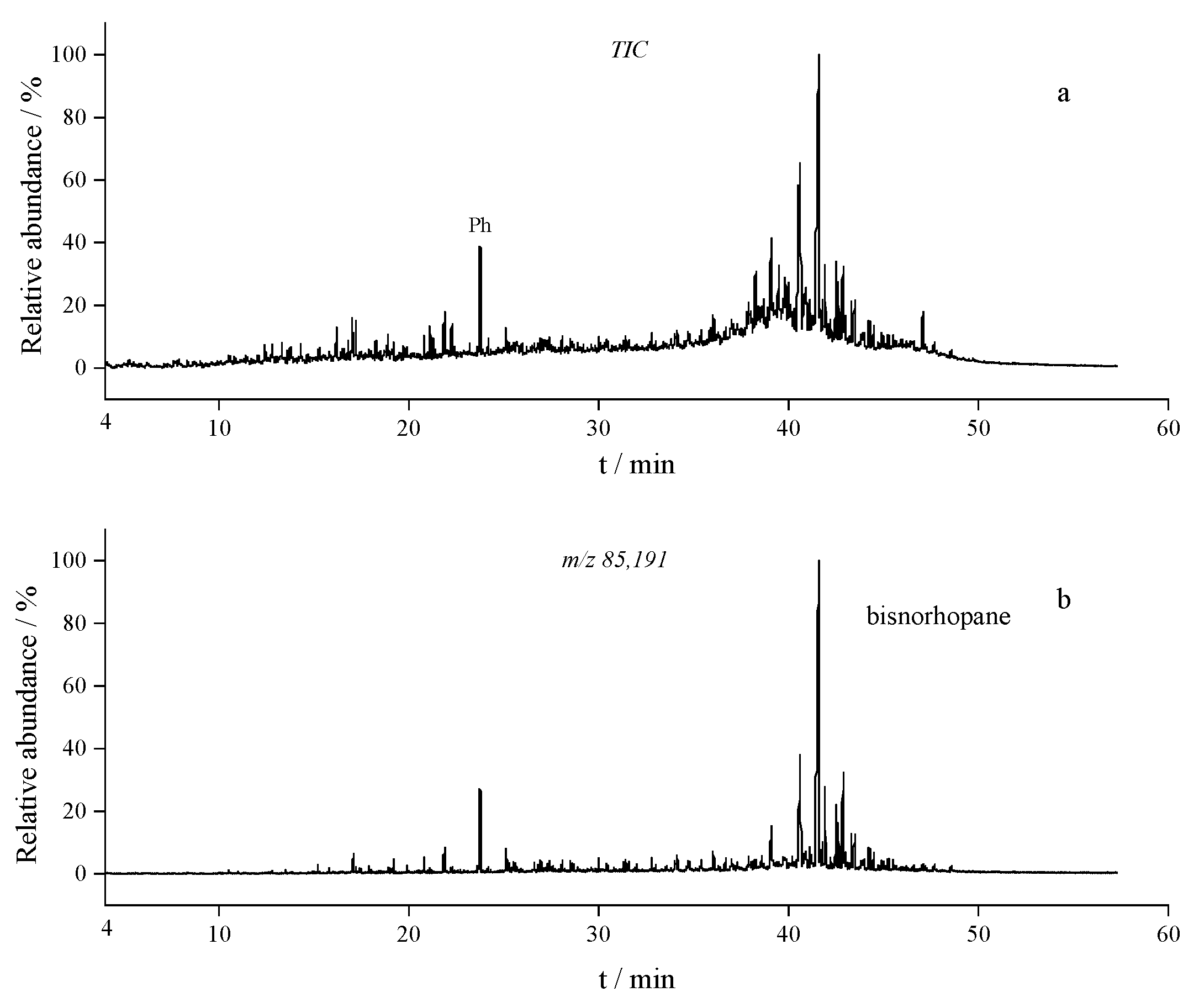
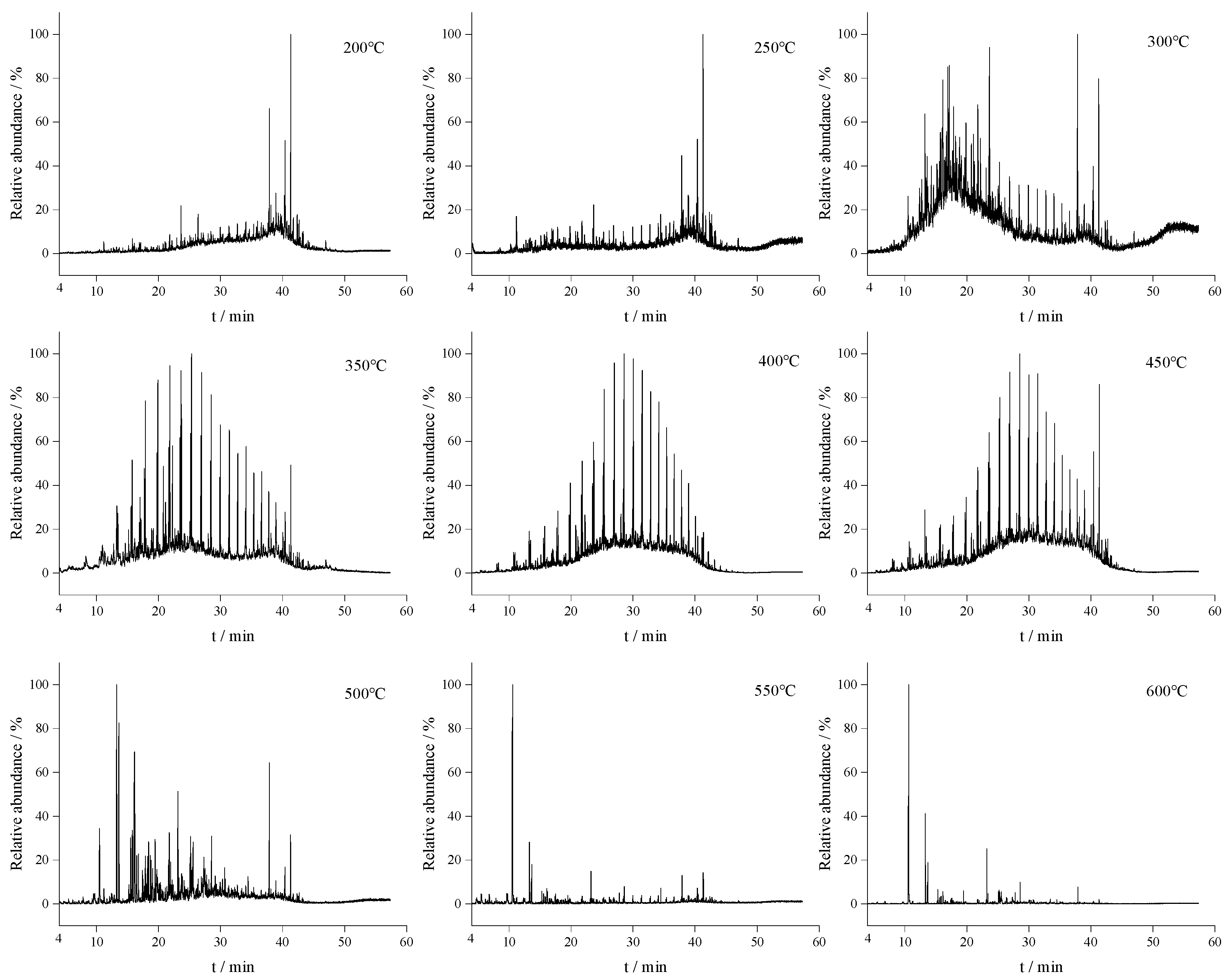
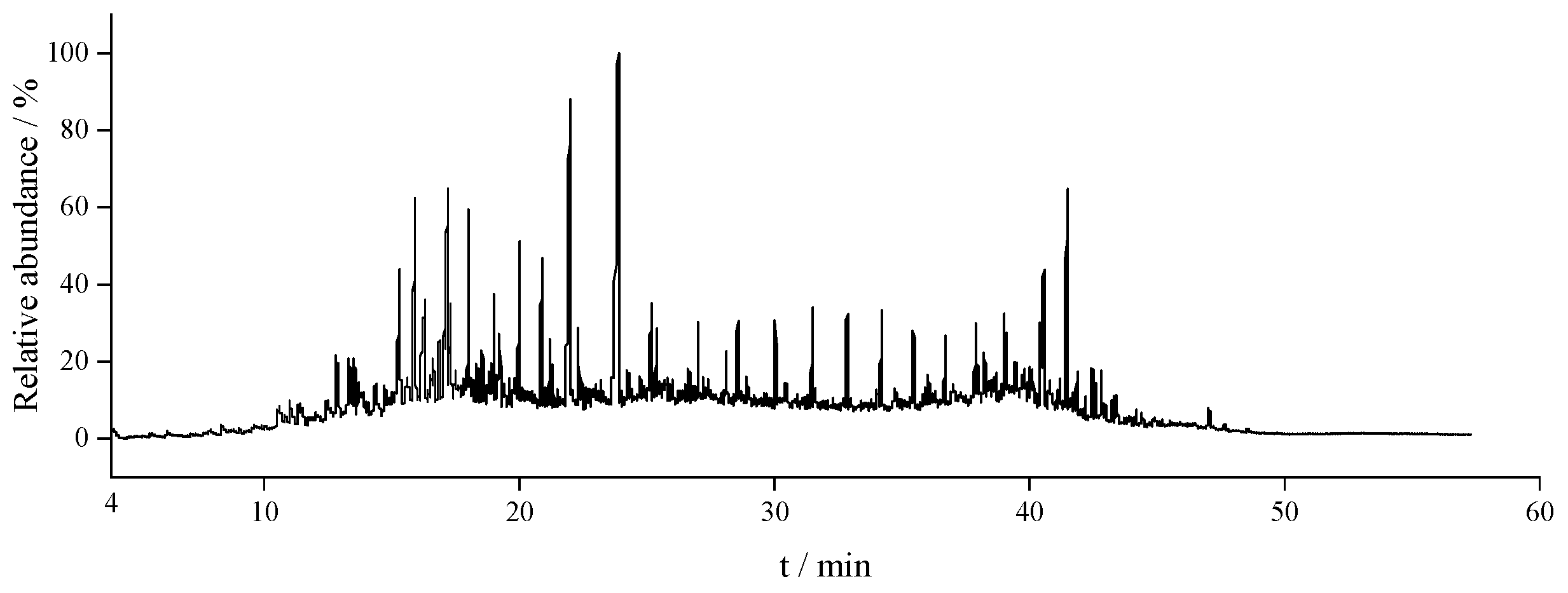
3.4. Characterization of Thermal Reaction Products by GC–MS
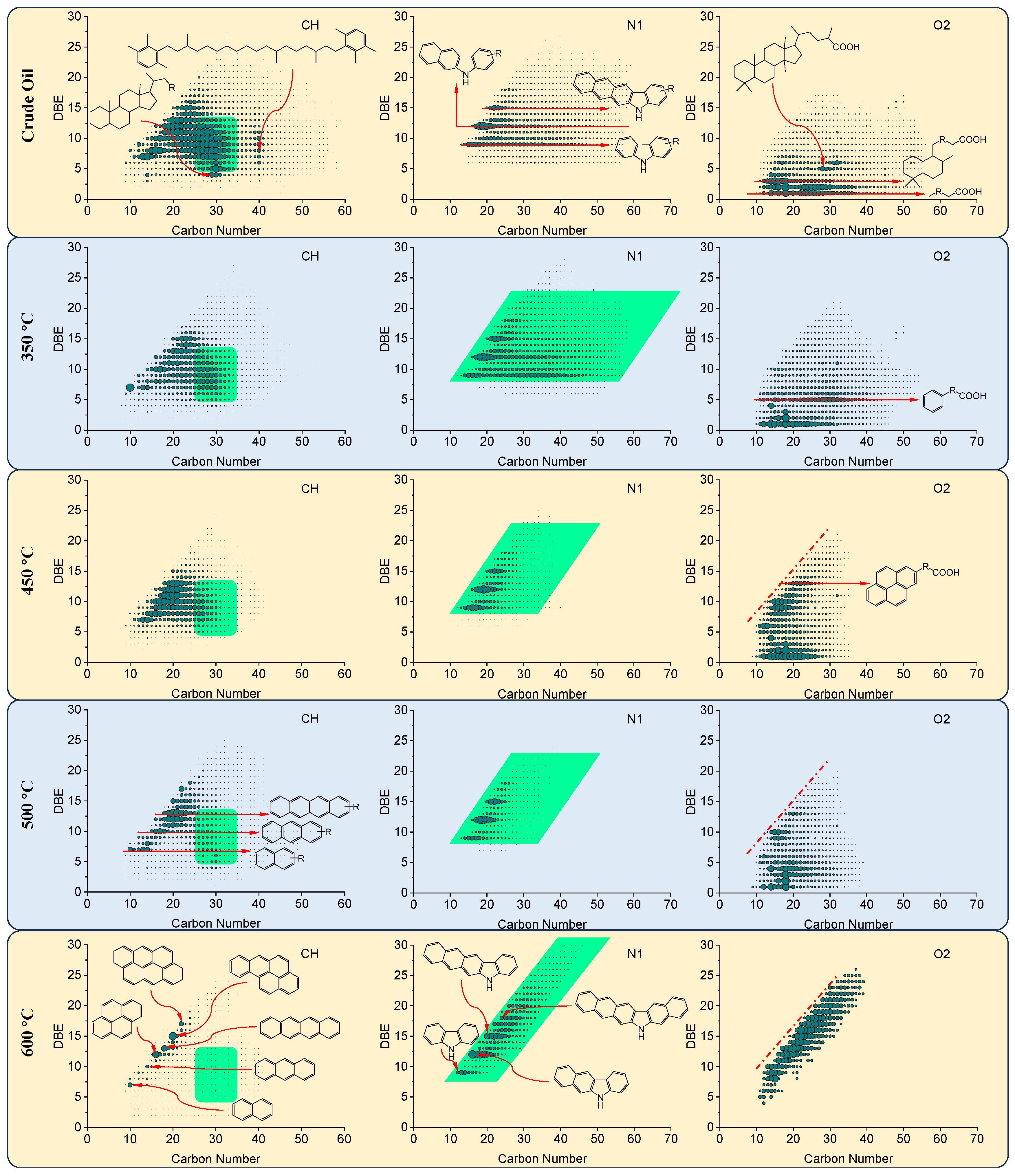
3.5. Characterization of Thermal Reaction Products by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
3.6. Analysis of Oil Samples from Fire-Flooding Wells
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, Q.; Zhao, S.Q.; Zhou, Y.S.; Gao, J.S.; Xu, C.M. Development of heavy oil upgrading technologies in China. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2020, 36, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakov, A.V.; Meshkova, V.D.; Guzey, D.V.; Pryazhnikov, M.I. Recent Advances in the Study of In Situ Combustion for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Energies 2023, 16, 4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Hu, Z.W.; Xu, Z.X.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Y.C.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, D.Q.; Li, S.Y. Experimental investigation of in situ combustion (ISC) in heavy oil thermal recovery. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 233, 212488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Liu, C.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Gong, Y.N.; Song, Y.; Tang, J.S. In-situ Combustion Simulation from Laboratory to Field Scale. Geofluids 2021, 2021, 8153583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, W.Y.; Chu, S.L.; Liu, H.Q.; Dong, X.H.; Luan, G.H. Experimental Simulation of the Zones Characteristics Considering Oily Bubble Behavior During in Situ Combustion. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 4964–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.G. Chemical society of petroleum aspects of in-situ combustion: Heat of combustion and kinetics. Eng. J. 1971, 12, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, N.P. Chemical-reaction mechanisms that govern oxidation rates during in-situ combustion and high-pressure air injection. SPE Res. Eval. Eng. 2016, 19, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.B.; Jiang, H.Y.; Yang, F.X.; Shi, Y.L.; Bai, Y.; Du, K. Research on characteristics of fire flooding zones based on core analysis. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 170, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahinpey, N.; Murugan, P.; Mani, T. Comparative kinetics and thermal behavior: The study of crude oils derived from Fosterton and Neilburg fields of Saskatchewan. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.G.; Wang, X.S.; Sun, J.H.; Tang, J.S.; Chen, S.; Pan, J.J.; Guo, Y. Formation and Combustion Heat Release of Naphthenic-Based Crude Oil Cokes at Different Reaction Temperatures. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 15106–15112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hascakir, B.; Ross, C.M.; Castanier, L.M.; Kovscek, A.R. Fuel formation and conversion during in-situ combustion of crude oil. SPE J. 2013, 18, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.L.; Zhang, X.L.; Xi, C.F.; Wang, X.C.; Yang, F.X.; Shi, X.R.; Li, Q. Displacement and development characteristics of fire flooding of vertical wells in old heavy oil areas. Pet. Res. 2018, 3, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anto-Darkwah, E.; Cinar, M. Effect of pressure on the isoconversional in situ combustion kinetic analysis of Bati Raman crude oil. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 143, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Pu, W.F.; Su, L.; Shang, C.; Song, Y.; Li, W.; He, Z.H.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, Z.Z. Properties, combustion behavior, and kinetic triplets of coke produced by low-temperature oxidation and pyrolysis: Implications for heavy oil in-situ combustion. Pet. Sci. 2021, 18, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.B.; Wei, Y.G.; Wang, Z.M.; Yang, W.; Yang, H.J.; Liu, S.J. Kinetics of Low-Temperature Oxidation of Light Crude Oil. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 2647–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.X.; Sun, X.G.; Xin, W.B.; Zhan, H.Y.; Gao, C.G.; Yuan, S.B. Study on the sweep control method of in-situ combustion reservoir in Xinjiang Hongqian oilfield based on asynchronous injection and production. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.F.; Liu, P.C.; Li, Q.; Tang, J.S.; Guan, W.L.; Chen, Y.J. Experiments and simulations on factors affecting the stereoscopic fire flooding in heavy oil reservoirs. Fuel 2022, 314, 123146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.C.; Che, H.C. Parameters Determination during In Situ Combustion of Liaohe Heavy Oil. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 3416–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.H.; Liu, W.M.; Pan, Y.H.; Wang, X.F.; Wang, Y.P.; Peng, P.A. Superimposed secondary alteration of oil reservoirs. Part I: Influence of biodegradation on the gas generation behavior of crude oils. Org. Geochem. 2020, 142, 103965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.H.; Liao, Y.H.; Zheng, Y.J. Effect of Biodegradation on the Molecular Composition and Structure of Asphaltenes: Clues from Quantitative Py-Gc and Thm-Gc. Org. Geochem. 2015, 86, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi-Nasab, F.S.; Parastar, H. Pattern recognition analysis of gas chromatographic and infrared spectroscopic fingerprints of crude oil for source identification. Microchem. J. 2020, 153, 104326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sviridenko, N.N.; Pevneva, G.S.; Voronetskaya, N.G. GC-MS analysis of hydrocarbons formed after catalytic cracking of heavy oil. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2023, 42, 2158–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelevic, A.; Geantet, C.; Moreaud, M.; Lorentz, C.; Souchon, V. Quantitative analysis of hydrocarbons in gas oils by two-dimensional comprehensive gas chromatography with vacuum ultraviolet detection. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 13766–13775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Liao, G.Z.; Wang, Z.M.; Su, R.G.; Ma, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.G.; Wang, X.S.; Pan, J.J.; Shi, Q. Molecular composition of low-temperature oxidation products in a simulated crude oil in-situ combustion. Fuel 2022, 316, 123297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Wang, P.F.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, X.Q.; Song, W.; Yang, J.S.; Yuan, C.D. Oxidation behaviors of Hongqian heavy crude oil characterized by TG-DSC-FTIR-MS within full temperature regions. Fuel 2023, 353, 129242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.L.; Xia, C.Q.; Wang, L.; Tang, J.C. Fingerprint analysis reveals sources of petroleum hydrocarbons in soils of different geographical oilfields of China and its ecological assessment. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Li, Y.Y.; Su, R.G.; Wang, X.S.; Pan, J.J.; Shi, Q.; Liao, G.Z.; Xu, C.M. Molecular composition of low-temperature oxidation products of the heavy oil. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 3264–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Li, Y.Y.; Su, R.G.; Wu, J.X.; Xie, L.Y.; Tang, J.S.; Wang, X.S.; Pan, J.J.; Wang, Y.F.; Shi, Q.; et al. Ketones in Low-Temperature Oxidation Products of Crude Oil. Processes 2023, 11, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | Saturates (wt%) | Aromatics (wt%) | Resins (wt%) | Asphaltenes (wt%) | Residue Oils (wt%) | Cokes (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude oil | 32.14 | 21.71 | 43.01 | 3.15 | - | - |
| Products at 200 °C | 24.43 | 8.95 | 51.32 | 15.30 | 84.5 | 0 |
| Products at 250 °C | 23.43 | 8.96 | 40.03 | 27.59 | 83.5 | 0.6 |
| Products at 300 °C | 14.14 | 10.57 | 55.34 | 8.15 | 59.2 | 2.3 |
| Products at 350 °C | 53.48 | 13.59 | 24.55 | 8.38 | 53.9 | 5.7 |
| Products at 400 °C | 36.40 | 10.56 | 44.78 | 8.26 | 53.1 | 9.3 |
| Products at 450 °C | 46.61 | 14.04 | 24.48 | 14.87 | 22.9 | 14.2 |
| Products at 500 °C | 2.44 | 7.66 | 8.32 | 81.57 | 8.2 | 13.9 |
| Temperature (°C) | Crude Oil | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | 550 | 600 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak area ratios (C21/bisnorhopane) | 0.014 | 0.051 | 0.082 | 0.16 | 1.6 | 6.5 | 0.91 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.01 |
| Peak area ratios (naphthalene/bisnorhopane) | 0.047 | 0.063 | 0.070 | 0.44 | 0.79 | 0.53 | 0.32 | 11 | 44 | 300 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, Y.; Song, Y.; Feng, T.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X. In Situ Combustion Characteristics of Heavy Oil in the Liaohe Oilfield at Different Temperatures. Processes 2024, 12, 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071320
Gong Y, Song Y, Feng T, Guo Y, Wang X. In Situ Combustion Characteristics of Heavy Oil in the Liaohe Oilfield at Different Temperatures. Processes. 2024; 12(7):1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071320
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Yuning, Yang Song, Tian Feng, Yong Guo, and Xusheng Wang. 2024. "In Situ Combustion Characteristics of Heavy Oil in the Liaohe Oilfield at Different Temperatures" Processes 12, no. 7: 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071320
APA StyleGong, Y., Song, Y., Feng, T., Guo, Y., & Wang, X. (2024). In Situ Combustion Characteristics of Heavy Oil in the Liaohe Oilfield at Different Temperatures. Processes, 12(7), 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071320







