The Application of Pipette-Tip and Magnetic Dummy-Template Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode Array and Spectrofluorimetric Detection for the Determination of Coumarins in Cosmetic Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Samples
2.2. Preparation of Standard Solutions
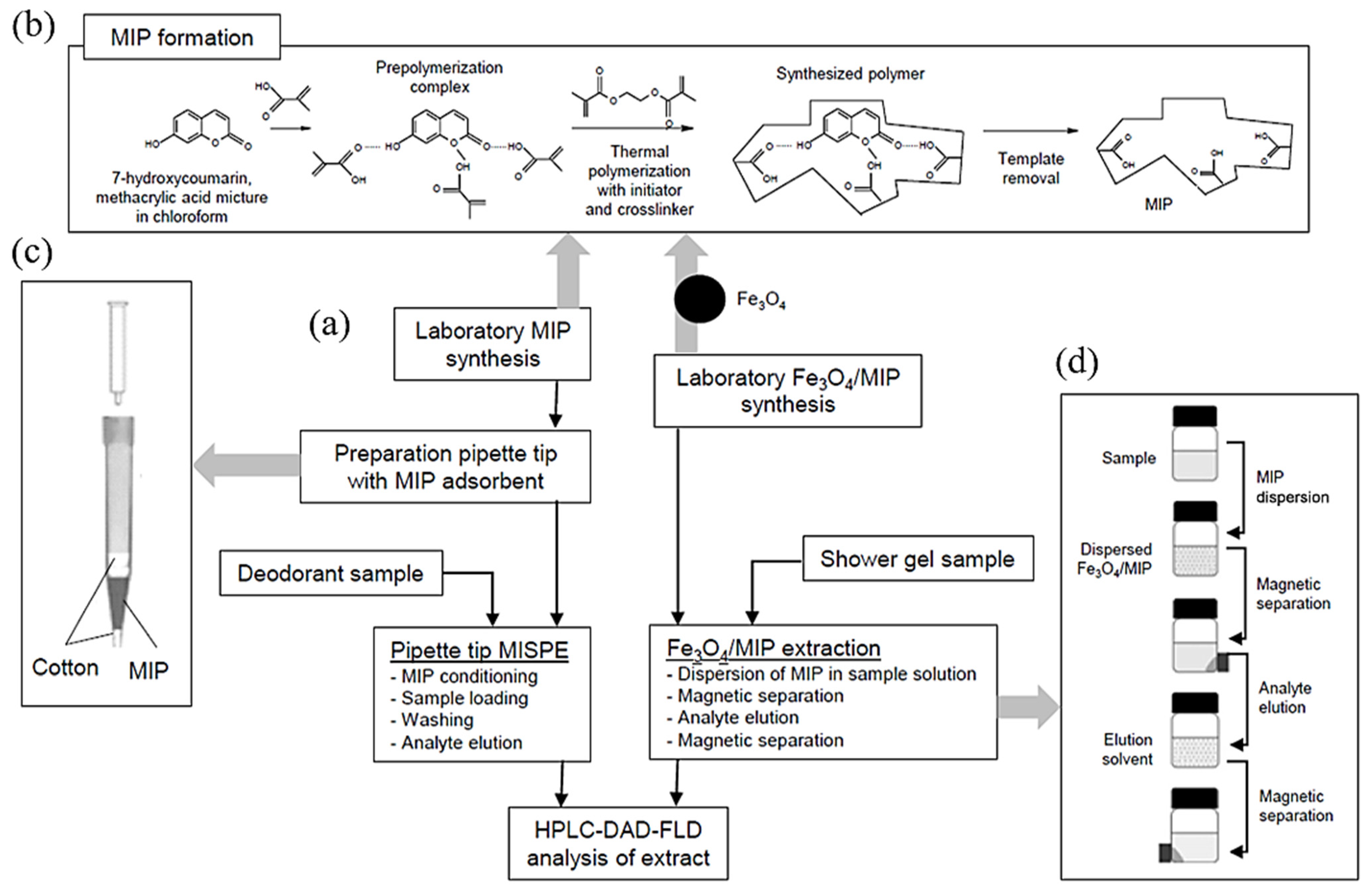
2.3. MIP and Fe3O4/MIP Synthesis
2.4. Sample Preparation
2.5. HPLC Instrumentation and Separation
2.6. Method Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
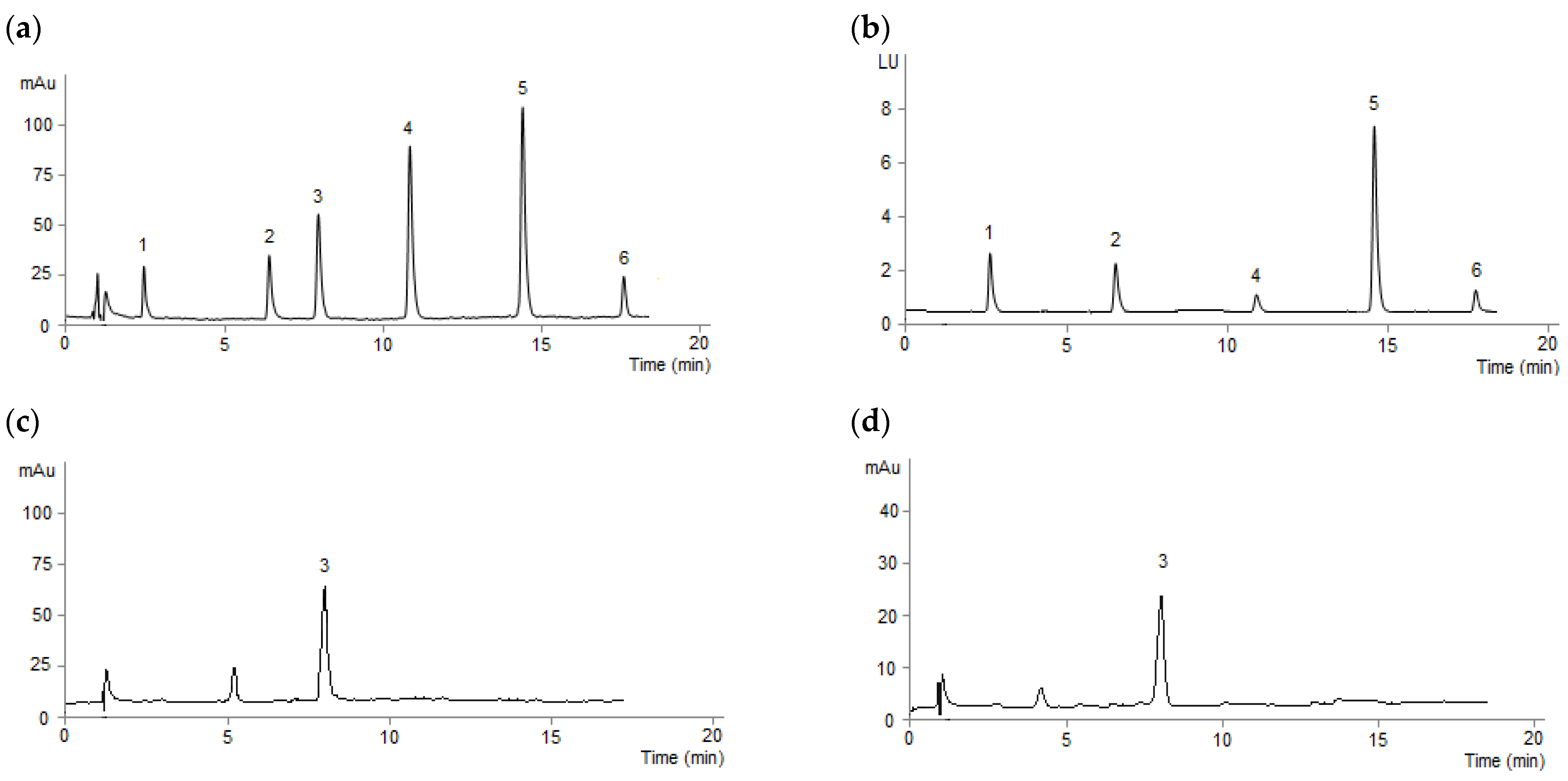
3.1. RP-HPLC-DAD-FLD Analysis
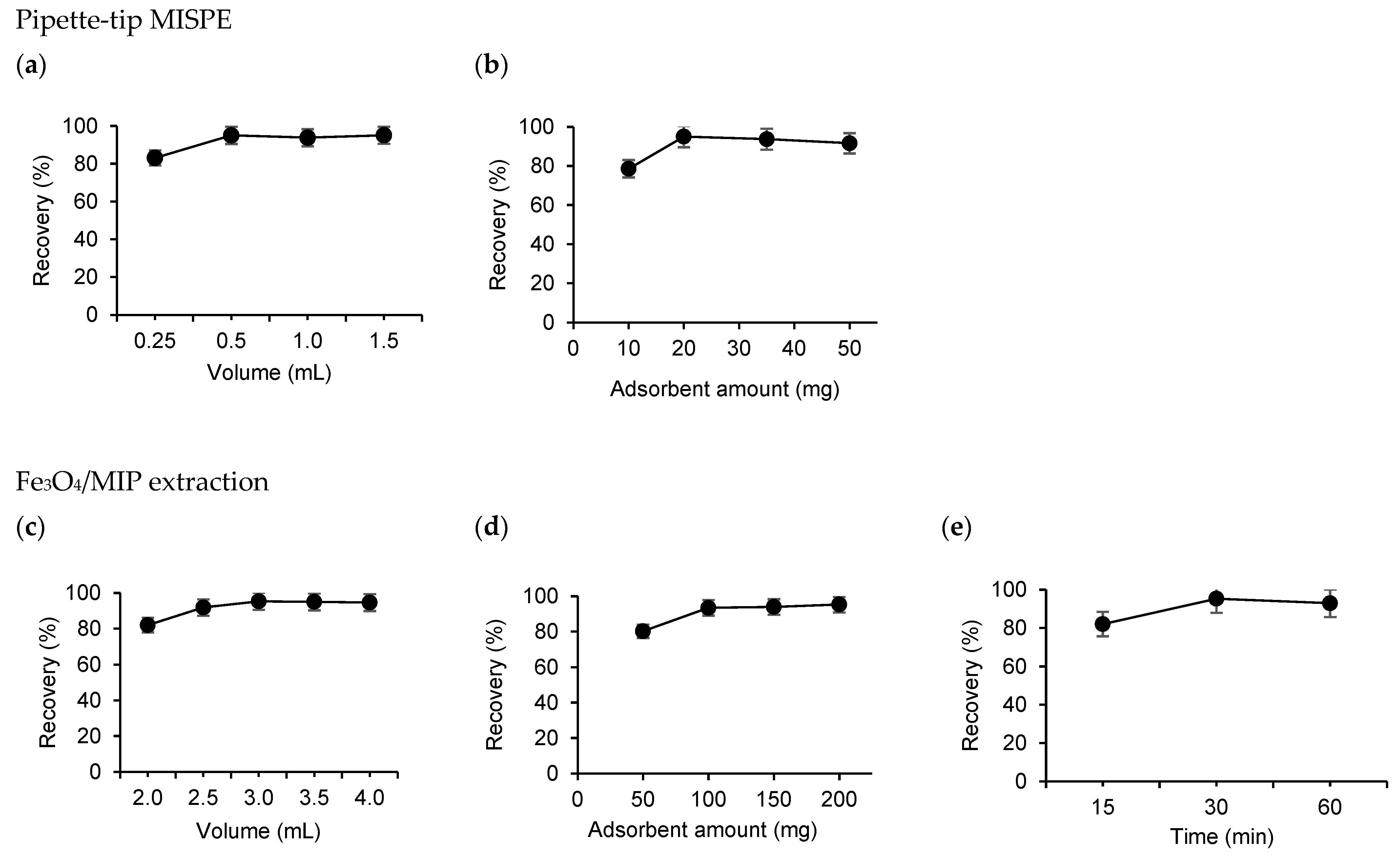
3.2. Extraction Procedure with MIP-Based Adsorbents
3.3. Method Evaluation
3.4. Comparison of the Methods and Analysis of the Method Performance
3.5. Analysis of Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hausen, B.M.; Schmieder, M. The sensitizing capacity of coumarins (I). Contact Dermat. 1986, 15, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausen, B.M.; Kallweit, M. The sensitizing capacity of coumarins (II). Contact Dermat. 1986, 15, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausen, B.M.; Berger, M. The sensitizing capacity of coumarins (III). Contact Dermat. 1989, 21, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Cruz-Martins, N.; López-Jornet, P.; Lopez, E.P.; Harun, N.; Yeskaliyeva, B.; Beyatli, A.; Sytar, O.; Shaheen, S.; Sharopov, F.; et al. Natural coumarins: Exploring the pharmacological complexity and underlying molecular mechanisms. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6492346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Pandey, A.; Manvati, S. Coumarin: An emerging antiviral agent. Helion 2020, 6, e03217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, F.; Roleira, F.; Milhazes, N.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E. Simple coumarins and analogues in medicinal chemistry: Occurrence, synthesis and biological activity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 887–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasperkiewicz, K.; Erkiert-Polguj, A.; Budzisz, E. Sunscreening and photosensitizing properties of coumarins and their derivatives. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2016, 13, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, Y.C. Emerging strategies to protect the skin from ultraviolet rays using plant-derived materials. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2021/1099 of 5 July 2021. Amending Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council on Cosmetic Products. Off. J. Eur. Union 2021, L238, 29–31. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32021R1099&rid=2 (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Pratiwi, R.; Auliya As, N.N.; Yusar, R.F.; Shofwan, A.A.A. Analysis of prohibited and restricted ingredients in cosmetics. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcolan, M.; Martins, P.A.; Pedrosa, V.A.; Rodrigues, M.R.; de Oliveira, H.P.; Codognoto, L. Spe ctrofluorimetric determination of coumarin in commercial tablets. J. Fluoresc. 2011, 21, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.F.; Wu, H.L.; Zhu, S.H.; Han, Q.J.; Fu, H.Y.; Li, S.F.; Yu, R.Q. Simultaneous determination of 6-methylcoumarin and 7-methoxycoumarin in cosmetics using three-dimensional excitation–emission matrix fluorescence coupled with second-order calibration methods. Talanta 2008, 75, 1260–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.G.; Li, J.; Xu, J.G.; Lv, Y.W.; Pan, X.J.; Dong, Y.Y. Determination of coumarins in cosmetics by high performance liquid chromatography. China Surfactant Deterg. Cosmet. 2020, 50, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Orsi, D.; Gagliardi, L.; Bolasco, A.; Tonelli, D. HPLC determination of 6-methylcoumarin and 3-pyridine methanol in toiletries for oral hygiene. Anal. Sci. 2000, 16, 1341–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiefel, C.; Schubert, T.; Morlock, G.E. Bioprofiling of cosmetics with focus on streamlined coumarin analysis. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 5242–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanalakshmi, E.; Rajesh, P.; Kandan, P.; Kesavan, M.; Jayaraman, G.; Selvaraj, A.; Priya, R. Stability of bonds, kinetic stability, energy parameters, spectral characterization, GC–MS and molecular descriptors studies on coumarine, 3-[2-(1-methyl-2-imidazolylthio)-1-oxoethyl]. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1295, 136544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmedt, B.; Canfyn, M.; Pype, M.; Baudewyns, S.; Hanot, V.; Courselle, P.; De Beer, J.O.; Rogiers, V.; De Paepe, K.; Deconinck, E. HS–GC–MS method for the analysis of fragrance allergens in complex cosmetic matrices. Talanta 2015, 131, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, R.; Yang, H. A novel up-conversion fluorescence resonance energy transfer sensor for the high sensitivity detection of coumarin in cosmetics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 290, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Li, G. Current trends in sample preparation for cosmetic analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celeiro, M.; Garcia-Jares, C.; Llompart, M.; Lores, M. Recent advances in sample preparation for cosmetics and personal care products analysis. Molecules 2021, 26, 4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Xi, H.; Ma, H.; Meng, X.; Wang, Z.; Bai, H.; Li, W.; Wang, C. Simultaneous separation and determination of 22 coumarin derivatives in cosmetics by UPLC-MS/MS. Chromatographia 2015, 78, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celeiro, M.; Vazquez, L.; Lamas, J.P.; Vila, M.; Garcia-Jares, C.; Llompart, M. Miniaturized matrix solid-phase dispersion for the analysis of ultraviolet filters and other cosmetic ingredients in personal care products. Separations 2019, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Sun, S.; Bai, H.; Ma, Q. Online coupling of matrix solid-phase dispersion to direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry for high-throughput analysis of regulated chemicals in consumer products. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1239, 340677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, D.; Yan, S.; Wen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Song, Z. Recent advances in molecularly imprinted polymers for antibiotic analysis. Molecules 2023, 28, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Song, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lv, M.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Lu, W.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Recent advances in molecular-imprinting-based solid-phase extraction of antibiotics residues coupled with chromatographic analysis. Front. Environ. Chem. 2021, 2, 703961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, L.; Erny, G.L.; Santos, L.; Alves, A. Applications of molecularly imprinted polymers to the analysis and removal of personal care products: A review. Talanta 2016, 146, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhu, C.; Liu, M.; Wu, Z.; Liu, L.; Tan, X.; Lei, F. Preparation and application of a molecular capture for safety detection of cosmetics based on surface imprinting and multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 527, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Zhao, W.; Zhai, M.; Wei, F.; Cai, Z.; Sheng, N.; Hu, Q. Molecularly imprinted layer-coated silica nanoparticles for selective solid-phase extraction of bisphenol A from chemical cleansing and cosmetics samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 658, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicario, A.; Solari, M.; Felici, E.; Aragón, L.; Bertolino, F.; Gomez, M.R. Molecular imprinting on surface of silica particles for the selective extraction of benzylparaben in flow system applied to cosmetics and water samples. Microchem. J. 2018, 142, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.Y.; Li, J.J.; Su, X.M.; Wu, Z.Y.; Li, P.F.; Lei, F.H.; Tan, X.C.; Shi, Z.W. Synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective separation and determination of metronidazole in cosmetic samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 3875–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raof, S.F.A.; Mohamad, S.; Abas, M.R. Synthesis and evaluation of molecularly imprinted silica gel for 2-hydroxybenzoic acid in aqueous solution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 5952–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Kou, L.; Chen, Z.; Qin, W. Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles based potentiometric sensor with a nanomolar detection limit. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Zhang, B.; Guo, P.; Chen, G.; Chang, C.; Fu, Q. Facile preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective extraction and determination of dexamethasone in skincare cosmetics using HPLC. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 2441–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, P.; Muhammad, T.; Wei, A.; Wu, B.; Zhou, T. A membrane-protected micro-solid-phase extraction method based on molecular imprinting and its application on the determination of local anesthetics in cosmetics. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 2675–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholami, H.; Ghaedi, M.; Arabi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Bagheri, A.R.; Mohamedian, H. Application of molecularly imprinted biomembrane for advancement of matrix solid-phase dispersion for clean enrichment of parabens from powder sunscreen samples: Optimization of chromatographic conditions and green approach. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 3839–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhu, L.; Yang, R. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer combined with solid-phase extraction for detection of kojic acid in cosmetic products. Microchem. J. 2022, 183, 108028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramina, N.A.; Asman, S. Synthesis and evaluation of green magnetic mesoporous molecularly imprinted polymers for adsorption removal of parabens from cosmetic samples. Curr. Chem. Lett. 2023, 12, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hroboňová, K.; Špačková, A.; Ondáková, M. Application of solid-phase extraction for isolation of coumarins from wine samples. Nova Biotechnol. Chim. 2019, 18, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machyňáková, A.; Hroboňová, K. Synthesis and evaluation of molecularly imprinted polymers as sorbents for selective extraction of coumarins. Chromatographia 2017, 80, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Choo, J.; Chen, L. Molecular imprinting: Green perspectives and strategies. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machyňáková, A.; Hroboňová, K. Preparation and application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective extraction of coumarins from food and plant samples. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 2168–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hroboňová, K.; Lehotay, J.; Čižmárik, J.; Sádecká, J. Comparison HPLC and fluorescence spectrometry methods for determination of coumarin derivatives in propolis. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2013, 36, 486–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machyňáková, A.; Hroboňová, K. Similtaneous determination of coumarin derivatives in natural samples by ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 56, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Xiongfeng, H.; Lvye, L.; Qun, X.; Rohre, J. Determination of Coumarins in Cosmetics; Application Note 118; Thermo Fisher Scientific: Sunnyvale, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kempinska-Kupczyk, D.; Kot-Wasik, A. The potential of LC-MS technique in direct analysis of perfume content. Monatshefte Chem. 2019, 15, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisneski, H.H. Determination of coumarin in fragrance products by capillary gas chromatography with electron capture detection. J. AOAC Int. 2001, 84, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, S.C. Analysis of fragrances in cosmetics by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. High Resolut. Chromatogr. 1995, 18, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyano, D.; Lima, T.; Ruiz Simões, F.; La-Scalea, M.; De Oliveira, H.; Codognoto, L. Electrochemical study of simple coumarin and its determination in aqueous infusion of mikania glomerata. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2014, 25, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hroboňová, K.; Špačková, A. Application of selective polymeric sorbents for extraction of coumarins from fragrance samples. Acta Chim. Slov. 2020, 13, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, M.E.I.; El-Nouby, M.A.M.; Kimani, P.K.; Lim, L.W.; Rabea, E.I. A review of the modern principles and applications of solid-phase extraction techniques in chromatographic analysis. Anal. Sci. 2022, 38, 1457–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Álvarez, M.; Turiel, E.; Martín-Esteban, A. Recent advances and future trends in molecularly imprinted polymers-based sample preparation. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, 2300157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagarová, I. Magnetic solid phase extraction as a promising technique for fast separation of metallic nanoparticles and their ionic species: A review of recent advances. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2020, 2020, 8847565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z.M.; Konieczka, P.; Namieśnik, J. Analytical eco-scale for assessing the greenness of analytical procedures. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J. A new tool for the evaluation of the analytical procedure: Green Analytical Procedure Index. Talanta 2018, 181, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Wojnowski, W. Complementary green analytical procedure index (ComplexGAPI) and sofrware. Green Chem. 2001, 23, 8657–8665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Fragrance Association. IFRA Standard—48th Amendment; International Fragrance Association: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
| Compound | tR (min) | Rs | As | HEPT (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin-6-β-D-glucoside | 2.52 | 12.18 | 1.2 | 8.5 |
| 7-Hydroxycoumarin | 6.55 | 4.40 | 1.2 | 7.1 |
| Coumarin | 8.31 | 7.57 | 1.1 | 5.7 |
| 7-Methoxycoumarin | 11.40 | 4.55 | 1.1 | 3.5 |
| 6-Methylcoumarin | 14.63 | 12.40 | 1.1 | 3.6 |
| Dicoumarol | 17.85 | 1.2 | 4.0 |
| Analyte | Detection Type | R2 | LOD (µg·mL−1) | LOQ (µg·mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin-6-β-D-glucoside | DAD | 0.9993 | 0.3 | 1.0 |
| FLD | 0.9993 | 0.001 | 0.003 | |
| Coumarin | DAD | 0.9995 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| FLD | na | na | na | |
| 7-Methoxycoumarin | DAD | 0.9987 | 0.1 | 0.4 |
| FLD | 0.9986 | 0.004 | 0.012 | |
| 6-Methylcoumarin | DAD | 0.9981 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| FLD | 0.9988 | 0.3 × 10−3 | 0.001 | |
| Dicoumarol | DAD | 0.9985 | 0.3 | 0.9 |
| FLD | 0.9878 | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| Compound | Recovery (%) | Intraday Precision a (RSD %) | Interday Precision b (RSD %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4/MIP extraction c | |||
| 6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin-6-β-D-glucoside | 73.2 | 4.2 | 4.8 |
| 7-Hydroxycoumarin | 93.7 | 3.6 | 5.0 |
| Coumarin | 86.9/81.2 | 3.7/4.1 | 3.8/5.2 |
| 7-Methoxycoumarin | 84.2 | 4.9 | 5.5 |
| 6-Methylcoumarin | 85.0 | 3.5 | 4.9 |
| Dicoumarol | 70.3 | 3.7 | 4.5 |
| Pipette-tip MISPE d | |||
| 6,7-dihydroxycoumarin-6-β-D-glucoside | 72.4 | 3.1 | 3.1 |
| 7-hydroxycoumarin | 94.6 | 2.4 | 3.8 |
| Coumarin | 94.1/102.0 | 3.5/2.8 | 4.5/3.3 |
| 7-methoxycoumarin | 89.5 | 2.9 | 4.3 |
| 6-methylcoumarin | 85.4 | 3.2 | 3.6 |
| Dicoumarol | 73.8 | 3.7 | 5.1 |
| Analyte | Sample | Method | Recovery (%) | LOD/LOQ | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-Methylcoumarin | Toothpaste | UAE–HPLC-DAD | - | 5 × 10−3 µg/ns | [14] |
| Coumarin; 7-Methoxycoumarin; 6-Methylcoumarin; Dicoumarol; 7-Ethoxy-4-methyl-coumarin | Cream | UAE–HPLC-UV | 80–94 | 0.032–0.045 µg·mL−1/ns | [44] |
| 6-Methyl-7-hydroxycoumarin; 7-Hydroxycoumarin; 4-Methyl-7-hydroxy-coumarin; 6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin; Dicoumarol; Coumarin; 7-Methoxycoumarin | Cream, lotion, shampoos, lipstick | SPE(Oasis HLB)–UPLC-MS/MS | 80–93 | ns/5 × 10−3–15 × 10−3 µg·mL−1 | [21] |
| Coumarin | Perfume | Dilution, HPLC-Q-TOF-MS | - | - | [45] |
| Coumarin | Deodorant, body lotion, cream, conditioner, bath additive | HPTLC with postchromatographic derivatization with KOH | - | 0.5 × 10−3/1.3 × 10−3 µg·mL−1 | [15] |
| Coumarin | Fragrance product | GC-ECD | 99–110 | 5 × 10−3 µg·mL−1/ns | [46] |
| Coumarin | Fragrance products | GC-MS | 80–116 | 1.0 µg·mL−1/ns | [47] |
| Coumarin | Sun block, mist spray, emulsion | Fluorescent sensor | 96–103 | 0.11 µg·mL−1/ns | [18] |
| Coumarin | Aqueous media | Square wave voltammetry with BDDE | 92–104 | 0.23/0.66 µg·mL−1 | [48] |
| 6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin-6-β-D-glucoside; 7-Hydroxycoumarin; Coumarin; 7-Methoxycoumarin; 6-Methylcoumarin; Dicoumarol | Perfume, shower gel | Pipette-tip MISPE–HPLC-DAD-FLD Fe3O4/MISPE–HPLC-DAD-FLD | 72–102 70–94 | 0.3 × 10−3–0.3/1 × 10−3–1 µg·mL−1 | This work |
| Pipette-Tip MISPE–HPLC-DAD-FLD | |||
| Eco-Scale | PPs | GAPI a | |
| Reagents | Methanol (8.2 mL) | 7 |  |
| Acetic acid (1 mL) | 5 | ||
| MIP (0.06 g) | 1 | ||
| Instruments | HPLC-DAD-FLD | 1 | |
| Occupational hazards | 0 | ||
| Waste (18.5 mL) | 8 | ||
| Total PPs | 22 | ||
| Score | 78 | ||
| Fe3O4/MISPE–HPLC-DAD-FLD | |||
| Eco-Scale | PPs | GAPI a | |
| Reagents | Methanol (9.5 mL) | 7 |  |
| Acetic acid (1.0 mL) | 5 | ||
| Fe3O4/MIP (0.3 g) | 1 | ||
| Instruments | HPLC-DAD-FLD | 1 | |
| Mixer | 0 | ||
| Vacuum evaporator | 1 | ||
| Occupational hazards | |||
| Waste (13.4 mL) | 8 | ||
| Total PPs | 23 | ||
| Score | 77 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Špačková, A.; Hroboňová, K.; Jablonský, M. The Application of Pipette-Tip and Magnetic Dummy-Template Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode Array and Spectrofluorimetric Detection for the Determination of Coumarins in Cosmetic Samples. Processes 2024, 12, 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12030582
Špačková A, Hroboňová K, Jablonský M. The Application of Pipette-Tip and Magnetic Dummy-Template Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode Array and Spectrofluorimetric Detection for the Determination of Coumarins in Cosmetic Samples. Processes. 2024; 12(3):582. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12030582
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠpačková, Andrea, Katarína Hroboňová, and Michal Jablonský. 2024. "The Application of Pipette-Tip and Magnetic Dummy-Template Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode Array and Spectrofluorimetric Detection for the Determination of Coumarins in Cosmetic Samples" Processes 12, no. 3: 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12030582
APA StyleŠpačková, A., Hroboňová, K., & Jablonský, M. (2024). The Application of Pipette-Tip and Magnetic Dummy-Template Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode Array and Spectrofluorimetric Detection for the Determination of Coumarins in Cosmetic Samples. Processes, 12(3), 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12030582






