Inclusion of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extracts and Varying Final Internal Temperatures to Influence the Antioxidant and Physicochemical Qualities of Low-Grade Beef Patties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Beef Patties
2.2. Crude Protein, Crude Fat, Moisture Content
2.3. pH Value
2.4. Cooking Loss
2.5. Water Holding Capacity
2.6. Shear Force Value
2.7. DPPH Scavenging Activity
2.8. Lipid Oxidation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. pH Value and Cooking Loss
3.2. Water Holding Capacity
3.3. Moisture, Crude Protein, and Crude Fat
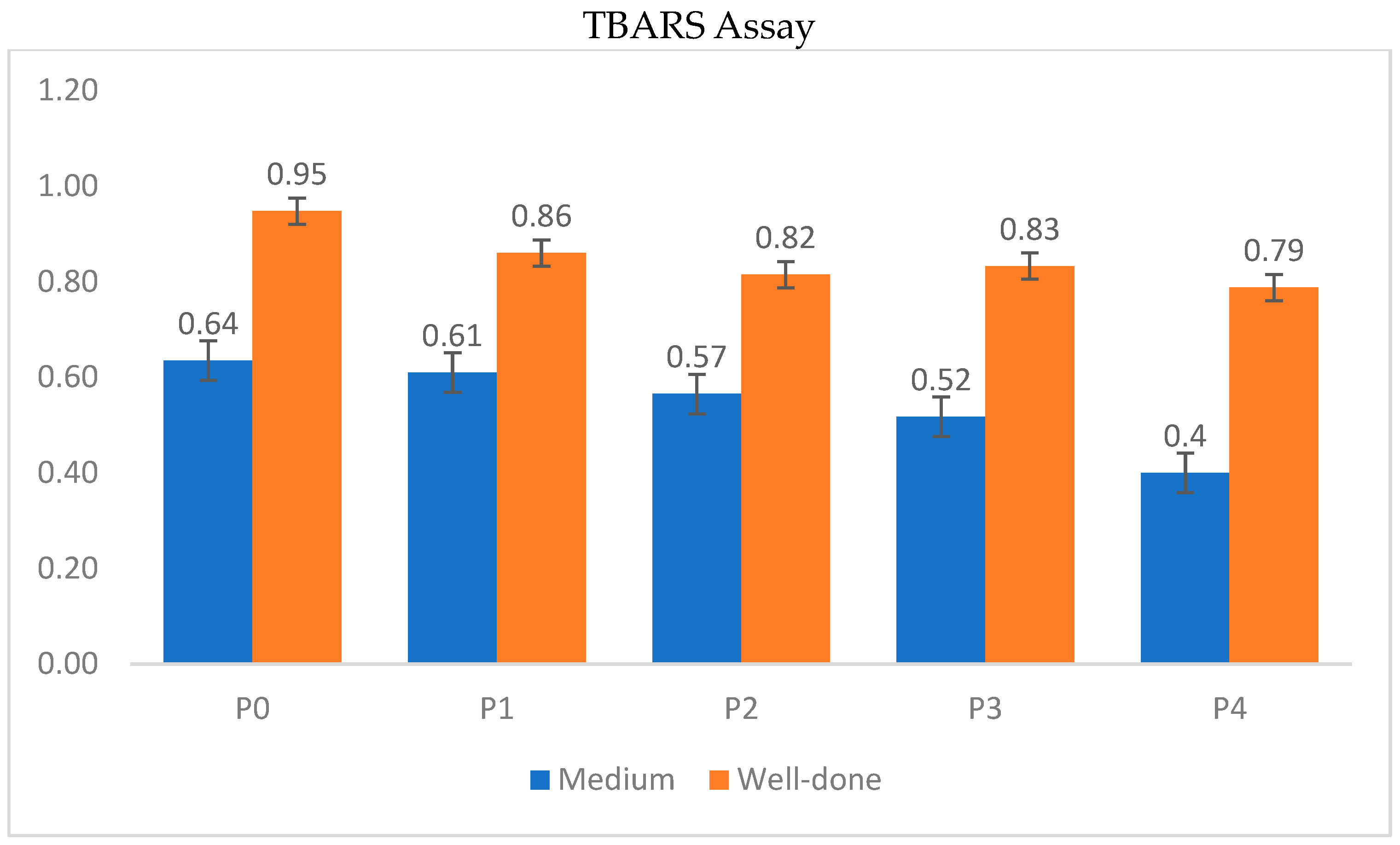
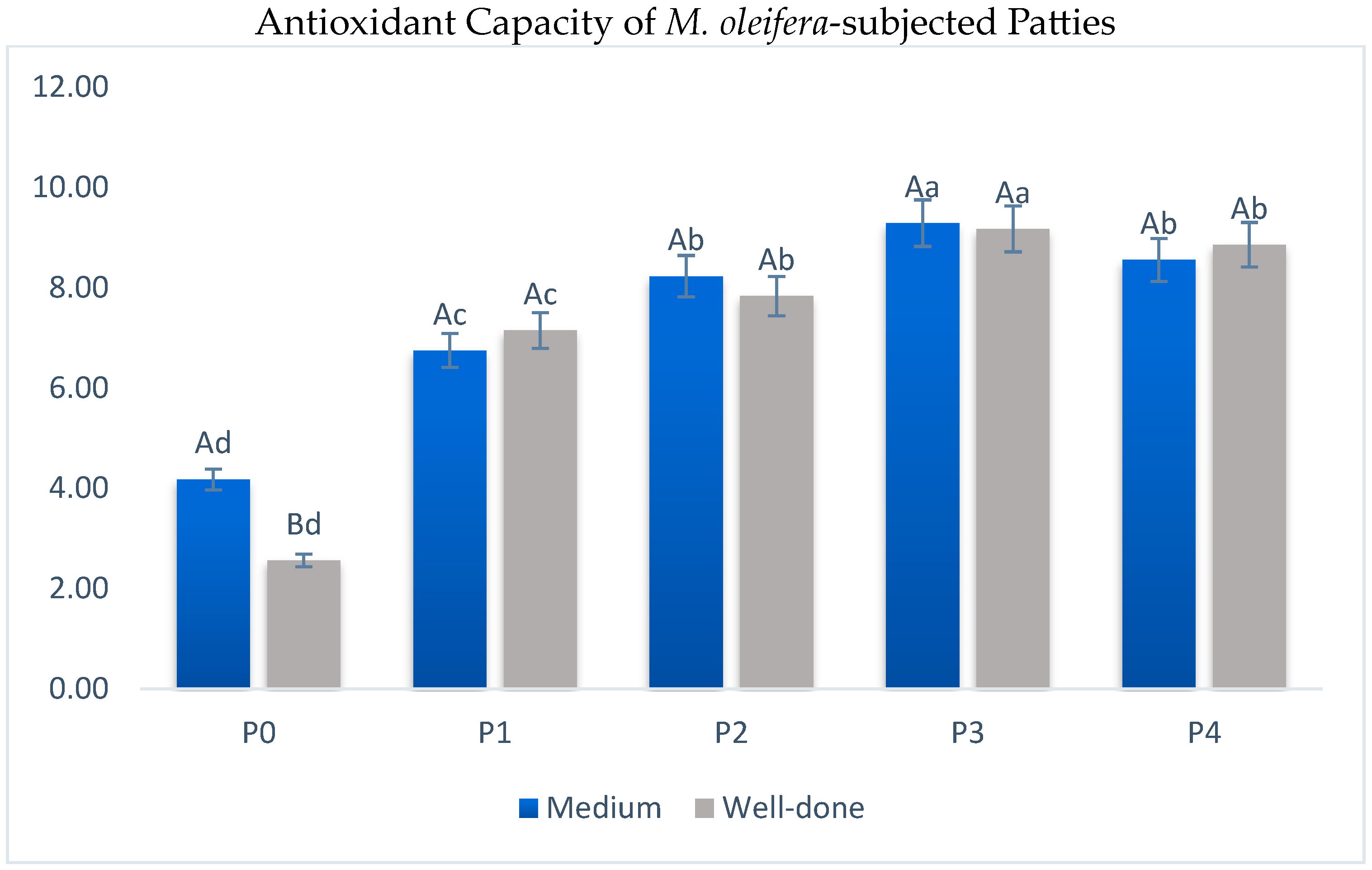
3.4. TBARS and Antioxidant Capacity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christensen, J.L.; Rama, R.; Von-Tunzelmann, N. Study on Innovation in the European Food Products and Beverages Industry; European Innovation Monitoring System, EIMS Publication, 35; European Commission, Directorate General XIII: Luxembourg, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, M.G.; Briz, J. Innovation in the Spanish food & drink industry. Int. Food Agribus. Manag. Rev. 2000, 3, 155–176. [Google Scholar]
- Bigliardi, B.; Galati, F. Innovation trends in the food industry: The case of functional foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, Z.; Islam, S.R.; Hossen, F.; Mahtab-ul-Islam, K.; Hasan, M.R.; Karim, R. Moringa oleifera is a prominent source of nutrients with potential health benefits. Int. J. Food Sci. 2021, 2021, 6627265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barido, F.H.; Jang, A.; Pak, J.I.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.K. Combined effects of processing method and black garlic extract on quality characteristics, antioxidative, and fatty acid profile of chicken breast. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Barido, F.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.; Shin, D.J.; Jang, A. Effect of Calamansi Pulp Ethanol Extracts on the Meat Quality and Biogenic Amine Formation of Pork Patty during Refrigerated Storage. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2023, 43, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varelis, P.; Melton, L.; Shahidi, F. Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Barido, F.H.; Kang, S.M.; Lee, S.K. The quality and functional improvement of retorted Korean ginseng chicken soup (Samgyetang) by enzymolysis pre-treatment with Cordyceps militaris mushroom extract. Foods 2022, 11, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barido, F.H.; Lee, S.K. Tenderness-related index and proteolytic enzyme response to the marination of spent hen breast by a protease extracted from Cordyceps militaris mushroom. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, L.C.; Monteiro, M.L.; da Costa-Lima, B.R.; Guedes-Oliveira, J.M.; Rodrigues, B.L.; Fortunato, A.R.; Baltar, J.D.; Tonon, R.V.; Koutchma, T.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Effect of microencapsulated extract of pitaya (Hylocereus costaricensis) peel on oxidative quality parameters of refrigerated ground pork patties subjected to UV-C radiation. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arihara, K. Strategies for designing novel functional meat products. Meat Sci. 2006, 74, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, S.; Samaraweera, H.; Lee, E.J.; Ahn, D.U. Improving functional value of meat products. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumar, M.; Naveena, B.M.; Vaithiyanathan, S.; Sen, A.R.; Sureshkumar, K. Effect of incorporation of Moringa oleifera leaves extract on quality of ground pork patties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 3172–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lungu, N.S.; Afolayan, A.J. Warmed-over flavour profiles, microbial changes, shelf-life and check-all-that-apply sensory analysis of cooked minced pork treated with varying levels of Moringa oleifera leaf and root powder. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10616. [Google Scholar]
- Naveena, B.M.; Muthukumar, M.; Muthulakshmi, L.; Anjaneyulu, A.S.; Kondaiah, N. Effect of different cooking methods on lipid oxidation and microbial quality of vacuum-packaged emulsion products from chicken. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2014, 38, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, H.R.; Stanfield, M.S.; Koch, E.J. Beef palatability as affected by cooking rate and final internal temperature. J. Anim. Sci. 1976, 43, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barido, F.H.; Lee, S.K. Effect of detoxified Rhus verniciflua extract on oxidative stability and quality improvement of raw chicken breast during cold storage. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2022, 64, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesteira, S.M.; Oliveira, R.L.; Silva, T.M.; Ribeiro, R.D.; Ribeiro, C.V.; Pereira, E.S.; Lanna, D.P.; Pinto, L.F.; Rocha, T.C.; Vieira, J.F.; et al. Physicochemical quality, fatty acid composition, and sensory analysis of Nellore steers meat fed with inclusion of condensed tannin in the diet. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hijazeen, M.; Lee, E.J.; Mendonca, A.; Ahn, D.U. Effects of tannic acid on lipid and protein oxidation, color, and volatiles of raw and cooked chicken breast meat during storage. Antioxidants 2016, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Prado, M.E.; Queiroz, V.A.; da Veiga Correia, V.T.; Neves, E.O.; Roncheti, E.F.; Gonçalves, A.C.; de Menezes, C.B.; de Oliveira, F.C. Physicochemical and sensorial characteristics of beef burgers with added tannin and tannin-free whole sorghum flours as isolated soy protein replacer. Meat Sci. 2019, 150, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohs, S.J.; Hartman, M.J. Review of the safety and efficacy of Moringa oleifera. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyinka, A.T.; Oyeyinka, S.A. Moringa oleifera as a food fortificant: Recent trends and prospects. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2018, 17, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razis, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.D.; Kntayya, S.B. Health benefits of Moringa oleifera. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 8571–8576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vongsak, B.; Sithisarn, P.; Gritsanapan, W. Simultaneous HPLC quantitative analysis of active compounds in leaves of Moringa oleifera Lam. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2014, 52, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, R.; Shetty, N.; Prakash, M.; Giridhar, P. Effect of dehydration methods on retention of carotenoids, tocopherols, ascorbic acid and antioxidant activity in Moringa oleifera leaves and preparation of a RTE product. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 2176–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, M.; Hekmat, S.; Ahmadi, L. Microbial and sensory evaluation of probiotic yoghurt supplemented with cereal/pseudo-cereal grains and legumes. Int. J. Dairy. Technol. 2018, 71, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nudel, A.; Cohen, R.; Abbo, S.; Kerem, Z. Developing a nutrient-rich and functional wheat bread by incorporating Moringa oleifera leaf powder and gluten. LWT 2023, 187, 115343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzana, T.; Mohajan, S.; Saha, T.; Hossain, M.N.; Haque, M.Z. Formulation and nutritional evaluation of a healthy vegetable soup powder supplemented with soy flour, mushroom, and moringa leaf. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 5, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, O.O.; Felix-Minnaar, J.V.; Jideani, V.A. Functional properties and amino acid profile of Bambara groundnut and Moringa oleifera leaf protein complex. Processes 2022, 10, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S. Determination of fat, moisture, and protein in meat and meat products by using the FOSS FoodScan near-infrared spectrophotometer with FOSS artificial neural network calibration model and associated database: Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 2007, 90, 1073–1083.Table. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoola, G.A.; Coker, H.A.; Adesegun, S.A.; Adepoju-Bello, A.A.; Obaweya, K.; Ezennia, E.C.; Atangbayila, T.O. Phytochemical screening and antioxidant activities of some selected medicinal plants used for malaria therapy in Southwestern Nigeria. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2008, 7, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Barido, F.H.; Jang, A.; Pak, J.I.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.K. The effect of pre-treated black garlic extracts on the antioxidative status and quality characteristics of Korean ginseng chicken soup (Samgyetang). Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2021, 41, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ingredients (%) | Treatments | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | |
| Beef | 81.5 | 81.5 | 81.5 | 81.5 | 81.5 |
| Ice | 7.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 |
| Egg | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| Emulsifier | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Seasonings | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Flour | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Subtotal | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| M. oleifera extracts | 0.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 |
| Variables | Doneness Level | Treatments | SEM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | |||
| pH value | Medium | 5.75 Aa | 5.72 Aa | 5.68 Aab | 5.62 Ab | 5.59 Ab | 0.00 |
| Well-done | 5.65 Aa | 5.62 Aa | 5.69 Aa | 5.68 Aa | 5.66 Aa | 0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 | ||
| Cooking Loss (%) | Medium | 5.16 B | 7.76 B | 8.41 B | 9.22 B | 8.24 B | 0.72 |
| Well-done | 11.21 A | 11.55 A | 13.47 A | 10.71 A | 16.15 A | 0.69 | |
| SEM | 0.78 | 0.24 | 0.81 | 0.52 | 0.39 | ||
| WHC (%) | Medium | 76.16 b | 80.34 a | 74.61 b | 81.63 a | 68.63 c | 0.51 |
| Well-done | 63.34 c | 81.15 a | 76.32 b | 78.15 ab | 61.46 c | 0.37 | |
| SEM | 0.46 | 0.35 | 0.68 | 0.41 | 0.55 | ||
| Variables | Doneness Level | Treatments | SEM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | |||
| Moisture (%) | Medium | 69.68 Aa | 68.11 Aa | 70.06 Aa | 70.43 Aa | 66.33 Ab | 0.10 |
| Well-done | 67.42 Bab | 66.49 Aab | 64.63 Bb | 69.34 Aa | 64.28 Bb | 0.07 | |
| SEM | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.12 | ||
| Crude Fat (%) | Medium | 2.56 Bb | 3.36 Ba | 3.67 Aa | 3.12 Ba | 2.60 Bb | 0.32 |
| Well-done | 3.53 Ab | 4.30 Aa | 4.24 Aa | 4.30 Aa | 3.48 Ab | 0.19 | |
| SEM | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.19 | 0.21 | ||
| Crude Protein (%) | Medium | 22.38 Ba | 22.13 Ba | 23.42 Ba | 23.43 Aa | 21.48 Bb | 0.15 |
| Well-done | 24.14 Ab | 24.42 Aab | 25.33 Aa | 23.73 Ab | 23.38 Ab | 0.22 | |
| SEM | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.20 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kartikasari, L.R.; Barido, F.H.; Hertanto, B.S.; Nuhriawangsa, A.M.P.; Swastike, W. Inclusion of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extracts and Varying Final Internal Temperatures to Influence the Antioxidant and Physicochemical Qualities of Low-Grade Beef Patties. Processes 2024, 12, 2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122818
Kartikasari LR, Barido FH, Hertanto BS, Nuhriawangsa AMP, Swastike W. Inclusion of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extracts and Varying Final Internal Temperatures to Influence the Antioxidant and Physicochemical Qualities of Low-Grade Beef Patties. Processes. 2024; 12(12):2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122818
Chicago/Turabian StyleKartikasari, Lilik Retna, Farouq Heidar Barido, Bayu Setya Hertanto, Adi Magna Patriadi Nuhriawangsa, and Winny Swastike. 2024. "Inclusion of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extracts and Varying Final Internal Temperatures to Influence the Antioxidant and Physicochemical Qualities of Low-Grade Beef Patties" Processes 12, no. 12: 2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122818
APA StyleKartikasari, L. R., Barido, F. H., Hertanto, B. S., Nuhriawangsa, A. M. P., & Swastike, W. (2024). Inclusion of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extracts and Varying Final Internal Temperatures to Influence the Antioxidant and Physicochemical Qualities of Low-Grade Beef Patties. Processes, 12(12), 2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122818









