The Effect of Chemical Composition on the Morphology of Pb/Zn-Containing Dust
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Method and Scheme
2.1. Materials
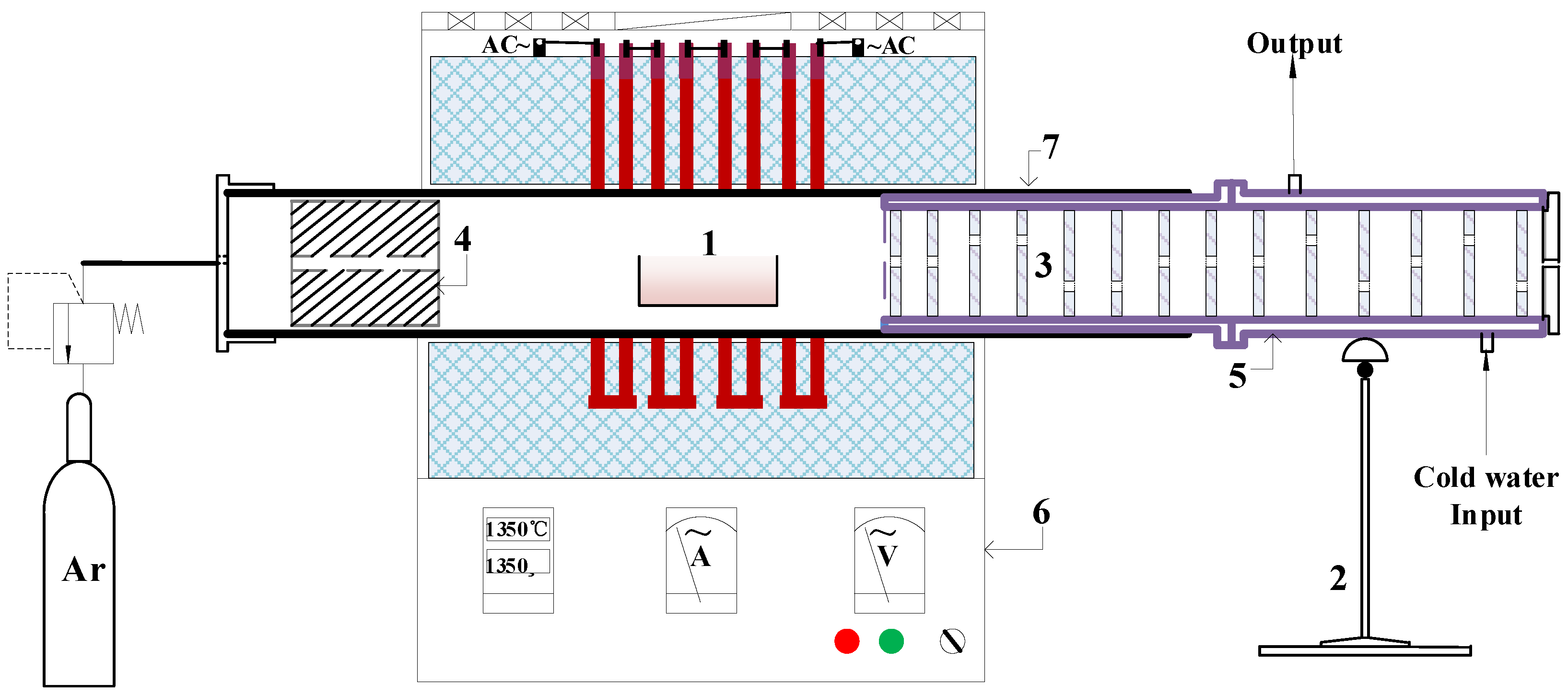
2.2. Experimental Apparatus and Procedure
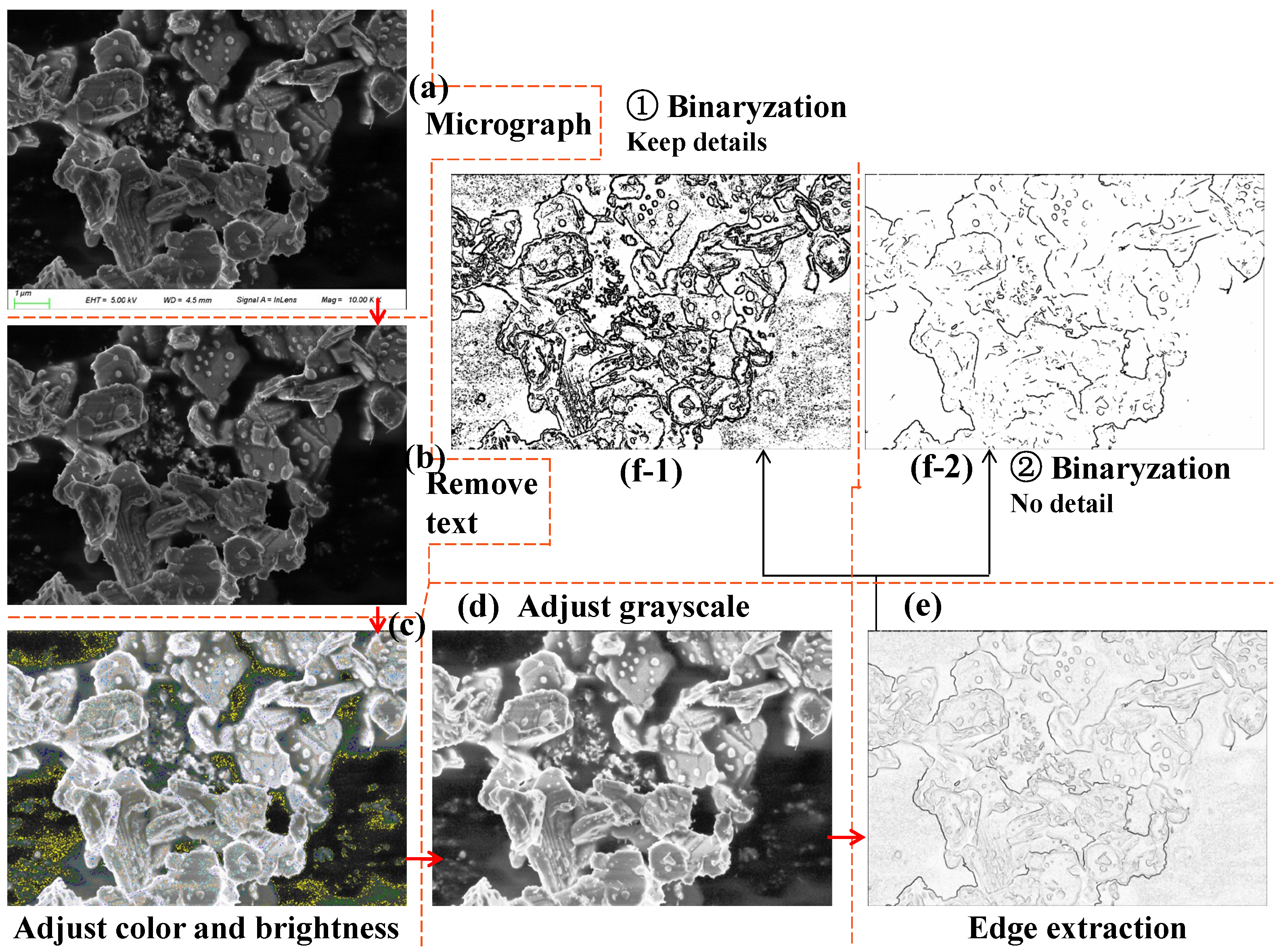
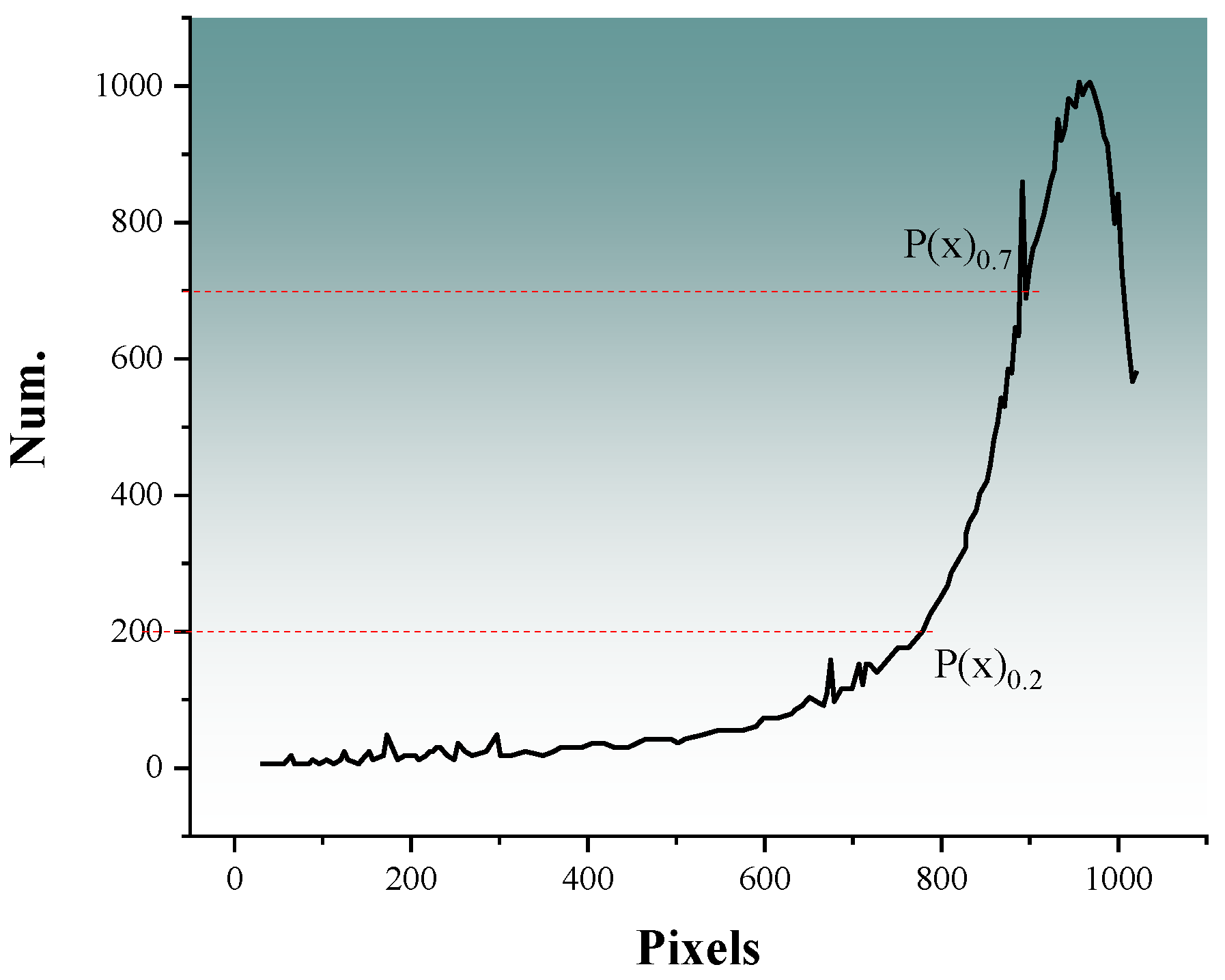
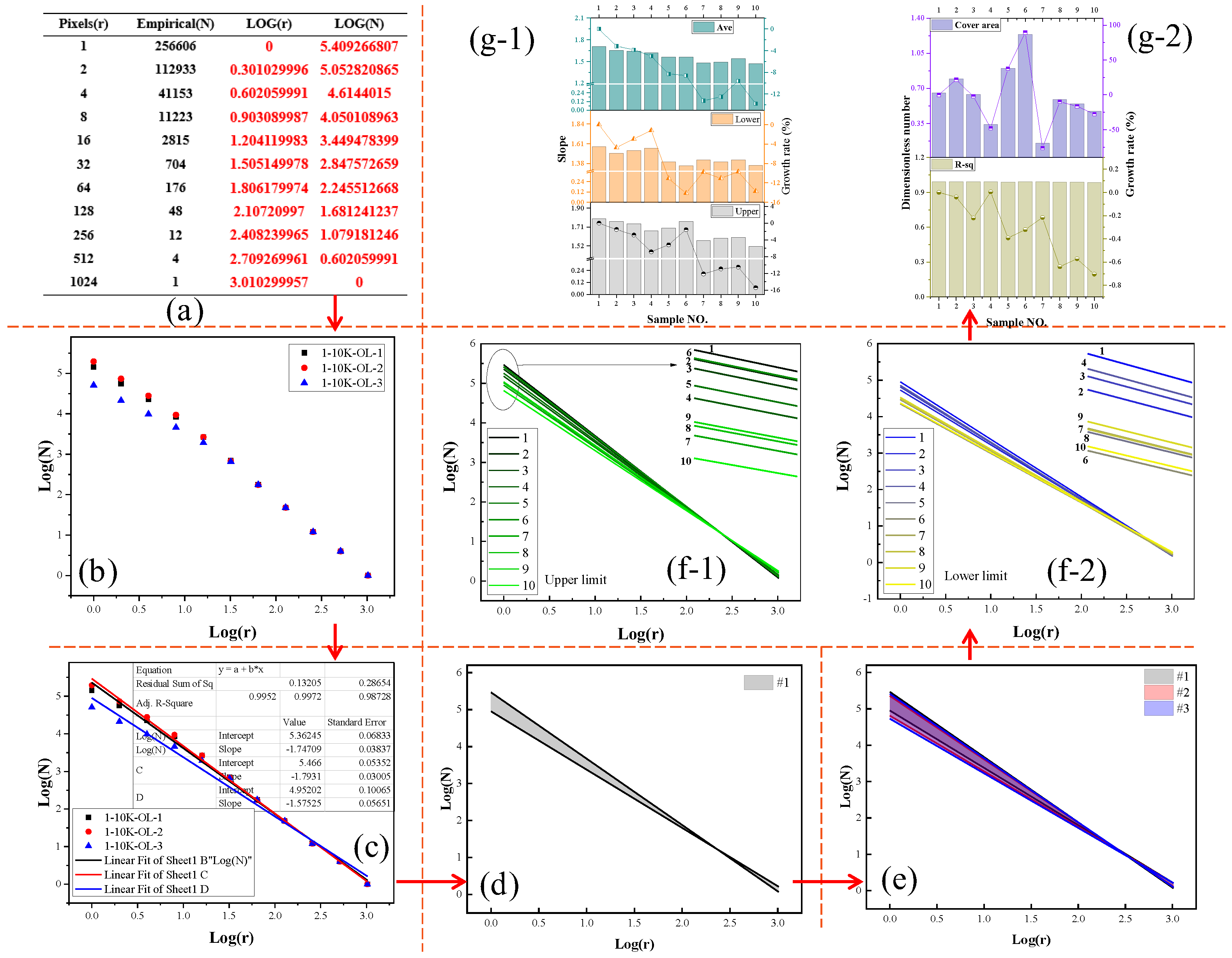
2.3. Data Processing Flow
3. Results and Discussion
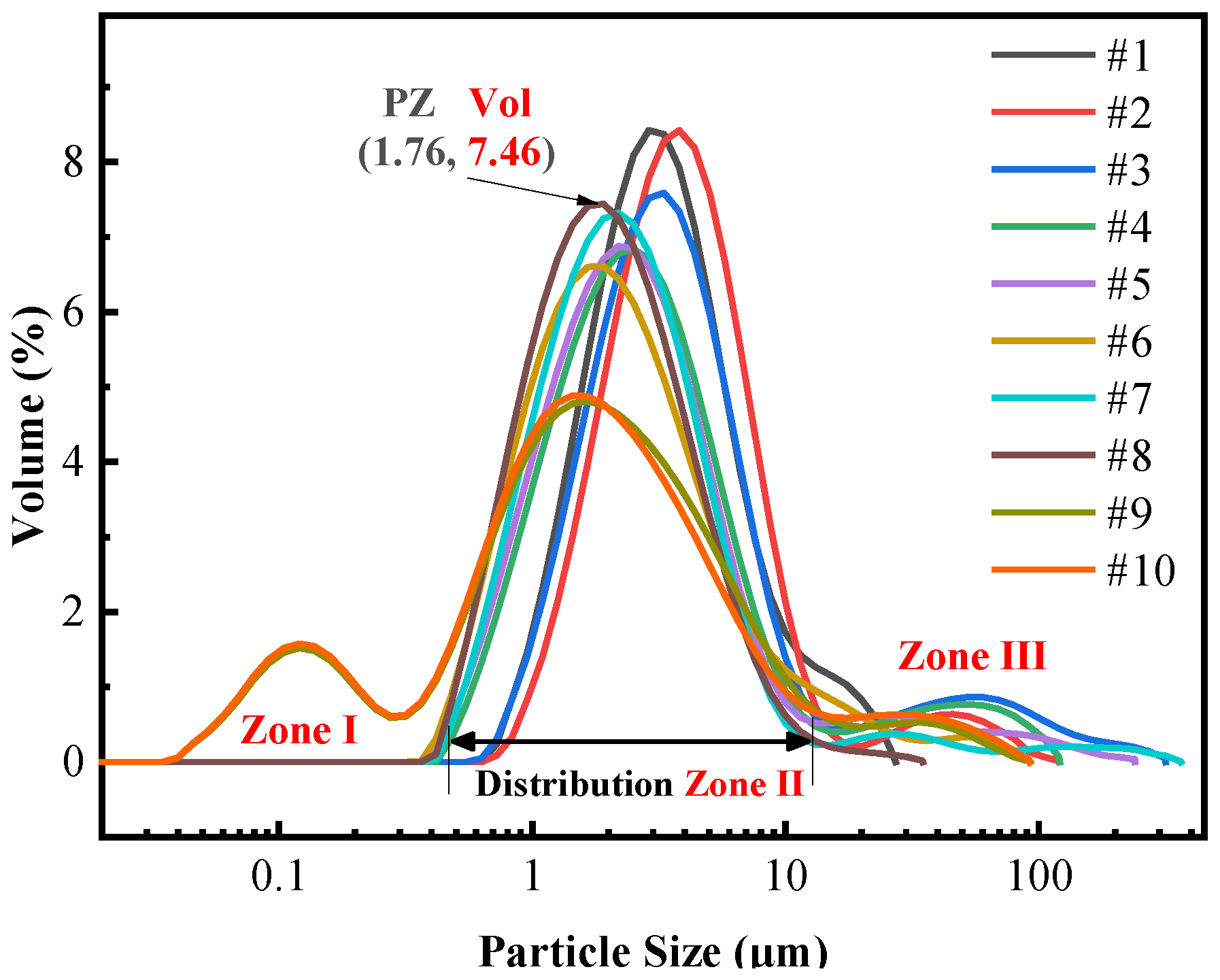
3.1. Particle Size Distribution of Dust
3.2. The Fractal Dimension of Dust
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruan, H.-J.; Su, W.-Y.; Yao, K. Box dimension and fractional integral of linear fractal interpolation functions. J. Approx. Theory 2009, 161, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowińska, K.; Adamczyk, Z. Zinc and Lead Metallurgical Slags as a Potential Source of Metal Recovery: A Review. Mater 2023, 16, 7295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kicińska, A. Physical and chemical characteristics of slag produced during Pb refining and the environmental risk associated with the storage of slag. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 2723–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.A.; Li, L.; Tian, X.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, N.; Yu, H. A review on lead slag generation, characteristics, and utilization. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurashima, K.; Matsuda, K.; Kumagai, S.; Kameda, T.; Saito, Y.; Yoshioka, T. A combined kinetic and thermodynamic approach for interpreting the complex interactions during chloride volatilization of heavy metals in municipal solid waste fly ash. Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, H.; Osada, S.; Nakata, H.; Kubota, M.; Matsuda, H. Effect of coexisting inorganic chlorides on lead volatilization from CaO–SiO2–Al2O3 molten slag under municipal solid waste gasification and melting conditions. Fuel 2013, 103, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, M.; Reiter, W.; Suer, J.; Di Sante, L.; Cirilli, F.; Praolini, F.; Mosconi, M.; Guzzon, M.; Malfa, E.; Algermissen, D.; et al. Towards the Circularity of the EU Steel Industry: Modern Technologies for the Recycling of the Dusts and Recovery of Resources. Metals 2024, 14, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D.J.C.; Barron, A.R. Pyrometallurgical removal of zinc from basic oxygen steelmaking dust—A review of best available technology. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 157, 104746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, C.-Q.; Tan, J.; Yin, Z.-L.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Liao, Z.; Zhang, P.-M.; Liu, Y. Recovery of iron from lead-zinc metallurgical slags by bath smelting. J. Cent. South Univ. 2015, 22, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.lseg.com/en/data-analytics/trading-solutions/world-bureau-metal-statistics#contact-sales (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Dehghani, S.; Moore, F.; Keshavarzi, B.; Hale, B.A. Health risk implications of potentially toxic metals in street dust and surface soil of Tehran, Iran. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 136, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, M.; Shao, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, N.; Zhou, H.; Li, W. Morphology and elemental composition of individual solid dust particles: From different sources to the atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 338, 120842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiszewski, M.; Marć, M.; Gałuszka, A.; Namieśnik, J. Green Chemistry Metrics with Special Reference to Green Analytical Chemistry. Molecules 2015, 20, 10928–10946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenta, S.; Garrigues, S.; de la Guardia, M. Green Analytical Chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 27, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.S.; Jonsson, H.H.; Maring, H.B.; Smirnov, A.; Savoie, D.L.; Cliff, S.S.; Reid, E.A.; Livingston, J.M.; Meier, M.M.; Dubovik, O.; et al. Comparison of size and morphological measurements of coarse mode dust particles from Africa. J. Geophys. Res-Atmos. 2003, 108, NO. D19, 8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reding, N.S.; Farrell, T.M.; Verma, A.; Shiflett, M.B. Effect of particle morphology on metal dust deflagration sensitivity and severity. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2021, 70, 104396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Schweizer, C.; Bagaria, P.; Kulatilaka, W.D.; Mashuga, C.V. Effect of particle morphology on dust cloud dynamics. Powder Technol. 2020, 379, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagaria, P.; Prasad, S.; Sun, J.; Bellair, R.; Mashuga, C. Effect of particle morphology on dust minimum ignition energy. Powder Technol. 2019, 355, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Song, Z.; Wang, B.; Lin, L.; Sun, L. High temperature corrosion of particulate matter during MSW combustion: Effects of particle size, inorganic minerals and additives on corrosion rates and mechanisms. Fuel 2024, 358, 130235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H. Application of fuzzy analytic evaluation method in occupational disease hazard control effect: Evaluation of a battery enterprise. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Application of Materials Science and Environmental Materials (AMSEM2016), Phuket Island, Thailand, 1–3 October 2015; pp. 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, C.; Fang, M.; Cen, J.; Wang, Q. Numerical investigation of particle re-entrainment mechanism and its suppression strategy in the high-temperature electrostatic precipitator. Powder Technol. 2024, 437, 119538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, D.; Ma, J.; Dong, Z.; Bai, L.; Kan, Q. Research on factors affecting the spread of dust pollution in conveyor belt workshop and research on wet dust reduction technology. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e299328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aust, A.E.; Cook, P.M.; Dodson, R.F. Morphological and Chemical Mechanisms of Elongated Mineral Particle Toxicities. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B. 2011, 14, 40–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciej, S.; Jerzy, M.; Luďka, H.; Martin, K.; Richard, K.; Lubos, K.; Marta, P.; Alena, O.; Tomasz, R. Fine dust after sanding untreated and thermally modified spruce, oak, and meranti wood. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2023, 81, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoli, A.; Favoni, O. Particle size, size distribution and morphological evaluation of airborne dust particles of diverse woods by Scanning Electron Microscopy and image processing program. Powder Technol. 2012, 225, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.M.G.; Addison, J.; McIntosh, C.; Miller, B.G.; Niven, K. Variations in the Carcinogenicity of Tremolite Dust Samples of Differing Morphology. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1991, 643, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coz, E.; Moreno, F.J.G.; Casuccio, G.S.; Artíñano, B. Variations on morphology and elemental composition of mineral dust particles from local, regional, and long-range transport meteorological scenarios. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Uno, I.; Wang, Z.; Nishizawa, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Sun, Y.; Fu, P.; Tang, X.; et al. Real-time observational evidence of changing Asian dust morphology with the mixing of heavy anthropogenic pollution. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, T.; Qu, C.; Bi, J.; Huang, L. Evaluation and source identification of trace element contamination of soils in the Qixia lead-zinc mining area, Jiangsu, China. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 1703–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Sun, K.; Surong, W.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. Monte Carlo Simulation-Based Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Soil Pollution: A Case Study in the Qixia Mining Area, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2012, 18, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ji, H. Microscopic morphology and seasonal variation of health effect arising from heavy metals in PM2.5 and PM10: One-year measurement in a densely populated area of urban Beijing. Atmos. Res. 2018, 212, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Niu, H.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Z.; Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Shang, D.; Hu, M. Insights into a dust event transported through Beijing in spring 2012: Morphology, chemical composition and impact on surface aerosols. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashek, W.V.; Olenchock, S.A.; Mayfield, J.E.; Wirtz, G.H.; Wolz, D.E.; Young, C.A. Carbohydrate and protein contents of grain dusts in relation to dust morphology. Environ. Health Perspect. 1986, 66, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshel, G.; Levy, G.J.; Mingelgrin, U.; Singer, M.J. Critical Evaluation of the Use of Laser Diffraction for Particle-Size Distribution Analysis. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature; Freeman and Co.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- King, R.D.; Brown, B.; Hwang, M.; Jeon, T.; George, A.T. Fractal dimension analysis of the cortical ribbon in mild Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage 2010, 53, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, M.; Chang, Y. Lower Assouad type dimensions of uniformly perfect sets in doubling metric spaces. Fractals 2020, 28, 2050039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, Z.; Abd, N.; Rashid; Fauzi, S.H.M.; Shahrim, Z.; Marangoni, A.G. Fractal dimension in palm oil crystal networks during storage by image analysis and rheological measurements. Marangoni 2015, 64, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, L.; Yu, X.; Zhou, B. Direct Numerical Simulation of Inclusion Cluster Floating Behavior in Molten Steel Using Lattice Boltzmann Method. Steel Res. Int. 2015, 86, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risović, D.; Poljaček, S.M.; Furić, K.; Gojo, M. Inferring fractal dimension of rough/porous surfaces—A comparison of SEM image analysis and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy methods. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 3063–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gneiting, T.; Ševčíková, H.; Percival, D.B. Estimators of Fractal Dimension: Assessing the Roughness of Time Series and Spatial Data. Stat. Sci. 2012, 27, 247–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bipin NB, J.; Rani, N.S. A modified deep semantic binarization network for degradation removal in palm leaf manuscripts. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 62937–62969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Xu, C.-Z.; Zhang, L.; Kong, H. GSB: Group superposition binarization for vision transformer with limited training samples. Neural Netw. 2024, 172, 106133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.-D.; Zhao, J.-X. Volatilisation Behaviour and Mechanism of Lead-Containing Slag during Physical Property Tests. Mater 2024, 17, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snodgrass, J.G.; Vanderwart, M. A standardized set of 260 pictures: Norms for name agreement, image agreement, familiarity, and visual complexity. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Learn. Mem. 1980, 6, 174–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
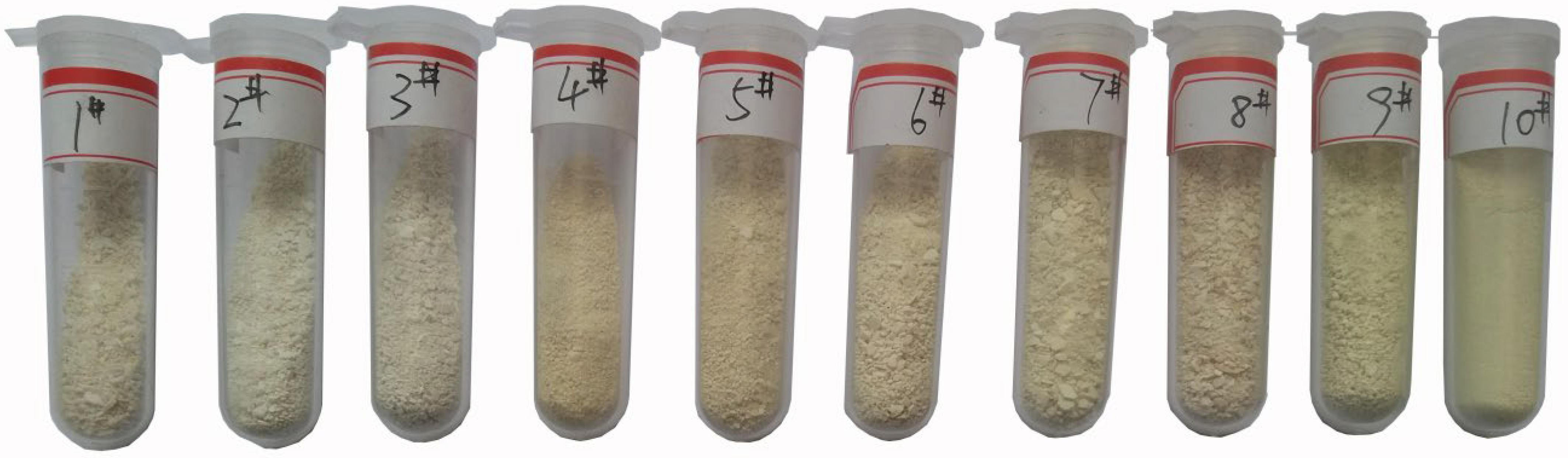


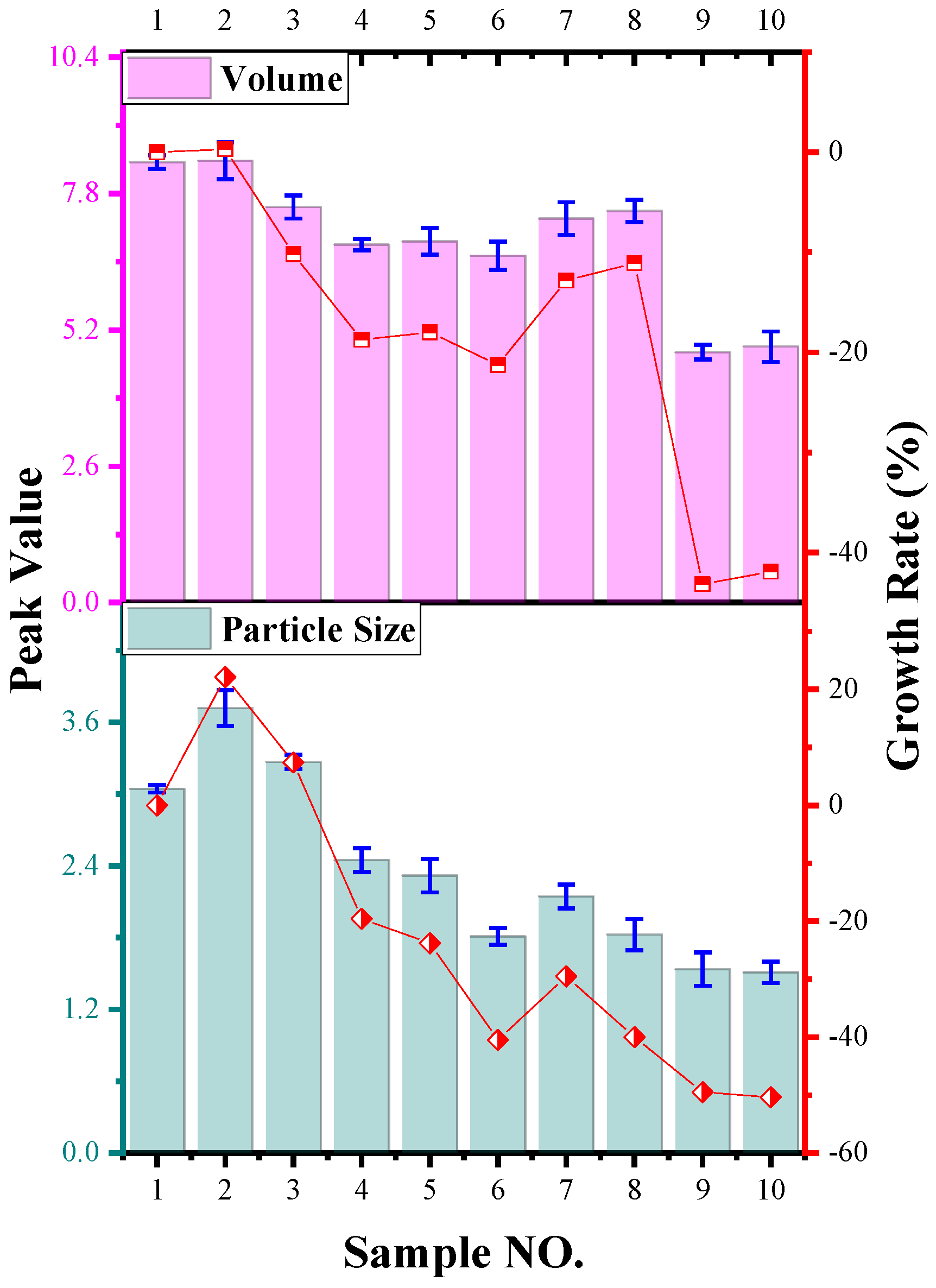
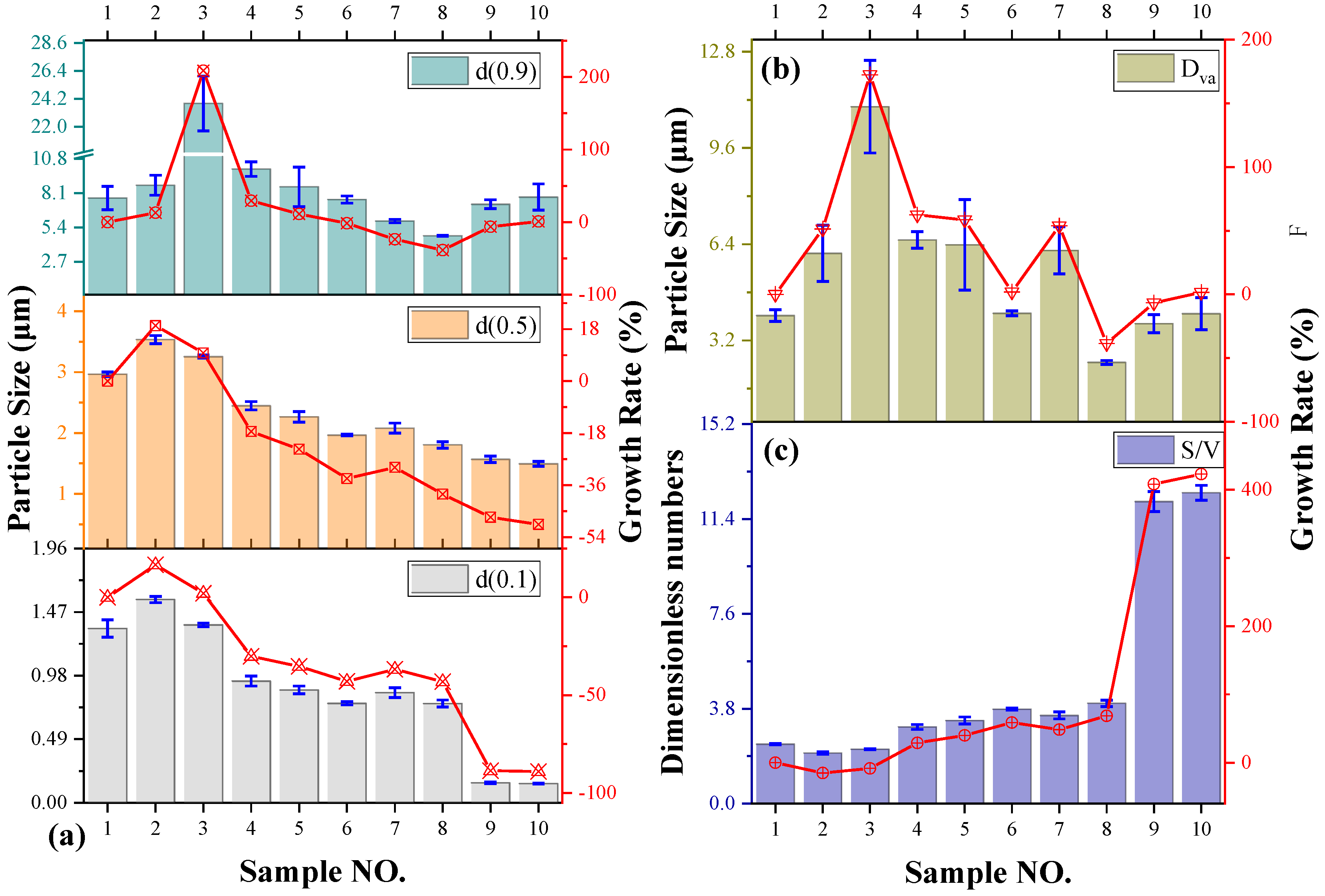
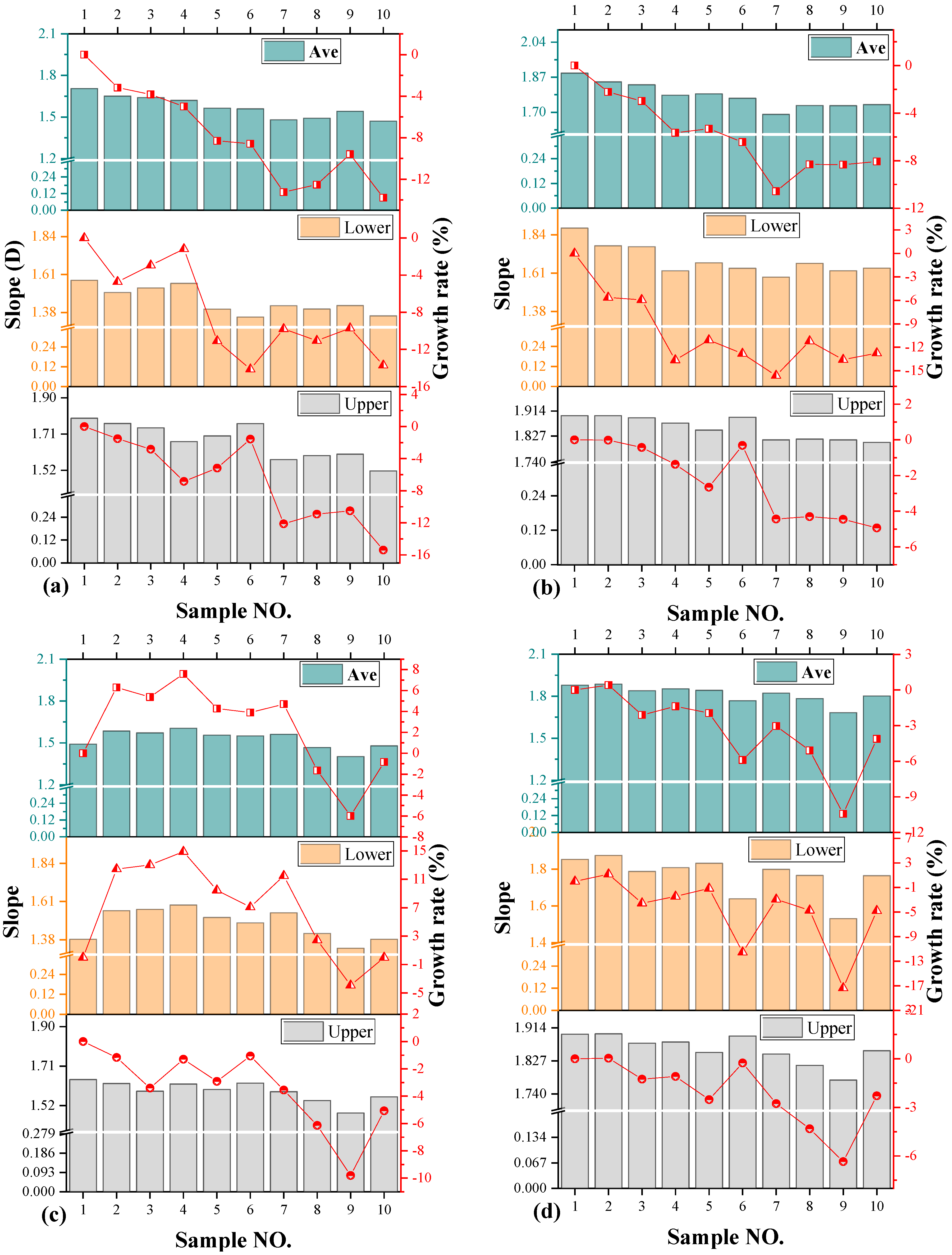

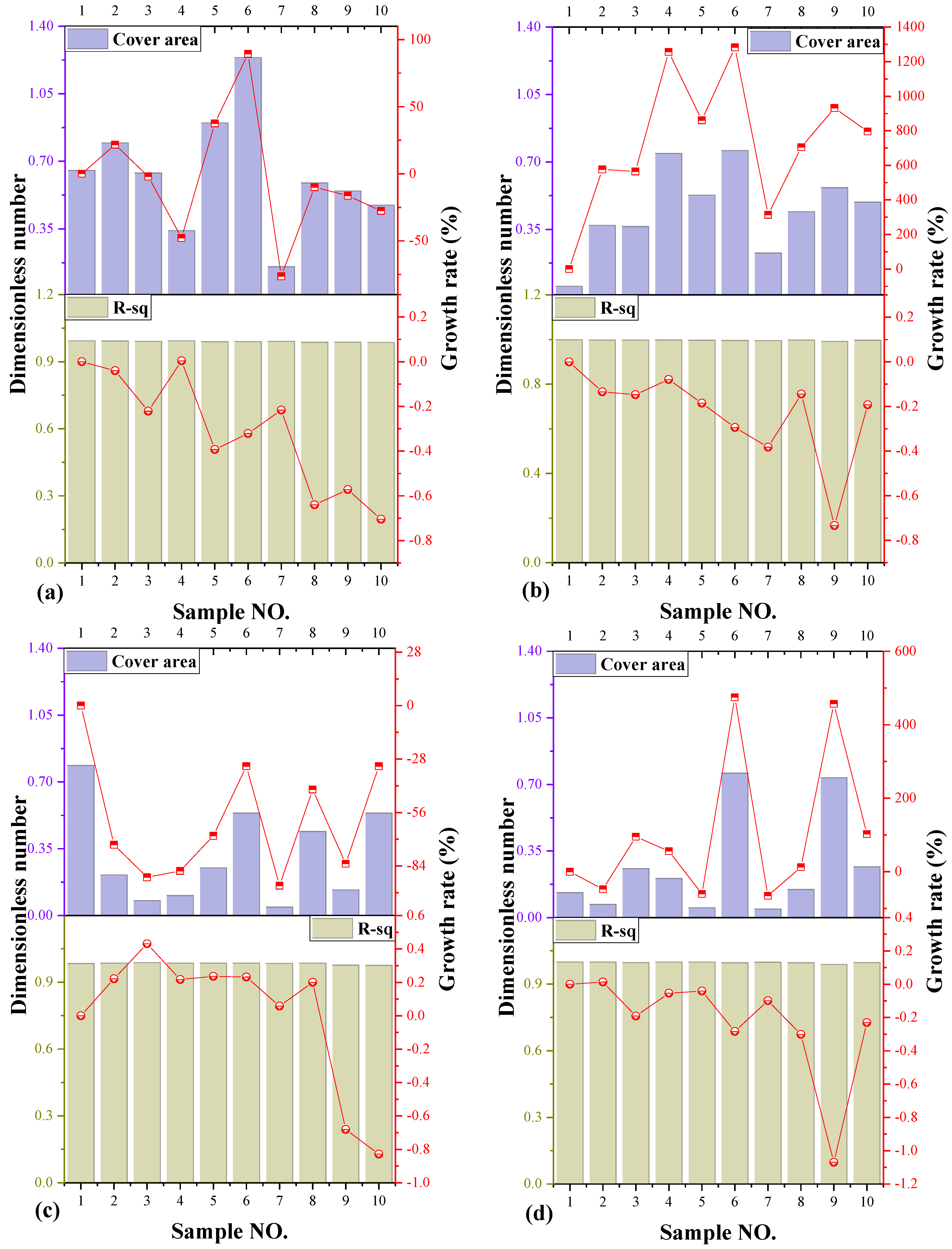
| NO. | Dust Composition (%, ω) | Slag Composition (%, ω) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO | PbO | PbO | ZnO | FeOt | CaO | SiO2 | |
| #1 | 9.607 | 90.393 | 2.69 | 13 | 44.97 | 11.24 | 28.10 |
| #2 | 4.884 | 95.116 | 10 | 11 | 42.13 | 10.53 | 26.33 |
| #3 | 3.898 | 96.102 | 20 | 10 | 37.33 | 9.33 | 23.33 |
| #4 | 1.457 | 98.543 | 40 | 6 | 28.42 | 11.37 | 14.21 |
| #5 | 1.368 | 98.632 | 40 | 6 | 27.00 | 10.13 | 16.88 |
| #6 | 1.313 | 98.687 | 40 | 6 | 30.38 | 6.75 | 16.88 |
| #7 | 1.095 | 98.905 | 40 | 6 | 25.41 | 12.71 | 15.88 |
| #8 | 0.797 | 99.202 | 40 | 6 | 28.80 | 7.20 | 18.00 |
| #9 | 0.719 | 99.281 | 40 | 6 | 28.59 | 9.53 | 15.88 |
| #10 | 0.552 | 99.448 | 40 | 6 | 31.76 | 6.35 | 15.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, W.; Li, Q.; Huang, N.; Wang, S. The Effect of Chemical Composition on the Morphology of Pb/Zn-Containing Dust. Processes 2024, 12, 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122734
Tang W, Li Q, Huang N, Wang S. The Effect of Chemical Composition on the Morphology of Pb/Zn-Containing Dust. Processes. 2024; 12(12):2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122734
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Wendan, Qian Li, Na Huang, and Shuoran Wang. 2024. "The Effect of Chemical Composition on the Morphology of Pb/Zn-Containing Dust" Processes 12, no. 12: 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122734
APA StyleTang, W., Li, Q., Huang, N., & Wang, S. (2024). The Effect of Chemical Composition on the Morphology of Pb/Zn-Containing Dust. Processes, 12(12), 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122734






