Linear Programming-Based Sparse Kernel Regression with L1-Norm Minimization for Nonlinear System Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Conversion of QP to LP in SVR
3. Kernel Regression Models with Guaranteed Modeling Accuracy and Sparsity
3.1. Kernel Regression Models with Guaranteed Modeling Accuracy
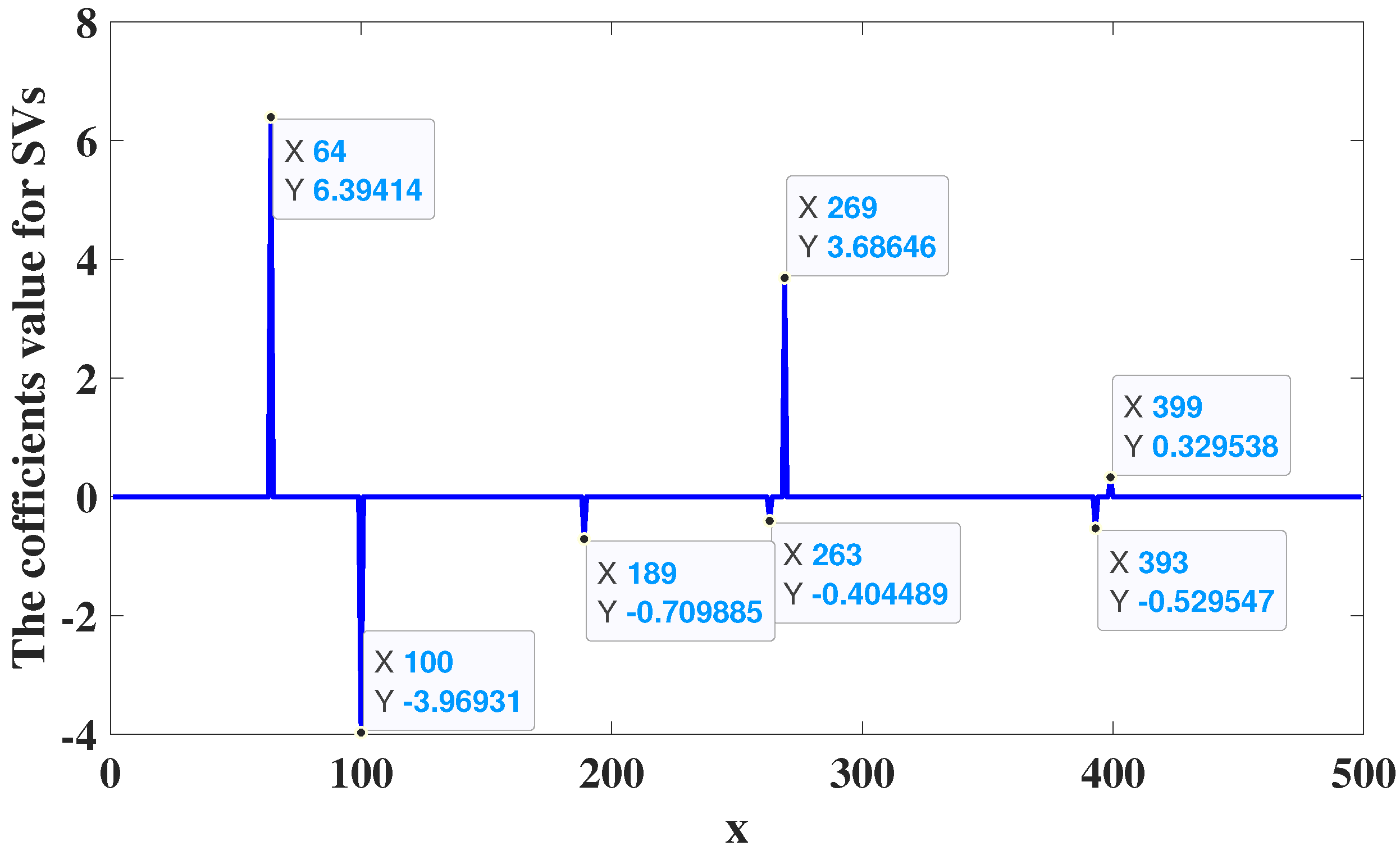
3.2. Kernel Regression Models with Guaranteed Sparsity
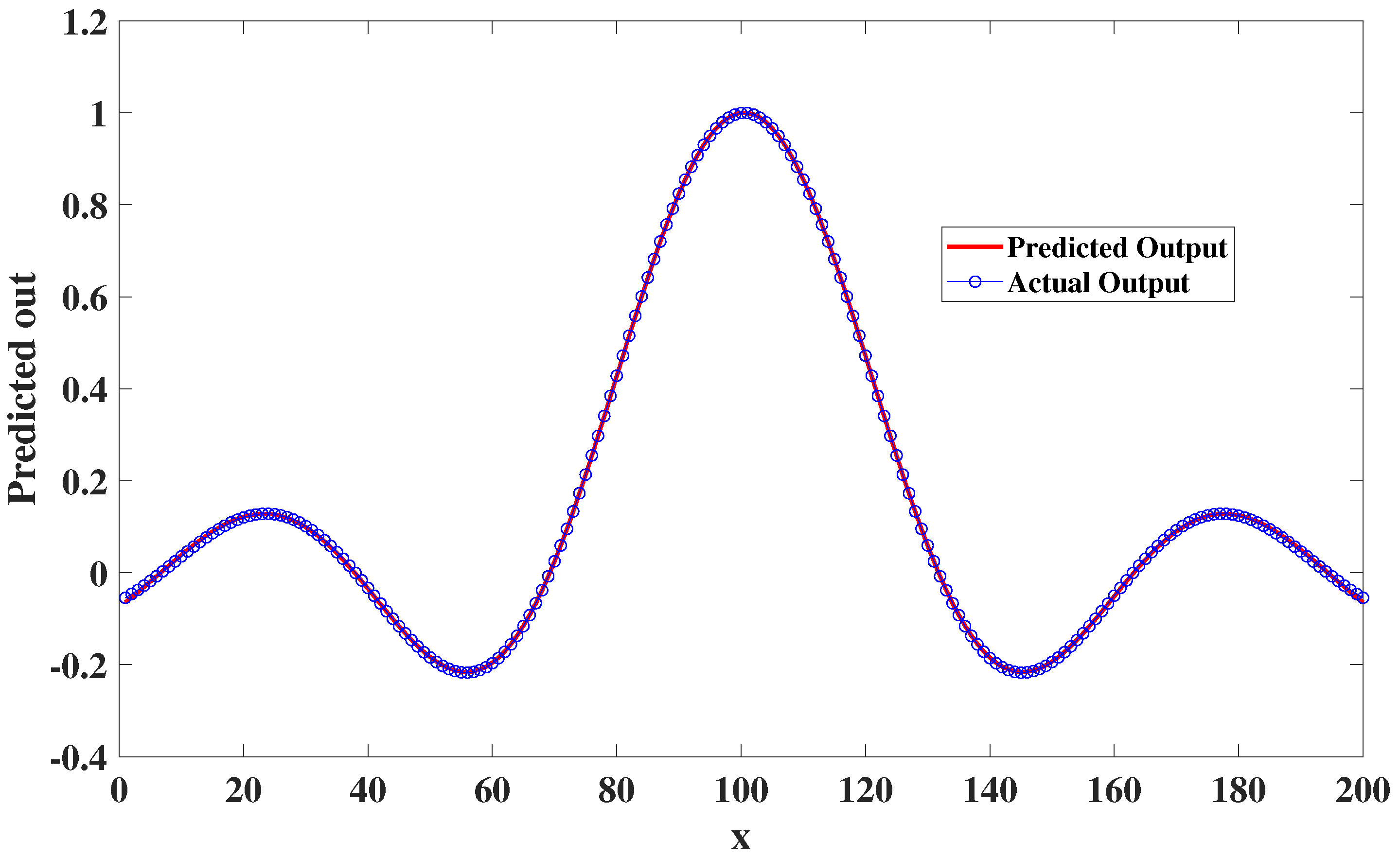
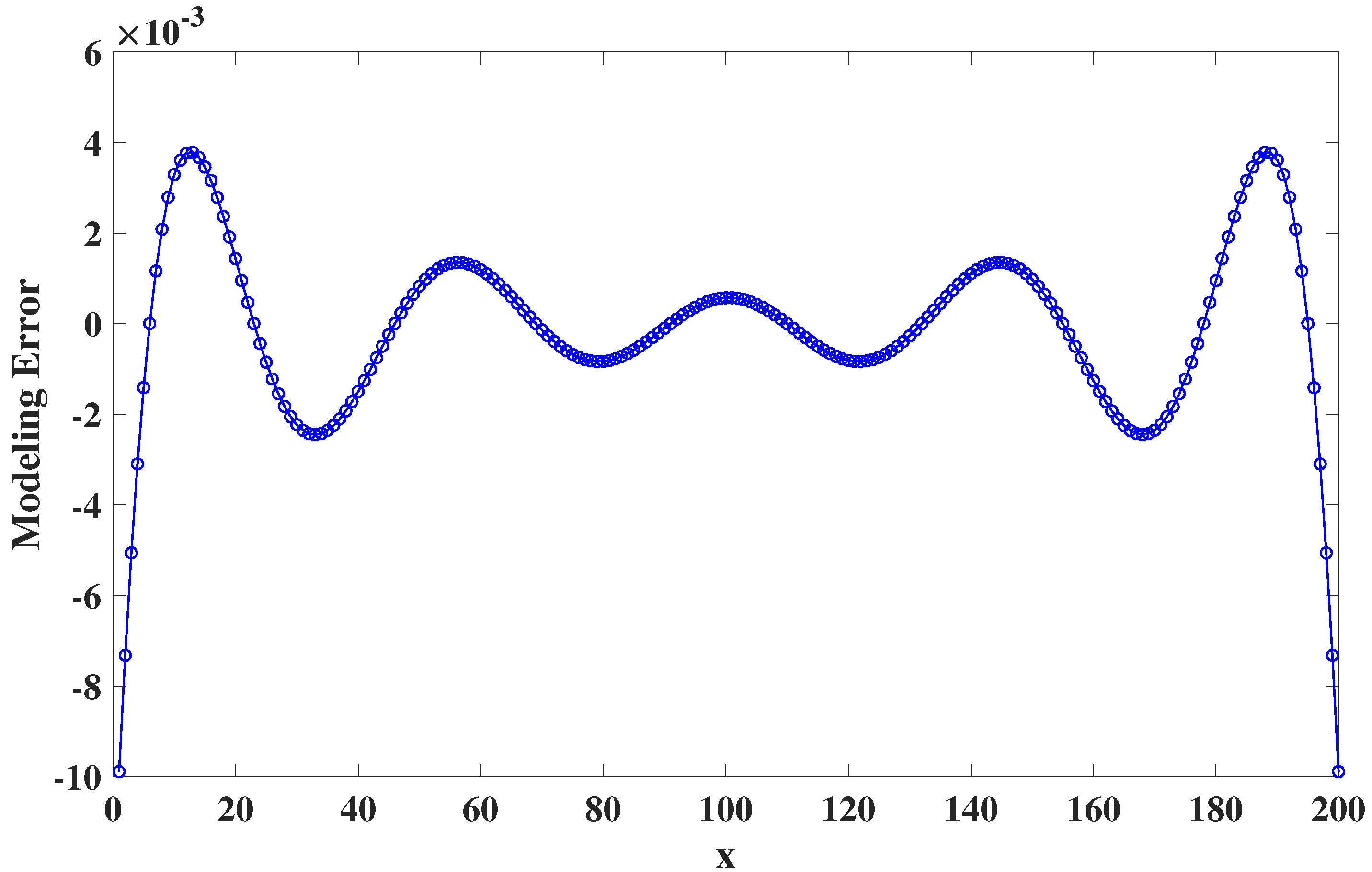
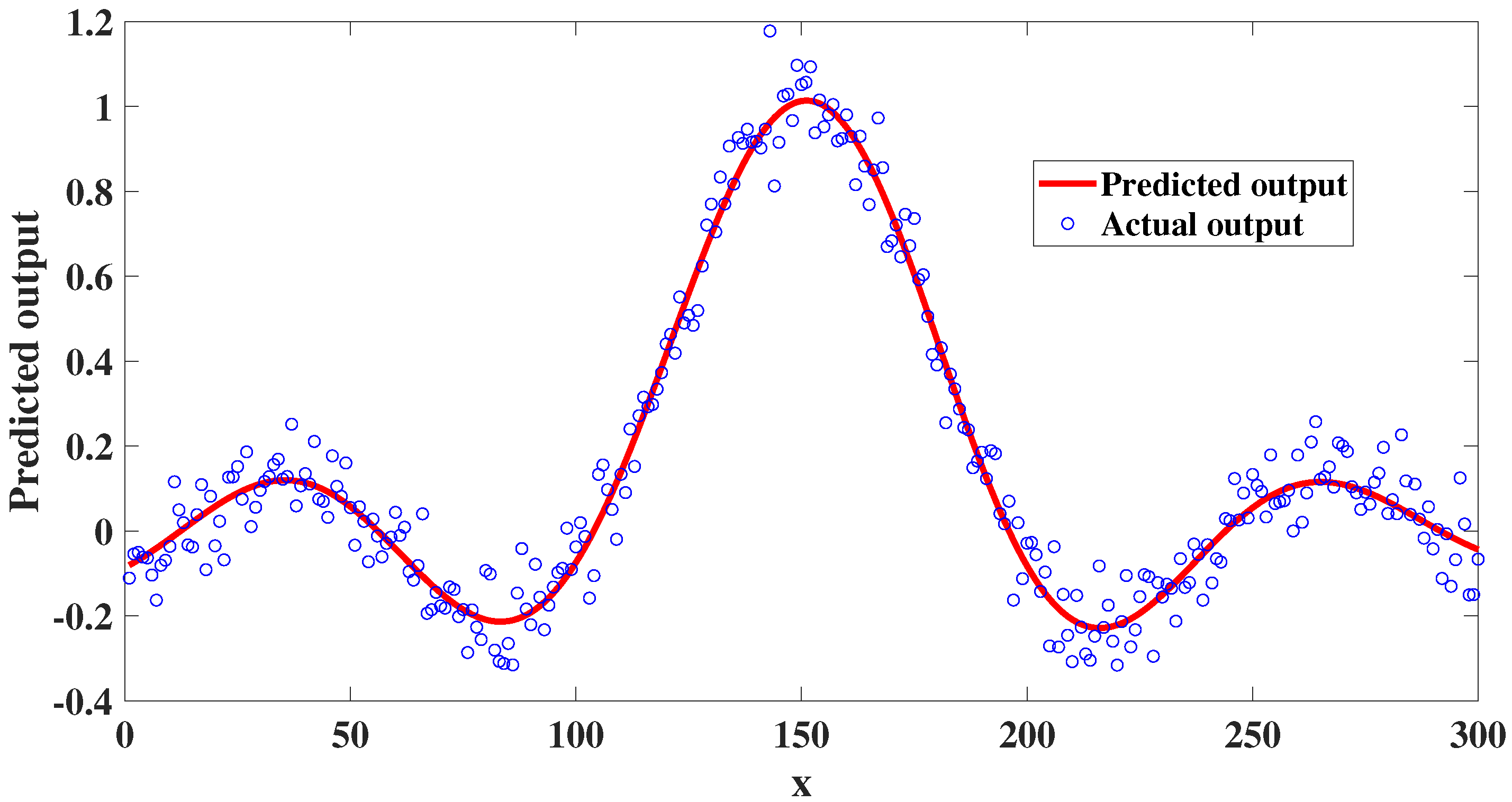
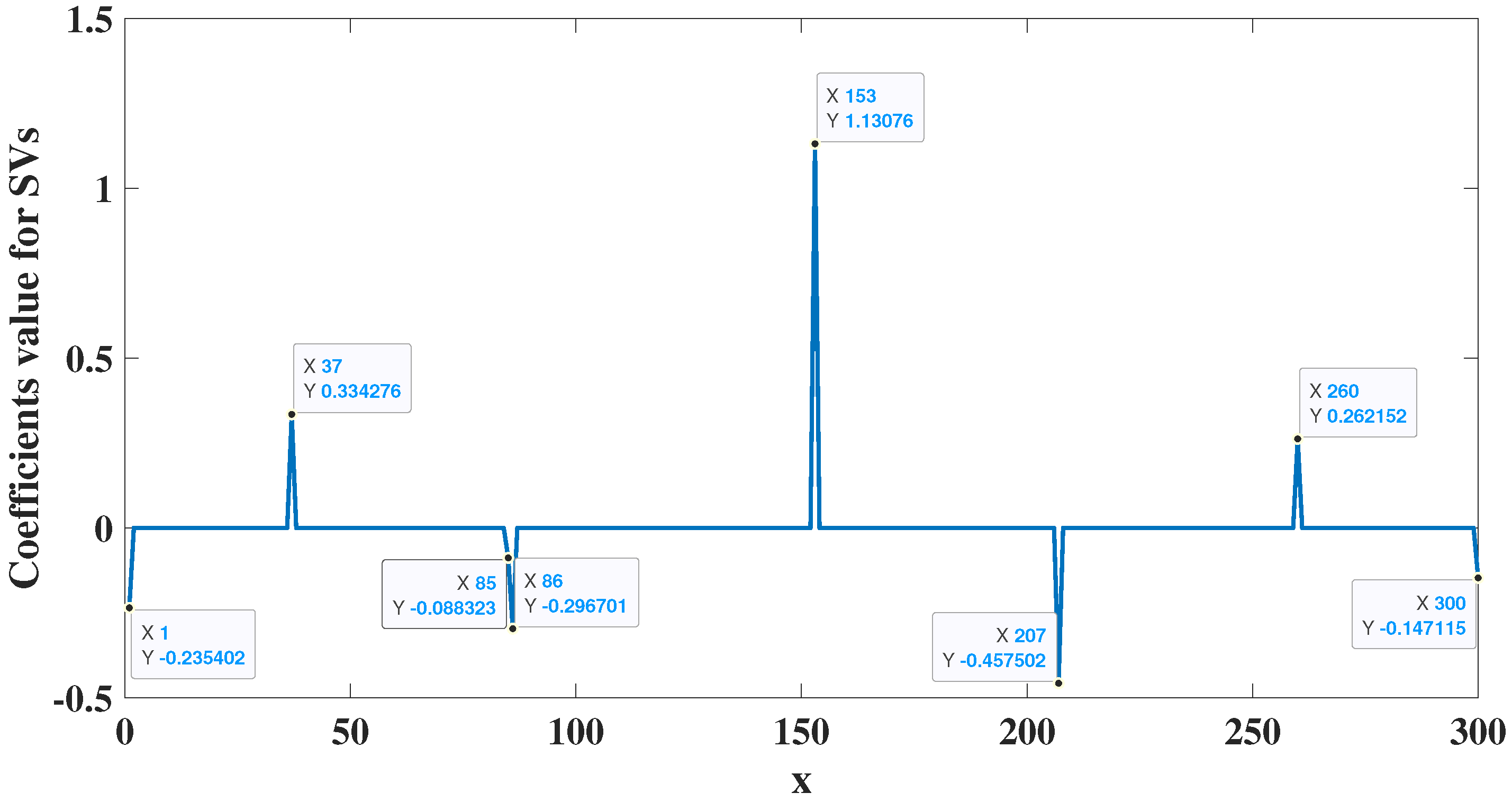
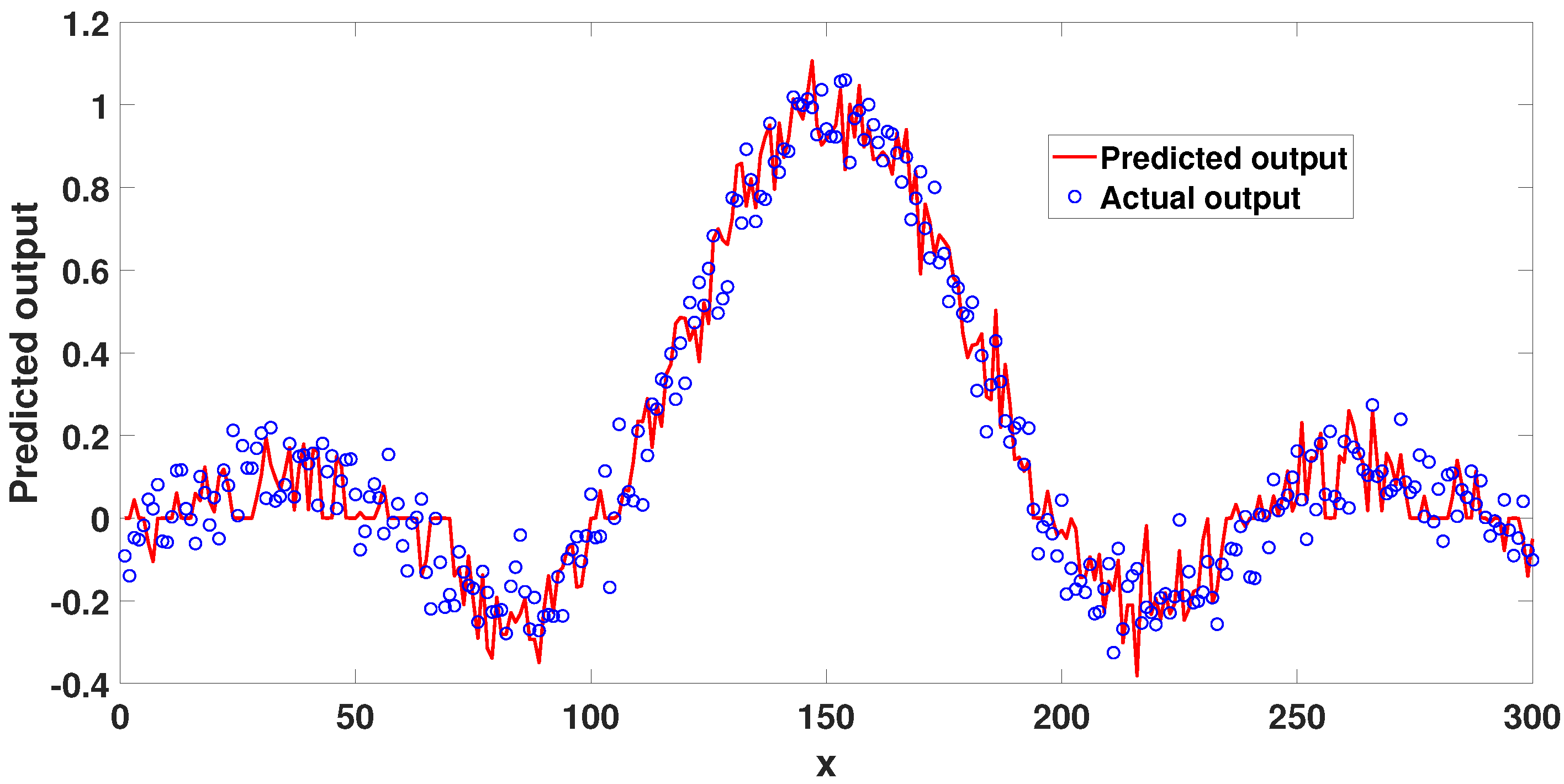
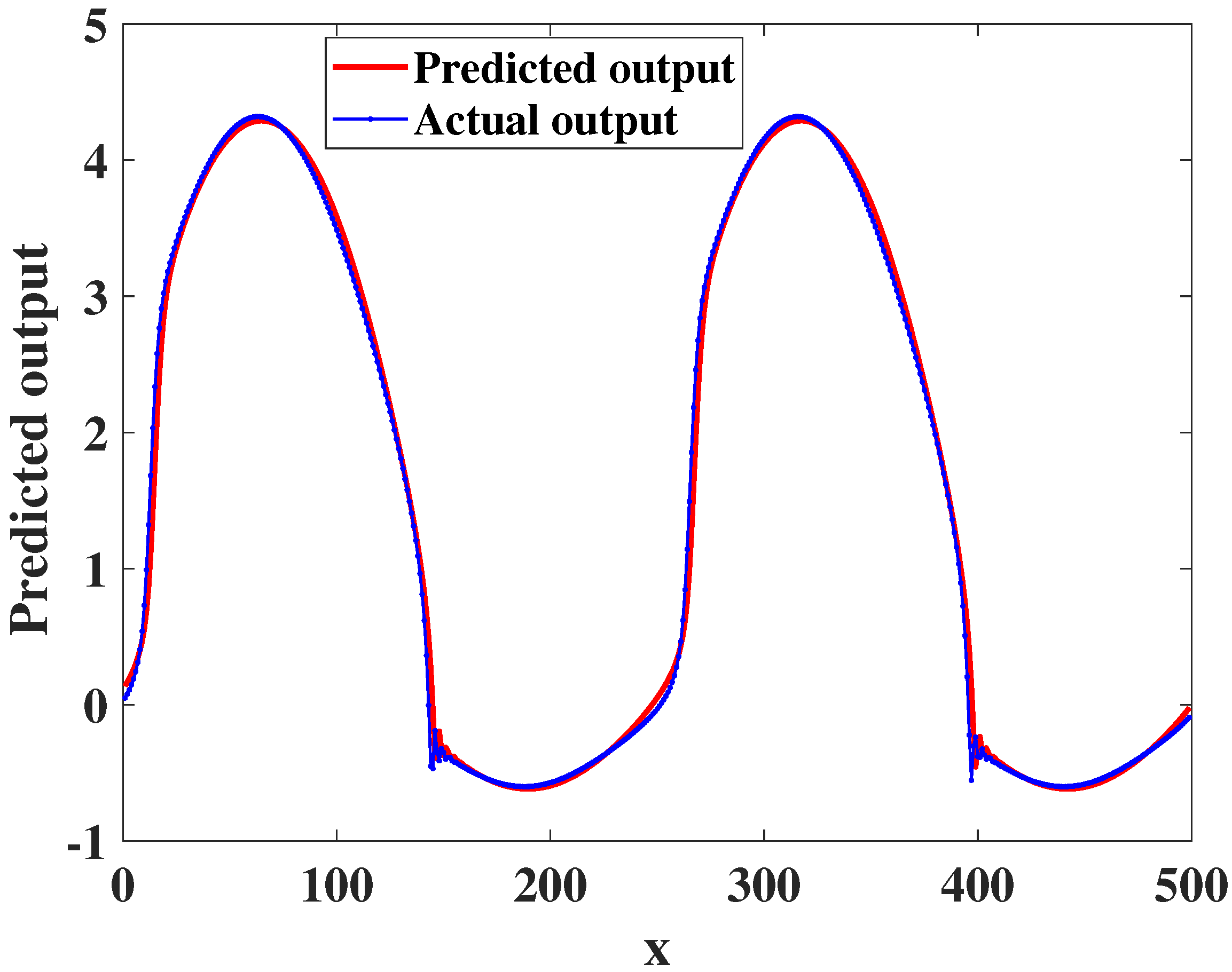
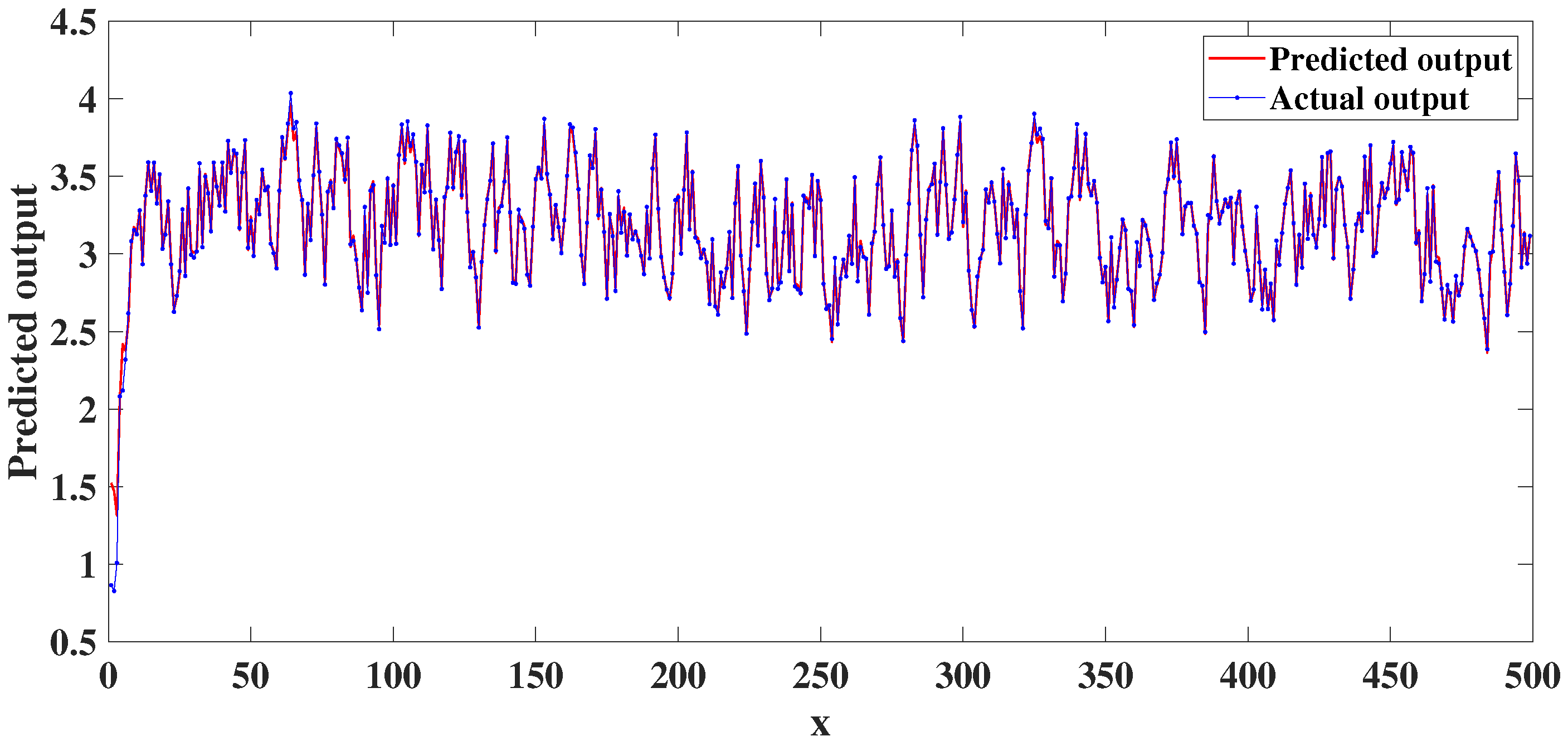
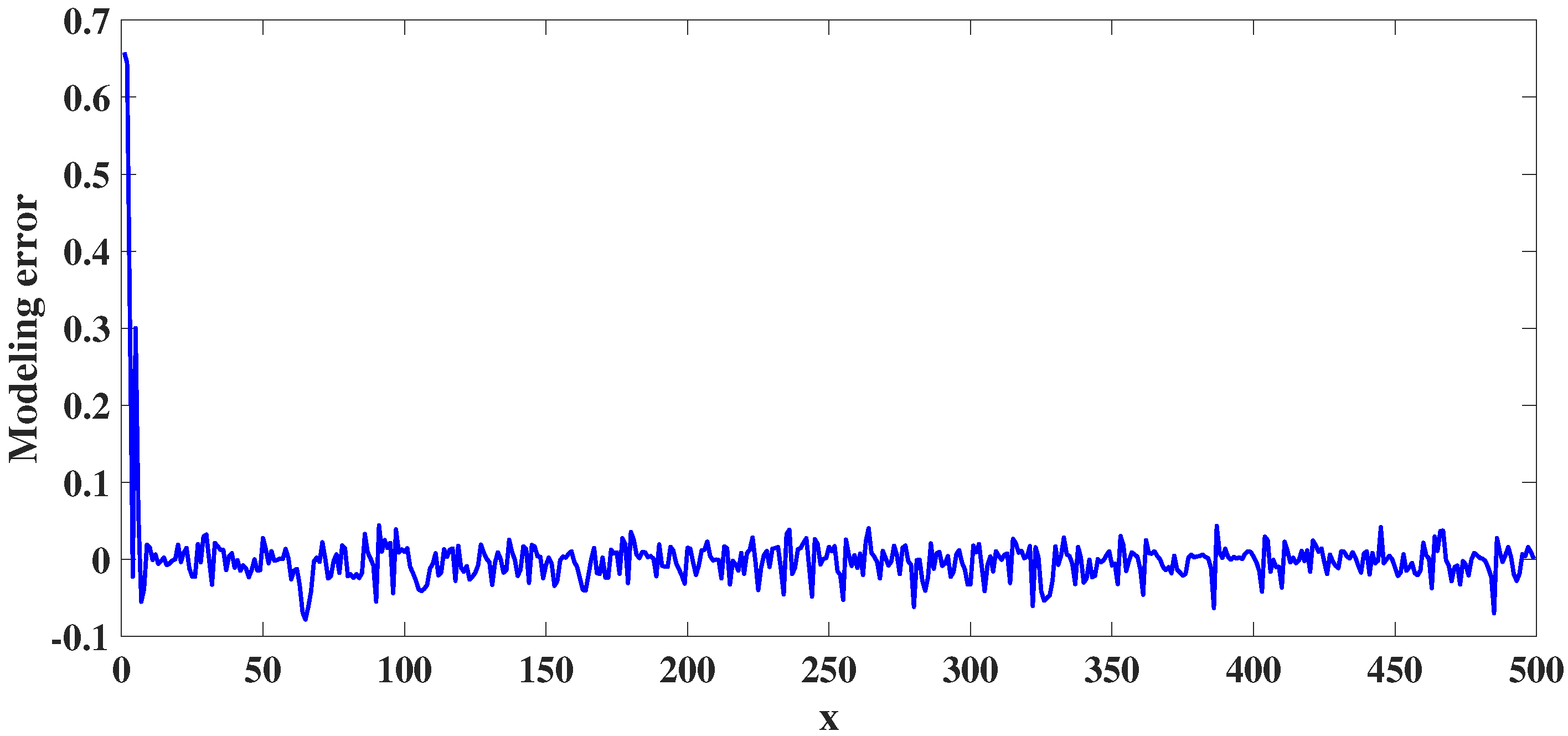
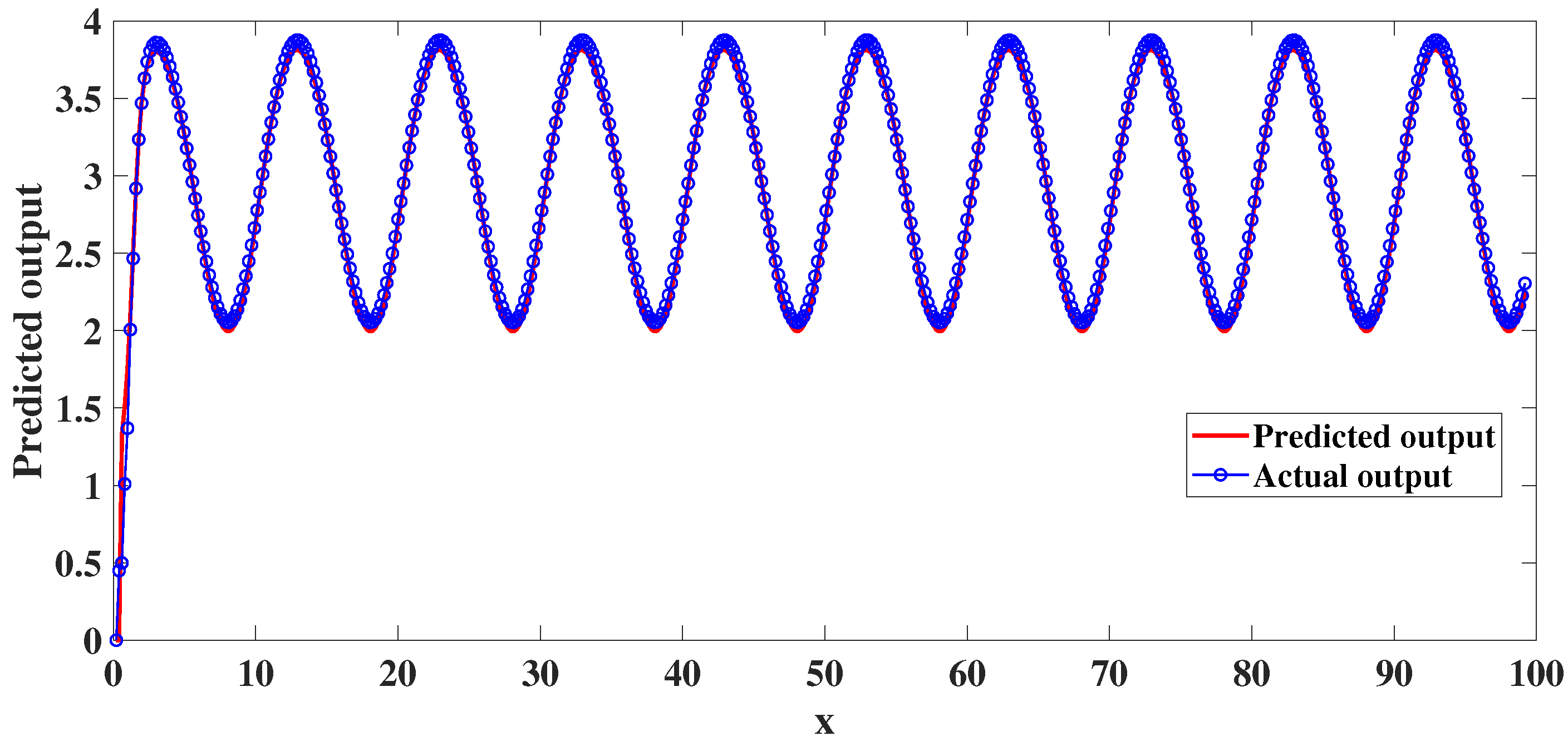
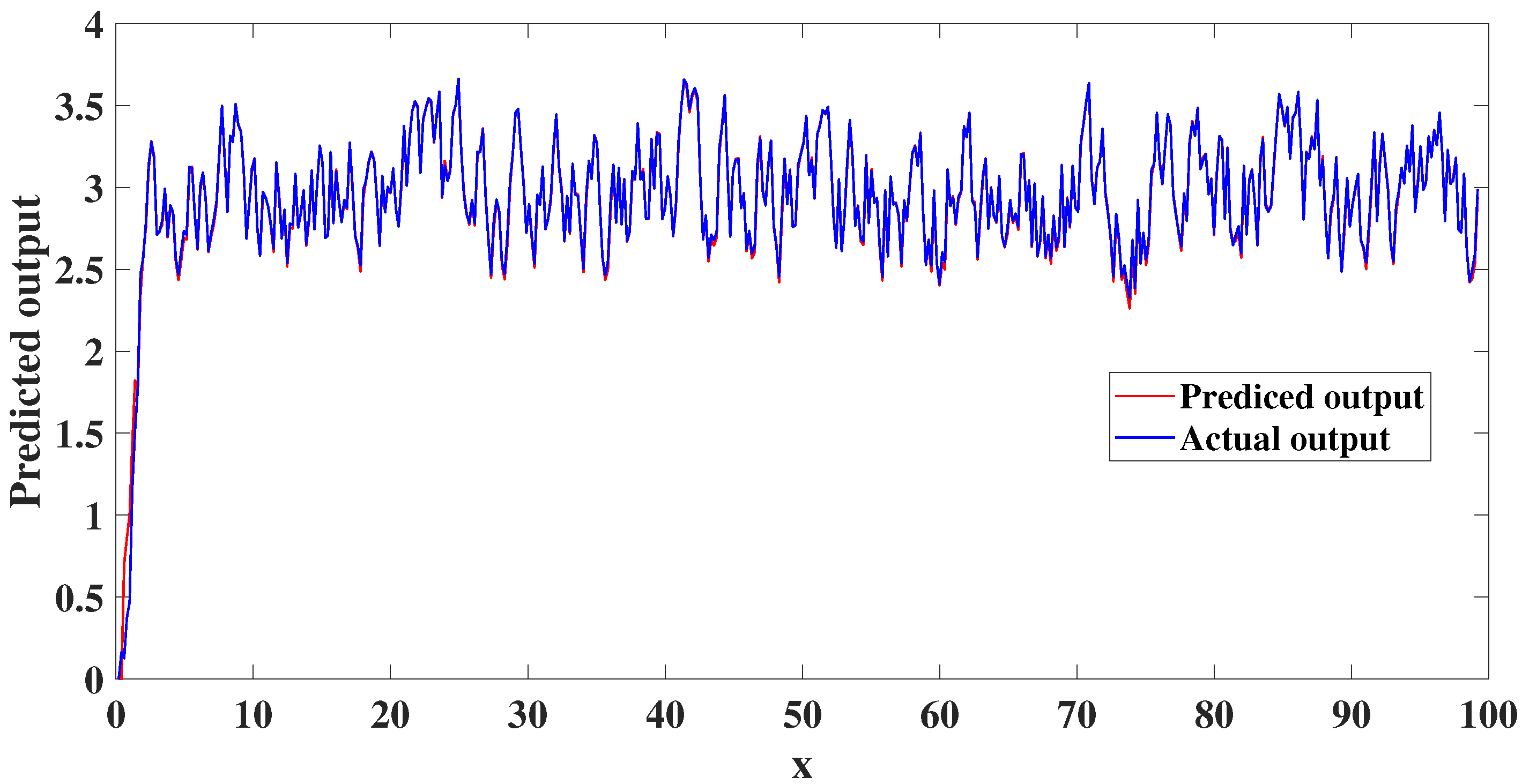
4. Experimental Studies
4.1. Static Nonlinear System Analysis
4.2. Dynamic Nonlinear System Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, X.; Song, R.; Shan, D.; Ren, X.; Zheng, Y.; Lv, F.; Deng, Q.; He, Y.; Li, X.; Li, R.; et al. Discovery of hepatoprotective activity components from Thymus quinquecostatus celak. by molecular networking, biological evaluation and molecular dynamics studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 140, 106790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Nuertayi, A.; Yan, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y. Hybrid physical and data driven modeling for dynamic operation characteristic simulation of wind turbine. Renew. Energy 2023, 215, 118958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Bhattarai, H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Hwang, H.; Wu, X.; Tang, Y.; Kang, S. Dynamic characteristics of segmental assembled HH120 wind turbine tower. Renew. Energy 2024, 303, 117438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, M.; Nguyen, M.; Bui, T. A novel thermo-mechanical local damage model for quasi-brittle fracture analysis. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2024, 130, 104329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffolo, K.; Meunier, S.; Ricardez-Sandoval, L. Reactor network modelling for biomass-fueled chemical-looping gasification and combustion processes. Fuel 2024, 366, 131254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeqi, A.; Moradi, S.; Heidari Shirazi, K. Nonlinear subspace system identification based on output-only measurements. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 12904–12937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeqi, A.; Moradi, S. Nonlinear system identification based on restoring force transmissibility of vibrating structures. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 172, 108978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, L.; Qiao, J. A self-organizing fuzzy neural network with hybrid learning algorithm for nonlinear system modeling. Inf. Sci. 2023, 642, 119145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Guo, Y.; Qiao, J. Nonlinear system modeling using a self-organizing recurrent radial basis function neural network. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 71, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Li, C.; Feng, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. A t-s fuzzy model identification approach based on evolving mit2-fcrm and wos-elm algorithm. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 92, 103653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goethals, I.; Pelckmans, K.; Suykens, J.; Moor, B. Subspace identification of hammerstein systems using least squares support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2005, 50, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilario, K.; Cao, Y.; Shafiee, M. A kernel design approach to improve kernel subspace identification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 6171–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigatos, G.; Tzafestas, G. Extended Kalman filtering for fuzzy modelling and multi-sensor fusion. Math. Model. Syst. 2007, 13, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Xia, D.; Erazo, D.; Nagarajaiah, S. A novel unscented kalman filter for recursive state-input-system identification of nonlinear systems. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 127, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipping, M. Sparse bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2001, 1, 211–244. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhong, Z. An active sparse polynomial chaos expansion approach based on sequential relevance vector machine. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 418, 116554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V. The support vector method. In International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 261–271. [Google Scholar]
- Smola, A.; Bernhard, S. A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat. Comput. 2004, 14, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucak, K.; Oke Gunel, G. Adaptive stable backstepping controller based on support vector regression for nonlinear systems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 129, 107533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Lee, S. Recurrent fuzzy neural network backstepping control for the prescribed output tracking performance of nonlinear dynamic systems. ISA Trans. 2014, 53, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwicker, J.; Rebennack, S. Support vector machines within a bivariate mixed-integer linear programming framework. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 245, 122998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharon, B.; Nemirovski, A. Robust solutions of linear programming problems contaminated with uncertain data. Math. Program. 2000, 88, 411–424. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Fang, H. Kernel regression model guaranteed by identifying accuracy and model sparsity for nonlinear dynamic system identification. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2020, 20, 7804–7814. [Google Scholar]
- Manngrd, M.; Kronqvist, J.; Bling, J. Structural learning in artificial neural networks using sparse optimization. Neurocomputing 2018, 272, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Yan, G.; Zhang, F.; Zeng, C.; Tian, P. Linear Programming-Based Sparse Kernel Regression with L1-Norm Minimization for Nonlinear System Modeling. Processes 2024, 12, 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112358
Liu X, Yan G, Zhang F, Zeng C, Tian P. Linear Programming-Based Sparse Kernel Regression with L1-Norm Minimization for Nonlinear System Modeling. Processes. 2024; 12(11):2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112358
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoyong, Genglong Yan, Fabin Zhang, Chengbin Zeng, and Peng Tian. 2024. "Linear Programming-Based Sparse Kernel Regression with L1-Norm Minimization for Nonlinear System Modeling" Processes 12, no. 11: 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112358
APA StyleLiu, X., Yan, G., Zhang, F., Zeng, C., & Tian, P. (2024). Linear Programming-Based Sparse Kernel Regression with L1-Norm Minimization for Nonlinear System Modeling. Processes, 12(11), 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112358







