Synergistic Catalysis of Reservoir Minerals and Exogenous Catalysts on Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of the Catalyst
2.3. Characterization of the Complex
2.4. Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil
2.5. Product Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Catalyst
3.2. Effect of Reaction Temperature on Aquathermolysis
3.3. Effect of Reaction Time on Aquathermolysis
3.4. Effect of Water
3.5. Effect of Reservoir Minerals on Aquathermolysis
3.6. The Effect of Hydrogen Donors on the Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil
3.7. Analysis of the Viscosity of Heavy Oil Catalyzed by Various Catalysts
3.8. Determination of SARA before and after Reaction
3.9. Elemental Analysis (EA)
3.10. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3.11. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Analysis (DSC)
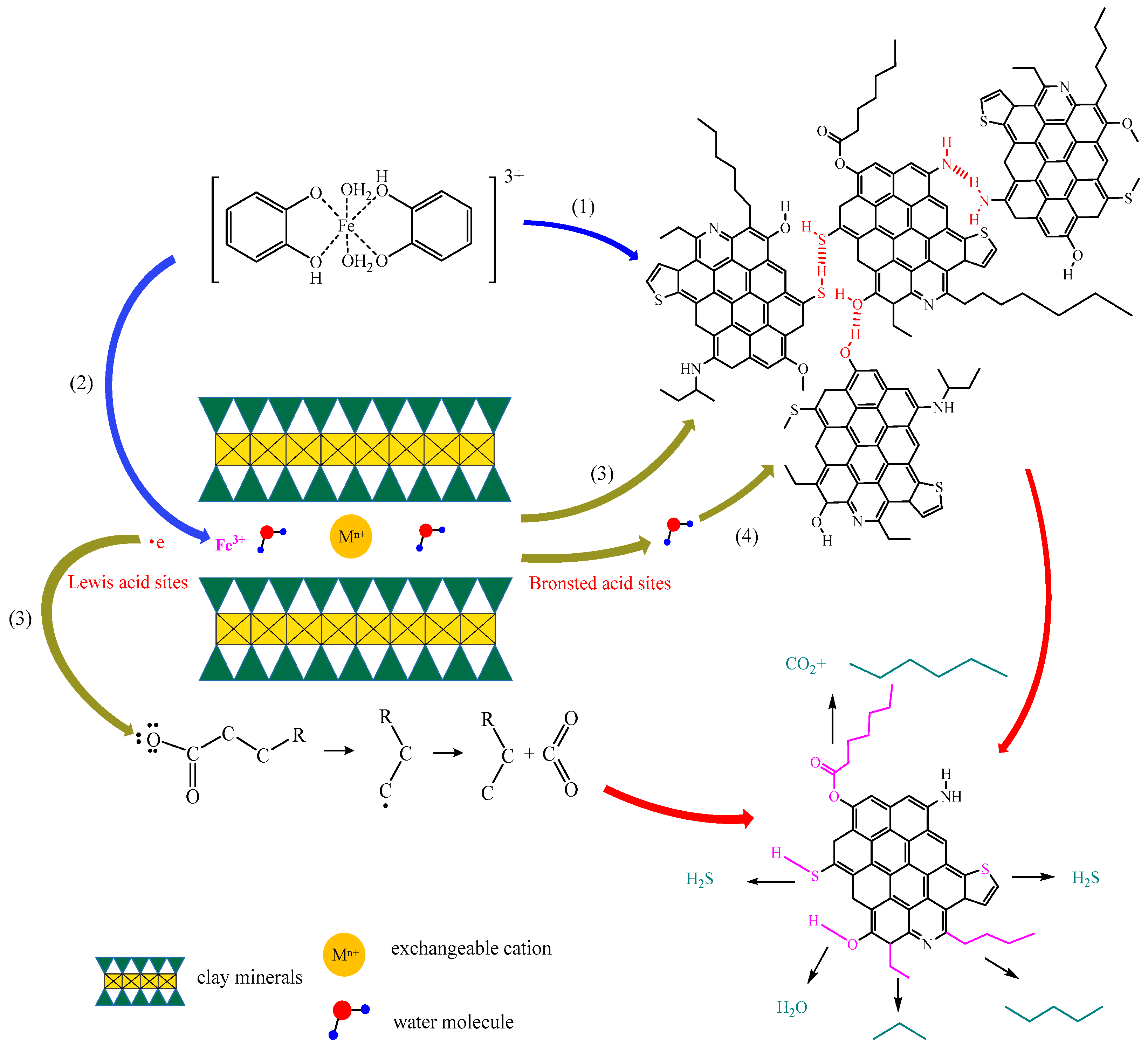
3.12. Mechanism
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaban, S.; Dessouky, S.; Badawi, A.E.F.; El Sabagh, A.; Zahran, A.; Mousa, M. Upgrading and viscosity reduction of Heavy oil by catalyst ionic liquid. Energy Fuel 2014, 28, 6545–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Yang, J. Aquathermolysis of heavy crude oil with ferric oleate catalyst. Pet. Sci. 2018, 15, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Tian, C.; Chen, J. Study on Hydrothermal Cracking of Heavy Oil under the Coexisting Conditions of Supercritical Water and Non-condensate Gas. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 18029–18040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Li, H.; Yu, Z. In-situ heavy and extra-heavy oil recovery: A review. Fuel 2016, 185, 886–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraza, O.; Galadima, A. Aquathermolysis of heavy oil: A review and perspective on catalyst development. Fuel 2015, 157, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakhin, A.V.; Khelkhal, M.A.; Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Mukhamatdinova, R.E.; Tajik, A.; Slavkina, O.V.; Malaniy, S.Y.; Gafurov, M.R.; Nasybullin, A.R.; Morozov, O.G. Changes in Heavy Oil Saturates and Aromatics in the Presence of Microwave Radiation and Iron-Based Nanoparticles. Catalysts 2022, 12, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Cao, M.; Huang, Q.; Liu, B.; Jiang, J. Study on reaction equations of heavy oil aquathermolysis with superheated steam. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 5023–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushakova, A.; Zatsepin, V.; Khelkhal, M.; Sitnov, S.; Vakhin, A. In Situ Combustion of Heavy, Medium, and Light Crude Oils: Low-Temperature Oxidation in Terms of a Chain Reaction Approach. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 7710–7721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A.; Bafail, A.; Nizami, A.S. Heavy oil upgrading: Unlocking the future fuel supply. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Li, C.; Gao, H.; Chen, M.; Huang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, C. Recyclable oleic acid modified magnetic NiFe2O4 nanoparticles for catalytic aquathermolysis of Liaohe heavy oil. Fuel 2017, 200, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Fujimoto, K.; Tsubaki, N. Effect of Initiative Additives on Hydro-Thermal Cracking of Heavy Oils and Model Compound. Energy Fuels 2003, 17, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yuan, W.; Yan, J.; Meng, M.; Guo, Z.; Gu, X.; Zhang, J.; Qu, C.; Song, H.; Jeje, A. Zn(II) Complex Catalyzed Coupling Aquathermolysis of Water-Heavy Oil-Methanol at Low Temperature. Pet. Chem. 2018, 58, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yan, J.; Bai, Y.; Gu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Jeje, A. Clean aquathermolysis of heavy oil catalyzed by Fe(III) complex at relatively low temperature. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhamed’yarova, A.N.; Gareev, B.I.; Nurgaliev, D.K.; Aliev, F.A.; Vakhin, A.V. A Review on the Role of Amorphous Aluminum Compounds in Catalysis: Avenues of Investigation and Potential Application in Petrochemistry and Oil Refining. Processes 2021, 9, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, P.; Dowling, N.; Hyne, J.; Lesage, K. The chemistry of organosulphur compound types occurring in heavy oils: 4. the high-temperature reaction of thiophene and tetrahydrothiophene with aqueous solutions of aluminium and first-row transition-metal cations. Fuel 1987, 66, 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Dong, S.; Yu, T.; Slaný, M.; Chen, G. Enhanced aquathermolysis of Heavy oil catalysed by bentonite supported Fe (III) complex in the present of ethanol. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.K.; Ancheyta, J.; Marroquín, G. Catalytic Aquathermolysis Used for Viscosity Reduction of Heavy Crude Oils: A Review. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2809–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H.; Jiang, S.J. Liaohe Extra-Heavy Crude Oil Underground Aquathermolytic Treatments Using Catalyst and Hydrogen Donors under Steam Injection Conditions. In Proceedings of the SPE International Improved Oil Recovery Conference in Asia Pacific, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 8–9 October 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, P.; Hyne, J. Chemistry of organosulphur compound types occurring in heavy oil sands: 3. Reaction of thiophene and tetrahydrothiophene with vanadyl and nickel salts. Fuel 1984, 63, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yuan, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, H.; Jeje, A.; Song, S.; Qu, C. Catalytic aquathermolysis of heavy oil by coordination complex at relatively low temperature. Pet. Chem. 2017, 57, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, Y.; Lu, N.; Xu, T.; Zhu, G.; Wang, K. A review on upgrading and viscosity reduction of heavy oil and bitumen by underground catalytic cracking. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 4249–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muntaser, A.A.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Suwaid, M.A.; Saleh, M.M.; Djimasbe, R.; Yuan, C.; Zairov, R.R.; Ancheyta, J. Effect of decalin as hydrogen-donor for in-situ upgrading of Heavy crude oil in presence of nickel-based catalyst. Fuel 2022, 313, 122652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Z.; Zhao, X. Using hydrogen donor with oil-soluble catalysts for upgrading Heavy oil. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2014, 87, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneer, A.S.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Al-muntaser, A.A.; Yuan, C.; Valentina, L.S.; Almaz, Z.; Farit, G.V.; Ilfat, Z.R.; Dmitrii, A.; Artem, E.C. In-situ catalytic upgrading of heavy oil using oil-soluble transition metal-based catalysts. Fuel 2020, 282, 118753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Study of catalytic aquathermolysis of heavy oil in the presence of a hydrogen donor. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2012, 48, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Slaný, M.; Kuzielová, E.; Zhang, W.; Ma, L.; Dong, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G. Influence of reservoir minerals and ethanol on catalytic aquathermolysis of Heavy oil. Fuel 2022, 307, 121871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmić, A.E.; Radošević, M.; Bogdanić, G.; Srića, V.; Vuković, R. Studies on the influence of long chain acrylic esters polymers with polar monomers as crude oil flow improver additives. Fuel 2008, 87, 2943–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Gan, J.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Wang, G.; Wu, L.; Gong, Y. Extraction of crude oil from petrochemical sludge: Characterization of products using thermogravimetric analysis. Fuel 2017, 188, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovalles, C.; Filgueiras, E.; Morales, A.; Scott, C.E.; Gonzalez-Gimenez, F.; Embaid, B.P. Use of a dispersed iron catalyst for upgrading extra-heavy crude oil using methane as source of hydrogen. Fuel 2003, 82, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliev, F.A.; Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Sitnov, S.A.; Ziganshina, M.R.; Onishchenko, Y.V.; Sharifullin, A.V.; Vakhin, A.V. In-situ Heavy oil aquathermolysis in the presence of nanodispersed catalysts based on transition metals. Processes 2021, 9, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, J.; Celis, R.; Pavlovic, I.; Ulibarri, M.A. Interactions of pesticides with clays and layered double hydroxides: A review. Clay Miner. 2008, 43, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulet, P.; Greenwell, H.C.; Stackhouse, S.; Coveney, P.V. Recent advances in understanding the structure and reactivity of clays using electronic structure calculations. Theochem 2005, 762, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.M.; Zhou, C.H.; Keeling, J.; Tong, D.S.; Yu, W.H. Towards an understanding of the role of clay minerals in crude oil formation, migration and accumulation. Earth. Sci. Rev. 2012, 115, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, W.D. Clay mineral catalysis and petroleum generation. Annu. Rev. Earth. Planet. Sci. 1979, 7, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.R.; Rhodes, C.N. Bronsted and Lewis acid catalysis with ion-exchanged clays. Catal. Lett. 1997, 45, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, C.H. Smectite dehydration-its relation to structural development and hydrocarbon accumulation in Northern Gulf of Mexico Basin. AAPG Bull. 1984, 68, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.R.; Bhat, Y.S.; Nagendrappa, G.; Prakash, B.J. Bronsted and Lewis acidity of modified montmorillonite clay catalysts determined by FT-IR spectroscopy. Catal. Today. 2009, 141, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Stucki, J.W. Effects of structural Fe oxidation state on the coupling of interlayer water and structural Si-O stretching vibrations in montmorillonite. Langmuir 1999, 15, 4648–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Pour Point/°C | Asphaltene, % | Saturated HC, % | Aromatic HC, % | Resin, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20.0 | 23.44 | 31.16 | 28.73 | 16.67 |
| Oil Sample | Saturates, % | Aromatics, % | Asphaltenes, % | Resins, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 23.44 | 31.16 | 28.73 | 16.67 |
| After reaction with C-Fe and sodium montmorillonite | 30.28 | 36.20 | 25.98 | 7.54 |
| After reaction with C-Fe and sodium montmorillonite and EtOH | 33.15 | 37.74 | 23.19 | 5.92 |
| Oil Sample | Elemental Content/% | C/H | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | N | S | ||
| Blank | 86.20 | 10.02 | 1.88 | 0.65 | 0.116 |
| After the aquathermolysis | 85.90 | 10.04 | 1.41 | 0.56 | 0.116 |
| After reaction with C-Fe and sodium montmorillonite | 86.19 | 10.10 | 1.58 | 0.44 | 0.117 |
| After reaction with C-Fe and sodium montmorillonite and EtOH | 83.99 | 10.29 | 1.30 | 0.44 | 0.122 |
| Reaction System | Weight Loss Ratio/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–150 °C | 150–350 °C | 350–450 °C | >450 °C | |
| Blank | 3.10 | 18.36 | 34.82 | 43.72 |
| Water | 4.42 | 24.05 | 31.90 | 39.63 |
| Water + C-Fe + sodium montmorillonite | 1.83 | 29.35 | 29.77 | 39.05 |
| Water + C-Fe + sodium montmorillonite + EtOH | 5.33 | 30.82 | 28.94 | 34.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zang, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Chen, G. Synergistic Catalysis of Reservoir Minerals and Exogenous Catalysts on Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil. Processes 2023, 11, 2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092635
Zang Y, Liu H, Chen D, Zhang S, Li S, Chen G. Synergistic Catalysis of Reservoir Minerals and Exogenous Catalysts on Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil. Processes. 2023; 11(9):2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092635
Chicago/Turabian StyleZang, Yunlei, Huaizhu Liu, Dong Chen, Shu Zhang, Shanjian Li, and Gang Chen. 2023. "Synergistic Catalysis of Reservoir Minerals and Exogenous Catalysts on Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil" Processes 11, no. 9: 2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092635
APA StyleZang, Y., Liu, H., Chen, D., Zhang, S., Li, S., & Chen, G. (2023). Synergistic Catalysis of Reservoir Minerals and Exogenous Catalysts on Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil. Processes, 11(9), 2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092635








