Abstract
This study aimed to evaluate the potential of utilizing aerated concrete (AC) and clay bricks (CB) sourced from construction and demotion waste (CDW) as low-cost adsorbents for the removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solutions. The effects of various parameters, including particle size, solution pH, contact time, adsorbent dosage, and initial Pb2+ concentration, were analyzed through batch experiments. The results indicated that AC performed more efficiently in removing lead ions than CB under all the tested conditions. The highest removal efficiency of Pb2+ with AC was 99.0%, which was achieved at a pH of 5.0, contact time of 1 h, an adsorbent dosage of 5 g/L, and an initial Pb2+ concentration of 100 mg/L. The maximum adsorption capacities of AC and CB were 201.6 mg/g and 56.3 mg/g, respectively. The adsorption isotherm data of the adsorbents were successfully modeled using both the Langmuir and Freundlich models. The removal of lead ions from aqueous solutions by both adsorbents is primarily achieved through adsorption and microprecipitation. Compared to CB, AC exhibited superior performance, attributed to its larger specific surface area, pore volume, and alkalinity. The cost-effectiveness and availability of AC make it a promising candidate for treating of Pb-contaminated wastewater, providing a new way for resource utilization of CDW.
1. Introduction
Water is an essential resource for the existence of life on the earth, yet its quality has been detrimentally altered due to fast industrialization, population expansion, and urbanization [1]. One of the primary causes of degradation in water quality is the presence of heavy metal pollutants [2,3], which pose a growing environmental issue of concern worldwide due to their tendency for accumulation, toxicity, and persistence [4]. Lead (II) is particularly hazardous, being one of the most toxic heavy metal ions found in aquatic environments [5]. Exposure to lead can have devastating effects on the human body, potentially causing harm to the brain and central nervous system, disrupting proper bone development, damaging the gastrointestinal tract, and leading to serious disorders or even death [6,7]. As a result, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) have classified lead as a carcinogen, and the World Health Organization (WHO) regulates its release to be less than 10 μg/L [8]. However, for industrial effluents, the lead (II) discharge limit is 100 μg/L in the United States and 1 mg/L in China [9]. To ensure safe release standards and prevent lead from contaminating the environment, it is crucial to effectively remove it from wastewater.
Several techniques have been employed for the removal of lead from aqueous solutions, including adsorption, membrane filtration, chemical coagulation and flocculation, chemical precipitation, electrochemical methods, ion exchange, and bio-remediation, etc. [10,11]. Among these methods, the adsorption process is currently viewed as an economical, effective, and simple-to-implement technology for the elimination of lead from wastewater [12,13]. Various adsorbents have been tested and utilized for removing lead, both in laboratory settings and in practical industrial applications [13,14,15]. However, certain adsorbents such as synthetic polymers, nanoparticles, and carbon nanotubes, despite exhibiting high efficiency in lead removal, have not been extensively adopted due to their high cost [16,17,18]. Thus, substantial efforts have been made to identify potential low-cost adsorbents for the removal of lead. Low-cost adsorbents can be broadly classified into geosorbents, biosorbents, industrial wastes, industrial byproducts and construction and demolition waste (CDW), and modified low-cost adsorbents [19]. Nonetheless, compared with other low-cost adsorbents, research on CDW as an adsorbent for the elimination of lead ions from wastewater is relatively scarce.
A vast amount of CDW is produced globally due to rapid economic growth and urbanization. China is the largest producer of CDW worldwide, generating 2.4 billion tons per year, accounting for nearly half of the world’s total [20]. However, the utilization rate of CDW in China is only 5%, which is significantly lower compared to Japan (90%), the Netherlands (75%), and most European countries (80%) [21]. Unutilized CDW in substantial amounts can lead to negative environmental consequences if not properly managed [22]. Therefore, efficient strategies for the reuse and recycling of CDW are imperative to mitigate the adverse effects of its generation. Clay bricks and aerated concrete as the most common building materials are the primary components of CDW in China [23]. Clay bricks are primarily made of clay minerals, which have experienced a stage of firing through kilns to enhance their hardness and durability. Aerated concrete blocks are manufactured by blending cement, lime, fly ash, and fine river sand. They are a light-weight porous building material that have the advantages of effective heat and sound insulation, fireproofing, and energy efficiency [24]. Clay bricks and aerated concrete are characterized by high porosity, with a porosity of about 40% and 68%, respectively [23]. Given their abundance, low cost, and high porosity, clay bricks or aerated concrete sourced from CDW appear to be promising candidates to be evaluated as alternative adsorbents in the remediation of wastewaters. Powdered clay bricks or aerated concrete wastes have been formerly utilized for the removal of organic pollutants and heavy metals, including cadmium (Cd), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), nickel (Ni), and copper (Cu), from wastewaters [25,26,27,28,29]. However, the use of aerated concrete and clay bricks from CDW as adsorbents for lead removal has not been fully examined. In order to gain a comprehensive understanding of lead adsorption onto aerated concrete and clay bricks, further studies are required to investigate the effect of various parameters, including particle size, contact time, solution pH, adsorbent dosage, and initial Pb2+ concentration on lead adsorption characteristics.
Hence, this research aimed to explore the feasibility of utilizing aerated concrete and clay bricks from construction and demolition wastes as adsorbents for lead removal. The objectives of the study were: (1) to investigate the adsorption characteristics of lead (II) ions from aqueous solutions using aerated concrete and clay bricks under various experimental conditions, and (2) to monitor changes in the concentration of metal ions (Pb2+, K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+) in water and lead solution, along with variations in pH and electric conductivity (EC), after the addition of the adsorbents, to gain insights into the adsorption mechanisms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
Aerated concrete and clay brick wastes were sourced from a two-story building that was demolished near Northeast Agricultural University (Harbin, China) in November 2019. The materials were thoroughly cleaned of surface impurities and dust before being crushed and sieved into six particle sizes: 2–5 mm, 1–2 mm, 0.5–1 mm, 0.25–0.5 mm, 0.1–0.25 mm, and less than 0.1 mm.
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
In the study, all reagents were of analytical reagent grade and were procured from Kermel Chemical Company in Tianjin, China. A stock solution of 1000 mg/L of Pb(II) was prepared by dissolving 1.60 g of lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2) in 1 L of deionized water. The required concentrations (50, 100, 150, 200, and 250 mg/L) for the experiments were obtained by diluting the stock solution with deionized water.
2.3. Material Characterization
The textural properties of the adsorbents were analyzed using the Surface Area and Porosity Analyzer (ASAP2020, Micromeritics, USA). The crystal structures formed during the adsorption process were studied using an X-ray diffraction (XRD) apparatus (D/max2200 model, Hitachi, Japan) at U = 40 kV and I = 30 mA. The scans were conducted between 5° and 100° with a scan rate of 5°/min and a step size of 0.0131° at room temperature. The presence of certain metal elements was detected using an X-ray fluorescence (XRF) apparatus (EDX6600, 3V, China). The chosen V/m ratio was 500 mL/g.
2.4. Batch Experiments
In batch experiments, the impact of adsorbent particle size (0.1–5 mm), solution pH (3.0–5.5), contact time (0.25–3 h), adsorbent dosage (2–10 g/L), and initial lead (II) concentration (50–250 mg/L) on the lead removal were evaluated. All adsorption experiments were conducted using a mechanical shaker equipped with a thermostatically controlled water bath, operating at 150 rpm and using 150 mL Erlenmeyer flasks. The experiment was performed at room temperature of 25 °C. The pH of the lead ion solution (in the range of 3.0–5.5) was adjusted using HCl (0.5 M) or NaOH (0.1 M) solution. A certain amount of adsorbent was weighed and added into the Pb2+ solution, and the mixture was shaken on a shaker under controlled conditions before the filtrate was collected. The concentration of lead ions (II) in the filtrate was measured using an Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AA-6800, Shimadzu-GL, Japan). All experiments were conducted in triplicate.
In the contact time-based batch experiment, the concentrations of other metal ions (K+, Ca2+, Na+, Mg2+), pH, and EC, along with that of lead ions, were measured at 0.25 h, 0.5 h, 1 h, 1.5 h, 2 h, 2.5 h, and 3 h intervals. The concentration of calcium and magnesium ions in the filtrate was measured using an Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AA-6800, Shimadzu-GL, Japan), while the concentration of sodium and potassium ions was analyzed using a Flame Photometer (6400A, Caihong, China). The pH of the solutions was measured with a pH meter (PB-10, Sartorius, Germany) and the EC of the solutions was measured with an EC meter (DDS-11A, Leici, China).
The removal efficiency (R, %), the adsorption capacity at time t (qt, mg/g), and the adsorption capacity (qe, mg/g) at equilibrium were calculated as follows:
where Ci (mg/L) and Ce (mg/L) represent the initial and equilibrium lead (II) concentrations, respectively; Ct (mg/L) is the concentration at time t; V (L) is the volume of reaction solution, which was standardized at 0.1 L; and m (g) is the mass of the adsorbent used.
2.5. Adsorption Isotherm Model
At a constant temperature, the interaction between a solid and a liquid phase in sorption is commonly described by Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models. These models were utilized to analyze the adsorption behavior within a range of medium concentrations. The commonly used form of the Langmuir isotherm model is represented as follows:
where qe (mg/g) represents the equilibrium adsorption capacity, qmax (mg/g) is the maximum monolayer capacity per unit mass of the adsorbent, Ce (mg/L) is the equilibrium concentration of lead ions in the solution, and KL (L/mg) is Langmuir equilibrium constant, which is related to affinity of the binding sites.
The general Freundlich equation is calculated as follows:
where Kf [(mg/g) (L/mg)1/n] is a Freundlich constant representing adsorption capacity and n is an empirical parameter describing the adsorption intensity.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
A statistical analysis was conducted utilizing SPSS 19.0 and included an analysis of variance (ANOVA) to assess the differences between the selected treatments. Further, a t-test was performed to determine the significant difference in treatment means, with a significance level of p < 0.05, based on three replicates. The graphics were generated using Origin 2021.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorbent Characterization
3.1.1. Pore Characteristics
The textural characteristics of the adsorbents were analyzed through N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm studies (Figure 1). All the isotherms exhibited a Type II isotherm with distinctive Type H3 hysteresis loop, suggesting the presence of slit-shaped pores in these materials [30,31]. The BET surface area, Langmuir surface area, total pore volume, and average pore width of AC and CB are shown in Table 1. According to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), solids possessing an average pore diameter within the range of 2–50 nm are classified as mesoporous materials, while those exhibiting average pore diameters greater than 50 nm are considered macroporous materials. Both AC and CB were found to be mesoporous solid with average pore diameters of 4.74 and 6.56 nm, respectively. AC exhibits higher surface area and pore volume compared to CB, which may contribute to its greater adsorption capacity.
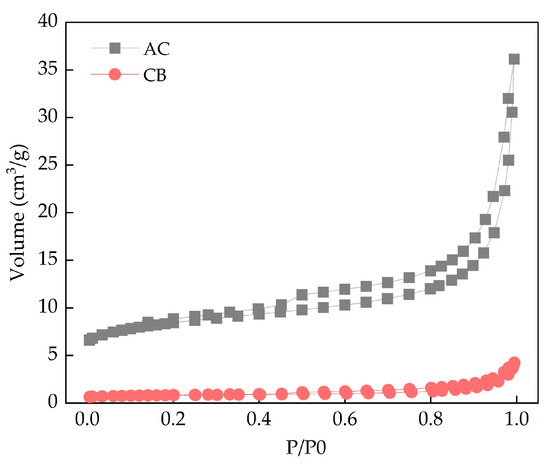
Figure 1.
N2 physisorption isotherms of the materials.

Table 1.
Pore characteristics of the adsorbents.
3.1.2. XRD Analysis
The XRD diffraction patterns of AC and CB before and after the loading of lead ions are presented in Figure 2. No additional peaks were observed in the spectra of AC-Pb and CB-Pb, suggesting that lead ions did not result in the formation of new crystal structures in either AC or CB. The diffraction peaks observed in the XRD pattern of AC-Pb are associated with calcite (syn, Ca(CO3), FOM value 2.0, PDF# 81-2027), clinotobermorite (Ca5Si6O16(OH)2·4H2O, FOM value 6.1, PDF# 88-1328), and magnesium calcite (syn, (Mg0.03Ca0.97)(CO3), FOM value 7.4, PDF# 89-1304) (Figure 2a). The diffraction peaks observed in the XRD pattern of CB-Pb correspond to quartz (SiO2) (FOM value 2.6, PDF# 87-2096) and albite (Ca-rich, ordered, (Na, Ca)Al(Si, Al)3O8, FOM value 10.1, PDF# 41-1480) (Figure 2b). In comparison to native materials, certain peak intensities in the lead-loaded materials were increased, which was related to the dissolution of the soluble components and the relative enhancement of the insoluble components [32,33].
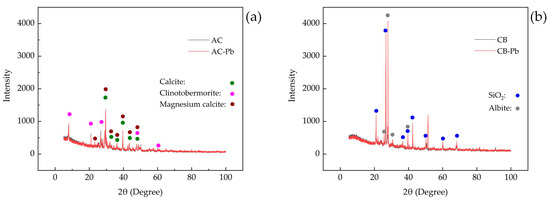
Figure 2.
X-ray diffraction patterns of native and lead-loaded materials. (a) A comparison between native aerated concrete (AC) and lead-loaded aerated concrete (AC-Pb); (b) a comparison between native clay bricks (CB) and lead-loaded clay bricks (CB-Pb).
3.1.3. XRF Analysis
X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF) was utilized to detect 31 metallic elements potentially present in the materials. The content of lead and other metallic elements that are relatively abundant in the materials is shown in Table 2. Calcium (Ca) was found to be the dominant metallic element detected in AC, while no significant amount of Ca was detected in CB, which is consistent with the XRD detection results. A comparison between native materials and lead-loaded materials revealed a significant increase in lead content (1.1% in AC-Pb and 0.5% in CB-Pb), along with a decrease in the content of Ca and Fe, suggesting the occurrence of ion exchange of calcium and iron ions with lead ions. However, it should be noted that the limited sample size and the inherent limitations of XRF in detecting certain elements, particularly light elements [34], necessitate the application of complementary chemical techniques for a more comprehensive analysis.

Table 2.
The content (%) of some metallic elements of native and lead-loaded materials.
3.2. Batch Experiments for Lead Ions Removal
3.2.1. Effect of Particle Size
The lead removal efficiency of AC was found to be significantly higher compared to CB under different experimental conditions (Figure 3). It was observed that smaller particle sizes facilitated the removal of lead ions (Figure 3a). This can be attributed to the fact that smaller particles generally have larger surface areas, which leads to improved adsorption performance and higher adsorption efficiency [35]. Upon reaching a particle size of 1–2 mm, the removal efficiency (R value) of AC had reached 98.0%, effectively removing almost all lead ions in the solutions. Therefore, it was challenging to further increase the R value with further decrease in particle size of AC. In contrast, the R value of CB increased with decreasing particle size. However, compared to AC, the R value of CB was significantly lower, ranging from 41.7% to 54.9%, making the effect of particle size on lead removal more pronounced.
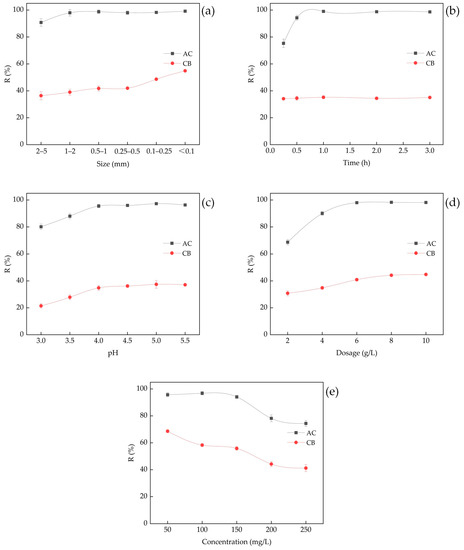
Figure 3.
Effect of experimental factors on the removal efficiency of lead ions (agitation rate: 150 rpm; T: 298 K; initial pH 5.2; particle size: 0.1–0.25 mm; dosage: 5 g/L; initial Pb2+ concentration: 100 mg/L; contact time: 1 h). (a) Effect of particle size; (b) effect of contact time; (c) effect of pH; (d) effect of adsorbent dosage; (e) effect of initial Pb2+ concentration.
3.2.2. Effect of Contact Time
The adsorption of Pb2+ onto AC occurred rapidly in the initial 0.5 h and proceeded at a slower pace thereafter. The removal efficiency of Pb2+ by AC increased from 75.3% to 99.0% at 1 h, reaching adsorption equilibrium (Figure 3b). The adsorption efficiency of CB was limited, with values ranging from 34.2% to 35.2%. The R value of CB did not change significantly over time, suggesting that the adsorption process reached saturation within 0.25 h. There was little change in the R value of CB with time, which was related to the fact that CB was a sintered material with less soluble substances and had relatively stable particles during the shaking process.
During the adsorption process of AC, the dissolution of more metal ions and the ion exchange may take a longer time. The particles of AC were prone to breakage during shaking, which could increase the adsorption capacity to some extent, leading to a more significant change in the R value of AC with contact time. Based on technical and economic considerations, the optimal contact time for Pb2+ removal with AC was determined to be 1 h in this study.
3.2.3. Effect of pH
The efficiency of removing pollutants from wastewater through adsorption is greatly influenced by the pH of the solution. This is because the pH affects the surface charge of the adsorbent, the degree of ionization, and speciation of the adsorbate [36]. In this study, the impact of pH was analyzed in the acidic range by using initial pH values ranging from 3.0 to 5.5. Initial pH levels above 5.5 were avoided due to the potential for metal hydroxide precipitation, which is likely to occur at higher pH levels, and to align with the practical interest of metal-contaminated waters, which typically present with an acidic pH [37]. The results indicated that the R values of both adsorbents rose as the initial pH increased and reached a relatively stable level at a pH of 4.0. The peak removal efficiency of both adsorbents was observed at a pH of 5.0. This indicated that a higher initial pH is more beneficial for the removal of lead ions due to the competition of hydrogen ions for the adsorption sites under low pH conditions [38,39].
3.2.4. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
The impact of adsorbent dosage on Pb2+ removal is presented in Figure 3d. It was observed that increasing the adsorbent dosage enhanced the lead removal efficiency. As the AC dosage was increased from 2 to 6 g/L, the removal efficiency improved correspondingly. At a dose of 6 g/L, the R value reached 98.0%. The removal efficiency of CB increased with an increase in dosage.
3.2.5. Effect of Initial Pb2+ Concentration and Adsorption Isotherms
The impact of initial concentration on the adsorption of Pb (II) by the adsorbents was examined through varying solution concentrations (50, 100, 150, 200, and 250 mg/L) as depicted in Figure 3e. The results indicated that as the initial concentration of Pb (II) increased, the removal efficiency of the adsorbents decreased. The regression analysis of the initial concentration (Ce) and the adsorption capacity (qe) revealed that the adsorption isotherm data of the adsorbents aligned well with the Langmuir and Freundlich models (Table 3). The Langmuir model estimated the maximum adsorption capacities of AC and CB to be 184.9 mg/g and 42.9 mg/g, respectively. In order to validate the theoretical values, a lead solution with a concentration of 1000 mg/L was employed, and the results indicated that the maximum adsorption capacities of AC and CB were 201.6 mg/g and 56.3 mg/g, respectively. It was found that the maximum adsorption capacity of AC was over three times that of CB.

Table 3.
Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm model for the adsorption of lead ions (T: 298 K, pH 5.2, adsorbent dosage of 5 g/L, contact time of 1 h, Pb2+ concentration at 50, 100, 150, 200, 250 mg/L).
Numerous studies have explored the adsorption of Pb (II) by inorganic mineral adsorbents and the adsorption capacities of various types of adsorbents used for Pb (II) removal were compared. It was revealed that AC reached the adsorption capacity that is comparable to that of zeolite and other mineral adsorbents (Table 4).

Table 4.
Comparison of maximum adsorption capacities of Pb (II) ions with some mineral adsorbents.
3.3. Mechanism of Pb(II) Removal by Adsorbents
The metal ions, including K+, Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+, leached from the adsorbents into water and lead solution were determined (Figure 4). During the adsorption process of AC in lead solution, the concentration of Pb2+ decreased sharply over time, while the concentrations of K+, Na+, and Ca2+ increased (Figure 4a). The concentrations of K+, Na+, and Ca2+ in lead solution with AC at each time point was found to be higher than their concentrations in water (Figure 4a,b). This suggests that K+, Na+, and Ca2+ in lead solution added with AC are derived partly from the naturally dissolved ions present in AC, and partly from the ions exchanged with Pb2+.
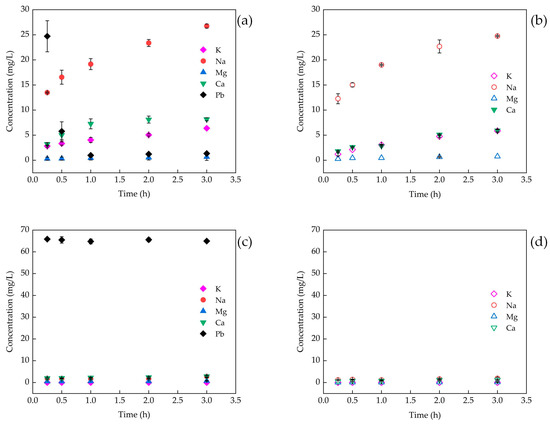
Figure 4.
Changes in the metal ions of the adsorbents in water and lead solution. (a) AC in lead solution; (b) AC in water; (c) CB in lead solution; (d) CB in water.
The difference between the concentration of each metal ion in lead solution and that in water is considered as the concentration of the ion exchanged with Pb2+ (Cie). The concentration of each ion exchanged with Pb2+ was added as the total metal ion exchange concentration (Csum). The correlation analysis showed that there was no significant correlation between Cie or Csum and the concentration of Pb2+ (CPb) (Table 5). This suggests that ion exchange is not the primary mechanism that influences the removal of lead ions by AC. There was only a small amount of metal ions that leached from CB into both lead solution and water (Figure 4c,d), and Cie can be disregarded. This observation indicates that ion exchange is also not the predominant mechanism for CB to remove lead ions.

Table 5.
Correlation coefficients of CPb, pH, EC, Cie-K, Cie-Na, Cie-Ca, and Csum.
Figure 5a demonstrates the change in the final pH of AC in lead solutions and water over time. AC exhibited higher alkalinity in water, but the pH values in lead solutions at each time point were lower compared to that in water. This can be explained by the fact that under alkaline conditions, Pb2+ and OH− quickly form lead hydroxide as precipitates, which results in the consumption of OH− and a surplus of H+. This, in turn, leads to a decrease in the solution pH. Similar findings were reported in previous studies on the use of compost to remove lead ions from aqueous solutions [33,52]. The final pH value of CB in water was close to 7.0. Similar to AC, the final pH value of CB in lead solutions at each time point was also lower than that in water (Figure 5b), indicating that both adsorbents utilize microprecipitation as a mechanism to remove lead. Studies have demonstrated that microprecipitation reactions can be effectively modeled using both the Langmuir and Freundlich models [53].
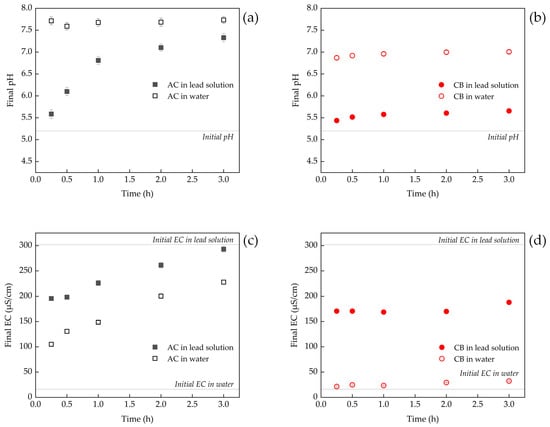
Figure 5.
Changes in the pH and EC of adsorbents in water and lead solution with time. (a) Changes in pH of AC in water and lead solution; (b) changes in the pH of CB in water and lead solution; (c) changes in the EC of AC in water and lead solution; (d) changes in the EC of CB in water and lead solution.
The EC value can reflect the salt content in the solution. The higher the concentration of salt in the solution, the greater the measured EC value. The results indicated that the addition of AC into water led to an increase in EC values with time, suggesting the leaching of salts from AC (Figure 5c). In lead solution, the removal of Pb2+ by AC resulted in an EC value that was lower than the initial value, but eventually, the dissolution of salt from AC caused the EC value to rise. The EC value of CB in water remained relatively constant and close to the initial EC value of the water. However, in lead solution, the removal of lead by CB caused the EC value to decrease, but due to a limited amount of salt leaching from CB, the EC value changed only slightly (168.7–180.0 μS/cm) (Figure 5d).
The release of other metal ions during the adsorption process of lead ions by AC may restrict its potential as a superior adsorbent to some degree. Despite this, the use of AC for the treatment of lead-contaminated wastewater for irrigation purposes appears to be a feasible option. Although sodium ions leached from AC may lead to soil salinization to some extent, calcium, magnesium, and potassium ions are essential plant nutrients required in large quantities that promote plant growth. Furthermore, the leaching of salt from AC is limited, and its hazards are considered acceptable when compared to those of lead ions. To optimize the benefits of using AC in future applications, a well-designed application process should be developed to maximize its benefits while minimizing any drawbacks.
Based on the results and analysis above, it can be concluded that adsorption and micro-precipitation are the main mechanisms for removing lead by these two adsorbents (Figure 6).
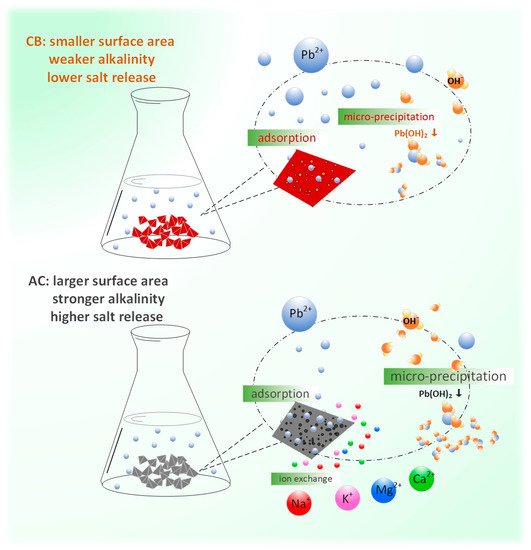
Figure 6.
Mechanism of Pb(II) removal by adsorbents.
4. Conclusions
In the present study, powdered aerated concrete (AC) and clay bricks (CB) from construction and demolition waste were investigated as low-cost adsorbents for the removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions by applying batch experiments. The adsorption characteristics were examined at different particle sizes, contact time, pH values, adsorbent dosage levels, and different initial Pb(II) concentrations. The results showed that AC outperformed CB in removing lead ions under all tested conditions, and the maximum adsorption capacity of AC for lead ions was over three times that of CB. The Langmuir and Freundlich models successfully described the adsorption isotherm data of both adsorbents. The exchange of lead ions with other metal ions was observed for both adsorbents, but this effect was weak, particularly for CB. The primary mechanism for removing lead ions from aqueous solutions using both adsorbents is through adsorption and microprecipitation. AC exhibited superior performance compared to CB due to its larger specific surface area, pore volume, and alkalinity. The cost-effectiveness and availability of AC make it a potentially attractive adsorbent for treating wastewater contaminated with lead, providing a new way for resource utilization of ever-increasing construction and demotion wastes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L. and Y.Y.; methodology, X.L., Y.Y., R.X. and X.M.; formal analysis, X.L., Y.Y. and X.M.; investigation, Y.Y., H.H. and L.Z.; data curation, X.L. and Y.Y.; resources, H.H., R.X. and L.Z.; writing—original draft, Y.Y.; writing—review and editing, X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M700742), Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Foundation (LBH-Z21109) and University Nursing Program for Young Scholars with Creative Talents in Heilongjiang Province (UNPYSCT-2018184).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vardhan, K.H.; Kumar, P.S.; Panda, R.C. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Negrete-Bolagay, D.; Figueroa, F.; Zamora-Ledezma, E.; Ni, M.; Alexis, F.; Guerrero, V.H. Heavy metal water pollution: A fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozera-Sucharda, B.; Gworek, B.; Kondzielski, I.; Chojnicki, J. The comparison of the efficacy of natural and synthetic aluminosilicates, including zeolites, in concurrent elimination of lead and copper from multi-component aqueous solutions. Processes 2021, 9, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Parihar, R.D.; Sharma, A.; Bakshi, P.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Bali, A.S.; Karaouzas, I.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.K.; Gyasi-Agyei, Y. Global evaluation of heavy metal content in surface water bodies: A meta-analysis using heavy metal pollution indices and multivariate statistical analyses. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonone, S.S.; Jadhav, S.; Sankhla, M.S.; Kumar, R. Water contamination by heavy metals and their toxic effect on aquaculture and human health through food Chain. Lett. Appl. Nanobiosci. 2020, 10, 2148–2166. [Google Scholar]
- Collin, M.S.; Venkataraman, S.K.; Vijayakumar, N.; Kanimozhi, V.; Arbaaz, S.M.; Stacey, R.S.; Anusha, J.; Choudhary, R.; Lvov, V.; Tovar, G.I. Bioaccumulation of lead (Pb) and its effects on human: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 7, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, X.; Wang, J.; Jiang, F.; Wei, L.; Chen, G.; Hao, X. Effects of lead and mercury on sulfate-reducing bacterial activity in a biological process for flue gas desulfurization wastewater treatment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, A.; Azari, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Ansarpour, M. Removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters: A review. ChemBioEng Rev. 2017, 4, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, N.; Yusof, N.; Lau, W.; Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A. Recent trends of heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by membrane technologies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 76, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.C.; Patel, R.K. Removal of lead and zinc ions from water by low cost adsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, I.R.; Chowdhury, S.; Mazumder, M.A.J.; Al-Ahmed, A. Removal of lead ions (Pb2+) from water and wastewater: A review on the low-cost adsorbents. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatiya, N.A.; Reshad, A.S.; Negie, Z.W. Chemical modification of neem (Azadirachta indica) biomass as bioadsorbent for removal of Pb2+ ion from aqueous waste water. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 7813513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Seyedin, O.; Aghamohammadhassan, M. Adsorptive removal of lead (II) ion from water and wastewater media using carbon-based nanomaterials as unique sorbents: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 254, 109814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahri, N.A.M.; Jamil, S.N.A.M.; Abdullah, L.C.; Huey, S.J.; Yaw, T.C.S.; Mobarekeh, M.N.; Rapeia, N.S.M. Equilibrium and kinetic behavior on cadmium and lead removal by using synthetic polymer. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 17, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiyadh, S.S.; AlSaadi, M.A.; Jaafar, W.Z.; AlOmar, M.K.; Fayaed, S.S.; Mohd, N.S.; Hin, L.S.; El-Shafie, A. Review on heavy metal adsorption processes by carbon nanotubes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahoon, M.A.; Siddeeg, S.M.; Alsaiari, N.S.; Mnif, W.; Rebah, F.B. Effective heavy metals removal from water using nanomaterials: A review. Processes 2020, 8, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumara, G.M.P.; Kawamoto, K. Steel slag and autoclaved aerated concrete grains as low-cost adsorbents to remove Cd2+ and Pb2+ in wastewater: Effects of mixing proportions of grains and liquid-to-solid ratio. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Miller, T.R.; Liu, G.; Tam, V.W. Construction debris becomes growing concern of growing cities. Waste Manag. 2019, 83, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Zhou, N.; Xiao, X.; Li, M.; Zhu, C. Environmental behavior of construction and demolition waste as recycled aggregates for backfilling in mines: Leaching toxicity and surface subsidence studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.; Azab, S. Environmental and economic impact assessment of construction and demolition waste disposal using system dynamics. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 82, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, B.; Xiao, J.; Singh, A. Utilization potential of aerated concrete block powder and clay brick powder from C&D waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 238, 117721. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmans, J.; Nielsen, P.; Snellings, R.; Broos, K. Recycling of autoclaved aerated concrete in floor screeds: Sulfate leaching reduction by ettringite formation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabyarmohammadi, H.; Salarirad, M.M.; Behnamfard, A. Characterization and utilization of clay-based construction and demolition wastes as adsorbents for zinc (II) removal from aqueous solutions: An equilibrium and kinetic study. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2014, 33, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djeribi, R.; Hamdaoui, O. Sorption of copper (II) from aqueous solutions by cedar sawdust and crushed brick. Desalination 2008, 225, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Kang, Y.; Luo, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q. Sustainable use of autoclaved aerated concrete waste to remove low concentration of Cd (II) ions in wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 82, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrzynska, K. Removal of cadmium from wastewaters with low-cost adsorbents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokokwe, G.; Letshwenyo, M.W. Utilisation of cement brick waste as low cost adsorbent for the adsorptive removal of copper, nickel and iron from aqueous solution: Batch and column studies. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2022, 126, 103156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmayanti, L.; Kadja, G.T.; Notodarmojo, S.; Damanhuri, E.; Mukti, R.R. Structural alteration within fly ash-based geopolymers governing the adsorption of Cu2+ from aqueous environment: Effect of alkali activation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 377, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ranst, E.; Utami, S.; Verdoodt, A.; Qafoku, N. Mineralogy of a perudic Andosol in central Java, Indonesia. Geoderma 2008, 144, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bai, X.; Dong, L.; Liang, J.; Jin, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, S.; Qu, J. Composting enhances the removal of lead ions in aqueous solution by spent mushroom substrate: Biosorption and precipitation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 200, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikongi, P.; Salvas, J.; Gosselin, R. Curve-fitting regression: Improving light element quantification with XRF. X-ray Spectrom. 2017, 46, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tan, X.; Xin, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Cui, K. Preparation of activated charcoal from pyrolusite-added sewage sludge and adsorption of lead ion in wastewater. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2010, 4, 2473–2478. [Google Scholar]
- Bibi, S.; Farooqi, A.; Yasmin, A.; Kamran, M.A.; Niazi, N.K. Arsenic and fluoride removal by potato peel and rice husk (PPRH) ash in aqueous environments. Int. J. Phytorem. 2017, 19, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filote, C.; Volf, I.; Santos, S.C.; Botelho, C.M. Bioadsorptive removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution by the biorefinery waste of Fucus spiralis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, B.; Li, W.; Xie, L.; Yu, J.; He, F. Performance analysis of demolition waste bricks for phosphorus removal from stormwater runoff. Urban Water J. 2020, 17, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Yin, N.; Ouyang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, P. Waste non-burn-free brick derived sulfhydryl functioned magnetic zeolites and their efficient removal of uranium (VI) ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 571, 151241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikyskova, E.; Dousova, B.; Mikysek, P.; Lhotka, M.; Kolousek, D. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study of Pb2+ removal from aqueous solution by waste brick dust. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 634, 127939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazy, S.E.; Gad, A.H. Lead separation by sorption onto powdered marble waste. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 7, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawket, A.; Abderyim, S.; Ismayil, N. Analysis of the adsorption properties of lead ion onto natural sand particles by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2011, 31, 3126–3129. [Google Scholar]
- Sarı, A.; Tuzen, M.; Soylak, M. Adsorption of Pb (II) and Cr (III) from aqueous solution on Celtek clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perić, J.; Trgo, M.; Medvidović, N.V. Removal of zinc, copper and lead by natural zeolite—A comparison of adsorption isotherms. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1893–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Jin, X.; Lu, X.; Chen, Z. Adsorption of Pb (II), Cd (II), Ni (II) and Cu (II) onto natural kaolinite clay. Desalination 2010, 252, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellaoui, Y.; Olguín, M.T.; Abatal, M.; Ali, B.; Méndez, S.E.D.; Santiago, A.A. Comparison of the divalent heavy metals (Pb, Cu and Cd) adsorption behavior by montmorillonite-KSF and their calcium-and sodium-forms. Superlattices Microstruct. 2019, 127, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantawong, V.; Harvey, N.; Bashkin, V. Comparison of heavy metal adsorptions by Thai kaolin and ballclay. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 148, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranđelović, M.; Purenović, M.; Zarubica, A.; Purenović, J.; Matović, B.; Momčilović, M. Synthesis of composite by application of mixed Fe, Mg (hydr) oxides coatings onto bentonite–a use for the removal of Pb (II) from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 199, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdus-Salam, N.; Adekola, F. The influence of pH and adsorbent concentration on adsorption of lead and zinc on a natural goethite. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. 2005, 6, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahfarokhi, S.S.H.; Landi, A.; Khademi, H.; Hojati, S. Removal of Cd2+ and Pb2+ ions from aqueous solutions using iranian natural zeolite and sepiolite. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 40, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, D.; Kim, H.U.; Lee, S.M. Removal behavior of sericite for Cu (II) and Pb (II) from aqueous solutions: Batch and column studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 57, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wei, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Xu, W.; Qu, J. Interpretation of lead removal by two biomasses at different size via monitoring the solution environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pap, S.; Kirk, C.; Bremner, B.; Sekulic, M.T.; Shearer, L.; Gibb, S.W.; Taggart, M.A. Low-cost chitosan-calcite adsorbent development for potential phosphate removal and recovery from wastewater effluent. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).