Coleus aromaticus Ethanolic Leaves Extract Mediates Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Plant Sample and Authentication
2.4. Coleus Aromaticus Extract Preparation
2.5. GC-MS Analysis
2.6. Assessment of EtOH-LCa-Mediated Cytotoxicity
2.7. Assessment of EtOH-LCa Mediated Effects on Morphology
2.8. EtOH-LCa-Mediated Effects on Nuclear Morphology
2.9. Assessment of EtOH-LCa Mediated Effects on Caspase-3 Activity
2.10. Evaluation of EtOH-LCa Mediated Effects on Intracellular ROS
2.11. Assessment of EtOH-LCa Mediated Effects on Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (ΔΨm)
2.12. Cell Cycle Assay
2.13. Assessment of EtOH-LCa Mediated Effects on NF-κB Levels
2.14. qRT-PCR-Based Assessment of Gene Expression
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Various Phytoconstituent
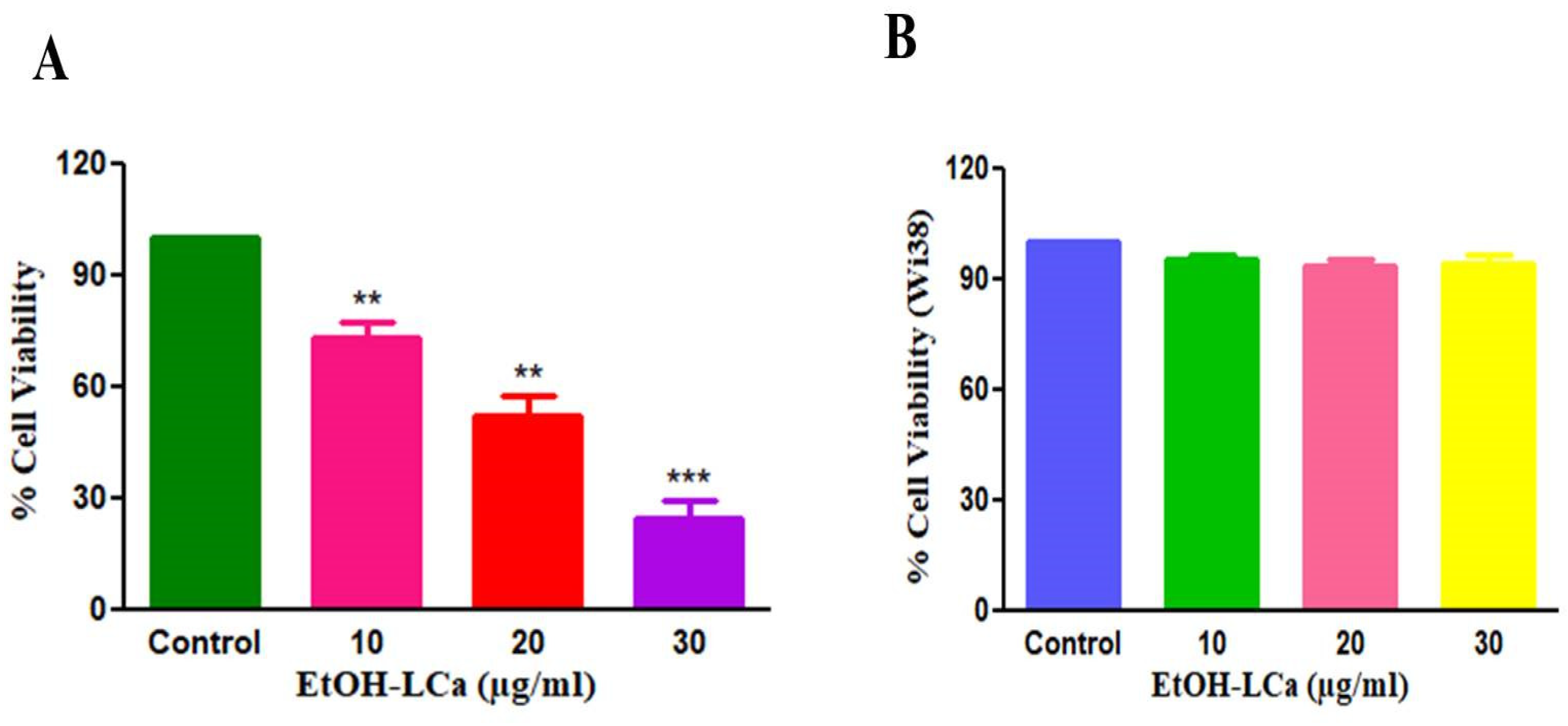
3.2. EtOH-LCa Exerts Cytotoxic Effects in Lung Carcinoma Cells
3.3. EtOH-LCa Induces Significant Morphological Aberrations in Lung Carcinoma Cells
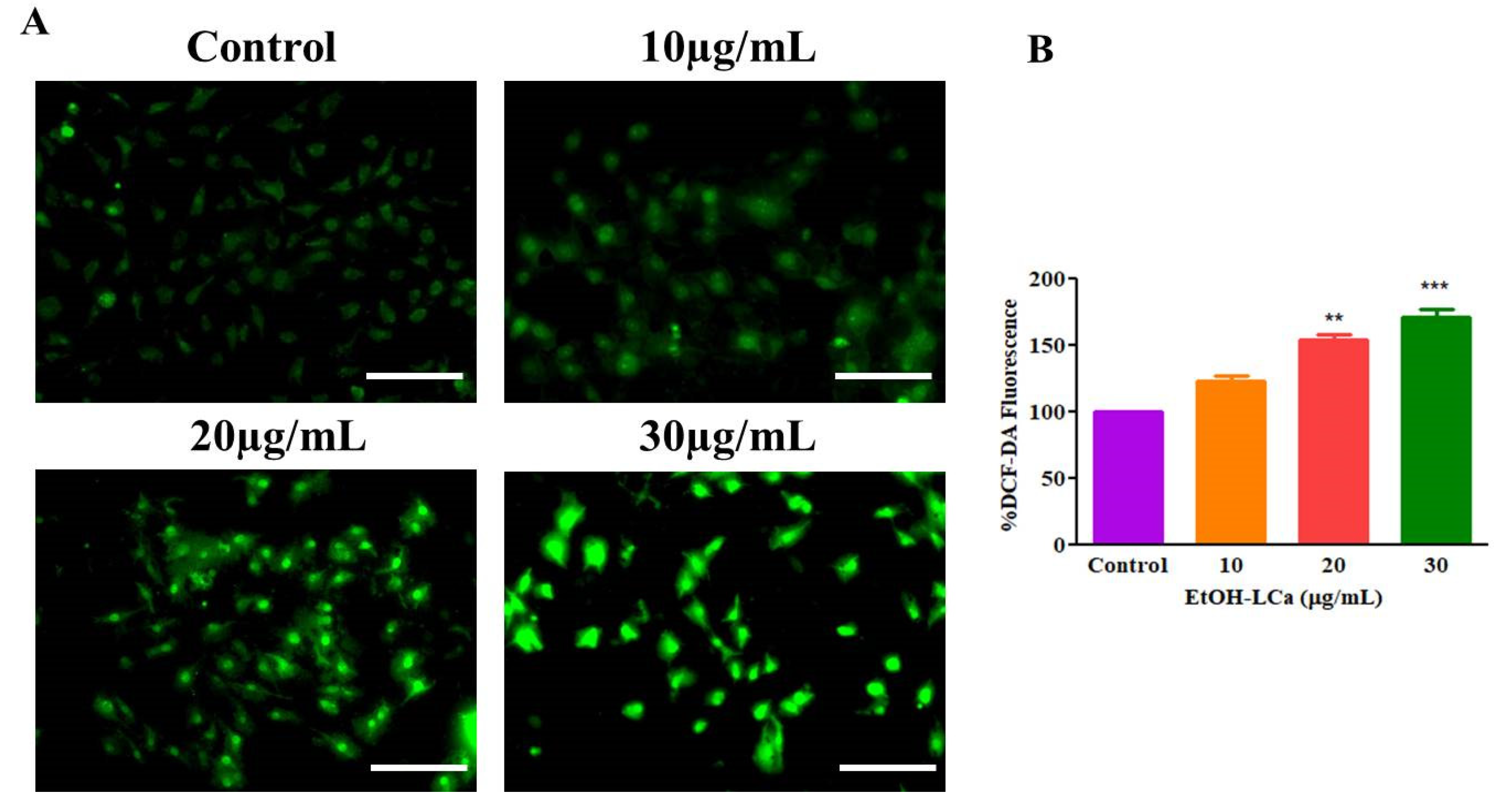
3.4. EtOH-LCa Generates High ROS -Mediated Oxidative Stress in Lung Carcinoma Cells
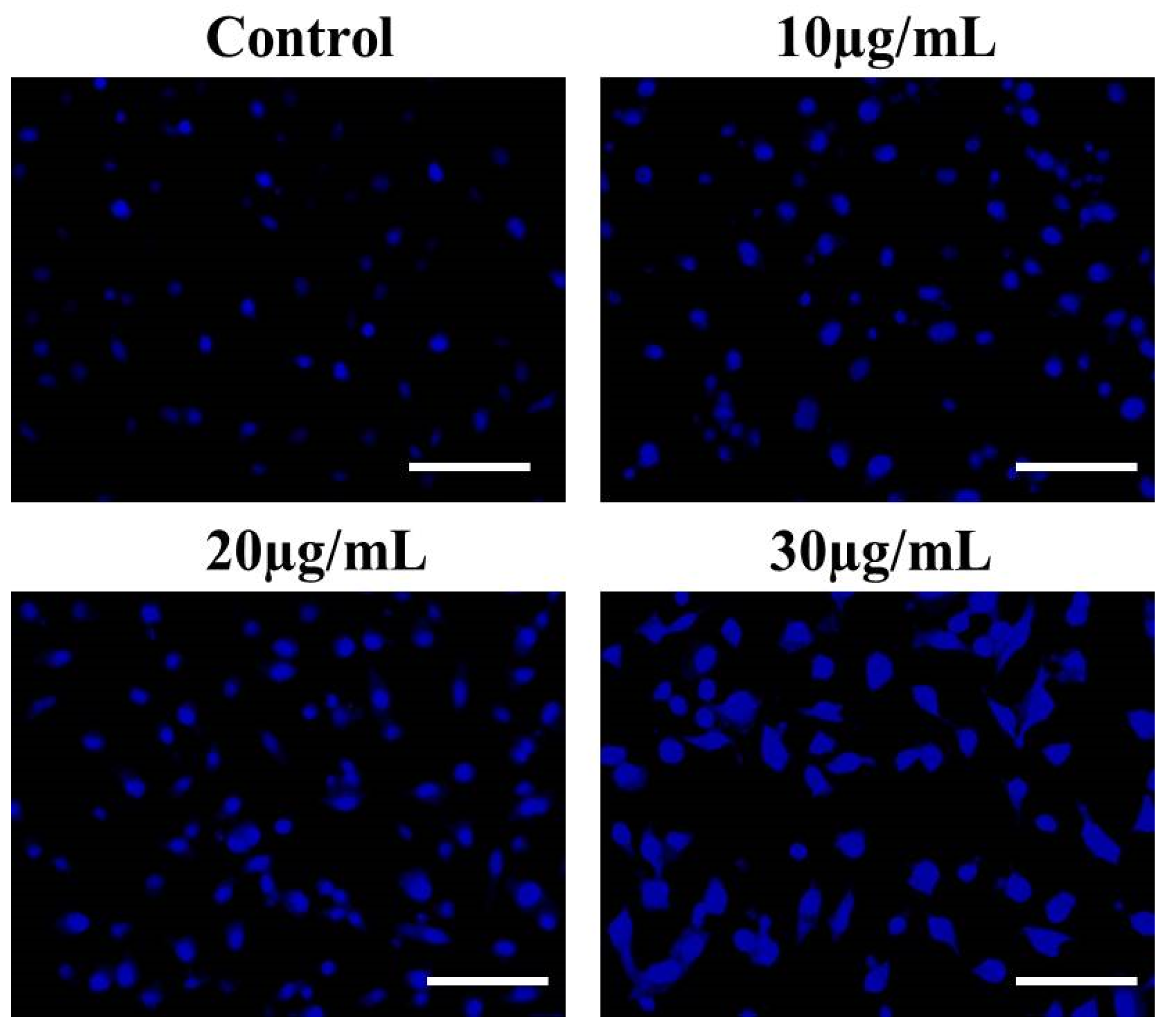
3.5. EtOH-LCa Induces Nuclear Condensation and Fragmentation in Lung Carcinoma Cells
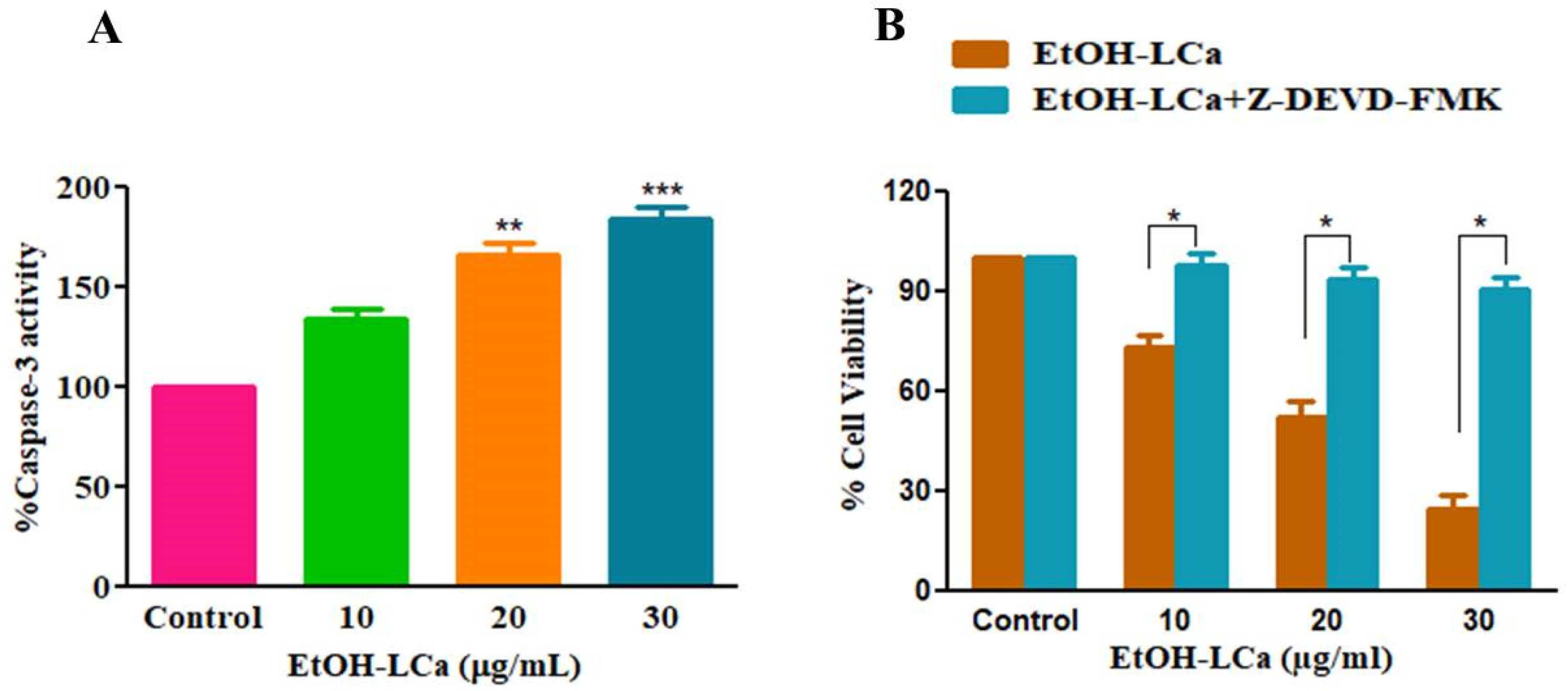
3.6. Effect of EtOH-LCa on Activation of Caspase-3 in A549 Lung Cancer Cells
3.7. Effect of EtOH-LCa on Mitochondrial Membrane Potential in Lung Carcinoma Cells
3.8. Effect of EtOH-LCa on Expression Levels of Bcl-2 Members in Lung Carcinoma Cells
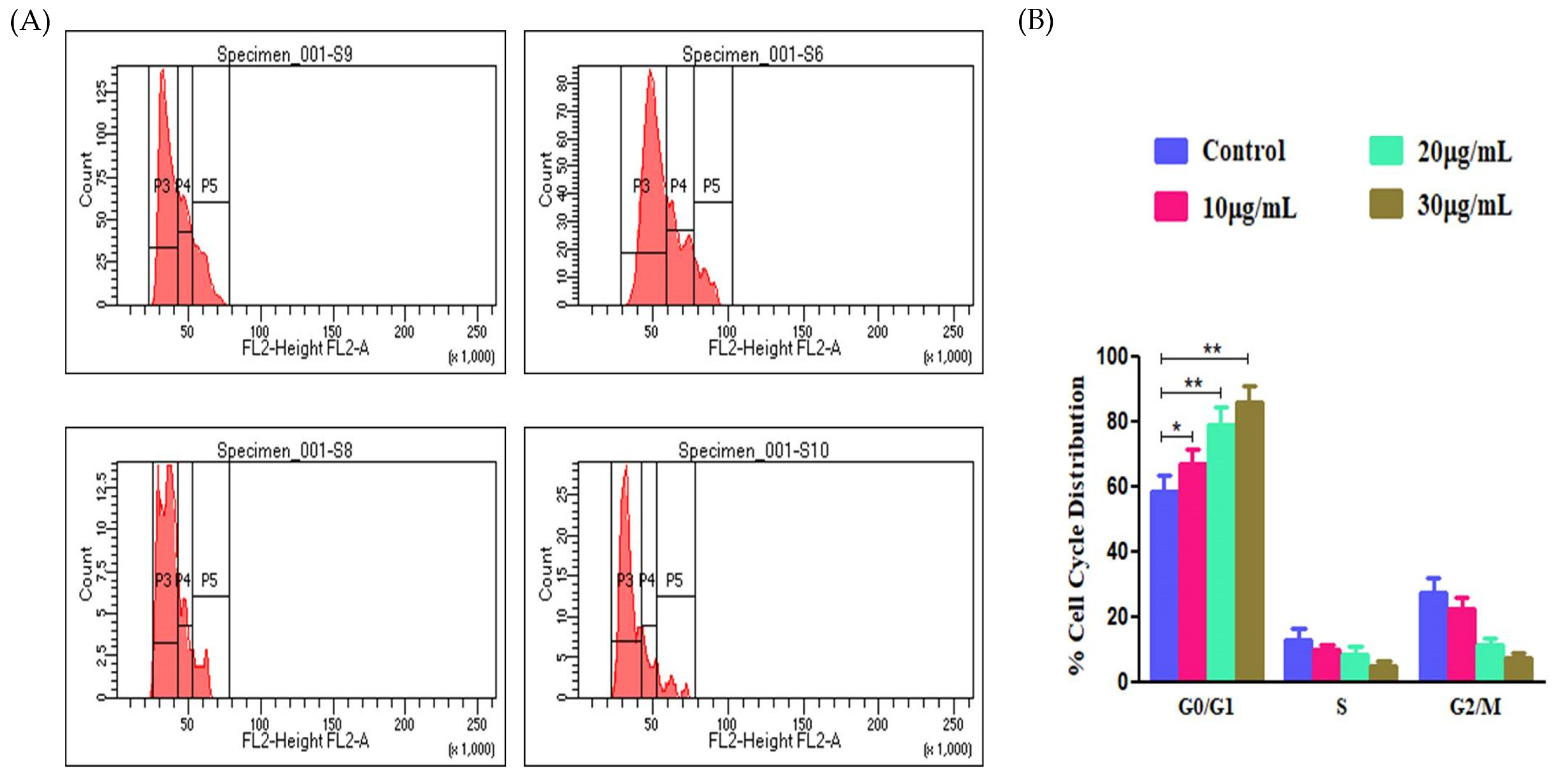
3.9. Effect of EtOH-LCa on Cell Cycle Progression of A549 Cells
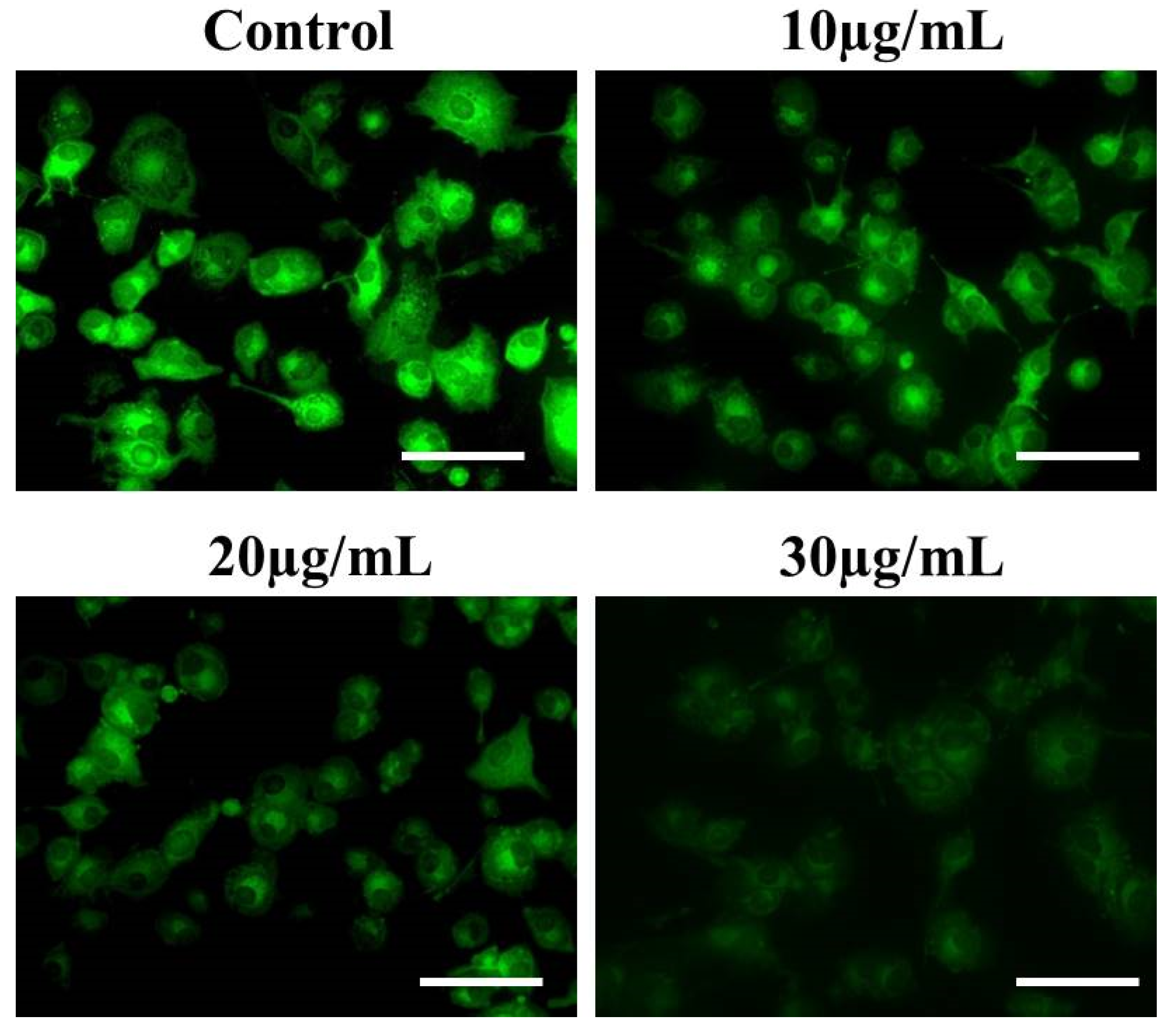
3.10. EtOH-LCa Inhibited the NF-kB Signaling Pathway in Lung Carcinoma Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawsari, M.F.; Alalaiwe, A.; Khafagy, E.S.; Al Saqr, A.; Alshahrani, S.M.; Alsulays, B.B.; Alshehri, S.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Danish Rizvi, S.M.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Efficacy of SPG-ODN 1826 Nanovehicles in Inducing M1 Phenotype through TLR-9 Activation in Murine Alveolar J774A.1 Cells: Plausible Nano-Immunotherapy for Lung Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subaiea, G.M.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Yadav, H.K.S.; Al Hagbani, T.; Abdallah, M.H.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Gangadharappa, H.V.; Hussain, T.; Abu Lila, A.S. Ganetespib with Methotrexate Acts Synergistically to Impede NF-κB/p65 Signaling in Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockswold, G.L.; Ramsey, H.E.; Buker, G.D. The results of treatment of lung cancer by surgery, radiation and chemotherapy at a USPHS hospital. Mil. Med. 1970, 135, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.J.; Qi, M.; Li, N.; Lei, Y.H.; Zhang, D.M.; Chen, J.X. Natural products and their derivatives: Promising modulators of tumor immunotherapy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, N.; Akram, M.; Yaniv-Bachrach, Z.; Daniyal, M. Is it safe to consume traditional medicinal plants during pregnancy? Phytother. Res. 2020, 35, 1908–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Plants as a source of anti-cancer agents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimmy, J.L. Coleus aromaticus Benth.: An update on its bioactive constituents and medicinal properties. All. Life 2021, 14, 756–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadikar, D.D.; Patki, P.E. Coleus aromaticus: A therapeutic herb with multiple potentials. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 2895–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariram, N. Coleus aromaticus Benth Synthesis of Potentially Nanomedicine as High Nutritive Value of Human Health and Immunomodulator. IJSRM 2016, 4, 18–38. [Google Scholar]
- Khare, R.S.; Kundu, S. Coleus Aromaticus Benth—A Nutritive Medicinal Plant Of Potential Therapeutic Value. Int. J. Pharma Bio Sci. 2011, 2, 488–500. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, V.M.; Pai, V.R.; Kedilaya, P. A preliminary evaluation of anticancer and antioxidant potential of two traditional medicinal plants from Lamiaceae—Pogostemon heyneanus and Plectranthus amboinicus. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 6, 073–078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulianto, W.; Andarwulan, N.; Giriwono, P.E.; Pamungkas, J. HPLC-based metabolomics to identify cytotoxic compounds from Plectranthus amboinicus (Lour.) Spreng against human breast cancer MCF-7Cells. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1039, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.S., Jr. The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996, 14, 649–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Lin, A. NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Bai, L.; Lin, Y. NF-kappaB in lung cancer, a carcinogenesis mediator and a prevention and therapy target. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2011, 16, 1172–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Lin, Y. Sensitization of TNF-induced cytotoxicity in lung cancer cells by concurrent suppression of the NF-kappaB and Akt pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 355, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ju, W.; Renouard, J.; Aden, J.; Belinsky, S.A.; Lin, Y. 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin synergistically potentiates tumor necrosis factor-induced lung cancer cell death by blocking the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyrd-Hansen, M.; Meier, P. IAPs: From caspase inhibitors to modulators of NF-kappaB, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kani, K.; Momota, Y.; Harada, M.; Yamamura, Y.; Aota, K.; Yamanoi, T.; Takano, H.; Motegi, K.; Azuma, M. γ-tocotrienol enhances the chemosensitivity of human oral cancer cells to docetaxel through the downregulation of the expression of NF-κB-regulated anti-apoptotic gene products. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, A.; Ahmad, A.; Tiwari, R.K.; Ahmad, I.; Alkhathami, A.G.; Alshahrani, M.Y.; Asiri, M.A.; Almeleebia, T.M.; Saeed, M.; Yadav, D.K.; et al. In Vitro Evaluation of Antioxidant, Anticancer, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Adenium obesum. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 847534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Tiwari, R.K.; Mishra, P.; Alkhathami, A.G.; Almeleebia, T.M.; Alshahrani, M.Y.; Ahmad, I.; Asiri, R.A.; Alabdullah, N.M.; Hussien, M.; et al. Antiproliferative and apoptotic potential of Glycyrrhizin against HPV16+ Caski cervical cancer cells: A plausible association with downreguation of HPV E6 and E7 oncogenes and Notch signaling pathway. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 3264–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Ansari, I.A. Carvacrol Exhibits Chemopreventive Potential against Cervical Cancer Cells via Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis and Abrogation of Cell Cycle Progression. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 2224–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Tiwari, R.K.; Saeed, M.; Al-Amrah, H.; Han, I.; Choi, E.H.; Yadav, D.K.; Ansari, I.A. Carvacrol instigates intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis with abrogation of cell cycle progression in cervical cancer cells: Inhibition of Hedgehog/GLI signaling cascade. Front. Chem. 2023, 10, 1064191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaltaev, N.; Axelrod, S. Global lung cancer mortality trends and lifestyle modifications: Preliminary analysis. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 1526–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder, C.; Bulliard, J.L.; Germann, S.; Konzelmann, I.; Bochud, M.; Leyvraz, M.; Chiolero, A. Estimating lifetime and 10-year risk of lung cancer. Prev. Med. Rep. 2018, 11, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lila, A.S.; Kiwada, H.; Ishida, T. Selective delivery of oxaliplatin to tumor tissue by nanocarrier system enhances overall therapeutic efficacy of the encapsulated oxaliplatin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, G.E.; Md Akim, A.; Sung, Y.Y.; Sifzizul, T.M.T. Cancer and apoptosis: The apoptotic activity of plant and marine natural products and their potential as targeted cancer therapeutics. Front. Pharm. 2022, 13, 842376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, C.M.; Singh, A.T.K. Apoptosis: A Target for Anticancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Lin, Z.Q.; Liu, B.; Wei, Y.Q. Caspase-mediated programmed cell death pathways as potential therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell. Prolif. 2012, 45, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khafagy, E.-S.; Al Saqr, A.; Alotaibi, H.F.; Abu Lila, A.S. Cytotoxic and Apoptotic Effect of Rubus chingii Leaf Extract against Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma A549 Cells. Processes 2022, 10, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelle, J.K.; Letai, A. Control of mitochondrial apoptosis by the Bcl-2 family. J. Cell. Sci. 2009, 122, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Saqr, A.; Khafagy, E.S.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Almansour, K.; Abu Lila, A.S. Screening of Apoptosis Pathway-Mediated Anti-Proliferative Activity of the Phytochemical Compound Furanodienone against Human Non-Small Lung Cancer A-549 Cells. Life 2022, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.Q.; Rashid, K.; AlAmodi, A.A.; Agha, M.V.; Akhtar, S.; Hakeem, I.; Raza, S.S.; Uddin, S. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cancer pathogenesis and therapy: An update on the role of ROS in anticancer action of benzophenanthridine alkaloids. Biomed. Pharm. 2021, 143, 112142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, S.; Giorgi, C.; Suski, J.M.; Agnoletto, C.; Bononi, A.; Bonora, M.; De Marchi, E.; Missiroli, S.; Patergnani, S.; Poletti, F.; et al. Mitochondria-ros crosstalk in the control of cell death and aging. J. Signal. Transduct. 2012, 2012, 329635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorov, D.B.; Juhaszova, M.; Sollott, S.J. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 909–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, B.H.; Funkhouser, W.K.; Calvo, B.F.; Meyers, M.O.; Kim, H.J.; Goldberg, R.M.; Bernard, S.A.; Caskey, L.; Deal, A.M.; Wright, F.; et al. Nuclear factor κ-light chain-enhancer of activated B cells is activated by radiotherapy and is prognostic for overall survival in patients with rectal cancer treated with preoperative fluorouracil-based chemoradiotheraphy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.P.; Zheng, C.C.; Huang, Y.N.; He, M.L.; Xu, W.W.; Li, B. Molecular mechanisms of chemo- and radiotherapy resistance and the potential implications for cancer treatment. MedComm 2021, 2, 315–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmi, R.R.; Sakthivel, K.M.; Guruvayoorappan, C. NF-κB inhibitors in treatment and prevention of lung cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Tchou-Wong, K.-M.; Rom, W.N. NF-kappaB in Lung Tumorigenesis. Cancers 2011, 3, 4258–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Range |
|---|---|
| Ion source temperature | 200 °C |
| Column flow rate | 1.24 mL/min |
| Column oven temperature | 280 °C |
| Column injector temperature | 250 °C |
| Pressure mode | 66.7 kPa |
| Total flow rate | 10.4 mL/min |
| Interface temperature | 260 °C |
| Gene Name | Forward Sequence | Reverse Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | CGACCACTTTGTCAAGCTCA | CCCCTCTTCAAGGGGTCTAC |
| Bcl2 | ATTGGGAAGTTTCAAATCAGC | TGCATTCTTGGACGAGGG |
| Bax | TCAGGATGCGTCCACCAAGAAG | TGTGTCCACGGCGGCAATCATC |
| Bad | CCTCAGGCCTATGCAAAAAG | AAACCCAAAACTTCCGATGG |
| Bcl-XL | GCCACTTACCTGAATGACCACC | AACCAGCGGTTGAAGCGTTCCT |
| S. No. | Retention Time | Area (%) | Compound Name | Molecular Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 6.504 | 0.02 | 2-Methylcyclopentanol | C6H12O |
| 2. | 9.398 | 0.03 | 1-Decene | C10H20 |
| 3. | 15.650 | 0.10 | 1-Dodecanol | C12H26O |
| 4. | 18.707 | 0.04 | Phenol, 5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)-, acetate | C12H16O |
| 5. | 18.957 | 0.03 | 1H-3a,7-Methanoazulene | C11H10 |
| 6. | 21.472 | 0.20 | 1-Tetradecanol | C14H30O |
| 7. | 23.689 | 0.85 | 1-Dodecanol | C12H26O |
| 8. | 26.695 | 0.21 | 1-Hexadecanol | C16H34O |
| 9. | 27.615 | 0.45 | Hexadecamethylcyclooctasiloxane | C16H48O8Si8 |
| 10. | 29.070 | 1.33 | n-Tridecan-1-ol | C13H28O |
| 11. | 29.231 | 0.24 | Propanoic acid | C₃H₆O₂ |
| 12. | 31.142 | 2.03 | Octadecamethylcyclononasiloxane | C18H54O9Si9 |
| 13. | 31.387 | 0.12 | Behenic alcohol | C22H46O |
| 14. | 32.335 | 0.12 | 6-Octen-1-ol, 3,7-dimethyl-, propanoate | C13H24O2 |
| 15. | 32.816 | 0.10 | 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis(2-methylpropyl) ester | C16H22O |
| 16. | 33.838 | 0.79 | Cyclodecasiloxane, eicosamethyl- | C20H60O10Si10 |
| 17. | 34.947 | 0.33 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | C₁₆H₃₂O₂ |
| 18. | 35.619 | 0.20 | Irganox 1076 TMS | C38H70O3Si |
| 19. | 37.921 | 0.33 | Phytol | C20H40O |
| 20. | 38.907 | 0.17 | 2-Propenoic acid, 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-, 2-ethylhexyl ester | C18H26O3 |
| 21. | 39.844 | 0.38 | Phytyl stearate | C38H74O2 |
| 22. | 44.396 | 7.28 | Tetracosamethyl-cyclododecasiloxane | C24H72O12Si12 |
| 23. | 44.848 | 0.13 | Tetrapentacontane | C54H110 |
| 24. | 45.344 | 4.45 | Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | C24H38O4 |
| 25. | 45.796 | 0.63 | 4,4’-Methylenebis(2,6-DI-tert-butylphenol) | C29H44O2 |
| 26. | 46.887 | 0.51 | Linalyl isobutyrate | C14H24O2 |
| 27. | 49.486 | 0.15 | Hexacontane | C60H122 |
| 28. | 49.699 | 2.07 | 4-Hydroxy-7,7’,8,8’,11,11’,12,12’,15,15’-decahydro-beta, psi-carotene | C40H66O |
| 29. | 50.935 | 0.31 | Tetracosane | |
| 30. | 51.967 | 0.04 | 2,6-Dichloro-4-nitrophenol | C6H3Cl2NO3 |
| 31. | 53.823 | 0.08 | Oxirane, hexadecyl | C18H36O |
| 32. | 54.382 | 0.65 | α-Tocopherol-β-D-mannoside | C24H50 |
| 33. | 56.341 | 0.78 | Lathosterol | C27H46O |
| 34. | 56.730 | 0.06 | Profenofos | C11H15BrClO3PS |
| 35. | 56.841 | 1.16 | Stigmasterol | C29H48O |
| 36. | 57.403 | 0.04 | Quebrachamine | C19H26N2 |
| 37. | 57.537 | 0.12 | Octanedioic acid dimethyl ester | C10H18O4 |
| 38. | 58.257 | 0.07 | Testosterone decanoate | C29H46O3 |
| 39. | 59.219 | 0.84 | Alpha-amyrin | C30H50O |
| 40. | 60.220 | 0.02 | Monocrotophos | C7H14NO5P |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Subaiea, G.; Alafnan, A.; Alamri, A.; Hussain, T.; Hassoun, S.M.; Lila, A.S.A.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Katamesh, A.A. Coleus aromaticus Ethanolic Leaves Extract Mediates Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells. Processes 2023, 11, 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11051332
Subaiea G, Alafnan A, Alamri A, Hussain T, Hassoun SM, Lila ASA, Khafagy E-S, Katamesh AA. Coleus aromaticus Ethanolic Leaves Extract Mediates Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells. Processes. 2023; 11(5):1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11051332
Chicago/Turabian StyleSubaiea, Gehad, Ahmed Alafnan, Abdulwahab Alamri, Talib Hussain, Shimaa Mahmoud Hassoun, Amr Selim Abu Lila, El-Sayed Khafagy, and Ahmed A. Katamesh. 2023. "Coleus aromaticus Ethanolic Leaves Extract Mediates Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells" Processes 11, no. 5: 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11051332
APA StyleSubaiea, G., Alafnan, A., Alamri, A., Hussain, T., Hassoun, S. M., Lila, A. S. A., Khafagy, E.-S., & Katamesh, A. A. (2023). Coleus aromaticus Ethanolic Leaves Extract Mediates Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells. Processes, 11(5), 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11051332











