Comparative Analysis of the Engine Performance and Emissions Characteristics Powered by Various Ethanol–Butanol–Gasoline Blends
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
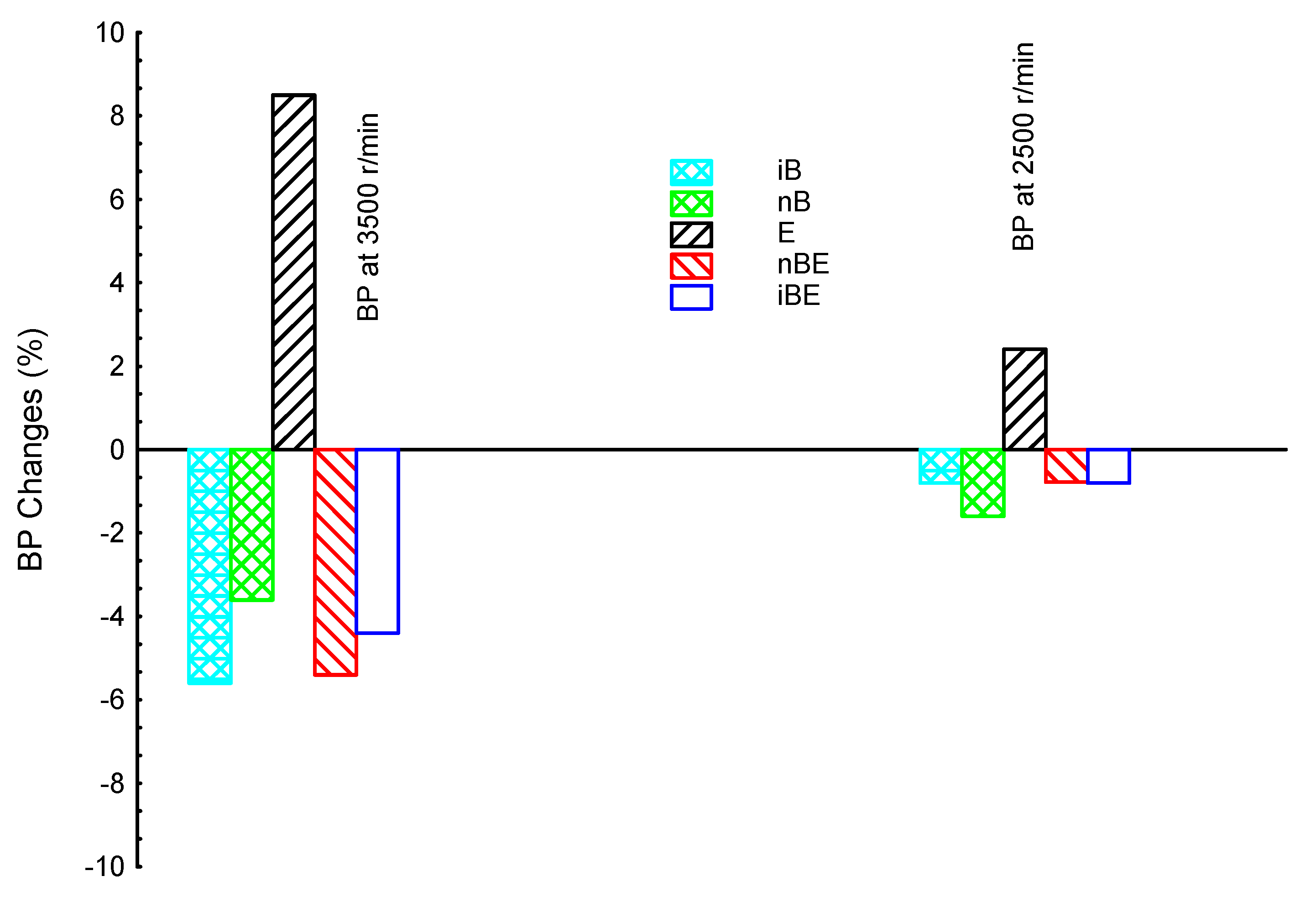
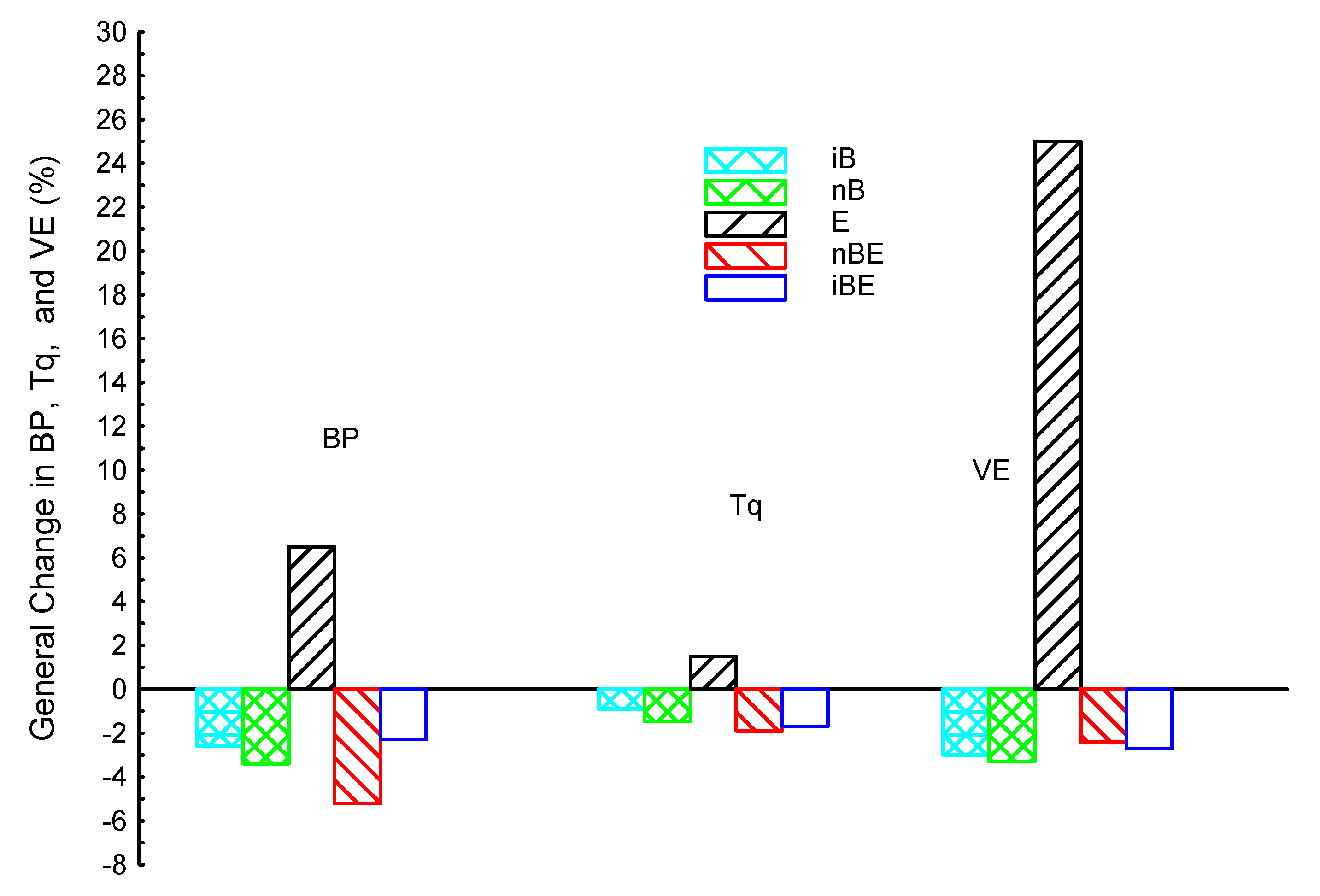
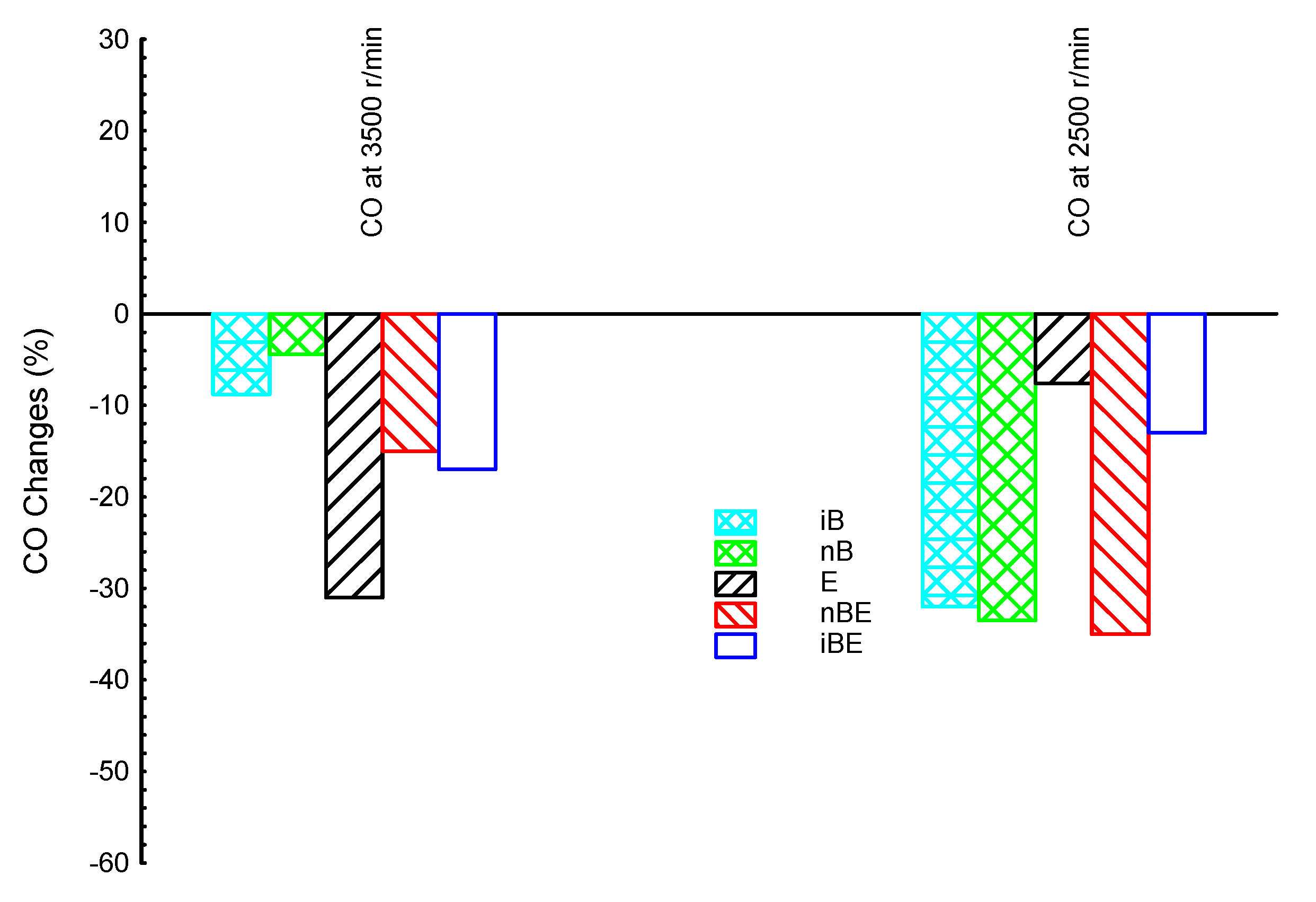
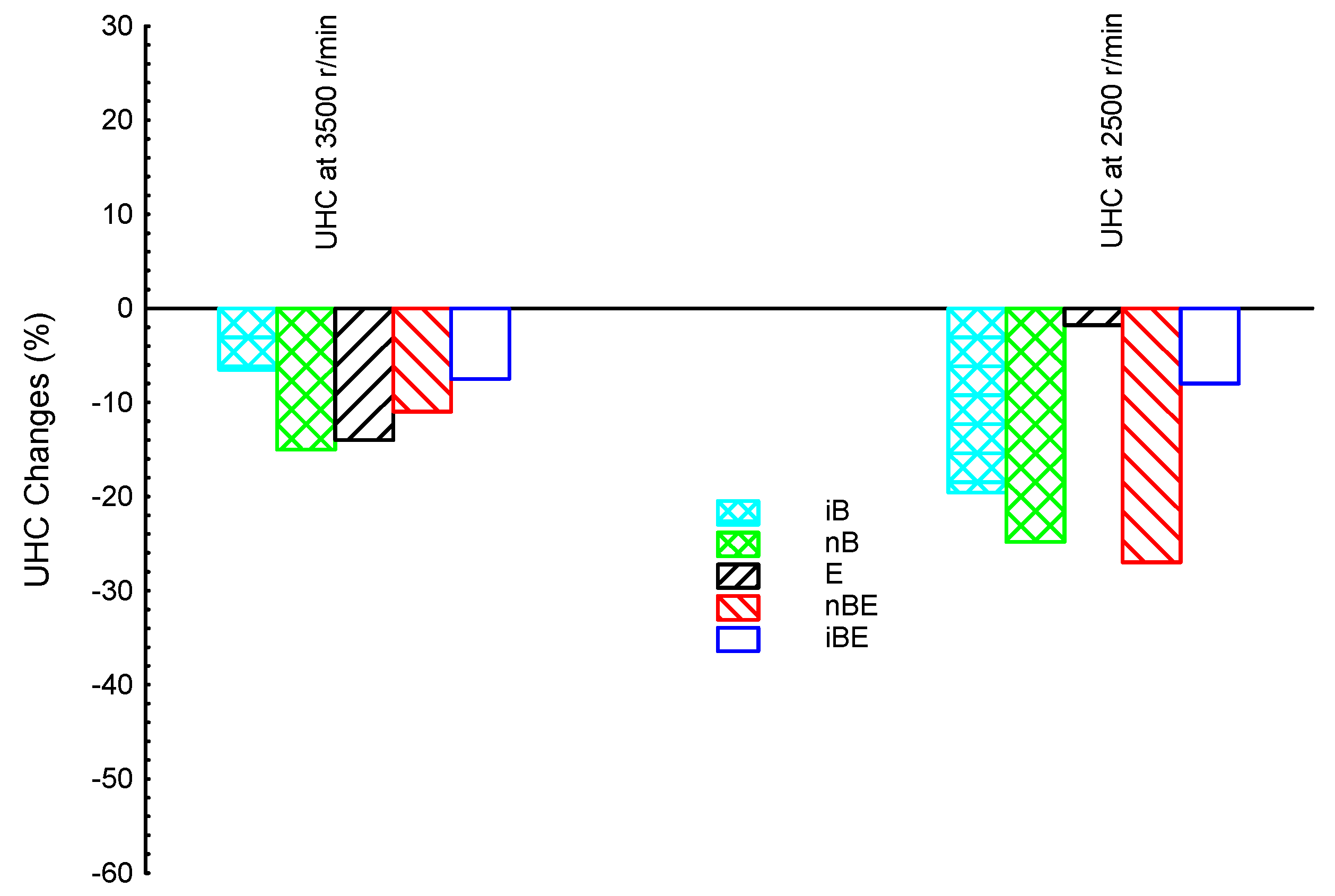
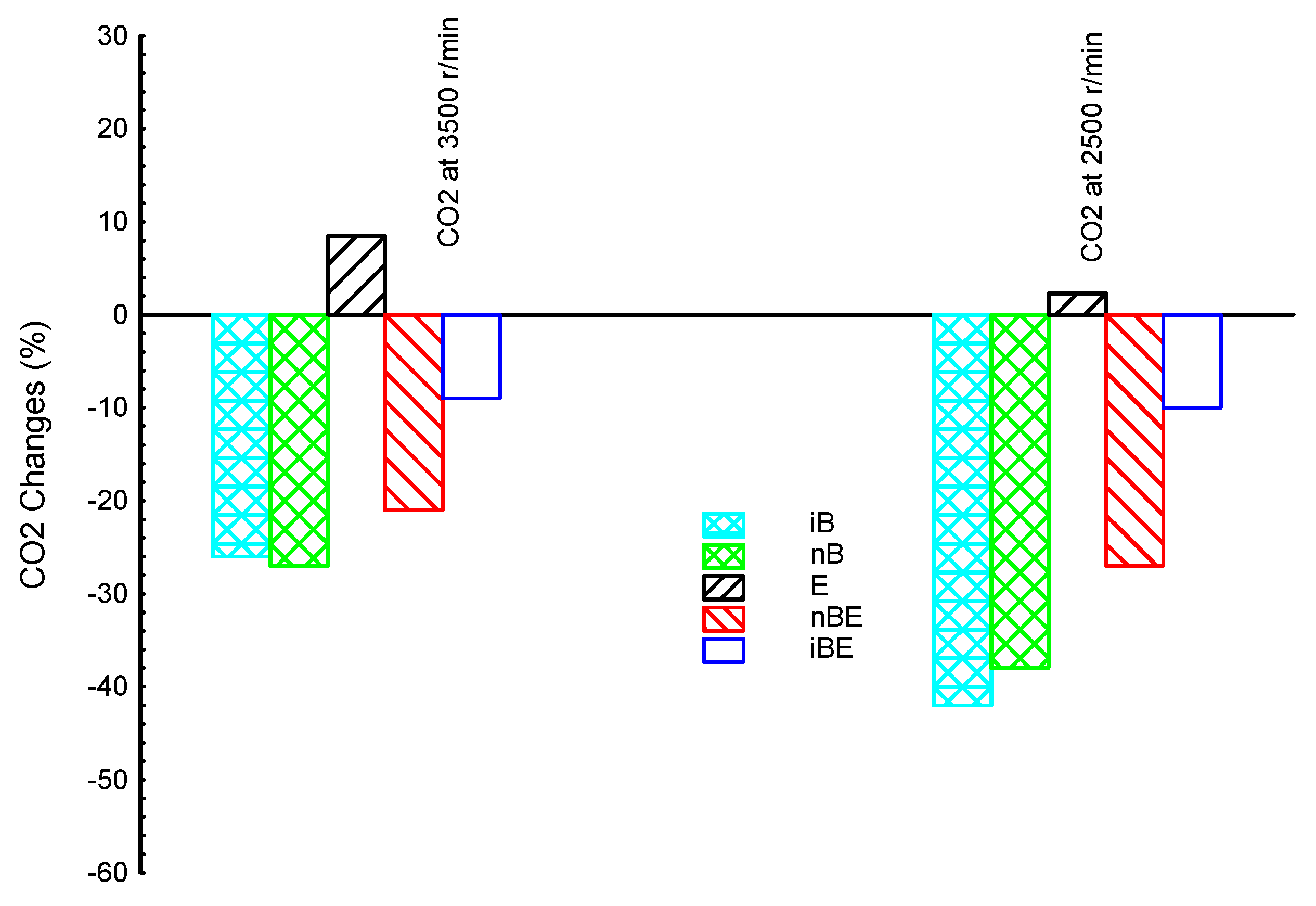
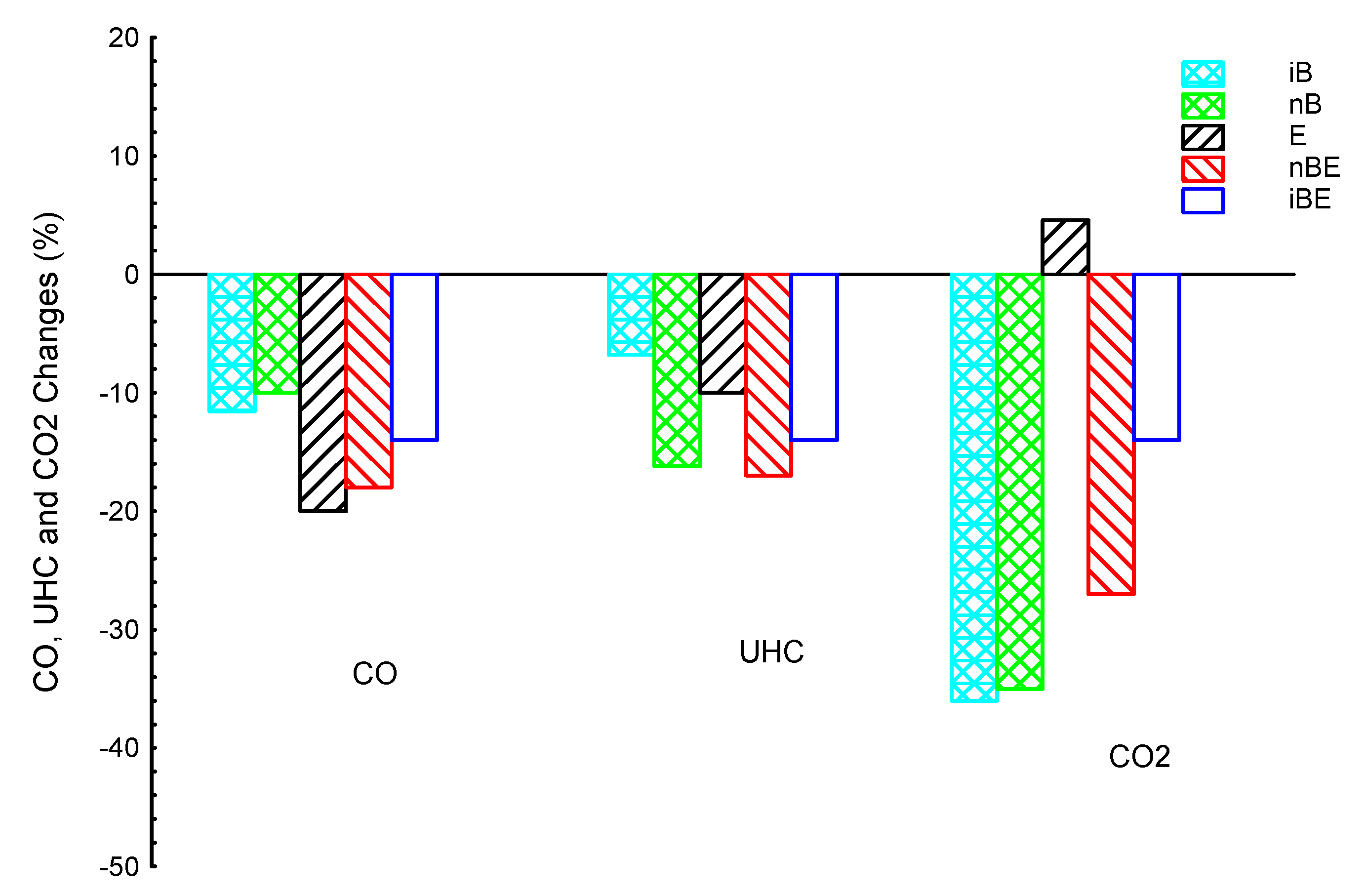
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations/Nomenclatures
| CO | Carbon monoxide |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| UHC | Unburned hydrocarbon |
| BP | Brake power |
| Tq | Engine torque |
| VE | Volumetric efficiency |
| iB | i-Butanol–gasoline blend |
| nB | n-Butanol– gasoline blend |
| E | Bio-ethanol–gasoline blend |
| nBE | n-Butanol–bio-ethanol–gasoline blend |
| iBE | i-Butanol–bio-ethanol–gasoline blend |
References
- Elfasakhany, A.; Klason, T.; Bai, X.S. Modeling of Pulverised Wood Combustion Using a Functional Group Model. Combust. Theory Model. 2008, 12, 883–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A.; Tao, L.; Espenas, B.; Larfeldt, J.; Bai, X.S. Pulverised Wood Combustion in a Vertical Furnace: Experimental and Computational Analyses. Appl. Energy 2013, 112, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A. Powder biomass fast pyrolysis as in combustion conditions: Numerical prediction and validation. Renew. Energy Focus 2018, 27, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A.; Bai, X.S. Numerical and experimental studies of irregular-shape biomass particle motions in turbulent flows. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2019, 22, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A. The Effects of Ethanol-Gasoline Blends on Performance and Exhaust Emission Characteristics of Spark Ignition Engines. Int. J. Automot. Eng. 2014, 4, 608–620. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Kang, D.; Fridlyand, A.; Goldsborough, S.S.; Vuilleumier, D. Autoignition behavior of gasoline/ethanol blends at engine-relevant conditions. Combust. Flame 2020, 216, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A. Experimental study on emissions and performance of an internal combustion engine fueled with gasoline and gasoline/n-butanol blends. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 88, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Fan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Nour, M.; Li, X. Combustion and emissions of isomeric butanol/gasoline surrogates blends on an optical GDI engine. Fuel 2020, 27215, 117690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A. Experimental investigation on SI engine using gasoline and a hybrid iso-butanol/gasoline fuel. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 95, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, D.; Qi, W. Comparative study on air dilution and hydrogen-enriched air dilution employed in a SI engine fueled with iso-butanol-gasoline. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 10895–10905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isam, E.Y.; Saleh, A.M. Butanol-gasoline blends impact on performance and exhaust emissions of a four stroke spark ignition engine. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 41, 102612. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, H.; Hajialimohammadi, A.; Gavzan, I.J.; Hajimousa, M.A. Numerical and experimental investigation on the effect of using blended gasoline-ethanol fuel on the performance and the emissions of the bi-fuel Iranian national engine. Fuel 2023, 337, 127252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadiri, U. Computational Investigations on MPFI Engine Fueled Blended Ethanol, H2O based Micro-Emulsions, and Conventional Gasoline. Environ. Adv. 2023; 100367, (in press). [CrossRef]
- Mortadha, K.M.; Hyder, H.B.; Zaid, M.H.A.-D.; Zaid, S.K.; Mudhaffar, S.A.-Z. Effect of ethanol-gasoline blends on SI engine performance and emissions. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 25, 100891. [Google Scholar]
- Iodice, P.; Amoresano, A.; Langella, G. A review on the effects of ethanol/gasoline fuel blends on NOX emissions in spark-ignition engines. Biofuel Res. J. 2021, 8, 1465–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehhaghi, M.; Panahi, H.K.S.; Aghbashlo, M.; Lam, S.S.; Tabatabaei, M. The effects of nanoadditives on the performance and emission characteristics of spark-ignition gasoline engines: A critical review with a focus on health impacts. Energy 2021, 225, 120259. [Google Scholar]
- Nazzal, T. Experimental study of gasoline –Alcohol blends on performance of internal combustion engine. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2011, 52, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Elfasakhany, A. Investigations on the effects of ethanol-methanol-gasoline blends in a spark-ignition engine: Performance and emissions analysis. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2015, 18, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, D.; Govindarajan, P.; Venkatesan, J. Influence of isobutanol blend in spark ignition engine performance operated with gasoline and ethanol. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2010, 2, 2859–2868. [Google Scholar]
- Sileghem, L.; Coppens, A.; Casier, B.; Vancoillie, J.; Verhelst, S. Performance and emissions of iso-stoichiometric ternary GEM blends on a production SI engine. Fuel 2014, 117, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A.; Mahrous, A.-F. Performance and emissions assessment of n-butanol–methanol–gasoline blends as a fuel in spark-ignition engines. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 3015–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.W.G.; Pearson, R.J.; Dekker, E.; Iosefa, B.; Johansson, K.; Bergstom, K. Extending the role of alcohols as transport fuels using iso-stoichiometric ternary blends of gasoline, ethanol and methanol. Appl. Energy 2013, 102, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, V.F.; Anderson, J.E.; Wallington, T.J.; Nielsen, O.J. Vapor pressures of alcohol–gasoline blends. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 3647–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A. Exhaust emissions and performance of ternary iso-butanol–bio-methanol–gasoline and n-butanol–bio-ethanol–gasoline fuel blends in spark-ignition engines: Assessment and comparison. Energy 2018, 158, 830–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A. Experimental study of dual n-butanol and iso-butanol additives on spark-ignition engine performance and emissions. Fuel 2016, 163, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwale, L.; Kristóf, L.; Bereczky, A.; Mbarawa, M.; Kolesnikov, A. Performance, combustion and emission characteristics of n-butanol additive in methanol–gasoline blend fired in a naturally-aspirated spark ignition engine. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 118, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A. Benefits and drawbacks on the use biofuels in spark ignition engines. In Mauritius; LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing: Saarland, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-620-2-05720-2. [Google Scholar]
- Elfasakhany, A. Biofuels in Automobiles: Advantages and Disadvantages: A Review. Curr. Altern. Energy 2019, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A. Gasoline engine fueled with bioethanol-bio-acetone-gasoline blends: Performance and emissions exploration. Fuel 2020, 274, 117825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A. Investigation on performance and emissions characteristics of an internal combustion engine fuelled with petroleum gasoline and a hybrid methanol–gasoline fuel. Int. J. Eng. Technol. (IJET-IJENS) 2013, 13, 24–43. [Google Scholar]
- Elfasakhany, A. Investigations on performance and pollutant emissions of spark-ignition engines fueled with n-butanol-, iso-butanol-, ethanol-, methanol-, and acetone-gasoline blends: A comparative study. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 71, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A. Alcohols as Fuels in Spark Ignition Engines: Second Blended Generation; LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing: Saarland, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-3-659-97691-9. [Google Scholar]
- Elfasakhany, A. Performance and emissions analysis on using acetone-gasoline fuel blends in spark ignition engine. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2016, 19, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A. State of Art of Using Biofuels in Spark Ignition Engines. Energies 2021, 14, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A. Comparisons of Using Ternary and Dual Gasoline-Alcohol Blends in Performance and Releases of SI Engines. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 7495–7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, D.; Feng, R.; Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Li, K.; Liu, X. The challenges and strategies of butanol application in conventional engines: The sensitivity study of ignition and valve timing. Appl. Energy 2013, 108, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, T.; Miers, S.A.; McConnell, S. A comparison of ethanol and butanol as oxygenates using a direct-injection, spark-ignition engine. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2009, 131, 032802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimescu, A. Performance and fuel conversion efficiency of a spark ignition engine fueled with iso-butanol. Appl. Energy 2012, 96, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Huo, M.; Wu, H.; Nithyanandan, K.; Lee, C.F.; Wang, Q. Low temperature spray combustion of acetone-butanol-ethanol (ABE) and diesel blends. Appl. Energy 2014, 117, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuerta, M.; Contreras, R.G.; Fernandez, J.C.; Dorado, M.P. Stability, lubricity, viscosity, and cold-flow properties of alcohol-diesel blends. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 4497–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfasakhany, A. Dual and Ternary Biofuel Blends for Desalination Process: Emissions and Heat Recovered Assessment. Energies 2021, 14, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gas Analyzer | Engine | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 9 kg | Type | SI (spark ignition) |
| Warm-up period | 10 min | No. of cylinders | 1 |
| Exhaust gas temp. range | 5–45 °C | No. of valves | 2 |
| Apparatus heating range | 0−130 °C, resolution ±1 °C | Bore (mm) | 65.1 |
| Voltage | 230 V (+10%/−15%) | Stroke (mm) | 44.4 |
| Frequency | 50 ± 1 Hz | Compression ratio | 7:1 |
| Power consumption | Max. 45 VA | Displacement (cm3) | 147.7 |
| Pollutant range | CO 0–10 vol.% CO2 0–20 vol.% UHC 0–2000 ppm | Maximum power (kW) | 1.5 |
| Weight | 17 kg | ||
| Fuel | Gasoline | Bio-Ethanol | i-Butanol | n-Butanol | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Property | |||||
| Formula | C8H15 | C2H6O | C4H10O | C4H10O | |
| C, H, O value (wt.%) | 86, 14, 0 | 52, 13, 35 | 65, 13.5, 21.5 | 65, 13.5, 21.5 | |
| LHV (MJ/kg) | 43.5 | 27 | 33.3 | 33.1 | |
| Heat of evap. (kJ/kg) | 223.2 | 725.4 | 474.3 | 582 | |
| Stoich. A/F ratio | 14.6 | 9 | 11.1 | 11.2 | |
| Oxygen wt.% | 0.0 | 34.7 | 21.6 | 21.6 | |
| Density (kg/m3) | 760 | 790 | 802 | 810 | |
| P sat. at 38 °C (kPa) | 31 | 13.8 | 2.3 | 2.27 | |
| Flash temp. (°C) | −45 to −38 | 21.1 | 28 | 35 | |
| Ignition temp. (°C) | 420 | 434 | 415 | 385 | |
| Boiling temp. (°C) | 25–215 | 78.4 | 108 | 117.7 | |
| Solubility in water (mL/100 mL H2O) | <0.1 | Fully miscible | 10.6 | 7.7 | |
| Vapor toxicity | Moderate irritant | Toxic even in small doses | Moderate irritant | Moderate irritant | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elfasakhany, A. Comparative Analysis of the Engine Performance and Emissions Characteristics Powered by Various Ethanol–Butanol–Gasoline Blends. Processes 2023, 11, 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041264
Elfasakhany A. Comparative Analysis of the Engine Performance and Emissions Characteristics Powered by Various Ethanol–Butanol–Gasoline Blends. Processes. 2023; 11(4):1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041264
Chicago/Turabian StyleElfasakhany, Ashraf. 2023. "Comparative Analysis of the Engine Performance and Emissions Characteristics Powered by Various Ethanol–Butanol–Gasoline Blends" Processes 11, no. 4: 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041264
APA StyleElfasakhany, A. (2023). Comparative Analysis of the Engine Performance and Emissions Characteristics Powered by Various Ethanol–Butanol–Gasoline Blends. Processes, 11(4), 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041264







