An Extension of the Poisson Distribution: Features and Application for Medical Data Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Statistical Properties
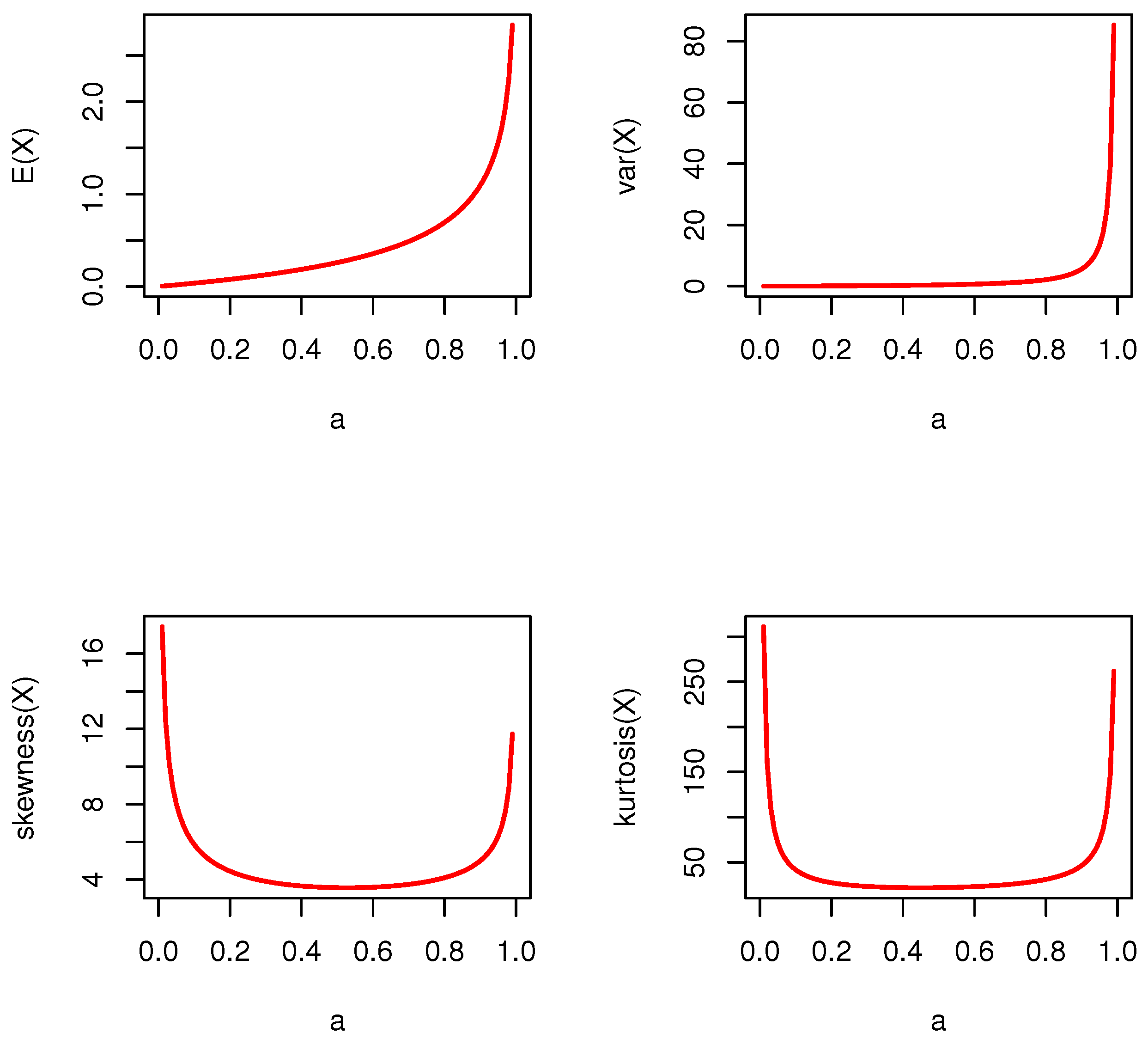
2.1. Moments and Auxiliary Statistical Measures
2.2. Conditional Expectation
2.3. Order Statistic (OrSc)
2.4. Lorenz Curve
3. Estimation Methods: Unbiased and Consistent Estimators
3.1. Maximal Likelihood Estimation
3.2. Moment Estimation
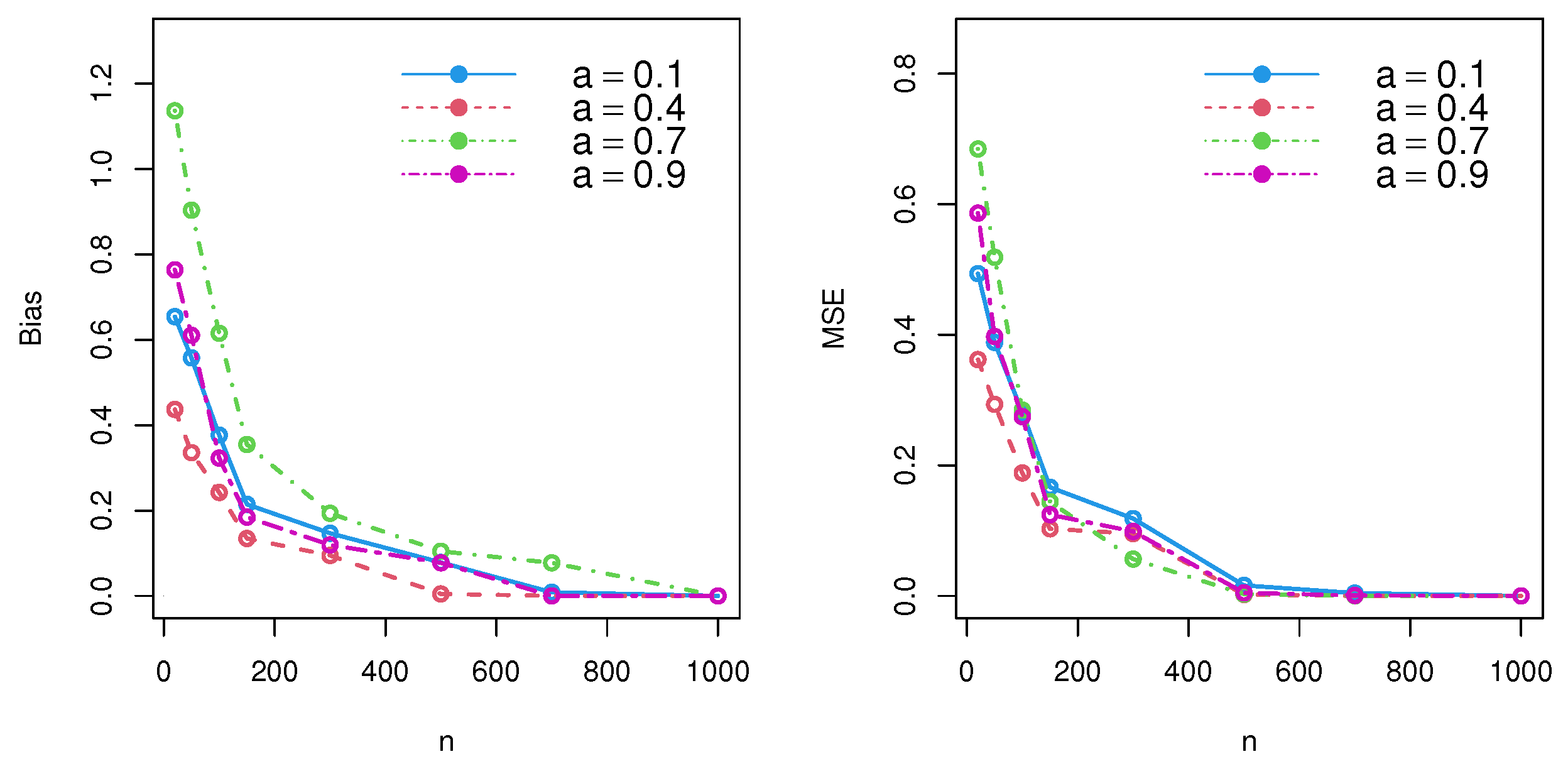
4. Estimator Performance: Simulation Results
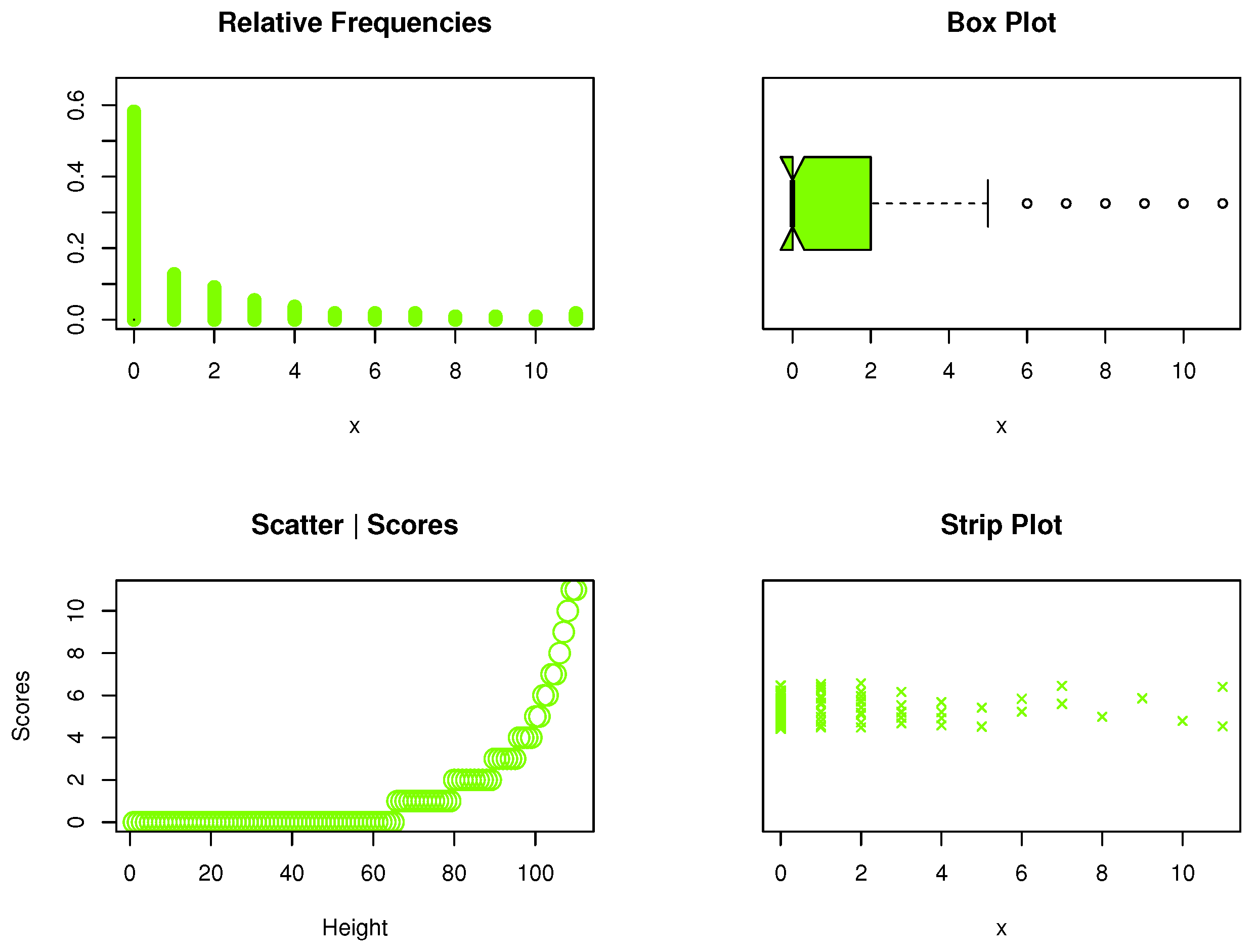
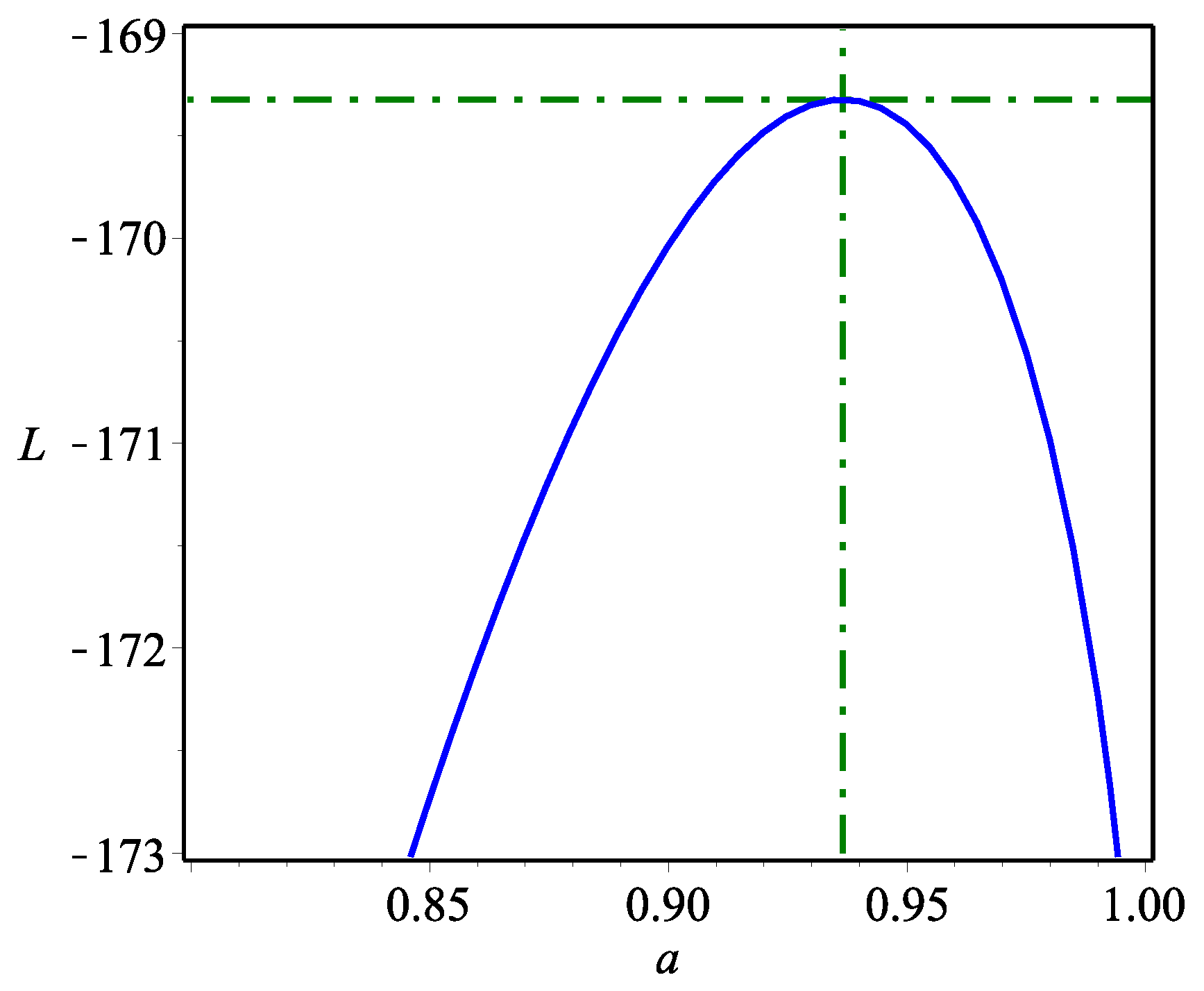
5. Data Analysis: Kidney Dysmorphogenetics
6. Results and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yari, G.; Tondpour, Z. Some new discretization methods with application in reliability. Appl. Appl. Math. Int. J. (AAM) 2018, 13, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, D. Discrete Rayleigh distribution. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2004, 53, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, H.; Pundir, P.S. Discrete Burr and discrete Pareto distributions. Stat. Methodol. 2009, 6, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Déniz, E. Another generalization of the geometric distribution. Test 2010, 19, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazi, M.A.; Lai, C.D.; Alamatsaz, M.H. A discrete inverse Weibull distribution and estimation of its parameters. Stat. Methodol. 2010, 7, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Huniti, A.A.; AL-Dayian, G.R. Discrete Burr type III distribution. Am. J. Math. Stat. 2012, 2, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekoukhou, V.; Alamatsaz, M.H.; Bidram, H. Discrete generalized exponential distribution of a second type. Statistics 2013, 47, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Ahmad, M. Discrete inverse Rayleigh distribution. Pak. J. Stat. 2014, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, T.; Aslam, M.; Ahmad, M. A two parameter discrete Lindley distribution. Rev. Colomb. Estad. 2016, 39, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, B.; Shanker, R.A. Discrete Lindley distribution with applications in biological sciences. Biom. Biostat. Int. J. 2018, 7, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Babtain, A.A.; Ahmed, A.H.N.; Afify, A.Z. A new discrete analog of the continuous Lindley distribution, with reliability applications. Entropy 2020, 22, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliwa, M.S.; Altun, E.; El-Dawoody, M.; El-Morshedy, M. A new three-parameter discrete distribution with associated INAR (1) process and applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 91150–91162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazah, M.M.A.; Erbayram, T.; Akdoğan, Y.; Al Sobhi, M.M.; Afify, A.Z. A new extended geometric distribution: Properties, regression model, and actuarial applications. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, S.D. Mémoire sur l’équilibre et le mouvement des corps élastiques. Mém. Acad. R. Sci. Inst. Fr. 1829, 8, 357–570. [Google Scholar]
- Del Castillo, J.; Pérez-Casany, M. Weighted Poisson distributions for overdispersion and underdispersion situations. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 1998, 50, 567–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.A. The effect of methods of ascertainment upon the estimation of frequencies. Ann. Eugen. 1934, 6, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, E.; Bhning, D. On estimation of the Poisson parameter in zero-modified Poisson models. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2000, 34, 441–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokonendji, C.C.; Mizere, D.; Balakrishnan, N. Connections of the Poisson weight function to overdispersion and underdispersion. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2008, 138, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Morshedy, M.; Eliwa, M.S.; Altun, E. Discrete Burr-Hatke distribution with properties, estimation methods and regression model. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 74359–74370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram Research. HurwitzLerchPhi Function. J. Appl. Stat. 2008, 32, 1461–1478. [Google Scholar]
- Altun, E.; El-Morshedy, M.; Eliwa, M.S. A study on discrete Bilal distribution with properties and applications on integervalued autoregressive process. Revstat-Stat. J. 2022, 20, 501–528. [Google Scholar]
- Poisson, S.D. Probabilité des jugements en matière criminelle et en matière civile, précédées des règles générales du calcul des probabilitiés; Bachelier: Paris, France, 1837; Volume 1, p. 1837. [Google Scholar]
- Eliwa, M.S.; El-Morshedy, M. A one-parameter discrete distribution for over-dispersed data: Statistical and reliability properties with applications. J. Appl. Stat. 2022, 49, 2467–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Para, B.A.; Jan, T.R. Discrete version of log-logistic distribution and its applications in genetics. Int. J. Mod. Math. Sci. 2016, 14, 407–422. [Google Scholar]
- Para, B.A.; Jan, T.R. On discrete three parameter Burr type XII and discrete Lomax distributions and their applications to model count data from medical science. Biom. Biostat. J. 2016, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Shanker, R.; Mishra, A. A two-parameter Poisson-Lindley distribution. Int. J. Stat. Syst. 2014, 9, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Almazah, M.M.A.; Alnssyan, B.; Ahmed, A.H.N.; Afify, A.Z. Reliability properties of the NDL family of discrete distributions with its inference. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeeb, A.S.; Ahsan-Ul-Haq, M.; Babar, A. A discrete analog of inverted Topp-Leone distribution: Properties, estimation and applications. Int. J. Anal. Appl. 2021, 19, 695–708. [Google Scholar]
- El-Morshedy, M.; Altun, E.; Eliwa, M.S. A new statistical approach to model the counts of novel coronavirus cases. Math. Sci. 2022, 16, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.K.; Riley, P.R.; Price, K.L.; McElduff, F.; Winyard, P.J.; Welham, S.J.; Long, D.A. Corticosteroid-induced kidney dysmorphogenesis is associated with deregulated expression of known cystogenic molecules, as well as Indian hedgehog. Am. J.-Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2010, 298, F346–F356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Scheme I () | Scheme II () | |||
| n | Bias | MSE | Bias | MSE |
| 20 | ||||
| 50 | ||||
| 100 | ||||
| 150 | ||||
| 300 | ||||
| 500 | ||||
| 700 | ||||
| 1000 | ||||
| scheme III () | scheme IV () | |||
| Bias | MSE | Bias | MSE | |
| 20 | ||||
| 50 | ||||
| 100 | ||||
| 150 | ||||
| 300 | ||||
| 500 | ||||
| 700 | ||||
| 1000 | ||||
| Scheme I () | Scheme II () | |||
| n | Bias | MSE | Bias | MSE |
| 20 | ||||
| 50 | ||||
| 100 | ||||
| 150 | ||||
| 300 | ||||
| 500 | ||||
| 700 | ||||
| 1000 | ||||
| scheme III () | scheme IV () | |||
| Bias | MSE | Bias | MSE | |
| 20 | ||||
| 50 | ||||
| 100 | ||||
| 150 | ||||
| 300 | ||||
| 500 | ||||
| 700 | ||||
| 1000 | ||||
| Observed | Expected Frequencies | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Frequencies | DWPLT | Geo | DR | DIR | DBL | Poi | DPa |
| 0 | 65 | |||||||
| 1 | 14 | |||||||
| 2 | 10 | |||||||
| 3 | 6 | |||||||
| 4 | 4 | |||||||
| 5 | 2 | |||||||
| 6 | 2 | |||||||
| 7 | 2 | |||||||
| 8 | 1 | |||||||
| 9 | 1 | |||||||
| 10 | 1 | |||||||
| 11 | 2 | |||||||
| Total | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 |
| a | ||||||||
| Ac | ||||||||
| Bc | ||||||||
| CAc | ||||||||
| Hc | ||||||||
| Chi | ||||||||
| Dm | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| Pv | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| Observed | Expected Frequencies | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Frequencies | DWPLT | DF-I | DLogL | DIW | DLo | Bin | DB-II |
| 0 | 65 | |||||||
| 1 | 14 | |||||||
| 2 | 10 | |||||||
| 3 | 6 | |||||||
| 4 | 4 | |||||||
| 5 | 2 | |||||||
| 6 | 2 | |||||||
| 7 | 2 | |||||||
| 8 | 1 | |||||||
| 9 | 1 | |||||||
| 10 | 1 | |||||||
| 11 | 2 | |||||||
| Total | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 |
| a | ||||||||
| X | Frequencies | DWPLT | DF-I | DLogL | DIW | DLo | Bin | DB-II |
| b | ||||||||
| Ac | ||||||||
| Bc | ||||||||
| CAc | ||||||||
| Hc | ||||||||
| Chi | ||||||||
| Dm | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | |
| Pv | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Observed | Expected Frequencies | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Frequencies | DWPLT | DL-I | DL-II | DL-III | NDL | PoiL | DITL | DGL |
| 0 | 65 | ||||||||
| 1 | 14 | ||||||||
| 2 | 10 | ||||||||
| 3 | 6 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 5 | 2 | ||||||||
| 6 | 2 | ||||||||
| 7 | 2 | ||||||||
| 8 | 1 | ||||||||
| 9 | 1 | ||||||||
| 10 | 1 | ||||||||
| 11 | 2 | ||||||||
| Total | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 |
| a | |||||||||
| b | |||||||||
| c | |||||||||
| Ac | |||||||||
| Bc | |||||||||
| CAc | |||||||||
| Hc | |||||||||
| Chi | |||||||||
| Dm | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | |
| Pv | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Dawoody, M.; Eliwa, M.S.; El-Morshedy, M. An Extension of the Poisson Distribution: Features and Application for Medical Data Modeling. Processes 2023, 11, 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041195
El-Dawoody M, Eliwa MS, El-Morshedy M. An Extension of the Poisson Distribution: Features and Application for Medical Data Modeling. Processes. 2023; 11(4):1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041195
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Dawoody, Mohamed, Mohamed S. Eliwa, and Mahmoud El-Morshedy. 2023. "An Extension of the Poisson Distribution: Features and Application for Medical Data Modeling" Processes 11, no. 4: 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041195
APA StyleEl-Dawoody, M., Eliwa, M. S., & El-Morshedy, M. (2023). An Extension of the Poisson Distribution: Features and Application for Medical Data Modeling. Processes, 11(4), 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041195








