Abstract
This research aims to provide insights into the biological efficacy of a newly formed hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent (DES). A DES based on menthol was successfully synthesized with fatty acids. The DESs’ properties as enzyme activators were examined against a neat counterpart. The menthol:decanoic acid (1:1) combination showed improved thermal stability, strong catalytic activity, and reusability for up to four subsequent cycles under ideal conditions (pH 7.0, 40 °C for 2 h). The hydrophobic DES replaced hexane in ester synthesis, where RNL@DES5 showed better fatty acid conversion compared to neat RNL. This study demonstrated promising applications of hydrophobic DESs in non-aqueous organic reactions.
1. Introduction
Green solvents that satisfy green chemistry standards have long been debated in the chemical community. In addition, in order to protect the environment, industries are focusing on green innovative practices (GIPs) [1] and achieving sustainable development goals (SDGs) [2]. Interestingly, a new class of solvents has been reported [3] which emerges as a replacement for typical organic solvents. A large number of known deep eutectic solvents (DESs) do not require sophisticated preparation. They are non-volatile, low cost (compared to some ionic liquids), biodegradable, sustainable, and non-toxic, defying most conventional solvent characteristics [4]. A DES is produced as a result of a notably lower melting point of the constituents when two or more elements are combined in a specified molar ratio, resulting in a homogenous liquid-state component at room temperature [5,6]. According to Pereira et al. [7], a certain combination of at least two solid components, called a eutectic mixture, causes a shift in phase from solid to liquid at a particular temperature. This temperature, also known as the eutectic point temperature, is the minimal melting point for all possible compositions. As a result, pure components have a greater melting point than a eutectic mixture. Typically, this mixture is correlated and distinguished by a decline in freezing point compared to the actual compounds [6]. This phenomenon occurs because of the hydrogen bond interaction among the acceptor (HBA) and donor (HBD) of the hydrogen bond.
There are limitless designations of a DES as it has tunable physicochemical traits that may be altered to produce diverse groups of DESs, thus expanding their applicability in both academic and industrial fields. He et al. [8] reported that a DES can increase biodiesel output (98.5%), resulting in a more thorough completion of the transesterification cycle. Moreover, Lynam et al. [9] found that a DES may dissolve lignin at 60 °C, increasing the glucose yield following enzymatic hydrolysis to more than seven times that of raw or glycerol-pretreated pine. A further discovery reported by Piemontese et al. [10] was that a DES can be utilized as an extraction media for Ochratoxin A (OTA), which is found in wheat and its derivatives. They showed that the DES mixture with the immunoaffinity column’s antibodies was outstanding since it could hold onto up to 96% of the OTA and produced better accuracy (70–88%) and precision (2–7%) results. Thus, DESs perform well, being adaptable for broad applications in various fields [11]. Hence, a wide array of DESs have been used in other applications such as extraction media for bioactive compounds [12,13,14], electrochemical processes [15], and molecular sensing [16]. DESs have also been portrayed as having high enzyme stability in lipase-catalyzed processes. For example, Putra et al. [17] found that enzyme immobilization with DES can enhance lipase catalytic activity, thermal stability, and reusability for up to seven cycles. Furthermore, Shehata et al. [18] offered suggestions for tailoring water-in-DES for the best possible stability and activity of the enzyme while also offering insights into designing effective lipase applications in DES-based reaction media. Furthermore, DESs as green reaction media can provide guidance for improving the catalytic performance of enzymes as reported by Cao et al. [19]. According to a study by Hayyan et al. [20], the association between the DES parameter combination and lipase activity can be explained by the impact of the DES mixture’s intrinsic features.
The stability limitation of chemicals based on hydrophilic ammonium salts when mixed with water has recently driven the discovery of hydrophobic DESs as an environmentally suitable substitute for conventional organic solvents [21]. Despite the fact that the DESs reported have been mentioned in previous publications [17,22], their biological activity was not assessed and their usage with recycled industrial enzymes using hydrophobic fatty acid-based DESs has not been addressed. Therefore, various chain fatty acids (Figure 1) such as butanoic, decanoic, propionic, octanoic, and hexanoic acids were utilized in this study and combined with menthol, as they have many numerous benefits for a broad range of applications. Most fatty acids exhibit a wide range of activities, and the mechanisms are non-specific, giving them the advantage in numerous fields such as cosmetics [23], nutraceuticals, agriculture, medicine [24], and, especially, food preservation. However, the choice of fatty acid is essentially dependent on the application and varies according to the process specifications. Unique mixtures that are finely tuned for potency and specifically tailored for target application could be generated. These may be combined with solvents, stabilizers, or other compounds, resulting in infinite mixtures.
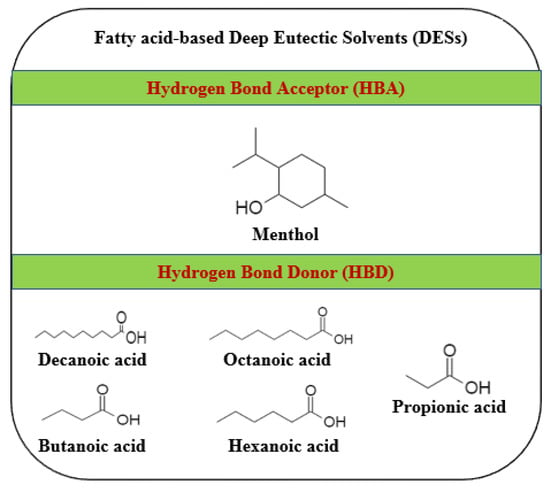
Figure 1.
Chemical compositions of different fatty acids (decanoic acid, butanoic acid, octanoic acid, hexanoic acid, and propionic acid) as the hydrogen bond donors required to synthesize hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents (DESs) with menthol (hydrogen bond acceptor).
In this study, menthol is used as a hydrogen bond acceptor or basic compound for naturally hydrophobic DESs. The terpene recognized as menthol, which is known to be derived from the Mentha species, has already been combined with a variety of chemicals for DES formulation [25]. It is a simple compound that can be obtained from natural sources (peppermint oil) or synthetically prepared by the hydrogenation of thymol. In general, it has been found that using an active, selective, and recyclable bifunctional (metal-acid) catalyst with selective features may result in a high yield of menthol synthesis by citral hydrogenation [26]. Their significance is mostly attributable to factors such as a high melting point and latent heat fusion within the ideal working range, minimal volume change during phase transition, and a good chemical stability [27]. Because hydrophobic DESs can increase the stability of DESs in water, the synthesized hydrophobic DESs can significantly broaden the range of biological applications.
In this paper, we examined the biological perspective of menthol-based hydrophobic DESs towards enzymatic activity by assessing the synergistic effect of fatty acids and menthol. The solvent miscibility test confirmed the presence of the menthol-based hydrophobic DESs and their thermal analysis was investigated using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The properties of all hydrophobic DES as enzyme activators were investigated and contrasted with their free enzyme counterparts. The enzymatic activity with different lipases and DESs was evaluated and the kinetic performance of DESs was determined at different substrate concentrations. A comparison of the enzymatic activity in the presence of natural deep eutectic solvents (NADESs) and ionic liquids (ILs) was also performed. Fourier-transformed infrared (FTIR) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analyses were used to further characterize the functional groups and morphology of the free and activated lipase, respectively. Therefore, the outcomes demonstrate the potential acquired DESs as new enzyme activators in numerous fields, especially in non-aqueous organic reactions.
2. Results and Discussion
This research demonstrates the biological perspective of fatty acids and menthol in a DES system due to the probable synergistic impacts between their components. Although recent, there has been insufficient research examining the interaction between menthol and antimicrobial fatty acids. In addition, there are also minimum studies exploring the effect of hydrophobic DESs on enzymes in the literature. The results obtained on the DESs are portrayed as follows.
2.1. DES Preparation and the Visual Aspect
Different types of fatty acids were used as HBAs, and menthol was used as an HBD to synthesize five samples of DESs. All L-menthol-based DESs were prepared with five different types of carboxylic acids (propionic acid, butanoic acid, hexanoic acid, octanoic acid, and decanoic acid), namely, DES 1, DES 2, DES 3, DES 4, and DES 5, respectively. With a one-to-one molar ratio, the mixture of menthol and chosen fatty acids successfully formed a transparent liquid that did not change upon cooling as seen in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
Hydrophobic DESs are obtained when menthol and various fatty acids (a) propanoic acid, (b) butanoic acid, (c) hexanoic acid, (d) octanoic acid, and (e) decanoic acid are combined in an equimolar ratio of 1:1.
From the observations throughout the preparation process, the liquid aspect is gradually obtained for menthol mixtures with all fatty acids. The colorless liquid form of DES 1 to 5 persisted even after cooling. This is because the ratio of fatty acids and menthol used is appropriate, as well as the temperature and duration of heating. The equivalent amount of HBA and HBD has formed a homogenous mixture as there is enough hydrogen bonding formed, causing a sudden drop in the melting point. If the amount of the HBD exceeded the HBA amount; even after prolonged shaking at a high temperature, no DES would form and the mixture would remain heterogeneous. The study by Hayyan et al. [28] confirms this case, demonstrating that when the amount of glucose exceeded the amount of choline chloride, a solid mixture resulted.
2.1.1. Solvent Miscibility Test Analyses
According to McGaughy and Reza [29], HBA and HBD can be changed to modify and enhance the physical properties of the DES, including substantially varying miscibility and solubility in water in contrast to the DESs’ individual components.
Therefore, in this study, hydrophobic DESs were produced as lipase enhancers. All DESs were observed to have a phase separation between the water (bottom layer) and the DES (top layer). We predicted that as the temperature changes, the ionic state would drastically change, thus prompting the transition from a hydrophilic to a hydrophobic state [30]. Indeed, the DESs created by combining menthol as a base with fatty acids have already been identified as hydrophobic DESs, forming H-bonds between a covalent organic compound and the carboxylic acid.
Miscibility is an absolute characteristic that is not expressed in numbers. Visual assessment is the most frequent determination of miscibility. When a mixture is miscible, there is no partial mixing, no layers or precipitates are formed, and no separation occurs. Miscibility can be defined using the same system as solubility, i.e., unlike dissolves unlike and like dissolves like. If a mixture is immiscible, it will form layers. Liquids have a tendency to be miscible with liquids of equal polarity. This works the same for nonpolar materials; the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules in the mixture will be almost the same even if other molecules have been included. A liquid with a different polarity to water would be immiscible in water. For example, hexane will not be miscible in water. This also applied to the five DESs that did not mix with water, demonstrating their hydrophobicity for further use as lipase enhancers.
2.1.2. Thermal Analysis
L-menthol melts at 42.96 °C. This is in agreement with a study by Schmitz et al. [31]. The melting temperatures in Table 1 clearly show that the solvents’ melting points varied from that of the initial pure components. From the thermogram obtained, all peaks are endothermic, implying a fusion method.

Table 1.
Melting points for menthol and DESs determined throughout the study.
One of the most used thermal analysis methods is differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), which measures the energy and temperature correlated with thermal events such as glass transitions, crystallization, and melting. This technique has been used in several works to examine the thermal changes that occur in the DESs [5]. When a material undergoes a thermal event, known as an endothermic reaction, the material effectively absorbs the energy. L-menthol is reported as a component with low melting enthalpy, suggesting that L-menthol is a good contender for formulating deep eutectic systems. When the compounds are in DES form, the peaks observed are different from those of the individual components, which shows a supramolecular transformation. This also confirms that these DESs are supramolecular complexes, ranging over a broad temperature spectrum in the liquid state. Less pure compounds will consequently exhibit a prolonged melting peak that starts at a lower temperature as compared to a pure compound. The charge delocalization caused by the hydrogen bonding between a chloride ion and molecules of fatty acids may be the cause of the melting point drop; a melting point depression occurs in all the DESs. Ribeiro et al. [11] reported similar trends for L-menthol DESs at the same ratio, where L-menthol:Octanoic acid and L-menthol:decanoic acid Tm were −10.35 and 14.35, respectively. We suggest that differences in readings could be due to systematic errors.
2.2. Screening of Lipases in Different Types of DESs
Four different types of lipases (RNL, CRL, AML, and PPL) were selected in this study due to their versatility and because they are widely used in the aroma and flavor industry, the fat and oil industry, and the pharmaceutical industry, and are applicable as biosensors that display a particularly wide substrate specificity on both triglycerides and sterol esters. For example, Hümmer et al. [32] reported hydrophobic DESs as reaction media for the lipase-catalyzed esterification to synthesize menthol fatty acid esters. They observed that the established DES reaction systems are pristine reactant mixtures that allow for solvent-free lipase-catalyzed esterification.
Therefore, this study demonstrates the fluctuation of lipase activity in the different hydrophobic DESs (Figure 3). The free lipase (control) corresponded to 100% of relative activity for all lipases. After being activated with different types of hydrophobic DESs, the relative activity of each lipase (RNL, CRL, AML, and PPL) was observed. In general, it was found that the long-chain fatty acid DESs used in this work were more stable than the other DESs. Similarities were observed in RNL and AML, as they both exhibited the highest activity in DES 5. This finding was in agreement with Hollenbach et al. [33], as DES 5 can result in the highest initial velocity reaction during the enzymatic synthesis of glucose monodecanoate.
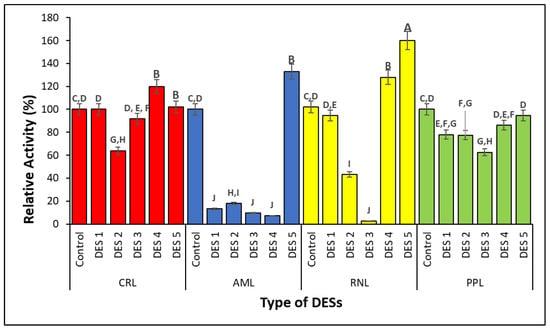
Figure 3.
Lipases’ activity in the presence of hydrophobic DESs. CRL = Candida rugosa lipase, ≥700 U mg−1 solid, AML = Amano lipase PS, from Burkholderia cepacian, ≥30,000 U g−1), RNL = Rhizopus niveus lipase, ≥1.5 U mg−1), and PPL = porcine pancreas lipase, 100–500 U mg−1 protein. Means with different superscript alphabets differ considerably (p < 0.05).
Lipase from PPL demonstrated a lower relative activity compared to the control (free lipase) when activated with different types of hydrophobic DESs (DES1–DES5). On the other hand, DES 3 caused a severe loss of activity in both AML and RNL, where only AML was negatively affected by DES 4 and RNL in DES 3. In DES 3, the CRL activity was seen to slightly decrease (an approximate 10% reduction in activity), whereas 38% of the activity was lost in DES2.
2.3. Comparison of Lipase Activity in Menthol-Based DESs and Other Solvents
The relative activities of lipases were assessed in different solvents based on the statistical analyses. Figure 4 depicts the relative lipase activity of the solvents and co-solvents used. The AML@DES-5 has the significantly (p < 0.05) highest lipase activity, followed by RNI-DES 4 and RNI-DES 5. The ranking of lipase activity as affected by the solvents and co-solvents is as follows: AML-DES 5 > RNL-DES 4 > RNI-DES 5 > PPL-NADES 2 > RNI-DES 1, where the lipase activity of these solvents and co-solvents was significantly different (p < 0.05). Figure 5 arranges the solvents and co-solvents into decreasing ranking indicators: from the highest lipase activity to the lowest lipase activity by computing the least (LS) means of the lipase activity. The RNL-DES 5, PPL-NADES 2, and PPL-NADES 1, which had the highest lipase activities with insignificant differences of means, were the most suitable reaction media, while AML-DES 3, AML-DES 4, and RNL-DES 3 were the least suitable reaction media for hydrolysis in this study.
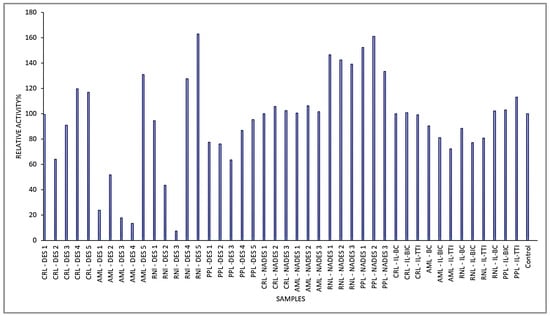
Figure 4.
Relative lipase activity of CRL, AML, RNL, and PPL in solvents and co-solvents. CRL = Candida rugosa lipase, ≥700 U mg−1 solid, AML = Amano lipase PS, from Burkholderia cepacian, ≥30,000 U g−1), RNL = Rhizopus niveus lipase, ≥1.5 U mg−1), and PPL = porcine pancreas lipase, 100–500 U mg−1 protein.

Figure 5.
Summary of the least square means of all lipases (CRL, AML, RNL, and PPL) with different types of NADESs/DESs. CRL = Candida rugosa lipase, ≥700 U mg−1 solid, AML = Amano lipase PS, from Burkholderia cepacian, ≥30,000 U g−1), RNL = Rhizopus niveus lipase, ≥1.5 U mg−1), and PPL = porcine pancreas lipase, 100–500 U mg−1 protein.
Based on this analysis, we examined both RNL and AML with DES 4 and 5 to validate the statistical findings. The results can be seen in Figure 6, where the data revealed that RNL in DES 5 as a reaction medium shows outstanding performance in terms of enhancing lipase activity; hence, it was selected as the study case.
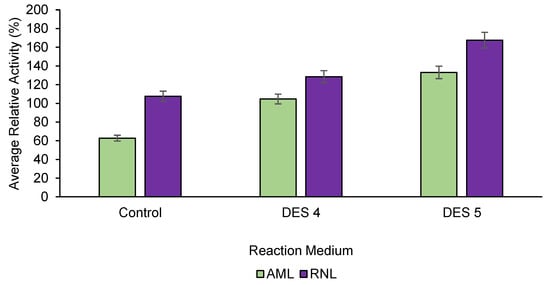
Figure 6.
Relative lipase activity in the presence of DES 4 and DES 5. AML = Amano lipase PS, from Burkholderia cepacian, ≥30,000 U g−1) and RNL = Rhizopus niveus lipase, ≥1.5 U mg−1). Means with different superscript alphabets differ considerably (p < 0.05). DES4 = Menthol:Octanoic acid and DES5 = menthol:decanoic acid (1:1). Conditions: concentration of lipase: 1 mg mL−1, 2 h, 300 rpm, 40 °C, and pH 7.0.
2.4. Activated Lipase Enzymatic Activity and Adsorption
The adsorption capacity of free and activated lipase with DES5 is presented in Table 2 along with their enzymatic activity. The outcome demonstrates that, compared to free RNL, the RNL@DES-5 specific activity increases by 1.18-fold. This result is in accordance with Cao et al. [34], who reported that the hydrophobic DES suspension (L-menthol:oleic acid) shows an increase in specific activity of 1.96 times and a higher release yield of intracellular enzyme of up to 114.58%. Remarkably, an increase of over 60% was observed in RNL@DES-5 activity. Lipase activity yields of free RNL and enhanced RNL@DES-5 were at 93.47% and 167.58%, respectively. Fungal lipases have received a lot of attention due to their well-known ability to be produced by local microorganisms and their distinct catalytic characteristics. Among those, lipase-producing fungi belong to the genera of Rhizopus sp. [35]. The unique stability of the RNL is demonstrated in these results. Lipases can be maintained in a DES mixture or be activated because of the hydrogen bond formation between HBD and salt, according to a study by Elgharbawy et al. [36]. This results in a major alteration in the DES chemical composition which increases the activity of enzymes by increasing the interaction of hydrogen bonds and lowering the thermodynamic water reaction medium of activity.

Table 2.
Measurements of lipase activity and efficiency when DES 5 is present.
The higher specific activity of RNL@DES-5 could be attributed to increased density and, hence, increased specific gravity, as it signifies how heavy the fluid is. With the incorporation of the DES, the density and viscosity rise. These outcomes are in accordance with our earlier research in which IL was used as an extractant [37]. Because of this, compared to free RNL (6.09%), the RNL@DES-5 (30.03%) has a higher rate of desorption.
2.5. Half-Life (t1/2) and Stability of Free and Activated Lipase in the Presence of DES
The stability of the lipase was measured by monitoring the activity experimentally over time until it reached 50% of the initial value (A = 0.5A0). The half-life (t1/2) was calculated using the exponential decay model and refers to the rate at which the activity is proportional to the value remaining; in other words, 50% of the initial value. The experimental results revealed that the half-life for free and activated lipase (RNL@DES-5) was approximately 9 and 29 days, respectively. The experimental results are in line with the model presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
One phase non-linear decay model of free and activated lipase.
The half-life of RNL was extended by 14 days when DES5 was used to activate it. The potential for an enzyme to be used in industry rises with a longer half-life since it is stable for a prolonged period of time. The free and activated lipase rate constant (k) for lipase activity is indicated in reference to how long that enzyme has been stored (days). Since lipase storage time is calculated as the reciprocal of k, the activated lipase tau value was larger than that of the free lipase. Tau is a constant time that is stated as storage time units. Additionally, compared to free lipase, the difference range between the plateau and Y0, which is represented in the same units as the relative activity of lipase, is greater. The one-phase non-linear decay model findings demonstrate that activated lipase has a longer half-life than free lipase. This can further be explained by the molecular interaction that enhances the stability and, hence, activity of lipase. When the DES is in contact with an enzyme, a hydrogen bond is formed between the two. The hydrogen bonding imparts stability and thus a greater half-life. Further, it can be caused by the hydroxy functionality presence in fatty acids and DES, enabling additional hydrogen bond donor/acceptor sites, and maximizing stability and lipase activity. The functionalization of IL for the activation of enzymes is well supported by these findings [38]. A study by Pätzold et al. [39] also demonstrated lipase-catalyzed esterification in a menthol and lauric acid (LA)-based DES. They found that the lipase-catalyzed with the DES could achieve a higher stability, up to 2.25 days, compared to LA (one day) substrates only. Hence, it indicates that hydrophobic DESs can enhance lipase stability.
2.6. Recyclability of Activated Lipase and Total Protein Recyclability
When compared to free lipase, activated RNL@DES-5 is observed to be more recyclable. By evaluating the lipase relative activity following recovery, it is possible to determine the lipase reusability (Figure 7) and total protein (Figure 8). Over two cycles, the remaining enhanced RNL (124%) is seen to be higher than free lipase (98%), whereas both samples retained 40% and 32%, respectively, by the 5th cycle. After the 5th cycle, the total protein is greater (~46%) than the free lipase (41%). These findings show that the hydrogen bonds provided by the DES in the reaction medium have improved the activated lipase (RNL@DES-5) stability.
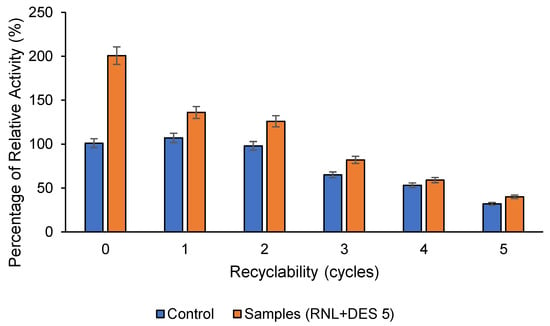
Figure 7.
Recyclability of RNL (control) and RNL@DES-5 (sample). DES5 = menthol:decanoic acid (1:1) and RNL = Rhizopus niveus lipase. Conditions: concentration of lipase: 1 mg mL−1, 2 h, 300 rpm, 40 °C, and pH 7.0.
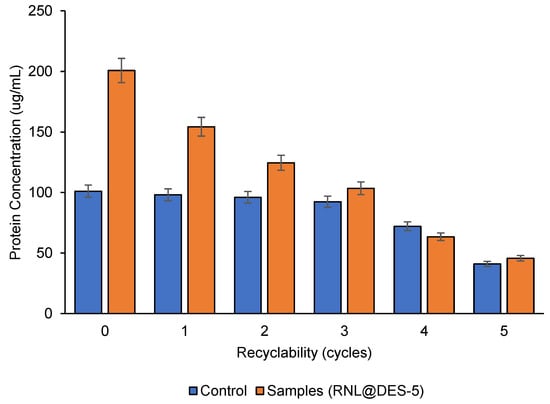
Figure 8.
Total protein recyclability of RNL (control) and RNL@DES-5 (sample). DES5 = menthol:decanoic acid (1:1) and RNL = Rhizopus niveus lipase. Conditions: concentration of lipase: 1 mg mL−1, 2 h, 300 rpm, 40 °C, and pH 7.0.
From the third to the fifth cycle, the RNL@DES-5 activity was observed to gradually decrease. A strong correlation of a gradual decrease from the fourth to the fifth cycle may be seen in the total protein reusability. The activity of RNL@DES-5 drops by 10% after the first reuse. This could be attributed to the slow enzyme denaturation during processing [40]. In addition, continuous recycling causes the DES amount to reduce and hence the reduced activity.
2.7. Kinetic Parameters of the Enhanced Lipase
To further prove the effectiveness of the tested menthol-based DESs, kinetics parameters were calculated, and the obtained data are presented in Table 4. Since KM values represent the affinity of the enzymes, it was seen that lipases, in general, had lower KM values in menthol-based DESs compared to the control samples (in the range of 6 to 16 times lower), which implies greater affinity. Furthermore, the values of Vmax were higher than the control samples, implying higher activity. In addition, the presence of menthol-based DESs increases the lipases’ catalytic efficiency, as suggested by the kcat values. The kcat/KM value represents the enzyme specificity for each substrate when the enzyme holds more than one possible substrate. The larger values of kcat/KM signify higher specificity of the lipases in the DESs, except for AML in DES 4. The value of kcat increased in the range of 2-fold to 5-fold for the lipases tested. In general, enzymes possess values of kcat/KM close to 1.67 × 1011–1.67 × 1012 mM−1 min−1 (108–109 M−1 s−1), implying that the reaction occurs as soon as the substrate and the enzyme colloid. When the KM is low and kcat is high, the best substrates are anticipated [41].

Table 4.
Lipase kinetic parameters when hydrophobic DESs are present.
The increased water content corresponded with polarity changes, which may influence the lipase selectivity towards the substrate, pNPP, which might be the reason for the inhibitory effect of DES 3. However, since the majority of the DESs used activated the lipases, we can assume the formation of the double layer, where the enzyme performed in the minimum amount of water needed. This could be due to the hydrophobic nature of the DESs; hence, lipases could function in the hydrophobic DESs by initiating the bonding of hydrogen with the carboxylic group of fatty acids or menthol hydroxy group [23]. The increased alkyl chain length of the HBD and fatty acids could be one reason for the activation of lipases as the molecule became larger and thus had a stronger intermolecular attraction. A large chain-length molecule experiences stronger London dispersion forces (part of van der Waals forces). This is because longer molecules possess more sites to be attracted to other molecules [42,43]. Therefore, it is expected that the lipase molecules have more places to locate and function within the DES layer rather than the buffer solution. Furthermore, the lipase structure contains both hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces.
The activation of some lipase surfaces suggests enzyme conformational changes in which a surface domain known as the lid shifts and displays the active site region. Compared to the enzyme’s closed state, this active lipase conformation is more hydrophobic. The individual enzyme mobility at the water-lipid interface is another important characteristic on the molecular level. If the lipase attaches to the surface in a possessive manner, the enzyme is considered to be acting in the ‘scooting mode’, whereas the ‘hopping mode’ allows for an interchange between the surface and the solution. By accumulating at interfaces, DESs might convert characteristics such as surface hydrophobicity and charge. In addition, protein adsorption might be affected by the presence of surfactants in many means, starting from completely restricted adsorption to cooperative adsorption, resulting in a higher adsorbed quantity [44]. Moreover, pre-absorbed proteins might also be displaced from solid surfaces by the presence of surfactants. This is accomplished by solubilizing it, either by protein replacement at the protein binding location or surface. In addition, the conformational stability and the protein surface hydrophobicity are affected by small complex surfactants of ionic concentrations with most solutions [44]. Based on that, we assume that the lipase, in this case, is adsorbed on the hydrophobic surface (DES layer), in which it is further activated (Figure 9).
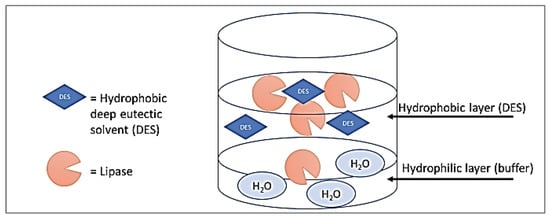
Figure 9.
Illustration of lipase molecules’ predicted behavior in a medium containing a hydrophobic layer (DES) and a buffer solution (in water).
Overall, the menthol and fatty acids DESs were suitable enhancers for lipases, although the effect of hydrophobic DESs on enzymes has not yet been fully explored. Hydrogen bonding and ionic interactions have been proven to play crucial roles in the structure of IL toward the activity of lipase. Because they can absorb water molecules in the enzyme area, they may inhibit lipase activity, causing inactivation due to a dehydrating effect [45]. This is because the IL network will be stretched and eventually disrupted when it is exposed to water molecules after dilution [46]. The aqueous solutions of ILs and lipase activity interactions reveal that anion IL behavior is determined by its water molecules’ interactions, supporting the dependency of biological IL activity in the water. A study by Di et al. [47] shows pretreated activated lipases (Rhizomucor miehei) using 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([BMIM][PF6]) and an enzymatic IL-strengthened technique. They found that when lipase was pre-treated with IL, its pH tolerance range decreased, and its hydrolysis activity was significantly inhibited. According to Bingham and Ballone [48], small hydrophilic anions such as IL-BC and IL-BIC stay in the lipase solution, while more hydrophobic solvents such as hydrophobic DESs create a film at the water interface. As mentioned by Makoś et al. [49], the lower water content in hydrophobic DESs decreases with the increasing length of the carbon chain, which in turn increases the hydrophobicity of the HBD. Hence, Hümmer [50] reported that when they examined the esterification of lipase-catalyzed DES compounds as a reaction medium, CRL was found to be significant in menthol:fatty acid DESs. Since commercial and natural lipase preparations have been demonstrated with DES activity, they have been considered environmentally friendly and cheaper for lipase-catalyzed reaction applications. As observed in the case of DES 3, increased fluctuations and the loss of the secondary structure, the partial loss of which was suggested by Shehata et al. [18], of a specific area may describe the lipase activity’s radical reduction. A recent study reported a successful DES made up of (-)-menthol and decanoic acid in the glucose mono-decanoate synthesis using iCALB (lipase B from Candida antarctica, activated on acrylic resin). The recently fabricated hydrophobic DESs show better yields than hydrophilic DESs. This group has demonstrated that the enzyme possessed remarkable reusability and stability in a menthol:decanoic acid DES for at least five cycles of the reaction without an activity loss [33].
2.8. Activated Lipase and DES Fourier Transformed Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
In order to ascertain the relationships between the active lipase and chemical shifts and infrared bands, FTIR analysis reveals how DES5 affects RNL. Table 5 presents the analysis. The addition of DES5 is what causes the significant variations in the FTIR spectra of both free and activated lipase (Figure 10).

Table 5.
FTIR spectra of key functional groups and their correspondence wavenumber (cm−1) of free lipase, DES5, and RNL@DES-5.
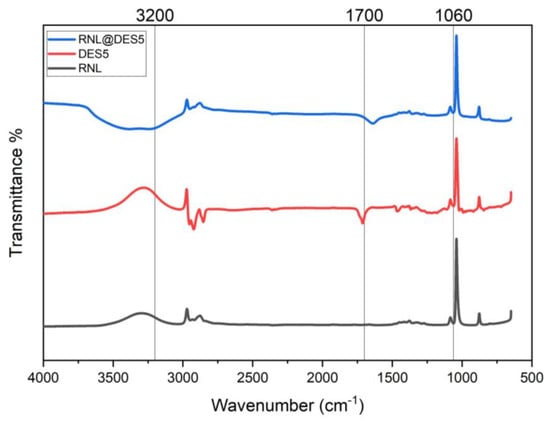
Figure 10.
FTIR stacking spectra expressed as a percentage of free lipase (%T), DES5, and RNL@DES-5 after incubation at the following conditions: lipase concentration: 1 mg mL−1, 2 h, 300 rpm, pH 7.00, and 40 °C.
From the spectrum, the free lipase, DES 5, and RNL@DES-5 show a band absorption between 3200 and 3600 cm−1, which is correlated to O-H vibration stretching. One potential explanation is that the force constant is significantly reduced when an oxygen atom cloud point is transferred to a hydrogen bond [50]. Furthermore, the peaks at 3022 and 2850 were observed in free lipase, DES 5, and RNL@DES-5, confirming the existence of a C-H stretching vibration. The O-H group shift in wavelength number in the RNL@DES-5 as compared to free lipase is evidence of hydrogen bonding and the synthesis of DES [51]. The peaks that appear at 1700 cm−1 are due to the vibration of C=O bonds stretching, confirming the existence of menthol-based DESs with decanoic acid (DES 5).
The vibration of the S=O stretching gives rise to an intense stretching peak normally found between 1065 and 1061 cm−1. The S=O stretching is most likely caused by the DES components’ robust intramolecular interactions [51]. Additionally, the bending of the C=C band at 991 and 842 cm−1 of DES 5 demonstrates that DES 5 was successfully activated with RNL.
2.9. Morphology of Free and Activated Lipase
The surface morphology of the free and enhanced lipase was observed under scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The RNL morphology as the control (a) and RNL@DES-5 (b) are shown in Figure 11, with 10k and 40k magnification, respectively. The SEM images of lipase molecules (RNL) as the control and RNL@DES-5 were examined; it was seen that polygonal granules are formed in the RNL morphology. Unlike the control (RNL), the SEM image revealed that the lipase molecules (RNL) were activated with DES-5, as it demonstrates a cloud-like appearance upon the introduction of DES 5. The figure shows that some of the enzyme clumps tend to adhere to the lipase molecules. According to Cao et al. [52], it has been widely accepted that the almost hydrophobic DESs have a significant impact on the activity and structure of enzymes. In a study reported by Guajardo et al. [53], the activated lipases in cross-linked aggregates (CLEA) generate an effective biocatalyst that is extremely stable in non-traditional, low-viscous DESs. Consequently, the FTIR results were supported by the morphology of the activated lipase (RNL@DES-5) from the SEM images. On the other hand, enhancing the enzymatic activity and behavior of enzyme immobilization will be greatly aided by the changes in the structure of lipases that result from immobilization.

Figure 11.
Morphology of (a) RNL as the control and (b) RNL@DES-5 at 10k and 40k magnification, respectively. Conditions: concentration of lipase: 1 mg mL−1, 300 rpm, 2 h, pH 7.0, 40 °C, and 2 h.
2.10. Application in Reverse Reactions: Synthesis
To illustrate the possibility of DES as a medium for ester synthesis, RNL was evaluated for its ability to synthesize esters in the presence of hexane and DES5. The result showed that the RNL@DES5 was able to catalyze the synthesis of ethyl decanoate (Figure 12). The results demonstrated that esterification occurs at 40 min. The free fatty acid conversion in the DES5 medium reached 78%, which is higher than the organic medium (58%) after 60 min.
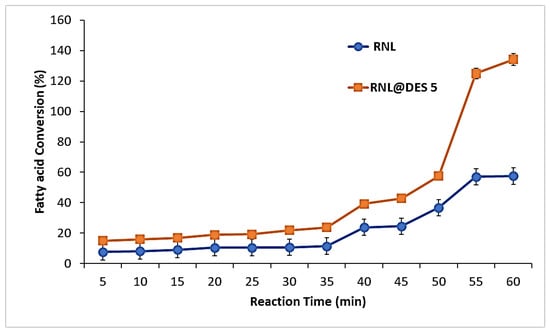
Figure 12.
Fatty acid conversion (%) in free lipase with organic solvents compared to RNL@DES-5. Conditions of activated RNL@DES5 = pH 7.0, 40 °C for 2 h.
Hümmer et al. [32] produced (-)-menthol fatty acid esters using the lipase-catalyzed esterification of the DES molecules themselves. DESs based on (-)-menthol and fatty acids (octanoic, decanoic, and dodecanoic acid) were used as the reaction medium. Without requiring the addition of a solvent, DES serves as both a reaction medium and substrate pool simultaneously. Their results showed that DES reaction systems demonstrated esterification under solvent-free conditions. The results of this study agree with what was reported, as RNL in DES5 was able to perform the esterification without the addition of organic solvents.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Sodium deoxycholate (purity 97%), isopropanol, and p-nitrophenyl palmitate (pNPP) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (U.S.). Fatty acids, including butanoic acid (Sigma Aldrich), decanoic acid (R&M, 99%), octanoic acid (R&M, 98%), hexanoic acid (Sigma Aldrich, 96%), and propionic acid (R&M, 99%), were analytical grade chemicals. All analytical and synthesis procedures were performed with deionized (DI) water. Descriptions of the lipases that were used are in Table 6.

Table 6.
The study abbreviations of the lipases.
3.2. Menthol-Based DESs Preparation
To synthesize DESs with a 1:1 molar ratio, a specific amount of menthol and several fatty acids (decanoic acid, propionic acid, hexanoic acid, butanoic acid, and octanoic acid) were combined. Figure 13 demonstrates the procedure to synthesize hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents (DESs) using menthol as a hydrogen bond acceptor and fatty acids as hydrogen bond donors. The molar ratio was designated based on the literature by Tang et al. [54]. Each DES was synthesized by placing the required components into a glass flask that was completely sealed and heated without stirring for four hours at 70 °C. It was expected that an effective DES would be formed by a homogeneous and transparent liquid. Prior to storage, the mixture was cooled to room temperature.
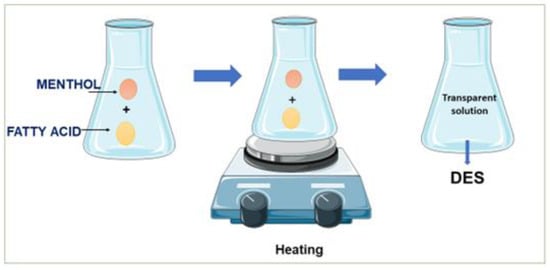
Figure 13.
Schematic of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent synthesis.
3.2.1. Solvent Miscibility Test of Hydrophobic DESs
To test the DES’s hydrophobicity, 2.5 mL of deionized water was transferred into a glass container. Then, 1 mL of each DES was transferred into the same container. The miscibility of the DES with the water was observed.
3.2.2. Thermal Analysis of Hydrophobic DESs
Aluminum cells were heated (10 °C min−1) for the differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis (Mettler Toledo DSC 1, USA). In the liquid aluminum pan, 10–15 mg of the DES sample was added. Samples were heated to temperatures ranging from −30 to 500 °C, and nitrogen was used for the analysis (50 mL min−1). The methods were executed according to Aroso et al. [5].
3.3. Assay (Enzyme Substrate Solution) Preparation
The pNPP (7 mg) was present in 4 mL of isopropanol in the substrate-enzyme solution (solution A). Arabic gum (0.07 g), sodium deoxycholate (0.14 g), and 65 mL of pH 7.0 phosphate buffer (50 mM) were mixed to make Solution B. To eliminate the turbidity, Triton X-100 (350 µL) was dissolved in Solution B. A mixture of solutions A and B was prepared quickly for every assay.
3.4. Lipase Activity Assay
A colorimetric assay was used to determine the activity of the lipase. The procedure was performed as reported previously by Elgharbawy et al. [36]. The hydrolysis of para-nitrophenyl palmitate (pNPP) to p-nitrophenol was chosen as the basic reaction to assess the activity of the enzyme. To start the reaction, 300 μL lipase or lipase/DES was added to 700 μL of the fresh solution (A + B). Then, all tubes were allowed for incubation in a pre-heated water bath (40 °C, 15 min). The reaction was terminated by the addition of 300 μL acetone:ethanol solution (1:1). The p-nitrophenol (pNP) absorbance at 410 nm was measured via the MultiskanTM GO microplate spectrometer. Measurements were performed in triplicate for each DES. The results were then recorded and reported as the average of the triplicates ± standard deviation (SD).
For each DES solution, individual standard curves were generated because the molar extinction coefficient can differ due to the different pH values and DES presence. The unit of measurement for lipase activity was mg−1 and the amount of enzyme required to produce one mole of pNP per minute was known as one unit. The optical density of DES without enzyme was measured and calculated for the correction of enzyme value. The relative activity in regard to the initial concentration of the enzyme at zero time (I0) and the activity (%) achieved after the incubation step was calculated using Equation (1).
3.5. Lipases Activities in DES Screening
To evaluate the influence of hydrophobic DESs on biological molecules, lipases were selected as the targeted protein molecules. The four lipases (CRL, RNL, AML, and PPL), with fixed concentrations (one mg enzyme in one mL buffer) were mixed in pH 7.00 sodium phosphate buffer (50 mM). Then, each DES was added at a ratio of 1:4 of the total reaction volume. All reaction mixtures were heated to 40 °C and agitated at 300 rpm in a thermomixer (BIOBASE).
3.6. Comparison of Lipase Activity in Menthol-based DESs and Other Solvents
To validate the exceptional enhancement and stability of lipases in the DESs, their activity was compared with natural deep eutectic solvents (NADESs) and ionic liquids (ILs) [55]. The relative activity was then assessed based on statistical analyses. The NADESs used were NADES 1 (ChCl:fructose:water (5:2:5)), NADES 2 (ChCl:sucrose:water (4:1:4)), and NADES 3 (ChCl:glucose:water (4:1:4)) [36]. The ILs used were IL-BC (1-butyl-2,3-dimethylimidazoliumimid chloride), IL-BIC (N-butylpyridinium chloride), and IL-TTI (Tetrabutylammonium bis(trifluormethylsulfonyl)amide), which are commercially available from MERCK.
3.7. Procedures for Chemical and Analytical Analysis
3.7.1. Protein Content Determination
The Bradford assay (using Bio-Rad reagent) and bovine serum albumin (BSA) were used, respectively, to measure the protein standard curve and its content. In total, 160 µL of reagent and 40 µL of the sample were mixed using the microplate mixer feature for each microplate well. Using a MultiskanTM GO spectrometer (Thermofisher), the absorbance was measured at 595 nm after 5 min.
3.7.2. Measurements of Enzyme Activity and Adsorption
The method by Li et al. [56] was used to study the lipase adsorption-desorption activity in this study. The selected pH of the buffer was combined with free (0.05 mL) or subsequently activated lipase in a 15 mL centrifuge tube. For 2 h, the centrifuge tube was incubated in a thermomixer (BIOBASE) at 40 °C. The supernatant was then obtained after centrifuging for 15 min at 4 °C. The total amount of protein for the unabsorbed enzyme was determined with the Bradford assay. The initial amount of protein in the supernatant and total enzyme following the 2 h of adsorption was determined to calculate the amount of lipase that had been absorbed into the substrate. The adsorption parameters were calculated using Equation (2) using the Langmuir-type adsorption isotherm.
where P is the total free enzyme (mg mL−1) after adsorption in the supernatant, is the total enzyme adsorbed (mg g−1), is constant adsorption (mL mg−1), and is a measurement for affinity adsorption. The graph plots of / against ; and were then determined. To calculate desorption at 40 °C, the sample volume was 5 mL, diluted with buffer, and incubated for 2 h. After 15 min, the samples were centrifuged, and the protein content was determined. The average percentages of enzymes are quantified by Equation (3).
where C and D are the amount of protein unabsorbed (mg g−1) and the sum of the adsorbed lipase (free and activated) (mg g−1) over the previous 2 h, respectively [57]. The enzyme relative activity (in percent) and the remaining activity yield was calculated according to Equation (4) [58] and (5) [59], respectively. Meanwhile, Equation (6) demonstrates the specific enzyme activity calculation [60].
3.7.3. Half-Life (t1/2)
For a period of time (days), until it reaches 50% of its initial value, lipase pre-incubation stability was observed. It was incubated at the optimum pH with DES at 4.0 ± 2.0 °C. When the activity of the enzyme reached 50% of its initial value, the results of free and activated lipase were recorded, and the relative activities were calculated. The half-life (t1/2) was computed statistically using version 9.0.0 GraphPad Prism and the one-phase non-linear decay model was obtained, following Equation (7):
where is in the time units and k is the constant rate in the enzymatic reaction.
3.8. Total Protein Recyclability and Activated Lipase Recovery in DES
In order to assess the total protein reusability of pNPP, the activity of activated lipase was continuously used in the hydrolysis reaction. After each recyclability cycle, the used activated lipase was isolated and retrieved for 2 h using pH 7.0 PBS at 40 °C. As stated in Section 2.4, the lipase activity was determined and recorded until the A0 reached 50%. To estimate the relative activity of the enzyme and determine the enhanced lipase potential for recycling, the initial activity of the enzyme (A0, specified as 100%) was employed.
3.9. Lipase Kinetic Parameter in the Presence of DES
To further evaluate the performance of the DESs, the kinetics parameters were calculated (in optimal conditions) at different substrate concentrations. The experimental kinetic data were plotted using the Lineweaver–Burk plot to evaluate the maximum velocity (Vmax) and Michaelis–Menten constant (KM). The enzymatic affinity is the KM value. The values were acquired using the GraphPad Prism version 9.0.0 and Michaelis–Menten model, applying a non-linear regression. Both the catalytic efficiency (kcat/KM) and turnover number (kcat) could be assessed using the GraphPad Prism Version 9.0.0 since the required enzyme total quantity is specified.
3.10. Statistical Analysis
Data were reported as the standard deviation ± the mean after being analyzed in triplicate. A Tukey’s test with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was identified at a 95% confidence level (p ˂ 0.05) between the means via XLSTAT-Pro (2019) statistical software (Addinsoft, Paris, France). Kinetics analyses were conducted using GraphPad Prism version 9.0.0.
3.11. Characterization
3.11.1. Fourier Transformed Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
An FTIR spectrometer 400 (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA) with a transmittance mode at 4000 to 500 cm−1 with 4 cm−1 resolution was used to perform the FTIR analysis. To ascertain modifications in functional groups, 0.1 g of free and activated lipase were evaluated.
3.11.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
Using an SEM (FEI Quanta 200, Hillsboro, Oregon, U.S.) at 5 kV, the morphologies of the free and activated lipase were examined. The samples, which weighed about 50 mg, were adhered on aluminum stubs with the aid of pad carbon before being coated with a tiny layer of platinum to improve the conductivity of electrons.
3.12. Application in Reverse Reactions: Synthesis
The reaction mixture consisted of ethanol, and decanoic acid diluted in hexane (6 mL of reaction medium) was used as the substrate. An esterification reaction in a DES system was also performed under similar conditions using DES to substitute hexane in the reaction medium. The reaction mixture was mixed in a 100 mL glass bottle sealed with a screwcap and incubated in an incubator shaker with controlled temperature under fixed agitation at 240 rpm for 60 min. The reaction was initiated by adding the RNL. The samples were withdrawn from the reaction mixture at various time intervals (0.1 mL), diluted in 10 mL of ethanol solution, and titrated with a standard 0.1 M NaOH using phenolphthalein as an indicator to determine the residual decanoic acid concentration [61]. The reaction can be observed in Scheme 1. The conversion percentage was determined as Equation 8:
where:
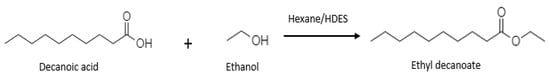
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of ethyl decanoate.
- Y = fatty acid conversion (%)
- C0 = initial decanoic acid concentration (mM)
- Ct = decanoic acid concentration (mM) after a certain time t (min) of reaction.
4. Conclusions
Eutectic mixtures based on menthol were described in this report, providing insights into the enzyme activation activity of hydrophobic DESs. Regarding enzyme activation, lipases showed a high stability and catalytic activity in the hydrophobic DESs, particularly in DES 4 and DES 5. Moreover, the reusability of activated RNL@DES-5 was up to four subsequent cycles under ideal conditions. These improvements were attributed to the unique hydrogen bonding of DES 5 that protected active conformations of RNL via immobilization that was seen upon examination using FTIR and SEM analyses. DES 5 also demonstrated the ability to catalyze ester synthesis with good performance and could replace the use of organic solvents such as hexane in multiple industries. This confirms that some of the developed hydrophobic DESs have potential applications in various organic and industrial reactions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.M.E. and A.H.; methodology, N.A.N.A. and S.S.S.P.; software, A.A.M.E. and M.S.A.S.; validation, W.J.B.; formal analysis, M.S.A.S. and A.A.M.E.; investigation, S.S.S.P., N.A.l. and N.A.N.A.; resources, A.H. and A.A.M.E.; data curation, N.A.N.A. and S.S.S.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.M.E., S.S.S.P. and H.W.K.; writing—review and editing, A.A.M.E.; visualization, S.S.S.P. and H.W.K.; supervision, A.A.M.E.; project administration, A.A.M.E.; funding acquisition, J.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Higher Education, MoHE-Malaysia [FRGS/1/2020/STG05/UM/02/11].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the artice.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the International Institute for Halal Research and Training (INHART) for providing the facilities to conduct this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Khan, P.A.; Johl, S.K.; Johl, S.K. Does Adoption of ISO 56002-2019 and Green Innovation Reporting Enhance the Firm Sustainable Development Goal Performance? An Emerging Paradigm. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021, 30, 2922–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, P.A.; Johl, S.K.; Akhtar, S. Vinculum of Sustainable Development Goal Practices and Firms’ Financial Performance: A Moderation Role of Green Innovation. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2022, 15, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel Solvent Properties of Choline Chloride/Urea Mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Tailoring Properties of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents with Water to Facilitate Their Applications. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroso, I.M.; Paiva, A.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents from Choline Chloride and Betaine—Physicochemical Properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 241, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyan, A.; Hashim, M.A.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hayyan, M.; AlNashef, I.M. A Novel Phosphonium-Based Deep Eutectic Catalyst for Biodiesel Production from Industrial Low Grade Crude Palm Oil. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 92, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; de la Calle, I. Solvents and Eutectic Solvents. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Science, 3rd ed.; Worsfold, P., Poole, C., Townshend, A., Miró, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 184–190. ISBN 978-0-08-101984-9. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Li, K.; Bo, G.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Yan, J.; Yang, M.; Yan, Y. Enhancing Biodiesel Production via Liquid Yarrowia Lipolytica Lipase 2 in Deep Eutectic Solvents. Fuel 2022, 316, 123342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynam, J.G.; Kumar, N.; Wong, M.J. Deep Eutectic Solvents’ Ability to Solubilize Lignin, Cellulose, and Hemicellulose; Thermal Stability; and Density. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piemontese, L.; Perna, F.M.; Logrieco, A.; Capriati, V.; Solfrizzo, M. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Novel and Effective Extraction Media for Quantitative Determination of Ochratoxin A in Wheat and Derived Products. Molecules 2017, 22, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, B.D.; Florindo, C.; Iff, L.C.; Coelho, M.A.Z.; Marrucho, I.M. Menthol-Based Eutectic Mixtures: Hydrophobic Low Viscosity Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2469–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Pertiwi, A.S.; Kembaren, Y.H.; Rahman, A.; Mun’im, A. Application of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Ultrasonic Assisted Extraction of Total Polyphenolic and Caffeine Content from Coffee Beans (Coffea Beans L.) for Instant Food Products. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 8, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents as a New Extraction Media for Phenolic Metabolites in Carthamus Tinctorius L. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6272–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravana, P.S.; Ho, T.C.; Chae, S.J.; Cho, Y.J.; Park, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Chun, B.S. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Extraction and Fabrication of Chitin Films from Crustacean Waste. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baby, J.N.; Sriram, B.; Wang, S.F.; George, M. Effect of Various Deep Eutectic Solvents on the Sustainable Synthesis of MgFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Simultaneous Electrochemical Determination of Nitrofurantoin and 4-Nitrophenol. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.K.; Chipatecua Godoy, Y. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Assisted Synthesis of Au Nanostars Supported on Graphene Oxide as an Efficient Substrate for SERS-Based Molecular Sensing. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putra, S.S.S.; Basirun, W.J.; Elgharbawy, A.A.M.; Hayyan, A.; Hayyan, M.; Mohammed, M.A. Nanocellulose and Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent as Potential Biocatalyst System toward Enzyme Immobilization. Mol. Catal. 2022, 528, 112422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, M.; Unlu, A.; Sezerman, U.; Timucin, E. Lipase and Water in a Deep Eutectic Solvent: Molecular Dynamics and Experimental Studies of the Effects of Water-in-Deep Eutectic Solvents on Lipase Stability. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 8801–8810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wu, R.; Zhu, F.; Dong, Q.; Su, E. How to Improve the Efficiency of Biocatalysis in Non-Aqueous Pure Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Case Study on the Lipase-Catalyzed Transesterification Reaction. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 179, 108336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyan, A.; Hadj-Kali, M.K.; Salleh, M.Z.M.; Hashim, M.A.; Rubaidi, S.R.; Hayyan, M.; Zulkifli, M.Y.; Rashid, S.N.; Mirghani, M.E.S.; Ali, E.; et al. Characterization of Tetraethylene Glycol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Potential Application for Dissolving Unsaturated Fatty Acids. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 312, 113284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Romero, L.; Rintoul, I.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. From Phase Change Materials to Green Solvents: Hydrophobic Low Viscous Fatty Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3888–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.N.; Hayyan, A.; Hayyan, M.; Hashim, M.A.; Elgharbawy, A.A.M.; Sani, F.S.; Basirun, W.J.; Lee, V.S.; Alias, Y.; Mohammed, A.K.; et al. Ternary Glycerol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Physicochemical Properties and Enzymatic Activity. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 169, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin Ting, H.; Warsi Khan, H.; Vijaya Bhaskar Reddy, A.; Goto, M.; Moniruzzaman, M. Extraction of Salicylic Acid from Wastewater Using Ionic Liquid-Based Green Emulsion Liquid Membrane: COSMO-RS Prediction and Experimental Verification. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 347, 118280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.W.; Reddy, A.V.B.; Bustam, M.A.; Goto, M.; Moniruzzaman, M. Development and Optimization of Ionic Liquid-Based Emulsion Liquid Membrane Process for Efficient Recovery of Lactic Acid from Aqueous Streams. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 176, 108216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.M.; Pereira, C.V.; Mano, F.; Silva, E.; Castro, V.I.B.; Sá-Nogueira, I.; Reis, R.L.; Paiva, A.; Matias, A.A.; Duarte, A.R.C. Therapeutic Role of Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Menthol and Saturated Fatty Acids on Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2019, 2, 4346–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simakova, I.L.; Vajglová, Z.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Eränen, K.; Hupa, L.; Peurla, M.; Mäkilä, E.M.; Wärnå, J.; Murzin, D.Y. Citral-to-Menthol Transformations in a Continuous Reactor over Ni/Mesoporous Aluminosilicate Extrudates Containing a Sepiolite Clay Binder. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2022, 26, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Tyagi, V.V.; Chen, C.R.; Buddhi, D. Review on Thermal Energy Storage with Phase Change Materials and Applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 318–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyan, A.; Mjalli, F.S.; Alnashef, I.M.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.M.; Al-Wahaibi, T.; Hashim, M.A. Glucose-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Physical Properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 178, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaughy, K.; Reza, M.T. Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Furfural from Water by Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents: Improvement of Density Function Theory Modeling with Experimental Validations. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 22305–22313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longeras, O.; Gautier, A.; Ballerat-Busserolles, K.; Andanson, J.-M. Deep Eutectic Solvent with Thermo-Switchable Hydrophobicity. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 12516–12520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, D.; Shubert, V.A.; Betz, T.; Schnell, M. Exploring the Conformational Landscape of Menthol, Menthone, and Isomenthone: A Microwave Study. Front. Chem. 2015, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hümmer, M.; Kara, S.; Liese, A.; Huth, I.; Schrader, J.; Holtmann, D. Synthesis of (-)-Menthol Fatty Acid Esters in and from (-)-Menthol and Fatty Acids—Novel Concept for Lipase Catalyzed Esterification Based on Eutectic Solvents. Mol. Catal. 2018, 458, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenbach, R.; Ochsenreither, K.; Syldatk, C. Enzymatic Synthesis of Glucose Monodecanoate in a Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Wu, R.; Dong, Q.; Zhao, L.; Cao, F.; Su, E. Effective Release of Intracellular Enzymes by Permeating the Cell Membrane with Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents. ChemBioChem 2020, 21, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Fernández, J.; Benaiges, M.D.; Valero, F. Rhizopus Oryzae Lipase, a Promising Industrial Enzyme: Biochemical Characteristics, Production and Biocatalytic Applications. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgharbawy, A.A.; Hayyan, A.; Hayyan, M.; Rashid, S.N.; Nor, M.R.M.; Zulkifli, M.Y.; Alias, Y.; Mirghani, M.E.S. Shedding Light on Lipase Stability in Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2018, 32, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.W.; Elgharbawy, A.A.M.; Bustam, M.A.; Goto, M.; Moniruzzaman, M. Vegetable Oil–Ionic Liquid-Based Emulsion Liquid Membrane for the Removal of Lactic Acid from Aqueous Streams: Emulsion Size, Membrane Breakage, and Stability Study. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 32176–32183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. What Do We Learn from Enzyme Behaviors in Organic Solvents?—Structural Functionalization of Ionic Liquids for Enzyme Activation and Stabilization. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 45, 107638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pätzold, M.; Weimer, A.; Liese, A.; Holtmann, D. Optimization of Solvent-Free Enzymatic Esterification in Eutectic Substrate Reaction Mixture. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 22, e00333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, M.L.; Pereira, M.M.; Freire, M.G.; Silva, J.P.A.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Tavares, A.P.M. Laccase Activation in Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11806–11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorsch, J.R. Chapter One—Practical Steady-State Enzyme Kinetics. In Laboratory Methods in Enzymology: Protein Part A; Lorsch, J.B.T.-M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; Volume 536, pp. 3–15. ISBN 0076-6879. [Google Scholar]
- Fabrizio, A.; Corminboeuf, C. How Do London Dispersion Interactions Impact the Photochemical Processes of Molecular Switches? J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, M.A.; Wegner, H.A. Exploring London Dispersion and Solvent Interactions at Alkyl–Alkyl Interfaces Using Azobenzene Switches. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 18552–18556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonesson, A.W.; Elofsson, U.M.; Brismar, H.; Callisen, T.H. Adsorption and Mobility of a Lipase at a Hydrophobic Surface in the Presence of Surfactants. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5810–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozhaev, V. Engineering Stability of Enzymes in Systems with Organic Solvents. In Stability and Stabilization of Biocatalysts; Ballesteros, A., Plou, F.J., Iborra, J.L., Halling, P.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 15, pp. 355–363. ISBN 0921-0423. [Google Scholar]
- Egorova, K.S.; Gordeev, E.G.; Ananikov, V.P. Biological Activity of Ionic Liquids and Their Application in Pharmaceutics and Medicine. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7132–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, J.; Yu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Z. Ionic Liquid-Strengthened Immobilized Rhizomucor Miehei Lipase for Catalytic Esterification of Itaconic Acid in Aqueous Media. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, R.J.; Ballone, P. Computational Study of Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids Interacting with a POPC Phospholipid Bilayer. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 11205–11216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoś, P.; Słupek, E.; Gębicki, J. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents in Microextraction Techniques—A Review. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Dai, E. A Deep Eutectic Solvent as an Extraction Solvent to Separate and Preconcentrate Parabens in Water Samples Using in Situ Liquid-Liquid Microextraction. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Lima, F.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Circular Approach to Purify Water Contaminated with Ciprofloxacin. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 14739–14746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wu, R.; Zhu, F.; Dong, Q.; Su, E. Enzymes in Nearly Anhydrous Deep Eutectic Solvents: Insight into the Biocompatibility and Thermal Stability. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2022, 157, 110022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guajardo, N.; Ahumada, K.; Domínguez de María, P. Immobilized Lipase-CLEA Aggregates Encapsulated in Lentikats® as Robust Biocatalysts for Continuous Processes in Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 310, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Dai, Y.; Row, K.H. Evaluation of Fatty Acid/Alcohol-Based Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents as Media for Extracting Antibiotics from Environmental Water. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 7325–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgharbawy, A.A.; Riyadi, F.A.; Alam, M.Z.; Moniruzzaman, M. Ionic Liquids as a Potential Solvent for Lipase-Catalysed Reactions: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 251, 150–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Ge, X.; Zhang, J. Effects of Lignin and Surfactant on Adsorption and Hydrolysis of Cellulases on Cellulose. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noori, M.S.; Karimi, K. Detailed Study of Efficient Ethanol Production from Elmwood by Alkali Pretreatment. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 105, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, S.; Yu, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Yang, Y.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, K.J.; Kan, E.; Lee, S.H. Effect of Deep Eutectic Solvent Mixtures on Lipase Activity and Stability. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2016, 128, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Zhu, H.; Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Hou, K.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y. Immobilized Lipase on Macroporous Polystyrene Modified by PAMAM-Dendrimer and Their Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgharbawy, A.A.M.; Syed Putra, S.S.; Hayyan, M.; Hayyan, A.; Basirun, W.J.; Mirghani, M.E.S.; Majrashi, A.A.; Nawawi, W.M.F.W.; Alias, Y.; Mohd Salleh, H.; et al. Polyamidoamine Dendrimers: Favorable Polymeric Nanomaterials for Lipase Activation. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, J.J.; Todero, L.M.; Lage, F.A.P.; Khedy, G.I.; Ducas, J.D.; Custódio, A.P.; Pinto, M.A.; Mendes, A.A. Interfacial Activation of Lipases on Hydrophobic Support and Application in the Synthesis of a Lubricant Ester. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).