Biosorption of Hexavalent Chromium by Bacillus megaterium and Rhodotorula sp. Inactivated Biomass
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biosorbents Preparation
2.2. Biosorption Studies
2.3. Determination of Metal Concentration in Solution
2.4. Quantification of Biosorption Performances
- biosorption capacity (q, mg/g) which is defined as the amount of metal taken up by the biosorbent per unit mass (or volume) of biosorbent under established experimental conditions, being calculated with Equation (1).
- removal efficiency (R, %) is the fraction of metal removed expressed in percent and can be calculated using Equation (2):where: C0, C—initial and residual concentration of metal ion in solution, respectively (mg/L); m—biosorbent mass (g); V—volume of aqueous solution that was used in biosorption studies (L).
2.5. Biosorption Kinetics
2.6. Adsorption Isotherms
2.7. Biosorbent Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
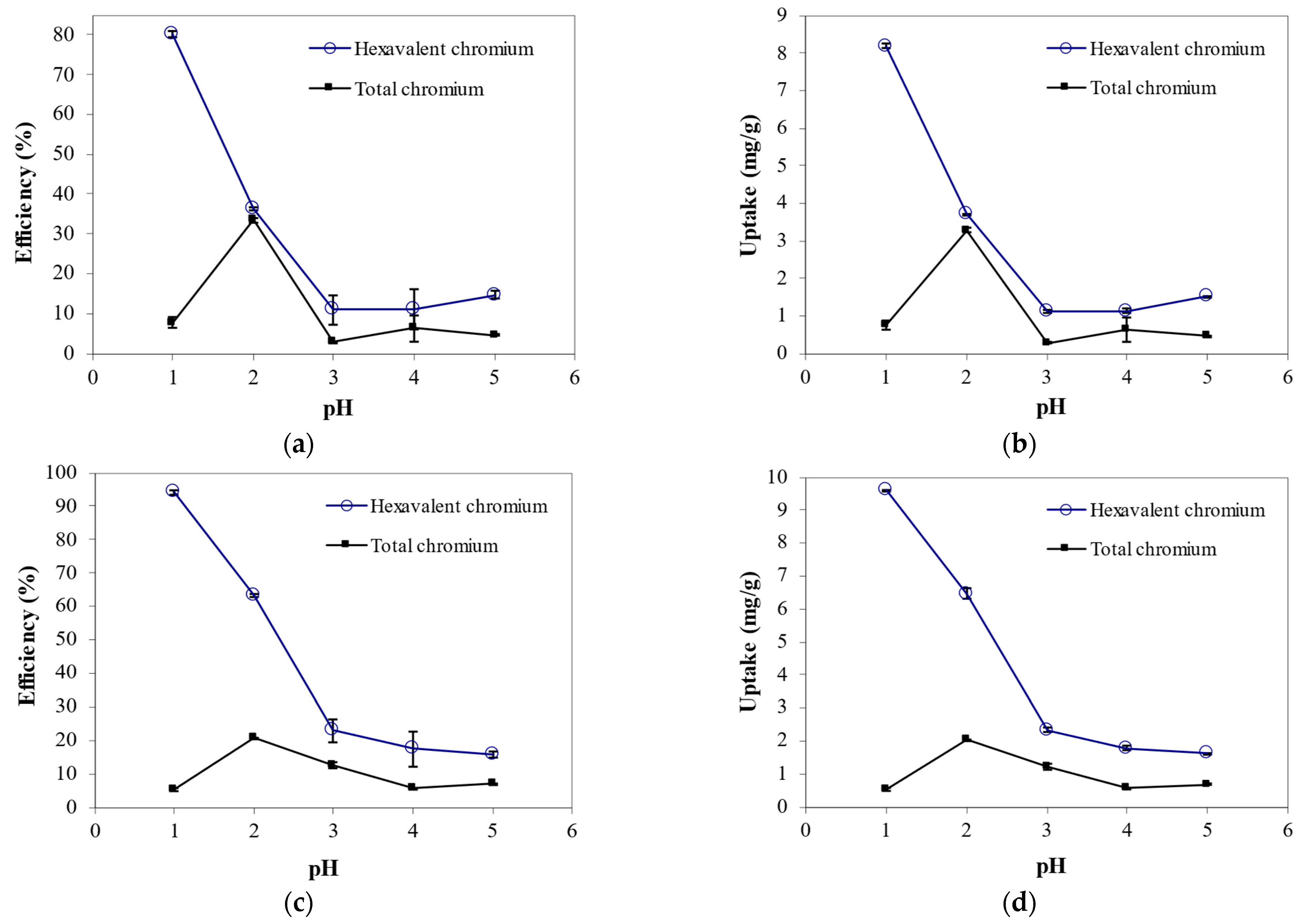
3.1. Effect of Initial pH on Cr6+ Biosorption
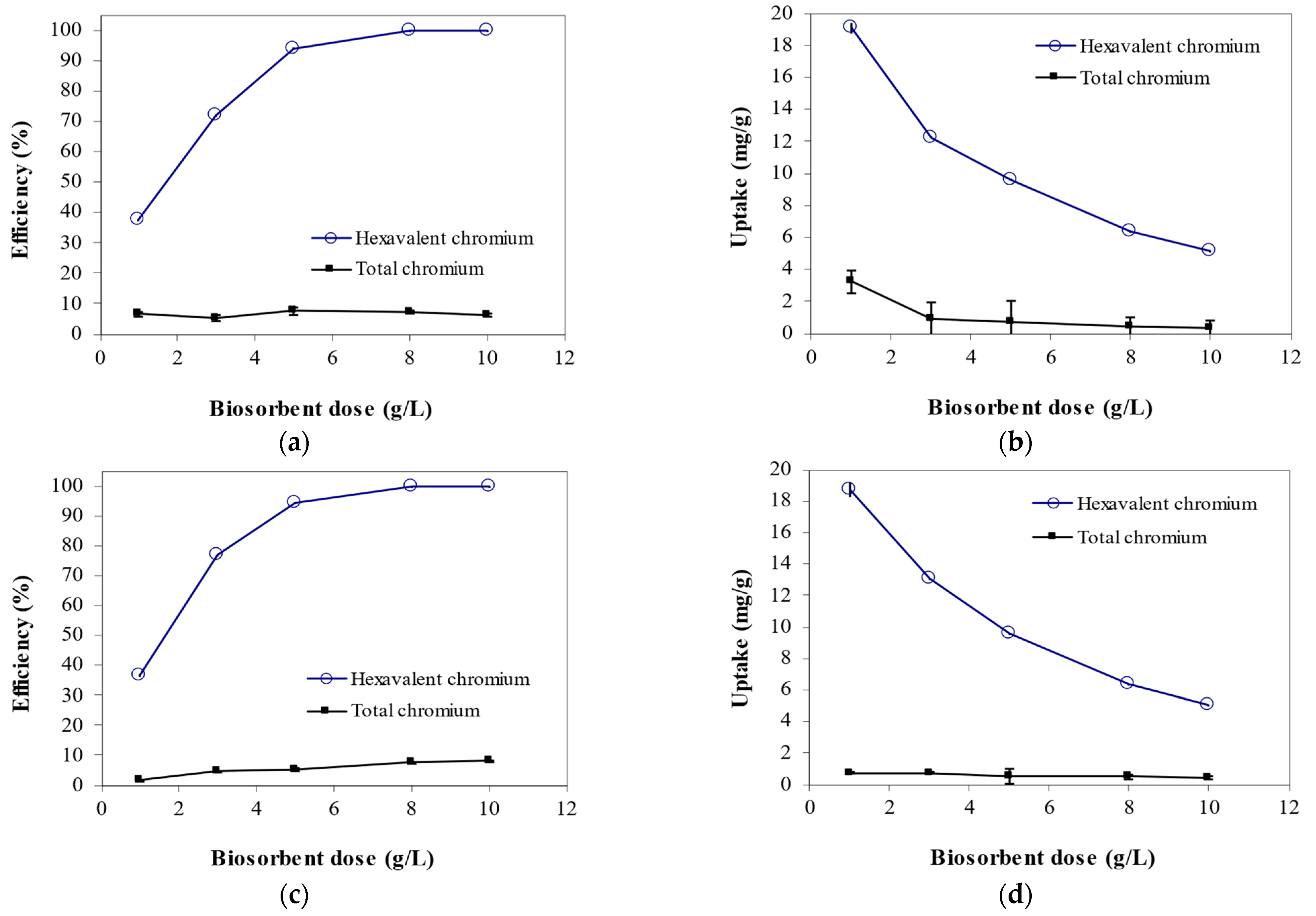
3.2. Effect of Biomass Dosage on Cr6+ Biosorption
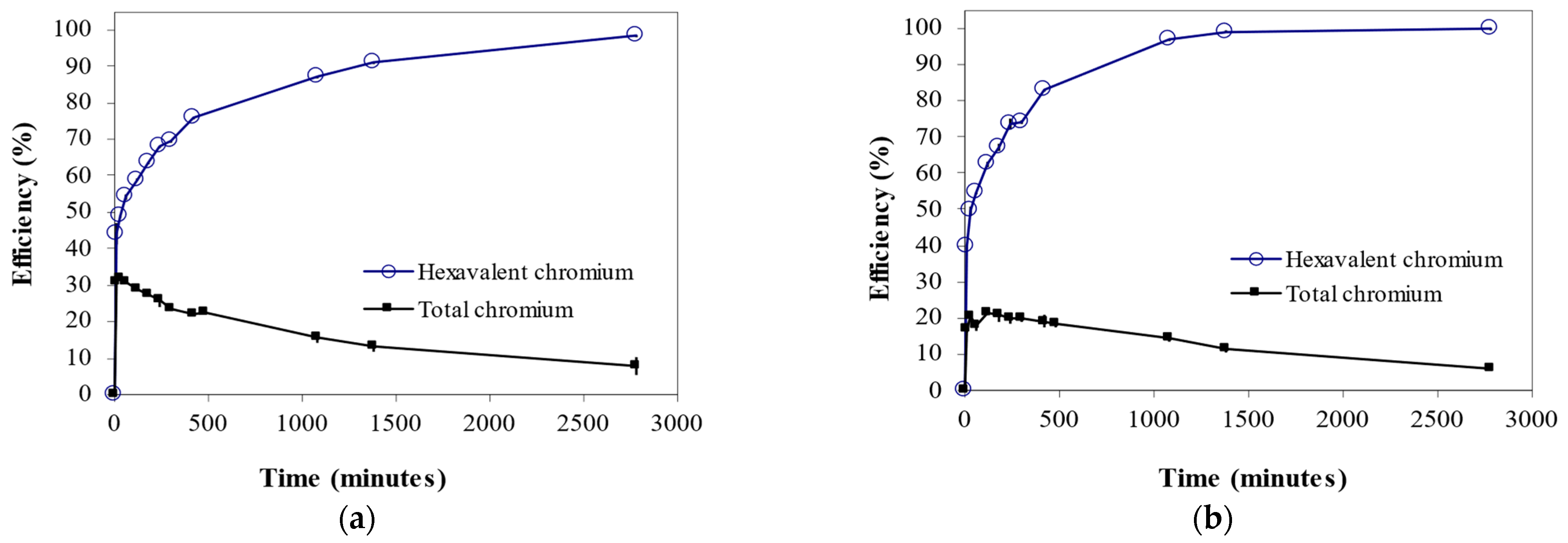
3.3. Effect of Contact Time on Cr6+ Biosorption
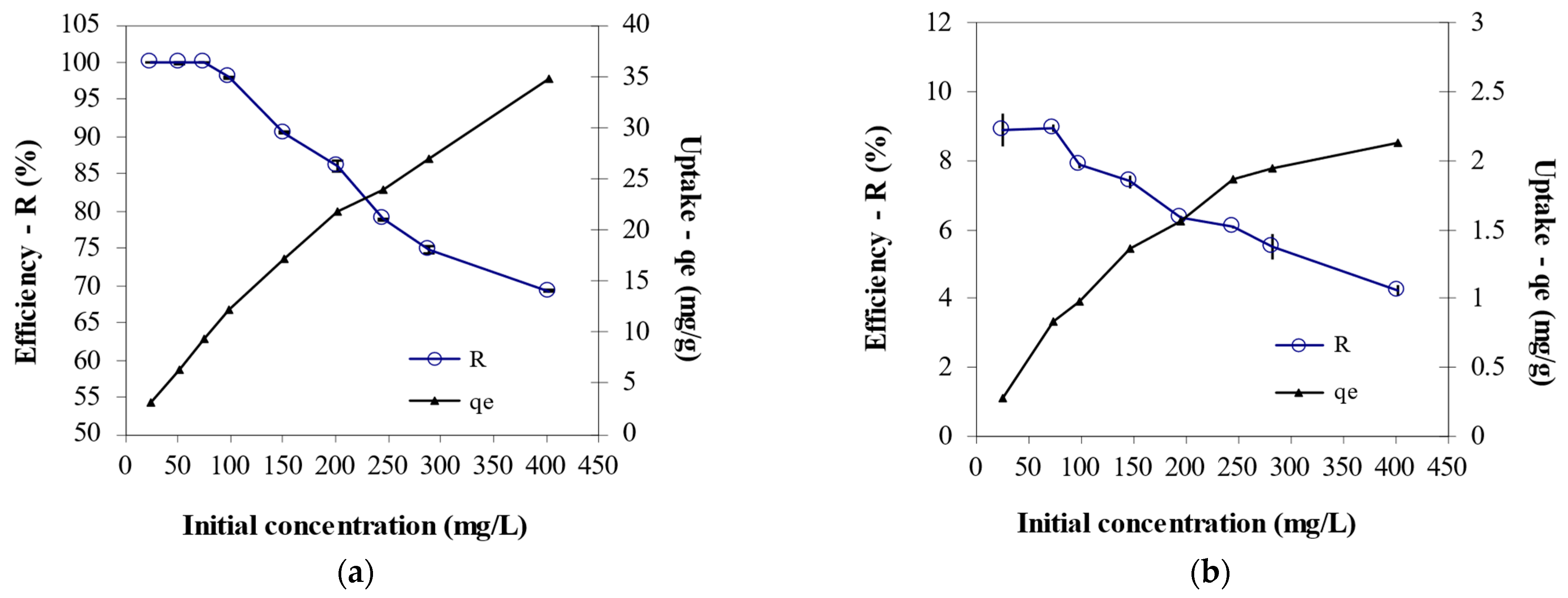
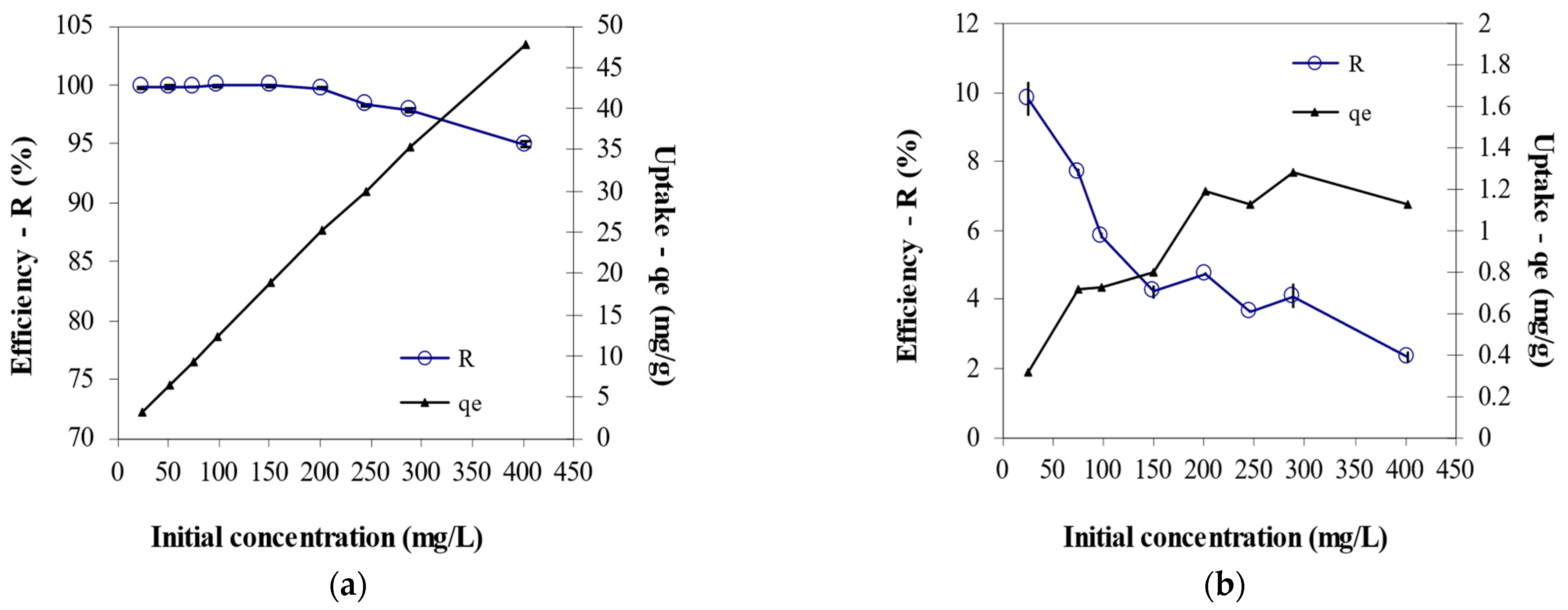
3.4. Effect of Initial Cr6+ Concentration on Biosorption
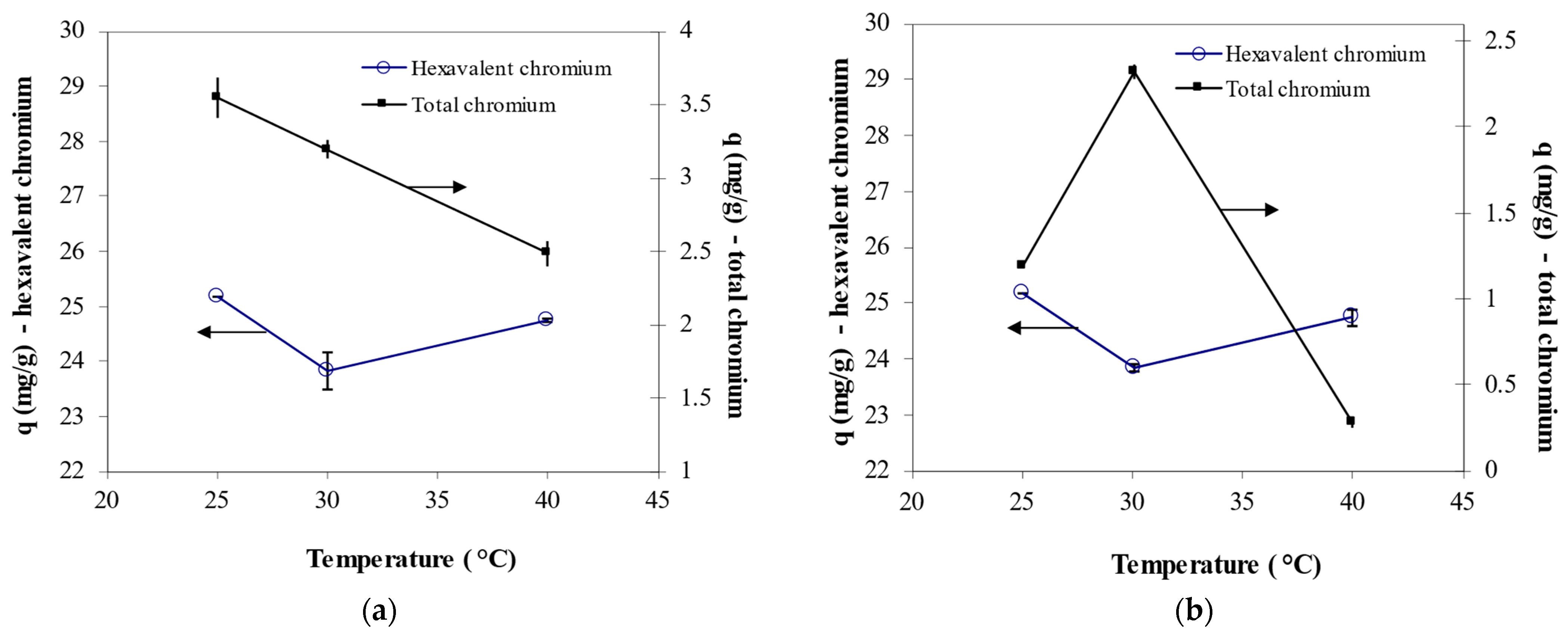
3.5. Effect of Temperature on Cr6+ Biosorption
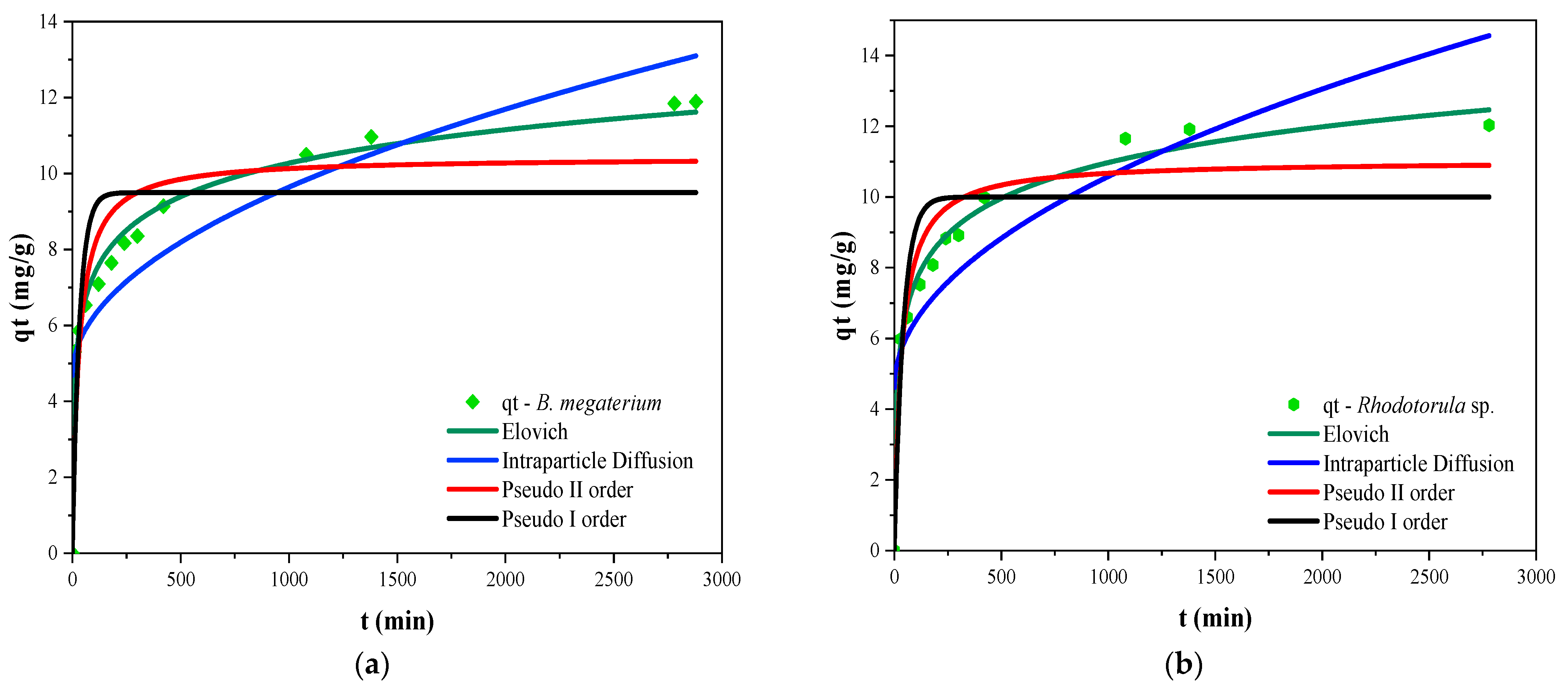
3.6. Sorption Kinetics
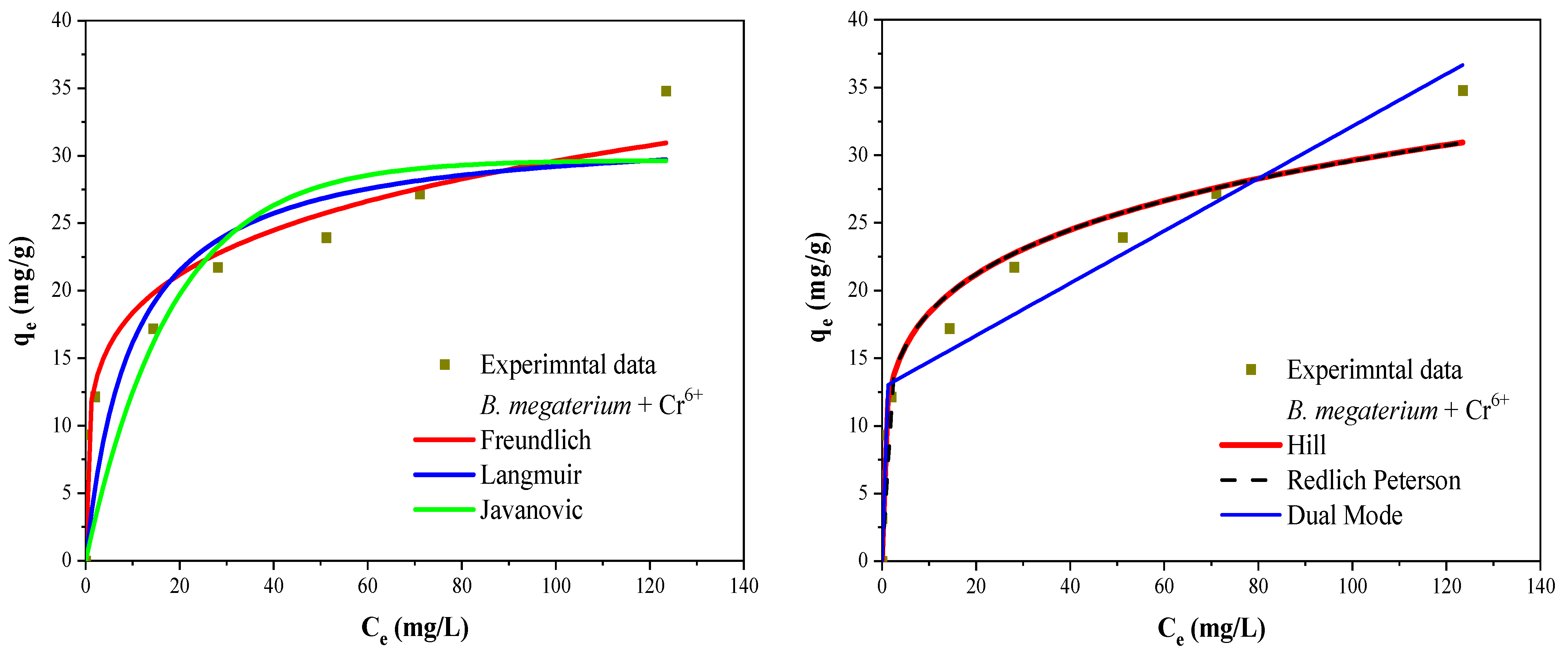
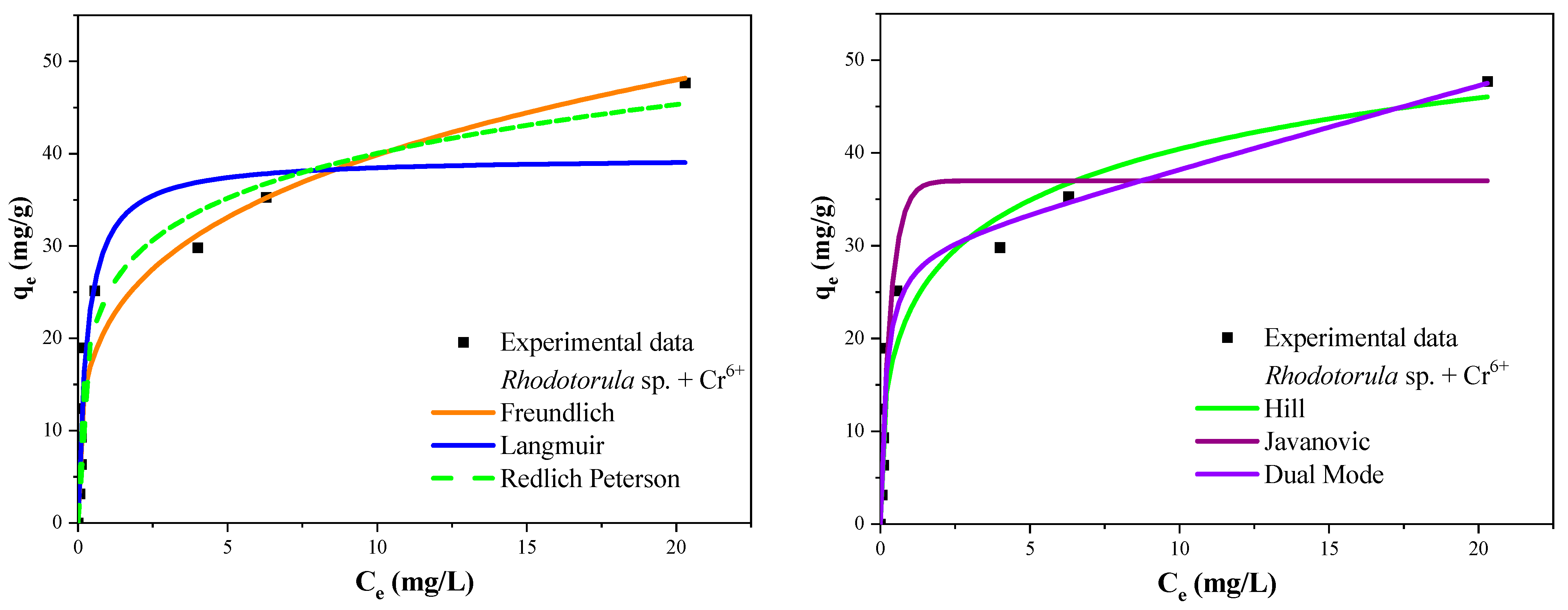
3.7. Biosorption Isotherms
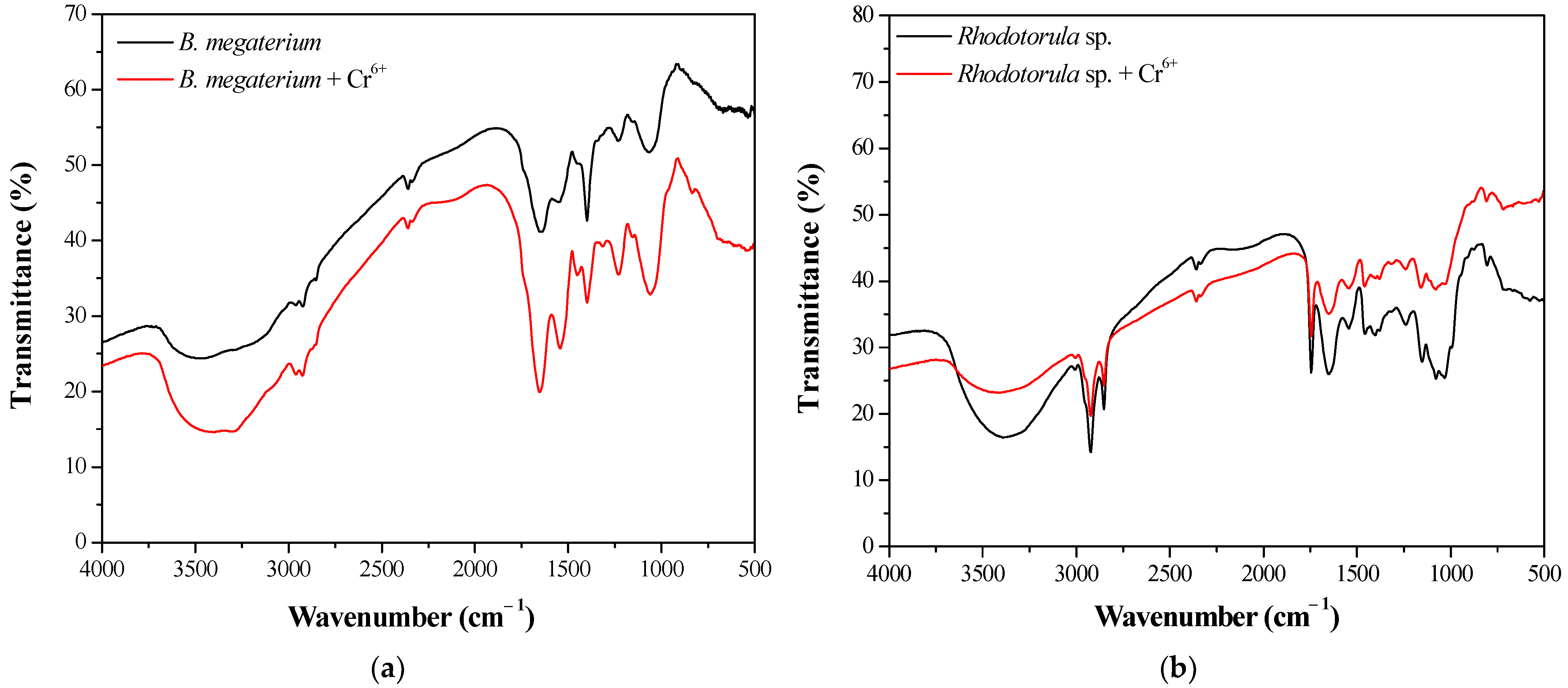
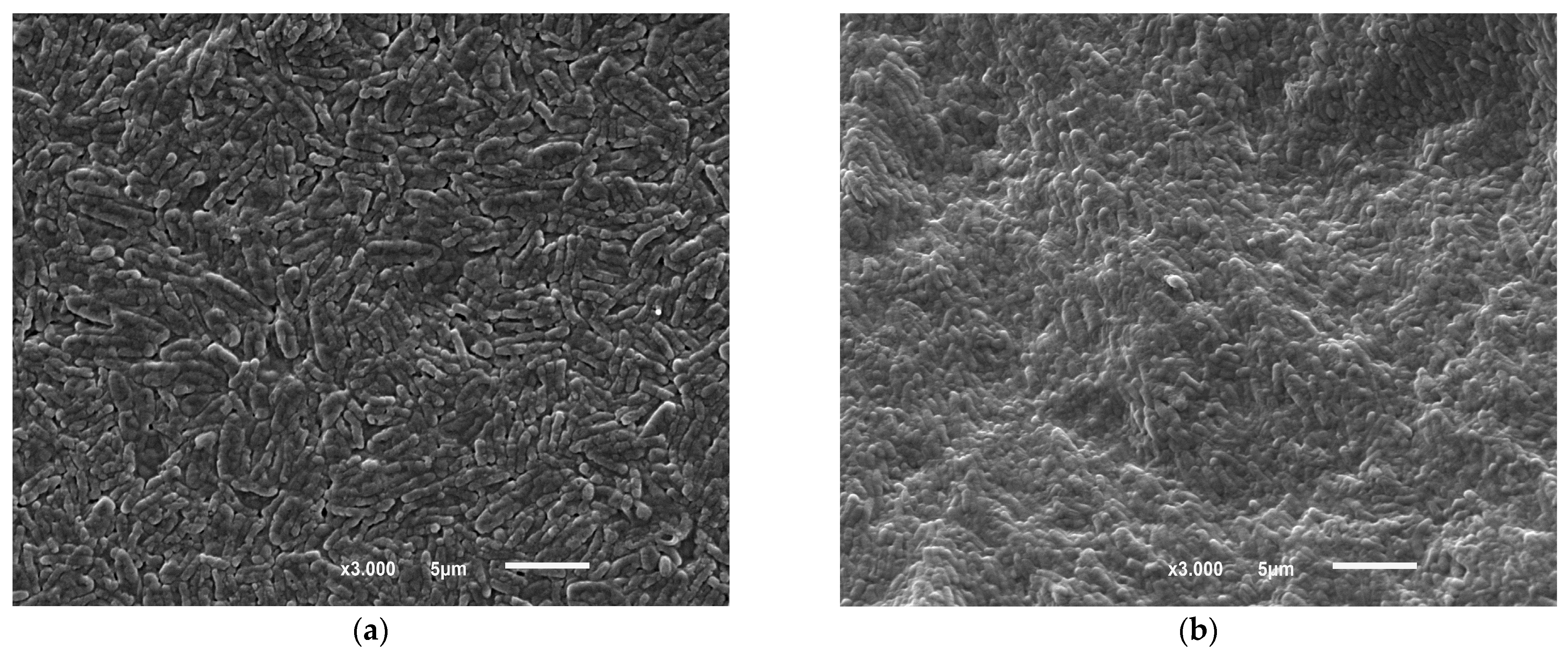
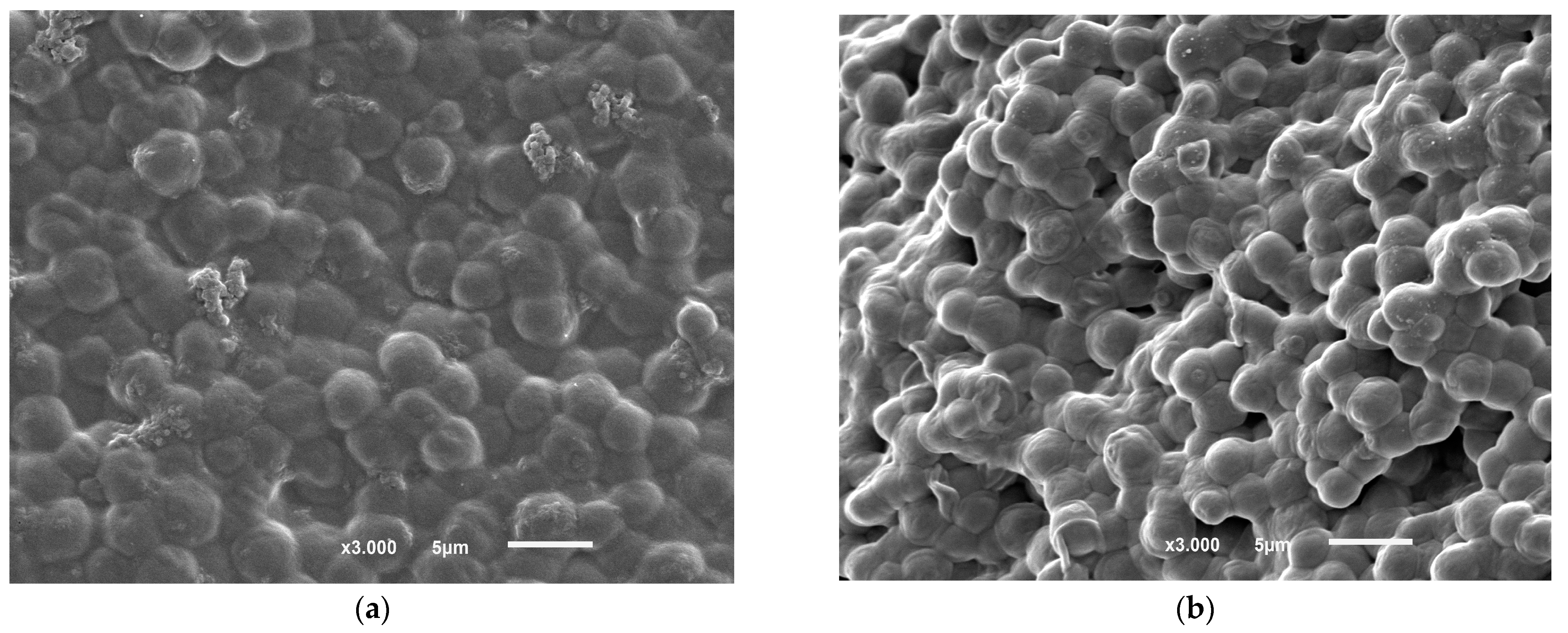
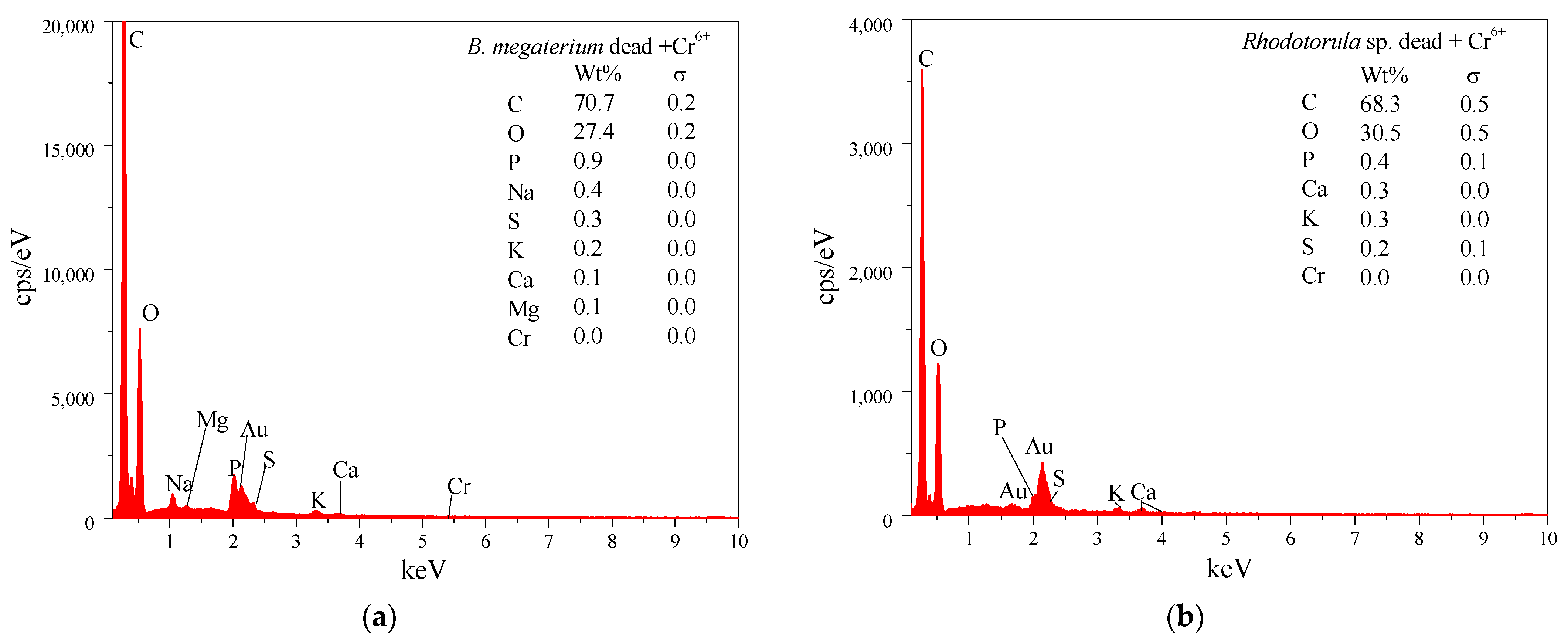
3.8. FTIR and SEM-EDS Analysis of the Biosorbent
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Environment Agency. The European Pollutant Release and Transfer Register (E-PRTR), Member States Reporting under Article 7 of Regulation (EC) No 166/2006—European Environment Agency. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/member-states-reporting-art-7-under-the-european-pollutant-release-and-transfer-register-e-prtr-regulation-10 (accessed on 11 December 2020).
- Namieśnik, J.; Rabajczyk, A. The Speciation and Physico-Chemical Forms of Metals in Surface Waters and Sediments. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2010, 22, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B.C. Mapping of Selected Trace Metals and Associated Risk in Coastal Sediments along the Northwest Anatolia Coasts of Turkey. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2021, 20, 1999–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubeah, R.; Altaher, H.; Khalil, T. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium Using Two Innovative Adsorbents. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2018, 17, 1621–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconu, M.; Rosca, M.; Cozma, P.; Minut, M.; Smaranda, C.; Hlihor, R.-M.; Gavrilescu, M. Toxicity and Microbial Bioremediation of Chromium Contaminated Effluents. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on E-Health and Bioengineering (EHB), Iasi, Romania, 29–30 October 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Langård, S.; Costa, M. Chromium. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 717–742. ISBN 978-0-444-59453-2. [Google Scholar]
- WHO Chromium. Air Quality Guidelines; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Daulton, T.L.; Little, B.J. Determination of Chromium Valence over the Range Cr(0)–Cr(VI) by Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy. Ultramicroscopy 2006, 106, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, R.; Nandi, R.; Saha, B. Sources and Toxicity of Hexavalent Chromium. J. Coord. Chem. 2011, 64, 1782–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology: Volume 3: Environmental Toxicology; Experientia Supplementum; Luch, A., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 133–164. ISBN 978-3-7643-8340-4. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, R.; Anjaneyulu, Y.; Krupadam, R.J. Cr (VI) Removal from Electroplating Industrial Effluents: A Greener and Cheaper Method. Zaštita Mater. 2009, 50, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sibi, G. Biosorption of Chromium from Electroplating and Galvanizing Industrial Effluents under Extreme Conditions Using Chlorella Vulgaris. Green Energy Environ. 2016, 1, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K.; Khandegar, V.; Saroha, A.K. Removal of Chromium from Electroplating Industry Effluent Using Electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2013, 17, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Chaudhari, P.K.; Prajapati, A.K. Removal of Chromium (VI) and Lead from Electroplating Effluent Using Electrocoagulation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, H.M.; Kamal, E.M.; Mohamed, A.H.; El-Bassuony, A.D. Chromium Removal from Tannery Wastewater Using Chemical and Biological Techniques Aiming Zero Discharge of Pollution. In Proceeding of Fifth Scientific Environmental Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 12–16 July 2010; pp. 171–183. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.-C.; Wang, M.-K.; Chiou, C.-S.; Li, Y.-S.; Lin, Y.-A.; Huang, S.-S. Chromium Removal and Sorption Mechanism from Aqueous Solutions by Wine Processing Waste Sludge. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 8891–8899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosca, M.; Hlihor, R.-M.; Gavrilescu, M. Bioremediation of Persistent Toxic Substances: From Conventional to New Approaches in Using Microorganisms and Plants. In Microbial Technology for the Welfare of Society; Microorganisms for Sustainability; Arora, P.K., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 17, pp. 289–312. ISBN 9789811388439. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilescu, M. Removal of Heavy Metals from the Environment by Biosorption. Eng. Life Sci. 2004, 4, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoudani, Y.E.; Dimane, F.; Ouarghi, H.E. Removal Efficiency of Heavy Metals by a Biological Wastewater Treatment Plant and Their Potential Risks to Human Health. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2021, 8, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgariu, L.; Gavrilescu, M. Bioremediation of Heavy Metals by Microalgae. In Handbook of Marine Microalgae; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 457–469. ISBN 978-0-12-800776-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hlihor, R.; Petronela, C.; Gavrilescu, M. Removal of Heavy Metals from the Environment by Phytoremediation and Microbial Remediation. In Sustainable Solutions for Environmental Pollution; El-Gendy, N.S., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 95–146. ISBN 978-1-119-82751-1. [Google Scholar]
- Filote, C.; Roșca, M.; Hlihor, R.M.; Cozma, P.; Simion, I.M.; Apostol, M.; Gavrilescu, M. Sustainable Application of Biosorption and Bioaccumulation of Persistent Pollutants in Wastewater Treatment: Current Practice. Processes 2021, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwastowski, J.; Staroń, P. Influence of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Yeast Cells Immobilized on Cocos Nucifera Fibers for the Adsorption of Pb(II) Ions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 632, 127735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, O.G.; Demir, A.; Gören, N. Investigation of Cobalt(II) Adsorption from Aqueous. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2022, 21, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, O.; Kazemi, M. A Review Study of Biosorption of Heavy Metals and Comparison between Different Biosorbents. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 1386–1399. [Google Scholar]
- Bulgariu, L.; Bulgariu, D.; Rusu, C. Marine Algae Biomass for Removal of Heavy Metal Ions. In Hb25_Springer Handbook of Marine Biotechnology; Kim, S.-K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 611–648. ISBN 978-3-642-53970-1. [Google Scholar]
- Shamim, S. Biosorption of Heavy Metals. In Biosorption; Derco, J., Vrana, B., Eds.; InTech: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 978-1-78923-472-5. [Google Scholar]
- Filote, C.; Roșca, M.; Simion, I.M.; Hlihor, R.M. Continuous Systems Bioremediation of Wastewaters Loaded with Heavy Metals Using Microorganisms. Processes 2022, 10, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlihor, R.M.; Diaconu, M.; Fertu, D.; Chelaru, C.; Sandu, I.; Tavares, T. Bioremediation of Cr(VI) Polluted Wastewaters by Sorption on Heat Inactivated Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Biomass. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2013, 7, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlihor, R.M.; Diaconu, M.; Leon, F.; Curteanu, S.; Tavares, T.; Gavrilescu, M. Experimental Analysis and Mathematical Prediction of Cd(II) Removal by Biosorption Using Support Vector Machines and Genetic Algorithms. New Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, A.; Guha, A.K.; Ray, L. Adsorption Behaviour of Cadmium by Bacillus Cereus M 116: Some Physical and Biochemical Studies. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2011, 23, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, H. Responses of Rhodotorula sp. Y11 to Cadmium. Biometals 2008, 21, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, N.; Vishwakarma, K.; Singh, J.; Mishra, M.; Kumar, V.; Rani, R.; Mishra, R.K.; Chauhan, D.K.; Tripathi, D.K.; Sharma, S. Tolerance and Reduction of Chromium(VI) by Bacillus sp. MNU16 Isolated from Contaminated Coal Mining Soil. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roşca, M.; Hlihor, R.-M.; Cozma, P.; Drăgoi, E.N.; Diaconu, M.; Silva, B.; Tavares, T.; Gavrilescu, M. Comparison of Rhodotorula sp. and Bacillus megaterium in the Removal of Cadmium Ions from Liquid Effluents. Green Process. Synth. 2018, 7, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. SW-846 Test Method 7196A: Chromium, Hexavalent (Colorimetric). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/hw-sw846/sw-846-test-method-7196a-chromium-hexavalent-colorimetric (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Kajjumba, G.W.; Emik, S.; Öngen, A.; Kurtulus Özcan, H.; Aydın, S. Modelling of Adsorption Kinetic Processes—Errors, Theory and Application. In Advanced Sorption Process Applications; Edebali, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1-78984-818-2. [Google Scholar]
- Netzahuatl-Muñoz, A.R.; del Carmen Cristiani-Urbina, M.; Cristiani-Urbina, E. Chromium Biosorption from Cr(VI) Aqueous Solutions by Cupressus lusitanica Bark: Kinetics, Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Studies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B. Cu(II) and As(V) Adsorption Kinetic Characteristic of the Multifunctional Amino Groups in Chitosan. Processes 2020, 8, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangabhashiyam, S.; Anu, N.; Giri Nandagopal, M.S.; Selvaraju, N. Relevance of Isotherm Models in Biosorption of Pollutants by Agricultural Byproducts. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, R.; Saadi, Z.; Fazaeli, R.; Fard, N.E. Monolayer and Multilayer Adsorption Isotherm Models for Sorption from Aqueous Media. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayawei, N.; Ebelegi, A.N.; Wankasi, D. Modelling and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherms. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 3039817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkia, Y.B.; Bouaziz, N.; Al-Muhtaseb, S.A.; Lamine, A.B. Adsorption Energy and Pore-Size Distributions of Activated Carbons Calculated Using Hill’s Model. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, D.N. Jovanovich Adsorption Isotherm for Heterogeneous Surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1973, 43, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieth, W.R.; Sladek, K.J. A Model for Diffusion in a Glassy Polymer. J. Colloid Sci. 1965, 20, 1014–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonen, Y.; Rytwo, G. Using the Dual-Mode Model to Describe Adsorption of Organic Pollutants onto an Organoclay. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 299, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda-García, E.; Cristiani-Urbina, E. Hexavalent Chromium Removal and Total Chromium Biosorption from Aqueous Solution by Quercus Crassipes Acorn Shell in a Continuous Up-Flow Fixed-Bed Column: Influencing Parameters, Kinetics, and Mechanism. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobby, R.; Jha, P.; Gupta, A.; Gupte, A.; Desai, N. Biotransformation of Chromium by Root Nodule Bacteria Sinorhizobium sp. SAR1. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlihor, R.M.; Figueiredo, H.; Tavares, T.; Gavrilescu, M. Biosorption Potential of Dead and Living Arthrobacter Viscosus Biomass in the Removal of Cr(VI): Batch and Column Studies. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 108, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rocha Ferreira, G.L.; Vendruscolo, F.; Antoniosi Filho, N.R. Biosorption of Hexavalent Chromium by Pleurotus Ostreatus. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-López, J.A.; Angosto, J.M.; Avilés, M.D. Biosorption of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Medium with Opuntia Biomass. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 670249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojiagu, D.K.; Odibo, C.F.J.; Ojiagu, C.; Agu, K.C.; Okafor, A.C. Biosorption of Hexavalent Chromium by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Strain ANSC: Equilibria Isothermic, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies. Bioeng. Biosci. 2018, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinath, T.; Verma, T.; Ramteke, P.W.; Garg, S.K. Chromium (VI) Biosorption and Bioaccumulation by Chromate Resistant Bacteria. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Al-Absi, R.S. Mechanistic Understanding of the Adsorption and Thermodynamic Aspects of Cationic Methylene Blue Dye onto Cellulosic Olive Stones Biomass from Wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volesky, B. Biosorption Process Simulation Tools. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 71, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Pei, X.; Zhou, D.; He, P.; Hughes, S.S. Study on Detoxification and Removal Mechanisms of Hexavalent Chromium by Microorganisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnanelli, F. Equilibrium, Kinetic and Dynamic Modelling of Biosorption Processes. In Microbial Biosorption of Metals; Kotrba, P., Mackova, M., Macek, T., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 59–120. ISBN 978-94-007-0442-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rosca, M.; Hlihor, R.M.; Cozma, P.; Simion, I.M.; Filote, C.; Grecu, C.; Stoleru, V.; Gavrilescu, M. Scaling-Up Strategies of Heavy Metals Microbial Bioremediation. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on e-Health and Bioengineering (EHB), Iasi, Romania, 18–19 November 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Temel, F.A.; Avci, E.; Turan, N.G. Investigation of Copper(II), Zinc(II) and Lead(II) Removal onto Expanded Perlite by Adsorption from the Wastes of Metal Casting Industry: Statistical Modeling and Optimization. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2022, 21, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmohammadi-Kalalagh, S.; Babazadeh, H.; Nazemi, A. Comparison of Linear and Nonlinear Forms of Isotherm Models for Zn(II) and Cu(II) Sorption on a Kaolinite. Arab J Geosci 2015, 8, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.-C.; Juang, K.-W. Comparison of Linear and Nonlinear Forms of Isotherm Models for Strontium Sorption on a Sodium Bentonite. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2000, 243, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaneva, Z.L.; Koumanova, B.K.; Georgieva, N.V. Linear and Nonlinear Regression Methods for Equilibrium Modelling of p -Nitrophenol Biosorption by Rhizopus Oryzae: Comparison of Error Analysis Criteria. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 517631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosca, M.; Diaconu, M.; Hlihor, R.-M.; Cozma, P.; Gavrilescu, M. Prediction of Equillibrium Sorption Isotherm for Cadmium Biosorption by Microorganisms: Comparison of Linear and Nonlinear Methods. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on e-Health and Bioengineering (EHB), Iasi, Romania, 29–30 October 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ayele, A.; Godeto, Y.G. Bioremediation of Chromium by Microorganisms and Its Mechanisms Related to Functional Groups. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 7694157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.; Thomas, L. Chemical-Assisted Microbially Mediated Chromium (Cr) (VI) Reduction Under the Influence of Various Electron Donors, Redox Mediators, and Other Additives: An Outlook on Enhanced Cr(VI) Removal. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 619766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossan, S.; Hossain, S.; Islam, M.R.; Kabir, M.H.; Ali, S.; Islam, M.S.; Imran, K.M.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Mou, T.J.; Parvez, A.K.; et al. Bioremediation of Hexavalent Chromium by Chromium Resistant Bacteria Reduces Phytotoxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, M.; Šoštarić, T.; Stojanović, M.; Petrović, J.; Mihajlović, M.; Ćosović, A.; Stanković, S. Mechanism of Adsorption of Cu2+ and Zn2+ on the Corn Silk (Zea mays L.). Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, M.; Petrović, J.; Šoštarić, T.; Ercegović, M.; Milojković, J.; Lopičić, Z.; Kojić, M. A Mechanism Assessment and Differences of Cadmium Adsorption on Raw and Alkali-Modified Agricultural Waste. Processes 2022, 10, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, M.; Šoštarić, T.; Stojanović, M.; Milojković, J.; Mihajlović, M.; Stanojević, M.; Stanković, S. Removal of Pb2+ Ions by Raw Corn Silk (Zea mays L.) as a Novel Biosorbent. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 58, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, D.; Sukla, L.B.; Mishra, B.B.; Devi, N. Biosorption for Removal of Hexavalent Chromium Using Microalgae Scenedesmus sp. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talari, A.C.S.; Martinez, M.A.G.; Movasaghi, Z.; Rehman, S.; Rehman, I.U. Advances in Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy of Biological Tissues. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2017, 52, 456–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duygu, D.Y.; Udoh, A.U.; Ozer, T.B.; Akbulut, A.; Erkaya, I.A.; Yildiz, K.; Guler, D. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy for Identification of Chlorella vulgaris Beijerinck 1890 and Scenedesmus obliquus (Turpin) Kützing 1833. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 3817–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Hao, R.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Ye, Y. Hexavalent Chromium Reduction and Bioremediation Potential of Fusarium Proliferatum S4 Isolated from Chromium-Contaminated Soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 78292–78302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Experiments | Factors Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Biosorbent Dose (g/L) | Contact Time (Minutes) | Initial Concentration (mg/L) | Temperature (°C) | |
| 1—Effect of initial pH | 1–5 | 5 | 2880 | 51.03 | 25 |
| 2—Effect of biosorbent dose | 1 | 1–10 | 2880 | 51.03 | 25 |
| 3—Effect of contact time | 1 | 8 | 10–4320 | 96.29 | 25 |
| 4—Effect of initial concentration | 1 | 8 | 2880 | 25.29–402.52 | 25 |
| 5—Effect of temperature | 1 | 8 | 2880 | 201.87 | 25–40 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Optimum pH | 2 |
| Color Reagent | Diphenyl carbazide in acetone, 5 g/L |
| Buffer | H2SO4, 10% |
| Wavelength (λmax, nm) | 540 |
| Reference sample | Blank |
| Linear range, (mg/L) | 0.1–1 |
| Equation | y = 0.7588x + 0.0127 |
| Regression coefficient | 0.9997 |
| Kinetic Model | Parameters | B. megaterium | Rhodotorula sp. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter Value | SE | Parameter Value | SE | ||
| Pseudo I order | k1 | 0.031 | 0.012 | 0.024 | 0.008 |
| qe (mg/g) | 9.496 | 0.611 | 10.001 | 0.635 | |
| R2 | 0.7169 | - | 0.7821 | - | |
| Pseudo II order | k2 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| qe (mg/g) | 10.427 | 0.584 | 11.029 | 0.587 | |
| R2 | 0.8451 | - | 0.8947 | - | |
| Elovich | α (mg/g·min) | 4.091 | 1.324 | 2.684 | 0.740 |
| β (mg/g·min) | 0.786 | 0.042 | 0.685 | 0.036 | |
| R2 | 0.9868 | 0.9887 | - | ||
| Intraparticle diffusion | kdiff (mg/g) | 0.157 | 0.027 | 0.189 | 0.036 |
| Ce (mg/L) | 4.684 | 0.725 | 4.614 | 0.855 | |
| R2 | 0.7559 | - | 0.7282 | - | |
| q experimental | 11.888 | 0.004 | 12.031 | 0.016 | |
| Isotherm Model | Isotherm Parameters | B. megaterium | Rhodotorula sp. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter Value | SE | Parameter Value | SE | ||
| Langmuir | qm (mg/g) | 32.072 | 5.292 | 39.597 | 3.392 |
| b (L/mg) | 0.101 | 0.078 | 3.426 | 1.158 | |
| RL | 0.281–0.024 | - | 0.011–0.0007 | - | |
| R2 | 0.7788 | - | 0.8829 | - | |
| Freundlich | k (mg/g) | 11.382 | 1.436 | 21.516 | 1.851 |
| n | 4.817 | 0.739 | 3.734 | 0.511 | |
| R2 | 0.9432 | - | 0.9382 | - | |
| Redlich-Peterson | AR (L/g) | 9.383 × 107 | 4.282 × 106 | 260.71 | 200.22 |
| BR (mg/mL) | 8.223 × 106 | 3.772 × 105 | 9.47 | 8.988 | |
| mR | 0.793 | 0.041 | 0.831 | 0.083 | |
| R2 | 0.9351 | - | 0.9167 | - | |
| Jovanovic | qm (mg/g) | 29.671 | 4.129 | 36.993 | 3.363 |
| KJ (L/mg) | 0. 054 | 0.028 | 2.942 | 0.929 | |
| R2 | 0.7357 | - | 0.8522 | - | |
| Hill | qm (mg/g) | 3.169 × 106 | 3.02 × 105 | 79.681 | 71.36 |
| KD | 278,679.31 | 2.66 × 104 | 2.451 | 3.445 | |
| nH | 0.207 | 0.111 | 0.402 | 0.194 | |
| R2 | 0.9351 | - | 0.9015 | - | |
| Dual Mode | qm (mg/g) | 12.815 | 1.591 | 29.899 | 3.970 |
| Kd (L/g) | 0.193 | 0.026 | 0.880 | 0.306 | |
| b (L/mg) | 284.31 | 215.75 | 5.713 | 2.035 | |
| R2 | 0.9386 | - | 0.9077 | - | |
| qmax experimental (mg/g) | 34.808 | 0.019 | 47.70 | 0.115 | |
| Peak | Types of Vibration | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Native Biomass | Cr6+ Loaded Biomass | ||
| Bacillus megaterium | |||
| - | 836.67 | S=O stretching | [65,67,69,70,71,72] |
| 1064.01 | 1060.15 | P=O symmetric stretching of phosphate groups, –OH group of polysaccharides; C–O stretching of alcoholic groups, of ethers | |
| 1233.54 | 1229.69 | P=O asymmetric stretching of phosphate groups, carbonyl stretch C=O of carboxylic acid | |
| 1545.65 | 1541.79 | C–N stretching in amide II group and N–H bending | |
| 1649.68 | 1653.53 | C=O and C–N stretching in amide I group | |
| 3476.05 | 3402.84 | Stretching vibrations of hydroxyl groups | |
| Rhodotorula sp. | |||
| 1033.18 | 1029.33 | P=O symmetric stretching of phosphate groups, –OH group of polysaccharides; C–O stretching of alcoholic groups, of ethers | [65,67,69,70,71,72] |
| 1152.63 | 1156.48 | P=O asymmetric stretching of phosphate groups, carbonyl stretch C=O of carboxylic acid | |
| 1403.08 | 1399.23 | –COO− symmetric stretching of carboxyl groups | |
| 1457.02 | 1460.87 | –CH2 bending, symmetric C=O | |
| 3391.28 | 3410.55 | Stretching vibrations of hydroxyl groups | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roșca, M.; Silva, B.; Tavares, T.; Gavrilescu, M. Biosorption of Hexavalent Chromium by Bacillus megaterium and Rhodotorula sp. Inactivated Biomass. Processes 2023, 11, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010179
Roșca M, Silva B, Tavares T, Gavrilescu M. Biosorption of Hexavalent Chromium by Bacillus megaterium and Rhodotorula sp. Inactivated Biomass. Processes. 2023; 11(1):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010179
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoșca, Mihaela, Bruna Silva, Teresa Tavares, and Maria Gavrilescu. 2023. "Biosorption of Hexavalent Chromium by Bacillus megaterium and Rhodotorula sp. Inactivated Biomass" Processes 11, no. 1: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010179
APA StyleRoșca, M., Silva, B., Tavares, T., & Gavrilescu, M. (2023). Biosorption of Hexavalent Chromium by Bacillus megaterium and Rhodotorula sp. Inactivated Biomass. Processes, 11(1), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010179









