Benzene Reduction Process Simulation and Optimization in Catalytic Cracking Gasoline Distillation
Abstract
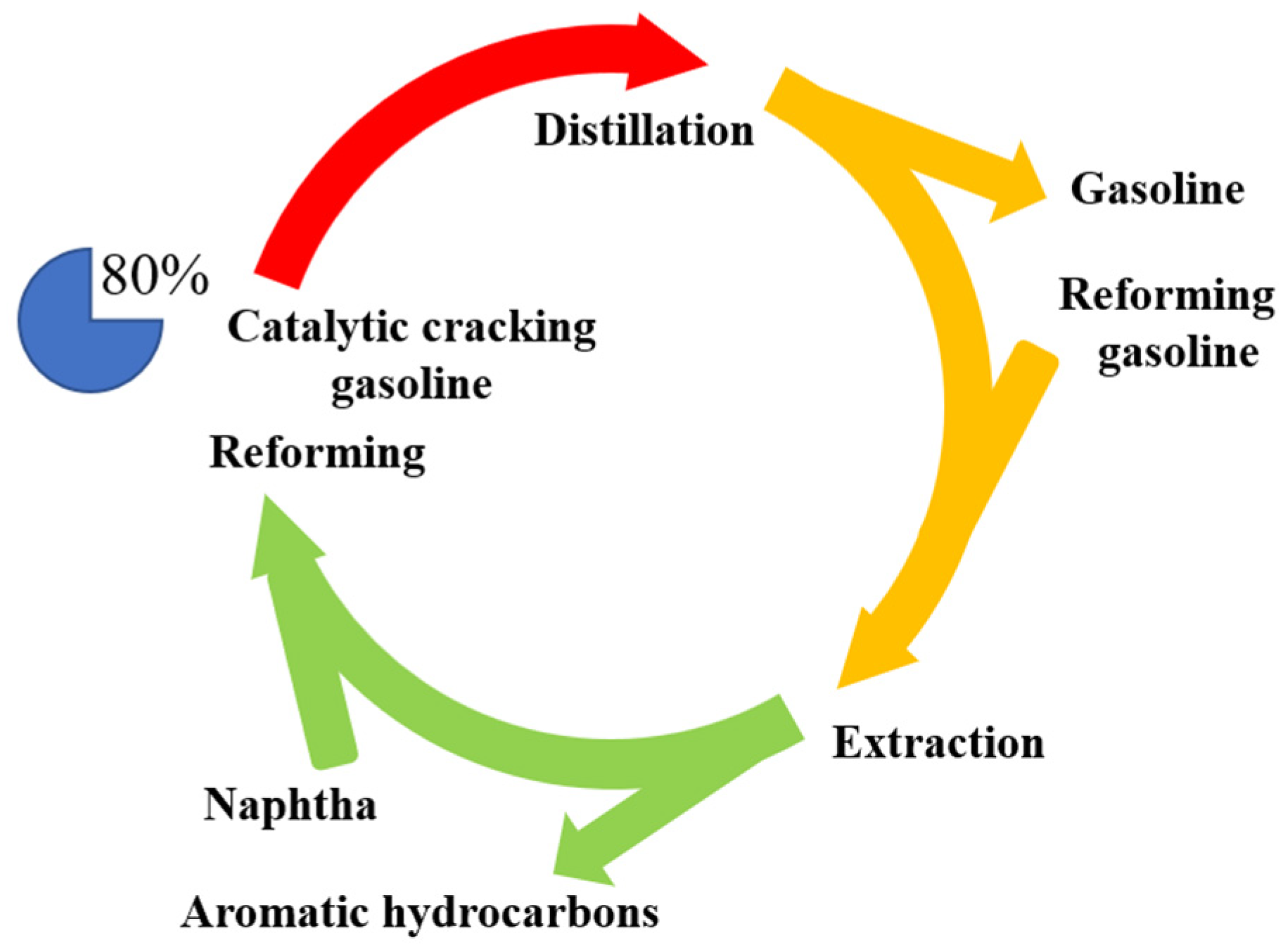
1. Introduction
2. Simulation Strategy
2.1. Material Composition
2.2. Simulation Module
3. Optimization Analysis
3.1. Divided Wall Distillation Model
3.1.1. Technological Process
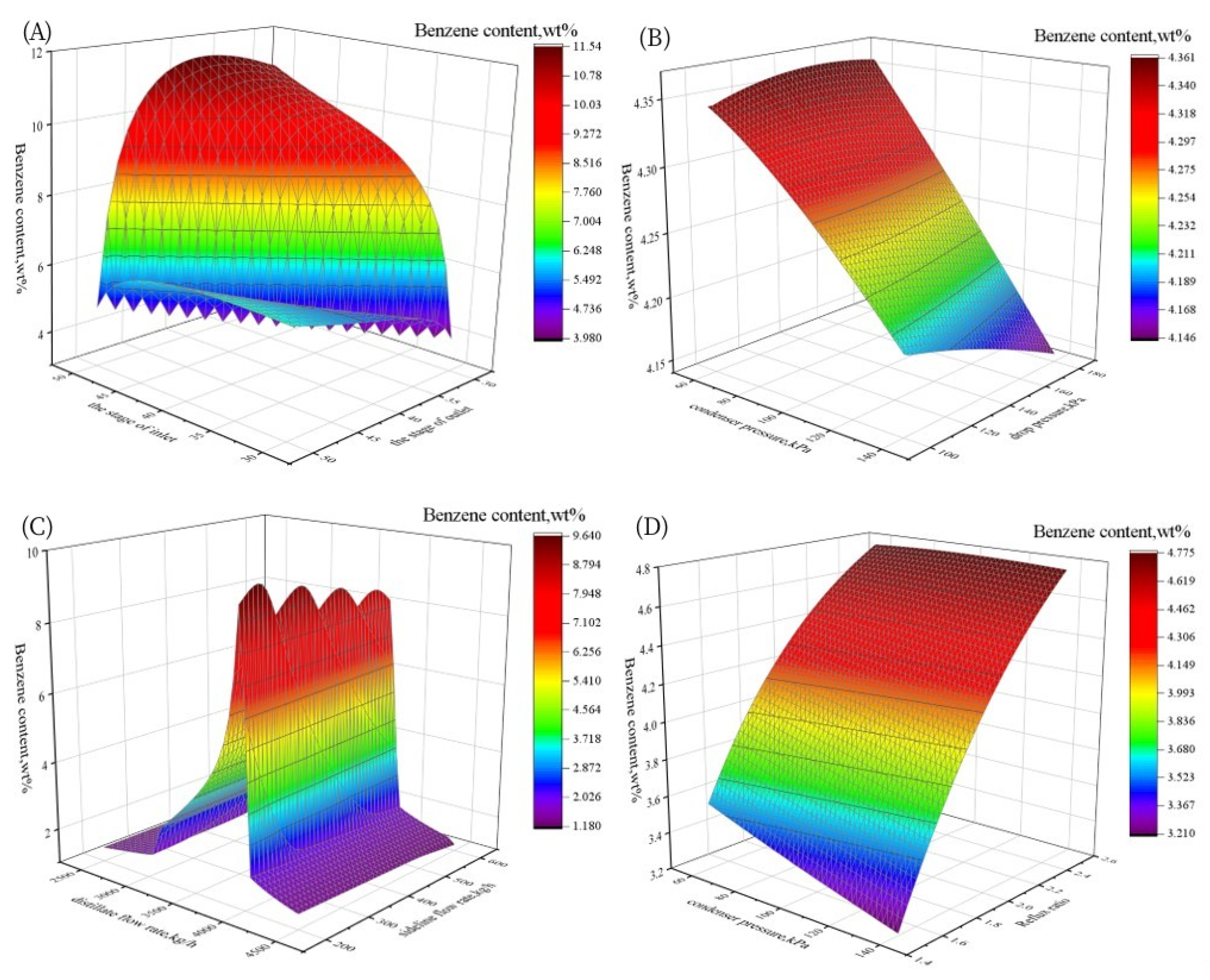
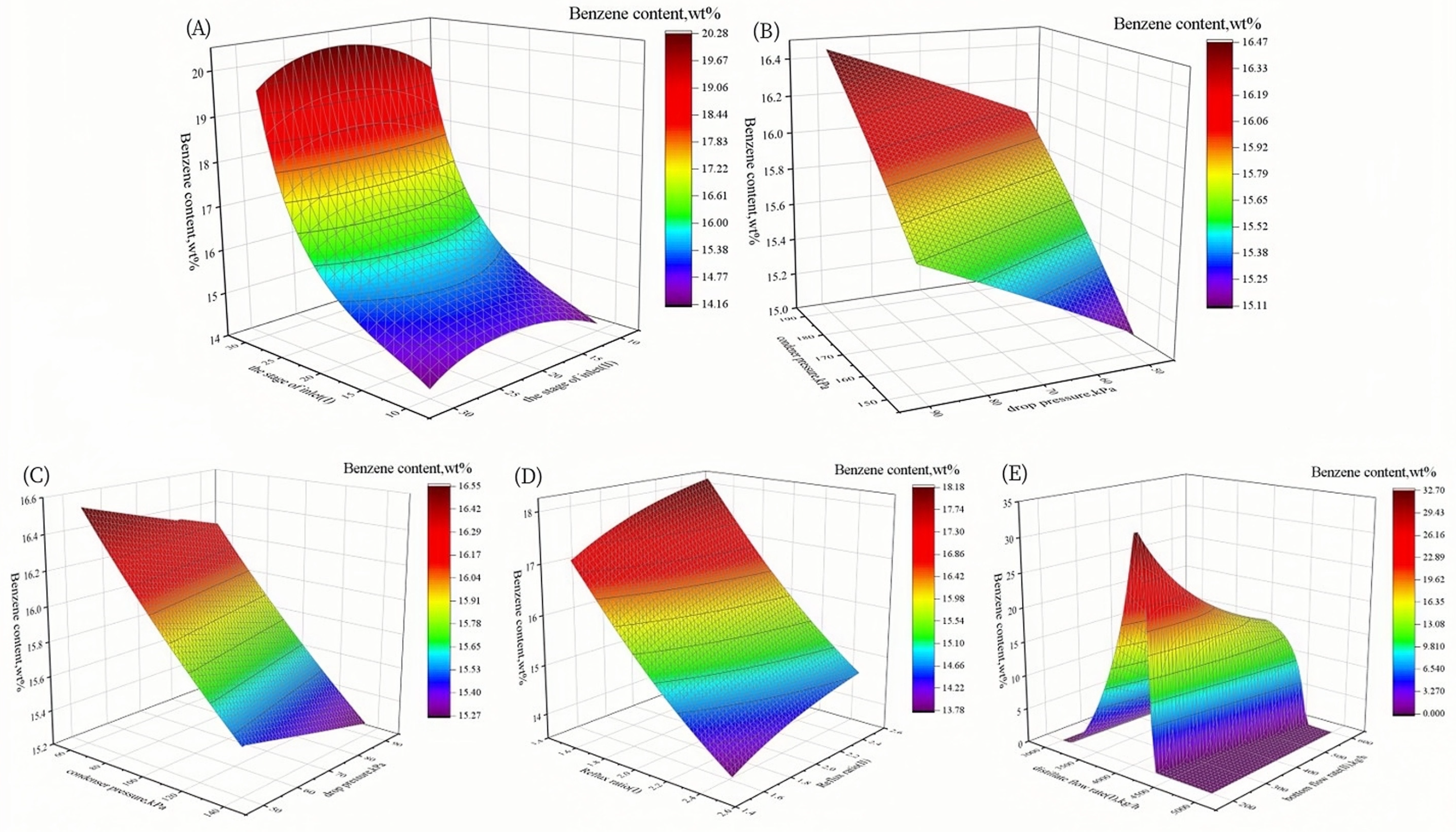
3.1.2. Sensitivity Analysis
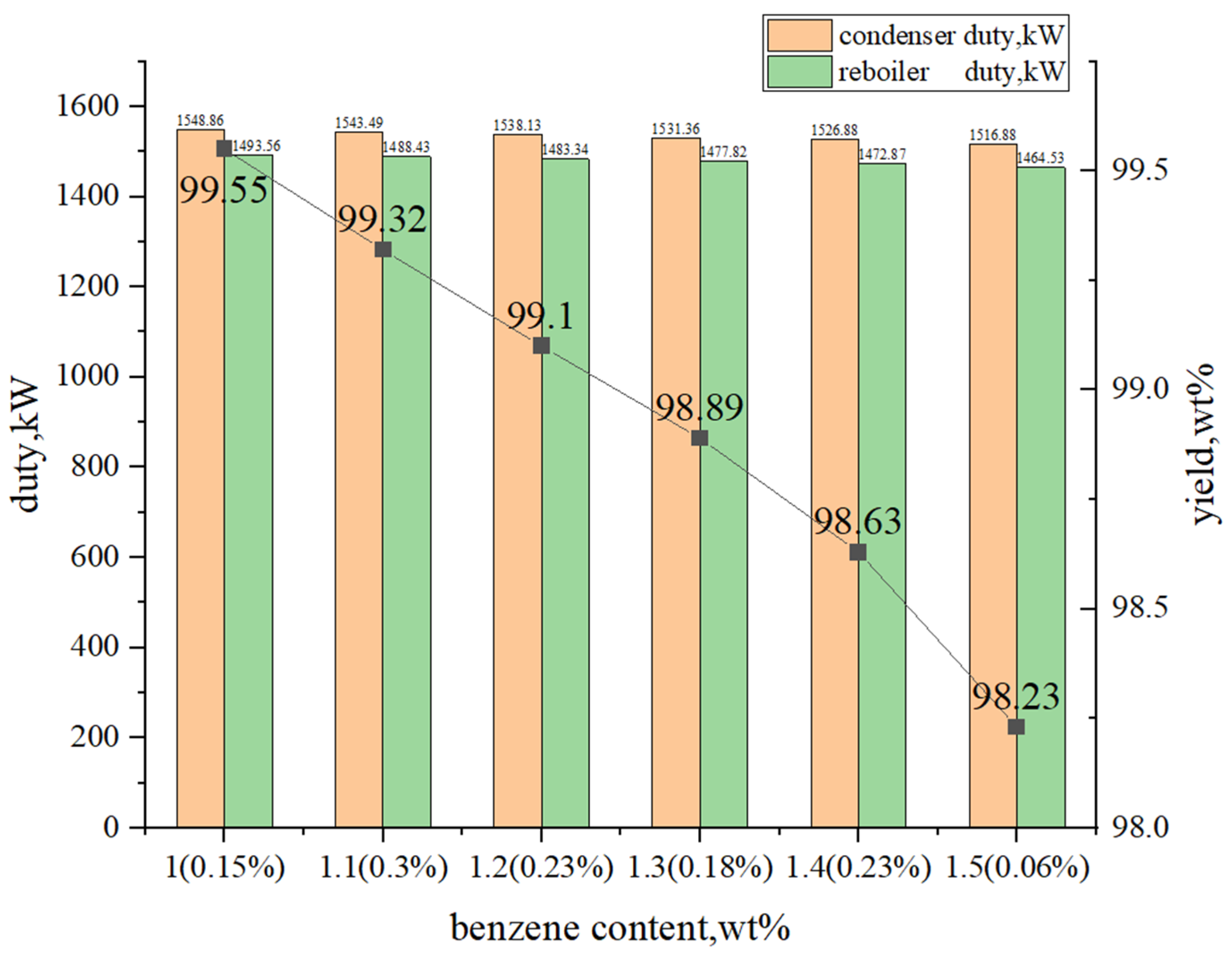
3.1.3. Multi-Objective Optimization Analysis
3.2. Single-Column Distillation Model
3.2.1. Sensitivity Analysis
3.2.2. Multi-Objective Optimization Analysis
3.3. Double-Column Distillation Model
3.3.1. Sensitivity Analysis
3.3.2. Multi-Objective Optimization Analysis
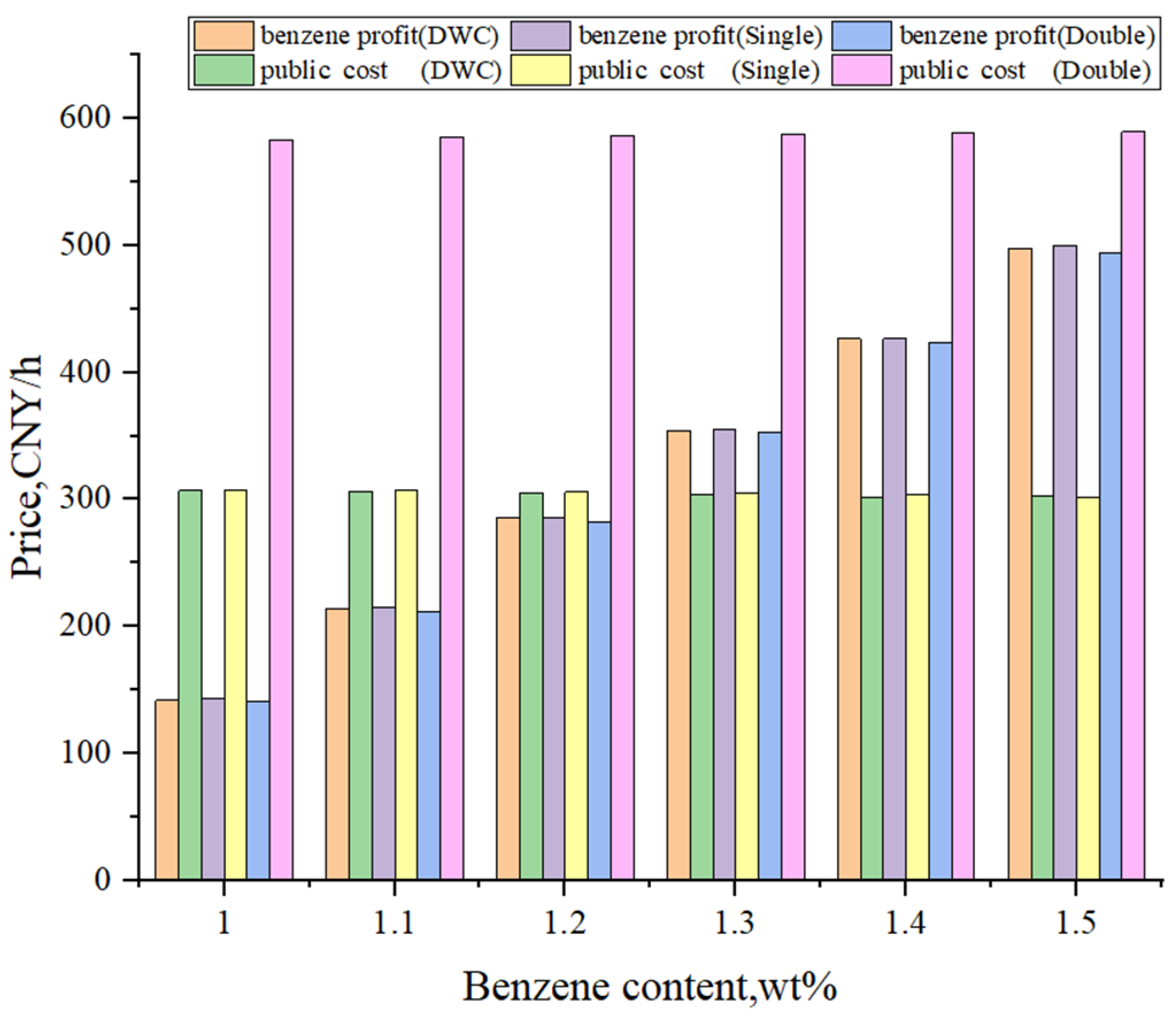
4. Comprehensive Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| p | pressure |
| V | mole volume |
| R | gas constant |
| T | absolute temperature |
| a&b | related to the characteristics of the component and can be expressed as a function of critical temperature |
| α (T) | temperature function |
| Tr | reduced temperature |
| ω | acentric factor |
References
- Brelsford, R. US refiners complete MSAT II-compliance projects. Oil Gas J. 2016, 114, 31–32. [Google Scholar]
- DIN EN 228-2013; Automotive Fuels—Unleaded Petrol—Requirements and Test Methods. Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V.: Berlin, Germany, 2013.
- GB 18352.6-2016; Limits and Measurement Methods for Emissions from Light-Duty Vehicles (CHINA 6). Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- GB 18352.5-2013; Limits and Measurement Methods for Emissions from Light-Duty Vehicles (CHINA 5). Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Spurling, R. Reducing Benzene in Gasoline: The National Challenge. In Proceedings of the 2007 NPRA Annual Meeting, San Antonio, TX, USA, 18–20 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Laredo, G.C.; Marroquin, J.O.; Castillo, J.; Perez-Romo, P.; Navarrete-Bolaños, J. Benzene reduction in gasoline by olefin alkylation: Effect of the catalyst on a C6-reformate heart-cut. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 363, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laredo, G.C.; Castillo, J.J.; Navarrete-Bolaños, J.; Perez-Romo, P.; Lagos, F.A. Benzene reduction in gasoline by alkylation with olefins: Comparison of beta and MCM-22 catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 413, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laredo, G.C.; Quintana-Solórzano, R.; Castillo, J.J.; Armendáriz-Herrera, H.; Garcia-Gutierrez, J.L. Benzene reduction in gasoline by alkylation with propylene over MCM-22 zeolite with a different Brønsted/Lewis acidity ratios. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 454, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laredo, G.C.; Castillo, J.; Marroquin, J.O.; Hernandez, F. Benzene reduction in gasoline by alkylation with olefins: Effect of the feedstock on the catalyst deactivation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 363, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laredo, G.C.; Castillo, J.; Armendariz-Herrera, H. Benzene reduction in gasoline by alkylation with olefins: Effect of the experimental conditions on the product selectivity. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 384, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, K. Benzene Reduction at Lowest Capital Cost. In Proceedings of the 2008 NPRA Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–11 March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Brian, J.S. Technology Advancements in Benzene Saturation; NPRA Q & A Technology Forum: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nocca, J.L. Benzene Management in a MSAT 2 Environment. In Proceedings of the 2008 NPRA Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–11 March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Podrebarac, G.G.; Foley, R. Benzene Removal from FCC Naphtha. U.S. Patent US7501549B2, 10 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Duan, A.J.; Xu, C.M.; Zheng, P.; Wang, X.L.; Jiang, G.Y.; Liu, J.; Wei, Y.C. Study on hydrodesulfurization of L/W coexistence zeolite modified by magnesium for FCC gasoline. Energy Fuels 2017, 32, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.L.; Chen, T.; Chen, T.; Li, Z.P.; Li, X.F. CFD analysis of flow field in aromatics extraction unit. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Proceedings of the 2020 4th International Workshop on Advances in Energy Science and Environment Engineering, Hangzhou, China, 10–12 April 2020; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 512, p. 012178. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.J.; Sun, L.N.; Wei, N.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.J. The characteristics and source analysis of VOCs emissions at roadside: Assess the impact of ethanol-gasoline implementation. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 263, 118670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantero, C.A.T.; Zúñiga, R.P.; García, M.M.; Cabral, S.R.; Calixto-Rodriguez, M.; Martínez, J.S.V.; Enriquez, M.G.M.; Estrada, A.J.P.; Torres, G.O.; Sorcia-Vázquez, F.J.; et al. Design and control applied to an extractive distillation column with salt for the production of bioethanol. Processes 2022, 10, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.Y.R.; López, G.L.; Martínez, V.M.A.; Vázquez, F.J.S.; Mendoza, J.A.B.; García, M.M. Parametric study and control of a pressure swing adsorption process to separate the water-ethanol mixture under disturbances. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 236, 116214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.Y.R.; Mendoza, J.A.B.; Torres, G.O.; Vázquez, F.J.S.; Rojas, A.C.; Vidal, A.F.P. Fault-tolerant control implemented to hammerstein–wiener model: Application to Bio-ethanol dehydration. Fuel 2022, 308, 121836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.Y.R.; Ortiz-Torres, G.; García, R.O.D.; Cantero, C.A.T.; Rodriguez, M.C.; Sarmiento-Bustos, E.; Oceguera-Contreras, E.; Hernández, A.A.F.; Cerda, J.C.R.; Molina, Y.A.; et al. Review of the pressure swing adsorption process for the production of biofuels and medical oxygen: Separation and purification technology. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantero, C.A.T.; Lopez, G.L.; Alvarado, V.M.; Jimenez, R.F.E.; Morales, J.Y.R.; Coronado, E.M.S. Control structures evaluation for a salt extractive distillation pilot plant: Application to bio-ethanol dehydration. Energies 2017, 10, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.P. A globally convergent method for nonlinear programming. J. Optim. Theory 1977, 22, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.J.D. A fast algorithm for nonlinearly constrained optimization calculations. Math. Program. 1978, 45, 547–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Peng, J.F.; Zhang, Q.J.; Sun, M.; Mao, H.J.; Min, J. Comprehensive analysis of the pollutant characteristics of gasoline vehicle emissions under different engine, fuel, and test cycles. Energies 2022, 15, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Billa, T.; Zhang, L.Z.; Shi, Q.; Zhao, S.Q.; Klein, M.T.; Xu, C.M. Molecular representation of the petroleum gasoline fraction. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinifar, P.; Shahverdi, H. Prediction of the ASTM and TBP distillation curves and specific gravity distribution curve for fuels and petroleum fluids. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 100, 3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.Y.; Robinson, D.B. A new two-constant equation of state. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1976, 15, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Gao, Y.H.; Xia, S.Q.; Shang, Q.Y.; Ma, P.S. Calculation of the phase equilibrium of CO2–Hydrocarbon binary mixtures by PR-BM EOS and PR EOS. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 2019, 25, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, W.; Liu, S.L.; Li, X.G.; Li, H.; Wang, S.X.; Lu, X.S. Thermodynamics fundamentals and energy efficiency for the separation and high-valued utilization of Fischer–Tropsch heavy oil. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2019, 58, 9118–9126. [Google Scholar]
- Tamayo-Galván, V.E.; Segovia-Hernández, J.G.; Hernández, S.; Hernández, H. Controllability analysis of modified Petlyuk structures. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 86, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laleh, T.M.; Yuan, X.G.; Luo, Y.Q.; Gong, C.; Yu, G.C. Numerical investigation on effect of vapor split ratio to performance and operability for dividing wall column. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 21, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.H. Rigorous design of extended fully thermally coupled distillation columns. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 89, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amminudin, K.A.; Smith, R.; Thong, D.Y.C.; Towler, G.P. Design and optimization of fully thermally coupled distillation columns Part 1: Preliminary design and optimization methodology. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2001, 79, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, S.; Röhm, H.J. Design of complex distillation columns by overall-cost optimization. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2004, 27, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SH/T 5000-2011; The Calculation Method of CO2 Emissions in Petrochemical Production. China Petrochemical Press: Beijing, China, 2011.





| Measured Data | ASTM (D86) | Assay | Simulation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| density | 736.1 kg/m3 | 0% | 30 °C | 15.0 °C |
| vapor pressure | 78.8 kPa | 10% | 48.6 °C | 45.4 °C |
| sulfur content | 647.4 ppm | 50% | 97.5 °C | 96.6 °C |
| chlorine content | 0.5 ppm | 90% | 174.9 °C | 175.0 °C |
| aromatic content | 25.6 wt% | 95% | 187.3 °C | 186.4 °C |
| olefin content | 28.3 wt% | 100% | 200 °C | 197.8 °C |
| Variables | Unit | Range | Step Size | Optimization Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sideline products | kg/hr | [10–300] | 0.01 | 37.68 |
| Condenser pressure | kPa | [60–140] | 0.01 | 60.02 |
| Drop pressure (M) | kPa | [100–180] | 0.01 | 124.91 |
| Top pressure (A) | kPa | [130–150] | 0.01 | 130.00 (lower) |
| Drop pressure (A) | kPa | [70–90] | 0.01 | 70.23 |
| Interconnect (V) | kg/hr | [1500–2500] | 0.01 | 1503.92 |
| Interconnect (L) | kg/hr | [3500–4500] | 0.01 | 4499.85 |
| Distillate products | kg/hr | [2500–4500] | 0.01 | 4016.65 |
| Reflux ratio | - | [1.5–2.5] | 0.01 | 2.5 (upper) |
| Variables | Unit | Range | Step Size | Optimization Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sideline products | kg/hr | [10–300] | 0.01 | 45.42 |
| Condenser pressure | kPa | [60–140] | 0.01 | 60 (lower) |
| Drop pressure | kPa | [100–180] | 0.01 | 100 (lower) |
| Distillate products | kg/hr | [2500–4500] | 0.01 | 4028.06 |
| Reflux ratio | - | [1.5–2.5] | 0.01 | 2.50 (upper) |
| Variables | Unit | Range | Step Size | Optimization Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Condenser pressure (I) | kPa | [150–190] | 0.01 | 150.00 (lower) |
| Drop pressure (I) | kPa | [50–90] | 0.01 | 75.15 |
| Reflux ratio (I) | - | [1.5–2.5] | 0.01 | 2.5 (upper) |
| Distillate products (I) | kg/hr | [3000–5000] | 0.01 | 3936.78 |
| Bottom products (II) | kg/hr | [10–300] | 0.01 | 21.74 |
| Condenser pressure (II) | kPa | [60–140] | 0.01 | 60.00 (lower) |
| Drop pressure (II) | kPa | [50–90] | 0.01 | 50.00 (lower) |
| Reflux ratio (II) | - | [1.5–2.5] | 0.01 | 2.5 (upper) |
| Energy | Price, CNY | Calorific Value | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benzene | 7/kg | - | - |
| Cooling water | 0.26/t | 45.071 MJ/t | 25 °C/35 °C |
| Standard coal | 1.5/kg | 29.271 MJ/kg | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Ke, M.; Song, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, J. Benzene Reduction Process Simulation and Optimization in Catalytic Cracking Gasoline Distillation. Processes 2023, 11, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010151
Wang Z, Ke M, Song Z, Li J, Sun J. Benzene Reduction Process Simulation and Optimization in Catalytic Cracking Gasoline Distillation. Processes. 2023; 11(1):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010151
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zijian, Ming Ke, Zhaozheng Song, Jiahan Li, and Jinru Sun. 2023. "Benzene Reduction Process Simulation and Optimization in Catalytic Cracking Gasoline Distillation" Processes 11, no. 1: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010151
APA StyleWang, Z., Ke, M., Song, Z., Li, J., & Sun, J. (2023). Benzene Reduction Process Simulation and Optimization in Catalytic Cracking Gasoline Distillation. Processes, 11(1), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010151





