Abstract
The deleterious consequences of snake envenomation are due to the extreme protein complexity of snake venoms. Therefore, the identification of their components is crucial for understanding the clinical manifestations of envenomation pathophysiology and for the development of effective antivenoms. In addition, snake venoms are considered as libraries of bioactive molecules that can be used to develop innovative drugs. Numerous separation and analytical techniques are combined to study snake venom composition including chromatographic techniques such as size exclusion and RP-HPLC and electrophoretic techniques. Herein, we present in detail these existing techniques and their applications in snake venom research. In the first part, we discuss the different possible technical combinations that could be used to isolate and purify SV proteins using what is known as bioassay-guided fractionation. In the second part, we describe four different proteomic strategies that could be applied for venomics studies to evaluate whole venom composition, including the mostly used technique: RP-HPLC. Eventually, we show that to date, there is no standard technique used for the separation of all snake venoms. Thus, different combinations might be developed, taking into consideration the main objective of the study, the available resources, and the properties of the target molecules to be isolated.
1. Introduction
Venomous animals are widely spread all over the world. Accordingly, animal–human encounters are frequent in endemic regions, possibly ending up with human envenomation. Animal venoms induce different types of symptoms, leading sometimes to death [1]. Snake venoms (SVs) are the highlights of research owing to their fascinating complexity and their deadly effects [2]. Snakebite envenoming is a global health issue affecting up to 2.7 million people per year. The death toll is estimated to reach 138,000 deaths per year (https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/snakebite-envenoming (accessed on 23 January 2022)). Due to their highly diverse composition, SVs cause a variety of clinical manifestations ranging from local tissue necrosis to systemic cardiovascular and neurologic symptoms. Nowadays, the single efficient treatment for snake envenomation is antivenom. Yet, the development of effective antivenoms is hampered by the complexity and the limited understanding of the composition and biological activities of SVs, among others [3]. In addition to the appropriate development of antivenoms, a detailed characterization of SV components will help in the interpretation of clinical symptoms. It will also pave the way for the discovery of novel biomolecules with therapeutic interest [4]. To date, various drugs originating from SVs have been approved for clinical use. The most prominent drug CaptoprilTM, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It was developed from a bradykinin-potentiating enzyme isolated from Bothrops jararaca venom [5]. AggrastatTM (Echistatin), another medication developed from Echis carinatus SV, is approved for the prevention of thrombotic complications. Reptilase isolated from different venoms of Bothrops species is approved for use during surgery for the prophylaxis and treatment of hemorrhage [6]. Accordingly, the exploration of SV components is of high significance to the medical field [7].
In fact, proteins and peptides constitute 90 to 95% of SV dry weight. They might contain more than 100 proteins mostly belonging to around 8–11 protein families [8]. Consequently, SVs are highly heterogeneous and require robust techniques to separate and identify protein isoforms. Recent advances in protein separation techniques provided means with higher resolution to evaluate these extremely heterogeneous mixtures. The separation of venom components is the first step in the process of venom decomplexation and analysis. It allows the repartition of molecules based on different biological, chemical, and physical properties [9]. Several techniques are currently available, but there is no standard technique used for the separation of SV proteins. Since they are relatively scarce and cannot be wasted to optimize separation techniques, an overview of previously used separation strategies is crucial. Accordingly, we present in this review the most used separation techniques currently available for the analysis of snake venoms. We then detail their implementation and use for different study purposes. In fact, it is the study objective that drives the choice of separation technique to be used. Therefore, we detail at first in this review the combinations of chromatographic techniques that are used to isolate and purify different snake venom proteins. On the other hand, we detail different workflows using different separation techniques for the evaluation of whole snake venom proteomic composition and distribution of SV protein families.
2. Methods Used for Separation of Venom Complex Mixtures
2.1. Chromatographic Techniques
Chromatographic methods are mostly employed for the separation of SVs and are preferred over electrophoretic techniques since they provide better resolution [10]. Liquid chromatography (LC) involves the partition of molecules between two phases: a stationary and a mobile phase. Molecules with different biochemical and physical features will interact differently with the stationary phase and thus will be separated from other components of the mixture [11]. Different types of chromatography are currently used for the separation of SVs, namely (i) size exclusion chromatography, (ii) ion-exchange chromatography, (iii) affinity chromatography and (iv) reversed-phase chromatography. A single chromatographic step is usually insufficient to isolate a molecule or reveal composition of the complex SV mixture. Hence, multiple chromatographic steps can be coupled together, which is known as multidimensional chromatography. Additionally, LC might be coupled with electrophoretic techniques for an improved protein isolation.
2.1.1. Size Exclusion Chromatography
Size exclusion chromatography (SEC), also known as gel filtration chromatography, intends to separate mixtures of molecules based on their size (Figure 1(Aa)). SEC is a highly versatile technique where multiple factors could be modified to obtain the optimal separation of the target proteins. Numerous column matrices are available that are made of a single type of polymer or a combination of different types. The matrices used most frequently for the separation of SVs include dextran (Sephadex), dextran–polyacrylamide (Sephacryl) and dextran–agarose (Superdex). In addition to the choice of matrix, other column parameters might be modified such as length and inner diameter that are directly related to the column fractionation range and resolution. Thus, if a high-resolution fractionation of molecule is required, then a narrow molecular weight (MW) range column should be used, covering the MW of the molecule. On the other hand, if whole venom fractionation is the objective, then selecting a column covering the molecular weight of all SV proteins is preferable [12]. Notably, SV proteins are distributed over a wide range of molecular weights (1.6–250 kDa); thus, columns with different molecular ranges (ranging from 1.5 to 1500 kDa) are used comprising Sephadex G50, Sephadex G75, Superdex G75, Superdex 200 and Sephacryl S-300. In addition to the choice of a column, the mobile phase selection is of high importance in every chromatographic process. Therefore, in SEC, a mobile phase with good ionic properties should be chosen to (i) minimize any type of interaction between the molecules and the matrix and (ii) to maintain proteins’ stability and activity. The most common eluents used for SV separation include 0.01 to 1 M of ammonium acetate, ammonium bicarbonate and sodium acetate. Sodium chloride can be added to the buffer to improve resolution. Since the separation is based on size only in SEC, the composition of the mobile phase remains constant during the process and is known as an isocratic elution [11]. The slower the flow, the better the resolution of compounds; however, the time required for separation will significantly increase. Thus, a balance between the separation time and resolution should be made to choose a convenient flow rate between 0.1 and 1 mL/min [12]. The protein elution is typically monitored using an UV detector at 280 nm. SEC has been extensively used in SV separation, usually as a first step, for the separation of large proteins from small peptides and toxins, allowing an improved analysis of each component. Accordingly, a Superdex 200 SEC was used as a first step in the process of purification of a trimeric phospholipase A2 from Oxyuranus scutellatus snake venom. The protein of interest was around 45 kDa, and thus, the fraction containing molecules of 45 kDa was collected and further fractionated to obtain a pure molecule [13]. Likewise, a snake venom serine proteinase was isolated from Vipera ammodytes ammodyets venom using Sephacryl S-200 SEC as a first chromatographic step. Further fractionation of the peak of interest yielded 11 fractions, demonstrating the low resolution of SEC [14]. Consequently, SEC is valuable for the partition of snake venom proteins by size groups; however, it must be followed by other separation techniques, since it has an inherently low resolution and is incapable alone of isolating a single molecule from the mixture. SEC might also be used with standards to measure the MW of each fraction eluted [15].
2.1.2. Ion Exchange Chromatography
Ion exchange chromatography (IEX) is a separation technique based on the net surface charge of molecules to be separated (Figure 1(Ab)). When opting for IEX as a separation technique, multiple parameters can be optimized to match the target of the separation [16]. Accordingly, choosing a convenient stationary phase is critical for effective separation. Different types of resins can be used including cellulose, agarose, polyacrylamide, and dextran. The most used strong and weak cation columns in SV separation are sulfonic acid (SP) and carboxymethyl (CM) columns, respectively, while the most used strong anion and weak anion exchangers are quaternary amine (Q) and diethylaminoethanol (DEAE), respectively. For SV separation, the most common salts used are Tris-HCl, sodium chloride or ammonium bicarbonate. They are used for the elution of molecules mostly as linear gradients since they provide a better resolution; however, step gradient might also be used [16]. In principle, proteins constituting SVs occupy a wide pH range, and thus, both weak and strong exchangers might be used. Similarly, both cationic and anionic exchangers might be used depending on the type of protein to be isolated. If the target protein is stable at pH below its pI value (when it is positively charged), then a cation-exchange chromatography (CEX) is preferable. CEX is used at a pH lower than the pI of molecules to isolate them from the mixture, and therefore, they are used under slightly acidic mobile phase conditions with pH ranging from 5.5 to 7 [16]. Under such conditions, CEX was used to isolate three hyaluronidases from the venom of Cerastes. In this study, CM-sepharose CEX was used to separate fractions previously generated by SEC. IEX provided a high resolution and an improved separation of venom components, since three different hyaluronidases were effectively purified to homogeneity using this chromatographic technique [17]. Similarly, a Mono S CEX column was used to further separate fractions generated by the SEC of Vipera ammodytes venom. The peak of interest was homogeneous, showing one band on SDS-PAGE and proving the high resolution of CEX as a second step of the purification process [14]. On the other hand, an SV metalloproteinase was isolated using CEX as a first step, which required a supplementary purification step to reach the pure protein [18]. In contrast, if the target protein is more stable at pH above its pI (when it is negatively charged), then an anion-exchange chromatography (AEX) is preferable. AEX is usually used with buffer pH ranging from 7 to 8.2. AEX was used as a second chromatographic step for the purification of a metalloproteinase and L-amino acid oxidase from Bothrops atrox and Bothrops mojeni. To do so, fractions eluted from SEC were re-fractionated on a Mono Q column to reach the pure protein [19]. In another study, a DEAE-Sephacel AEX column was used as a first step to separate metalloproteinase from Bothrops moojeni and required two successive chromatographic techniques to reach the pure protein [20]. In SV separation, IEX is widely used in both facets, knowing that SV proteins have a wide distribution across pH. In several research studies, IEX was used as a first step to separate the crude SV before evaluating its components. Mostly, it is used as a more specific intermediate step to separate a fraction originating from a previous chromatographic step.
2.1.3. Reversed-Phase High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography
Reversed-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) is a high-resolution separation technique used for the partitioning of molecules with different polarities (Figure 1(Ac)). Due to its high resolution, RP-HPLC is used in almost every SV separation, since it provides a fair separation of protein isoforms that are very abundant in these mixtures [21]. Numerous columns are developed and are commercially available constituting of hydrophobic alkyl groups usually attached to silica beads. The most common columns are the butylsilane (C4), octylsilane (C8), and octadecylsilane (C18), which are made of 4-, 8- or 18-carbon chains, respectively. These columns differ in their hydrophobicity: the longer the carbon chain, the more hydrophobic the column, and therefore the stronger the interaction with the sample, causing an increased retention and better separation. Consequently, C18 is the most employed column for the separation of complex mixtures such as SVs [22]. The use of C4 and C8 columns has also been noted in SV separation. Molecules bound with different strengths to the matrix are then eluted using organic solvents such as propanol, methanol and acetonitrile [23]. The latter is the most used for SV separation. The application of a gradient organic solvent allows the elution of molecules in order of increasing hydrophobicity, and the gradients used could be linear or step gradients, depending on the features of the molecules to be isolated. RP-HPLC is very versatile and can be employed for several objectives. This technique was thoroughly used for the isolation and purification of SV molecules. For this purpose, RP-HPLC is usually coupled with other separation techniques and used as the last step for better purification. C18-based RP-HPLC was used to isolate a CRiSP from Crotalus oreganus helleri venom. Crude venom was fractionated in 27 fractions with F7 having molecules of 25 KDa (MW range of CRiSP family) and thus was further chromatographed using CEX. The chromatographic profile showed one major peak that was identified as CRiSP and a minor peak demonstrating the high resolution of C18 columns [24]. A C4 column was used as a last step to purify a metalloproteinase from Bothrops pauloensis venom after IEX and SEC. C4 fractionation resulted in a highly pure protein [15]. C4 was also used for the analysis of Peruvian pit vipers’ whole venom. The SDS-PAGE of resulting fractions was extremely heterogeneous, indicating the need for another separation technique [25]. Another usage of RP-HPLC is to confirm the purity of isolated proteins. Accordingly, the purity of hyaluronidase isolated from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom using three successive chromatographic steps (CEX, SEC and hydrophobic chromatography) was confirmed using a C18 column showing a single peak on chromatogram [26]. RP-HPLC might also be used for the analysis of whole SV composition or the comparison of SVs variability [27,28]. Most importantly, RP-HPLC is the most compatible chromatographic method to be used for the downstream identification of SV proteins with mass spectrometry.
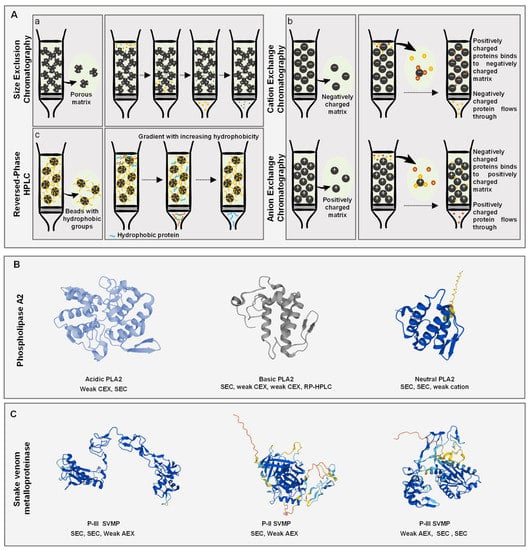
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic representation of the following chromatographic techniques. (Aa) Porous matrix of size exclusion chromatography (i.e., dextran, dextran–agarose, or dextran–polyacrylamide) and the separation process using an isocratic elution buffer (i.e., 0.01 to 0.1 M of ammonium acetate, ammonium bicarbonate or sodium acetate). (Ab) Anion-exchange chromatography (AEX) positively charged matrix (i.e., quaternary amine or diethylaminoethanol) and cation-exchange chromatography (CEX), negatively charged matrix (i.e., sulfonic acid or carboxymethyl) and their corresponding separation process using linear or stepwise elution gradients (i.e., sodium chloride or ammonium bicarbonate can be used as elution buffers). (Ac) Hydrophobic matrix of reversed-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography (i.e., silica matrix beads with varied length alkyl groups and the separation process in RP-HPLC using linear or stepwise gradients of acetonitrile. (B) Examples of three phospholipase A2 (acidic, basic, and neutral PLA2) isolated using the aforementioned chromatographic techniques. From the left to the right an acidic PLA2 from Daboia siamensis [29], a basic PLA2 from Protobothrops flavoviridis [30] and a neutral PLA2 from Naja naja sputatrix [31] (C) Snake venom metalloproteinases (PIII and PII SVMP) isolated using the aforementioned chromatographic techniques. From the left to the right a PIII SVMP from Bothrops leucurus [32], a PII SVMP from Gloydius brevicaudus [33], and a PIII SVMP from Trimeresurus gramineus [34]. ((B): acidic PLA2 UniProt: P31100, basic PLA2 UniProt: P0DJJ9, neutral PLA2 UniProt: Q92084; (C) PIII SVMP UniProt: P86092, PII SVMP UniProt: Q9YI19, PIII SVMP Uniprot: P0C6E8).
2.1.4. Affinity Chromatography
Affinity chromatography is a separation technique used to isolate a specific molecule or group of similar molecules from a complex mixture (Figure 2). This type of chromatography is considerably deployed for the separation and purification of a variety of SV proteins, since it provides a less costly and less time-consuming method [35]. Several molecules have been developed and customized as substrates to bind specific SV proteins from the crude mixture. For instance, an SV metalloproteinase having a strong interaction with ssp-3 protein was isolated by immobilizing ssp-3 on a matrix [36]. The substrate of PLA2 enzyme was synthesized and immobilized on an affinity column for the purification of the protein from Crotalus durissus venom [37]. Likewise, PLA2 was isolated from Bothrops jararaca venom using immunoaffinity chromatography. For this process, an anti-crotoxin IgG, with high affinity to PLA2, was developed and immobilized on Sepharose polymer, allowing the purification of the protein [38]. Alternatively, commercially available affinity columns can be used along with other chromatographic steps to separate a specific group of proteins. Since these columns are not specific to a single molecule, a series of chromatographic steps are used to reach protein purity. Three types of columns are commonly used for the separation of SVs bearing lactose, heparin and benzamidine substrates. Columns with immobilized lactose were used to isolate C-type lectins from Bothrops atrox and Cerastes cerastes venoms, resulting in a highly pure protein [39,40]. Similarly, these columns can be used to generate a lectin-free sample to further isolate molecules from the eluate [41]. Heparin columns are used to isolate coagulation factors having affinity for heparin, while benzamidine columns are preferably used to isolate serine proteases. For example, a heparin affinity column was used to isolate a metalloproteinase from Bothrops moojeni venom after two chromatographic steps: IEX and SEC [20]. On the other hand, serine protease was isolated from Bothrops pirajai venom using benzamidine columns along with size exclusion and reverse phase chromatography [42]. Other serine proteinases were isolated from Bothrops atrox and Bothrops brazili venoms using SEC and benzamidine affinity chromatography [43]. To elute molecules from affinity columns, different types of buffers can be used such as decreasing the pH step gradient, salt gradient or introduction of a competitor molecule for the binding sites. Affinity chromatography requires in some cases the use of strongly acidic buffers (pH = 2.5) to disrupt interactions between the molecule and the stationary phase. This might interfere with the protein structure and function; thus, appropriate buffers should be selected depending on the objective of the separation. Another limitation to be aware of is the non-specific binding of proteins that would contaminate the eluted protein [35].
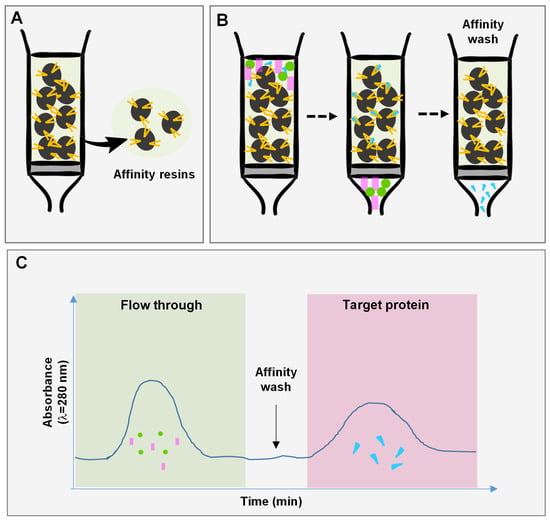
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of affinity chromatography. (A) The affinity resins (i.e., agarose) that binds the molecule of interest and (B) the separation process, which includes an equilibration step (using Tris-HCl or sodium acetate) followed by the elution (using Tris-HCL/Glycine-HCl, PBS). (C) A typical chromatogram of affinity chromatography with the first flow through containing only molecules with no affinity to the matrix, which is followed by affinity wash to disrupt the interaction between the matrix and the target protein and elute the latter.
2.2. Electrophoretic Techniques
The high versatility, feasibility, and practicality of chromatographic techniques outweighed those of electrophoretic techniques; nevertheless, the latter remain an important means for the separation of a variety of venoms (Table 1). For SVs, electrophoretic techniques are used rigorously for the separation and identification of protein content of whole venom and fractions. Even though electrophoretic methods have several limitations, their use is integral in the process of SV analysis. Two major types of electrophoretic methods are currently used: one-dimensional gel electrophoresis and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis.

Table 1.
The advantages and disadvantages of different separation techniques used for snake venom analysis.
2.2.1. One-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis (1-DGE)
SDS-PAGE is considerably used in the process of SV separation for distinct objectives, including proteomic analysis. In fact, SVs are separated by SDS-PAGE followed by in-gel protein digestion and mass spectrometry for protein identification [44]. A chromatography step might also be added before gel separation to improve resolution and enhance protein coverage [14]. For example, HPLC fractions of Crotalus durissus crude venom were separated using SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions; bands were excised, digested, and subjected to mass spectrometry for protein identification [45]. In addition to proteomic analysis, SDS-PAGE is frequently used during the multidimensional chromatography of SVs. It is useful as an intermediate step to determine the protein content of each fraction and the target fractions to be further separated. It might be used after an initial chromatographic step to evaluate the distribution of proteins [46], as it might be used as the last step to confirm the purity and molecular weight of the isolated protein. An example is the use of SDS-PAGE to analyze a fraction from RP-HPLC, which showed a single band with a molecular weight corresponding to PLA2, indicating the purity of the isolated molecule [47]. However, mass spectrometry (MS) identification of the molecular weight remains more accurate. SDS-PAGE might be used to unravel the intra- and inter-protein interactions. A reducing agent is added to the sample to reduce disulfide bonds and allow each protein subunit to migrate independently in the gel [48]. The process can therefore be conducted under both reducing and non-reducing conditions to compare protein migration under different conditions [49].
2.2.2. Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis (2-DGE)
This technique is also significantly used in SV analysis for several purposes. In general, 2-DGE is useful to unravel the overall distribution pattern of venom proteins and obtain information regarding their pI and MW distribution [50]. It is fairly used for the identification of protein families constituting the venom. It was therefore used to perform the proteomic characterization of several SVs such as coral snake Micrurus pyrrhocryptus [51], Macrovipera lebetina obtusa [52], and Bothrops insularis [53]. The procedure used to analyze these venoms involves the excision of proteins spots from the gel, trypsin digestion followed by mass spectrometry analysis for protein identification. Additionally, 2-DGE could be used coupled with other chromatographic steps to isolate proteins from SV mixtures. 2-DGE was used after affinity chromatography to evaluate the flow through of the column for separation of several SVs [54]. PLA2 was isolated from Bothrops mattogrossensis venom using two chromatographic steps; then, 2-DGE was performed to determine the MW (13.55 kDa) and pI (9.5) of the isolated molecule [55] Moreover, 2-DGE could be used for the comparison of SV proteomes. Venoms of same species could be compared for snakes living under different conditions; otherwise, venoms from different species could be compared to obtain a better understanding of the similarities and differences among species. For example, Wongtay et al. used 2-DGE to evaluate the differences in SV composition of three different Ophiophagus hannah snakes originating from different locations in Thailand. Results showed differences in protein migration in the gels and in protein spot identification [56]. Lastly, 2-DGE plays an important role in identifying the selectivity of antivenoms, since proteins from the gel could be transferred onto a membrane for immunoblotting analysis using antivenoms. This technique was used to identify the reactivity of a polyclonal antivenom against proteins of Egyptian cobras and indicated a weak immunoreactivity toward low molecular weight proteins, suggesting the need for the further development of more specialized antivenoms for these species [57].
Table 1 summarizes the main advantages and disadvantages of chromatographic and electrophoretic techniques used in SV analysis.
3. Implementation of Separation Methods for SVs
In the following part, we will detail the implementation of separation strategies used for SV analysis. Appropriately, different separation techniques are used to meet the objectives of the study that could be to (i) isolate and purify a single component or to (ii) analyze whole venom proteome.
3.1. Bioassay-Guided Fractionation
It uses biological assays to perform a fractionation aiming to isolate a specific molecule. During the process, a complex mixture is separated typically by chromatographic techniques, and each fraction is tested separately for a specific biological feature. The fractions of interest are then re-fractionated until a pure protein is recovered (Figure 3) [58]. The choice of the assay to be used is directly related to the molecule to be isolated. For SVs, numerous bioassays are currently used for different specific components. In fact, SVs induce a wide spectrum of effects once injected in prey, since they target several organ systems: namely, the nervous and the cardiovascular systems [59]. Different bioassays are developed for the isolation of cardiotoxic and neurotoxic components. Since SV cardiotoxic components are known to have effects on the cardiac muscle or vascular smooth muscle [59], several bioassays might be used for the isolation of cardiotoxic components. Firstly, Langendorff model heart preparations could be used to screen for cardiotoxic molecules. For example, this model was used to screen for the cardiotoxic component of Vipera ammodytes venom. First, the venom was fractionated using SEC and generated four fractions with fraction C having the highest cardiotoxicity. The subfraction C1 induced an irreversible cardiac arrest of the isolated heart, while subfraction C2 induced an irreversible significant decrease in heart rate without inducing cardiac arrest. Consequently, both fractions were re-fractionated using an RP-HPLC C4 column, and Ammodytin L (AtnL) was identified as the major protein inducing cardiotoxicity [60]. Another robust biological model to analyze cardiotoxicity could be the zebrafish model. This model is used to monitor atrial and ventricular rates, blood flow and clot formation. Recently, we took advantage of zebrafish embryos transparency to assess the direct cardiotoxicity of SV [61]. In addition, the zebrafish model was used to isolate the cardiotoxic molecule from Lachesis muta venom. First, crude venom was fractionated using SEC; then, the active fractions were fractionated using AEX, and fraction 8 with the highest cardiotoxicity was further purified using an RP-HPLC C18 column, generating a pure protein “mutacytin-1” [62]. Moreover, isolated rat mesenteric arteries might also be used to evaluate the vasorelaxant effect of fractions. This technique was used to isolate the vasorelaxant molecule in Bothrops leucurus venom. Crude venom was fractionated with CEX followed by RP-HPLC for the vasorelaxant fraction. After MS analysis, the molecule inducing vasorelaxation turned to be a PLA2 [63]. On the other hand, several neurotoxic components have been isolated and identified from SVs by the means of bioassay-guided fractionation. One of the most common neurotoxic assays used is the chick biventer cervicis nerve-muscle preparation. Neurotoxic components usually induce an inhibition of indirect twitches, leading to a decrease in muscle contraction in a concentration-dependent manner. This assay was used in tandem with SEC to isolate hostoxin-1 from Hoplocephalus stephensi [64], rufoxin from Rhamphiophis oxyrhynchus [65], and SPAN from Austrelaps species [66]. Another method to test neurotoxicity is the evaluation of neurotoxic effects on the sciatic nerve. The neurotoxic component of the venom of Daboia russelii was identified using this bioassay. The venom was fractionated by SEC and fraction 13 induced neurotoxic symptoms, such as respiratory distress, hind limb paralysis, lacrimation, convulsions, and profuse urination. This fraction was further purified using RP-HPLC, and the isolated protein was shown to inhibit indirectly stimulated twitches of sciatic nerve–muscle preparations [67]. Of note, SDS-PAGE is very useful in bioassay-guided fractionation, since it can indicate the protein content of each fraction eluted and the purity of the isolated protein [61]. Different combinations of separation techniques have been used for the isolation of novel SV molecules that upon biological characterization implicate the clinical outcome of the toxins or their potential use for drug development. Table 2 summarizes the most recent techniques used for the purification of the most common SV protein families.
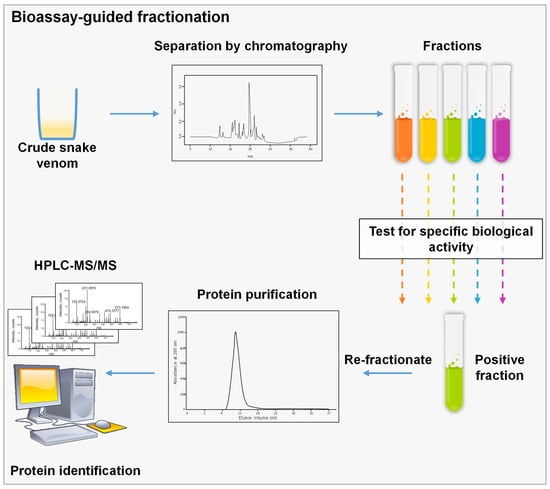
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of bioassay-guided fractionation, crude venom is separated using a chromatographic technique; then, fractions are assessed using a specified biological assay to choose the corresponding fraction. This step could be repeated several times until we reach a single peak or a pure molecule that could be identified by MS.

Table 2.
Different separation strategies used most recently to isolate the most abundant SV protein families. Da: Dalton, ND: Not Determined, a MW determined by SDS-PAGE, b MW determined by MS.
3.2. Whole Proteome Characterization and Identification
The currently available separation and analytical techniques allowed researchers to isolate and identify the most abundant constituents of the venoms. However, given the complexity of SVs, numerous molecules remain unexplored. More recently, the fundamental analysis of complex SV proteomes was made less challenging owing to the evolution of proteomics field. Accordingly, several proteomic techniques have been adapted, providing a rapid and relatively inexpensive method for the decomplexation of venom mixtures [96,97,98]. Both proteomic approaches, bottom–up (BU) and top–down (TD), might be used to analyze SVs composition. The latter has not been used in snake venomics until recently, since it is still in the course of progression [98,99]. On the other hand, bottom–up proteomics is more frequently used and typically involves the identification of trypsin-digested proteins by tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) after separation by both chromatographic and/or electrophoretic techniques. Multiple workflows are used for the BU proteomic analysis of SVs (Figure 4).
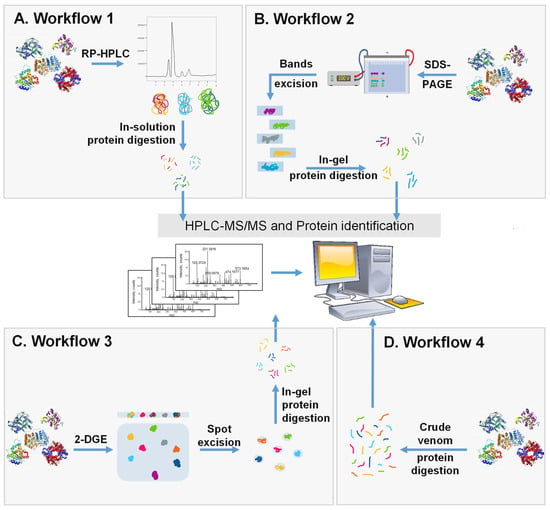
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of the 4 major workflows used for whole venom separation and proteome identification. (A) Crude SV is separated with RP-HPLC followed by in-solution trypsin digestion and the identification of components by LC-MS/MS. (B) Crude SV is separated by SDS-PAGE and protein bands are cut, digested, and analyzed using LC-MS/MS. (C) Crude venom is separated using 2-DGE followed by protein spot excision, in-gel digestion, and then protein identification by LC-MS/MS. (D) Crude venom is directly digested into peptides and analyzed using LC-MS/MS.
The first workflow (Figure 4A) involves the separation of venom mixture with RP-HPLC using a stepwise or linear acetonitrile gradient. This step is followed by an in-solution trypsin digestion of fractions and LC-MS/MS. Prior to digestion, collected fractions can be tested using SDS-PAGE to evaluate the distribution of proteins in each fraction regarding the MW and number of protein bands. This technique was extensively used in the venomics field to reveal the proteomic composition of SVs such as Bungarus sindanus, Calliophis intestinalis, Deinagkistrodon acutus, Trimeresurus wiroti, Trimeresurus puniceus, and Hydrophis curtus [100,101,102,103,104,105]. This technique was also used in several studies to compare the variability between different SVs [106].
The second workflow (Figure 4B) involves the use of a electrophoretic separation. In this approach, crude venom is separated by SDS-PAGE, and protein bands are visualized using Coomassie Blue or silver stain. Later, the protein bands are cut, digested, and then analyzed by LC-MS/MS. An RP-HPLC step might be added before the gel separation to increase the resolution of the workflow. This approach was considerably used in venomics for distinct SVs. For example, it was used to characterize and compare venoms of Trimeresurus macrops and Trimeresurus hageni and led to the identification of 187 and 216 proteins, respectively [107].
In the third workflow (Figure 4C), 2-DGE is first performed and followed by the in-gel digestion of all protein spots that are then analyzed by LC-MS/MS. The strategy was shown to be effective for the separation and identification of several SV proteomes [108,109]. As with every technique, 2-DGE has its own advantages and disadvantages. In fact, it provides the advantage of high molecular weight proteins recovery; however, it is sometimes hard to distinguish protein spots due to inaccurate separation and spot trains [110]. In addition, if protein quantity is insufficient in protein spots, then further analysis might not be performed [111]. This technique has been used to analyze several snake proteomes such as Gloydius intermedius, Agkistrodon contortrix and Naja asehi [108,109,110]. A study comparing different workflows indicated that the in-gel digestion of proteins provides a lower resolution compared with direct in-solution digestion [112]. However, after HPLC, in-gel protein digestion provides higher resolution compared to in-solution protein digestion [113]. These findings show that the choice of the method should be related to the properties of the proteins present in the mixture and to the overall workflow adopted for the analysis.
The fourth workflow (Figure 4D) is known as shotgun analysis. This technique involves the tryptic digestion of crude venom proteins. Ultimately, the resulting peptides are separated by RP-HPLC using a C18 column followed by MS to identify proteins. Shotgun analysis has numerous advantages over other techniques, since it does not require a decomplexation process at the beginning that is time consuming and, in some cases, expensive. This strategy allows the recovery of low abundant proteins, since they may be lost during the separation step performed in other techniques [114]. This is reflected with a relatively high number of protein hits compared to other techniques. For example, the analysis of Vipera ammodytes ammodytes venom with the shotgun technique identified 99 proteins that is folds higher than other workflows used to analyze this SV [115]. This technique was also used for the analysis of Deinagkistrodon acutus venom and led to the identification of 84 proteins [116]. Despite the numerous advantages, some limitations have been reported such as the challenging identification of low molecular weight protein [115]. One way to overcome this limitation is to employ a combinatorial peptide ligand library and membrane filtration to recuperate low MW proteins [117]. This allows concentrating low-abundance proteins in the mixture, leading to a better protein coverage by shotgun analysis. The analysis of Naja ashei venom by Hus et al. indicated that the shotgun technique uncovers proteins that are not identified by other techniques such as 2-DGE, in which 19 proteins were identified compared to 39 proteins identified with shotgun. In this study, the authors indicate that a decomplexation step, although being time and labor consuming, provides higher coverage of proteins [110]. In another study, Bothrops leucurus venom yielded 137 proteins hits for shotgun analysis compared to 62 proteins identified using the first workflow [114].
Ultimately, even with the great advancement in the proteomic field, there is still no standard technique for SV analysis. Rather, a combination of several techniques could be used depending on the available resources and objectives of the study. This has been shown to provide a better coverage of the proteomes, since each technique might identify different sets of proteins. Proteomes of Naja mossambica and Naja naja nigricincta were analyzed using three different approaches, and the merged data identified 75 and 73 proteins, respectively, which was higher than the proteins identified by each approach alone [106]. Similarly, Naja naja nigricincta and Bungarus caeruleus venoms were analyzed by three different approaches simultaneously, using the second and fourth workflows, identifying a total of 81 and 46 proteins, respectively, for each SV [118].
To date, the literature available on snake venomics indicates undoubtedly that bottom–up proteomics is the strategy of choice for venom proteomes analysis. Yet, the use of such a strategy for the analysis of complex mixtures such as SVs is particularly challenging. This is due, in general, to the protein digestion step required prior to MS analysis. TD analysis provides an alternative to solve this problem, since intact proteins might be analyzed directly [119]. TD was not used in the field of venomics until a few years ago, and its use is limited, since it requires very sophisticated and costly instrumentation. As with any other type of analysis, TD requires the separation of complex protein mixtures prior to MS. Therefore, RP-HPLC constitutes the best method for separation, since it is compatible with the top–down downstream analysis [120]. However, other separation methods might be used as well [121]. A multidimensional separation seems to provide the best resolution, and it includes the use of gel-based separations followed by RP-HPLC [121]. TD proteomics was used successfully for the analysis of several SV proteomes including Dendroaspis jamesoni, Dendroaspis kaimosae, Dendroaspis viridis, and Ophiophagus hannah venoms [122,123]. In addition to being costly, TD analysis has other limitations, including its inconvenience for the identification of high molecular weight proteins that are an abundant constituent of viperid snakes [119,121]. Thus, to overcome the limitations of both strategies, an integration of TD and BU proteomics is currently employed and is designated as ‘middle–down proteomics’. This approach was used for the analysis of Echis carinatus sochureki, Protobothrops flavoviridis, and Vipera anatolica senliki venoms and proved to be the most effective compared to each method alone [124,125]. In Table 3, we summarize the different workflows and strategies detailed previously with corresponding examples of analyzed SVs and consequent findings.

Table 3.
Different workflows and strategies used in SV proteomic analysis, applications, and consequent findings. Da: Dalton.
4. Conclusions
Protein separation techniques are the basis on which proteomics analysis rely; thus, the choice of the convenient method is critical to reach the desired goal. Even with the scientific advancement, there is still no standard technique to be employed for the separation of SVs. Therefore, separation and analytical methods should be carefully chosen based on the objectives of research and the available resources. Clearly, snake venomics is of interest not only for fundamental research but also for the therapeutic field. It is true that venoms are toxic; however, they were shown to be an invaluable library for the development of pharmaceuticals. Thus, SV separation techniques play a pivotal role in the isolation and purification of biologically active molecules that could be used as model to develop drugs specifically to treat cardiovascular and neurological diseases. Another important field of venom studies is anti-venomics. Multiple whole proteome analysis techniques might be used including 2-DGE, immunoaffinity chromatography and RP-HPLC to assess the immune reactivity of the antivenom to each component of the venom and to evaluate cross-reactivity with other species, altogether aiming to improve the specificity of antivenoms and reduce snakebite-related complications and mortalities [96].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.F.; validation, M.R., Z.F., C.M., J.-M.S. and C.L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.S.; writing—review and editing, M.R., C.M., Z.F. and C.L.; visualization, M.R. and C.S.; supervision, Z.F., C.M. and C.L.; project administration, Z.F. and C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the PHC CEDRE (46541TH) and the French MENESR. C.S is recipient of doctoral fellowship award from the Lebanese University in cooperation with the federation of Zgharta casa municipalities and also recipient of the Eiffel scholarship from Campus France.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Charbel Mouawad and Jacinthe Frangieh for the helpful discussion.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Utkin, Y.N. Animal Venom Studies: Current Benefits and Future Developments. World J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 6, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite Envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, M.K.; Fung, S.Y.; Tan, K.Y.; Tan, N.H. Proteomic Characterization of Venom of the Medically Important Southeast Asian Naja Sumatrana (Equatorial Spitting Cobra). Acta Trop. 2014, 133, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed Abd El-Aziz, T.; Soares, A.G.; Stockand, J.D. Snake Venoms in Drug Discovery: Valuable Therapeutic Tools for Life Saving. Toxins 2019, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kini, R.M.; Koh, C.Y. Snake Venom Three-Finger Toxins and Their Potential in Drug Development Targeting Cardiovascular Diseases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 181, 114105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomback, B.; Blomback, M.; Nilsson, I.M. Coagulation Studies on Reptilase, an Extract of the Venom from Bothrops Jararaca. Thromb. Diath. Haemorrh. 1958, 1, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangieh, J.; Rima, M.; Fajloun, Z.; Henrion, D.; Sabatier, J.M.; Legros, C.; Mattei, C. Snake Venom Components: Tools and Cures to Target Cardiovascular Diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, H.; Moin, S.F.; Choudhary, M.I. Snake Venom: From Deadly Toxins to Life-Saving Therapeutics. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1874–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.S.; Cheung, R.C.F.; Xia, L.; Wong, J.H.; Ng, T.B.; Chan, W.Y. Snake Venom Toxins: Toxicity and Medicinal Applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6165–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.; Tan, K.Y.; Tan, N.H. A Protein Decomplexation Strategy in Snake Venom Proteomics. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1871, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, I.M. High Performance Liquid Chromatography: Principles and Clinical Applications. BMJ 1989, 299, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ó’Fágáin, C.; Cummins, P.M.; O’Connor, B.F. Gel-Filtration Chromatography. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1485, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cendron, L.; Mičetić, I.; Polverino de Laureto, P.; Paoli, M. Structural Analysis of Trimeric Phospholipase A2 Neurotoxin from the Australian Taipan Snake Venom. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 3121–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latinović, Z.; Leonardi, A.; Koh, C.Y.; Kini, R.M.; Trampuš Bakija, A.; Pungerčar, J.; Križaj, I. The Procoagulant Snake Venom Serine Protease Potentially Having a Dual, Blood Coagulation Factor V and X-Activating Activity. Toxins 2020, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naves de Souza, D.L.; Gomes, M.S.; Ferreira, F.B.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Achê, D.C.; Richardson, M.; Borges, M.H.; Rodrigues, V.M. Biochemical and Enzymatic Characterization of BpMP-I, a Fibrinogenolytic Metalloproteinase Isolated from Bothropoides pauloensis Snake Venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 161, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, S.; Beck, A.; Veuthey, J.L.; Guillarme, D. Ion-Exchange Chromatography for the Characterization of Biopharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 113, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahby, A.F.; Mahdy, E.-S.; El-Mezayen, H.A.; Salama, W.H.; Abdel-Aty, A.M.; Fahmy, A.S. Egyptian Horned Viper Cerastes cerastes Venom Hyaluronidase: Purification, Partial Characterization and Evidence for Its Action as a Spreading Factor. Toxicon 2012, 60, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, G.H.M.; Borges, R.J.; Eulálio, M.M.C.; Dos Santos, L.D.; Fontes, M.R.M. Biochemical, Pharmacological and Structural Characterization of BmooMP-I, a New P-I Metalloproteinase from Bothrops moojeni Venom. Biochimie 2020, 179, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.K.; Joshi, M.B.; Vasishta, S.; Jagadale, R.N.; Biligiri, S.G.; Coronado, M.A.; Arni, R.K.; Satyamoorthy, K. P-I Metalloproteinases and L-Amino Acid Oxidases from Bothrops species inhibit angiogenesis. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 27, e20200180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, C.P.; Santos-Filho, N.A.; Costa, T.R.; Gomes, M.S.; Torres, F.S.; Costa, J.; Borges, M.H.; Richardson, M.; dos Santos, D.M.; de Castro Pimenta, A.M.; et al. Isolation and Structural Characterization of a New Fibrin(Ogen)Olytic Metalloproteinase from Bothrops moojeni Snake Venom. Toxicon 2008, 51, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisakul, J.; Khow, O.; Wiwatwarayos, K.; Rusmili, M.R.A.; Prasert, W.; Othman, I.; Abidin, S.A.Z.; Charoenpitakchai, M.; Hodgson, W.C.; Chanhome, L. A Biochemical and Pharmacological Characterization of Phospholipase A2 and Metalloproteinase Fractions from Eastern Russell’s Viper (Daboia siamensis) Venom: Two Major Components Associated with Acute Kidney Injury. Toxins 2021, 13, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Kariu, T.; Takazaki, S.; Hattori, S.; Chijiwa, T.; Ohno, M.; Oda-Ueda, N. Island Specific Expression of a Novel [Lys(49)]Phospholipase A(2) (BPIII) in Protobothrops flavoviridis Venom in Amami-Oshima, Japan. Toxicon 2009, 54, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, S.; Tu, A.T. Phospholipase A2 from Naja naja sputatrix Venom Is a Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor Inhibitor. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1996, 328, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.F.; Gabriel, L.M.; Gontijo, S.; Gremski, L.H.; Veiga, S.S.; Evangelista, K.S.; Eble, J.A.; Richardson, M. Structural and Functional Characterization of a P-III Metalloproteinase, Leucurolysin-B, from Bothrops leucurus Venom. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 468, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, S.; Hori, J.; Fujimura, S.; Kimoto, E. Purification and Amino Acid Sequence of Brevilysin L6, a Non-Hemorrhagic Metalloprotease from Agkistrodon halys brevicaudus Venom. J. Biochem. 1999, 125, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.B.; Chang, S.C.; Liau, M.Y.; Huang, T.F. Purification, Molecular Cloning and Mechanism of Action of Graminelysin I, a Snake-Venom-Derived Metalloproteinase That Induces Apoptosis of Human Endothelial Cells. Biochem. J. 2001, 357, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage, D.S.; Matsuda, R. Affinity Chromatography: A Historical Perspective. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1286, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioi, N.; Nishijima, A.; Terada, S. Flavorase, a Novel Non-Haemorrhagic Metalloproteinase in Protobothrops Flavoviridis Venom, Is a Target Molecule of Small Serum Protein-3. J. Biochem. 2015, 158, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, S.L.; Acosta, G.; Ávila, L.; Giudicessi, S.L.; Camperi, S.A.; Albericio, F.; Cascone, O.; Martínez Ceron, M.C. Use of a Phosphopeptide as a Ligand to Purify Phospholipase A. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1146, 122070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, P.C.; Machado de Avila, R.A.; Selena Maria, W.; Richardson, M.; Fortes-Dias, C.L.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C. The Co-Purification of a Lectin (BJcuL) with Phospholipases A2 from Bothrops jararacussu Snake Venom by Immunoaffinity Chromatography with Antibodies to Crotoxin. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samah, S.; Fatah, C.; Jean-Marc, B.; Safia, K.T.; Fatima, L.D. Purification and Characterization of Cc-Lec, C-Type Lactose-Binding Lectin: A Platelet Aggregation and Blood-Clotting Inhibitor from Cerastes cerastes Venom. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonça-Franqueiro, E.e.P.; Alves-Paiva, R.e.M.; Sartim, M.A.; Callejon, D.R.; Paiva, H.H.; Antonucci, G.A.; Rosa, J.C.; Cintra, A.C.; Franco, J.J.; Arantes, E.C.; et al. Isolation, Functional, and Partial Biochemical Characterization of Galatrox, an Acidic Lectin from Bothrops atrox Snake Venom. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2011, 43, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ameziani, M.; Chérifi, F.; Kiheli, H.; Saoud, S.; Hariti, G.; Kellou-Taîri, S.; Laraba-Djebari, F. Isolation and Functional Identification of an Antiplatelet RGD-Containing Disintegrin from Cerastes cerastes Venom. Protein J. 2020, 39, 574–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaqueo, K.D.; Kayano, A.M.; Simões-Silva, R.; Moreira-Dill, L.S.; Fernandes, C.F.; Fuly, A.L.; Maltarollo, V.G.; Honório, K.M.; da Silva, S.L.; Acosta, G.; et al. Isolation and Biochemical Characterization of a New Thrombin-like Serine Protease from Bothrops pirajai Snake Venom. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 595186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhat, S.K.; Joshi, M.B.; Ullah, A.; Masood, R.; Biligiri, S.G.; Arni, R.K.; Satyamoorthy, K. Serine Proteinases from Bothrops Snake Venom Activates PI3K/Akt Mediated Angiogenesis. Toxicon 2016, 124, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kakati, H.; Patra, A.; Kalita, B.; Chanda, A.; Rapole, S.; Mukherjee, A.K. A Comparison of Two Different Analytical Workflows to Determine the Venom Proteome Composition of Naja kaouthia from North-East India and Immunological Profiling of Venom against Commercial Antivenoms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, K.K.; Liapis, A.I. Adsorbents and Columns in Analytical High-Performance Liquid Chromatography: A Perspective with Regard to Development and Understanding. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandera, P.; Skeifíková, V.; Rehová, L.; Hájek, T.; Baldriánová, L.; Skopová, G.; Kellner, V.; Horna, A. RP-HPLC Analysis of Phenolic Compounds and Flavonoids in Beverages and Plant Extracts Using a CoulArray Detector. J. Sep. Sci. 2005, 28, 1005–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntravat, M.; Cromer, W.E.; Marquez, J.; Galan, J.A.; Zawieja, D.C.; Davies, P.; Salazar, E.; Sánchez, E.E. The Isolation and Characterization of a New Snake Venom Cysteine-Rich Secretory Protein (SvCRiSP) from the Venom of the Southern Pacific Rattlesnake and Its Effect on Vascular Permeability. Toxicon 2019, 165, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlhoff, M.; Borges, M.H.; Yarleque, A.; Cabezas, C.; Richardson, M.; Sanchez, E.F. Exploring the Proteomes of the Venoms of the Peruvian Pit Vipers Bothrops Atrox, B. Barnetti and B. Pictus. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 2181–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordon, K.C.; Perino, M.G.; Giglio, J.R.; Arantes, E.C. Isolation, Enzymatic Characterization and Antiedematogenic Activity of the First Reported Rattlesnake Hyaluronidase from Crotalus durissus terrificus Venom. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2740–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Malhotra, A.; Giri, S.; Lalremsanga, H.T.; Bharti, O.K.; Santra, V.; Martin, G.; Doley, R. Venom of Several Indian Green Pit Vipers: Comparison of Biochemical Activities and Cross-Reactivity with Antivenoms. Toxicon 2022, 210, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Wu, C.J.; Hsiao, Y.C.; Yang, Y.H.; Liu, K.L.; Huang, G.J.; Hsieh, C.H.; Chen, C.K.; Liaw, G.W. Snake Venom Proteome of Protobothrops mucrosquamatus in Taiwan: Delaying Venom-Induced Lethality in a Rodent Model by Inhibition of Phospholipase A2 activity with varespladib. J. Proteom. 2021, 234, 104084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanuopadath, M.; Raveendran, D.; Nair, B.G.; Nair, S.S. Venomics and Antivenomics of Indian Spectacled Cobra (Naja naja) from the Western Ghats. Acta Trop. 2022, 228, 106324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.R.; Molina Molina, D.A.; de Souza, D.L.N.; Cardenas, J.; Costal-Oliveira, F.; Guerra-Duarte, C.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C. Biological and Proteomic Characterization of the Venom from Peruvian Andes Rattlesnake Crotalus durissus. Toxicon 2022, 207, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, A.; Zahid, A.; Negm, A.; Akrem, A.; Spencer, P.; Betzel, C. Isolation and Characterization of Bradykinin Potentiating Peptides from Agkistrodon bilineatus Venom. Proteome Sci. 2016, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Posada Arias, S.; Rey-Suárez, P.; Pereáñez, J.A.; Acosta, C.; Rojas, M.; Delazari Dos Santos, L.; Ferreira, R.S.; Núñez, V. Isolation and Functional Characterization of an Acidic Myotoxic Phospholipase A2 from Colombian Bothrops asper Venom. Toxins 2017, 9, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Sharma, R.; Rajput, Y.S.; Mann, B.; Singh, R.; Gandhi, K. Separation Methods for Milk Proteins on Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis: Critical Analysis and Options for Better Resolution. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 114, 104920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereañez, J.A.; Quintana, J.C.; Alarcón, J.C.; Núñez, V. Isolation and Functional Characterization of a Basic Phospholipase A2 from Colombian Bothrops asper Venom. Vitae 2014, 21, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Franco-Servín, C.; Neri-Castro, E.; Bénard-Valle, M.; Alagón, A.; Rosales-García, R.A.; Guerrero-Alba, R.; Poblano-Sánchez, J.E.; Silva-Briano, M.; Guerrero-Barrera, A.L.; Sigala-Rodríguez, J.J. Biological and Biochemical Characterization of Coronado Island Rattlesnake (Crotalus helleri caliginis) Venom and Antivenom Neutralization. Toxins 2021, 13, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olamendi-Portugal, T.; Batista, C.V.F.; Pedraza-Escalona, M.; Restano-Cassulini, R.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Benard-Valle, M.; de Roodt, A.R.; Possani, L.D. New Insights into the Proteomic Characterization of the Coral Snake Micrurus pyrrhocryptus Venom. Toxicon 2018, 153, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igci, N.; Demiralp, D.O. A Preliminary Investigation into the Venom Proteome of Macrovipera Lebetina Obtusa (Dwigubsky, 1832) from Southeastern Anatolia by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry and Comparison of Venom Protein Profiles with Macrovipera lebetina lebetina (Linnaeus, 1758) from Cyprus by 2D-PAGE. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, R.H.; Guimarães, P.R.; Junqueira, M.; Neves-Ferreira, A.G.; Soares, M.R.; Chapeaurouge, A.; Trugilho, M.R.; León, I.R.; Rocha, S.L.; Oliveira-Carvalho, A.L.; et al. Bothrops insularis Venomics: A Proteomic Analysis Supported by Transcriptomic-Generated Sequence Data. J. Proteom. 2009, 72, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, S.L.; Neves-Ferreira, A.G.; Trugilho, M.R.; Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B.; Valente, R.H.; Domont, G.B.; Perales, J. Screening for Target Toxins of the Antiophidic Protein DM64 through a Gel-Based Interactomics Approach. J. Proteom. 2017, 151, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonso, J.J.; Kayano, A.M.; Garay, A.F.G.; Simões-Silva, R.; Sobrinho, J.C.; Vourliotis, S.; Soares, A.M.; Calderon, L.A.; Gómez, M.C.V. Isolation, Biochemical Characterization and Antiparasitic Activity of BmatTX-IV, A Basic Lys49-Phospholipase A2 from the Venom of Bothrops mattogrossensis from Paraguay. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongtay, P.; Sangtanoo, P.; Sangvanich, P.; Karnchanatat, A. Variation in the Protein Composition and Biological Activity of King Cobra (Ophiophagus hannah) Venoms. Protein J. 2019, 38, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almehdar, H.A.; Adel-Sadek, M.A.; Redwan, E.M. Immunoreactivity and Two-Dimensional Gel-Electrophoresis Characterization of Egyptian Cobra Venom Proteome. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 28, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Kadi-Saci, A.; Laraba-Djebari, F. Purification and Characterization of a Thrombin-like Enzyme Isolated from Vipera Lebetina Venom: Its Interaction with Platelet Receptor. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2020, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averin, A.S.; Utkin, Y.N. Cardiovascular Effects of Snake Toxins: Cardiotoxicity and Cardioprotection. Acta Nat. 2021, 13, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabuva, S.; Lukšić, B.; Brizić, I.; Latinović, Z.; Leonardi, A.; Križaj, I. Ammodytin L Is the Main Cardiotoxic Component of the Vipera ammodytes ammodytes Venom. Toxicon 2017, 139, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahyoun, C.; Krezel, W.; Mattei, C.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Legros, C.; Fajloun, Z.; Rima, M. Neuro- and Cardiovascular Activities of Montivipera bornmuelleri Snake Venom. Biology 2022, 11, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotty, Y.; Álvarez, M.; Perdomo, L.; Sánchez, E.E.; Giron, M.E.; Jimenez, J.C.; Suntravat, M.; Guerrero, B.; Ibarra, C.; Montero, Y. Mutacytin-1, a New C-Type Lectin-like Protein from the Venezuelan Cuaima (Lachesis muta muta Linnaeus, 1766)(Serpentes: Viperidae) Snake Venom Inducing Cardiotoxicity in Developing Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Zebrafish 2019, 16, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, T.N.; Naumann, G.B.; Peixoto, P.; Rouver, W.N.; Gomes, H.L.; Campos, F.V.; Borges, M.H.; Dos Santos, R.L.; Bissoli, N.S.; Sanchez, E.F.; et al. Bothrops leucurus Venom Induces Acute Hypotension in Rats by Means of Its Phospholipase A2 (blD-PLA2). Toxicon 2020, 185, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.C.; Kuruppu, S.; Smith, A.I.; Reeve, S.; Hodgson, W.C. Isolation and Pharmacological Characterisation of Hostoxin-1, a Postsynaptic Neurotoxin from the Venom of the Stephen’s Banded Snake (Hoplocephalus stephensi). Neuropharmacology 2006, 51, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumsden, N.G.; Banerjee, Y.; Kini, R.M.; Kuruppu, S.; Hodgson, W.C. Isolation and Characterization of Rufoxin, a Novel Protein Exhibiting Neurotoxicity from Venom of the Psammophiine, Rhamphiophis oxyrhynchus (Rufous Beaked Snake). Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcon, F.; Purtell, L.; Santos, J.; Hains, P.G.; Escoubas, P.; Graudins, A.; Nicholson, G.M. Characterization of Monomeric and Multimeric Snake Neurotoxins and Other Bioactive Proteins from the Venom of the Lethal Australian Common Copperhead (Austrelaps superbus). Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1555–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, M.; Prasad, N.; Sing, T.; Gowda, V. Purification, Characterization, and Chemical Modification of Neurotoxic Peptide from Daboia Russelii Snake Venom of India. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2013, 27, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano-Pérez, F.; Rangel-López, E.; Robles-Bañuelos, B.; Franco-Vásquez, A.M.; García-Arredondo, A.; Navarro-García, J.C.; Zavala-Moreno, A.; Gómez-Manzo, S.; Santamaría, A.; Arreguín-Espinosa, R. Chemical Structure of Three Basic Asp-49 Phospholipases A2 Isolated from Crotalus molossus nigrescens Venom with Cytotoxic Activity against Cancer Cells. Toxicon 2022, 210, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, N.A.H.; Rusmili, M.R.A.; Zainal Abidin, S.A.; Shaikh, M.F.; Hodgson, W.C.; Othman, I. Isolation and Characterization of A2-EPTX-Nsm1a, a Secretory Phospholipase A. Toxins 2021, 13, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proleón, A.; Torrejón, D.; Urra, F.A.; Lazo, F.; López-Torres, C.; Fuentes-Retamal, S.; Quispe, E.; Bautista, L.; Agurto, A.; Gavilan, R.G.; et al. Functional, Immunological Characterization, and Anticancer Activity of BaMtx: A New Lys49- PLA. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 990–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, N.F.T.; Imberg, A.D.; Mariano, D.O.; Moraes, A.C.; Andrade-Silva, J.; Fernandes, C.M.; Sobral, A.C.; Giannotti, K.C.; Kuwabara, W.M.T.; Pimenta, D.C. β-Micrustoxin (Mlx-9), a PLA 2 from Micrurus lemniscatus Snake Venom: Biochemical Characterization and Anti-Proliferative Effect Mediated by P53. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 28, e20210094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennacer, A.; Boukhalfa-Abib, H.; Laraba-Djebari, F. Computational and Functional Characterization of a Hemorrhagic Metalloproteinase Purified from Cerastes cerastes Venom. Protein J. 2021, 40, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Požek, K.; Leonardi, A.; Pungerčar, J.; Rao, W.; Gao, Z.; Liu, S.; Laustsen, A.H.; Trampuš Bakija, A.; Reberšek, K.; Podgornik, H.; et al. Genomic Confirmation of the P-IIIe Subclass of Snake Venom Metalloproteinases and Characterisation of Its First Member, a Disintegrin-like/Cysteine-Rich Protein. Toxins 2022, 14, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burin, S.M.; Cacemiro, M.D.C.; Cominal, J.G.; Grandis, R.A.; Machado, A.R.T.; Donaires, F.S.; Cintra, A.C.O.; Ambrosio, L.; Antunes, L.M.G.; Sampaio, S.V.; et al. L-Amino Acid Oxidase Induces Apoptosis and Epigenetic Modulation on Bcr-Abl. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 26, e20200123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelkafi-Koubaa, Z.; Jebali, J.; Othman, H.; Morjen, M.; Aissa, I.; Zouari-Kesentini, R.; Bazaa, A.; Ellefi, A.A.; Majdoub, H.; Srairi-Abid, N.; et al. A Thermoactive L-Amino Acid Oxidase from Cerastes cerastes Snake Venom: Purification, Biochemical and Molecular Characterization. Toxicon 2014, 89, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, W.H.; Ibrahim, N.M.; El Hakim, A.E.; Bassuiny, R.I.; Mohamed, M.M.; Mousa, F.M.; Ali, M.M. L-Amino Acid Oxidase from Cerastes vipera Snake Venom: Isolation, Characterization and Biological Effects on Bacteria and Tumor Cell Lines. Toxicon 2018, 150, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey-Suárez, P.; Acosta, C.; Torres, U.; Saldarriaga-Córdoba, M.; Lomonte, B.; Núñez, V. MipLAAO, a New L-Amino Acid Oxidase from the Redtail Coral Snake. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carone, S.E.I.; Menaldo, D.L.; Sartim, M.A.; Bernardes, C.P.; Caetano, R.C.; da Silva, R.R.; Cabral, H.; Barraviera, B.; Ferreira Junior, R.S.; Sampaio, S.V. BjSP, a Novel Serine Protease from Bothrops Jararaca Snake Venom That Degrades Fibrinogen without Forming Fibrin Clots. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 357, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vander Dos Santos, R.; Villalta-Romero, F.; Stanisic, D.; Borro, L.; Neshich, G.; Tasic, L. Citrus Bioflavonoid, Hesperetin, as Inhibitor of Two Thrombin-like Snake Venom Serine Proteases Isolated from Crotalus simus. Toxicon 2018, 143, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrini-França, J.; Santos Rodrigues, R.; Santos-Silva, L.K.; de Souza, D.L.; Gomes, M.S.; Cologna, C.T.; de Pauw, E.; Quinton, L.; Henrique-Silva, F.; de Melo Rodrigues, V.; et al. Expression of a New Serine Protease from Crotalus durissus collilineatus Venom in Pichia Pastoris and Functional Comparison with the Native Enzyme. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 9971–9986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, F.G.; Menaldo, D.L.; Carone, S.E.I.; Silva, T.A.; Sartim, M.A.; De Pauw, E.; Quinton, L.; Sampaio, S.V. New Insights on Moojase, a Thrombin-like Serine Protease from Bothrops moojeni Snake Venom. Toxins 2018, 10, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, D.F.D.C.; Matias Ribeiro, M.S.; de Sousa Simamoto, B.B.; Dias, E.H.V.; Costa, J.O.; Santos-Filho, N.A.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Arantes, E.C.; Dantas, N.O.; Silva, A.C.A.; et al. Baltetin: A New C-Type Lectin-like Isolated from Bothrops Alternatus Snake Venom Which Act as a Platelet Aggregation Inhibiting. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2021, 1173, 122695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon-Filho, S.; Naves-de-Souza, D.L.; Lopes-de-Souza, L.; Silvano-de-Oliveira, J.; Bonilla Ferreyra, C.; Costal-Oliveira, F.; Guerra-Duarte, C.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C. Micrurus surinamensis Peruvian Snake Venom: Cytotoxic Activity and Purification of a C-Type Lectin Protein (Ms-CTL) Highly Toxic to Cardiomyoblast-Derived H9c2 Cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1908–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebali, J.; Zakraoui, O.; Aissaoui, D.; Abdelkafi-Koubaa, Z.; Srairi-Abid, N.; Marrakchi, N.; Essafi-Benkhadir, K. Lebecetin, a Snake Venom C-Type Lectin Protein, Modulates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Human THP-1-Derived Macrophages. Toxicon 2020, 187, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, W.L.; Kayano, A.M.; de Castro, O.B.; Paloschi, M.V.; Lopes, J.A.; Boeno, C.N.; Pereira, S.D.S.; Antunes, M.M.; Rodrigues, M.M.S.; Stábeli, R.G.; et al. Lectin Isolated from Bothrops jararacussu Venom Induces IL-10 Release by TCD4. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 106, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, A.; Sharma, M.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Devi, A.; Doley, R. Naja kaouthia Venom Protein, Nk-CRISP, Upregulates Inflammatory Gene Expression in Human Macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, C.P.; Menaldo, D.L.; Zoccal, K.F.; Boldrini-França, J.; Peigneur, S.; Arantes, E.C.; Rosa, J.C.; Faccioli, L.H.; Tytgat, J.; Sampaio, S.V. First Report on BaltCRP, a Cysteine-Rich Secretory Protein (CRISP) from Bothrops alternatus Venom: Effects on Potassium Channels and Inflammatory Processes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodovicho, M.E.; Costa, T.R.; Bernardes, C.P.; Menaldo, D.L.; Zoccal, K.F.; Carone, S.E.; Rosa, J.C.; Pucca, M.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Arantes, E.C.; et al. Investigating Possible Biological Targets of Bj-CRP, the First Cysteine-Rich Secretory Protein (CRISP) Isolated from Bothrops jararaca Snake Venom. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 265, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas Mercado, E.; Neri Castro, E.; Bénard Valle, M.; Rucavado-Romero, A.; Olvera Rodríguez, A.; Zamudio Zuñiga, F.; Alagón Cano, A.; Garza Ocañas, L. Disintegrins Extracted from Totonacan Rattlesnake (Crotalus totonacus) Venom and Their Anti-Adhesive and Anti-Migration Effects on MDA-MB-231 and HMEC-1 Cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2020, 65, 104809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.S.; Manzini, R.V.; Ferreira, I.G.; Cardoso, I.A.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Machado, A.R.T.; Antunes, L.M.G.; Rosa, J.C.; Arantes, E.C. Cell Migration Inhibition Activity of a Non-RGD Disintegrin from Crotalus durissus collilineatus venom. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 24, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allane, D.; Oussedik-Oumehdi, H.; Harrat, Z.; Seve, M.; Laraba-Djebari, F. Isolation and Characterization of an Anti-Leishmanial Disintegrin from Cerastes cerastes Venom. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryukova, E.V.; Potapenko, A.S.; Andreeva, T.V.; Ivanov, I.A.; Ryabinin, V.V.; Ziganshin, R.H.; Starkov, V.G.; Ayvazyan, N.M.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. Dimeric Disintegrins from the Steppe Viper V. ursinii Venom. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 488, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, J.M.; Attoub, S.; Musale, V.; Leprince, J.; Casewell, N.R.; Sanz, L.; Calvete, J.J. Isolation and Characterization of Cytotoxic and Insulin-Releasing Components from the Venom of the Black-Necked Spitting Cobra Naja nigricollis (Elapidae). Toxicon X 2020, 6, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonte, B.; Camacho, E.; Fernández, J.; Salas, M.; Zavaleta, A. Three-Finger Toxins from the Venom of Micrurus tschudii tschudii (Desert Coral Snake): Isolation and Characterization of Tschuditoxin-I. Toxicon 2019, 167, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, L.; Kryukova, E.; Ziganshin, R.; Andreeva, T.; Kudryavtsev, D.; Kasheverov, I.; Tsetlin, V.; Utkin, Y. Novel Three-Finger Neurotoxins From Naja melanoleuca Cobra Venom Interact with GABAA and Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Toxins 2021, 13, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonte, B.; Calvete, J.J. Strategies in “snake Venomics” Aiming at an Integrative View of Compositional, Functional, and Immunological Characteristics of Venoms. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 23, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd El-Aziz, T.M.; Soares, A.G.; Stockand, J.D. Advances in Venomics: Modern Separation Techniques and Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1160, 122352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slagboom, J.; Kaal, C.; Arrahman, A.; Vonk, F.J.; Somsen, G.W.; Calvete, J.J.; Wüster, W.; Kool, J. Analytical Strategies in Venomics. Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasoulis, T.; Pukala, T.L.; Isbister, G.K. Investigating Toxin Diversity and Abundance in Snake Venom Proteomes. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 768015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.Y.; Liew, J.L.; Tan, N.H.; Quah, E.S.H.; Ismail, A.K.; Tan, C.H. Unlocking the Secrets of Banded Coral Snake (Calliophis intestinalis, Malaysia): A Venom with Proteome Novelty, Low Toxicity and Distinct Antigenicity. J. Proteom. 2019, 192, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, A.M.F.; Tan, C.H.; Tan, K.Y.; Quraishi, N.H.; Tan, N.H. Venom Proteome of Bungarus sindanus (Sind Krait) from Pakistan and in Vivo Cross-Neutralization of Toxicity Using an Indian Polyvalent Antivenom. J. Proteom. 2019, 193, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Huang, M.N.; Chang, J.F.; Liu, C.C.; Chen, C.K.; Hsieh, C.H. Snake Venom Proteome and Immuno-Profiling of the Hundred-Pace Viper, Deinagkistrodon Acutus, in Taiwan. Acta Trop. 2019, 189, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.P.; Tan, K.Y.; Tan, C.H. Snake Venom Proteomics and Antivenomics of Two Sundaic Lance-Headed Pit Vipers: Trimeresurus wiroti (Malaysia) and Trimeresurus puniceus (Indonesia). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 40, 100875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.; Tan, K.Y.; Ng, T.S.; Sim, S.M.; Tan, N.H. Venom Proteome of Spine-Bellied Sea Snake (Hydrophis curtus) from Penang, Malaysia: Toxicity Correlation, Immunoprofiling and Cross-Neutralization by Sea Snake Antivenom. Toxins 2018, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, K.Y.; Wong, K.Y.; Tan, N.H.; Tan, C.H. Quantitative Proteomics of Naja annulifera (Sub-Saharan Snouted Cobra) Venom and Neutralization Activities of Two Antivenoms in Africa. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hia, Y.L.; Tan, K.Y.; Tan, C.H. Comparative Venom Proteomics of Banded Krait (Bungarus fasciatus) from Five Geographical Locales: Correlation of Venom Lethality, Immunoreactivity and Antivenom Neutralization. Acta Trop. 2020, 207, 105460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumkate, S.; Chanhome, L.; Thiangtrongjit, T.; Noiphrom, J.; Laoungboa, P.; Khow, O.; Vasaruchapong, T.; Sitprija, S.; Chaiyabutr, N.; Reamtong, O. Venomics and Cellular Toxicity of Thai Pit Vipers (Trimeresurus macrops and T. hageni). Toxins 2020, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.M.; Yang, Y.E.; Chen, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, L.L.; Wang, Z.Z.; Wang, X.M.; Wang, Y.M.; Tsai, I.H. Transcriptome and Proteome of the Highly Neurotoxic Venom of Gloydius intermedius. Toxicon 2015, 107, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocian, A.; Urbanik, M.; Hus, K.; Łyskowski, A.; Petrilla, V.; Andrejčáková, Z.; Petrillová, M.; Legáth, J. Proteomic Analyses of Agkistrodon Contortrix Contortrix Venom Using 2D Electrophoresis and MS Techniques. Toxins 2016, 8, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hus, K.K.; Buczkowicz, J.; Petrilla, V.; Petrillová, M.; Łyskowski, A.; Legáth, J.; Bocian, A. First Look at the Venom of Naja ashei. Molecules 2018, 23, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonardi, A.; Sajevic, T.; Pungerčar, J.; Križaj, I. Comprehensive Study of the Proteome and Transcriptome of the Venom of the Most Venomous European Viper: Discovery of a New Subclass of Ancestral Snake Venom Metalloproteinase Precursor-Derived Proteins. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 2287–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choksawangkarn, W.; Sriswasdi, S.; Kalpongnukul, N.; Wongkongkathep, P.; Saethang, T.; Chanhome, L.; Laoungbua, P.; Khow, O.; Sumontha, M.; Chaiyabutr, N.; et al. Combined Proteomic Strategies for In-Depth Venomic Analysis of the Beaked Sea Snake (Hydrophis schistosus) from Songkhla Lake, Thailand. J. Proteom. 2022, 259, 104559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katali, O.; Shipingana, L.; Nyarangó, P.; Pääkkönen, M.; Haindongo, E.; Rennie, T.; James, P.; Eriksson, J.; Hunter, C.J. Protein Identification of Venoms of the African Spitting Cobras. Toxins 2020, 12, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, Ê.; de Oliveira, L.A.; Sales Lauria, P.S.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Rodrigues Domênico, A.M.; da Silva Guerreiro, M.L.; Wiezel, G.A.; Cardoso, I.A.; Rossini, B.C.; Marino, C.L.; et al. Bothrops Leucurus Snake Venom Protein Profile, Isolation and Biological Characterization of Its Major Toxin PLA. Toxicon 2022, 213, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopcevic, K.; Karadzic, I.; Izrael-Zivkovic, L.; Medic, A.; Isakovic, A.; Popović, M.; Kekic, D.; Stanojkovic, T.; Hozic, A.; Cindric, M. Study of the Venom Proteome of Vipera ammodytes ammodytes (Linnaeus, 1758): A Qualitative Overview, Biochemical and Biological Profiling. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 37, 100776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; He, Q.; Zhou, B.; Huang, D.; Chen, J.; Chen, Q.; Yang, S.; Yu, X. Exploring the Five-Paced Viper (Deinagkistrodon acutus) Venom Proteome by Integrating a Combinatorial Peptide Ligand Library Approach with Shotgun LC-MS/MS. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 27, e20200196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hus, K.K.; Marczak, Ł.; Petrilla, V.; Petrillová, M.; Legáth, J.; Bocian, A. Different Research Approaches in Unraveling the Venom Proteome of Naja Ashei. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, M.; McCleary, R.J.R.; Kesherwani, M.; Kini, R.M.; Velmurugan, D. Comparison of Proteomic Profiles of the Venoms of Two of the “Big Four” Snakes of India, the Indian Cobra (Naja naja) and the Common Krait (Bungarus caeruleus), and Analyses of Their Toxins. Toxicon 2017, 135, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezellou, P.; Garikapati, V.; Kazemi, S.M.; Strupat, K.; Ghassempour, A.; Spengler, B. A Perspective View of Top-down Proteomics in Snake Venom Research. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 33 (Suppl. 1), 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvete, J.J.; Pla, D.; Els, J.; Carranza, S.; Damm, M.; Hempel, B.F.; John, E.B.O.; Petras, D.; Heiss, P.; Nalbantsoy, A.; et al. Combined Molecular and Elemental Mass Spectrometry Approaches for Absolute Quantification of Proteomes: Application to the Venomics Characterization of the Two Species of Desert Black Cobras, Walterinnesia aegyptia and Walterinnesia morgani. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 5064–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melani, R.D.; Skinner, O.S.; Fornelli, L.; Domont, G.B.; Compton, P.D.; Kelleher, N.L. Mapping Proteoforms and Protein Complexes From King Cobra Venom Using Both Denaturing and Native Top-down Proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2016, 15, 2423–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ainsworth, S.; Petras, D.; Engmark, M.; Süssmuth, R.D.; Whiteley, G.; Albulescu, L.O.; Kazandjian, T.D.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Rowley, P.; Wüster, W.; et al. The Medical Threat of Mamba Envenoming in Sub-Saharan Africa Revealed by Genus-Wide Analysis of Venom Composition, Toxicity and Antivenomics Profiling of Available Antivenoms. J. Proteom. 2018, 172, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petras, D.; Heiss, P.; Harrison, R.A.; Süssmuth, R.D.; Calvete, J.J. Top-down Venomics of the East African Green Mamba, Dendroaspis angusticeps, and the Black Mamba, Dendroaspis polylepis, Highlight the Complexity of Their Toxin Arsenals. J. Proteom. 2016, 146, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezellou, P.; Albuquerque, W.; Garikapati, V.; Casewell, N.R.; Kazemi, S.M.; Ghassempour, A.; Spengler, B. Integrating Top-Down and Bottom-Up Mass Spectrometric Strategies for Proteomic Profiling of Iranian Saw-Scaled Viper, Echis carinatus sochureki, Venom. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempel, B.F.; Damm, M.; Mrinalini; Göçmen, B.; Karış, M.; Nalbantsoy, A.; Kini, R.M.; Süssmuth, R.D. Extended Snake Venomics by Top-Down In-Source Decay: Investigating the Newly Discovered Anatolian Meadow Viper Subspecies. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1731–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Liu, J.; Peng, L.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Z. Compositional and Toxicological Investigation of Pooled Venom from Farm-Raised. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 28, e20210040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanhome, L.; Khow, O.; Reamtong, O.; Vasaruchapong, T.; Laoungbua, P.; Tawan, T.; Suntrarachun, S.; Sitprija, S.; Kumkate, S.; Chaiyabutr, N. Biochemical and Proteomic Analyses of Venom from a New Pit Viper, Protobothrops kelomohy. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 28, e20210080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, M.; Xue, C.; Liang, J.; Huang, F. Analysis of the Composition of Deinagkistrodon acutus Snake Venom Based on Proteomics, and Its Antithrombotic Activity and Toxicity Studies. Molecules 2022, 27, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitprija, S.; Chanhome, L.; Reamtong, O.; Thiangtrongjit, T.; Vasaruchapong, T.; Khow, O.; Noiphrom, J.; Laoungbua, P.; Tubtimyoy, A.; Chaiyabutr, N.; et al. Proteomics and Immunocharacterization of Asian Mountain Pit Viper (Ovophis monticola) Venom. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).