Effect of Cooling Rate on the Grain Morphology and Element Segregation Behavior of Fe-Mn-Al-C Low-Density Steel during Solidification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
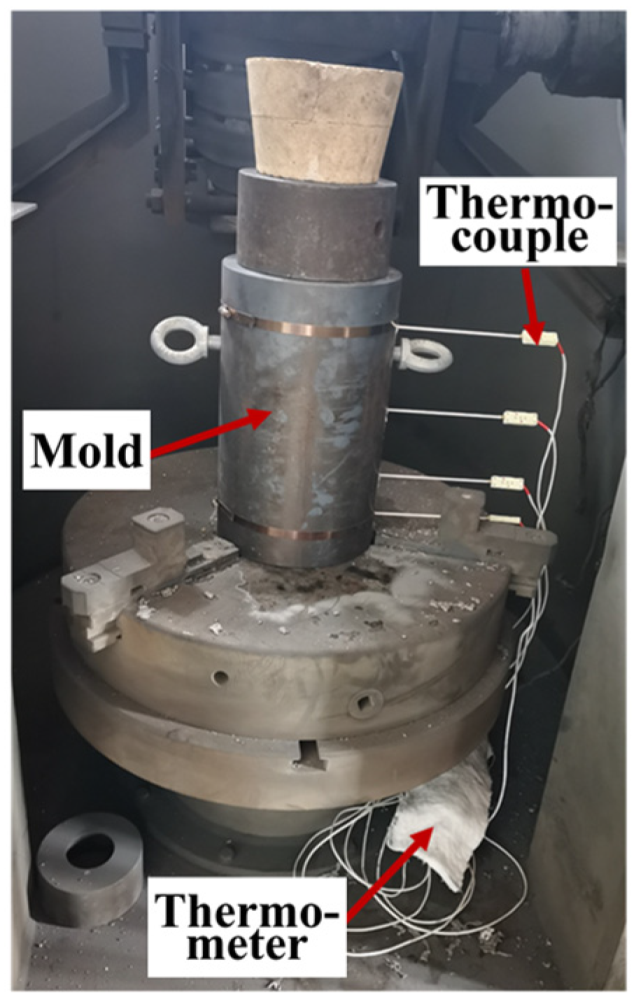
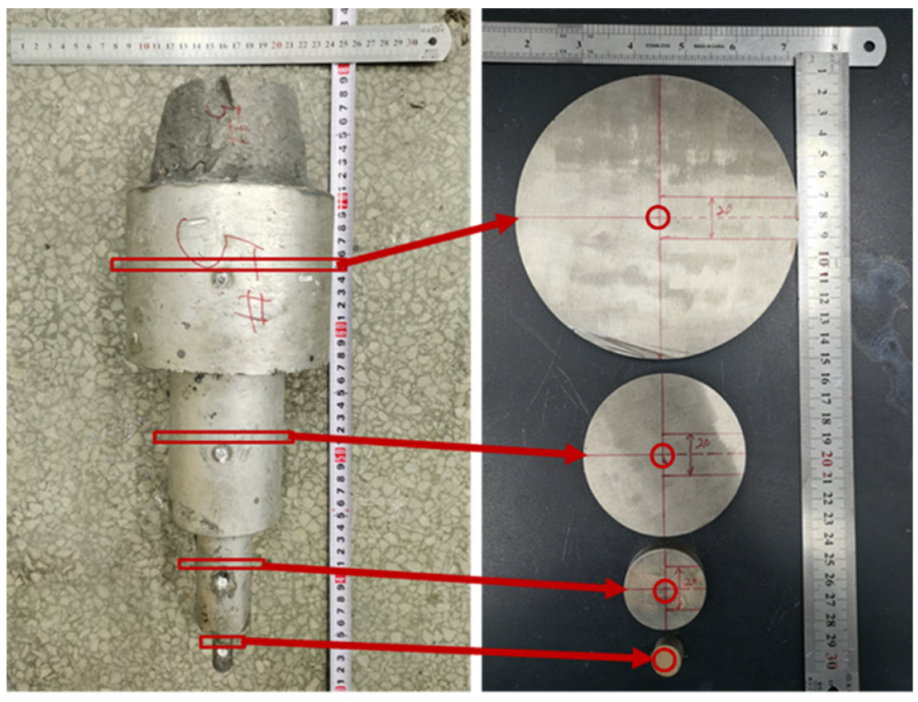
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Solidification Mode of Fe-Mn-Al-C Steel
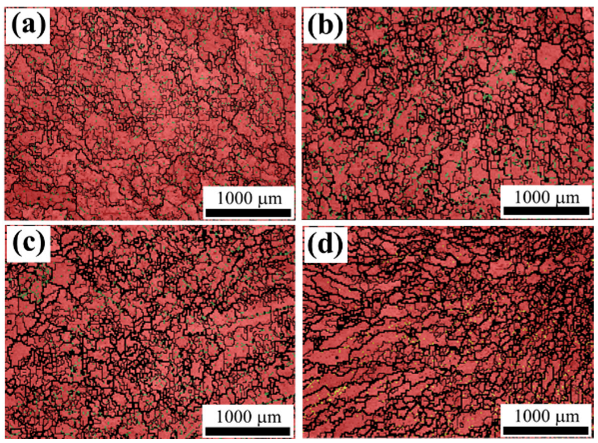
3.2. Effect of Cooling Rate on Grain Morphology of Fe-Mn-Al-C Steel
3.3. Effect of Cooling Rate on the Macroscopic Segregation of Fe-Mn-Al-C Steel Elements
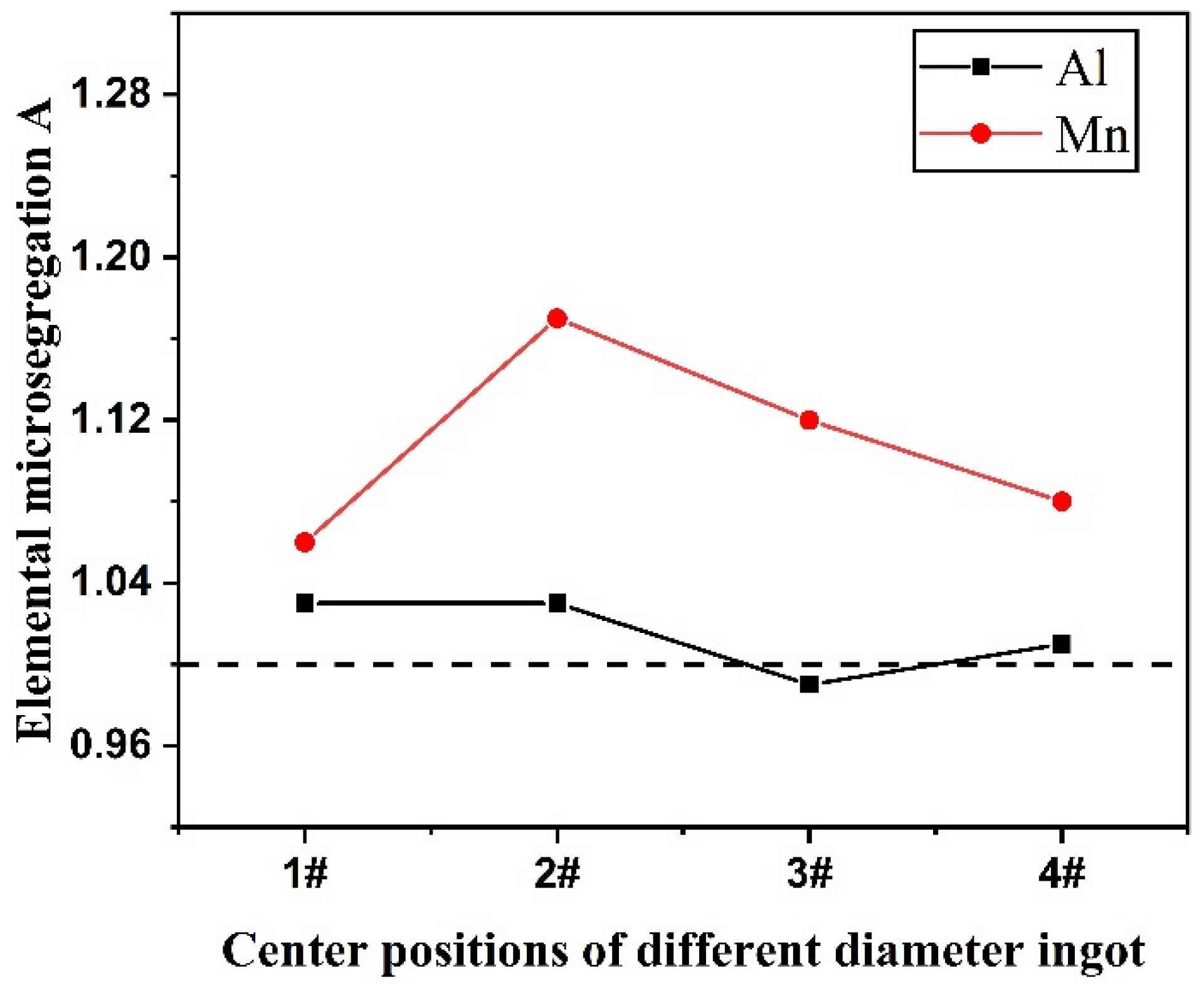
3.4. Effect of Cooling Rate on Microsegregation of Fe-Mn-Al-C Steel Elements
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The cooling rate has a significant influence on the content, size and distribution of the ferrite phase precipitation in Fe-30Mn-10Al-1.1C steel. With the increase in cooling rate, the ferrite phase precipitation content increases, the size of the ferrite grains is visibly reduced and the distribution of the ferrite phase becomes more uniform.
- (2)
- As the cooling rate increases, the austenitic phase grain size in the isometric crystal region at the center of the ingot decreases significantly. While the cooling rate increases from 1.69 °C/s to 10.28 °C/s, the average grain size of the austenitic phase transforms from 120 μm to 89 μm, which is a 26% reduction.
- (3)
- During the solidification process, the Mn and Al content are enriched on the grain boundary. With the cooling rate increasing, the micro-segregation value of Al is close to 1 and the extent of segregation decreases. Mn micro-segregation shows a trend of increasing first and subsequently decreasing. An increase in cooling rate helps to prevent Al and Mn segregation in Fe-30Mn-10Al-1.1C steel.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raabe, D.; Springer, H.; Gutiérrez-Urrutia, I.; Roters, F.; Bausch, M.; Seol, J.-B.; Koyama, M.; Choi, P.-P.; Tsuzaki, K. Alloy design, combinatorial synthesis, and microstructure-property relations for low-density Fe-Mn-Al-C austenitic steels. JOM 2014, 66, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikov, I.; Acselrad, O.; Shalkevich, A.; Pereira, L.C. Chemical Composition Optimization for Austenitic Steels of the Fe-Mn-Al-C System. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2000, 9, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Suh, D.W.; Kim, N.J. Fe-Al-Mn-C lightweight structural alloys: A review on the microstructures and mechanical properties. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2013, 14, 014205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frommeyer, G.; Brüx, U. Microstructures and mechanical properties of high-strength Fe-Mn-Al-C light-weight TRIPLEX steels. Steels Automot. Appl. 2006, 77, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, J.; Berghezan, A.; Lutts, A. High manganese-aluminium austenitic steel for cryogenic applications, some mechanical and physical properties. J. Phy. Colloq. 1984, 45, 619–623. [Google Scholar]
- Köster, W.; Tonn, W. Die Eisenecke des Systems Eisen-Mangan-Aluminium. Steel Res. Int. 1933, 7, 365–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.J.; Wan, C.M. The study of deformation twins in the austenitic Fe-Mn-C and Fe-Mn-Al-C alloys. Scr. Metall. 1989, 23, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassel, O.; Frommeyer, G. Effect of martensitic phase transformation and deformation twinning on mechanical properties of Fe-Mn-Si-Al steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1998, 14, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.D.; Park, K.T. Microband-induced plasticity in a high Mn-Al-C light steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2008, 496, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.D.; Hwang, S.W.; Park, K.T. Factors influencing the tensile behavior of a Fe-28Mn-9Al-0.8C Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 508, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutou, Y.; Kamiya, N.; Umino, R.; Ohnuma, I.; Ishida, K. High-Strength Fe-20Mn-Al-C-Based Alloys with Low Density. ISIJ Int. 2010, 50, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koyama, M.; Springer, H.; Merzlikin, S.V.; Tsuzaki, K.; Akiyama, E.; Raabe, D. Hydrogen embrittlement associated with strain localization in a precipitation-hardened Fe-Mn-Al-C light weight austenitic steel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 4634–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuazo, I.; Hallstedt, B.; Lindahl, B.; Selleby, M.; Soler, M.; Etienne, A.; Perlade, A.; Hasenpouth, D.; Massardier-Jourdan, V.; Cazottes, S.; et al. Low-Density Steels: Complex Metallurgy for Automotive Applications. JOM 2014, 66, 1747–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Hu, X. Deformation mechanisms and microstructure control in Fe-Mn-Al-C steels with high stacking fault energies. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 17, 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Li, W.; Ren, P.; Cao, W.; Liu, Q. Effects of C content on microstructure and properties of Fe-Mn-Al-C low-Density steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2019, 55, 951–957. [Google Scholar]
- Grajcar, A.; Kalinowska-Ozgowicz, E.; Opiela, M.; Grzegorczyk, B.; Gołombek, K. Effects of Mn and Nb on the macro-and microsegregation in high-Mn high-Al content TRIP steels. Arch. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 49, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Senk, D.; Emmerich, H.; Rezende, J.; Siquieri, R. Estimation of Segregation in Iron-Manganese Steels. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2007, 9, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, P.; Tang, H.; Zhang, J. Hot ductility of high alloy Fe-Mn-C austenite TWIP steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 660, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, P.; Zhang, J. Thermophysical Properties and Solidification Defects of Fe-22Mn-0.7C TWIP Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2016, 87, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.B. Analysis of Metallurgical Fundamental and Solidification Characteristics of Fe-Mn-C (-Al) TWIP Steel; University of Science and Technology Beijing: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.W.; Lu, X.-G.; Chang, Y.A. Solidification Simulation Using Scheil Model in Multicomponent Systems. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2009, 30, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.X.; Qin, Y.C. Metallography and Heat Treatment, 2nd ed.; Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 52–53. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]










| Elements | Mn | Al | C | Nb | V | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content, wt (%) | 30 | 10 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 58.7 |
| Ingot Position | Diameter of Ingot, mm | Cooling Rate, °C/s |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 140 | 1.69 |
| 2 | 80 | 2.01 |
| 3 | 40 | 5.87 |
| 4 | 15 | 10.28 |
| Elements | Ingot Point | Cooling Rate, °C/s | Content, wt% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | 1 | 1.69 | 29.92 |
| 2 | 2.01 | 29.84 | |
| 3 | 5.87 | 29.94 | |
| 4 | 10.28 | 29.93 | |
| Al | 1 | 1.69 | 9.56 |
| 2 | 2.01 | 9.68 | |
| 3 | 5.87 | 9.70 | |
| 4 | 10.28 | 9.81 | |
| C | 1 | 1.69 | 1.11 |
| 2 | 2.01 | 1.09 | |
| 3 | 5.87 | 1.11 | |
| 4 | 10.28 | 1.11 |
| Position | Ingot | Cooling Rate, °C/s | Content, wt% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grain boundary | 1 | 1.69 | 37.24 |
| 2 | 2.01 | 37.92 | |
| 3 | 5.87 | 37.62 | |
| 4 | 10.28 | 34.93 | |
| Inside the grain | 1 | 1.69 | 34.97 |
| 2 | 2.01 | 32.47 | |
| 3 | 5.87 | 33.61 | |
| 4 | 10.28 | 32.44 |
| Position | Ingot | Cooling Rate, °C/s | Content, wt% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grain boundary | 1 | 1.69 | 10.32 |
| 2 | 2.01 | 10.27 | |
| 3 | 5.87 | 9.62 | |
| 4 | 10.28 | 9.77 | |
| Inside the grain | 1 | 1.69 | 10.06 |
| 2 | 2.01 | 9.95 | |
| 3 | 5.87 | 9.75 | |
| 4 | 10.28 | 9.68 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, Q.; Zhu, G. Effect of Cooling Rate on the Grain Morphology and Element Segregation Behavior of Fe-Mn-Al-C Low-Density Steel during Solidification. Processes 2022, 10, 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061101
Huang S, Li G, Zhang Z, Tan Q, Zhu G. Effect of Cooling Rate on the Grain Morphology and Element Segregation Behavior of Fe-Mn-Al-C Low-Density Steel during Solidification. Processes. 2022; 10(6):1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061101
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shihui, Guangqiang Li, Zhan Zhang, Qingbiao Tan, and Guoliang Zhu. 2022. "Effect of Cooling Rate on the Grain Morphology and Element Segregation Behavior of Fe-Mn-Al-C Low-Density Steel during Solidification" Processes 10, no. 6: 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061101
APA StyleHuang, S., Li, G., Zhang, Z., Tan, Q., & Zhu, G. (2022). Effect of Cooling Rate on the Grain Morphology and Element Segregation Behavior of Fe-Mn-Al-C Low-Density Steel during Solidification. Processes, 10(6), 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061101






