Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Coating Sorbent for Preconcentration of Formaldehyde by Thin-Film Solid-Phase Microextraction Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
2.2. Real Samples
2.3. Equipment and Measuring Apparatus
2.4. Synthesis of DES-Based Sorbents
2.5. Preparation of Supports with DES-Based Sorbents
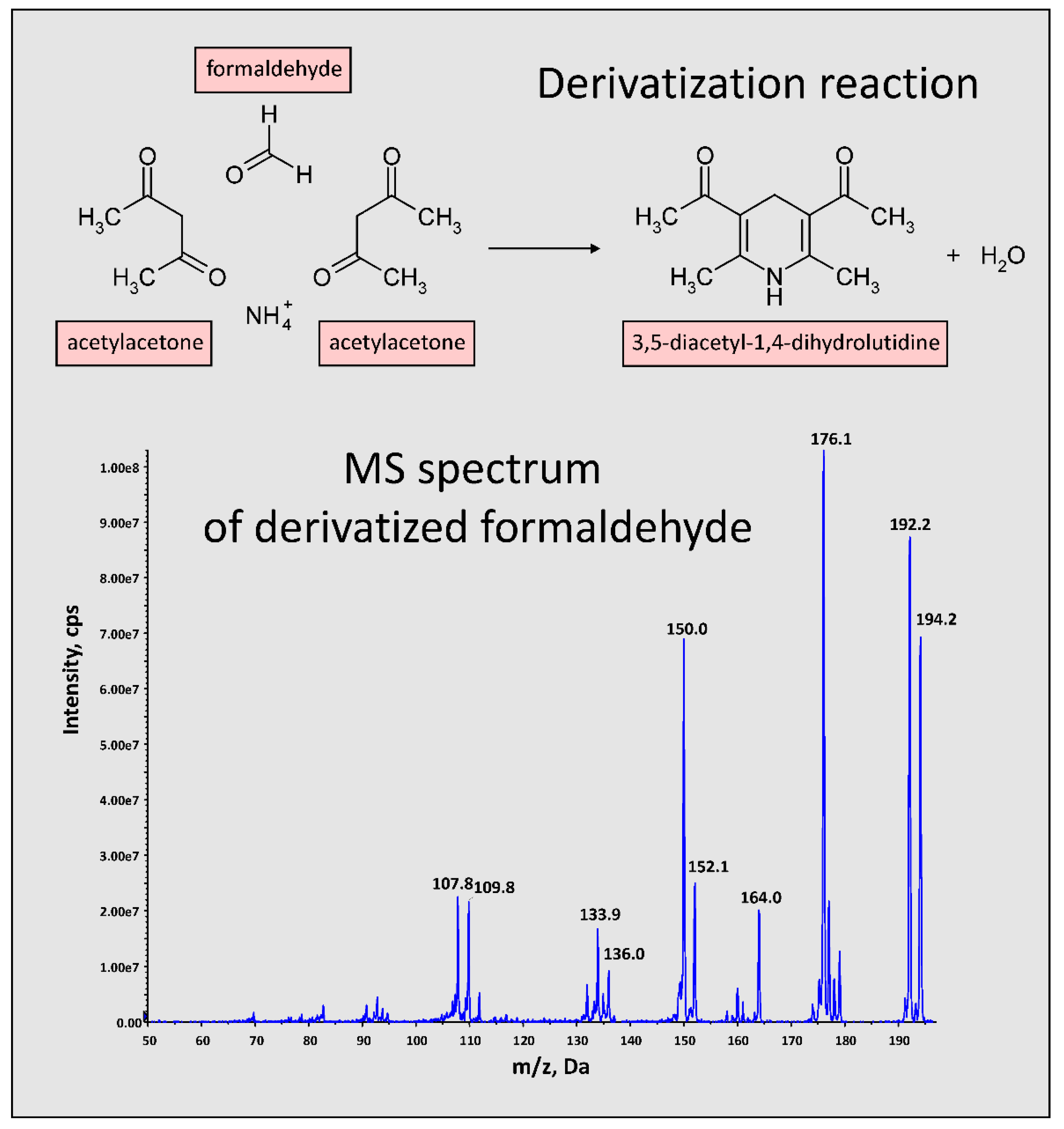
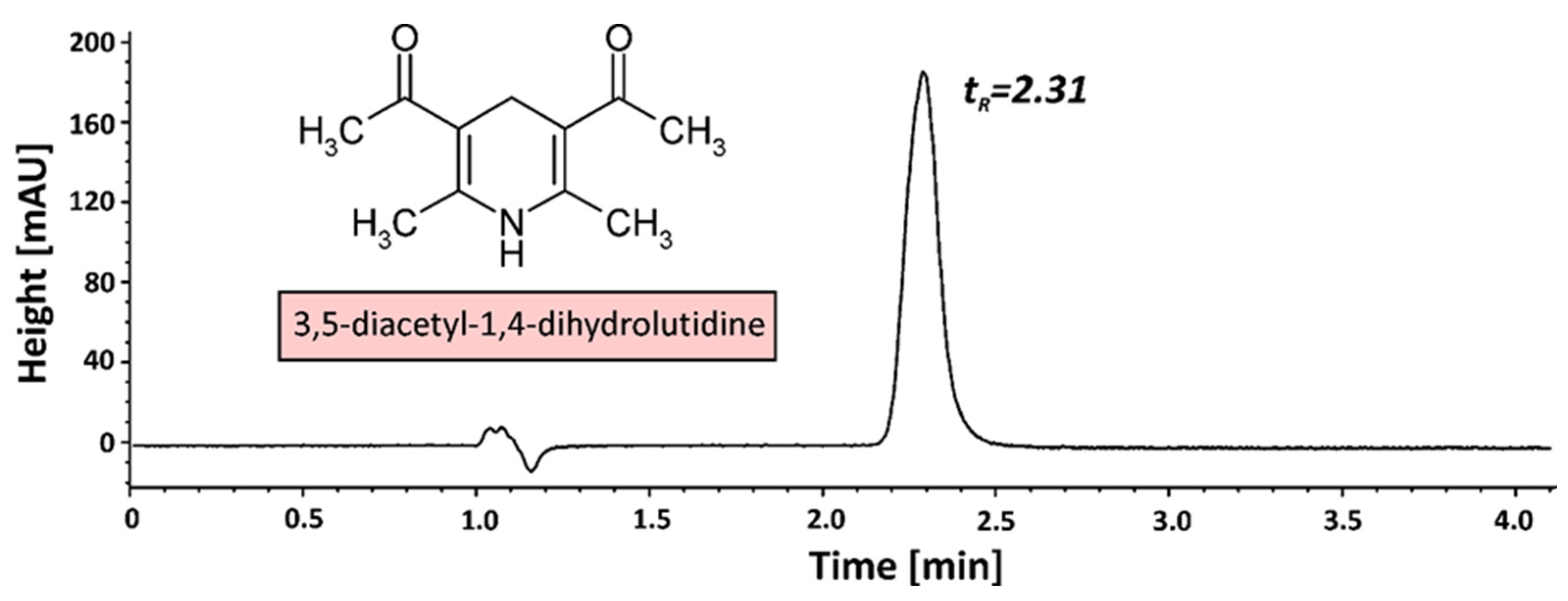
2.6. Derivatization of Formaldehyde
2.7. DES-TF-SPME Procedure
2.8. HPLC Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Sorbent Material and Solvent for Desorption
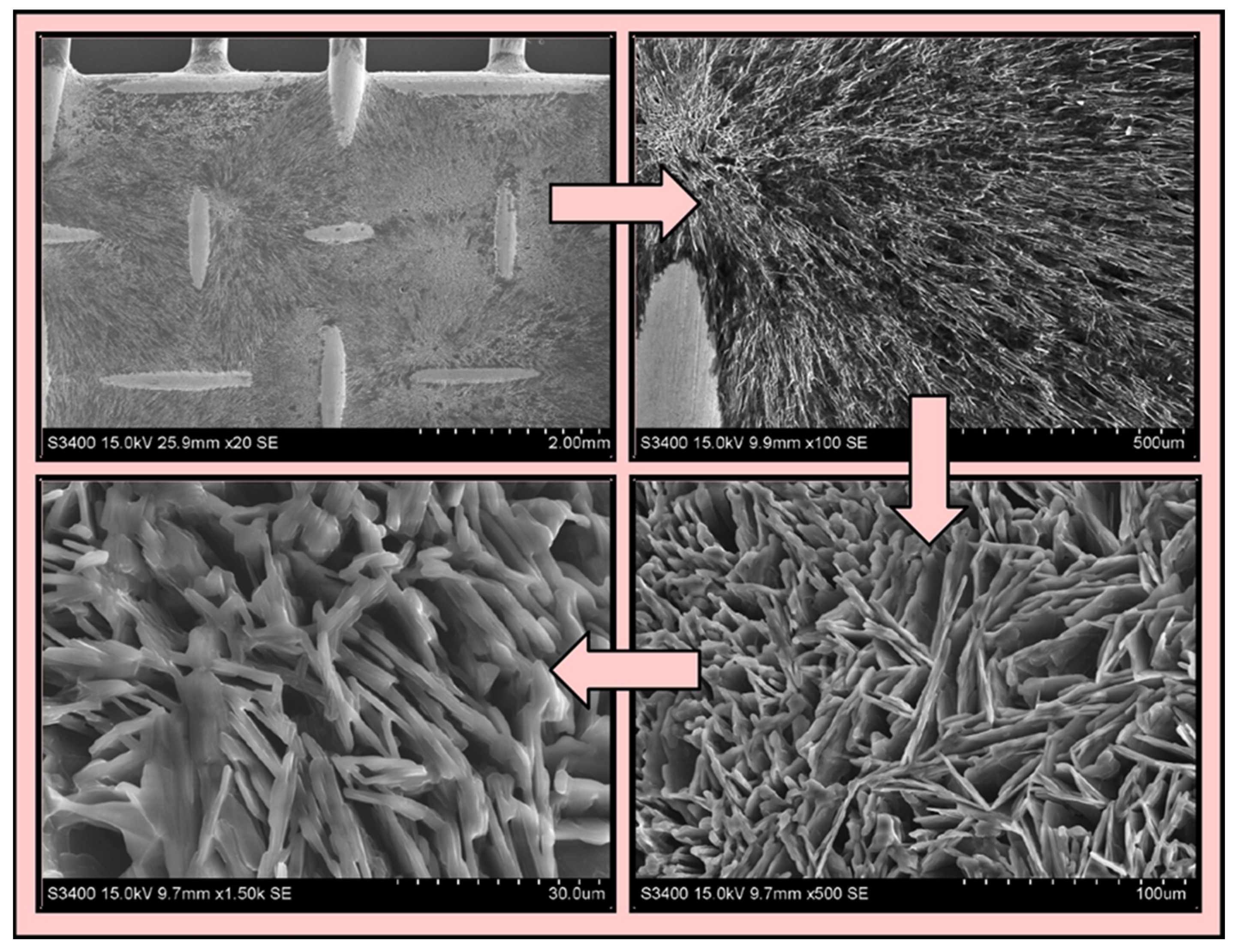
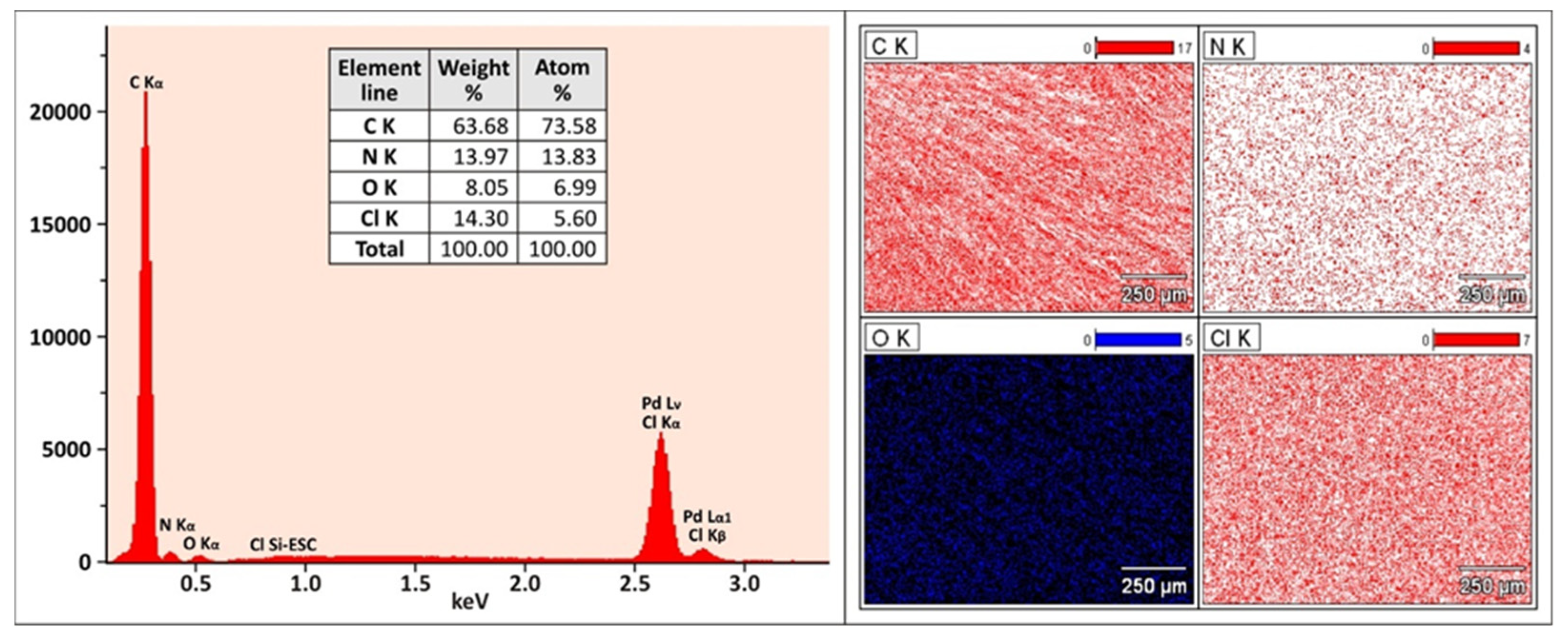
3.2. Characterization of the Selected Coating Sorbent
3.3. Optimization of DES-TF-SPME Conditions
3.3.1. Volume of Samples
3.3.2. The pH of Samples
3.3.3. The Addition of NaCl
3.3.4. The Time of Extraction
3.3.5. The Time of Desorption
3.4. Analytical Performance
3.5. Application of the Method to Surface Water Samples
3.6. Reusability of the Sorbent
3.7. Comparison with Different Microextraction Methods Used for Determination of Formaldehyde in Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qu, M.; Lu, J.; He, R. Formaldehyde from Environment. In Formaldehyde and Cognition; He, H., Ed.; Springer Science + Business Media B.V.: Berlin, Germany, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.H.; Jahan, S.A.; Lee, J.T. Exposure to formaldehyde and its potential human health hazards. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2011, 29, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammalleri, V.; Pocino, R.N.; Marotta, D.; Protano, C.; Sinibaldi, F.; Simonazzi, S.; Petyx, M.; Iavicoli, S.; Vitali, M. Occupational scenarios and exposure assessment to formaldehyde: A systematic review. Indoor Air 2022, 32, e12949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norliana, S.; Abdulamir, A.S.; Abu Bakar, F.; Salleh, A.B. The health risk of formaldehyde to human beings. Am. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 4, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenberg, J.A.; Moeller, B.C.; Lu, K.; Rager, J.E.; Fry, R.C.; Starr, T.B. Formaldehyde carcinogenicity research: 30 years and counting for mode of action, epidemiology, and cancer risk assessment. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 41, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.F.; Peng, J.F.; Chi, Y.G.; Jiang, G.B. Determination of formaldehyde in shiitake mushroom by ionic liquid-based liquid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography. Talanta 2005, 65, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, J.; Shams, G.R.; Meighani, H. Application of low density miniaturized dispersive liquid-liquid extraction method for determination of formaldehyde in aqueous samples (water, fruit juice and Streptococcus vaccine) by HPLC-UV. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 70, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Lu, R.; Zhou, W. Use of ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and high-performance liquid chromatography to detect formaldehyde in air, water, and soil samples. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2014, 37, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, P.; Chisvert, A.; Alonso, A.J.; Hernandorena, S.; Salvador, A. Determination of free formaldehyde in cosmetics containing formaldehyde-releasing preservatives by reversed-phase dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and liquid chromatography with post-column derivatization. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1543, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, A.; Ahmadi, R.; Ramezani, A.M. Vortex-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction based on hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for determination of malondialdehyde and formaldehyde by HPLC-UV approach. Microchem. J. 2018, 143, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, C.; Li, S.; Fan, J. A hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent based vortex-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of formaldehyde from biological and indoor air samples by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1589, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Su, R.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Determination of formaldehyde in beverages using microwave-assisted derivatization and ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 2011, 85, 2632–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Ghambarian, M.; Salemi, A.; Es-Haghi, A. Trace determination of free formaldehyde in DTP and DT vaccines and diphtheria–tetanus antigen by single drop microextraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zali, S.; Jalali, F.; Es-Haghi, A.; Shamsipur, M. Determination of free formaldehyde in vaccines and biological samples using solid-phase microextraction coupled to GC–MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 3883–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos, P.A.; Pawliszyn, J. Sampling and determination of formaldehyde using solid-phase microextraction with on-fiber derivatization. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 2311–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziel, J.A.; Noah, J.; Pawliszyn, J. Field sampling and determination of formaldehyde in indoor air with solid-phase microextraction and on-fiber derivatization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavilla, I.; Cabaleiro, N.; Pena, F.; de la Calle, I.; Bendicho, C. Ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction with simultaneous derivatization coupled to fibre optics-based cuvetteless UV–vis micro-spectrophotometry for formaldehyde determination in cosmetic samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 674, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochetkova, M.; Timofeeva, I.; Bulatov, A. A derivatization and microextraction procedure with organic phase solidification on a paper template: Spectrofluorometric determination of formaldehyde in milk. Spectrochim. Acta A 2021, 263, 120160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, C.F.; Brasil, M.A.S.; Costa, S.P.F.; Pinto, P.C.A.G.; Saraiva, M.L.M.F.S.; Rocha, F.R.P. Exploitation of pulsed flows for on-line dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction: Spectrophotometric determination of formaldehyde in milk. Talanta 2015, 144, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz, M.; Alvarado, J.; Pena-Pereira, F.; Senra-Ferreiro, S.; Lavilla, I.; Bendicho, C. Liquid-phase microextraction with in-drop derivatization combined with microvolume fluorospectrometry for free and hydrolyzed formaldehyde determination in textile samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 687, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beránek, J.; Kubátová, A. Evaluation of solid-phase microextraction methods for determination of trace concentration aldehydes in aqueous solution. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1209, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvand, M.; Bozorgzadeh, E.; Shariati, S.; Zanjanchi, M.A. Ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of formaldehyde in wastewaters and detergents. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 7597–7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, R.T.; Topiwala, V. Quantitative determination of formaldehyde in cosmetics using a combined solid-phase microextraction–isotope dilution mass spectrometry method. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1029, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, C.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid phase microextraction with thermal desorption using fused silica optical fibers. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 2145–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Garces, N.; Gionfriddo, E.; Gomez-Rıos, G.A.; Alam, M.N.; Boyacı, E.; Bojko, B.; Singh, V.; Grandy, J.; Pawliszyn, J. Advances in solid phase microextraction and perspective on future directions. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 302–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M.; Nazal, M.K.; Rutkowska, M.; Szczepańska, N.; Namieśnik, J.; Płotka-Wasylka, J. Solid phase microextraction: Apparatus, sorbent materials, and application. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2019, 49, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piri-Moghadam, H.; Alam, M.N.; Pawliszyn, J. Review of geometries and coating materials in solid phase microextraction: Opportunities, limitations, and future perspectives. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 984, 42–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barkhordari, A.; Ghiasvand, A.; Jalili, V. A comprehensive look at solid-phase microextraction technique: A review of reviews. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104319. [Google Scholar]
- Lashgaria, M.; Yaminia, Y. An overview of the most common lab-made coating materials in solid phase microextraction. Talanta 2019, 191, 283–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruheim, I.; Liu, X.; Pawliszyn, J. Thin-film microextraction. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olcer, Y.A.; Tascon, M.; Eroglu, A.E.; Boyacı, E. Thin film microextraction: Towards faster and more sensitive microextraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.; et al. Deep eutectic solvents: A review of fundamentals and applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Achkar, T.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fourmentin, S. Basics and properties of deep eutectic solvents: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Zhang, H.; Row, K.H. Application of deep eutectic solvents in the extraction and separation of target compounds from various samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, J.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Grześkowiak, T. Development of novel thin-film solid-phase microextraction materials based on deep eutectic solvents for preconcentration of trace amounts of parabens in surface waters. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14184-1:2011; Textiles—Determination of Formaldehyde—Part 1: Free and Hydrolysed Formaldehyde (Water Extraction Method). International Organization of Standarization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Rohyami, Y.; Pribadi, R.M. Validation of Methods on Formalin Testing in Tofu and Determination of 3,5-diacetyl-dihydrolutidine Stability by UV-Vis Spectrophotometry. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1911, 020018. [Google Scholar]
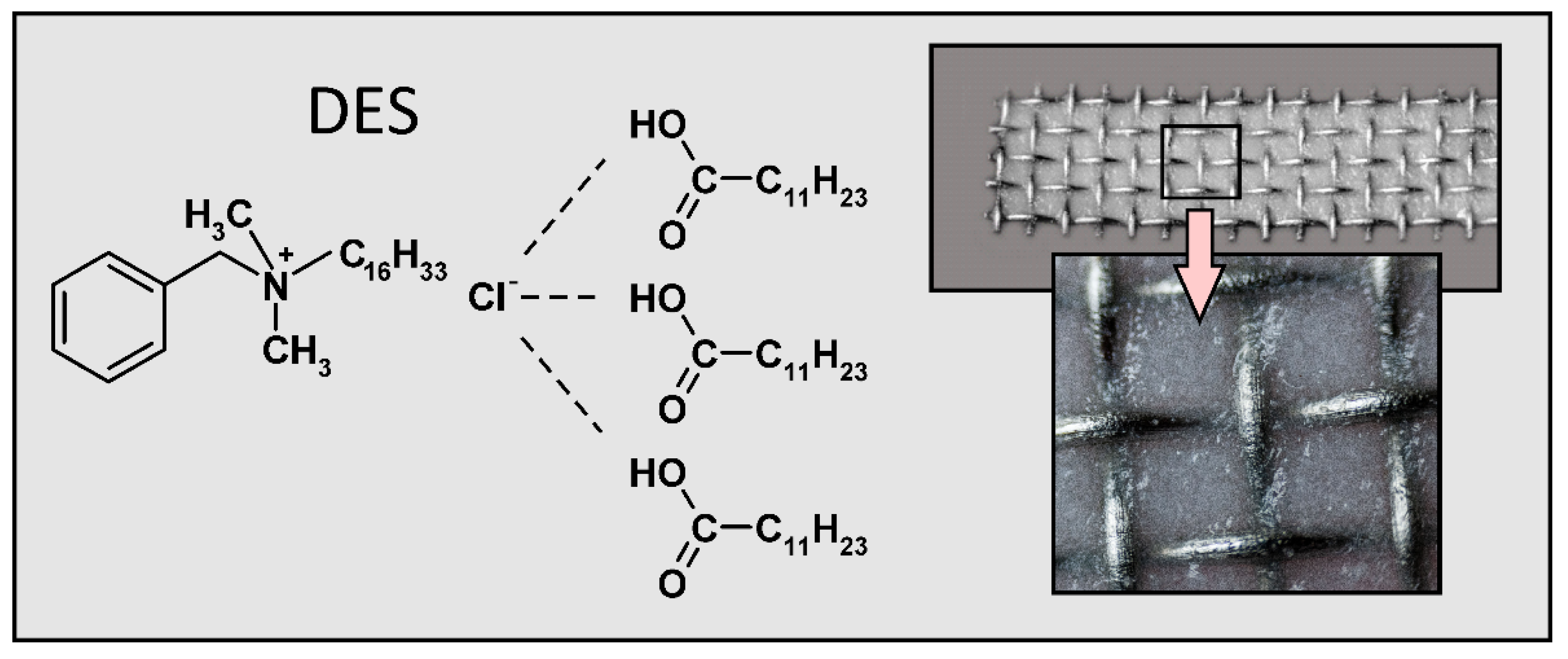
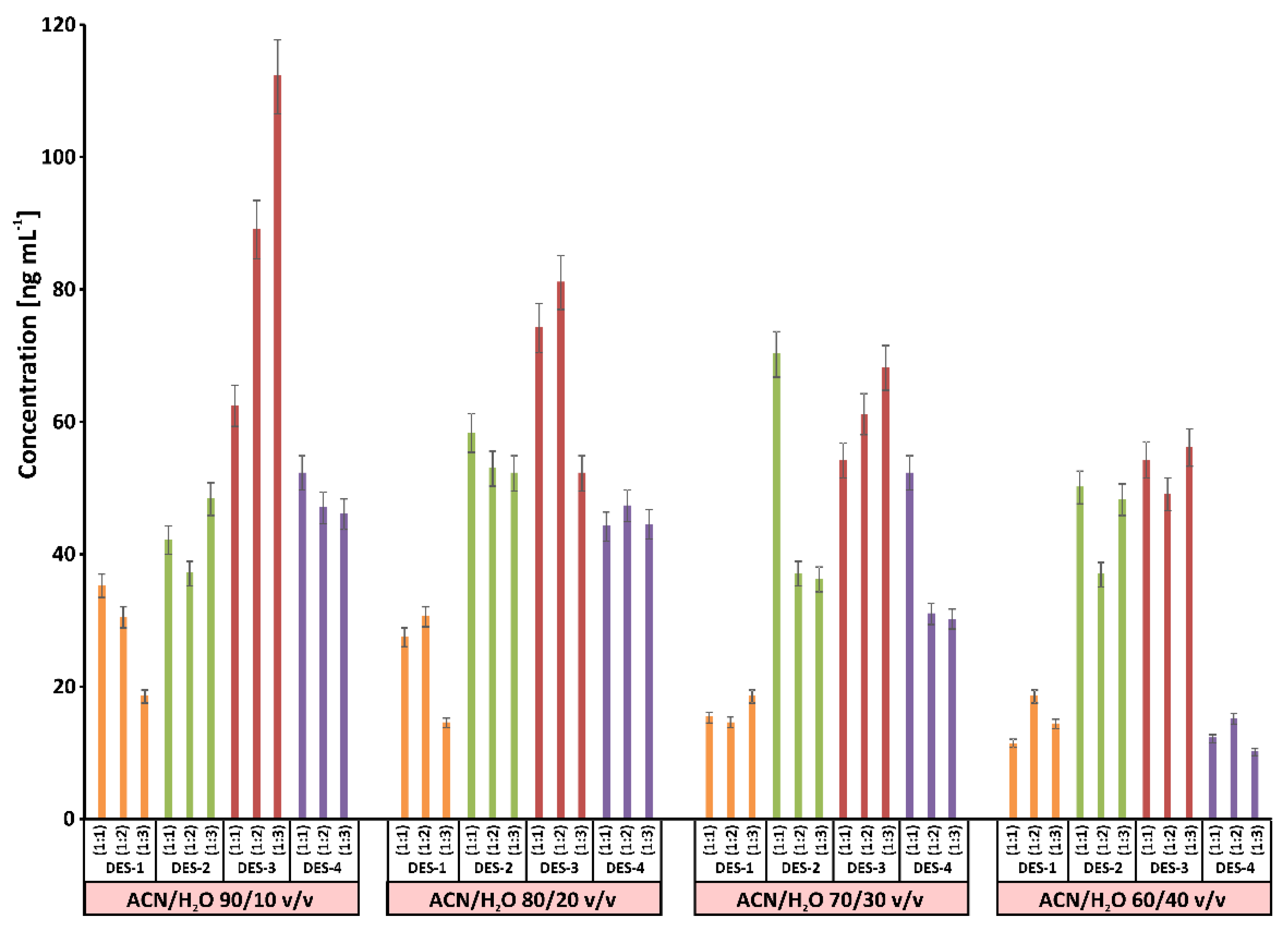


| DES | HBA:HBD (Molar Ratio) | Structure of HBA | Structure of HBD |
|---|---|---|---|
| DES-1 | 1:1 | 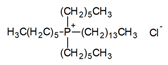 | 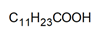 |
| 1:2 | |||
| 1:3 | |||
| DES-2 | 1:1 |  | 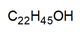 |
| 1:2 | |||
| 1:3 | |||
| DES-3 | 1:1 | 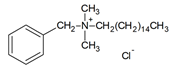 |  |
| 1:2 | |||
| 1:3 | |||
| DES-4 | 1:1 | 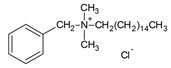 |  |
| 1:2 | |||
| 1:3 |
| Tested Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Linear range [ng mL−1] | 0.5–125 |
| Regression equation | y = 28.37x + 1.23 |
| Determination coefficient (r2) | 0.9995 |
| Single sorbent RSD [%] (n = 4) | 3.3 |
| Sorbent-to-sorbent RSD [%] (n = 4) | 4.8 |
| Recovery [%] | 86.1 |
| Enrichment Factor | 178 |
| LOD [ng mL−1] | 0.15 |
| LOQ [ng mL−1] | 0.50 |
| Sample of Natural Water | Initial [ng mL−1] | Spiked [ng mL−1] | Measured [ng mL−1] | RSD [%] (n = 4) | RR [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malta Lake | nd | 0.5 | 0.41 ± 0.06 | 14.6 | 82.0 |
| 5.0 | 4.55 ± 0.19 | 4.2 | 91.0 | ||
| 10.0 | 9.88 ± 0.45 | 4.6 | 98.8 | ||
| Baba Lake | nd | 0.5 | 0.39 ± 0.07 | 17.9 | 78.0 |
| 5.0 | 4.58 ± 0.22 | 4.8 | 91.6 | ||
| 10.0 | 9.74 ± 0.40 | 4.1 | 97.4 | ||
| Kórnickie Lake | nd | 0.5 | 0.48 ± 0.09 | 18.8 | 96.0 |
| 5.0 | 4.34 ± 0.43 | 9.9 | 86.8 | ||
| 10.0 | 9.91 ± 0.38 | 3.8 | 99.1 | ||
| Cybina River | nd | 0.5 | 0.43 ± 0.07 | 16.3 | 86.0 |
| 5.0 | 4.45 ± 0.14 | 3.2 | 89.0 | ||
| 10.0 | 9.67 ± 0.35 | 3.6 | 96.7 | ||
| Warta River | nd | 0.5 | 0.45 ± 0.08 | 17.8 | 90.0 |
| 5.0 | 4.21 ± 0.17 | 4.0 | 84.2 | ||
| 10.0 | 9.54 ± 0.31 | 3.3 | 95.4 |
| Extraction Cycle | Concentration [ng mL−1] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sorbent 1 | Sorbent 2 | Sorbent 3 | |
| 1 | 41.5 | 41.9 | 42.0 |
| 2 | 41.9 | 41.7 | 41.6 |
| 3 | 41.4 | 41.3 | 41.7 |
| 4 | 41.2 | 41.4 | 41.1 |
| 5 | 38.4 | 38.9 | 39.1 |
| Average | 40.9 | 41.0 | 41.1 |
| RSD [%] | 3.4 | 3.0 | 2.8 |
| Microextraction Method | Detection Technique | Sorbent or Extractant | Derivatization Agent | Sample | LOD [ng mL−1] | RSD [%] | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPME | GC-FID | PDMS/DVB | PFBHA | hair gel particle board indoor air | - * | - * | [15,16] |
| SPME | ID-MS | PDMS/DVB | PFPH | Cosmetic products | 3.9 | 3.8–7.8 | [23] |
| USAEME | micro-SP | CH2Cl2 | Nash reagent | Cosmetic products | 0.02 | 5.9 | [17] |
| IL-DLLME | HPLC-UV | [C8MIM][PF6] | DNPH | room air, tap water, soils | 0.01 | 1.3–6.8 | [8] |
| LDM-DLLME | HPLC-UV | BA:MEOH | DNPH | tap water, juice, vaccine | 0.05 | 3.0–8.0 | [7] |
| RP-DLLME | HPLC-UV/Vis | H2O | Nash reagent | Cosmetic products | 0.7 | 1.9–9.2 | [9] |
| DES-VA-LLME | HPLC-DAD | TAC:CP (1:1) | DNPH | indoor air | 0.2 ** | 1.1–3.5 | [10] |
| AA-DLLME-SPO | SF | thymol | Nash reagent | milk | 15 | ˂9.0 | [18] |
| DES-TF-SPME | HPLC-UV/Vis | DES | Nash reagent | lake water river water | 0.15 | 3.3–4.8 | this work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Werner, J.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Grześkowiak, T. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Coating Sorbent for Preconcentration of Formaldehyde by Thin-Film Solid-Phase Microextraction Technique. Processes 2022, 10, 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10050828
Werner J, Zgoła-Grześkowiak A, Grześkowiak T. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Coating Sorbent for Preconcentration of Formaldehyde by Thin-Film Solid-Phase Microextraction Technique. Processes. 2022; 10(5):828. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10050828
Chicago/Turabian StyleWerner, Justyna, Agnieszka Zgoła-Grześkowiak, and Tomasz Grześkowiak. 2022. "Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Coating Sorbent for Preconcentration of Formaldehyde by Thin-Film Solid-Phase Microextraction Technique" Processes 10, no. 5: 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10050828
APA StyleWerner, J., Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A., & Grześkowiak, T. (2022). Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Coating Sorbent for Preconcentration of Formaldehyde by Thin-Film Solid-Phase Microextraction Technique. Processes, 10(5), 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10050828








