Abstract
Waste management solutions including the valorization of waste materials in biotechnological processes is an important issue needing to be explored. A significant amount of waste is being generated by the food industry. In this study, an attempt was made to utilize two fish industry wastes simultaneously—waste brine and post-frying oil from frying fish fillets in Yarrowia lipolytica culture with high single cell oil synthesis yield. Oxygenation in the culture medium had a positive effect on the biosynthesis efficiency of microbial oil, resulting in the highest content of lipids in yeast cells at the level of 0.431 g/g d.m (dry mass). Y. lipolytica yeast preferentially accumulated oleic acid and linoleic acid, and the high content of linolenic acid, valuable from a nutritional point of view, was also found in microbial oil. This study proved that the use of post-frying rapeseed oil gives a chance to obtain valuable storage lipids in Y. lipolytica yeast cells via ex novo biosynthesis pathway. Furthermore, the wastewater stream could be limited using a waste brine as a solvent in medium preparation, but the brine share should not exceed 30% so as not to inhibit yeast cell growth.
1. Introduction
In 2015, the total amount of fishery products was estimated at 169.2 million tonnes, of which 6.4 million tonnes were accounted for by European Union countries. The largest producers of fishery and fish products in the EU are Spain, Denmark, Great Britain and France [1]. In 2018, the global fish production exceeded 178 million tonnes, and the world’s appetite for fish and fish products shows no sign of slowing. China, Indonesia, Peru, India, the Russian Federation, the United States of America and Vietnam are countries accounting for almost 50% of total global capture fish production, but global aquaculture production of farmed aquatic animals has been dominantly in Asia (89% share) [2].
The maritime economy includes fishing and fish processing, and in the light of circular economy, the waste management solutions related to the fish industry are particularly important. Food waste is a global problem, and it is closely related to the unnecessary use of water, packaging and energy [3,4]. Failure to reuse industrial by-products leads to an increase in the costs of their disposal. Industrial waste can pose a serious burden to the environment through its impact on flora and fauna. Unprocessed wastes are a habitat for pathogenic microflora that can reach farmlands, and thus, along with the crops, reach consumers’ tables [5,6]. It is recommended by the Sustainable Development Goals by United Nations to halve per capita global food waste at the retail and consumer levels and reduce food losses along production and supply chains, including postharvest losses [7].
A large proportion of fisheries and aquaculture production is either lost or wasted (35% of the global harvest) [2]. Fish is a perishable food that has a high potential for waste and loss [7]. Wastes generated by the fish industry are one of the most onerous in terms of sewage disposal. Difficulties in their management are related to high content of water, organic matter and susceptibility to oxidation. On the other hand, the waste can be a source of protein, fats or mineral salts [8]. The by-products of the fish processing are rejected in the technological process and are not intended for consumption and therefore cannot be called “food”. However, they can be used in the production of silages, forages, biogas, biodiesel, etc. [3,4]. Still, a significant part of them is neither consumed nor utilized.
Biotechnological methods for utilizing food processing wastes are desired. Bacteria or yeasts are involved to colonize contaminated environments and allow the reuse of wastes by their valorization into, e.g., various enzymatic proteins or metabolites of microbiological origin [9,10]. For the described purposes, especially Yarrowia lipolytica yeast can be used due to its ability to grow in media with various energy and carbon waste sources. The yeast use hydrophobic substrates, e.g., waste oils and other lipid-rich materials [11,12,13]. In recent years, many efforts have been made to produce microbial lipids using waste materials as substrates to lower cost of the biotechnological production. In the current study, batch cultures of Y. lipolytica KKP 379 were carried out in a laboratory bioreactor with the use of fishery industry wastes. Rapeseed waste oil from the frying process of fish fillets was applied as a carbon source, and waste brine was investigated as a solvent for yeast growth medium ingredients. Some factors influencing ex novo single cell oil synthesis such as oil alkaline hydrolysis, culture oxygenation regulation and variable content of the inorganic nitrogen source were studied. A concept of the simultaneous utilization of two different fish industry wastes has been proposed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yeast Strain
The Y. lipolytica KKP 379 wild-type strain was purchased from the Collection of Industrial Microorganisms at the prof. Wacław Dąbrowski Institute of Agricultural and Food Biotechnology-State Research Institute in Warsaw, Poland. The strain was stored in 20% (v/v) glycerol solution in nutrient YPG broth (yeast extract 1%, peptone 2%, glucose 2%) at −20 °C.
2.2. Fish Processing Wastes
The rapeseed post-frying waste oil was collected in tanks after the frying of fish fillets of cod in the fish factory located in the Podlaskie Voivodeship in Poland. The brine was gained from the same fish factory and was characterized by 17.6% NaCl concentration, 3.0% (m/m) lipid content, 0.23 g/dm3 reducing sugars content and pH 6.4.
2.3. Culture Conditions
Inoculum shaken cultures were provided in YPG medium (in 1.0 dm3: yeast extract, 10.0 g; peptone, 20.0 g; glucose, 20.0 g; pH 5.0) at 28 °C for 24 h.
Shaken cultures were provided in modified YPG medium with post-frying waste oil (20.0 g/dm3) replacing glucose (YPpfWO medium). Waste brine was used to dissolve medium ingredients in amounts from 0 to 100% along with distilled water. Additionally mineral media with 50 g/dm3 post-frying waste oil and 2.5 g/dm3 (NH4)2SO4 were prepared using from 0 to 30% waste brine along with distilled water for medium preparation. Mineral media also contained g/dm3: KH2PO4, 7.0; Na2HPO4, 2.5; FeSO4 × H2O, 0.16; CaCl2, 0.15; MnCl2 × 4H2O, 0.08; ZnSO4, 0.02. The initial pH of medium was estimated at 6.0 based on previous work [13,14].
Bioreactor cultures in a BIO FLO 3000 (New Brunswick, Hamburg, Germany) were provided at 28 °C and 0.0375% (v/v) inoculum, as described by Fabiszewska et al. [14]. Mineral media with 50 g/dm3 post-frying waste oil were prepared for bioreactor cultures, as described previously. (NH4)2SO4 was added as nitrogen source according to Table 1. Post-frying waste oil was pre-treated with 3.0% (m/v) NaOH at 70 °C for 24 h and neutralized with HCl. Brine was added to some variants of media replacing the corresponding amount of water. All medium ingredients were purchased from BTL (Łódź, Poland) and Avantor Performance Materials Poland S.A (Gliwice, Poland).

Table 1.
Media and culture conditions in bioreactor experiments.
To determine the pH of culture, a pH glass electrode was used. Medium was aerated with compressed air at a flow of 150 dm3/h per 1 dm3 medium. During batch culture with regulated aeration, variable speed of the agitator changed from 200 to 600 rpm, so that the oxygen level remained within 20% of the initial oxygenation of the substrate (the cascade system of regulation of the oxygenation level). The detailed parameters of batch cultures are presented in Table 1.
2.4. Simple Culture Measurements
Yeast cells were harvested by centrifugation (8000 rpm, 10 min, 4 °C) and washed twice in distilled water in order to remove residual waste oil. Cell dry mass of yeast biomass was measured by drying at 105 °C until constant weight.
Yeast cells were enumerated by pour plating of YPG medium with 2% agar. Subsequent serial 10-fold dilutions were made. Microorganisms were determined in triplicate.
Determination of citric acid content was conducted by enzymatic method according to the manufacturer’s protocols for colorimetric citric acid assay kit (Boehringer, Mannheim, Germany).
2.5. Cellular oil Extraction and Fatty Acids Profile Determination
Cellular lipids were extracted and analyzed by gas chromatography method with FID detector according to Fabiszewska et al. [15]. Fatty acids were derivatized to methyl esters with 10% BF3 and 1M sodium methoxide. Moreover, 30 g of wet biomass was dried at 80 °C. Extraction was performed in Soxhlet extractor using n-hexane as a solvent. The residual content of lipid carbon source in medium was determined by twice lipid extraction from 10 cm3 of medium with n-hexane and measuring of oil weight after solvent evaporation under 360 mbar pressure.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed of repeated measurements with the one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test and analysis of correlation using STATISTICA 13.1 (Statsoft, Poland). p-values lower than 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. The Shapiro–Wilk test was used to check if the populations were normally distributed, while Levene’s test and the Brown–Forsythe test were used to assess the equality of variances for a variable calculated for groups. Flask cultures were provided in triplicate, and bioreactor cultures were provided in duplicate. Data are expressed as mean with standard deviation.
3. Results
3.1. Waste Post-Frying Rapeseed Oil Management in Y. lipolytica Culture
In order to evaluate the ability of Y. lipolytica KKP 379 to grow in medium with waste post-frying rapeseed oil as a carbon source, three batch cultures yeast were carried out in a laboratory bioreactor under the parameters presented in Table 1; the results are presented in Figure 1. Alongside the effect of the regulation of medium oxygenation, the method of waste oil pre-treatment and the ratio of the carbon source to the nitrogen source were investigated.
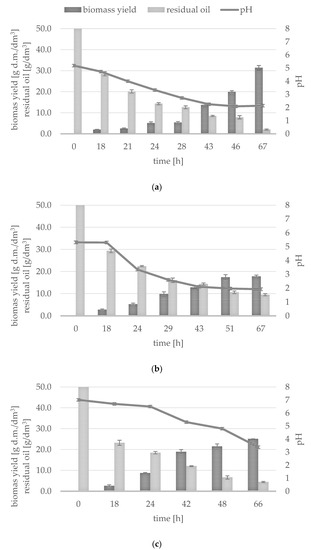
Figure 1.
Changes in biomass yield, residual oil and medium pH during Y. lipolytica culture in media: (a) A -pfWO-N-0.25-Aer-reg, (b) B-pfWO-N-0.50-no-Aer-reg, (c) C-H-pfWO-N-0.25-no-Aer-reg (for abbreviation see Table 1).
The first batch of culture was carried out in a synthetic medium with a 5% addition of post-frying waste as a carbon source (A-pfWO-N-0.25-Aer-reg; Figure 1a). The substrate oxygenation control was also applied, which consisted in maintaining the level of aeration at no lower than 20% of the initial oxygen concentration. The lag phase of the yeast culture lasted about 12 h (data not shown). After this time, the cells entered the logarithmic growth phase, which continued until the end of the experiment. Initially, the pH of the substrate was 5.19. At 33 h of cultivation, a decrease in pH to 2.21 was observed. An increase in the biomass yield was observed, initially insignificant up to 28 h, amounting to 5.37 g d.m./dm3, and then from 28 to 43 h during the logarithmic growth phase, when the biomass yield increased more than twice (13.70 g d.m./dm3). During the next 3 h of culture, the biomass yield increased to 19.93 g/dm3, and finally, after 67 h, it amounted 31.73 g/dm3. The residual oil content was also analyzed. The decrease in the waste oil content in the medium was observed, and after 18 h, its concentration was almost twofold lower and subsequently decreased throughout the culture, where, at the end of the cultivation, only 2 g/dm3 of residual oil was determined, which means 96% of the initial amount of post-frying oil was used by yeasts.
The second batch of culture was carried out in a synthetic medium with the same carbon source, but no oxygenation regulation was applied (B-pfWO-N-0.50; Figure 1b). The modification of the medium composition concerned the nitrogen level. The medium was supplemented with a double dose of ammonium sulphate (5.0 g/dm3) in relation to its concentration in the first culture described above. In the case of pH, both cultures were comparable, and the decrease in the pH level to 1.92 was observed. Taking into account the changes in the analyzed parameter and the course of the previous culture, it can be concluded that the lag phase was longer and lasted about 17 h. After this time, the phase of logarithmic growth of yeast cells began, as evidenced by an abrupt drop in the pH of the medium. This is also confirmed by the analysis of the yeast biomass yield. During the 67-h culture, the biomass yield was 2.81 g/dm3 in 18 h, 5.29 g/dm3 in 24 h and 12.88 g/dm3 in 43 h. Then, in 51 h and in the last hour, it was similar and did not exceed the value of 18.0 g/dm3. Waste oil decreased the most at the time when the cells were in the logarithmic growth phase. From the initial concentration of 50 g/dm3, its content decreased to about 30 g/dm3 after 18 h, and then its amount lowered. After the first day of the cultivation, it was at the level of 22.46 g/dm3. Finally, the content of the lipid substrate in the medium decreased five times from the initial value.
In the third culture carried out in a laboratory bioreactor (C-H-pfWO-N-0.25; Figure 1c), the waste carbon source in the form of post-frying rapeseed oil was subjected to alkaline hydrolysis. Compared to other cultures, the initial pH of the culture was much higher, but in a similar way, it decreased during yeast growth. After 2 days of cultivation, the pH value was approximately 5.0, reaching the value of 3.38 at the end of the culture.
In the yeast growth period lasting 66 h, the biomass content in the culture medium was 8.76 g/dm3 at the end of the first day. After the yeast cells entered the logarithmic growth phase, a twofold increase in the biomass yield was observed, and at the end of the culture, it reached the value of 25.14 g/dm3. In the case of the third culture, the course of utilization of the lipid carbon source was similar to that obtained in the previous cultures. Initially, a bright decrease in the oil content to 20.35 g/dm3 was measured. After 24 h of cultivation, its amount dropped to 18.45 g/dm3, and on the second day, it was only 6.61 g/dm3.
In order to evaluate the influence of selected factors on the efficiency of the biosynthesis of microbial oils by the yeast strain Y. lipolytica KKP 379, the results were compiled in the form of lipid content in yeast biomass cells (Table 2). The amounts of lipids extracted from yeast cells were statistically significantly different for each of the three culture variants. On the basis of the obtained results, it can be concluded that access to oxygen played a key role in the cultivation process, where the highest cellular lipid content (0.43 g/g d.m.) was obtained for the culture in which the regulation of the oxygenation of the culture medium was applied.

Table 2.
Citric acid concentration in medium and cellular lipids content in yeast cells grown in culture media with waste post-frying oil.
Citric acid concentration was determined in tested media during lag phase (approx. 24th h of the culture) and log phase (at the end of the culture). The results presented in Table 2 acknowledge that Y. lipolytica KKP 379 is capable of synthesizing citric acid alongside the single cell oil. The measurement of the content of this organic acid after 24 h of cultivation revealed that its content was low and ranged from 0.01 to 0.08 g/dm3. Definitely higher results were obtained when the yeasts were in the logarithm growth phase, and citric acid concentrations ranged from 0.08 to 0.78 g/dm3. The highest concentration of the described acid was found in the culture with hydrolyzed waste oil and amounted to 0.78 g/dm3.
3.2. Brine Management in Y. lipolytica Culture
Shaken cultures were performed to investigate Y. lipolytica yeast biomass growth in rich media with post-frying oil prepared with various contents of brine (Table 3). Additionally, it was assessed how the brine influenced the number of viable yeast cells in the culture medium during the experiment.

Table 3.
Cell dry mass and yeast cells number in YPpfWO flask shaken cultures of Y. lipolytica. Medium ingredients were dissolved with distilled water and waste brine at different proportions. The values with the same letter in a column did not differ significantly (α = 0.05).
The highest average yield of biomass was obtained in medium without brine (16.2 g d.m./dm3, Table 3). An equally high average yield and insignificant yield was obtained with the contents of 10% and 20%, respectively, 15.7 and 14.7 g d.m./dm3. However, from 40% of the brine content in the culture medium, the average biomass yield decreased. At 80% and 100% brine share, a significant reduction in the yield of biomass could be observed. Research showed that the number of yeast cells in the medium decreased with the increase in the brine share. The highest number of cells at the level of 9.0 log CFU/cm3 was observed at the brine content up to 20% that corresponded to the biomass yield. Slightly lower cell numbers (7.0–8.0 log CFU/cm3) were observed with the brine content of 40% and 60%, while with 80% and 100% brine share, the yeast cells’ growth was significantly inhibited.
The first set of analyses in shaken culture experiment highlighted the possibility of Y. lipolytica growth in medium with waste brine. Secondly, there were selected parameters of culture in a laboratory bioreactor which aimed at the synthesis of microbial oil. The key ingredient of the culture medium was post-frying waste oil. In the experiment, brine was used in an amount of 20% of the final medium volume (NaCl concentration in medium was 5.6%), and inorganic salts were the source of nitrogen, phosphorus and other elements. The culture medium was intensively oxygenated, and the oxygen concentration was kept at a level not lower than 20% of its initial content in the medium. The lag phase lasted about 16 h, while after 2 h there was a sharp decrease in the level of medium oxygenation (Figure 2a). Only after 56 h the yeast cells entered the stationary growth phase, and the medium oxygenation increased to about 40%. In the logarithmic growth phase, a decrease in pH to about 2 could be observed that is typical for intracellular lipid synthesis process. The biomass yield was significantly twice lower than that measured in medium A (Figure 1a) and amounted to 14.3 g d.m./dm3 after 64 h (Figure 2b). The highest content of intracellular lipids was recorded in the stationary growth phase, and it slightly exceeded 0.2 g/g d.m. The decrease in waste substrate content took place until the end of the culture, however, after 24 h, a milder decrease in the concentration of waste carbon source could be noticed. In the lag phase, the greatest use of the carbon source from the culture medium was noted, while in the logarithmic phase, the biomass yield and the synthesis efficiency of microbial oil increased.
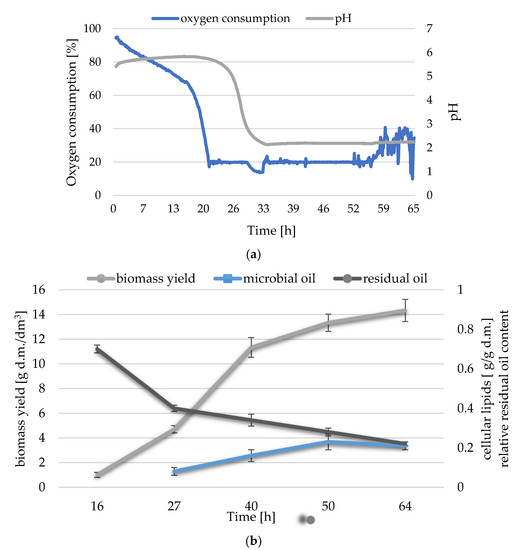
Figure 2.
Changes in (a) pH and oxygen consumption and (b) biomass yield, cellular lipids content and relative residual oil content during a batch culture of Y. lipolytica in medium D-pfWO-N-0.25-Aer-reg.
3.3. Characteristics of Microbial Oil—Fatty Acids Profile
Waste oil after frying the fish is characterized by a high content of oleic acid, 60.12%, of which belongs to the group of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) (Table 4). It also contained linoleic and linolenic acids, which amounted 11.90% and 4.26%, respectively. Unsaturated fatty acids accounted for 23.71%. A significant fact was that the fatty acid profile in microbial oil reflected the composition of initial carbon substrate and was characterized by 62.42% content of oleic acid, and unsaturated fatty acids were present at the level of 19.76%. The highest content of oleic acid could be found in residual oil. The substrate remaining in the medium did not contain myristic, behenic and erucic acids. Nevertheless, comparing the fatty acid profile of initial substrate and residual oil, it can be concluded that the yeast cell did not absorb any fatty acid preferentially.

Table 4.
Comparison of fatty acid content in lipids synthesized in cells during Y. lipolytica batch cultures in D-pfWO-N-0.25 medium with fatty acid content in initial carbon substrate and lipids remaining in culture medium—residual oil (abbreviations: C14:0—myristic acid, C16:0—palmitic acid, C18:0—stearic acid, C18:1—oleic acid, C18:2—linoleic acid, C18:3—linolenic acid, C20:0—arachidic acid, C22:0—behenic acid, C22:1—erucic acid).
4. Discussion
4.1. Bioreactor Batch Cultures of Y. lipolytica in Media with Post-Frying Oil
Waste post-frying rapeseed oil occurred as an easily digestible source of carbon for the yeast species and allowed for growth and the production of some metabolites such as storage lipids and citric acid. Strong evidence was found that factors influencing the biomass yield and the synthesis of microbial oil by Y. lipolytica yeast were the access of oxygen and the pH of the culture medium. Oxygenation of the culture medium is an important parameter referring to biomass yield and lipid synthesis efficiency of both de novo and ex novo routes. Interesting observations were made by Rakicka et al. [16]. Using the strain Y. lipolytica JMY4086, the effect of various oxygenation conditions was analyzed. Three strategies were applied: (a) the oxygenation degree of the culture was not regulated, agitation speed of 800 rpm and the airflow rate of 1.5 dm3/min; (b) oxygenation maintained at the level of 50% with amplitude of stirrer of 200–1000 rpm and air-flow of 0–3.5 dm3/min; (c) a high level of culture oxygenation with 800 rpm and air-flow in the range from 0–3.5 dm3/min. In the case of the obtained results, increasing the oxygenation did not increase the lipid yield, and the highest efficiency of lipids production (0.31 g/g) was obtained in the culture without the regulation of aeration. On the other hand, the highest biomass yield (59 g d.m./dm3) was recorded using the third strategy, but at the same time, the lowest lipid production was observed (0.13 g/g). Interestingly, for the discussed yeast species, it was found that higher oxygen concentration correlated with higher citric acid production, and it is associated with reduced lipid accumulation. Hence, in order to obtain a satisfactory efficiency of the lipid production process, it is advantageous to keep the oxygenation of the culture at a lower level [17]. It seems that the oxygenation level chosen for ex novo lipid synthesis in cultures A and D was satisfactory.
As mentioned in the current study, an important factor in the cultivation process in order to obtain microbial oils is the source of nitrogen, as well as its amount in the culture medium. The efficiency of the lipid biosynthesis process obtained in the experiment confirmed the validity of the hypothesis that ex novo oil synthesis occurs simultaneously with cell growth and was dependent on the nitrogen concentration in the medium [14]. The use of a culture medium with an increased share of the nitrogen source in relation to the carbon source (C/N ratio = 10:1 in culture B) resulted in a significantly lower efficiency of lipid biosynthesis (0.310 g/g d.m.) than in the case of substrate with a lower concentration of the nitrogen source (C/N ratio = 20:1 in culture A), but this result differed by about 30%, which was still a satisfactory result from the point of view of the efficiency of the process.
Papanikolaou et al. [18] conducted an experiment with shaken cultures of Y. lipolytica ACA-DC 50109 in media with different C/N ratios. Stearin was used as a sole carbon source in two initial concentrations, 10 or 20 g/dm3. The source of nitrogen was ammonium sulphate at concentrations ranging from 0 to 10 g/dm3. It has been proven that for each of the used variants of culture media, significant amounts of biomass and lipids were produced. However, larger amounts of lipids were accumulated when the availability of extracellular nitrogen was lower. The highest lipid yield (53%) was obtained in the medium containing 20 g/dm3 of stearin and 1 g/dm3 of ammonium sulphate (C/N ratio = 20:1 [18]). The same ratio of these elements was used in the second culture of the current study (B-pfWO-N-0.50; Figure 1b). Manipulation of the medium composition enables to obtain benefits resulting from lowering the costs of the culture process along with higher metabolites production.
Y. lipolytica is a well-known organic acids producer [19]. Organic acids, including citric acid, are a by-product of de novo as well as ex novo pathways of lipid biosynthesis [20,21]. The production of citric acid is influenced by the growing conditions, such as the used carbon source or oxygenation [17]. The secreted organic acids are responsible for lowering the pH of culture media in each of the carried batch cultures in the study.
Surprisingly, low contents of single cell oil in culture C were achieved, where post-frying oil was subjected to alkaline hydrolysis and used as a carbon source in yeast growth. It is hypothesized that in the medium alongside free fatty acids, a high concentration of glycerol was present. As a result of the fats’ saponification reaction, glycerol was being released and might have determined the accumulation of lipids by the de novo pathway. Although in the current study the ex novo pathway was investigated, it cannot be denied that the de novo pathway did not occur [14]. Moreover, higher pH of the culture medium at the beginning of culture C compared to cultures A and B seemed to be important. It certainly influenced the level of metabolites synthesized by cells, as evidenced by the higher level of citric acid in the medium with hydrolyzed post-frying waste oil in relation to the content of this compound in substrates with non-hydrolyzed waste. In the study by Tomaszewska et al. [22], citric acid and erythritol biosynthesis from glycerol, both pure and crude, by three mutants of Y. lipolytica were evaluated. Batch cultures in a wide pH range from 3.0 to 6.5 were carried out, and the citric acid biosynthesis production was the highest in pH 5.0–5.5, and decreasing the pH value changed the direction of metabolites’ biosynthesis to erythritol instead of citric acid. Those two factors may explain, in part, the relatively low efficiency of oil biosynthesis in yeast cells cultured in the medium with the pre-treated carbon source and intensive synthesis of citric acid (0.79 g/dm3 in 66 h).
4.2. Waste Brine Utilization in Yeast Cultures
Brine is considered as the nuisance waste that contains chlorides (e.g., NaCl), which constitute the greatest challenge in its management. Their removal by osmosis, membrane techniques or evaporation is uneconomical. Moreover, due to the presumably smaller market needs and lack of cost-effective treatment technology options, brine water has been considered as the waste product of desalination and is typically disposed of without further treatment [23]. Waste brine was successfully applied in Y. lipolytica culture using a previously investigated medium with waste cooking oil. The proposed solution could be a method of reusing the residual wastewater streams, e.g., waste brine, thus reducing the amount of water used in another technological process.
Importantly, Y. lipolytica yeasts are characterized as microorganisms tolerating quite high salinity in the culture medium, even up to 12% [24]. Dobrowolski et al. described an experiment in which Y. lipolytica yeast biomass with a lipid content of 21% d.m. was obtained when grown in a medium prepared on the basis of a 3.6% sodium chloride solution which imitated sea water [25]. The growth of Yarrowia cells in a medium containing waste water after washing tuna carcasses with the simultaneous synthesis of intracellular lipids in the amount of 30% has also been reported [26]. Still, to the best of our knowledge there are so far no reports indicating the use of fishery brine applied in yeast culture aimed for the synthesis of storage lipids.
4.3. Single Cell Oil Composition of Yeast Cultured in Waste Medium
It can be concluded that the Y. lipolytica yeast accumulated oleic acid (C18: 1) and linoleic acid (C18: 2) to a great extent. The composition of the extracted oil, synthesized ex novo, imitated the initial composition of the oily substrate. This is in good agreement with studies by Papanikolaou et al. [27], who used stearin, a blend of stearic acid and palmitic acid, as the carbon source. Shaken cultures of the strain Y. lipolytica ACA-DC 5010 were grown for 85 h at 28 °C, and intracellular lipids consisted of fatty acid residues similar in proportions to the initial substrate used, where the predominant acid was stearic acid (83%) [27]. At the same time, Papanikolaou and Aggelis [28,29] proved that the cells of this species of yeast absorbed more oleic acid (C18: 1) and linoleic acid (C18: 2) than palmitic acid (C16: 0) or stearic acid (C18: 0) regardless of the initial concentrations of these acids. It is also claimed that Y. lipolytica yeast has two transport systems for fatty acids dependent on the length of the carbon chain. The first one is specific for C12 and C14 acids, the second one for C16 and C18. C18 fatty acids are stored in the form of storage lipids while others are assimilated for cell growth purposes. Meanwhile, some stored lipids can be used biotransformated to fatty acids absent in the lipid substrate This may be due to a better dispersion of unsaturated fatty acids in the medium or a higher affinity of protein carriers for acids containing double bonds [30]. Nevertheless, the proportions of the individual acids in the initial substrate are also important. It was observed that the presence of larger amounts of oleic acid (C18: 1) in the environment adversely affects the absorption of stearic acid by the cells (C18: 0) and vice versa [28]. It can be concluded that our results are in line with previous results.
5. Conclusions
This work aimed at evaluating the possibility of using a combination of two fishery industry wastes to introduce in the medium for Y. lipolytica growth and microbial oil synthesis. After the optimization of some culture conditions in medium with post-frying rapeseed oil, an efficient combination of waste oil and waste brine contents in culture medium was developed. Factors that can be optimized to increase the waste disposal in yeast culture could be increasing the oxygenation of the medium and changing the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio. In summary, this established solution would be helpful for producing intracellular lipids and the valorization of some industry wastes via biotechnological means. In the context of the use of microbial oils in human nutrition, an important aspect seems to be further research on the content of substances potentially harmful to human health when microorganisms are grown in media with waste substrates.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.F.; methodology, A.F.; investigation, A.F., K.W., B.Z., M.W. and D.N.; resources, A.F.; data curation, A.F.; writing—original draft preparation, A.F. and B.Z.; writing—review and editing, A.F., B.Z. and D.N.; visualization, A.F.; supervision, A.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was financially supported by sources of the Ministry of Education and Science within funds of the Institute of Food Sciences of Warsaw University of Life Sciences (WULS), for scientific research.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pauly, D.; Zeller, D. Comments on FAOs State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture (SOFIA 2016). Mar. Policy 2017, 77, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture (SOFIA 2020), Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations 2020. Available online: https://www.fao.org/publications/sofia/en (accessed on 27 December 2021).
- Bücker, F.; Marder, M.; Peiter, M.R.; Lehn, D.N.; Esquerdo, V.M.; Pinto, L.A.; Konrad, O. Fish waste: An efficient alternative to biogas and methane production in an anaerobic mono-digestion system. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 708–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, K.; Ouanji, F.; Lotfi, E.M.; Mahi, M.E.; Kacimi, M.; Ziyad, M. Biodiesel production from waste fish oil with high free fatty acid content from Moroccan fish-processing industries. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, W.Y.; Man, Y.B.; Wong, M.H. Use of food waste, fish waste and food processing waste for China’s aquaculture industry: Needs and challenge. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.; Antelo, L.T.; Franco-Uría, A.; Alonso, A.A.; Pérez-Martín, R. Valorisation of fish by-products against waste management treatments—Comparison of environmental impacts. Waste Manag. 2015, 46, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruijssen, F.; Tedesco, I.; Ward, A.; Pincus, L.; Love, D.; Thorne-Lyman, A.L. Loss and waste in fish value chains: A review of the evidence from low and middle-income countries. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 26, 100434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebah, F.B.; Miled, N. Fish processing wastes for microbial enzyme production: A review. 3 Biotech 2013, 3, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coppola, D.; Lauritano, C.; Palma Esposito, F.; Riccio, G.; Rizzo, C.; de Pascale, D. Fish Waste: From Problem to Valuable Resource. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzchowska, K.; Zieniuk, B.; Fabiszewska, A. Use of Non-Conventional Yeast Yarrowia lipolytica in Treatment or Upgradation of Hydrophobic Industry Wastes. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 13, 757–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzchowska, K.; Zieniuk, B.; Nowak, D.; Fabiszewska, A. Phosphorus and Nitrogen Limitation as a Part of the Strategy to Stimulate Microbial Lipid Biosynthesis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snopek, P.; Nowak, D.; Zieniuk, B.; Fabiszewska, A. Aeration and Stirring in Yarrowia lipolytica Lipase Biosynthesis during Batch Cultures with Waste Fish Oil as a Carbon Source. Fermentation 2021, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiszewska, A.U.; Zieniuk, B.; Kozłowska, M.; Mazurczak-Zieniuk, P.M.; Wołoszynowska, M.; Misiukiewicz-Stępień, P.; Nowak, D. Studies on Upgradation of Waste Fish Oil to Lipid-Rich Yeast Biomass in Yarrowia lipolytica Batch Cultures. Foods 2021, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiszewska, A.; Misiukiewicz-Stępień, P.; Paplińska-Goryca, M.; Zieniuk, B.; Białecka-Florjańczyk, E. An Insight into Storage Lipid Synthesis by Yarrowia lipolytica Yeast Relating to Lipid and Sugar Substrates Metabolism. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabiszewska, A.; Pielińska, A.; Mazurczak, P.; Zieniuk, B.; Wołoszynowska, M. Impact of the selected factors on extraction yield and composition of fatty acids of microbial oil produced by the yeast cells of Yarrowia lipolytica. Żywność. Nauka. Technol. Jakość. 2017, 24, 58–68. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Rakicka, M.; Lazar, Z.; Dulermo, T.; Fickers, P.; Nicaud, J.M. Lipid production by the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica using industrial by-products under different culture conditions. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sabra, W.; Bommareddy, R.R.; Maheshwari, G.; Papanikolaou, S.; Zeng, A.P. Substrates and oxygen dependent citric acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica: Insights through transcriptome and fluxome analyses. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Chevalot, I.; Galiotou-Panayotou, M.; Komaitis, M.; Marc, I.; Aggelis, G. Industrial derivative of tallow: A promising renewable substrate for microbial lipid, single-cell protein and lipase production by Yarrowia lipolytica. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 10, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otto, C.; Holz, M.; Barth, G. Production of Organic Acids by Yarrowia lipolytica. In Yarrowia lipolytica. Microbiol. Monographs; Barth, G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 25, pp. 137–149. [Google Scholar]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Aggelis, G. Lipids of oleaginous yeasts. Part II: Technology and potential applications. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2011, 113, 1052–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Aggelis, G. Lipids of oleaginous yeasts. Part I: Biochemistry of single-cell oil production. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2011, 113, 1031–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, L.; Rakicka, M.; Rymowicz, W.; Rywińska, A. A comparative study on glycerol metabolism to erythritol and citric acid in Yarrowia lipolytica yeast cells. FEMS Yeast Res. 2014, 14, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.; Kwak, R.; Kwon, H.; Pham, V.S.; Kim, M.; Al-Anzi, B.; Lim, G.; Han, J. Purification of high salinity brine by multi-stage ion concentration polarization desalination. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Groenewald, M.; Boekhout, T.; Neuvéglise, C.; Gaillardin, C.; van Dijck, P.W.; Wyss, M. Yarrowia lipolytica: Safety assessment of an oleaginous yeast with a great industrial potential. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 40, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrowolski, A.; Drzymała, K.; Rzechonek, D.; Mituła, P.; Mirończuk, A. Lipid production from waste materials in seawater-based medium by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamimed, S.; Barkaoui, T.; Trabelsi, I.; Landoulsi, A.; Chatti, A. High-performance biological treatment of tuna wash processing wastewater using Yarrowia lipolytica. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Chevalot, I.; Komaitis, M.; Aggelis, G.; Marc, I. Kinetic profile of the cellular lipid composition in an oleaginous Yarrowia lipolytica capable of producing a cocoa-butter substitute from industrial fats. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2001, 80, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Aggelis, G. Selective uptake of fatty acids by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2003, 105, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Muniglia, L.; Chevalot, I.; Aggelis, G.; Marc, I. Accumulation of a cocoa-butter-like lipid by Yarrowia lipolytica cultivated on agro-industrial residues. Curr. Microbiol. 2003, 46, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saygün, A.; Şahin-Yeşilçubuk, N.; Aran, N. Effects of different oil sources and residues on biomass and metabolite production by Yarrowia lipolytica YB 423-12. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).