Hypoglycemic Effect and Experimental Validation of Scutellariae Radix based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Chemical Components and Targets
2.3. Selection of Targets for SR in Diabetes
2.4. Network of Targets
2.5. Gene Ontology (GO) and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.6. Network Analysis
2.7. Animal Experiment
2.8. Molecular Docking Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hypoglycemic Ingredients and Targets
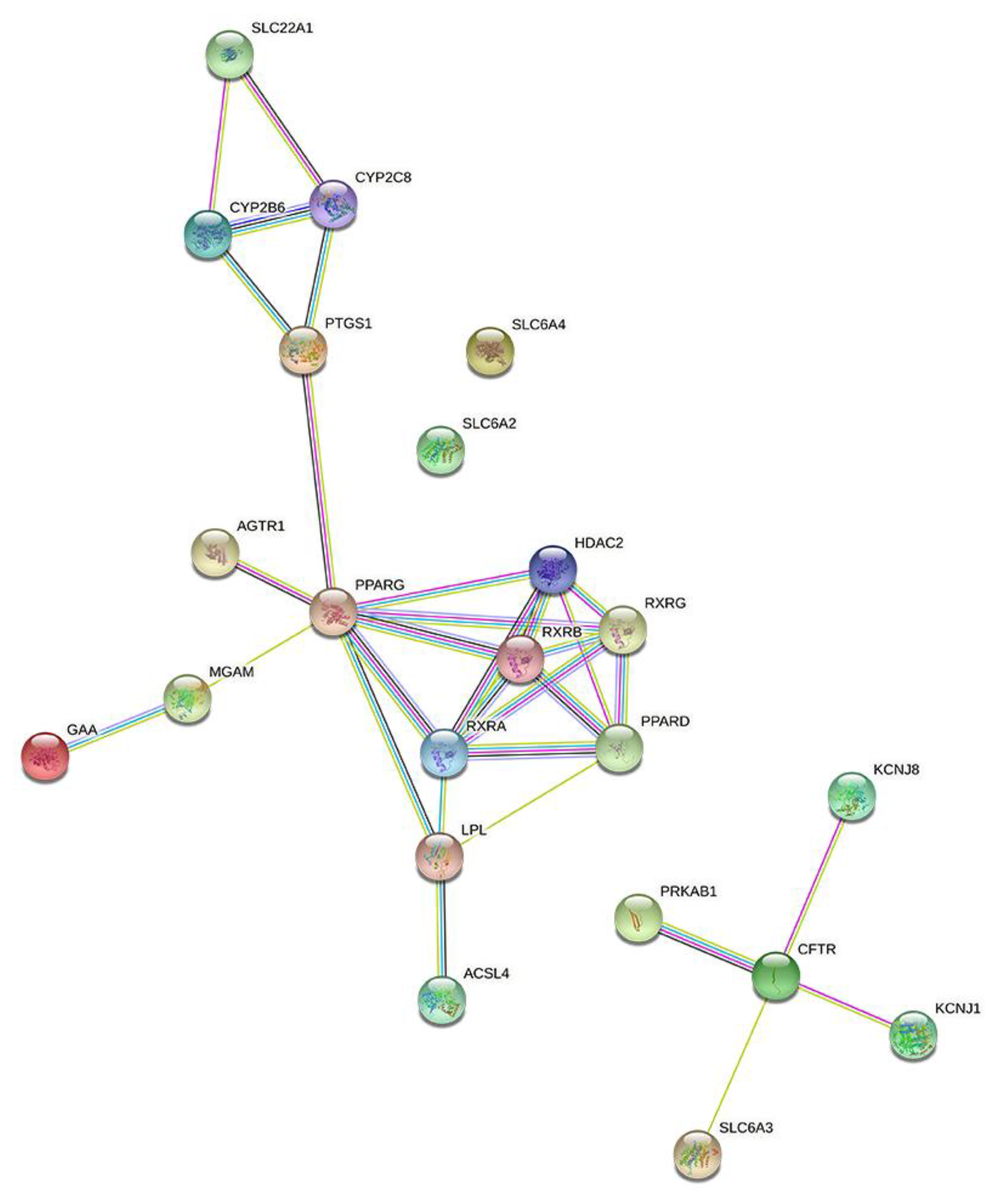
3.2. Relationship between Targets
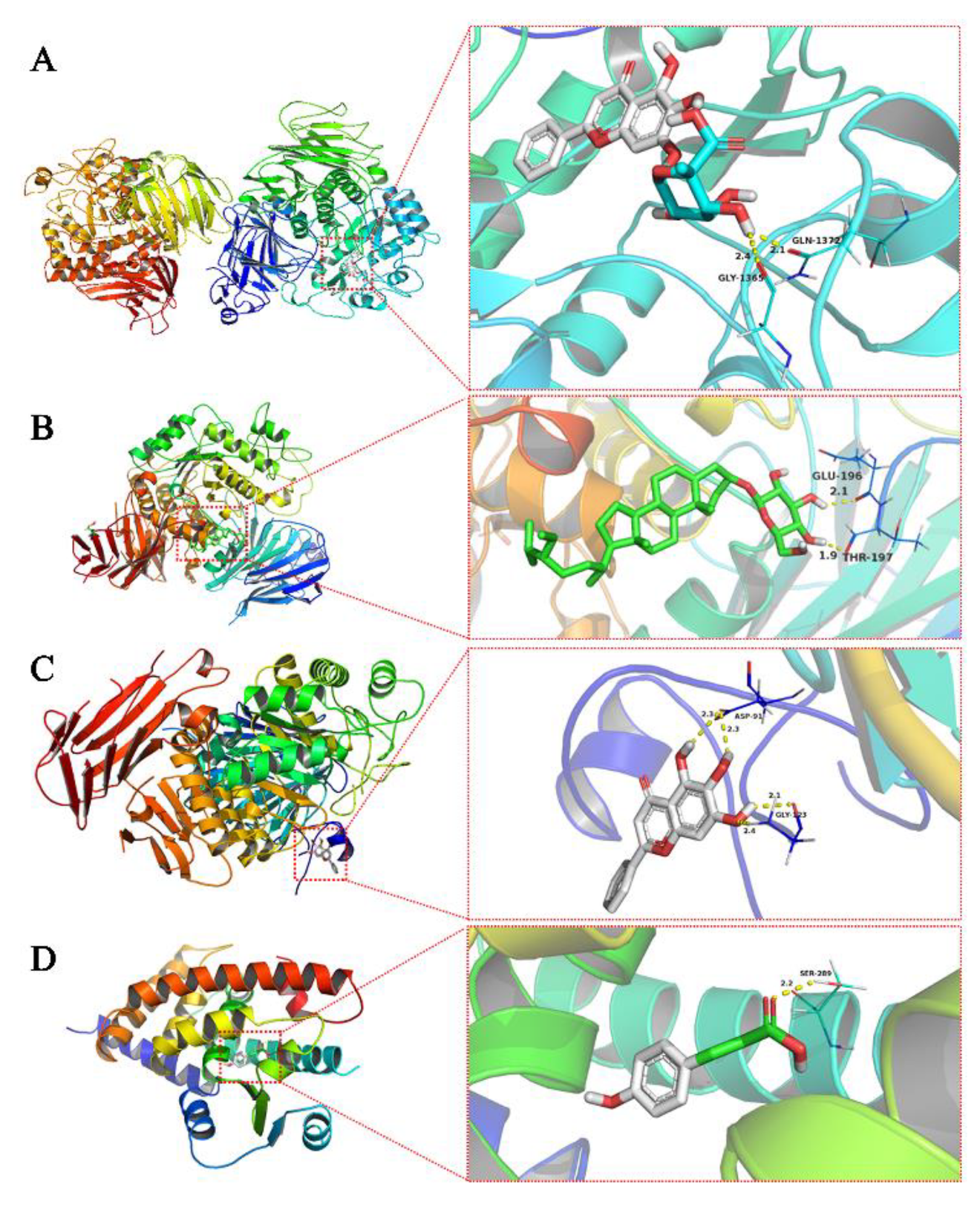
3.3. Molecular Docking Results
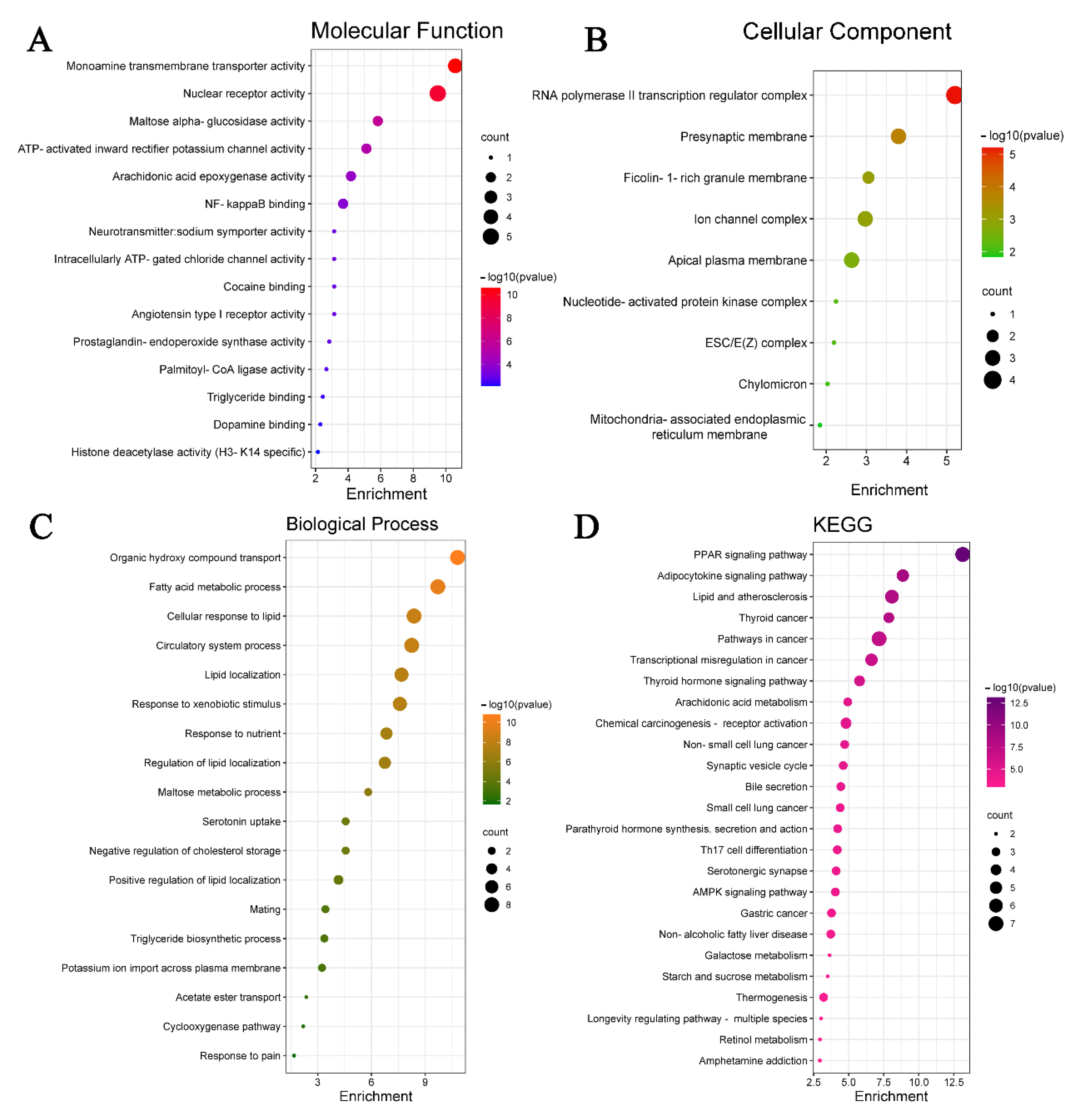
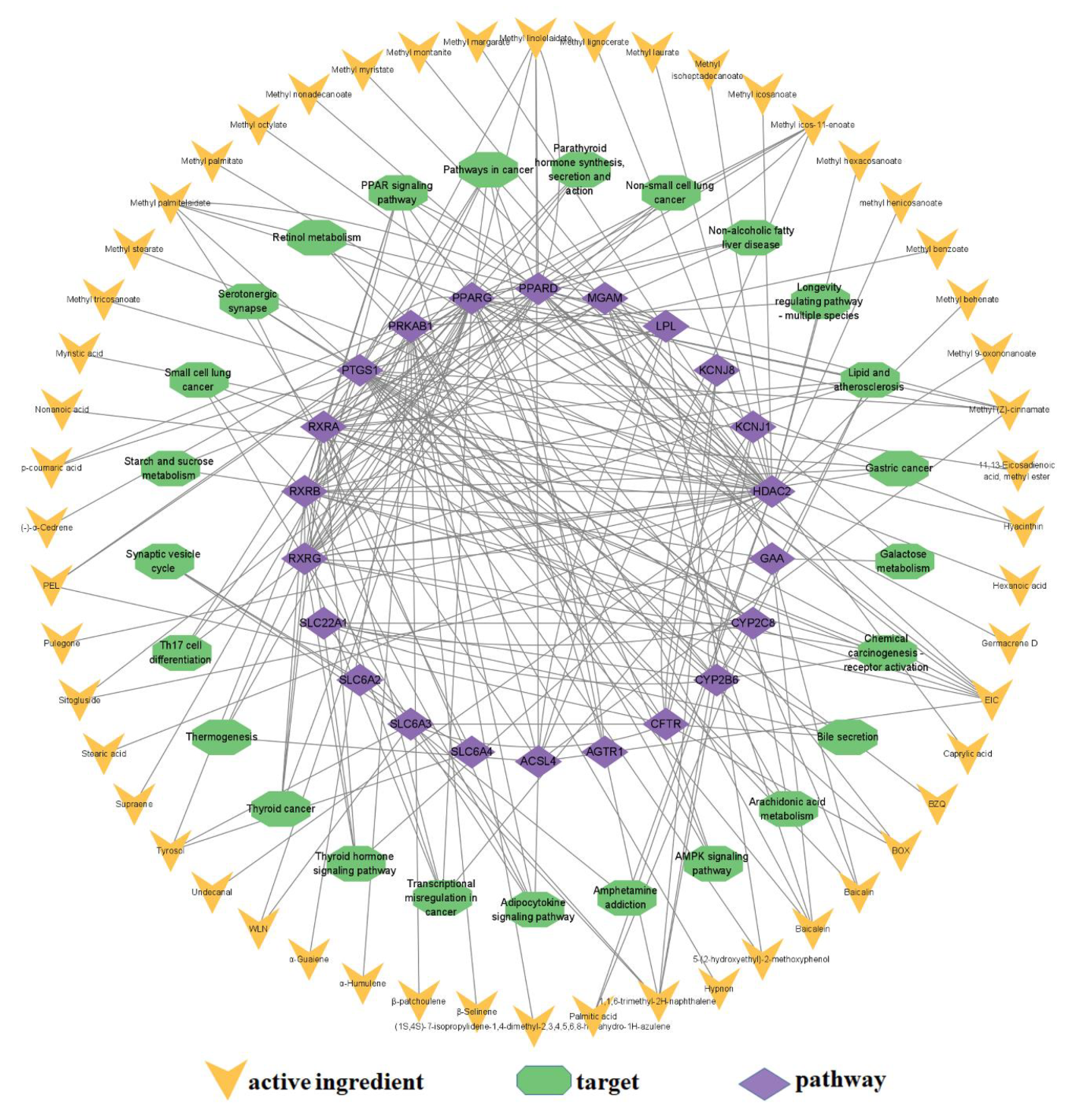
3.4. GO Analysis, KEGG Analysis and Ingredient–Target–Pathway Network
3.5. Animal Experiment
3.5.1. Blood Glucose
3.5.2. Body Weight and Water Drunk
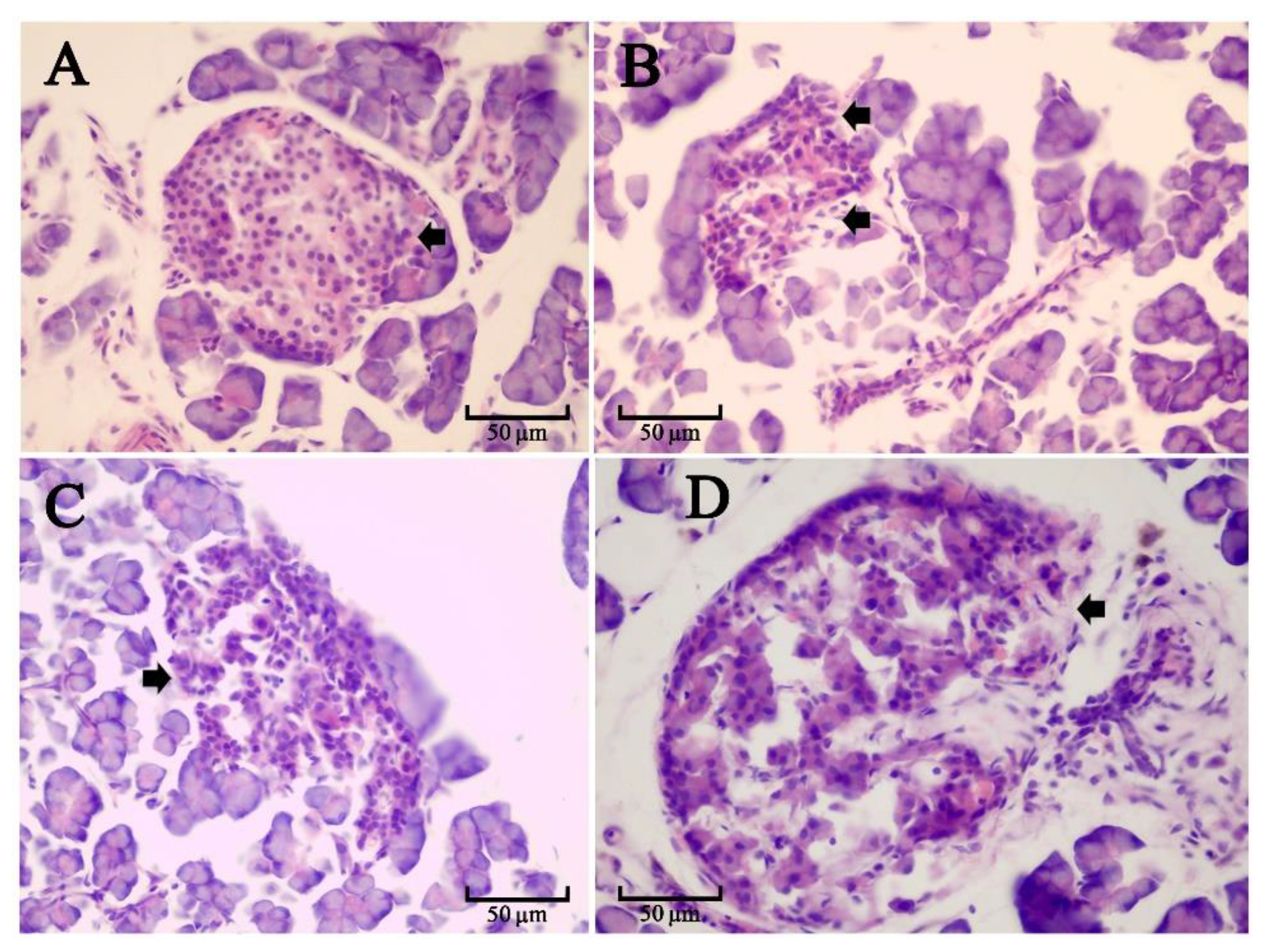
3.5.3. Effect of SR on the Pancreas in Diabetic Rats
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padhi, S.; Nayak, A.K.; Behera, A. Type II diabetes mellitus: A review on recent drug based therapeutics. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artasensi, A.; Pedretti, A.; Vistoli, G.; Fumagalli, L. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Multi-Target Drugs. Molecules 2020, 25, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Deng, X.; Zhang, D.; Xie, F.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Tavallaie, M.S.; Jiang, F.; Fu, L. Anti-diabetic potential of Pueraria lobata root extract through promoting insulin signaling by PTP1B inhibition. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Yang, Y.; Deng, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, W.; Feng, X. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese patent medicine Jinqi Jiangtang Tablet in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Complement. Ther. Med. 2019, 47, 102021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ma, P.; Peng, Y.; Wang, M.; Peng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Amelioration of hyperglycaemia and hyperlipidaemia by adjusting the interplay between gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism: Radix Scutellariae as a case. Phytomedicine 2021, 83, 153477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Liu, C.; Chen, M.; Zou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, X.; Jiang, S.; Shang, E.; Qian, D.; Duan, J. Scutellariae radix and coptidis rhizoma ameliorate glycolipid metabolism of type 2 diabetic rats by modulating gut microbiota and its metabolites. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Hong, S.M.; Sung, S.R.; Lee, J.E.; Kwon, D.Y. Extracts of Rehmanniae radix, Ginseng radix and Scutellariae radix improve glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and beta-cell proliferation through IRS2 induction. Genes. Nutr. 2008, 2, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Yu, M.; Shi, M.; Bo, P.; Gu, X.; Zhang, Z. Baicalin and its aglycone: A novel approach for treatment of metabolic disorders. Pharmaco. Rep. 2020, 72, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Ji, J.; Feng, Z.; Hou, X.; Luo, Y.; Mei, Z. A network pharmacology approach to explore the potential targets underlying the effect of sinomenine on rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 80, 106201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lv, D.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ye, G.; Chai, Y. Network pharmacology-based strategy for predicting active ingredients and potential targets of Yangxinshi tablet for treating heart failure. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 219, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, Q.; Huang, X.; Xu, A.; Liu, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. Revealing active components, action targets and molecular mechanism of Gandi capsule for treating diabetic nephropathy based on network pharmacology strategy. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinlong, R.; Peng, L.; Jinan, W.; Wei, Z.; Li, B.; Chao, H.; Pidong, L.; Zihu, G.; Weiyang, T.; Yinfeng, Y.; et al. TCMSP: A database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbalmedicines. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Diao, L.; Gu, J.; Wang, W.; Li, D.; et al. BATMAN-TCM: A Bioinformatics Analysis Tool for Molecular Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Lai, L.; Pei, J.; Li, H. PharmMapper 2017 update: A web server for potential drug target identification with a comprehensive target pharmacophore database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W356–W360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Morris, J.H.; Cook, H.; Kuhn, M.; Wyder, S.; Simonovic, M.; Santos, A.; Doncheva, N.T.; Roth, A.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D362–D368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortuño Sahagún, D.; Márquez-Aguirre, A.L.; Quintero-Fabián, S.; López-Roa, R.I.; Rojas-Mayorquín, A.E. Modulation of PPAR-γ by Nutraceutics as Complementary Treatment for Obesity-Related Disorders and Inflammatory Diseases. PPAR Res. 2012, 2012, 318613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, S. Berberine regulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and positive transcription elongation factor b expression in diabetic adipocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 649, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auwerx, J.; Schoonjans, K.; Fruchart, J.C.; Staels, B. Transcriptional control of triglyceride metabolism: Fibrates and fatty acids change the expression of the LPL and apo C-III genes by activating the nuclear receptor PPAR. Atherosclerosis 1996, 124, S29–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auwerx, J.; Leroy, P.; Schoonjans, K. Lipoprotein lipase: Recent contributions from molecular biology. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1992, 29, 243–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Qin, X.; Cao, X.; Wang, L.; Bai, F.; Bai, G.; Shen, Y. Structural insight into substrate specificity of human intestinal maltase-glucoamylase. Protein. Cell. 2011, 2, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, F.; van Buuringen, N.; Voermans, N.C.; Lefeber, D.J. Galactose in human metabolism, glycosylation and congenital metabolic diseases: Time for a closer look. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2021, 1865, 129898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaie, T.; Waldon, A.M.; Jacob, J.M.; Floyd, R.A.; Kotake, Y. COX-2 inhibition prevents insulin-dependent diabetes in low-dose streptozotocin-treated mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 273, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litherland, S.A.; She, J.X.; Schatz, D.; Fuller, K.; Hutson, A.D.; Peng, R.H.; Li, Y.; Grebe, K.M.; Whittaker, D.S.; Bahjat, K.; et al. Aberrant monocyte prostaglandin synthase 2 (PGS2) expression in type 1 diabetes before and after disease onset. Pediatr. Diabetes 2003, 4, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siewiera, K.; Kassassir, H.; Talar, M.; Wieteska, L.; Watala, C. Long-term untreated streptozotocin-diabetes leads to increased expression and elevated activity of prostaglandin H2 synthase in blood platelets. Platelets 2016, 27, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Normal Group | Model Group | Positive Group | Scutellariae Radix Group | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Diet before modeling | Standard diet | High-fat and high-sugar diet | High-fat and high-sugar diet | High-fat and high-sugar diet |
| Streptozotocin | / | 50 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg |
| Dosage (g/kg) | Normal saline | Normal saline | Metformin, 0.16 g/kg | Scutellariae Radix extract, 1.05 g/kg * |
| Target Gene | Targets | Uniprot ID | Number of Ingredients |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDAC2 | Histone deacetylase 2 | Q92769 | 24 |
| PTGS1 | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 1 | P23219 | 17 |
| PPARG | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma | P37231 | 12 |
| PPARD | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta | Q03181 | 10 |
| PRKAB1 | 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit beta-1 | Q9Y478 | 9 |
| ACSL4 | Long-chain-fatty-acid–CoA ligase 4 | O60488 | 5 |
| GAA | Lysosomal alpha-glucosidase | P10253 | 3 |
| MGAM | Maltase-glucoamylase, intestinal | O43451 | 3 |
| CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | P13569 | 3 |
| SLC6A3 | Sodium-dependent dopamine transporter | Q01959 | 2 |
| AGTR1 | Type-1 angiotensin II receptor | P30556 | 1 |
| CYP2B6 | Cytochrome P450 2B6 | P20813 | 1 |
| CYP2C8 | Cytochrome P450 2C8 | P10632 | 1 |
| KCNJ1 | ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11 | Q14654 | 1 |
| KCNJ8 | ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 8 | Q15842 | 1 |
| LPL | Lipoprotein lipase | P06858 | 1 |
| RXRA | Retinoic acid receptor RXR-alpha | P19793 | 1 |
| RXRB | Retinoic acid receptor RXR-beta | P28702 | 1 |
| RXRG | Retinoic acid receptor RXR-gamma | P48443 | 1 |
| SLC22A1 | Solute carrier family 22 member 1 | O15245 | 1 |
| SLC6A2 | Sodium-dependent noradrenaline transporter | P23975 | 1 |
| SLC6A4 | Sodium-dependent serotonin transporter | P31645 | 1 |
| No. | Ingredient | Molecular Formula | CAS No. | Number of Targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | EIC | C18H32O2 | 60-33-3 | 7 |
| 2 | 1,1,6-trimethyl-2H-naphthalene | C13H16 | 30364-38-6 | 5 |
| 3 | Baicalin | C21H18O11 | 21967-41-9 | 4 |
| 4 | Baicalein | C15H10O5 | 491-67-8 | 4 |
| 5 | Methyl linolelaidate | C19H34O2 | 2566-97-4 | 4 |
| 6 | Methyl palmitelaidate | C17H32O2 | 3913-63-1 | 4 |
| 7 | Methyl (Z)-cinnamate | C10H10O2 | / | 4 |
| 8 | Methyl icos-11-enoate | C21H40O2 | 2390-09-2 | 4 |
| 9 | Tyrosol | C8H10O2 | 501-94-0 | 3 |
| 10 | Palmitic acid | C16H32O2 | 57-10-3 | 2 |
| 11 | Sitoside | C35H60O6 | 474-58-8 | 2 |
| 12 | 5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-methoxyphenol | C9H12O3 | 50602-41-0 | 2 |
| 13 | P-coumaric acid | C9H8O3 | 501-98-4 | 2 |
| 14 | Hyacinthin | C8H8O | 122-78-1 | 2 |
| 15 | WLN | C7H6O | 100-52-7 | 2 |
| Group | Normal Group | Model Group | Positive Group | Scutellariae Radix Group | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| Blood glucose (mmol/L) | Before modeling | 5.2 ± 0.3 | 4.7 ± 0.9 | 5.1 ± 0.5 | 5.1 ± 0.4 |
| After modeling | 4.9 ± 1.0 | 23.1 ± 2.4 # | 20.6 ± 3.0 # | 22.7 ± 4.4 # | |
| After 4 weeks of treatment | 4.7 ± 0.9 * | 23.4 ± 6.2 | 6.2 ± 0.8 * | 6.2 ± 0.7 * | |
| Body weight change (g) | After 4 weeks of treatment | 37.5 ± 7.7 * ↑ | 66.3 ± 15.9 ↓ | 54.5 ± 12.5 *↓ | 45.3 ± 8.8 * ↓ |
| Drinking water (mL) | Before modeling | 19.9 ± 2.0 | 20.1 ± 2.0 | 20.4 ± 1.4 | 19.9 ± 1.3 |
| After 4 weeks of treatment | 54.7 ± 3.1 * | 195.5 ± 30.2 | 198.5 ± 14.0 | 144.3 ± 24.3 * | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Li, C.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, X.; Li, M.; Xue, J. Hypoglycemic Effect and Experimental Validation of Scutellariae Radix based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Processes 2022, 10, 2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10122553
Liu X, Li C, Chen Q, Xiao X, Li M, Xue J. Hypoglycemic Effect and Experimental Validation of Scutellariae Radix based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Processes. 2022; 10(12):2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10122553
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaolong, Chunyan Li, Qijian Chen, Xian Xiao, Manman Li, and Jintao Xue. 2022. "Hypoglycemic Effect and Experimental Validation of Scutellariae Radix based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking" Processes 10, no. 12: 2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10122553
APA StyleLiu, X., Li, C., Chen, Q., Xiao, X., Li, M., & Xue, J. (2022). Hypoglycemic Effect and Experimental Validation of Scutellariae Radix based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Processes, 10(12), 2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10122553








