Degradation of Hydroquinone Coupled with Energy Generation through Microbial Fuel Cells Energized by Organic Waste
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Source of Inoculation
2.3. Preparation of MFC Set-Up
2.4. MFC Electrochemical Test
2.5. Degradation Efficiency Calculation
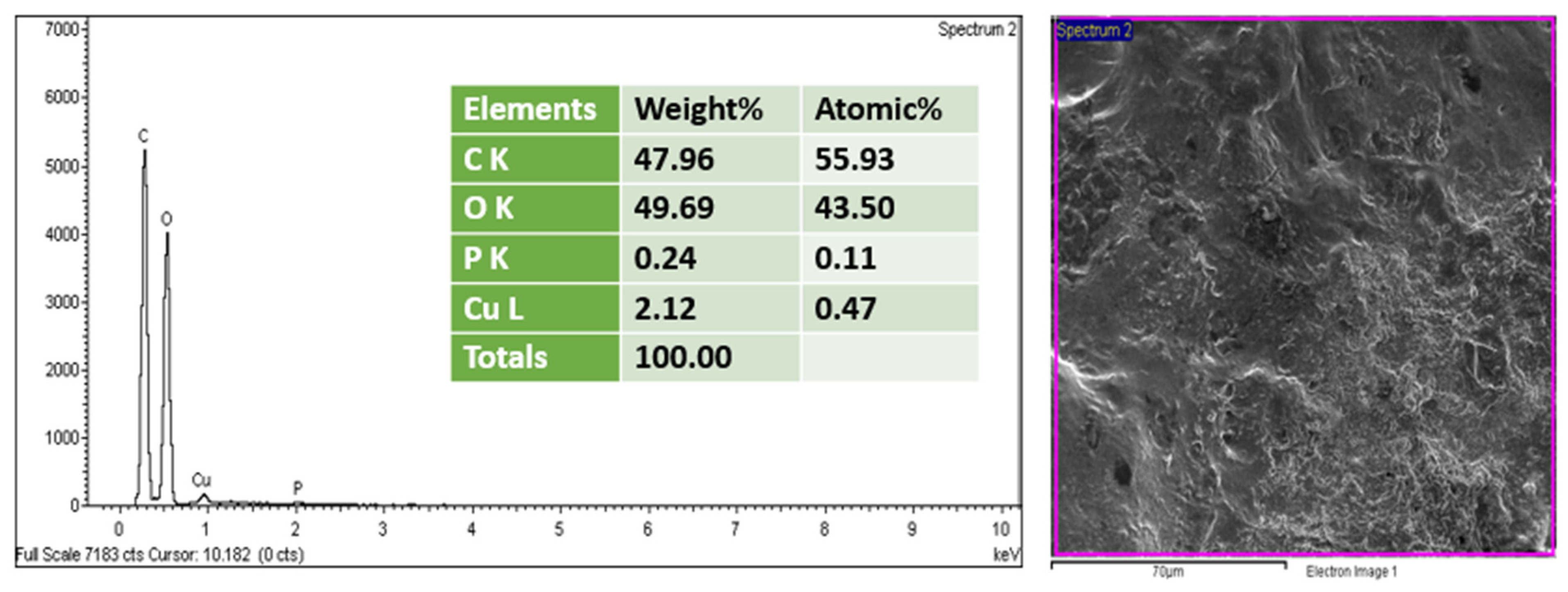
2.6. Biological Characterization
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Voltage Trend, Internal Resistance, and Polarization Behavior
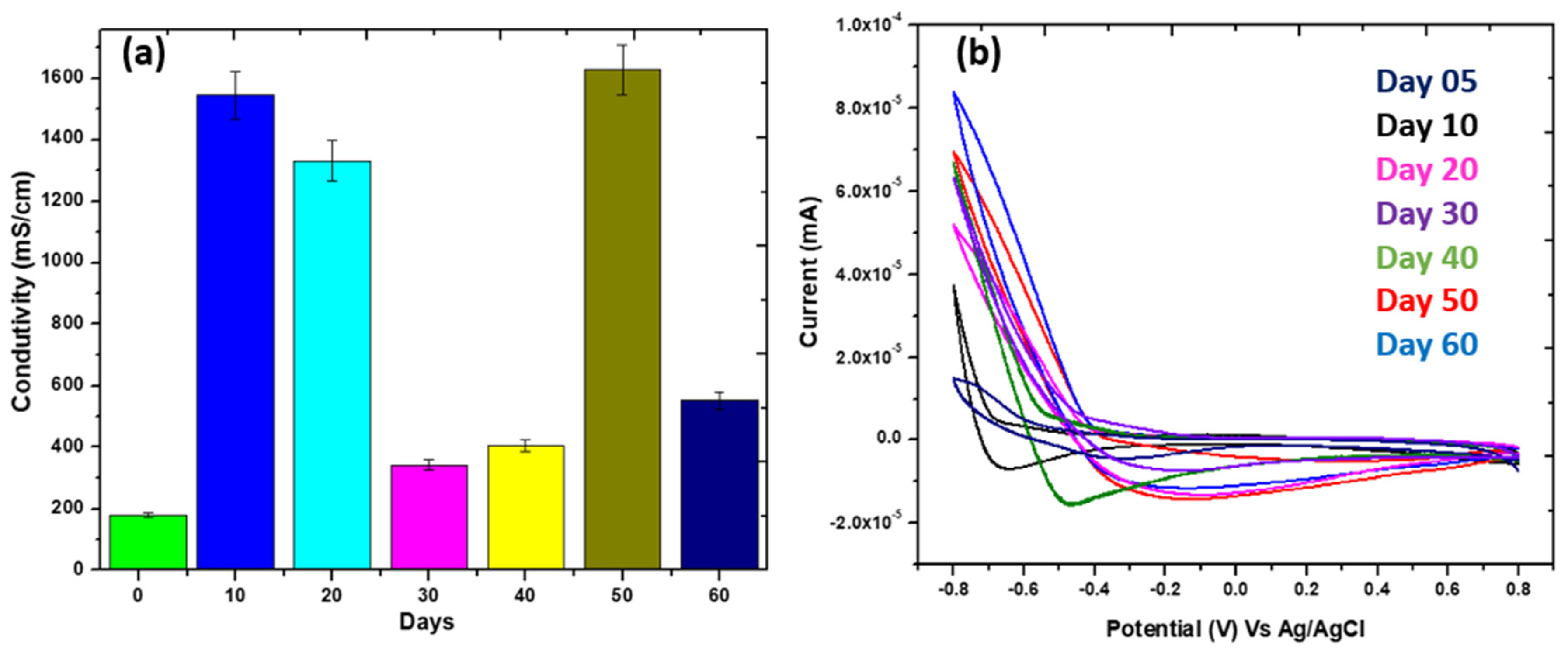
3.2. Conductivity Test and Cyclic Voltammetry Study
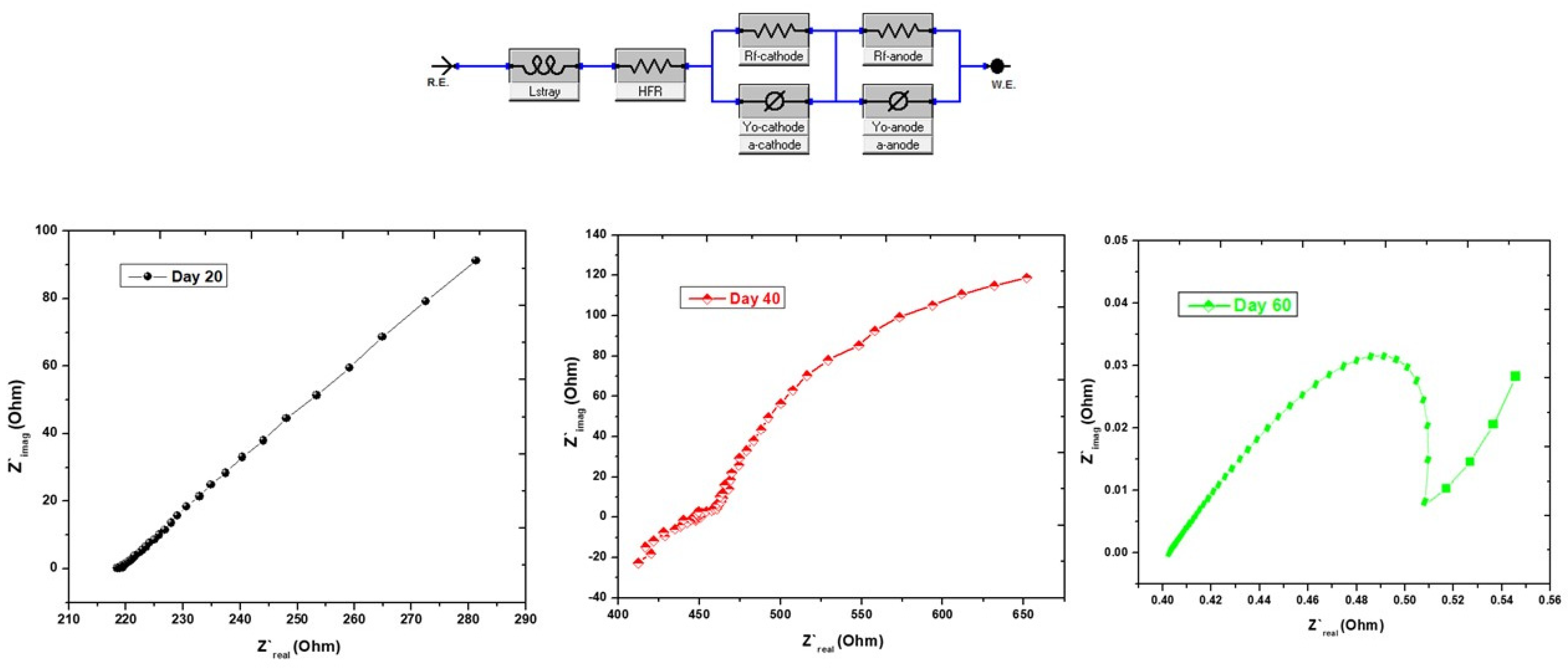
3.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Test
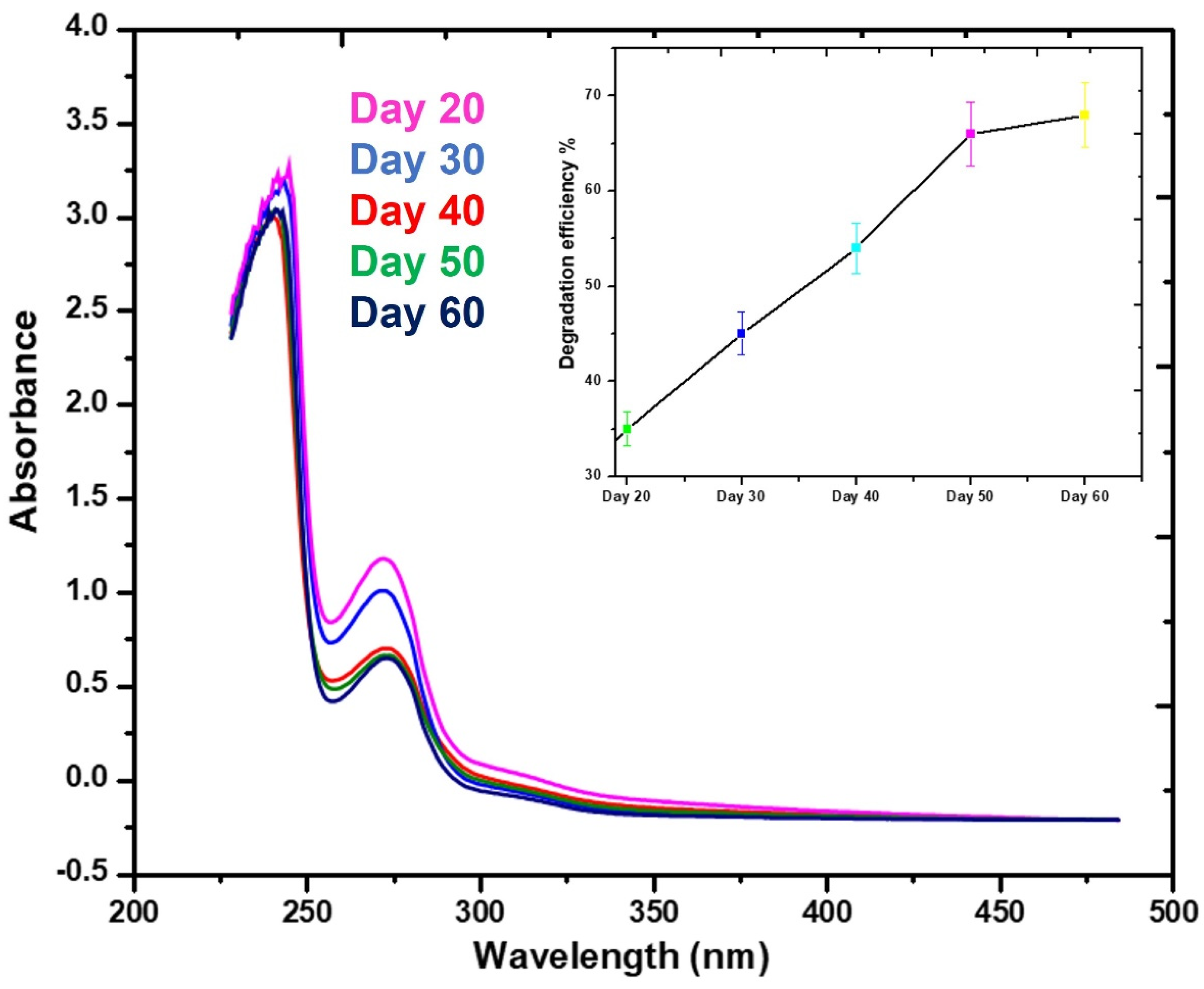
3.4. Hydroquinone Degradation Efficiency

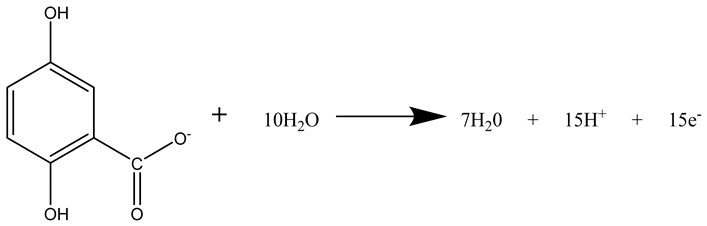
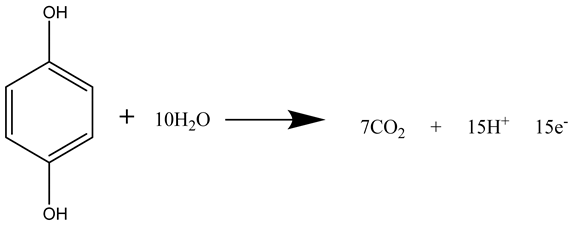
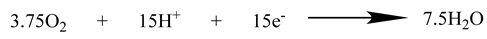
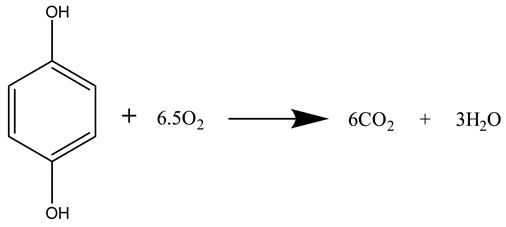
3.5. Oxidation of Rotten Rice in MFCs
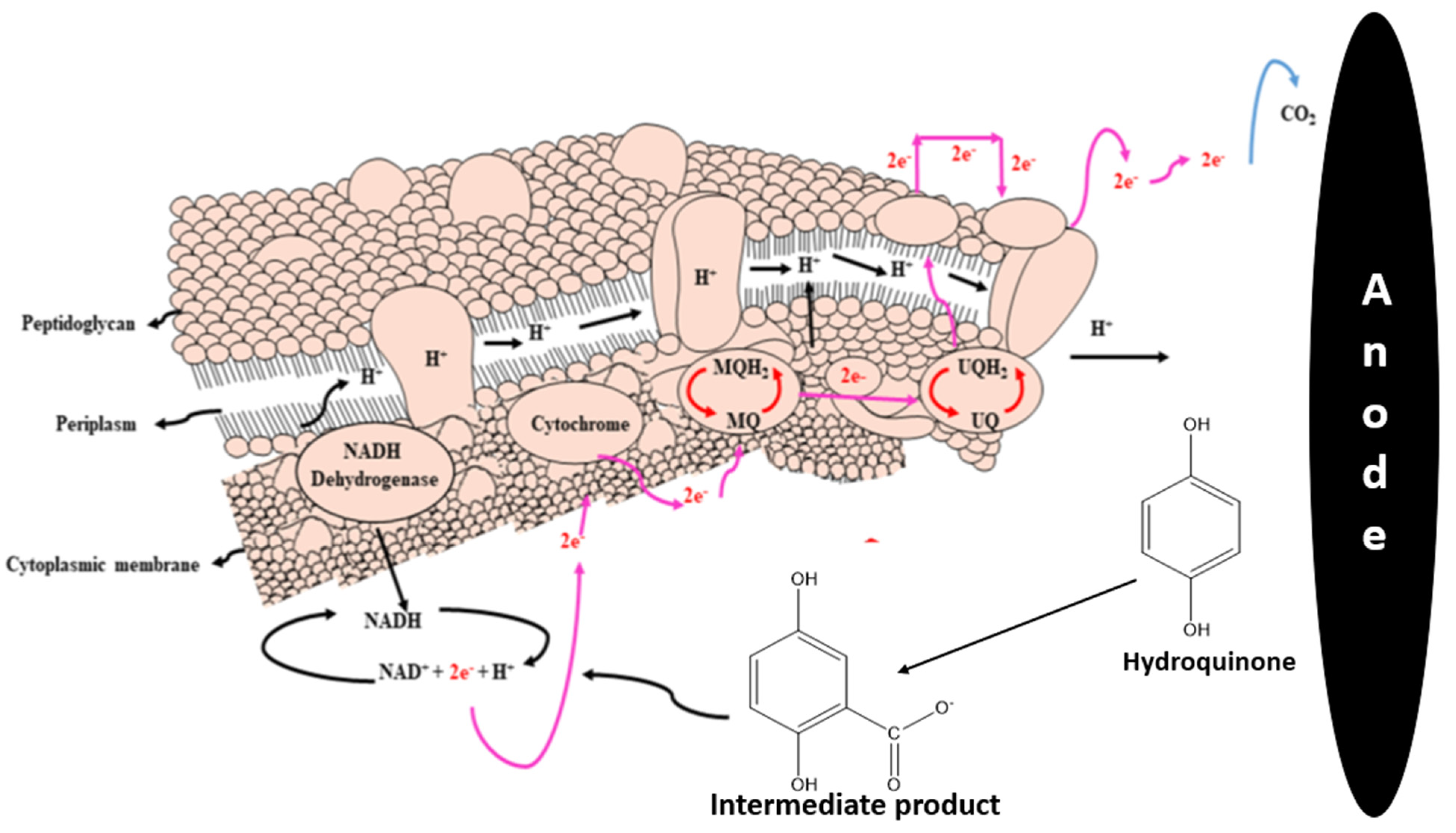
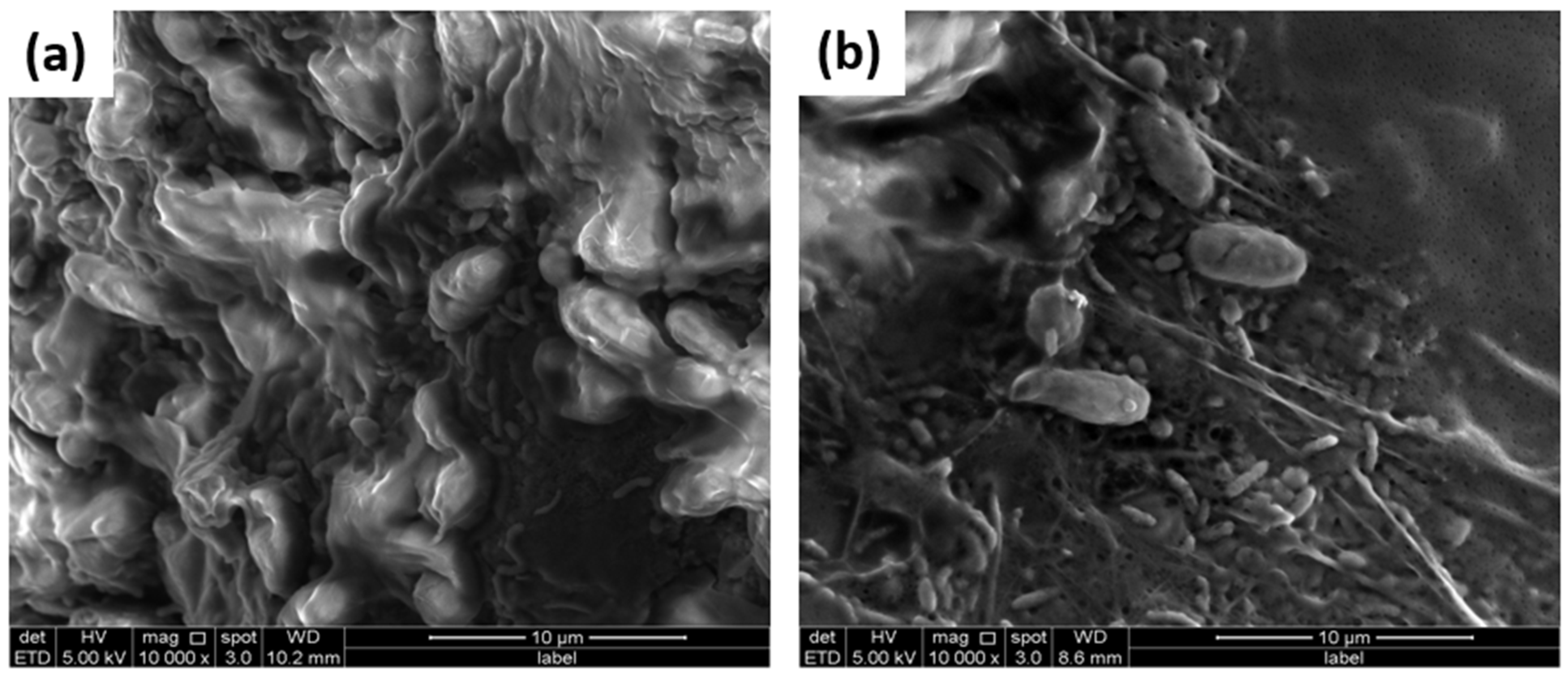
3.6. Biofilm Study
3.7. Bacterial Identification from Anode Electrode
4. Challenges and Future Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santoro, C.; Arbizzani, C.; Erable, B.; Ieropoulos, I. Microbial fuel cells: From fundamentals to applications. A review. J. Power Sources 2017, 356, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, B.E.; Regan, J.M. Microbial fuel cells—Challenges and applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5172–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Logan, B.E.; Hamelers, B.; Rozendal, R.; Schröder, U.; Keller, J.; Freguia, S.; Aelterman, P.; Verstraete, W.; Rabaey, K. Microbial fuel cells: Methodology and technology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5181–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Al-Zaqri, N.; Adnan, A.B.M.; Hussin, M.H.; Oh, S.E.; Umar, K. Impact of bakery waste as an organic substrate on microbial fuel cell performance. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, R.K.; Kim, Y.-K.; Lee, H.-J.; Tripathi, K.M. Upgrading of seafood waste as a carbon source: Nano-world outlook. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Khatoon, A.; Mohd Setapar, S.H.; Umar, K.; Parveen, T.; Mohamad Ibrahim, M.N.; Ahmad, A.; Rafatullah, M. Outlook on the role of microbial fuel cells in remediation of environmental pollutants with electricity generation. Catalysts 2020, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Regan, J.M.; Quan, X. Electron transfer mechanisms, new applications, and performance of biocathode microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, N.N.M.; Ahmad, A.; Ibrahim, M.N.M. Application of rotten rice as a substrate for bacterial species to generate energy and the removal of toxic metals from wastewater through microbial fuel cells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 62816–62827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissato, S.R.; Galhiane, M.S.; de Almeida, M.V.; Gerenutti, M.; Apon, B.M. Multiresidue determination of pesticides in honey samples by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and application in environmental contamination. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Kumar, V.; Malyan, S.K.; Sharma, J.; Mathimani, T.; Maskarenj, M.S.; Ghosh, P.C.; Pugazhendhi, A. Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) for bioelectrochemical treatment of different wastewater streams. Fuel 2019, 254, 115526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D. A bioelectrochemical system that converts waste to watts. In Microbial Fuel Cell; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Idris, M.O.; Kim, H.C. Exploring the effectiveness of microbial fuel cell for the degradation of organic pollutants coupled with bio-energy generation. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 102183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordlund, J.; Grimes, P.; Ortonne, J.P. The safety of hydroquinone. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2006, 20, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enguita, F.J.; Leitão, A.L. Hydroquinone: Environmental pollution, toxicity, and microbial answers. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 542168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suresh, S.; Srivastava, V.C.; Mishra, I.M. Adsorption of catechol, resorcinol, hydroquinone, and their derivatives: A review. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2012, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, D. Hydroquinone: An evaluation of the human risks from its carcinogenic and mutagenic properties. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2007, 37, 887–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrà, A.; Yaakop, A.S. Self-assembled oil palm biomass-derived modified graphene oxide anode: An efficient medium for energy transportation and bioremediating Cd (II) via microbial fuel cells. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103121. [Google Scholar]
- Greenman, J.; Gajda, I.; You, J.; Mendis, B.A.; Obata, O.; Pasternak, G.; Ieropoulos, I. Microbial fuel cells and their electrified biofilms. Biofilm 2021, 3, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Yaakop, A.S.; Umar, K.; Ahmad, A. Modified Graphene Oxide Anode: A Bioinspired Waste Material for Bioremediation of Pb2+ with Energy Generation through Microbial Fuel Cells. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 417, 128052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, A.; Mecheri, B.; Garavaglia, V.; Licoccia, S.; Di Nardo, P.; Traversa, E. Engineering materials and biology to boost performance of microbial fuel cells: A critical review. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; He, Z. Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification with electricity generation in dual-cathode microbial fuel cells. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Lee, H.-S.; Chae, J. Miniaturizing microbial fuel cells for potential portable power sources: Promises and challenges. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2012, 13, 353–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Li, H.; Gu, T. A state of the art review on microbial fuel cells: A promising technology for wastewater treatment and bioenergy. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 464–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, M.; Ngo, H.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Chang, S.; Nguyen, D.; Nghiem, L.; Ni, B. Challenges in the application of microbial fuel cells to wastewater treatment and energy production: A mini review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, K.-J.; Choi, M.-J.; Kim, K.-Y.; Ajayi, F.; Park, W.; Kim, C.-W.; Kim, I.S. Methanogenesis control by employing various environmental stress conditions in two-chambered microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5350–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkenkamp, S.; Menzel, C.; Karas, M.; Hillenkamp, F. Performance of infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry with lasers emitting in the 3 μm wavelength range. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1997, 11, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Umar, K. Biomass-derived composite anode electrode: Synthesis, characterizations, and application in microbial fuel cells (MFCs). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Rodríguez-Couto, S.; Ahmad, A. Preparation, characterization, and application of modified carbonized lignin as an anode for sustainable microbial fuel cell. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 155, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Flores, S.; Benites, S.M.; La Cruz-Noriega, D.; Cabanillas-Chirinos, L.; Valdiviezo-Dominguez, F.; Quezada Álvarez, M.A.; Vega-Ybañez, V.; Angelats-Silva, L. Bioelectricity Production from Blueberry Waste. Processes 2021, 9, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Mohamad Ibrahim, M.N.; Umar, K.; Bhawani, S.A.; Khan, A.; Asiri, A.M.; Khan, M.R.; Azam, M.; AlAmmari, A.M. Cellulose Derived Graphene/Polyaniline Nanocomposite Anode for Energy Generation and Bioremediation of Toxic Metals via Benthic Microbial Fuel Cells. Polymers 2021, 13, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Call, D.F.; Werner, C.M.; Logan, B.E. Adaptation to high current using low external resistances eliminates power overshoot in microbial fuel cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, A.; Khan, M.; Khan, N.; Nizami, A.; Rehan, M.; Khan, M. Development of novel MnO2 coated carbon felt cathode for microbial electroreduction of CO2 to biofuels. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasar, A.; Rahman, M.M. Applications of chitosan (CHI)-reduced graphene oxide (rGO)-polyaniline (PAni) conducting composite electrode for energy generation in glucose biofuel cell. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10428. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Chang, I.S.; Dinsdale, R.M.; Guwy, A.J. Accurate measurement of internal resistance in microbial fuel cells by improved scanning electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 366, 137388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, V.; Mohebbi-Kalhori, D.; Samimi, A. Equivalent electrical circuit modeling of ceramic-based microbial fuel cells using the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) analysis. J. Renew. Energy Environ. 2019, 6, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.D.; Li, D.; Tabraiz, S.; Shamurad, B.; Scott, K.; Khan, M.Z.; Yu, E.H. Integrated air cathode microbial fuel cell-aerobic bioreactor set-up for enhanced bioelectrodegradation of azo dye Acid Blue 29. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, B.-A.; Munteshari, O.; Lau, J.; Dunn, B.; Pilon, L. Physical interpretations of Nyquist plots for EDLC electrodes and devices. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paitier, A.; Godain, A.; Lyon, D.; Haddour, N.; Vogel, T.M.; Monier, J.-M. Microbial fuel cell anodic microbial population dynamics during MFC start-up. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhou, M.; Tian, X.; Tan, C.; McDaniel, C.T.; Hassett, D.J.; Gu, T. Microbial fuel cell (MFC) power performance improvement through enhanced microbial electrogenicity. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.-X.; Chen, T.; Wang, D.; Wan, L.-J. Potential dependent adsorption geometry of 2, 5-dihydroxybenzoic acid on a Au (111) surface: An in situ electrochemical scanning tunneling microscopy study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 6208–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibac, A.L.; Buruiana, T.; Melinte, V.; Buruiana, E.C. Photocatalysis applications of some hybrid polymeric composites incorporating TiO2 nanoparticles and their combinations with SiO2/Fe2O3. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bourcier, S.; Bouchonnet, S.; Hoppilliard, Y. Ionization of 2, 5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHB) matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization experiments and theoretical study. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 210, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.F.; Rafatullah, M.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Ismail, N. Bioelectricity production and xylene biodegradation through double chamber benthic microbial fuel cells fed with sugarcane waste as a substrate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, K.; Subramanian, S.; Basu, S. Microbial fuel cells for azo dye treatment with electricity generation: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Kundu, P. Biocatalysts in microbial fuel cells. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2010, 47, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadzli, F.S.; Rashid, M. Electricity generation and heavy metal remediation by utilizing yam (Dioscorea alata) waste in benthic microbial fuel cells (BMFCs). Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 172, 108067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Idris, M.O.; Ahmad, A.; Daud, N.N.M.; Ibrahim, M.N.M. Removal of Toxic Metal Ions from Wastewater Through Microbial Fuel Cells. In Microbial Fuel Cells for Environmental Remediation; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 299–325. [Google Scholar]
- Yaakop, A.S. Application of oil palm lignocellulosic derived material as an efficient anode to boost the toxic metal remediation trend and energy generation through microbial fuel cells. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 128062. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero–Barajas, C.; Umar, K.; Yaakop, A.S. Local fruit wastes driven benthic microbial fuel cell: A sustainable approach to toxic metal removal and bioelectricity generation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 32913–32928. [Google Scholar]
- Nimje, V.R.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-C.; Jean, J.-S.; Reddy, A.S.; Fan, C.-W.; Pan, K.-Y.; Liu, H.-T.; Chen, J.-L. Stable and high energy generation by a strain of Bacillus subtilis in a microbial fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2009, 190, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayangbenro, A.S.; Babalola, O.O. Genomic analysis of Bacillus cereus NWUAB01 and its heavy metal removal from polluted soil. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Al-Zaqri, N.; Yaakop, A.S.; Umar, K. Potato waste as an effective source of electron generation and bioremediation of pollutant through benthic microbial fuel cell. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, M.A.B.A.; Kim, H.-C.; Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B.; Yaakop, A.S. Oxidation of food waste as an organic substrate in a single chamber microbial fuel cell to remove the pollutant with energy generation. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 102282. [Google Scholar]
- Fadzli, F.; Yaakop, A. Benthic microbial fuel cells: A sustainable approach for metal remediation and electricity generation from sapodilla waste. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, S.B.; Bhawani, S.A.; Ismail Abdulrahman, R.M. Utilization of Mangifera indica as Substrate to Bioremediate the Toxic Metals and Generate the Bioenergy through a Single-Chamber Microbial Fuel Cell. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 8552701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadzli, F.S.; Bhawani, S.A.; Adam Mohammad, R.E. Microbial fuel cell: Recent developments in organic substrate use and bacterial electrode interaction. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 4570388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Guerrero-Barajas, C. Modern trend of anodes in microbial fuel cells (MFCs): An overview. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrà, A.; Bhawani, S.A.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Khan, A.; Alorfi, H.S.; Asiri, A.M.; Hussein, M.A.; Khan, I.; Umar, K. Utilizing Biomass-Based Graphene Oxide–Polyaniline–Ag Electrodes in Microbial Fuel Cells to Boost Energy Generation and Heavy Metal Removal. Polymers 2022, 14, 845. [Google Scholar]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Yaakop, A.S.; Rafatullah, M. Utilization of biomass-derived electrodes: A journey toward the high performance of microbial fuel cells. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
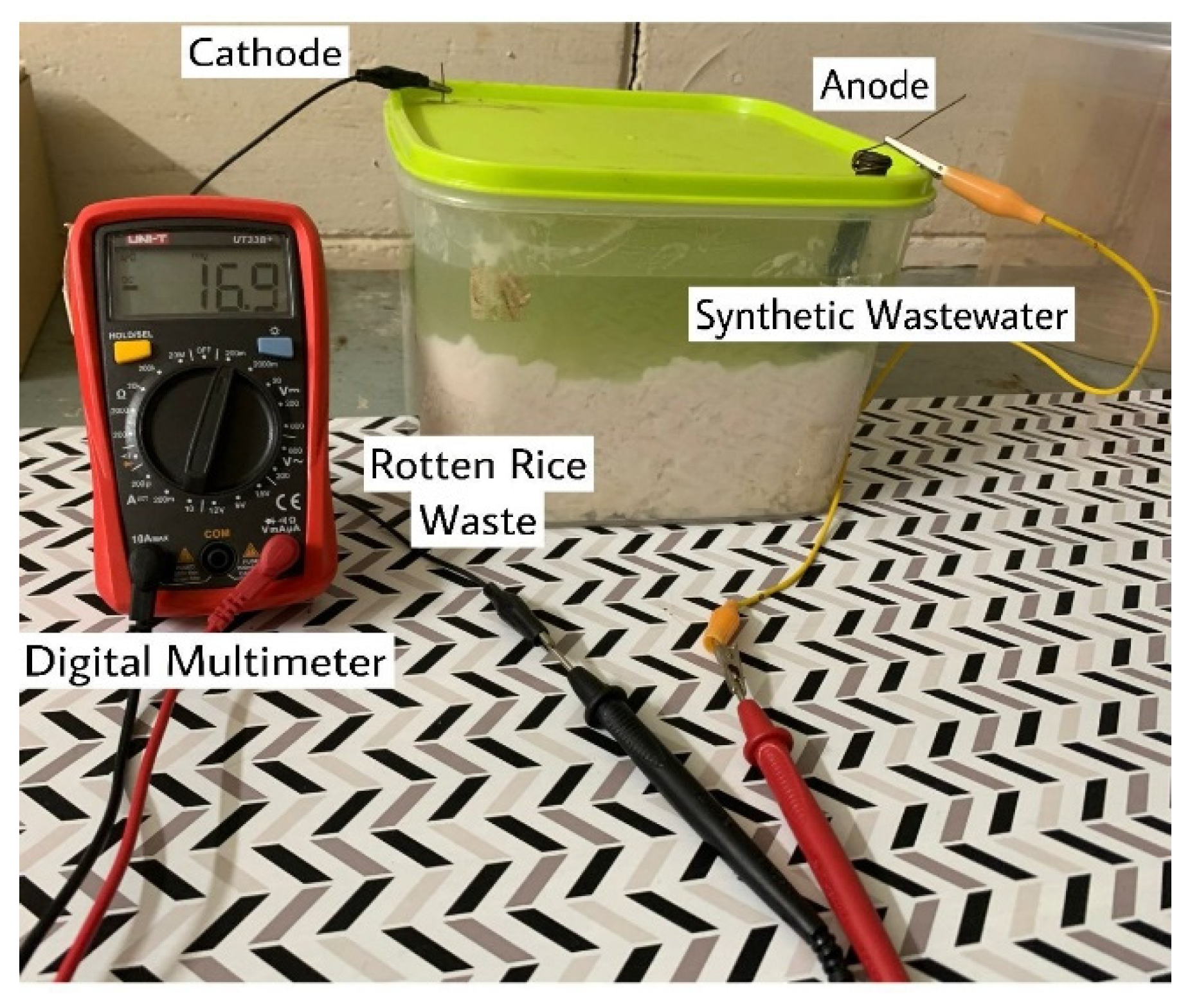


| Parameters | Lake Wastewater | Synthetic Wastewater |
|---|---|---|
| Color | Greenish | Cloudy |
| Electrical conductivity | 5.60 µs/cm | 11.05 µs/cm |
| Temperature | 25 ± 2 °C | 25 ± 2 °C |
| pH | 6.90 | 7.19 |
| Odor | Unpleasant smell | Unpleasant smell |
| Hydroquinone Concentration | 0 ppm | 10 ppm |
| Measurement Time Interval | Capacitance (F/g) |
|---|---|
| 5th | 7.20 × 10−5 |
| 10th | 2.70 × 10−4 |
| 20th | 2.76 × 10−4 |
| 30th | 2.82 × 10−4 |
| 40th | 2.88 × 10−4 |
| 50th | 3.00 × 10−4 |
| 60th | 5.04 × 10−4 |
| Bacterial Species | Identity (%) | Query Cover (%) | Accession Number (16S rRNA Gene) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lacticaseibacillus paracasei | 98.03 | 99 | NR_025880.1 |
| Lacticaseibacillus paracasei | 98.00 | 99 | NR_113337.1 |
| Pediococcus acidilactici | 93.08 | 99 | NR_042057.1 |
| Latilactobacillus species | 93.00 | 99 | NR_042443.1 |
| Loigolactobacillus backii | 93.49 | 98 | NR_114385.1 |
| Pediococcus stilesii | 93.59 | 98 | NR_042401.1 |
| Secundilactobacillus silagincola | 92.90 | 98 | NR_158059.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torlaema, T.A.M.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Ahmad, A.; Guerrero-Barajas, C.; Alshammari, M.B.; Oh, S.-E.; Hussain, F. Degradation of Hydroquinone Coupled with Energy Generation through Microbial Fuel Cells Energized by Organic Waste. Processes 2022, 10, 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102099
Torlaema TAM, Ibrahim MNM, Ahmad A, Guerrero-Barajas C, Alshammari MB, Oh S-E, Hussain F. Degradation of Hydroquinone Coupled with Energy Generation through Microbial Fuel Cells Energized by Organic Waste. Processes. 2022; 10(10):2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102099
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorlaema, Tasnim Aisya Mahmuelee, Mohamad Nasir Mohamad Ibrahim, Akil Ahmad, Claudia Guerrero-Barajas, Mohammed B. Alshammari, Sang-Eun Oh, and Fida Hussain. 2022. "Degradation of Hydroquinone Coupled with Energy Generation through Microbial Fuel Cells Energized by Organic Waste" Processes 10, no. 10: 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102099
APA StyleTorlaema, T. A. M., Ibrahim, M. N. M., Ahmad, A., Guerrero-Barajas, C., Alshammari, M. B., Oh, S.-E., & Hussain, F. (2022). Degradation of Hydroquinone Coupled with Energy Generation through Microbial Fuel Cells Energized by Organic Waste. Processes, 10(10), 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102099













