Deep Hierarchical Interval Type 2 Self-Organizing Fuzzy System for Data-Driven Robot Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Interval Type-2 Fuzzy System
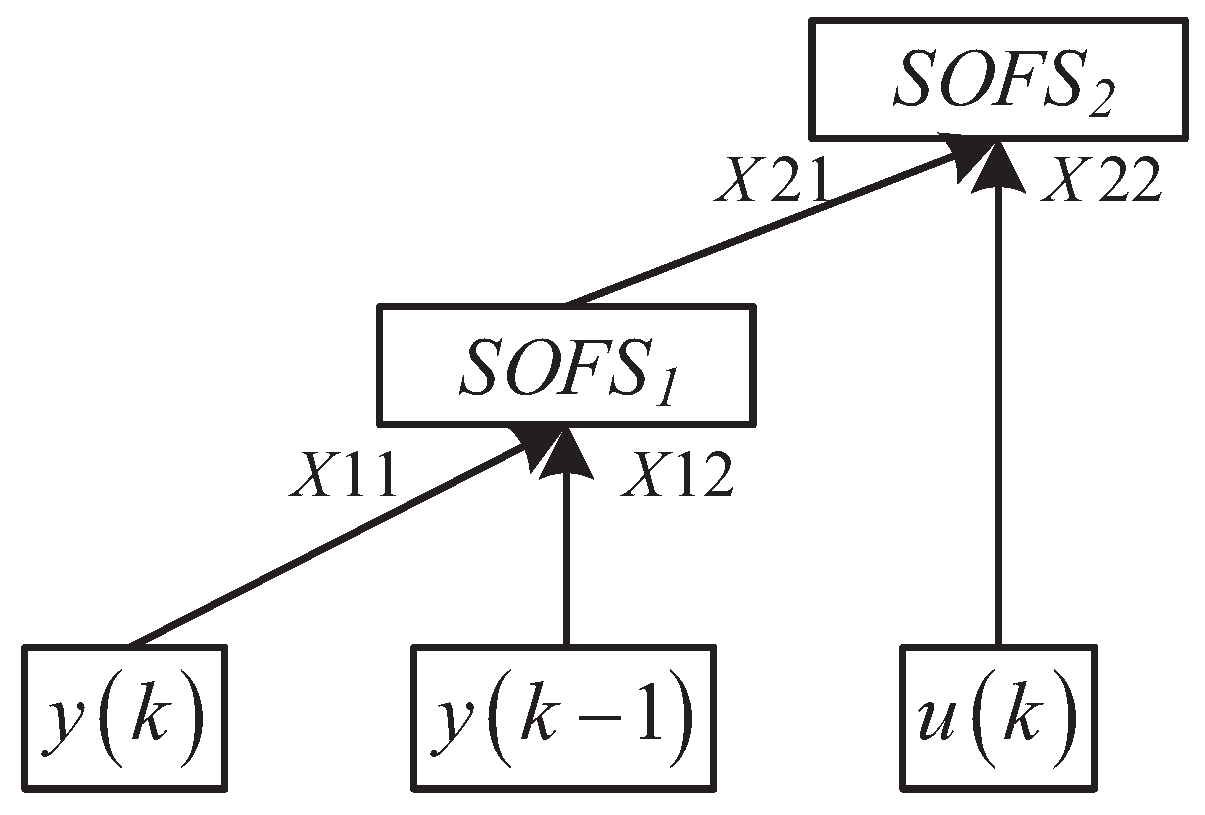
3. Deep Hierarchical Self-Organizing Interval Type 2 Fuzzy System
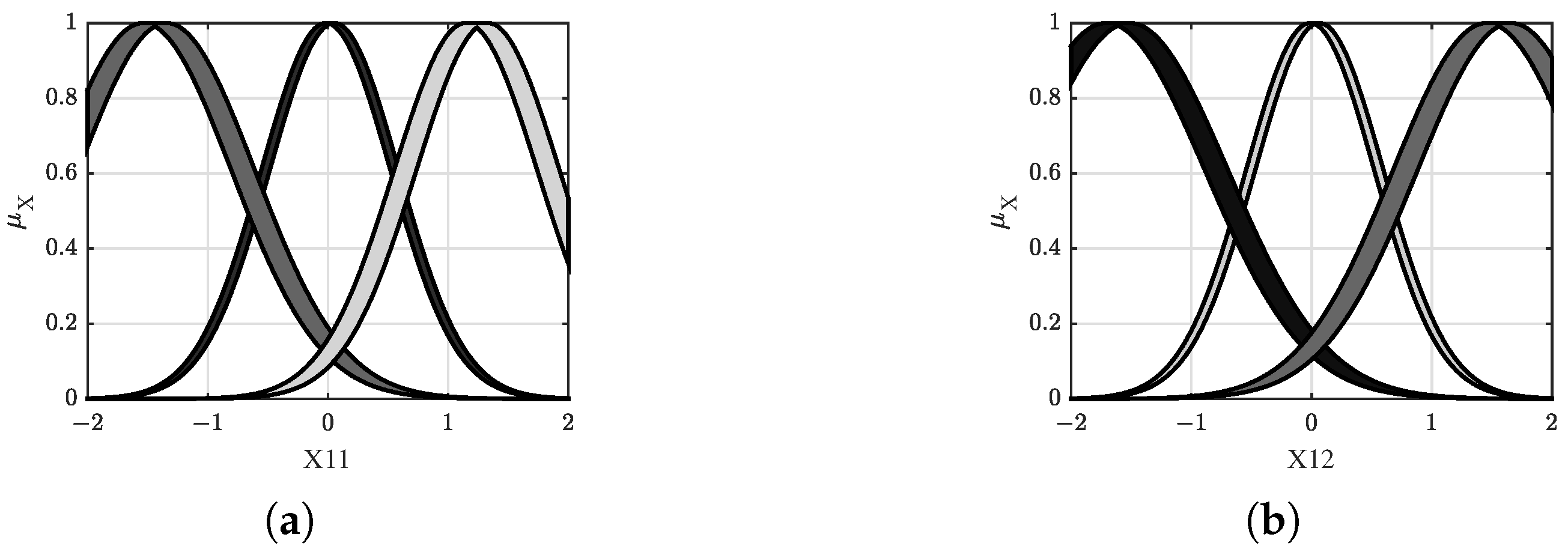
3.1. SOFS Systems Structure Learning
3.2. SOFS Systems Parameters Learning
3.3. DHSOIT2FS Structure and Learning
4. Simulation
4.1. Nonlinear Dynamic System Identification
4.2. Higher Dimensional System Identification
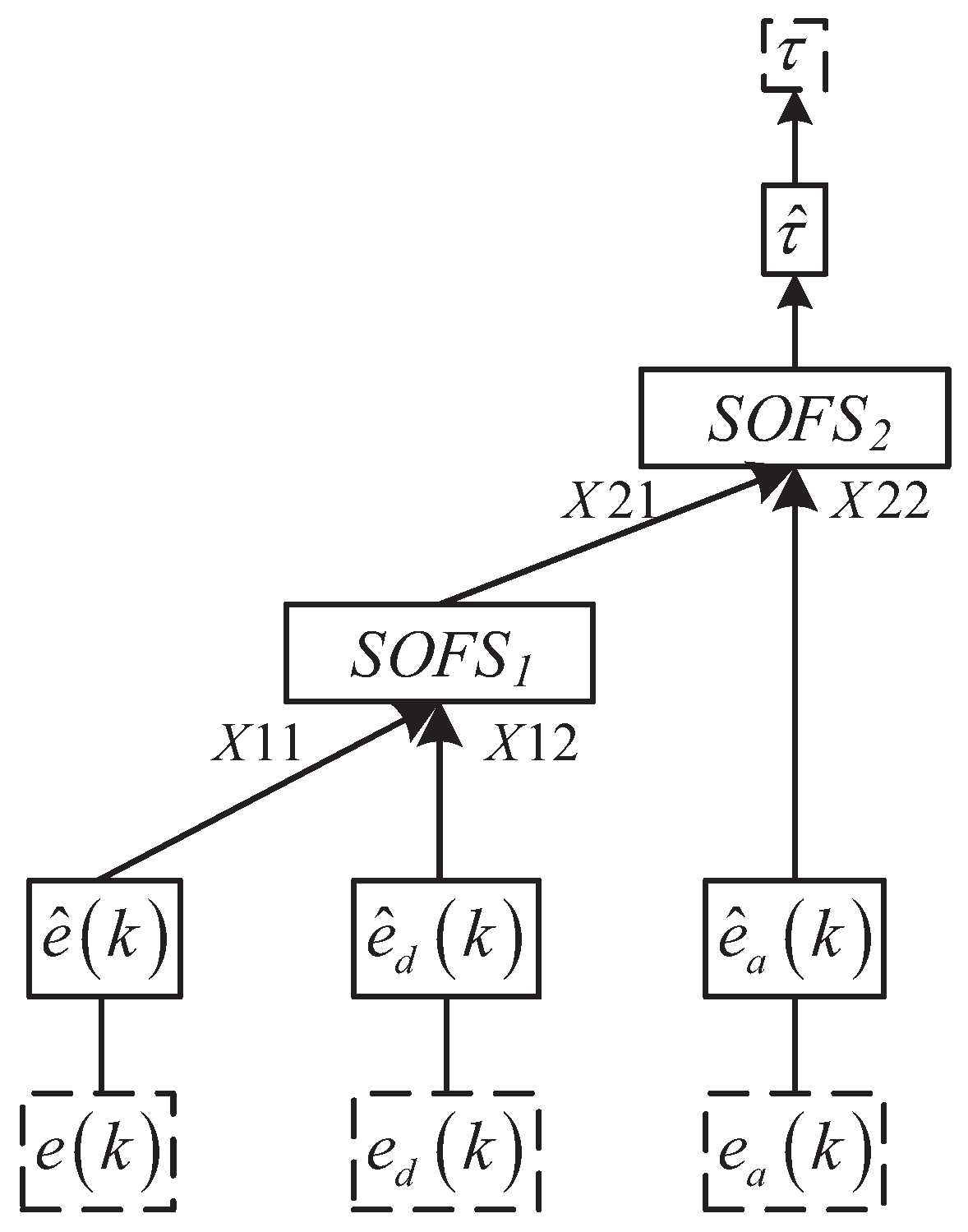
4.3. Data-Driven Single Linkage Robot Control
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ge, D.; Zeng, X.J. A self-evolving fuzzy system which learns dynamic threshold parameter by itself. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 27, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Shen, Q. A self-adaptive fuzzy learning system for streaming data prediction. Inf. Sci. 2021, 579, 623–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.X.; Doctor, F.; Liu, Y.X.; Fan, S.Z.; Shieh, J.S. An optimized type-2 self-organizing fuzzy logic controller applied in anesthesia for propofol dosing to regulate BIS. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 28, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdaus, M.M.; Pratama, M.; Anavatti, S.G.; Garratt, M.A.; Pan, Y. Generic evolving self-organizing neuro-fuzzy control of bio-inspired unmanned aerial vehicles. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 28, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X. Multilayer ensemble evolving fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 29, 2425–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Tong, W.; Mao, Y. Hybrid Non-singleton Fuzzy Strong Tracking Kalman Filtering for High Precision Photoelectric Tracking System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Chen, C.; Cao, H. Evolutionary self-organizing fuzzy system using fuzzy-classification-based social learning particle swarm optimization. Inf. Sci. 2022, 606, 92–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Cao, H.; Dian, S. A Self-Organized Method for a Hierarchical Fuzzy Logic System based on a Fuzzy Autoencoder. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Chen, C.; Cao, H.; Dian, S.; Xie, X. Multiobjective Optimization Design of Interpretable Evolutionary Fuzzy Systems With Type Self-Organizing Learning of Fuzzy Sets. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnik, N.N.; Mendel, J.M.; Liang, Q. Type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 1999, 7, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendel, J.M.; John, R.B. Type-2 fuzzy sets made simple. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2002, 10, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Choi, K.S.; Cao, L.; Wang, S. T2FELA: Type-2 fuzzy extreme learning algorithm for fast training of interval type-2 TSK fuzzy logic system. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2013, 25, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Mendel, J.M. Interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems: Theory and design. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2000, 8, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Mendel, J.M. Equalization of nonlinear time-varying channels using type-2 fuzzy adaptive filters. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2000, 8, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, H.B. Pattern recognition using type-II fuzzy sets. Inf. Sci. 2005, 170, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorozu, T.; Hirano, M.; Oka, K.; Tagawa, Y. Electron spectroscopy studies on magneto-optical media and plastic substrate interface. IEEE Transl. J. Magn. Jpn. 1987, 2, 740–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.X. Analysis and design of hierarchical fuzzy systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 1999, 7, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.L.; Chung, H.Y.; Yu, F.M. Modeling of hierarchical fuzzy systems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2003, 138, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ishibuchi, H.; Wang, S. Deep Takagi–Sugeno–Kang fuzzy classifier with shared linguistic fuzzy rules. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 26, 1535–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Shimojima, K. Structure organization of hierarchical fuzzy model using by genetic algorithm. Proc. 1995 IEEE Int. Conf. Fuzzy Syst. 1995, 1, 295–300. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E.; Osindero, S.; Teh, Y.W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput. 2006, 18, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Qiao, J. An Efficient Self-Organizing Deep Fuzzy Neural Network for Nonlinear System Modeling. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 30, 2170–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, D.; Huang, A.; Maddison, C.J.; Guez, A.; Sifre, L.; Van Den Driessche, G.; Schrittwieser, J.; Antonoglou, I.; Panneershelvam, V.; Lanctot, M.; et al. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature 2016, 529, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, R.; Banerjee, T.; Romine, W. Early hospital mortality prediction using vital signals. Smart Health 2018, 9, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.X. Fast Training Algorithms for Deep Convolutional Fuzzy Systems With Application to Stock Index Prediction. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 28, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Nojima, Y.; Ishibuchi, H.; Wang, S. Realizing deep high-order TSK fuzzy classifier by ensembling interpretable zero-order TSK fuzzy subclassifiers. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 29, 3441–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, X.; Peng, W.; Li, C.; Wang, H. Compression and regularized optimization of modules stacked residual deep fuzzy system with application to time series prediction. Inf. Sci. 2022, 608, 551–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, C.F.; Tsao, Y.W. A self-evolving interval type-2 fuzzy neural network with online structure and parameter learning. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2008, 16, 1411–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendel, J.M. Computing derivatives in interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2004, 12, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Methods | WM | DHSOIT2FS |
|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 0.0926 | 0.0476 |
| Number of rules | 343 | 20 |
| Total number of fuzzy sets | 21 | 20 |
| TrainRunTime | 0.1570 s | 2.1560 s |
| TestRunTime | 0.0342 s | 0.1790 s |
| Methods | WM | DHSOIT2FS |
|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 0.2390 | 0.05185 |
| Number of rules | 3125 | 48 |
| Total number of fuzzy sets | 375 | 58 |
| TrainRunTime | 8.180 s | 46.404 s |
| TestRunTime | 2.159 s | 4.457 s |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mei, Z.; Zhao, T.; Liu, N. Deep Hierarchical Interval Type 2 Self-Organizing Fuzzy System for Data-Driven Robot Control. Processes 2022, 10, 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102091
Mei Z, Zhao T, Liu N. Deep Hierarchical Interval Type 2 Self-Organizing Fuzzy System for Data-Driven Robot Control. Processes. 2022; 10(10):2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102091
Chicago/Turabian StyleMei, Zhen, Tao Zhao, and Nian Liu. 2022. "Deep Hierarchical Interval Type 2 Self-Organizing Fuzzy System for Data-Driven Robot Control" Processes 10, no. 10: 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102091
APA StyleMei, Z., Zhao, T., & Liu, N. (2022). Deep Hierarchical Interval Type 2 Self-Organizing Fuzzy System for Data-Driven Robot Control. Processes, 10(10), 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102091







