Human-Health and Environmental Risks of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soil and Groundwater at a Riverside Site, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of the Survey Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Hydrogeological Test
3.2. Soil and Groundwater Investigation
3.3. Sampling Method and Preservation
3.4. Sample Detection and Quality Control
3.5. Human-Health Risk Assessment Methods
3.6. Ecological Health Risk Assessment Method
3.7. Data Processing and Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Site Hydrogeological Parameters
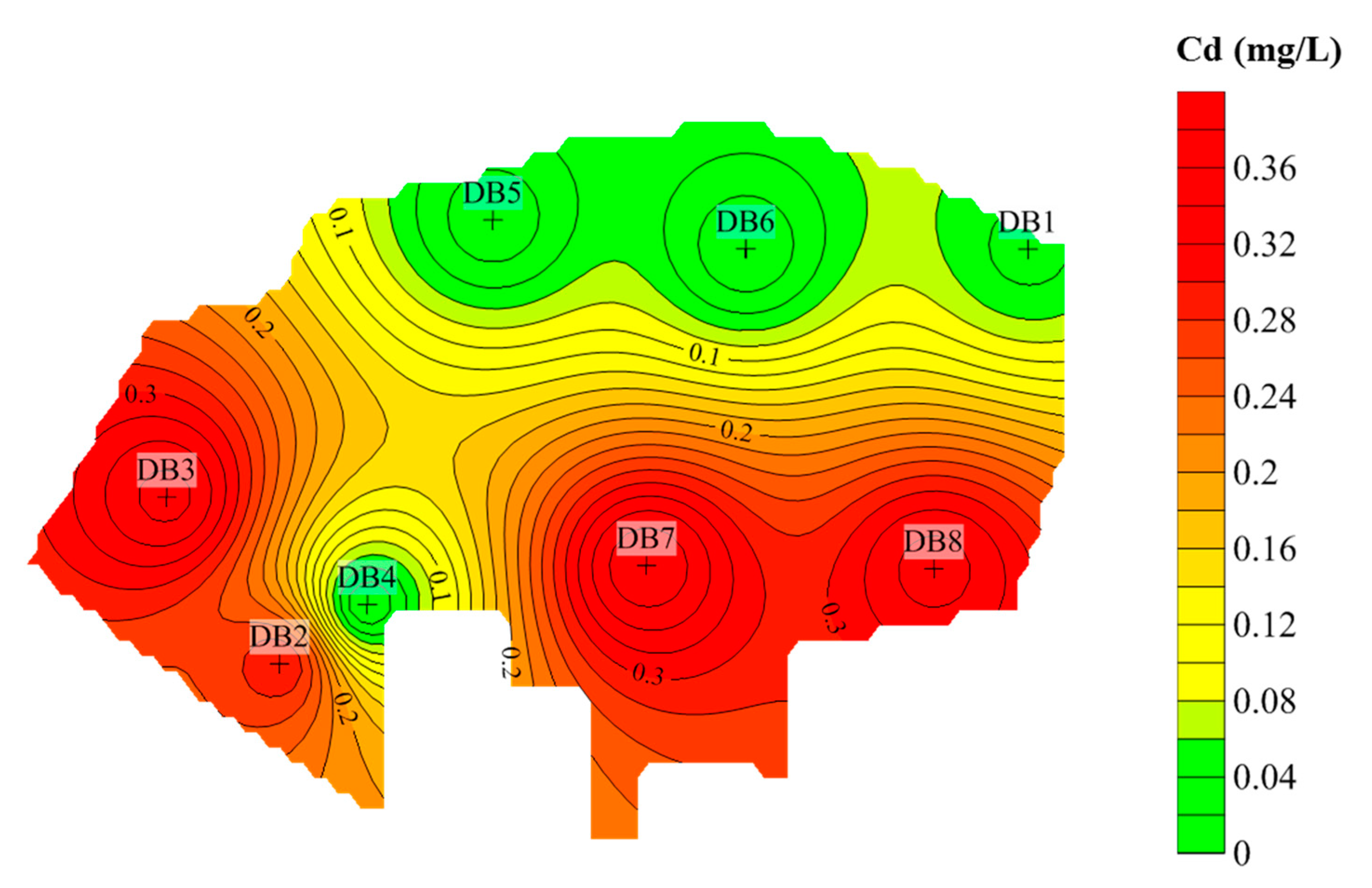
4.2. Site-Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metal Pollution
4.3. Human-Health Risk Assessment
4.4. Ecological Health Risk Assessment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, Q.; Lee, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Hu, H. Distribution of Heavy Metal Pollution in Surface Soil Samples in China: A Graphical Review. B. Environ. Contam. Tox. 2016, 97, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Xue, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X. Concentration of heavy metals in vegetables and potential health risk assessment in China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 40, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lin, C.; Cheng, H.; Duan, X.; Lei, K. Contamination and health risks of soil heavy metals around a lead/zinc smelter in southwestern China. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Liao, R.; Ali, A.; Mahar, A.; Guo, D.; Li, R.; Xining, S.; Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil near a Pb/Zn smelter in Feng County, China. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2017, 139, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar-Camacho, C.; Salas-Moreno, M.; Marrugo-Madrid, S.; Paternina-Uribe, R.; Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Díez, S. A human health risk assessment of methylmercury, arsenic and metals in a tropical river basin impacted by gold mining in the Colombian Pacific region. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; van der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 468–469, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Kirkwood, N.; Maksimović, Č.; Zheng, X.; O’Connor, D.; Jin, Y.; Hou, D. Nature based solutions for contaminated land remediation and brownfield redevelopment in cities: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pan, F.; Xiao, K.; Li, H.; Zheng, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L. An integrated study of the spatiotemporal character, pollution assessment, and migration mechanism of heavy metals in the groundwater of a subtropical mangrove wetland. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Wang, L.; Yang, R.; Hou, W.; Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Zhao, W. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil of a construction waste landfill site. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 70, 101700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, T. Review of soil heavy metal pollution in China: Spatial distribution, primary sources, and remediation alternatives. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 181, 106261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Long, J.; Fan, J.; Wu, P.; Chen, M.; Liu, P.; Li, T. Migration mechanism of pollutants in karst groundwater system of tailings impoundment and management control effect analysis: Gold mine tailing impoundment case. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 350, 131434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; Shi, Y.; Guo, G.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Su, Y.; Zhang, C. Spatial distribution prediction of soil As in a large-scale arsenic slag contaminated site based on an integrated model and multi-source environmental data. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Xu, X.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, P.; Li, Y. Pollution characteristics, influencing factors and health risks of personal heavy metals exposure: Results from human environmental exposure study in China. Build. Environ. 2022, 220, 109217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.C.; Ndambuki, J.M. Optimal design of groundwater pollution management systems for a decanting contaminated site: A simulation-optimization approach. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 15, 100664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janža, M. Optimization of well field management to mitigate groundwater contamination using a simulation model and evolutionary algorithm. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Huang, G.H.; Lu, H.W. A simulation-based fuzzy chance-constrained programming model for optimal groundwater remediation under uncertainty. Adv. Water Resour. 2008, 31, 1622–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wu, H.; Tian, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J. Migration and fate of characteristic pollutants migration from an abandoned tannery in soil and groundwater by experiment and numerical simulation. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badmus, G.O.; Ogungbemi, O.S.; Enuiyin, O.V.; Adeyeye, J.A.; Ogunyemi, A.T. Delineation of leachate plume migration and appraisal of heavy metals in groundwater around Emirin dumpsite, Ado-Ekiti, Nigeria. Sci. Afr. 2022, 17, e01308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, R.J.; Gronow, J.R.; Hall, D.H.; Voulvoulis, N. Household hazardous waste disposal to landfill: Using LandSim to model leachate migration. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 146, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Luo, Q.; Wu, J. An effective multi-objective optimization approach for groundwater remediation considering the coexisting uncertainties of aquifer parameters. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedpour, S.M.; Kirmizakis, P.; Brennan, P.; Doherty, R.; Ricken, T. Optimal remediation design and simulation of groundwater flow coupled to contaminant transport using genetic algorithm and radial point collocation method (RPCM). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K. Formulating surrogate pumping test data sets to assess aquifer hydraulic conductivity. J. Hydrol. X 2018, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulson, B.; Taylor, A.; Stifelman, M. Lead exposure in young children over a 5-year period from urban environments using alternative exposure measures with the US EPA IEUBK model—A trial. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidlaw, M.A.S.; Mohmmad, S.M.; Gulson, B.L.; Taylor, M.P.; Kristensen, L.J.; Birch, G. Estimates of potential childhood lead exposure from contaminated soil using the US EPA IEUBK Model in Sydney, Australia. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 781–790. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, H.T.; Rühaak, W.; Schuster, V.; Sass, I. Fully hydro-mechanical coupled Plug-in (SUB+) in FEFLOW for analysis of land subsidence due to groundwater extraction. SoftwareX 2019, 9, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, M.; Hemker, K. A Dupuit formulation for flow in layered, anisotropic aquifers. Adv. Water. Resour. 2002, 25, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Xu, X.; Chen, Q.; Liu, H.; Min, X.; Fourie, A.; Chai, L. Ab initio calculation of the adsorption of As, Cd, Cr, and Hg heavy metal atoms onto the illite(001) surface: Implications for soil pollution and reclamation. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 312, 120072. [Google Scholar]







| Heavy Metal | DB1 | DB2 | DB3 | DB4 | DB5 | DB6 | DB7 | DB8 | Standard | Detection Limits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb (mg/L) | 0.0023 | 0.0025 | 0.0034 | 0.0034 | 0.0022 | 0.0025 | 0.0042 | 0.0038 | 0.1 | 0.001 |
| Cd (mg/L) | 0.0033 | 0.2980 | 0.3680 | 0.0027 | 0.0067 | 0.0039 | 0.3790 | 0.3490 | 0.01 | 0.001 |
| Cr (mg/L) | <0.00011 | <0.00011 | <0.00011 | <0.00011 | <0.00011 | <0.00011 | <0.00011 | <0.00011 | 0.1 | 0.00011 |
| Zn (mg/L) | 0.2240 | 0.2130 | 2.5250 | 2.6390 | 0.2080 | 0.2260 | 2.6800 | 2.5470 | 5 | 0.004 |
| Fe (mg/L) | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.2600 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 2 | 0.01 |
| As (mg/L) | 0.0016 | 0.0016 | 0.0013 | 0.0012 | 0.0016 | 0.0014 | 0.0013 | 0.0013 | 0.05 | 0.001 |
| Hg (mg/L) | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.002 | 0.0001 |
| Ba (mg/L) | 0.0570 | 0.0551 | 0.0659 | 0.0629 | 1.0800 | 1.2500 | 0.0624 | 0.0629 | 4 | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, D.; Liang, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, S.; He, Y.; Du, J.; Chen, X.; Pu, S. Human-Health and Environmental Risks of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soil and Groundwater at a Riverside Site, China. Processes 2022, 10, 1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101994
Luo D, Liang Y, Wu H, Li S, He Y, Du J, Chen X, Pu S. Human-Health and Environmental Risks of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soil and Groundwater at a Riverside Site, China. Processes. 2022; 10(10):1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101994
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Dongyuan, Yuan Liang, Hao Wu, Shudi Li, Yaoye He, Junyan Du, Xixi Chen, and Shengyan Pu. 2022. "Human-Health and Environmental Risks of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soil and Groundwater at a Riverside Site, China" Processes 10, no. 10: 1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101994
APA StyleLuo, D., Liang, Y., Wu, H., Li, S., He, Y., Du, J., Chen, X., & Pu, S. (2022). Human-Health and Environmental Risks of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soil and Groundwater at a Riverside Site, China. Processes, 10(10), 1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101994







