Various Approaches for the Detoxification of Toxic Dyes in Wastewater
Abstract
1. Background
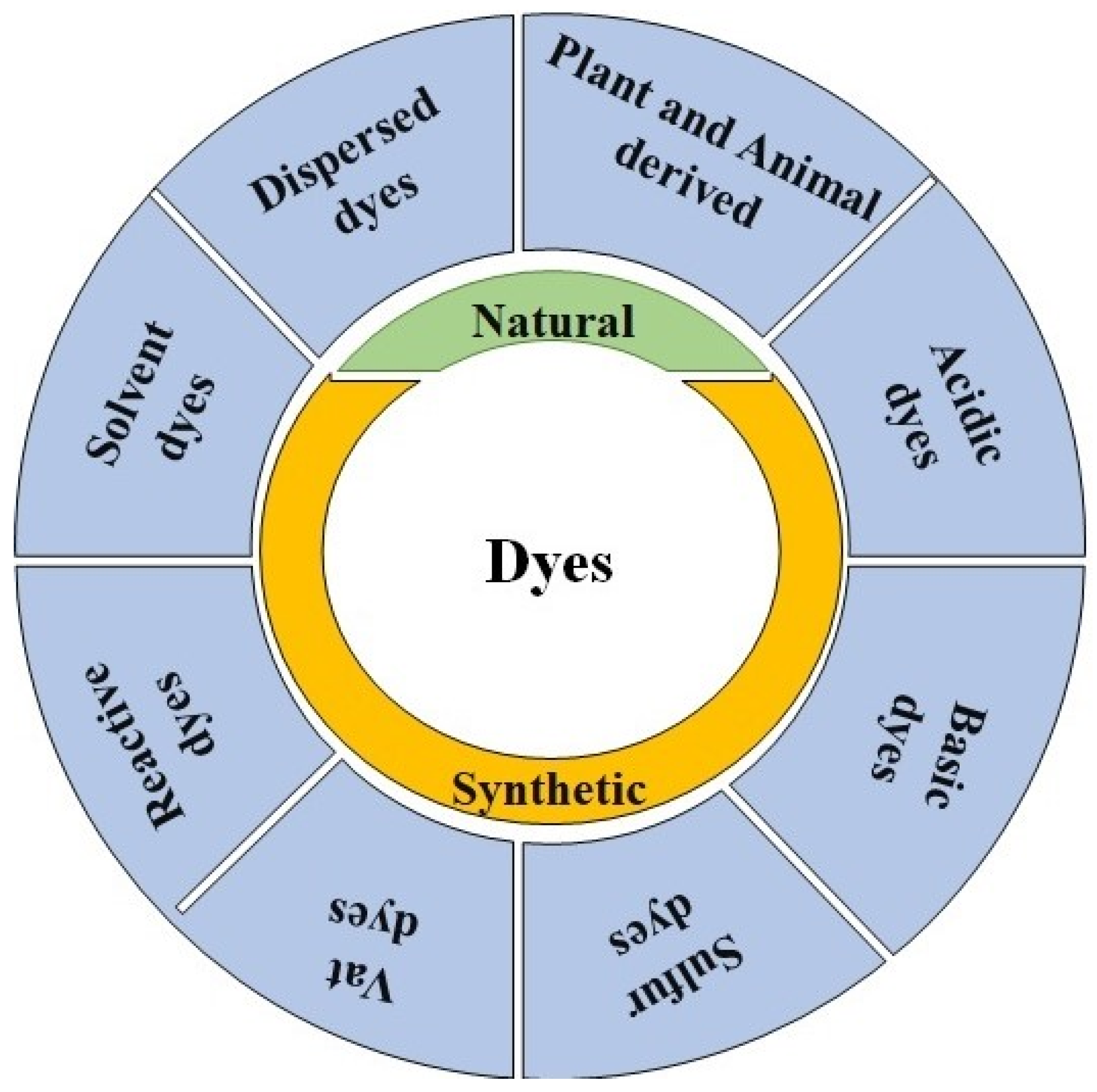
2. Production and Discharge of Dyes
3. Toxicity of Dyes
4. Environmental Impacts of Dyes
4.1. Air Pollution
4.2. Soil Pollution
4.3. Water Pollution
5. Negative Effects of Dyes on Various Populations
5.1. Effect on Microbial Population
5.2. Impact of Dyes on Fish
5.3. Impact on Algae
5.4. Effect on Agriculture
5.5. Impact on Human Health
5.5.1. Cancer
5.5.2. Effect on Liver
5.5.3. Allergies
5.5.4. Effect on Hormones and Central Nervous System
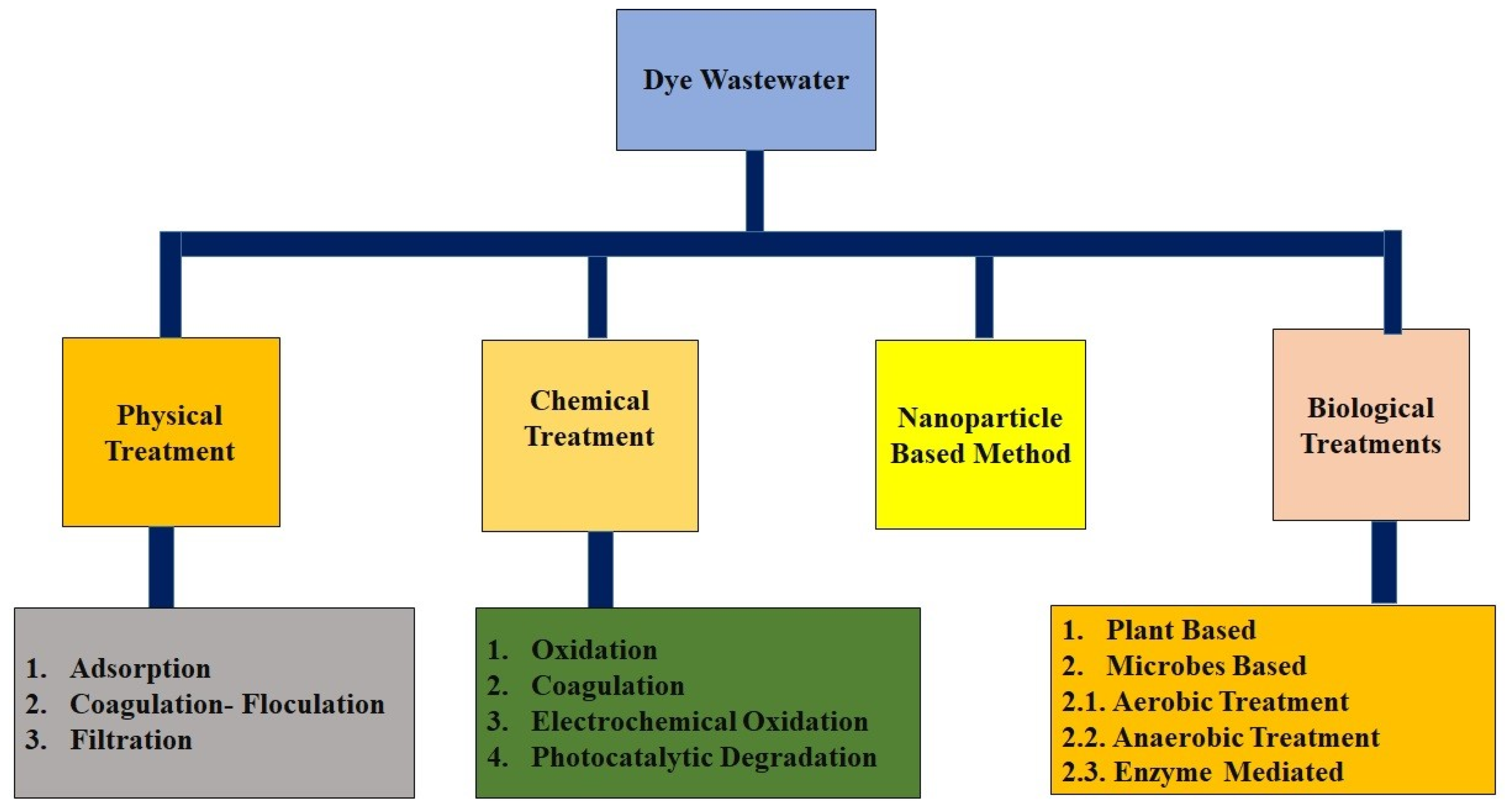
6. Dye removal Techniques
6.1. Physical Treatment
6.1.1. Filtration Technology
6.1.2. Adsorption
6.2. Chemical Treatment
6.2.1. Oxidation
6.2.2. Coagulation–Flocculation Method
6.2.3. Electrochemical Oxidation
6.2.4. Photocatalytic Degradation
6.3. Biological Techniques
6.3.1. Decolorization and Degradation of Dyes by Plants (Phytoremediation)
6.3.2. Treatment by Fungus
6.3.3. Treatment by Algae
6.3.4. Treatment by Lichen
6.3.5. Microbial Treatment
Aerobic Treatment
Anaerobic Treatment
7. Enzyme-Mediated Dye Removal
7.1. Types of Enzymes Participating in the Decolorization and Degradation of Dyes
7.1.1. Oxidative Enzymes
7.1.2. Reductive Enzymes
7.2. Immobilized Enzymes
8. Nanoparticle-Based Dye Degradation
8.1. Types of Nanomaterials Used in the Treatment of Water and Wastewater
8.1.1. Zero-Valent Meal Nanoparticles
Silver Nanoparticles
Iron Nanoparticles
8.1.2. Metal Oxide Nanoparticles
Iron Oxides Nanoparticles
Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
Titanium dioxide Nanoparticles
8.1.3. Carbon Nanotubes
8.1.4. Nanocomposite
8.2. Type of Nanomaterials in Wastewater Treatment
8.2.1. Nano-Adsorbents
8.2.2. Nano-Catalysts
8.2.3. Nano-Membranes
8.3. Use of Nanoparticles in Waste Water Treatment
9. Reuse of Industrial Wastewater
10. Wastewater Reuse: Advantages for Textile Industries
10.1. Lesser Environmental Issues
10.2. Improved Performance
10.3. Economically Beneficial
10.4. Dealing with the Issue of Rising Water Demand
10.5. Remedy for a Drought-Stricken Area
10.6. Better Quality Product
10.7. Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD)
11. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koop, S.H.A.; van Leeuwen, C.J. The challenges of water, waste and climate change in cities. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2017, 19, 385–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, I.; Lone, F.A.; Bhat, R.A.; Mir, S.A.; Dar, Z.A.; Dar, S.A. Concerns and Threats of Contamination on Aquatic Ecosystems. Bioremediation Biotechnol. 2020, 27, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithra, K.G.; Kumar, P.S.; Jaikumar, V.; Rajan, P.S. Removal of colorants from wastewater: A review on sources and treatment strategies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 75, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, D.W.; Birkinshaw, C.; O’Dwyer, T.F. Heavy metal adsorbents prepared from the modification of cellulose: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6709–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawad, H.; El-Rahim, W.M.; Khalafallah, M. Evaluation of biotoxicity of textile dyes using two bioassays. J. Basic Microbiol. 2003, 43, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, T.; McMullan, G.; Marchant, R.; Nigam, P. Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: A critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaskar, A.A.; Hassabo, A.G. Recent Use of Natural Animal Dyes in Various Field. J. Text. Color. Polym. Sci. 2021, 18, 191–210. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, I.M.C.; Gomes, A.; Brás, R.; Ferra, M.I.A.; Amorim, M.T.P.; Porter, R.S. Biological treatment of effluent containing textile dyes. Color. Technol. 2000, 116, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- O’Neill, C.; Hawkes, F.R.; Hawkes, D.L.; Lourenço, N.D.; Pinheiro, H.M.; Delée, W. Colour in textile effluents–sources, measurement, discharge consents and simulation: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1999, 74, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobylewski, S.; Jacobson, M.F. Toxicology of food dyes. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2012, 18, 220–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D. Food Colors and Associated Oxidative Stress in Chemical Carcinogenesis. In Handbook of Oxidative Stress in Cancer: Mechanistic Aspects; Chakraborti, S., Ray, B.K., Roychowdhury, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dixit, U.; Singh, K.; Gupta, S.P.; Beg, M.S.J. Structure and Properties of Dyes and Pigments. In Dyes and Pigments-Novel Applications and Waste Treatment; Papadakis, R., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banat, I.M.; Nigam, P.; Singh, D.; Marchant, R. Microbial decolorization of textile-dyecontaining effluents: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 1996, 58, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsantali, R.I.; Raja, Q.A.; Alzahrani, A.Y.A.; Sadiq, A.; Naeem, N.; Mughal, E.U.; Al-Rooqi, M.M.; El Guesmi, N.; Moussa, Z.; Ahmed, S.A. Miscellaneous azo dyes: A comprehensive review on recent advancements in biological and industrial applications. Dye. Pigment. 2022, 199, 110050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markandeya; Shukla, S.; Mohan, D. Toxicity of Disperse Dyes and its Removal from Wastewater Using Various Adsorbents: A Review. Res. J. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 11, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Suhas. Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2313–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandanshive, V.; Kadam, S.; Rane, N.; Jeon, B.H.; Jadhav, J.; Govindwar, S. In situ textile wastewater treatment in high rate transpiration system furrows planted with aquatic macrophytes and floating phytobeds. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhals, H. Color Chemistry. Synthesis, Properties and Applications of Organic Dyes and Pigments, 3rd ed.; Zollinger, H., Ed.; John Wiley & Son: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 43, pp. 5291–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgacs, E.; Cserháti, T.; Oros, G. Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: A review. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbasar, E.P.A.; Körlü, A.E. Textile Wastewater Treatment; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmen, Z.; Suteu, D. Textile Organic Dyes–Characteristics, Polluting Effects and Separation/Elimination Procedures from Industrial Effluents–A Critical Overview, IntechOpen. In Organic Pollutants Ten Years After the Stockholm Convention-Environmental and Analytical Update; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/29369 (accessed on 22 August 2022).
- Allen, S.; Kowmanova, B. Decolorization of water/wastewater using adsorption. J. Univ. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2005, 40, 175–192. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, P. Removing colour from dyehouse waste waters—A critical review of technology available. J. Soc. Dye. Colour. 1993, 109, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallas, G.; Choi, J.-H. Synthesis and spectral properties of azo dyes derived from 2- aminothiophenes and 2-aminothiazoles. Dye. Pigment. 1999, 42, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Cerniglia, C.E.; Chen, H. Toxicological significance of azo dye metabolism by human intestinal microbiota. Front. Biosci. 2012, 4, 568–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, B.; Sorial, G.A.; Bahrami, H.; Arami, M. Adsorption of binary mixtures of cationic dyes. Dye. Pigment. 2008, 3, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, A.; Singh, S. Myco-decontamination of azo dyes: Nano-augmentation technologies. 3 Biotech. 2020, 10, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, R.; Freeman, H.S. Environmental Chemistry of Dyes and Pigments; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Available online: https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Environmental+Chemistry+of+Dyes+and+Pigments-p-9780471589273 (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Kusic, H.; Juretic, D.; Koprivanac, N.; Marin, V.; Božić, A.L. Photooxidation processes for an azo dye in aqueous media: Modeling of degradation kinetic and ecological parameters evaluation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Qada, E.; Allen, S.; Walker, G. Adsorption of basic dyes from aqueous solution onto activated carbons. Chem. Eng. J. Granulation Process. Spec. Issue 2008, 135, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodaglio, A.G. Integrated, Decentralized Wastewater Management for Resource Recovery in Rural and Peri-Urban Areas. Resources 2017, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.R.; van Vliet, M.T.H.; Qadir, M.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Country-level and gridded estimates of wastewater production, collection, treatment and reuse. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iscen, C.F.; Kiran, I.; Ilhan, S. Biosorption of Reactive Black 5 dye by Penicillium restrictum: The kinetic study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosvi, S.; Kher, X.; Madamwar, D. Isolation, characterization and decolorization of textile dyes by a mixed bacterial consortium JW-2. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 3, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanbeigi, A.; Price, L. A technical review of emerging technologies for energy and water efficiency and pollution reduction in the textile industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 95, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.G.; Biswas, J.K.; Agarwal, K.M. Air Pollution From Bleaching and Dyeing Industries Creating Severe Health Hazards in Maheshtala Textile Cluster, West Bengal, India. Air Soil Water Res. 2017, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, R.; Selim, M.; Shamim, A.M.; Chowdhury, M.; Sultana, S. Review on various types of pollution problem in textile dyeing & printing industries of Bangladesh and recommandation for mitigation. J. Text. Eng. Fash. Technol. 2019, 5, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandare, R.V.; Govindwar, S.P. Phytoremediation of textile dyes and effluents: Current scenario and future prospects. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1697–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lellis, B.; Fávaro-Polonio, C.Z.; Pamphile, J.A.; Polonio, J.C. Effects of textile dyes on health and the environment and bioremediation potential of living organisms. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2019, 3, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunberg Calls out Climate Impact of Fashion Brands in Vogue Interview. BBC News 9 August 2021. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-58145465 (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Bae, J.S.; Freeman, H.S.; Kim, S.D. Influences of new azo dyes to the aquatic ecosystem. Fiber Polym. 2006, 7, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puvaneswari, N.; Muthukrishnan, J.; Gunasekaran, P. Toxicity assessment and microbial degradation of azo dyes. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 44, 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Gradíssimo, D.G.; Xavier, L.P.; Santos, A.V. Degradation of Azo Dyes: Bacterial Potential for Bioremediation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samchetshabam, G.; Ajmal, H.; Choudhury, T.G. Impact of Textile Dyes Waste on Aquatic Environments and Its Treatment. Environ. Ecol. 2016, 35, 2349–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Yasser, A.G.; Naser, M.D. Impact of pollutants on fish collected from different parts of Shatt Al-Arab River: A histopathological study. Environ Monit Assess. 2011, 181, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, B.; Yaseen, H.; Al-Ghanim, K.; Al-Misned, F.; Qasim, M.; Al-Mulhm, N.; Mahboob, S. A study on risk assessment of effect of hematoxylin dye on cytotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in freshwater fish: Food and water security prospective research. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2267–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesci, A.; Cicero, N.; Fumia, A.; Petrarca, C.; Mangifesta, R.; Nava, V.; Lo Cascio, P.; Gangemi, S.; Di Gioacchino, M.; Lauriano, E.R. Histological and Chemical Analysis of Heavy Metals in Kidney and Gills of Boops boops: Melanomacrophages Centers and Rodlet Cells as Environmental Biomarkers. Toxics 2022, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Li, F.; Okasha, K.M.; Mahmoud, Y.A.G.; Elsamahy, T.; Jiao, H.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J. A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, A.K.; Rathi, B.G.; Shukla, S.P.; Kumar, K.; Bharti, V.S. Acute toxicity of textile dye Methylene blue on growth and metabolism of selected freshwater microalgae. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 82, 103552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Thakur, A.; Goyal, A. CHAPTER 1:Industrial Wastewater and Its Toxic Effects. In Biological Treatment of Industrial Wastewater; 2021; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, M.B.; Hassan, J.; Saif, H.B.; Biswas, A.; Sultana, S. Toxic Effect of Textile Dyeing Effluents on Germination, Growth, Yield and Nutritional Quality of Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus). Int. J. Ecotoxicol. Ecobiol. 2016, 1, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Karunanidhi, D.; Subramani, T.; Srinivasamoorthy, K. Sources and Consequences of Groundwater Contamination. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belessi, V.; Romanos, G.; Boukos, N.; Lambropoulou, D.; Trapalis, C. Removal of reactive red 195 from aqueous solutions by adsorption on the surface of TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Hazard Mater. 2009, 170, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Z.; Chadha, P. Textile industry and occupational cancer. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2016, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berradi, M.; Hsissou, R.; Khudhair, M.; Assouag, M.; Cherkaoui, O.; El Bachiri, A.; El Harfi, A. Textile finishing dyes and their impact on aquatic environs. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, S.C.; Preethi, K.A.; Ross, K.; Tusubira, D.; Khan, M.W.A.; Mani, P.; Rao, T.N.; Sekar, D. CRISPR/Cas9 and next generation sequencing in the personalized treatment of Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, I.; Bacioglou, I.A.; Tuhkanen, T.; Bahnemann, D. H2O2/UV-C and Fe2+/H2O2/UV-C versus TiO2/UV-A Treatment for reactive dye wastewater. J. Environ. Eng. 2000, 126, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildenbrand, S.; Schmahl, F.W.; Wodarz, R.; Kimmel, R.; Dartsch, P.C. Azo dyes and carcinogenic aromatic amines in cell cultures. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 1999, 72, M52–M56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzek, T.; Lang, C.; Grohmann, G.; Baltes, W. Formation of a carcinogenic aromatic amine from an azo dye by human skin bacteria in vitro. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 1999, 18, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vineis, P.; Pirastu, R. Aromatic amines and cancer. Cancer Causes Control. 1997, 8, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golka, K.; Kopps, S.; Myslak, Z.W. Carcinogenicity of azo colorants: Influence of solubility and bioavailability. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 151, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, J.R.; Beltran, J.; Rodriguez, O. Vis and UV photocatalytic detoxification methods (using TiO2, TiO2/H2O2,TiO2/O3, TiO2=S2O28, O3, H2O2, S2O28, Fe3þ=H2O2 and Fe3þ=H2O2=C2O24) for dyes treatment. Catal.Today 2005, 101, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gago-Dominguez, M.; Castelao, J.E.; Yuan, J.-M.; Yu, M.C.; Ross, R.K. Use of permanent hair dyes and bladder-cancer risk. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 91, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Birmann, B.M.; Han, J.; Giovannucci, E.L.; E Speizer, F.; Stampfer, M.J.; A Rosner, B.; Schernhammer, E.S. Personal use of permanent hair dyes and cancer risk and mortality in US women: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 2020, 370, 2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, B.; Sharma, S. Food Color Induced Hepatotoxicity in Swiss Albino Rats, Rattus norvegicus. Toxicol. Int. 2015, 22, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, H.J.; Zhang, H. Targeting oxidative stress in disease: Promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 689–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, G.; Cataudella, E.; Giordano, M.; Nunnari, G.; Chisari, G.; Malaguarnera, M. Toxic hepatitis in occupational exposure to solvents. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2012, 18, 2756–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, J.; Kong, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Z. Serum activities of liver enzymes in workers exposed to sub-TLV levels of dimethylformamide. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2015, 28, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.P.; Ding, Y.L.; Han, C.H. Lessons from a case exposed to dimethylformamide of severe chronic toxic liver disease. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2012, 30, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pratt, M.; Taraska, V. Disperse blue dyes 106 and 124 are common causes of textile dermatitis and should serve as screening allergens for this condition. Am. J. Contact Dermat. Off. J. Am. Contact Dermat. Soc. 2000, 11, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, K.L.; Maibach, H.I. Textile dye allergic contact dermatitis prevalence. Contact Dermat. 2000, 42, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidenari, S.; Mantovani, L.; Manzini, B.M.; Pignatti, M. Cross-sensitizations between azo dyes and para-amino compound. A study of 236 azo-dye-sensitive subjects. Contact Dermat. 1997, 36, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solid, Water & Air Pollution from the Fashion Industry. Fabric of The World. 16 March 2020. Available online: https://www.fabricoftheworld.com/post/solid-water-air-pollution-from-the-fashion-industry (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Forida, P.; Shariful, I.; Zakia, U.; Shaharia, A.; Islam, A.K.M.S. A Study on the Solutions of Environment Pollutions and Worker’s Health Problems Caused by Textile Manufacturing Operations. Biomed J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2020, 28, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Besten, C.; Vet, J.J.; Besselink, H.T.; Kiel, G.S.; van Berkel, B.J.; Beems, R.; van Bladeren, P.J. The liver, kidney, and thyroid toxicity of chlorinated benzenes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1991, 111, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miret, N.V.; Pontillo, C.A.; Zárate, L.V.; de Pisarev, D.K.; Cocca, C.; Randi, A.S. Impact of endocrine disruptor hexachlorobenzene on the mammary gland and breast cancer: The story thus far. Environ. Res. 2019, 173, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, R.; Purchase, P.; Saratale, G.D.; Saratale, R.G.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Bilal, M.; Chandra, R.; Bharagava, R.N. Ecotoxicological and health concerns of persistent coloring pollutants of textile industry wastewater and treatment approaches for environmental safety. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, P.; Malik, A. Fungal dye decolourization: Recent advances and future potential. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsami, S.; Mohamadizaniani, M.; Sarrafzadeh, M.H.; Rene, E.R.; Firoozbahr, M. Recent advances in the treatment of dye-containing wastewater from textile industries: Overview and perspectives. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 143, 138–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, O.J.; Kim, H.; Chiang, P.-C. Decolorization of Wastewater. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 30, 449–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piaskowski, K.; Świderska-Dąbrowska, R.; Zarzycki, P.K. Dye Removal from Water and Wastewater Using Various Physical, Chemical, and Biological Processes. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 1371–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyah, Y.; Lahrichi, A.; Kachkoul, R.; El Mouhri, G.; Idrissi, M.; Iaich, S.; Zerrouq, F. Multi-parametric filtration effect of the dyes mixture removal with the low cost materials. Arab J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2020, 27, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledakowicz, S.; Paździor, K. Recent Achievements in Dyes Removal Focused on Advanced Oxidation Processes Integrated with Biological Methods. Molecules 2021, 26, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, H.J. Removal of Acid Orange 7 Dye from Wastewater: Review. Int. J. Waste Resour. 2019, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmagne, O.; Coste, C. Color removal from textile plant effluents. Am. Dyest. Report. 1996, 85, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Gunatilake, S. Methods of Removing Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater. J. Multidiscip. Eng. Sci. Stud. JMESS 2015, 1, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chidambaram, T.; Oren, Y.; Noel, M. Fouling of nanofiltration membranes by dyes during brine recovery from textile dye bath wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, V.; Saravanan, K.; Bharathi, P.; Dharanya, V.; Meiaraj, C. An overview of treatments for the removal of textile dyes. J. Chem. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 7, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Nqombolo, A.; Mpupa, A.; Moutloali, R.M.; Nomngongo, P.N. Wastewater Treatment Using Membrane Technology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/60850 (accessed on 22 August 2022).
- Nguyen, T.A.; Juang, R.S. Treatment of waters and wastewaters containing sulfur dyes: A. review. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, K.K.H.; McKay, G.; Porter, J.F. Sorption of acid dyes from effluents using activated carbon. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 1999, 1, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Sorption of dyes and copper ions onto biosorbents. Process Biochem. 2003, 7, 1047–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.; Roriz, C.L.; Morales, P.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Food colorants: Challenges, opportunities and current desires of agro-industries to ensure consumer expectations and regulatory practices. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 52, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yargeau, V. Chapter 17: Water and Wastewater Treatment: Chemical Processes; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Thorston, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.H.; Park, C.; Shin, E.B.; Kim, S. Decolorization of disperse and reactive dye solutions using ferric chloride. Desalination 2004, 61, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.G. Decolorizing dye wastewater with Fenton reagent. Water Res. 1992, 26, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mutairi, N.Z. Coagulant toxicity and effectiveness in a slaughterhouse wastewater treatment plant. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 65, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmudabadi, T.Z.; Ebrahimi, A.A.; Eslami, H.; Mokhtari, M.; Salmani, M.H.; Ghaneian, M.T.; Mohamadzadeh, M.; Pakdaman, M. Optimization and economic evaluation of modified coagulation–flocculation process for enhanced treatment of ceramic-tile industry wastewater. AMB Express 2018, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathuram, M.; Meera, R.; Vijayaraghavan, G. Application of locally sourced plants as natural coagulants for dye removal from wastewater: A review. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2018, 9, 2058–2070. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zheng, B.; He, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Ruan, S.; Yang, Y.; Dai, C.; Tang, L. Antimony contamination, consequences and removal techniques: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 156, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, J.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Veit, M.T.; Palácio, S.M.; Bergamasco, R. Performance of different coagulants in the coagulation/flocculation process of textile wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A.K.; Zaher, K. Hybrid treatment system for real textile wastewater remediation based on coagulation/flocculation, adsorption and filtration processes: Performance and economic evaluation. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzouk, B.; Gourich, B.; Madani, K.; Vial, C.; Sekki, A. Removal of a disperse red dye from synthetic wastewater by chemical coagulation and continuous electrocoagulation. A comparative study. Desalination 2011, 272, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamee, R.; Siddique, R. Biodegradation of Synthetic Dyes of Textile Effluent by Microorganisms: An Environmentally and Economically Sustainable Approach. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 9, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reza, K.M.; Kurny, A.; Gulshan, F. Parameters affecting the photocatalytic degradation of dyes using TiO2: A review. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavacharya, C. Colour removal from industrial effluents: A comparative review of available technologies. Chem. Eng. World 1997, 32, 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- López-Grimau, V.; Gutiérrez, M.C. Decolourisation of simulated reactive dyebath effluents by electrochemical oxidation assisted by UV light. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golob, V.; Vinder, A.; Simonič, M. Efficiency of the coagulation/flocculation method for the treatment of dyebath effluents. Dye. Pigment. 2005, 67, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, K.; Sandhya, S.; Carmalin Sophia, A.; Pachhade, K.; Subrahmanyam, Y.V. Decolorization and degradation of H-acid and other dyes using ferrous-hydrogen peroxide system. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. Recent advances in azo dye degrading enzyme research. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2006, 7, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Yan, B.; Du, C. Decolorization of azo dyes by Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 1815–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saratale, R.G.; Saratale, G.D.; Chang, J.S.; Govindwar, S.P. Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes: A review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2011, 42, 138–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, G.; Kalme, S.; Bhosale, S.; Govindwar, S. Biodegradation of kerosene by Aspergillus ochraceus NCIM-1146. J. Basic Microbiol. 2007, 47, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatvani, N.; Mecs, I. Production of laccase and manganese peroxidase by Lentinus edodes on malt-containing by-product of the brewing process. Process Biochem. 2001, 37, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Esposito, E. Potential applications of oxidative enzymes and phenoloxidase-like compounds in wastewater and soil treatment: A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2000, 2, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, S.; Saratale, G.; Govindwar, S. Biotransformation enzymes in Cunninghamella blakesleeana (NCIM-687). J. Basic Microbiol. 2006, 46, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Flurkey, W.H. Phenoloxidases in Portabella Mushrooms. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salokhe, M.D.; Govindwar, S.P. Effect of carbon source on the biotransformation enzymesin Serratia marcescens. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Singh, P.; Iyengar, L. Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2007, 2, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Chen, W.M.; Wu, F.; Chen, P.K.; Yen, C.Y. Revealing azo-dye decolorization of indigenous Aeromonas hydrophila from fountain spring in Northeast Taiwan. J. Chin. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2008, 39, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humnabadkar, R.P.; Saratale, G.D.; Govindwar, S.P. Decolorization of purple 2R by Aspergillus ochraceus (NCIM-1146). Asian J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Environ. Sci. 2008, 10, 693–697. [Google Scholar]
- Saratale, R.G.; Saratale, G.D.; Chang, J.S.; Govindwar, S.P. Decolorization and biodegradation of textile dye Navy blue HER by Trichosporon beigelii NCIM-3326. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, K.M.G.; Compart, L.C.A.; Morais, R.O.; Rosa, L.H.; Santos, M.H. Biodegradation of reactive textile dyes by basidiomycetous fungi from brazilian ecosystems. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2006, 37, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Rastogi, A.; Saini, V.K.; Jain, N. Biosorption of copper(II) from aqueous solutions by Spirogyra species. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 296, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, P.; Desai, N.; Govindwar, S.; Jadhav, J.P.; Bapat, V. Degradation analysis of Reactive Red 198 by hairy roots of Tagetes patula L. (Marigold). Planta 2009, 230, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagalkar, A.N.; Jagtap, U.B.; Jadhav, J.P.; Bapat, V.A.; Govindwar, S.P. Biotechnological strategies for phytoremediation of the sulfonated azo dye Direct Red 5B using Blumea malcolmii Hook. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4104–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilratnisakorn, S.; Thiravetyan, P.; Nakbanpote, W. Synthetic reactive dye wastewater treatment by narrow-leaved cattails (Typha angustifolia Linn.): Effects of dye, salinity and metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 1, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbuligwe, S.E. Comparative treatment of dye-rich wastewater in engineered wetland systems (EWSs) vegetated with different plants. Water Res. 2005, 39, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodake, G.S.; Talke, A.A.; Jadhav, J.P.; Govindwar, S.P. Potential of Brassica Juncea in Order to Treat Textile—Effluent—Contaminated Sites. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2009, 11, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Banerjee, A. Combined Application of Physico-Chemical & Microbiological Processes for Industrial Effluent Treatment Plant; Springer International Publishing: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, S.; Perumalsamy, M.; Prabhu, H.J. Decolourization potential of white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium on synthetic dye bath effluent containing Amido black 10B. J. Saudi. Chem. Soc. 2014, 18, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Yadav, S.; Nigam, V.K.; Sharma, S.R. Fungal-Mediated Solid Waste Management: A Review. In Mycoremediation and Environmental Sustainability; Prasad, R., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindhal, T.; Rakholiya, P.; Varjani, S.; Pandey, A.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Ng, H.Y.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A critical review on advances in the practices and perspectives for the treatment of dye industry wastewater. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgarahy, A.M.; Elwakeel, K.Z.; Elshoubaky, G.A.; Mohammad, S.H. Microwave-accelerated sorption of cationic dyes onto green marine algal biomass. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 22704–22722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayazıt, G.; Gül, Ü.D.; Ünal, D. Biosorption of Acid Red P-2BX by lichens as low-cost biosorbents. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 76, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.N.; Kadam, A.A.; Kachole, M.S.; Govindwar, S.P. Lichen Permelia perlata: A novel system for biodegradation and detoxification of disperse dye Solvent Red 24. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 276, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, R.M. Why is indigo blue? Biotech. Histochem. Off. Publ. Biol. Stain Comm. 2007, 82, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodake, G.; Jadhav, S.; Dawkar, V.; Govindwar, S. Biodegradation of diazo dye Direct brown MR by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus NCIM 2890. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarayu, K.; Sandhya, S. Current technologies for biological treatment of textile wastewater—A review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 645–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uday, U.S.P.; Bandyopadhyay, T.K.; Bhunia, B. Bioremediation and Detoxification Technology for Treatment of Dye(s) from Textile Effluent; Kumbasar, E.P.A., Körlü, A.E., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítězová, M.; Jančiková, S.; Dordević, D.; Vítěz, T.; Elbl, J.; Hanišáková, N.; Jampílek, J.; Kushkevych, I. The Possibility of Using Spent Coffee Grounds to Improve Wastewater Treatment Due to Respiration Activity of Microorganisms. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosz-Wilkołazka, A.; Kochmańska-Rdest, J.; Malarczyk, E.; Wardas, W.; Leonowicz, A. Fungi and their ability to decolourize azo and anthraquinonic dyes. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2002, 30, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popli, S.; Patel, U.D. Destruction of azo dyes by anaerobic–aerobic sequential biological treatment: A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, E.A.; Liu, Z.; Smith, S.R. Organic Contaminant Biodegradation by Oxidoreductase Enzymes in Wastewater Treatment. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grelska, A.; Noszczyńska, M. White rot fungi can be a promising tool for removal of bisphenol A, bisphenol S, and nonylphenol from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 39958–39976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Basak, B.; Dutta, S.; Bhunia, B.; Dey, A. Decolorization and biodegradation of congo red dye by a novel white rot fungus Alternaria alternata CMERI F6. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 147, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beg, Q.K.; Kapoor, M.; Mahajan, L.; Hoondal, G.S. Microbial xylanases and their industrial applications: A review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 56, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalby, P.A. Engineering Enzymes for Biocatalysis. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2007, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reetz, M.T.; Carballeira, J.D. Iterative saturation mutagenesis (ISM) for rapid directed evolution of functional enzymes. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, W.; Ng, T.B.; Deng, X.; Lin, J.; Ye, X. Laccases: Production, Expression Regulation, and Applications in Pharmaceutical Biodegradation. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlan, M.P.; Hazlewood, G.P. Hemicellulose and hemicellulases; Portland Press: London, UK; Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Homaei, A.A.; Sariri, R.; Vianello, F.; Stevanato, R. Enzyme immobilization: An update. J. Chem. Biol. 2013, 6, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fersi, C.; Gzara, L.; Dhahbi, M. Treatment of textile effluents by membrane technologies. Desalination 2005, 185, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, P.; Mishra, A.; Malik, A. Dual application of agricultural residues for xylanase production and dye removal through solid state fermentation. Int. Biodeterior. Amp Biodegrad. 2015, 96, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieille, C.; Zeikus, G.J. Hyperthermophilic Enzymes: Sources, Uses, and Molecular Mechanisms for Thermostability. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2001, 65, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, Q. Potential applications of the oxidoreductive enzymes in the decolorization and detoxification of textile and other synthetic dyes from polluted water: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2006, 26, 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.K.; Singh, R.L. Bio-removal of Azo Dyes: A Review. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 5, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, A.C.R.; Tischler, D. Microbial Degradation of Azo Dyes: Approaches and Prospects for a Hazard-Free Conversion by Microorganisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, J.C.; Moreira, P.R.; Queiroga, A.C.; Morgado, J.; Malcata, F.X.; Pintado, M.E. Application of immobilized enzyme technologies for the textile industry: A review. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2011, 29, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, F.; Bagheri, A.R.; Rasheed, T.; Bilal, M.; Rizwan, K.; Nguyen, T.A.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Chapter 7-Nanomaterials for removal of heavy metals from wastewater. In Micro and Nano Technologies, Nano-Biosorbents for Decontamination of Water, Air, and Soil Pollution; Denizli, A., Ali, N., Bilal, M., Khan, A., Nguyen, T.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 135–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hou, B.; Wang, J.; Tian, B.; Bi, J.; Wang, N.; Li, X.; Huang, X. Nanomaterials for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gola, D.; Kriti, A.; Bhatt, N.; Bajpai, M.; Singh, A.; Arya, A.; Chauhan, N.; Srivastava, S.K.; Tyagi, P.K.; Agrawal, Y. Silver nanoparticles for enhanced dye degradation. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albeladi, S.S.R.; Malik, M.A.; Al-thabaiti, S.A. Facile biofabrication of silver nanoparticles using Salvia officinalis leaf extract and its catalytic activity towards Congo red dye degradation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 10031–10044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraro, P.C.L.; Mortari, S.R.; Vizzotto, B.; Chuy, G.P.; Dos Santos, C.; Brum, L.F.W.; Da Silva, W.L. Iron oxide nanocatalyst with titanium and silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity on the degradation of Rhodamine B dye. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandhru, M.; Rani, S.K.; Vasimalai, N. Reductive degradation of toxic six dyes in industrial wastewater using diaminobenzoic acid capped silver nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.H.; Lim, M.; Hwang, Y.S. Potential environmental implications of nanoscale zero-valent iron particles for environmental remediation. Environ Health Toxicol. 2014, 29, e2014022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galatage, S.T.; Hebalkar, A.S.; Dhobale, S.V.; Mali, O.R.; Kumbhar, P.S.; Nikade, S.V.; Killedar, S.G. Silver Nanoparticles: Properties, Synthesis, Characterization, Applications and Future Trends. In Silver Micro-Nanoparticles-Properties, Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications; Kumar, S., Kumar, P., Pathak, C.S., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oghyanous, F. Nanoparticles in Wastewater Treatment. In Water Conservation-Inevitable Strategy; Eyvaz, M., Albahnasawi, A., Gürbulak, E., Yüksel, E., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekli, L.; Bayatsarmadi, B.; Sekine, R.; Sarkar, B.; Shen, A.M.; Scheckel, K.G.; Skinner, W.; Naidu, R.; Shon, H.K.; Lombi, E.; et al. Analytical characterisation of nanoscale zero-valent iron: A methodological review. Anal. Chim. Act. 2016, 903, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, C.; Segovia, M.; Valenzuela, M.L. Solid State Nanostructured Metal Oxides as Photocatalysts and Their Application in Pollutant Degradation: A Review. Photochem 2022, 2, 609–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, P.N.; Chopda, L.V. Application of Iron Oxide Nanomaterials for the Removal of Heavy Metals. J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 2014, 398569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.K.; Ali, D.; Khan, S.H.; Gnanamoorthy, G.; Choudhary, N.; Yadav, K.K.; Thai, V.N.; Hussain, S.A.; Manhrdas, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Amorphous Iron Oxide Nanoparticles by the Sonochemical Method and Their Application for the Remediation of Heavy Metals from Wastewater. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, K.; Ahmad, P.; Khan, A.; Muhammad, S.; Khandaker, M.U.; Alam, M.M.; Asim, M.; Din, I.U.; Chaudhary, R.G.; Kumar, D.; et al. Effect of Cu Doping on ZnO Nanoparticles as a Photocatalyst for the Removal of Organic Wastewater. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2022, 2022, 9459886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.Z.; Ahmad, A.; Tabassum, H.; Kuddus, M. Applications of Nanoparticles in the Treatment of Wastewater. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Martínez, L., Kharissova, O., Kharisov, B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anucha, C.B.; Altin, I.; Bacaksiz, E.; Stathopoulos, V.N. Titanium dioxide (TiO₂)-based photocatalyst materials activity enhancement for contaminants of emerging concern (CECs) degradation: In the light of modification strategies. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 10, 100262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utami, F.D.; Rahman, D.Y.; Sutisna; Kamirul; Margareta, D.O.; Abdullah, M. Photocatalyst based on TiO2 and its application in organic wastewater treatment using simple spray method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1204, 012086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, P.; Siciliano, C.; Macario, A.; Nagy, J.B. The Role of Carbon Nanotube Pretreatments in the Adsorption of Benzoic Acid. Materials 2021, 14, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soffian, M.S.; Halim, F.Z.A.; Aziz, F.; Rahman, M.A.; Amin, M.A.M.; Chee, D.N.A. Carbon-based material derived from biomass waste for wastewater treatment. Environ. Adv. 2022, 9, 100259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiri, F.; Andra, S.; Kommineni, N.; Balu, S.K.; Bulusu, R.; Boseila, A.A.; Akamo, D.O.; Ahmad, Z.; Khan, F.S.; Rahman, M.H.; et al. Recent Advances in Adsorptive Nanocomposite Membranes for Heavy Metals Ion Removal from Contaminated Water: A Comprehensive Review. Materials 2022, 15, 5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.K. (Ed.) Nanocomposites in Wastewater Treatment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sadegh, H.; Ali, G.A.M.; Gupta, V.K.; Makhlouf, A.S.H.; Shahryari-Ghoshekandi, R.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Sillanpää, M.; Megiel, E. The role of nanomaterials as effective adsorbents and their applications in wastewater treatment. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadavenkatesan, T.; Selvaraj, R.; Vinayagam, R. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Thunbergia grandiflora flower extract and its catalytic action in reduction of Congo red dye: Advanced Materials for Clean Energy and Health Applications, AMCEHA 2019. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 23, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadavenkatesan, T.; Vinayagam, R.; Selvaraj, R. Green synthesis and structural characterization of silver nanoparticles synthesized using the pod extract of Clitoria ternatea and its application towards dye degradation: Advanced Materials for Clean Energy and Health Applications, AMCEHA 2019. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 23, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.; Moldovan, B. Green Synthesis of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles for Efficient Catalytic Removal of Harmful Organic Dyes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.A.; Salunke, B.K.; Saha, P.; Deshmukh, A.R.; Kim, B.S. Comparison of dye degradation potential of biosynthesized copper oxide, manganese dioxide, and silver nanoparticles using Kalopanax pictus plant extract. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscio, V.; García-Jiménez, M.; Vilaseca, M.; López-Grimau, V.; Crespi, M.; Gutiérrez-Bouzán, C. Reuse of Textile Dyeing Effluents Treated with Coupled Nanofiltration and Electrochemical Processes. Materials 2016, 9, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englande, J.; Krenkel, P.; Shamas, J. Wastewater Treatment &Water Reclamation. Ref. Module Earth Syst. Environ. Sci. 2015, B978-0-12-409548-9.09508–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Shaikh, I.A.; Abid, T.; Samina, F.; Islam, S.; Khalid, A.; Firdour, N.; Javed, M.T. Reuse of textile wastewater after treating with combined process of chemical coagulation and electrocoagulation. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 2565–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; Gao, W. Reviewing textile wastewater produced by industries: Characteristics, environmental impacts, and treatment strategies. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 2076–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, D. Waste water treatment in Textile Industries- the concept and current removal Technologies. J. Biodivers. Environ. Sci. 2015, 7, 501–525. [Google Scholar]
- Sachidananda, M.; Webb, D.P.; Rahimifard, S. A Concept of Water Usage Efficiency to Support Water Reduction in Manufacturing Industry. Sustainability 2016, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 5 Advantages of Recycling Wastewater. Micronics Engineered Filtration Group, Inc. 2022. Available online: https://www.micronicsinc.com/filtration-news/advantages-of-recycling-wastewater/ (accessed on 22 August 2022).
- Rathoure, A.K. Zero liquid discharge treatment systems: Prerequisite to industries. MOJ Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2020, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| S. N. | Chromophore | Structure | Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Carbonyl | >C=O | 280 |
| 2 | Azo | -N=N- | 262 |
| 3 | Nitro | -O-N=O | 270 |
| 4 | Nitroso | -N=O | 330 |
| 5 | Triphenylmethane | -NO2 | 230 |
| 6 | Conjugated diene | -C=C-C=C- | 233 |
| 7 | Conjugated triene | -C=C-C=C-C=C- | 268 |
| 8 | Conjugated tetraene | -C=C-C=C-C=C-C=C- | 315 |
| 9 | Benzene |  | 261 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsukaibi, A.K.D. Various Approaches for the Detoxification of Toxic Dyes in Wastewater. Processes 2022, 10, 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101968
Alsukaibi AKD. Various Approaches for the Detoxification of Toxic Dyes in Wastewater. Processes. 2022; 10(10):1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101968
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsukaibi, Abdulmohsen K. D. 2022. "Various Approaches for the Detoxification of Toxic Dyes in Wastewater" Processes 10, no. 10: 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101968
APA StyleAlsukaibi, A. K. D. (2022). Various Approaches for the Detoxification of Toxic Dyes in Wastewater. Processes, 10(10), 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101968






