Helical-Track Bioreactors for Bacterial, Mammalian and Insect Cell Cultures
Abstract
:Nomenclature
| c*G | interfacial oxygen concentration in the gas phase [M] |
| cG | oxygen concentration in the atmospheric air [M] |
| cL | dissolved concentration of oxygen [M] |
| c*L | dissolved oxygen concentration at saturation [M] |
| kGa | oxygen mass transfer coefficient in the gas phase [h−1] |
| kLa | oxygen mass transfer coefficient in the liquid phase [h−1] |
| OTR | oxygen transfer rate through the gas-liquid interface [M·h−1] |
| OTRplug | oxygen transfer rate through the sterile closure [M·h−1] |
| t | time [h] |
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. The 250-mL HT Tube and Other Standard Vessels
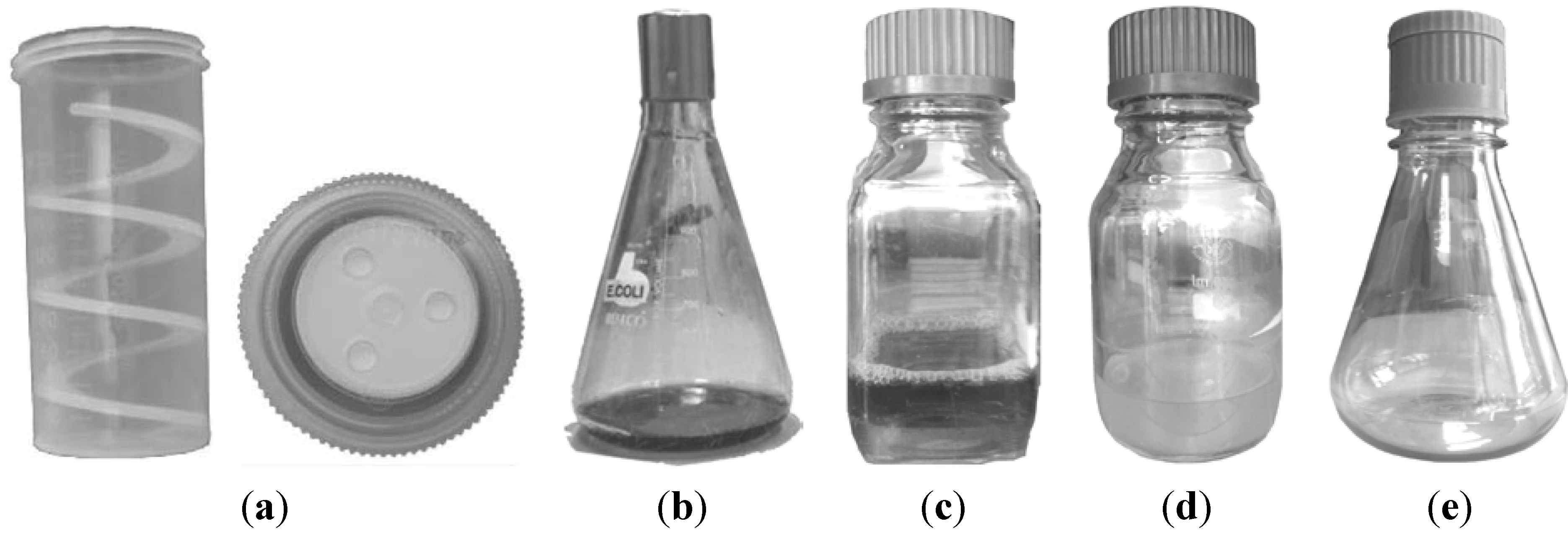
2.2. Gas Transfer


2.3. Bacterial Cultivation and Plasmid Production
2.4. Mammalian Cell Cultivation
2.5. Insect Cell Cultivation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. kLa in 250-mL HT Tubes

3.2. Bacterial Cultivation and Plasmid Production

| Yield | 1-L Erlenmeyer flasks | 250-mL HT tubes |
|---|---|---|
| a Total amount of plasmid | 1.9 ± 0.1 mg | 2.7 ± 0.3 mg |
| b OD600 | 21 ± 0.5 | 29 ± 0.7 |
3.3. Cultivation of Mammalian Cells
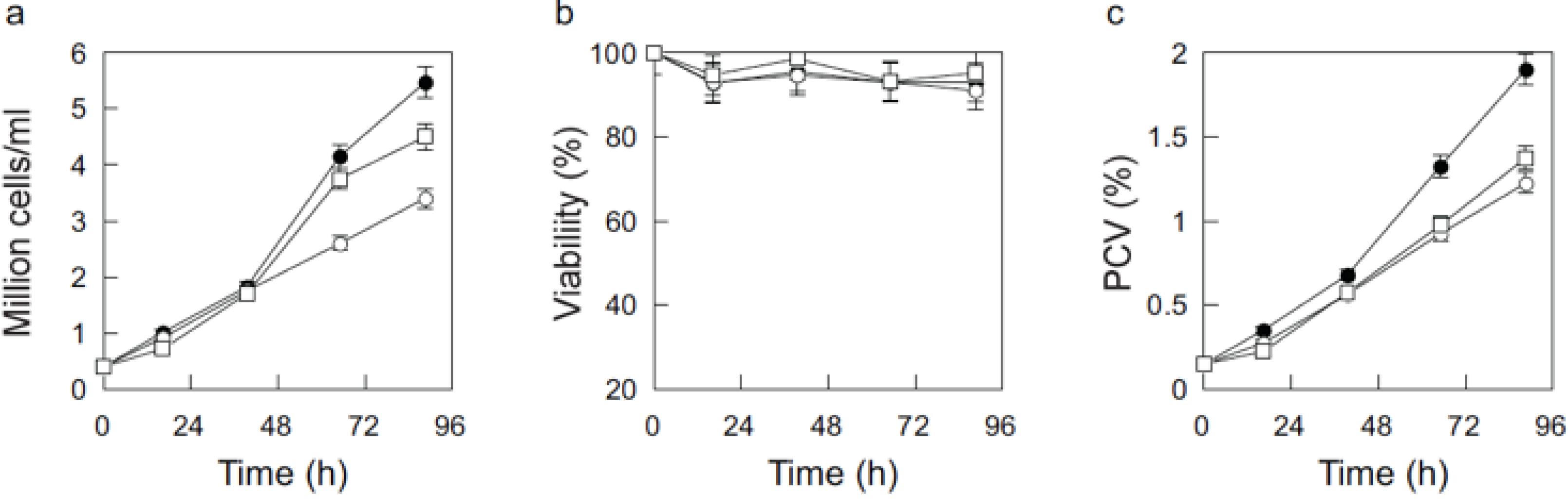
3.4. Cultivation of Insect Cells
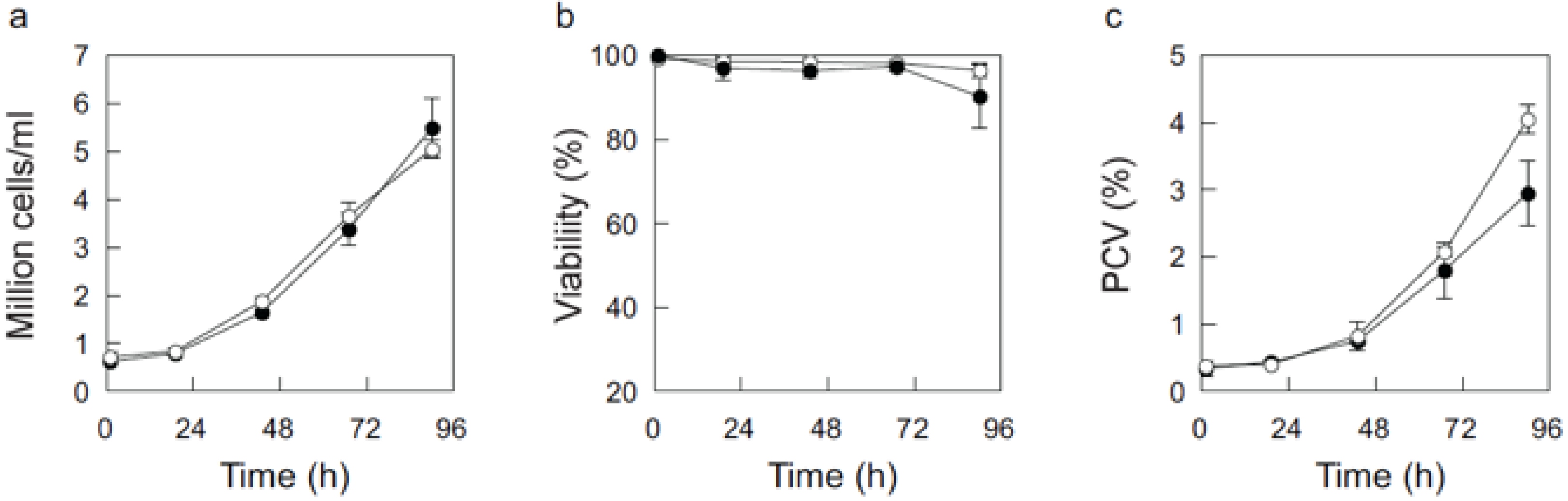
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Büchs, J. Introduction to advantages and problems of shaken cultures. Biochem. Eng. J. 2001, 7, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöckner, W.; Büchs, J. Advances in shaking technologies. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.S. Cotton closure as aeration barrier in shaken flask fermentations. Appl. Microbiol. 1964, 12, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Mrotzek, C.; Anderlei, T.; Henzler, H.J.; Büchs, J. Mass transfer resistance of sterile plugs in shaking bioreactors. Biochem. Eng. J. 2001, 7, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Stettler, M.; Reif, O.; Kocourek, A.; DeJesus, M.; Hacker, D.L.; Wurm, F.M. Shaken helical track bioreactors: Providing oxygen to high-density cultures of mammalian cells at volumes up to 1000 L by surface aeration with air. N. Biotechnol. 2008, 25, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Rao, G. A study of oxygen transfer in shake flasks using a non-invasive oxygen sensor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2003, 84, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikakhtari, H.; Hill, G.A. Closure effects on oxygen transfer and aerobic growth in shake flasks. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2006, 95, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoabediny, G.; Buchs, J. Modelling and advanced understanding of unsteady-state gas transfer in shaking bioreactors. Biotechnol. Appl. Bioc. 2007, 46, 57–67. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendra, Y.; Kiseljak, D.; Baldi, L.; Hacker, D.L.; Wurm, F.M. Reduced glutamine concentration improves protein production in growth-arrested CHO-DG44 and HEK-293E cells. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 34, 619–626. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, N.; Girard, P.; Hacker, D.L.; Jordan, M.; Wurm, F.M. Orbital shaker technology for the cultivation of mammalian cells in suspension. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 89, 400–406. [Google Scholar]
- Stettler, M.; Zhang, X.; Hacker, D.L.; de Jesus, M.; Wurm, F.M. Novel orbital shake bioreactors for transient production of CHO derived IgGs. Biotechnol. Prog. 2007, 23, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Michel, P.O.; Baldi, L.; Hacker, D.L.; Zhang, X.; Wurm, F.M. TubeSpin bioreactor 50 for the high-density cultivation of Sf-9 insect cells in suspension. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, M.; Ukkonen, K.; Haataja, T.; Ruottinen, M.; Glumoff, T.; Neubauer, A.; Neubauer, P.; Vasala, A. A novel fed-batch based cultivation method provides high cell-density and improves yield of soluble recombinant proteins in shaken cultures. Microb. Cell Fact. 2010, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettleship, J.E.; Assenberg, R.; Diprose, J.M.; Rahman-Huq, N.; Owens, R.J. Recent advances in the production of proteins in insect and mammalian cells for structural biology. J. Struct. Biol. 2010, 172, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissot, S.; Michel, P.O.; Hacker, D.L.; Baldi, L.; de Jesus, M.; Wurm, F.M. k(L)a as a predictor for successful probe-independent mammalian cell bioprocesses in orbitally shaken bioreactors. N. Biotechnol. 2012, 29, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Williams-Dalson, W.; Keshavarz-Moore, E.; Shamlou, P.A. Computational-fluid-dynamics (CFD) analysis of mixing and gas-liquid mass transfer in shake flasks. Biotechnol. Appl. Bioc. 2005, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Tissot, S.; Michel, P.O.; Douet, C.J.; Grezet, S.; Baldi, L.; Hacker, D.L.; Wurm, F.M. Helical-Track Bioreactors for Bacterial, Mammalian and Insect Cell Cultures. Processes 2013, 1, 3-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr1010003
Tissot S, Michel PO, Douet CJ, Grezet S, Baldi L, Hacker DL, Wurm FM. Helical-Track Bioreactors for Bacterial, Mammalian and Insect Cell Cultures. Processes. 2013; 1(1):3-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr1010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleTissot, Stéphanie, Patrik O. Michel, Clara J. Douet, Sarah Grezet, Lucia Baldi, David L. Hacker, and Florian M. Wurm. 2013. "Helical-Track Bioreactors for Bacterial, Mammalian and Insect Cell Cultures" Processes 1, no. 1: 3-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr1010003
APA StyleTissot, S., Michel, P. O., Douet, C. J., Grezet, S., Baldi, L., Hacker, D. L., & Wurm, F. M. (2013). Helical-Track Bioreactors for Bacterial, Mammalian and Insect Cell Cultures. Processes, 1(1), 3-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr1010003





