Forward Hand Gesture Spotting and Prediction Using HMM-DNN Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- To accurately detect meaningful number gestures, a stochastic method for building a non-gesture model using HMMs without training data is proposed (0–9).
- A confidence measure that the non-gesture model offers can be used as an adaptive threshold to establish the start and end points of meaningful gestures in the input video stream.
- DNNs are extremely efficient, and perform exceptionally well when it comes to real-time object detection. According to our experimental results, the proposed method can successfully spot and predict significant motions with high reliability.
- Our main goal is to provide accurate, robust, and online application results while also removing the lag between meaningful gesture spotting and identification.
2. Related Work
3. Pre-Processing and Feature-Based Tacking
4. Deep Neural Network
5. Spotting and Prediction Approach
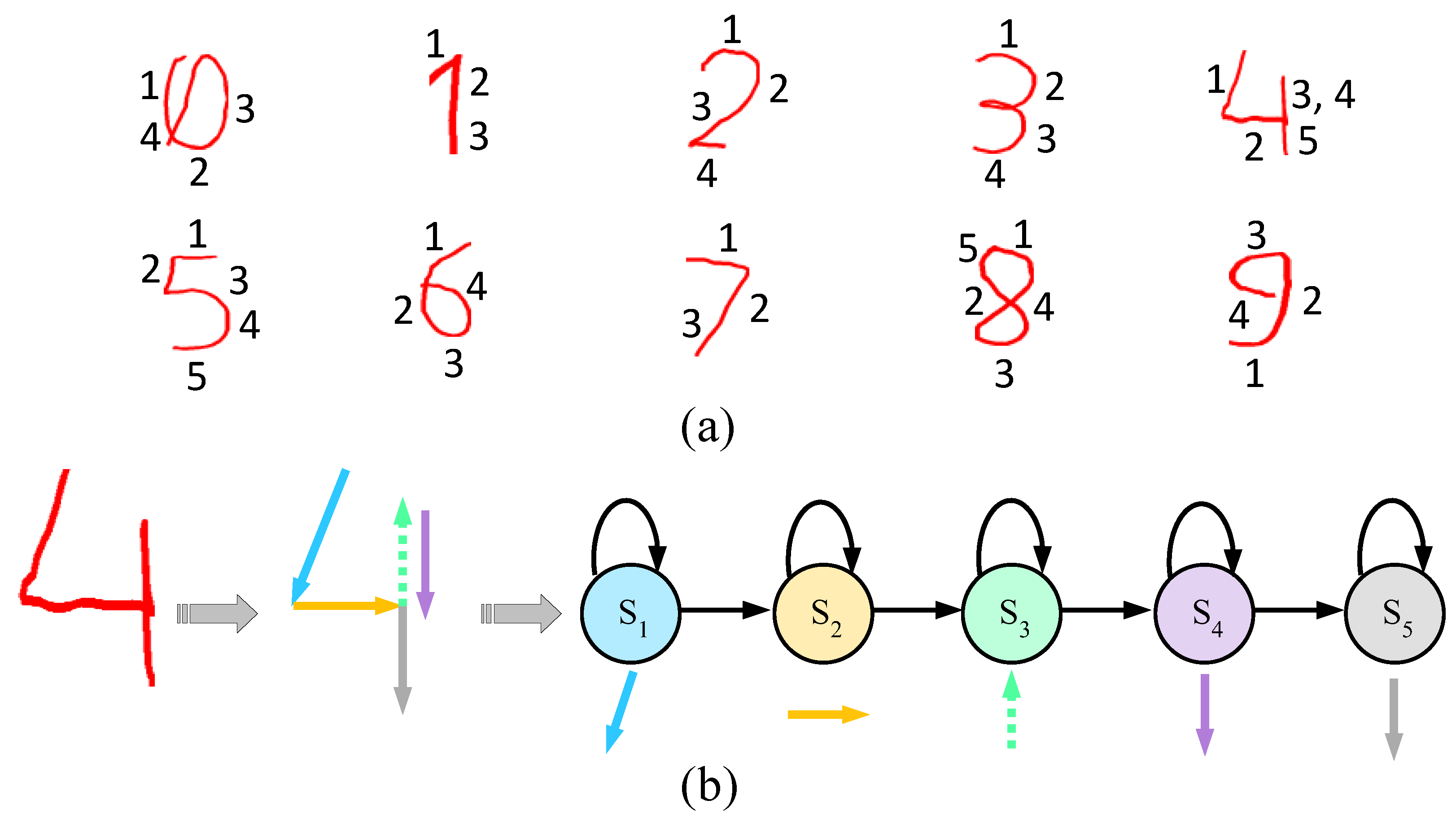
5.1. Spotting with HMMs
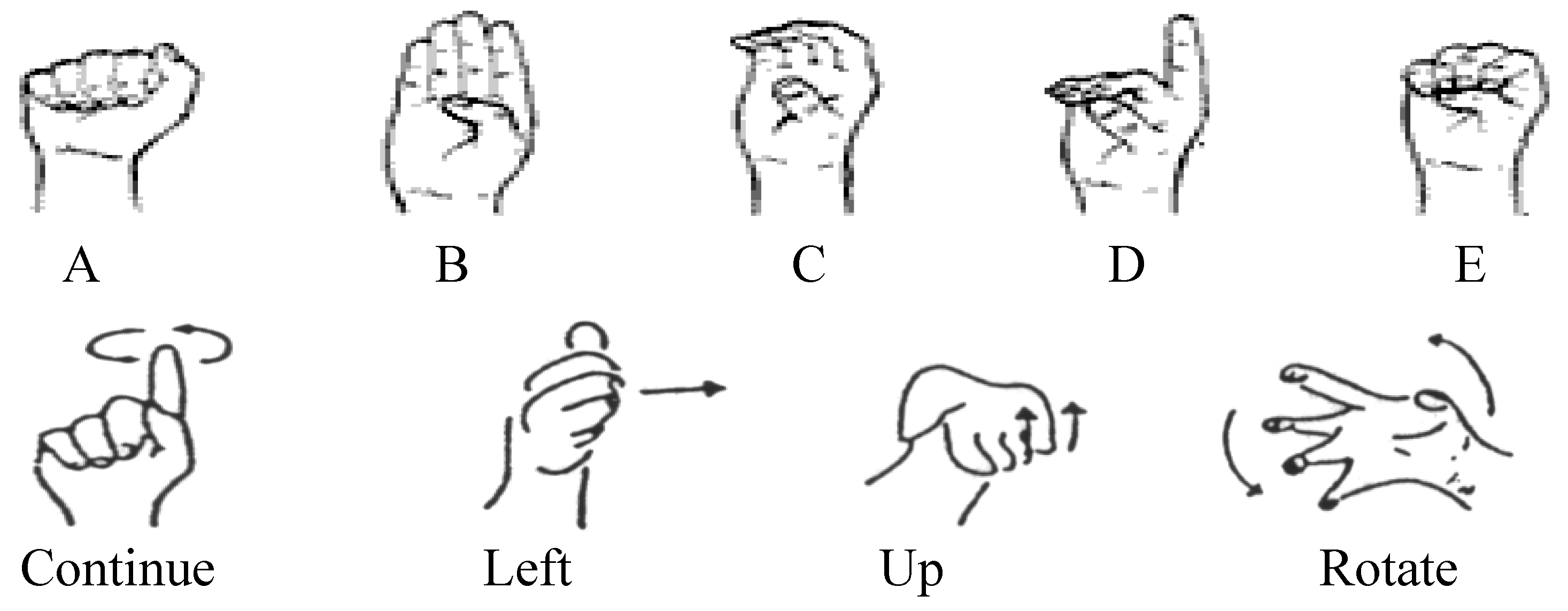
5.2. Gesture Model
5.3. Non-Gesture Model
- First, we copy all states of each hand gesture model along with their output observation . Then, using a Gaussian distribution smoothing filter, we re-estimate the probabilities to define the states such that they act for any pattern. Then, the floor process is smoothed.
- We replicate the probability of self-transition states in the gesture models, as every state reflects a meaningful unit (i.e., segmented graphical pattern) of the hand gesture. Therefore, the quantity of those components determines the target gestures.
- The following formula is used to calculate all outbound transition probabilities:
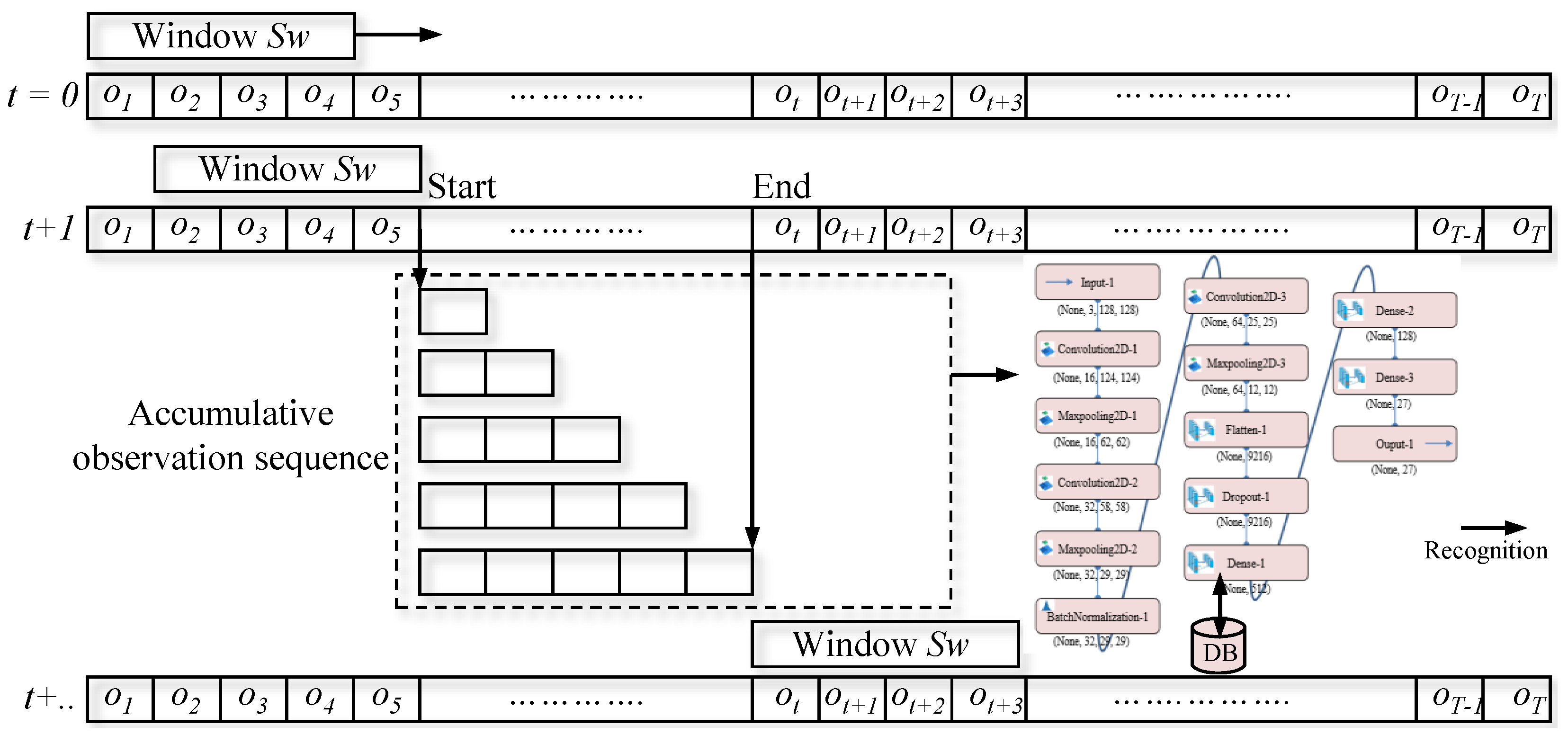
5.4. Gesture Spotting Network
5.5. Spotting and Recognition
6. Experimental Results and Discussion
7. Evaluation
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. A real-time hand gesture recognition method. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electronics, Communications and Control (ICECC), Ningbo, China, 9–11 September 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudah, M.; Al-Naji, A.; Chahl, J. Hand Gesture Recognition Based on Computer Vision: A Review of Techniques. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Žemgulys, J.; Raudonis, V.; Maskeliūnas, R.; Damaševičius, R. Recognition of basketball referee signals from real-time videos. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2019, 11, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hammadi, M.; Muhammad, G.; Abdul, W.; Alsulaiman, M.; Bencherif, M.A.; Alrayes, T.S.; Mathkour, H.; Mekhtiche, M.A. Deep Learning-Based Approach for Sign Language Gesture Recognition With Efficient Hand Gesture Representation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 192527–192542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaitkevičius, A.; Taroza, M.; Blažauskas, T.; Damaševičius, R.; Maskeliūnas, R.; Woźniak, M. Recognition of American Sign Language Gestures in a Virtual Reality Using Leap Motion. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezende, T.M.; Almeida, S.G.M.; Guimarães, F.G. Development and validation of a Brazilian sign language database for human gesture recognition. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 10449–10467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afza, F.; Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Kadry, S.; Manogaran, G.; Saba, T.; Ashraf, I.; Damaševičius, R. A framework of human action recognition using length control features fusion and weighted entropy-variances based feature selection. Image Vis. Comput. 2021, 106, 104090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaidis, A.; Pitas, I. Facial feature extraction and pose determination. Pattern Recognit. 2000, 33, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikajevas, A.; Maskeliunas, R.; Damaševičius, R. Detection of sitting posture using hierarchical image composition and deep learning. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryselis, K.; Petkus, T.; Blažauskas, T.; Maskeliūnas, R.; Damaševičius, R. Multiple Kinect based system to monitor and analyze key performance indicators of physical training. Hum.-Centric Comput. Inf. Sci. 2020, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An ANN-based gesture recognition algorithm for smart-home applications. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 2020, 14, 1967–1983. [CrossRef]
- Abraham, L.; Urru, A.; Normani, N.; Wilk, M.; Walsh, M.; O’Flynn, B. Hand Tracking and Gesture Recognition Using Lensless Smart Sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.; Cho, S.H. Hand Gesture Recognition Using an IR-UWB Radar with an Inception Module-Based Classifier. Sensors 2020, 20, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alkemade, R.; Verbeek, F.J.; Lukosch, S.G. On the Efficiency of a VR Hand Gesture-Based Interface for 3D Object Manipulations in Conceptual Design. Int. J. Hum.–Comput. Interact. 2017, 33, 882–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Sohn, B.S. Immersive Gesture Interfaces for Navigation of 3D Maps in HMD-Based Mobile Virtual Environments. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2018, 2018, 2585797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.H.; Hong, K.S. Game interface using hand gesture recognition. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer Sciences and Convergence Information Technology, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 30 November–2 December 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negin, F.; Rodriguez, P.; Koperski, M.; Kerboua, A.; Gonzàlez, J.; Bourgeois, J.; Chapoulie, E.; Robert, P.; Bremond, F. PRAXIS: Towards automatic cognitive assessment using gesture recognition. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 106, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Rio Guerra, M.S.; Martin-Gutierrez, J.; Acevedo, R.; Salinas, S. Hand Gestures in Virtual and Augmented 3D Environments for Down Syndrome Users. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaczmarek, W.; Panasiuk, J.; Borys, S.; Banach, P. Industrial Robot Control by Means of Gestures and Voice Commands in Off-Line and On-Line Mode. Sensors 2020, 20, 6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, P.; Simão, M.; Mendes, N.; Safeea, M. Gesture-based human-robot interaction for human assistance in manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 101, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, G.; Milne, H.; Griffiths, D.; Padfield, E.; Blenkinsopp, R.; Georgiou, O. Designing Mid-Air Haptic Gesture Controlled User Interfaces for Cars. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2020, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Fan, X.; Zhao, L.; Guo, X. A novel hand gesture recognition method based on 2-channel sEMG. Technol. Health Care 2018, 26, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Li, S. Object Detection Algorithm Based on Improved YOLOv3. Electronics 2020, 9, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulikajevas, A.; Maskeliūnas, R.; Damaševičius, R.; Ho, E.S.L. 3D Object Reconstruction from Imperfect Depth Data Using Extended YOLOv3 Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neto, P.; Pereira, D.; Pires, J.N.; Moreira, A.P. Real-time and continuous hand gesture spotting: An approach based on artificial neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mujahid, A.; Awan, M.J.; Yasin, A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Damaševičius, R.; Maskeliūnas, R.; Abdulkareem, K.H. Real-Time Hand Gesture Recognition Based on Deep Learning YOLOv3 Model. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strezoski, G.; Stojanovski, D.; Dimitrovski, I.; Madjarov, G. Hand Gesture Recognition Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In ICT Innovations 2016; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Z. Deep learning for sequence pattern recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC), Zhuhai, China, 27–29 March 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmezain, M. Hand Gesture Spotting and Recognition Using HMM and CRF in Color Image Sequences. Ph.D. Thesis, Otto-von-Guericke-Universitaet, Magdeburg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Elmezain, M.; Al-Hamadi, A.; Niese, R.; Michaelis, B. A Robust Method for Hand Tracking Using Mean-shift Algorithm and Kalman Filter in Stereo Color Image Sequences. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, Open Science Index 35. Int. J. Electron. Commun. Eng. 2009, 35, 2151–2155. [Google Scholar]
- Elmezain, M.; Al-Hamadi, A.; Michaelis, B. A Novel System for Automatic Hand Gesture Spotting and Recognition in Stereo Color Image Sequences. J. WSCG 2009, 17, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Elmezain, M.; Al-Hamadi, A.; Michaelis, B. A Robust Method for Hand Gesture Segmentation and Recognition Using Forward Spotting Scheme in Conditional Random Fields. In Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 August 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmezain, M.; Al-Hamadi, A.; Sadek, S.; Michaelis, B. Robust methods for hand gesture spotting and recognition using Hidden Markov Models and Conditional Random Fields. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology, Luxor, Egypt, 15–18 December 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




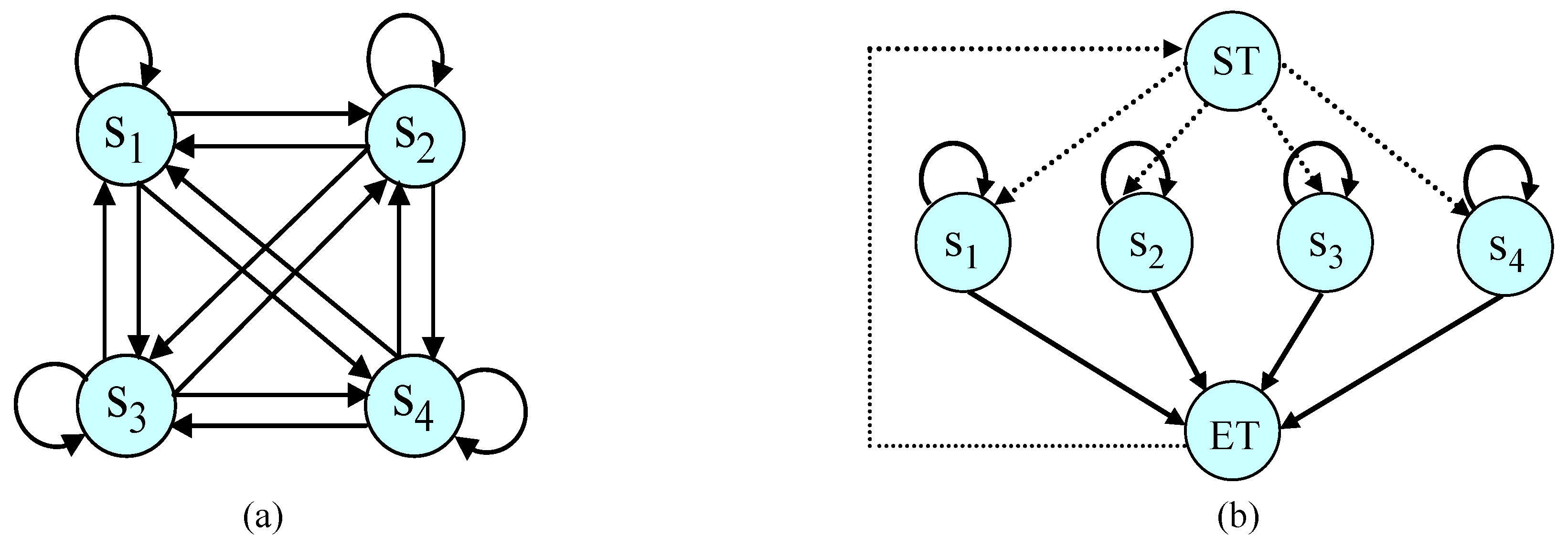






| Gesture Path | Train Data | Test Data | Key Gestures Spotting Outcomes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | D | S | Correct | Rec. (%) | |||
| ‘0’ | 60 | 28 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 25 | 89.29 |
| ‘1’ | 60 | 28 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 26 | 92.86 |
| ‘2’ | 60 | 28 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 27 | 96.43 |
| ‘3’ | 60 | 28 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28 | 100.00 |
| ‘4’ | 60 | 28 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 27 | 96.43 |
| ‘5’ | 60 | 28 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 27 | 96.43 |
| ‘6’ | 60 | 28 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 26 | 92.85 |
| ‘7’ | 60 | 28 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28 | 100.00 |
| ‘8’ | 60 | 28 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 27 | 96.43 |
| ‘9’ | 60 | 28 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 27 | 96.43 |
| Total | 600 | 280 | 3 | 4 | 8 | 268 | 95.71 |
| Spotting Key Gestures Results | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train Data | Test Data | Error Types | Spotting (%) | ||||
| I | D | S | Rec. | Rel. | |||
| 1 | 600 | 280 | 10 | 18 | 30 | 82.86 | 80.00 |
| 2 | 600 | 280 | 7 | 15 | 28 | 84.64 | 82.85 |
| 3 | 600 | 280 | 5 | 7 | 13 | 92.86 | 91.23 |
| 4 | 600 | 280 | 3 | 7 | 13 | 92.86 | 91.87 |
| 5 | 600 | 280 | 3 | 4 | 8 | 95.71 | 94.70 |
| 6 | 600 | 280 | 3 | 7 | 10 | 93.93 | 92.93 |
| 7 | 600 | 280 | 4 | 6 | 11 | 93.93 | 92.61 |
| 8 | 600 | 280 | 5 | 6 | 12 | 93.57 | 91.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elmezain, M.; Alwateer, M.M.; El-Agamy, R.; Atlam, E.; Ibrahim, H.M. Forward Hand Gesture Spotting and Prediction Using HMM-DNN Model. Informatics 2023, 10, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics10010001
Elmezain M, Alwateer MM, El-Agamy R, Atlam E, Ibrahim HM. Forward Hand Gesture Spotting and Prediction Using HMM-DNN Model. Informatics. 2023; 10(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics10010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleElmezain, Mahmoud, Majed M. Alwateer, Rasha El-Agamy, Elsayed Atlam, and Hani M. Ibrahim. 2023. "Forward Hand Gesture Spotting and Prediction Using HMM-DNN Model" Informatics 10, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics10010001
APA StyleElmezain, M., Alwateer, M. M., El-Agamy, R., Atlam, E., & Ibrahim, H. M. (2023). Forward Hand Gesture Spotting and Prediction Using HMM-DNN Model. Informatics, 10(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics10010001







