Estimating the BIS Capital Adequacy Ratio for Korean Banks Using Machine Learning: Predicting by Variable Selection Using Random Forest Algorithms
Abstract
1. Background
2. Literature Review
2.1. Financial Stability and BIS Capital Adequacy Ratios of Korean Banks
2.2. Korean Laws and Regulations about BIS Capital Adequacy Ratio
2.3. Predicting Financial Ratio with Machine Learning Techniques
3. Theoretical Background: BIS Capital Adequacy Ratio
4. Statistical Background: Machine Learning Algorithms
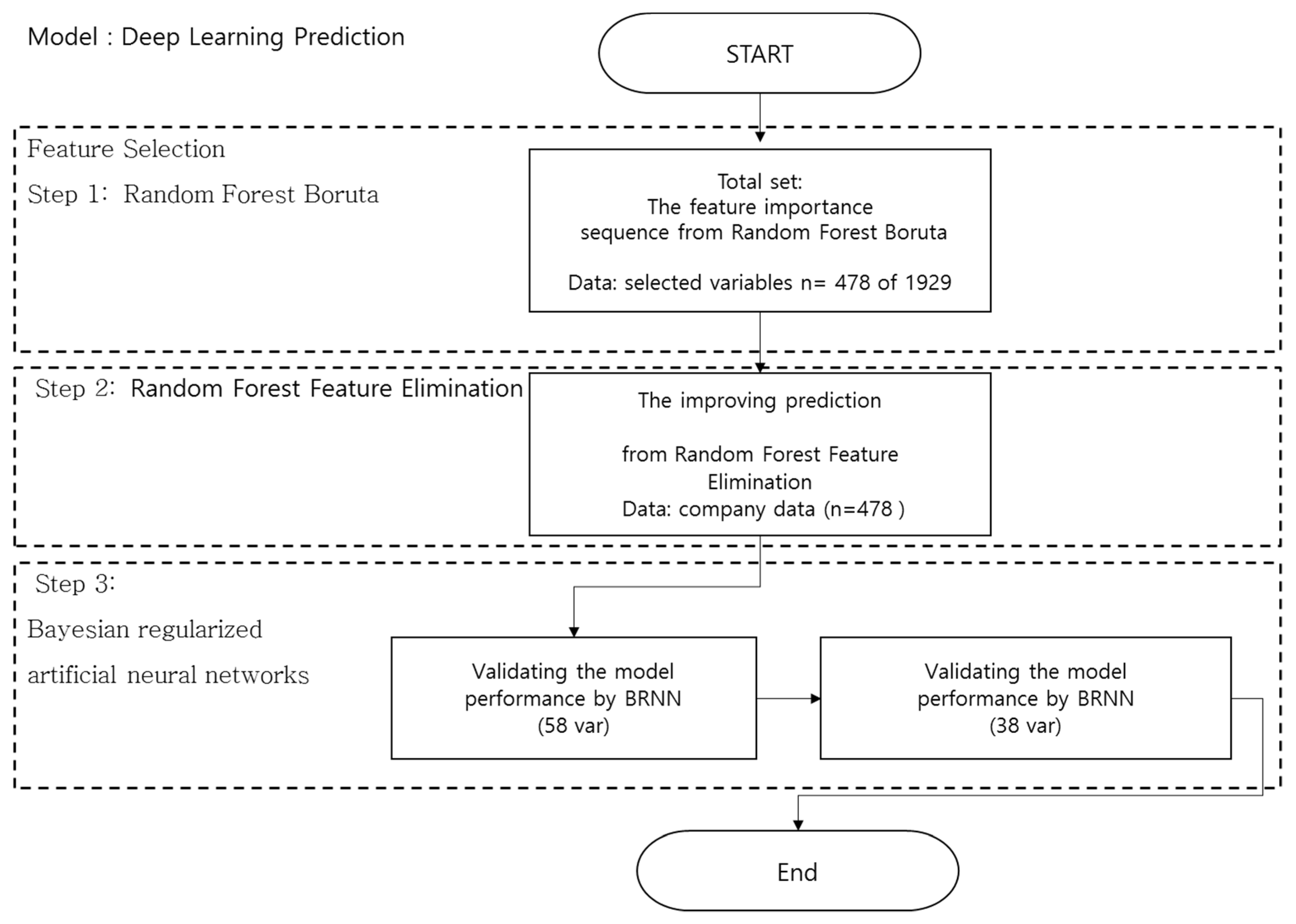
5. Methods
6. Results
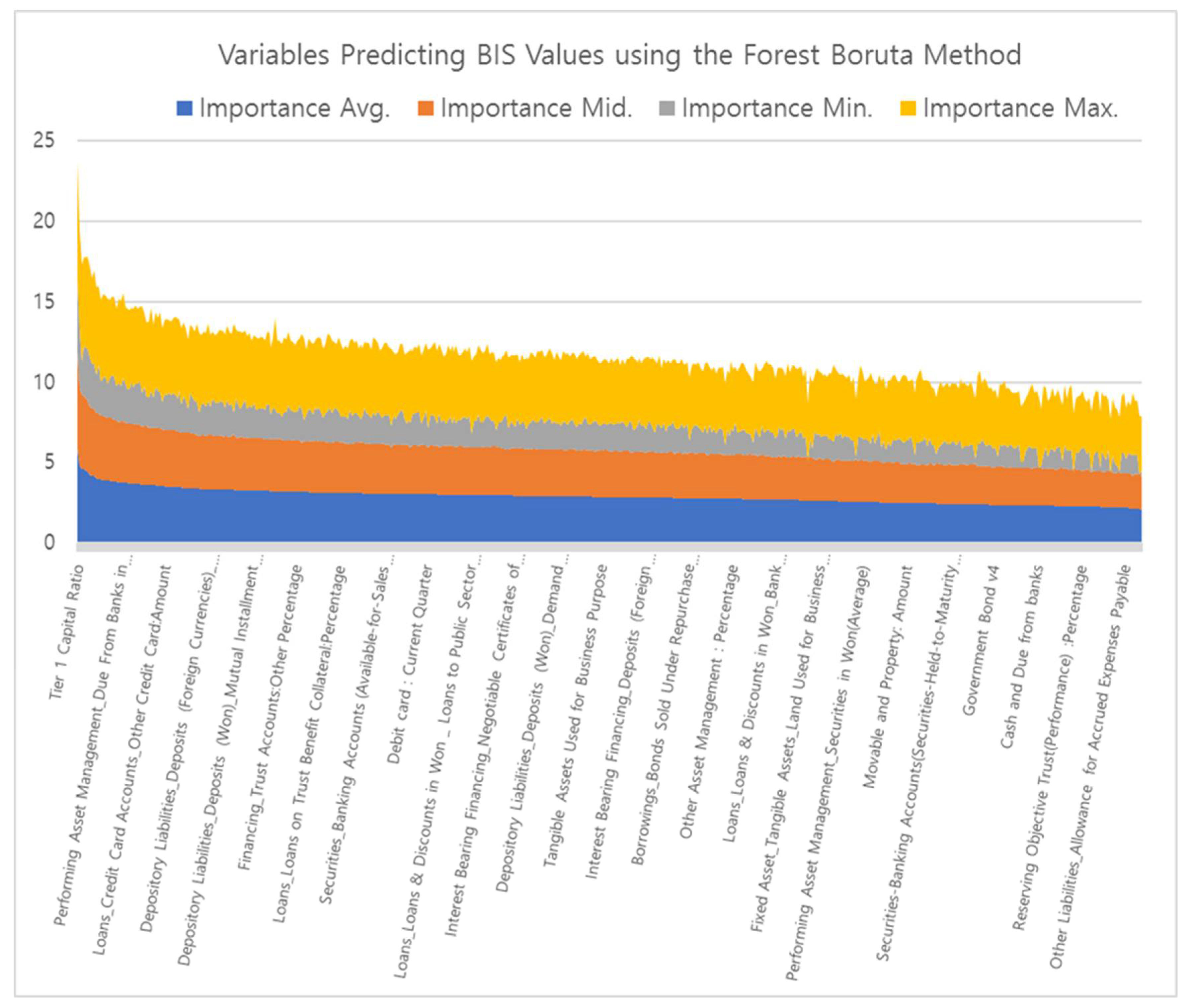
6.1. Stage 1. Feature Selection Using Random Forest Boruta
6.2. Stage 2. Feature Selection by Importance Rank Using Random Forest Feature Elimination
6.3. Stage 3. BIS Prediction Using Bayesian Regularized Neural Network Model
7. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
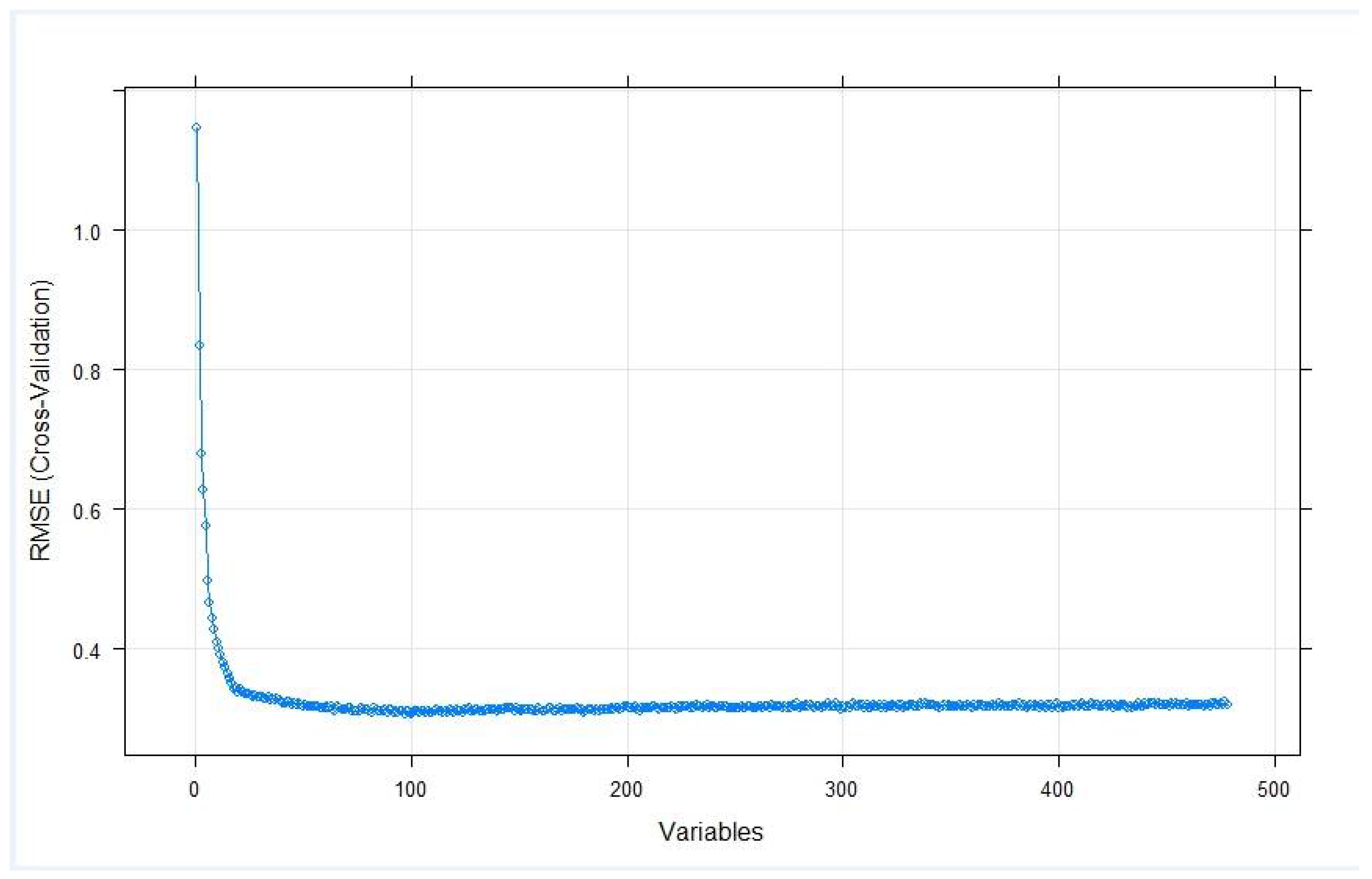
Appendix A. Resampling Performance Over Subset Size
| Variables | RMSE | Rsquared | MAE | RMSESD | Rsquaredsd | MAESD |
| 1 | 1.14645624 | 0.52161392 | 0.91597048 | 0.36944915 | 0.25013672 | 0.30473594 |
| 2 | 0.83488915 | 0.69543209 | 0.65871893 | 0.28540853 | 0.24394932 | 0.23308458 |
| 3 | 0.67893878 | 0.79362339 | 0.54014738 | 0.24017445 | 0.20280734 | 0.20077234 |
| 4 | 0.62692811 | 0.83468561 | 0.50001168 | 0.21732637 | 0.17058545 | 0.17891839 |
| 5 | 0.57497985 | 0.86323263 | 0.45396974 | 0.2005359 | 0.12218131 | 0.16157981 |
| 6 | 0.49643268 | 0.89350869 | 0.38584788 | 0.19108713 | 0.10980485 | 0.14230643 |
| 7 | 0.46477758 | 0.91060933 | 0.36186155 | 0.1849704 | 0.09282203 | 0.14001393 |
| 8 | 0.44432276 | 0.91851811 | 0.34425833 | 0.16859113 | 0.08582431 | 0.12287298 |
| 9 | 0.42694648 | 0.92633685 | 0.33015263 | 0.16704546 | 0.07508313 | 0.11987712 |
| 10 | 0.41042964 | 0.93148302 | 0.31652693 | 0.1591851 | 0.0778689 | 0.1117455 |
| 11 | 0.40045495 | 0.93270929 | 0.30961061 | 0.1577901 | 0.07636589 | 0.10924144 |
| 12 | 0.39109651 | 0.93500684 | 0.30124706 | 0.15665837 | 0.07570652 | 0.11049778 |
| 13 | 0.37949307 | 0.93999163 | 0.29305774 | 0.15246007 | 0.07213541 | 0.10936046 |
| 14 | 0.3747662 | 0.94274916 | 0.28856782 | 0.14681898 | 0.06354868 | 0.10608978 |
| 15 | 0.36460401 | 0.94557023 | 0.28159099 | 0.14678479 | 0.05899202 | 0.10561506 |
| 16 | 0.35801908 | 0.94814348 | 0.27776522 | 0.14022683 | 0.0590924 | 0.10467481 |
| 17 | 0.35161432 | 0.9503722 | 0.27264381 | 0.14029614 | 0.05575943 | 0.10401329 |
| 18 | 0.34306366 | 0.95269971 | 0.26457882 | 0.13749041 | 0.05533791 | 0.09966472 |
| 19 | 0.34346663 | 0.95415872 | 0.26487792 | 0.13132092 | 0.04871966 | 0.09553778 |
| 20 | 0.33867216 | 0.95426285 | 0.26067439 | 0.13142173 | 0.05040102 | 0.09473011 |
| 21 | 0.34125451 | 0.95226657 | 0.26075325 | 0.13809573 | 0.0571921 | 0.0977487 |
| 22 | 0.33740905 | 0.95361833 | 0.25860115 | 0.13957096 | 0.06041624 | 0.09890045 |
| 23 | 0.33451822 | 0.95309857 | 0.25596187 | 0.14202812 | 0.06127314 | 0.09942867 |
| 24 | 0.33585402 | 0.95350444 | 0.25592416 | 0.14270643 | 0.06258873 | 0.09930184 |
| 25 | 0.33440436 | 0.95371627 | 0.25683429 | 0.14407921 | 0.0643146 | 0.10102568 |
| 26 | 0.33309569 | 0.95497805 | 0.25530976 | 0.14001755 | 0.05874175 | 0.09814218 |
| 27 | 0.33059904 | 0.95465301 | 0.25294532 | 0.13792976 | 0.05935399 | 0.09573769 |
| 28 | 0.3326236 | 0.95406408 | 0.25504138 | 0.14039886 | 0.06459986 | 0.09684133 |
| 29 | 0.33070512 | 0.95423625 | 0.25471799 | 0.13988459 | 0.06143998 | 0.09745162 |
| 30 | 0.33026133 | 0.95437832 | 0.25394703 | 0.14270839 | 0.06413126 | 0.09832754 |
| 31 | 0.3314382 | 0.95483292 | 0.25452592 | 0.13697178 | 0.05975762 | 0.09509734 |
| 32 | 0.32950484 | 0.95535379 | 0.25411515 | 0.13907456 | 0.05805611 | 0.09703359 |
| 33 | 0.32951393 | 0.95553131 | 0.25386125 | 0.13939743 | 0.05872402 | 0.09830013 |
| 34 | 0.33021771 | 0.95548004 | 0.25430648 | 0.1402402 | 0.05673706 | 0.09915603 |
| 35 | 0.32709189 | 0.95600184 | 0.25101174 | 0.13678294 | 0.05795215 | 0.09605582 |
| 36 | 0.3287237 | 0.95555893 | 0.25298414 | 0.13940936 | 0.05596266 | 0.09943597 |
| 37 | 0.32690524 | 0.95650936 | 0.25045244 | 0.13706089 | 0.05292801 | 0.09645311 |
| 38 | 0.32903835 | 0.95533334 | 0.25032301 | 0.13927293 | 0.05454318 | 0.09675861 |
| 39 | 0.32595764 | 0.95616563 | 0.24930408 | 0.13698386 | 0.05553099 | 0.09553185 |
| 40 | 0.32334027 | 0.95752941 | 0.24737394 | 0.13580949 | 0.0549632 | 0.09521656 |
| 41 | 0.32298461 | 0.95756363 | 0.24815907 | 0.13296681 | 0.05177316 | 0.09404707 |
| 42 | 0.32119002 | 0.95789169 | 0.24544974 | 0.13752653 | 0.05510958 | 0.09449879 |
| 43 | 0.32329842 | 0.95752497 | 0.24776468 | 0.13657025 | 0.05486717 | 0.09473953 |
| 44 | 0.32446705 | 0.95739704 | 0.24895191 | 0.13672597 | 0.05607182 | 0.09412781 |
| 45 | 0.32005437 | 0.9590659 | 0.24430884 | 0.13759181 | 0.05003251 | 0.09617369 |
| 46 | 0.32301006 | 0.95843716 | 0.24760451 | 0.1372733 | 0.05021254 | 0.09559924 |
| 47 | 0.32080698 | 0.95862485 | 0.24543791 | 0.13473029 | 0.04856581 | 0.09411708 |
| 48 | 0.3209867 | 0.95894209 | 0.24464988 | 0.13712268 | 0.05111523 | 0.09657376 |
| 49 | 0.31926599 | 0.95900948 | 0.24396994 | 0.13760497 | 0.05116915 | 0.09720571 |
| 50 | 0.31770839 | 0.95986892 | 0.24167917 | 0.13685467 | 0.04782006 | 0.09547324 |
| 51 | 0.31975591 | 0.95916842 | 0.24299139 | 0.13772705 | 0.05335469 | 0.09567098 |
| 52 | 0.31759363 | 0.96003622 | 0.2421658 | 0.13634134 | 0.04886002 | 0.09466409 |
| 53 | 0.31824483 | 0.95970273 | 0.24286984 | 0.13192711 | 0.0497733 | 0.0929538 |
| 54 | 0.31859278 | 0.95967006 | 0.24238003 | 0.13649142 | 0.05269658 | 0.09526267 |
| 55 | 0.31716627 | 0.96080082 | 0.24218971 | 0.13396621 | 0.04801456 | 0.09443763 |
| 56 | 0.3164921 | 0.96084916 | 0.24044904 | 0.13153527 | 0.04782532 | 0.09130198 |
| 57 | 0.31723576 | 0.96012941 | 0.24097047 | 0.13678016 | 0.05194551 | 0.09499573 |
| 58 | 0.31443086 | 0.96133116 | 0.23965306 | 0.13413816 | 0.04642494 | 0.09368547 |
Appendix B. Resampling Performance Over Subset Size: Important Predictors by RFE
| Num | Overall | Variance (English) |
| 1 | 22.151384 | Tier 1 Capital Ratio |
| 2 | 11.111107 | Borrowings_Bonds Payable_(Discount Present Value):Percentage |
| 3 | 9.3877522 | Borrowings:Percentage |
| 4 | 8.9370711 | Acceptances and guarantees others |
| 5 | 8.6561452 | Acceptances and Guarantees |
| 6 | 8.2861521 | Borrowings_Bonds Payable:Percentage |
| 7 | 7.9801142 | Borrowings_Borrowings:Percentage |
| 8 | 7.8963313 | Receivable Charge-Offs |
| 9 | 7.7832859 | Other Liabilities_(Transfer from National Pension):Amount |
| 10 | 7.7440828 | Fixed Asset_Tangible Assets Used for Business Purpose_((Accumulated Depreciation)):Amount |
| 11 | 7.6228497 | Construction |
| 12 | 7.5957596 | Financing Without Cost_Other Non-cost Bearing Financing:(Average) |
| 13 | 7.2821885 | Financing Without Cost_Provision for Other Allowances:Percentage |
| 14 | 7.24095 | Performing Asset Management_Due From Banks in Won:(Average) |
| 15 | 6.6978429 | Other Liabilities_Account for Agency Business_Grio Account:Amount |
| 16 | 6.5836249 | Financing Without Cost_Demand Deposits:Percentage |
| 17 | 6.4640151 | Loans in won _ Average Interest rate |
| 18 | 6.4579122 | Financing With Cost_Borrowings in Won:Percentage |
| 19 | 6.4524425 | Non-Performing Asset Management_Others:Average |
| 20 | 6.4328985 | Performing Asset Management_Due From Banks in Won:Percentage |
| 21 | 6.4170021 | General and Administrative Expenses_Amortization of Intangible assets:Current Quarter |
| 22 | 6.3741191 | Financing Without Cost_Other Non-cost Bearing Financing:Percentage |
| 23 | 6.3035924 | Operation_Loans & Discounts:Percentage |
| 24 | 6.2622486 | Non-Performing Asset Management_Cash & Checks and Foreign Currency:Percentage |
| 25 | 6.1880531 | Derivative Contracts |
| 26 | 6.1864739 | Other Liabilities_Allowance Accounts_Allowance for Severance and Retirement Benefits_(Plan Assets)_(Due from Pension Plan):Percentage |
| 27 | 6.0419083 | Loans_Loans & Discounts in Won Loans to Enterprise:Percentage |
| 28 | 6.0393983 | Fixed Asset_Tangible Assets_Buildings Used for Business Purpose:Amount |
| 29 | 6.0326002 | Asset Management for Benefit_Other Won-Denomiated Currency Asset Management:Average |
| 30 | 6.0161628 | Securities_Banking Accounts (Available-for-Sales Securities)_ Available-for-Sales Securities in Won_Others: Amount |
| 31 | 5.9820987 | Bond Accounts:Amount |
| 32 | 5.9736885 | Personal Pension Trust:Percentage |
| 33 | 5.9424913 | Deposits in Won _ Average Interest rate |
| 34 | 5.9243753 | Interest_Interest and Dividends on Securities_Interest on Trading Securities:Current Quarter |
| 35 | 5.8140847 | Loans_Credit Card Accounts_Cash Service:Percentage |
| 36 | 5.7222446 | Securities-Banking Accounts (Subsidiaries)_Equity Investment (Won)_Consolidated Subsidiary Stock: Amount |
| 37 | 5.7078509 | Loans & Discounts_Loans on Real Estate Collateral:Amount |
| 38 | 5.7019038 | Non-Performing Asset Management_Fixed Assets Used for Business Purposes:Percentage |
| 39 | 5.6784716 | Other Liabilities_Accrued Expenses Payable:Percentage |
| 40 | 5.6422311 | Interest_Available-for-Sales Securities Interest:Current Quarter |
| 41 | 5.6110259 | Deposits in Won_Mutual Installment Deposits |
| 42 | 5.6005534 | Loans_Allowance for Credit Losses on Other Loans_Credit Card Accounts:Percentage |
| 43 | 5.5961849 | (Allowance for Credit Losses) Amount |
| 44 | 5.5531814 | Collateral_Others |
| 45 | 5.4702801 | Nonoperating Income_Rental income:Current Quarter |
| 46 | 5.4684209 | Securities-Banking Accounts (Subsidiaries)_Equity Investment (Won)_Consolidated Subsidiary Stock:Percentage |
| 47 | 5.4506053 | Allowance for Credit Losses on Other Loans:Amount |
| 48 | 5.4476118 | Loansoff-Shore Loans in Foreign Currency:Percentage |
| 49 | 5.4371039 | Loans_Loans & Discounts in Won Interbank Loans:Amount |
| 50 | 5.4077926 | Total Financing & Operation:Average |
| 51 | 5.4046407 | Securities-Banking Accounts (Securities-Held-to-Maturity Securities):Securities (Foreign Currencies):Percentage |
| 52 | 5.380378 | Financing_Trust Accounts:Average |
| 53 | 5.3780784 | Depository Liabilities_Deposits (Won)_Trust Account:Percentage |
| 54 | 5.3771052 | Performing Asset Management_Securities (Foreign Currencies):Percentage |
| 55 | 5.3696979 | Securities-Banking Accounts (Securities-Held-to-Maturity Securities):Securities (Foreign Currencies)_Debentures:Amount |
| 56 | 5.3564302 | Performing Asset Management_Loans in Foreign Currency:Percentage |
| 57 | 5.3204636 | Loans_Loans on Trust Benefit Collateral:Percentage |
| 58 | 5.3196173 | Consolidated Capital Surplus:Amount |
References
- Bazarbash, Majid. 2019. FinTech in Financial Inclusion Machine Learning Applications in Assessing Credit Risk. IMP Working Paper No. WP/19/109. Basel: International Monetary Fund. [Google Scholar]
- Bank for International Settlements. 2020. About BIS—Overview. Bank for International Settlement. Available online: https://www.bis.org/about/index.htm?m=1%7C1 (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- Bosarge, W. E. 1993. Adaptive processes to exploit the nonlinear structure of financial markets. In Neural Networks in Finance and Investing. Chicago: Probus Publishing, pp. 371–402. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, Leo. 2001. Random forests. Machine Learning 45: 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burden, Frank, and Dave Winkler. 2008. Bayesian regularization of neural networks. In Artificial Neural Networks. Tolowa: Humana Press, pp. 23–42. [Google Scholar]
- Fsc.go.kr. 2020. Financial Services Commission, Early Implementation of Basel III Credit Risk Framework. Available online: https://www.fsc.go.kr/eng/pr010101/22439 (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Gambacorta, Leonardo, Yiping Huang, Han Qiu, and Jingyi Wang. 2019. How do Machine Learning and Non-Traditional Data Affect Credit Scoring? New Evidence from a Chinese Fintech Firm (BIS Working Paper No. 834). Bank of International Settlements. Available online: https://www.bis.org/publ/work834.htm (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Genuer, Robin, Jean-Michel Poggi, and Christine Tuleau-Malot. 2010. Variable selection using random forests. Pattern Recognition Letters 31: 2225–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyon, Isabelle, Jason Weston, Stephen Barnhill, and Vladimir Vapnik. 2002. Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Machine Learning 46: 389–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Wookjae. 2020. Theoretical background: A new theoretical framework for financial planning with the case of life insurance demand—Dynamic ecological systemic framework. In The Demand for Life Insurance. Cham: Palgrave Pivot, pp. 19–46. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, Wookjae, Jae Min Lee, Narang Park, and John E. Grable. 2020. Using artificial neural network techniques to improve the description and prediction of household financial ratios. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance 25: 100273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Tin Kam. 1998. The random subspace method for constructing decision forests. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 20: 832–44. [Google Scholar]
- Hyndman, Rob J., and Anne B. Koehler. 2006. Another look at measures of forecast accuracy. International Journal of Forecasting 22: 679–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Institute of Financia. 2016. The improvement and implications for risk-weighted asset calculation method of Basel Bank Supervisory Commission. International Financial Issues 25: 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kohavi, Ron, and George H. John. 1997. Wrappers for feature subset selection. Artificial Intelligence 97: 273–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursa, Miron B., and Witold R. Rudnicki. 2010. Feature selection with the Boruta package. Journal of Statistical Software 36: 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, Andy, and Matthew Wiener. 2002. Classification and regression by random forest. R News 2: 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Linoff, Gordon S., and Michael J. A. Berry. 2011. Data Mining Techniques: For Marketing, Sales, and Customer Relationship Management. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- MacKay, David J. C. 1992. Bayesian Interpolation. Neural Computation 4: 415–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, Roland, José M. Peña, Johan Björkegren, and Jesper Tegnér. 2007. Consistent feature selection for pattern recognition in polynomial time. Journal of Machine Learning Research 8: 589–612. [Google Scholar]
- Petropoulos, Anastasios, Vasilis Siakoulis, Evaggelos Stavroulakis, and Aristotelis Klamargias. 2019. A robust machine learning approach for credit risk analysis of large loan level datasets using deep learning and extreme gradient boosting. In Bank for International Settlements. IFC Bulletins. Basel: Bank for International Settlements, vol. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Sariev, Eduard, and Guido Germano. 2020. Bayesian regularized artificial neural networks for the estimation of the probability of default. Quantitative Finance 20: 311–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, Wayne. 2014. Data mining methods and the rise of big data. In Big Data, Mining, and Analytics. New York: Auerbach, p. 71. [Google Scholar]
- Wooldridge, Jeffrey M. 2016. Introductory Econometrics: A Modern Approach. Mason: Nelson Education. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Nong. 2013. Data Mining: Theories, Algorithms, and Examples. Boca Raton: CRC Press. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Qifeng, Hao Zhou, Qingqing Zhou, Fan Yang, and Linkai Luo. 2014. Structure damage detection based on random forest recursive feature elimination. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 46: 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fss.or.kr. 2020. Financial Supervisory Service, Basel Regulations Related Report. Available online: http://www.fss.or.kr/fss/kr/bbs/list.jsp?bbsid= 1207396739395&url=/fss/kr/1207396739395 (accessed on 25 August 2020).
- National Law Information Center. 2020a. Banking Act §34. Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/%eb%b2% 95%eb%a0%b9/%ec%9d%80%ed%96%89%eb%b2%95 (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- National Law Information Center. 2020b. Detailed Regulations on Supervision of Banking Business. Appendix §17. Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/%ed%96%89%ec% a0%95%ea%b7%9c%ec%b9%99/%ec%9d%80%ed%96%89%ec%97%85%ea%b0%90%eb%8f%85%ec%97%85%eb%ac%b4%ec%8b%9c%ed%96%89%ec%84%b8%ec%b9%99 (accessed on 25 August 2020).
- National Law Information Center. 2020c. Detailed Regulations on Supervision of Banking Business. Appendix §3-2-2. Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/%ed%96%89%ec%a0%95% ea%b7%9c%ec%b9%99/%ec%9d%80%ed%96%89%ec%97%85%ea%b0%90%eb%8f%85%ec%97%85%eb%ac%b4%ec%8b%9c%ed%96%89%ec%84%b8%ec%b9%99 (accessed on 25 August 2020).
- National Law Information Center. 2020d. Detailed Regulations on Supervision of Banking Business. Appendix §3. Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/%ed%96%89% ec%a0%95%ea%b7%9c%ec%b9%99/%ec%9d%80%ed%96%89%ec%97%85%ea%b0%90%eb%8f%85%ec%97%85%eb%ac%b4%ec%8b%9c%ed%96%89%ec%84%b8%ec%b9%99 (accessed on 25 August 2020).
- National Law Information Center. 2020e. Detailed Regulations on Supervision of Banking Business. Appendix §3-3. Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/%ed%96%89%ec% a0%95%ea%b7%9c%ec%b9%99/%ec%9d%80%ed%96%89%ec%97%85%ea%b0%90%eb%8f%85%ec%97%85%eb%ac%b4%ec%8b%9c%ed%96%89%ec%84%b8%ec%b9%99 (accessed on 25 August 2020).
- National Law Information Center. 2020f. Detailed Regulations on Supervision of Banking Business. Appendix §3-4. Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/%ed%96%89%ec% a0%95%ea%b7%9c%ec%b9%99/%ec%9d%80%ed%96%89%ec%97%85%ea%b0%90%eb%8f%85%ec%97%85%eb%ac%b4%ec%8b%9c%ed%96%89%ec%84%b8%ec%b9%99> (accessed on 25 August 2020).
- National Law Information Center. 2020g. Enforcement Decree of The Banking Act §20. Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/%eb%b2%95%eb%a0%b9/%ec%9d%80%ed%96%89%eb%b2%95%ec%8b%9c%ed%96%89%eb%a0%b9 (accessed on 25 August 2020).
- National Law Information Center. 2020h. Regulations on Supervision of Banking Business §26. Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/%ed%96%89%ec%a0%95%ea%b7%9c%ec%b9%99/%ec%9d%80%ed%96%89%ec%97%85%ea%b0%90%eb%8f%85%ea%b7%9c%ec%a0%95 (accessed on 25 August 2020).
- National Law Information Center. 2020i. Regulations on Supervision of Banking Business §33. Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/%ed%96%89%ec%a0%95%ea%b7%9c%ec%b9%99/%ec%9d%80%ed%96%89%ec%97%85%ea%b0%90%eb%8f%85%ea%b7%9c%ec%a0%95 (accessed on 25 August 2020).
- National Law Information Center. 2020j. Regulations on Supervision of Banking Business §34. Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/%ed%96%89%ec%a0%95%ea%b7%9c%ec%b9%99/%ec%9d%80%ed%96%89%ec%97%85%ea%b0%90%eb%8f%85%ea%b7%9c%ec%a0%95 (accessed on 25 August 2020).
- National Law Information Center. 2020k. Regulations on Supervision of Banking Business §35. Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/%ed%96%89%ec%a0%95%ea%b7%9c%ec%b9%99/%ec%9d%80%ed%96%89%ec%97%85%ea%b0%90%eb%8f%85%ea%b7%9c%ec%a0%95 (accessed on 25 August 2020).
- National Law Information Center. 2020l. Regulations on Supervision of Banking Business §36. Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/%ed%96%89%ec%a0%95%ea%b7%9c%ec%b9%99/%ec%9d%80%ed%96%89%ec%97%85%ea%b0%90%eb%8f%85%ea%b7%9c%ec%a0%95 (accessed on 25 August 2020).
|
| Iteration | Indicator | BRNN With 38 vars | BRNN With 58 vars | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Model | Prediction Model | Training Model | Prediction Model | ||
| 1 | Neuron # | 20 | 20 | 16 | 16 |
| MAE | 0.4008 | 0.4059 | 0.3807 | 0.4072 | |
| RMSE | 0.5265 | 0.5737 | 0.5288 | 0.5775 | |
| R2 | 0.8901 | 0.8937 | |||
| 2 | Neuron # | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| MAE | 0.4475 | 0.3858 | 0.4461 | 0.3849 | |
| RMSE | 0.6214 | 0.5507 | 0.5801 | 0.5497 | |
| R2 | 0.8577 | 0.8727 | |||
| 3 | Neuron # | 5 | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| MAE | 0.4742 | 0.4429 | 0.4815 | 0.4430 | |
| RMSE | 0.6551 | 0.8090 | 0.6360 | 0.8091 | |
| R2 | 0.8270 | 0.8505 | |||
| 4 | Neuron # | 4 | 4 | 10 | 10 |
| MAE | 0.4330 | 0.4040 | 0.3878 | 0.4065 | |
| RMSE | 0.5617 | 0.6254 | 0.5445 | 0.6274 | |
| R2 | 0.8808 | 0.8996 | |||
| 5 | Neuron # | 18 | 18 | 3 | 3 |
| MAE | 0.4177 | 0.3851 | 0.3961 | 0.3854 | |
| RMSE | 0.5788 | 0.5469 | 0.5383 | 0.5471 | |
| R2 | 0.8731 | 0.8690 | |||
| 6 | Neuron # | 16 | 16 | 20 | 30 |
| MAE | 0.4437 | 0.4455 | 0.4082 | 0.3493 | |
| RMSE | 0.5975 | 0.6718 | 0.5575 | 0.5102 | |
| R2 | 0.8374 | 0.8768 | |||
| 7 | Neuron # | 3 | 3 | 10 | 10 |
| MAE | 0.4394 | 0.3954 | 0.3688 | 0.4604 | |
| RMSE | 0.5701 | 0.5843 | 0.8042 | 0.6297 | |
| R2 | 0.8694 | 0.8950 | |||
| 8 | Neuron # | 4 | 4 | 20 | 20 |
| MAE | 0.4114 | 0.3585 | 0.3752 | 0.3667 | |
| RMSE | 0.5413 | 0.5586 | 0.4988 | 0.5977 | |
| R2 | 0.8893 | 0.9086 | |||
| 9 | Neuron # | 3 | 3 | 10 | 10 |
| MAE | 0.4539 | 0.3971 | 0.3502 | 0.4984 | |
| RMSE | 0.5771 | 0.5757 | 0.4764 | 0.7602 | |
| R2 | 0.8752 | 0.9176 | |||
| BRNN With 38 vars | BRNN With 58 vars | Bayesian GLM With 38 vars | Bayesian GLM With 58 vars | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE (S.D.) | 0.4022 (0.4663) | 0.4113 (0.4776) | 0.5477 (1.0433) | 0.5119 (0.7689) |
| RMSE (S.D.) | 0.6107 (0.0796) | 0.6232 (0.0943) | 1.000 (0.6229) | 0.8583 (0.3412) |
| BRNN (38 var) | BRNN (58 var) | BGLM (38 var) | BGLM (58 var) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRNN (38 var) | ||||
| BRNN (58 var) | −0.7542 | |||
| BGLM (38 var) | −7.0432 *** | −6.5759 *** | ||
| BGLM (58 var) | −6.7482 *** | −5.6656 *** | 1.5280 |
| BRNN (38 var) | BRNN (58 var) | BGLM (38 var) | BGLM (58 var) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 0.6107 | 0.6232 | 1.000 | 0.8583 |
| 70% of RMSE | 0.700 | 0.6008 |
| Report (Financial Statics Information System) | (Importance Rank) by Variance (Item) of Domestic Bank |
|---|---|
| Capital Adequacy | (1) Tier 1 Capital Ratio |
| Consolidated Balance Sheet (Liabilities & Shareholders’ Equity-Banking Account) | (2) Borrowings_Bonds Payable_(Discount Present Value):Percentage (3) Borrowings:Percentage (6) Borrowings_Bonds Payable:Percentage (7) Borrowings_Borrowings:Percentage |
| Loans Receivable (Industries) | (11) Construction |
| Off-balance Accounts (Bank Accounts) | (4) Acceptances and Guarantees Others (5) Acceptances and Guarantees (8) Receivable Charge-Offs (25) Derivative Contracts |
| Principal Sources of Cash Flows in Bank Accounts | (12) Financing Without Cost_Other Non-cost Bearing Financing:(Average) (13) Financing Without Cost_Provision for Other Allowances:Percentage (14) Performing Asset Management_Due From Banks in Won:(Average) (16) Financing Without Cost_Demand Deposits:Percentage (18) Financing With Cost_Borrowings in Won:Percentage (19) Non-Performing Asset Management_Others:Average (20) Performing Asset Management_Due From Banks in Won:Percentage (22) Financing Without Cost_Other Non-cost Bearing Financing:Percentage (24) Non-Performing Asset Management_Cash & Checks and Foreign Currency:Percentage (29) Asset Management for Benefit_Other Won-Denomiated Currency Asset Management:Average (38) Non-Performing Asset Management_Fixed Assets Used for Business Purposes:Percentage |
| Principal Sources of Cash Flows in Trust Accounts | (23) Operation_Loans & Discounts:Percentage |
| Profitability | (17) Loans in won _ Average Interest rate (33) Deposits in Won _ Average Interest rate |
| Summarized Balance Statement (Assets-Banking Account) | (10) Fixed Asset_Tangible Assets Used for Business Purpose_(Accumulated Depreciation):Amount (27) Loans_Loans & Discounts in Won Loans to Enterprise:Percentage (28) Fixed Asset_Tangible Assets_Buildings Used for Business Purpose:Amount (30) Securities_Banking Accounts (Available-for-Sales Securities) Available-for-Sales Securities in Won_Others: Amount (35) Loans_Credit Card Accounts_Cash Service:Percentage (36) Securities-Banking Accounts(Subsidiaries)_Equity Investment (Won) Consolidated Subsidiary Stock: Amount |
| Summarized Balance Statement (Assets-Trust Account) | (31) Bond Accounts:Amount (37) Loans & Discounts_Loans on Real Estate Collateral:Amount |
| Summarized Balance Statement (Liabilities & Trust Account) | (32) Personal Pension Trust:Percentage |
| Summarized Balance Statement (Liabilities &Shareholders’ Equity-Banking Account) | (9) Other Liabilities_(Transfer from National Pension):Amount (15) Other Liabilities_Account for Agency Business_Grio Account:Amount (26) Other Liabilities_Allowance Accounts_Allowance for Severance and Retirement Benefits_(Plan Assets)_(Due from Pension Plan):Percentage |
| Summarized Income Statement (Banking Account) | (21) General and Administrative Expenses_Amortization of Intangible assets:Current Quarter (34) Interest_Interest and Dividends on Securities_Interest on Trading Securities:Current Quarter |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Shin, M.; Heo, W. Estimating the BIS Capital Adequacy Ratio for Korean Banks Using Machine Learning: Predicting by Variable Selection Using Random Forest Algorithms. Risks 2021, 9, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks9020032
Park J, Shin M, Heo W. Estimating the BIS Capital Adequacy Ratio for Korean Banks Using Machine Learning: Predicting by Variable Selection Using Random Forest Algorithms. Risks. 2021; 9(2):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks9020032
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jaewon, Minsoo Shin, and Wookjae Heo. 2021. "Estimating the BIS Capital Adequacy Ratio for Korean Banks Using Machine Learning: Predicting by Variable Selection Using Random Forest Algorithms" Risks 9, no. 2: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks9020032
APA StylePark, J., Shin, M., & Heo, W. (2021). Estimating the BIS Capital Adequacy Ratio for Korean Banks Using Machine Learning: Predicting by Variable Selection Using Random Forest Algorithms. Risks, 9(2), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks9020032






