Abstract
In light of the function of Internal Auditing and its significance in assessing and ensuring the validity of data, information, reports, and high lists generated by the Accounting Information System and improving its credibility and dependability, the purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between Internal Auditing (IA) and Accounting Information System (AIS) in Jordanian banks, with a focus on the mediator role of Organizational Commitment (OC). A cross-sectional survey method was used to collect data from a sample of employees who work in banks, including those who work in the internal audit department. The collected data were analyzed using SPSS 26.0 and PROCESS V4.1. The study sample includes 193 employees who work in banks, including those who work in the internal audit department. Descriptive statistical methods, such as frequencies, percentages, means, and standard deviations, were employed to depict both the characteristics of the sample and the participants’ responses to the study items. The results indicate that IA has a positive relationship with AIS. Moreover, the results indicate that OC partially mediates the relationship between IA and AIS in Jordanian banks.
1. Introduction
Internal Auditing is an essential component that helps distribute resources as efficiently as possible. It is also beneficial for reducing corruption’s outward signs and achieving economic success (Al-Taee and Flayyih 2023). Therefore, considered IA is a practice that safeguards resources against misuse, confirms the veracity of corporate data, and guarantees adherence to applicable laws and regulations. IA also aims to stop events from occurring in the bank on purpose or by accident; rather, choices should be created through the IA strategy, and “top management” refers to the data analyzed during auditing when making decisions (Napitupulu 2020). Employee loyalty to the organization in accomplishing common goals is shown in OC. Employees will endeavor to be innovative and productive in carrying out their jobs with a high level of devotion (Sumardjo and Supriadi 2023). Concerns about ethical behavior in the workplace are raised by unethical behavior in both public and private organizations (Limpo and Junaidi 2023). To make choices that are in line with the demands and objectives of the bank, it is vital to have information that is consistent with the AIS characteristics of each current department. Meanwhile, the OC that each person possesses may be used to create accurate information. This is so that information generated by each employee’s performance may be measured against the OC evaluation (Fauzi et al. 2023). Moreover, OC is a key factor that affects and defines audit consistency, where OC is at the heart of a bank’s operations and has an impact on both the performance as a whole as well as the caliber of its goods and services (Aldegis 2018).
Moreover, IA must also confirm that all pertinent economic events are gathered by the AIS and the process of changing and translating financial data (Al-Taee and Flayyih 2023). The dissemination of information has been accelerated by the advent of the big data era, the rise of the network economy, and advances in technology, while accounting computerization has gradually replaced the conventional manual bookkeeping system employed by banks, and the stage of computer information has officially begun (Alqudah et al. 2023). The success or loss of bank operations throughout the bank expansion process, however, can be somewhat influenced by accounting information statistics (Ye and Hu 2020). An AIS is a crucial instrument for managers looking to maintain a competitive edge. The AIS is sometimes thought of as one of the supportive information systems used in managerial tasks (Jarah et al. 2023a). Therefore, the AIS used by banks must be of a high caliber (Jarah and Almatarneh 2021). Every bank also needs an AIS that has been correctly created, is kept up to date, and enables the bank to conduct its purposes in order to keep the path of incoming and outgoing accounts. An information technology-based solution that aids in the control of a bank’s economic and financial activities is an AIS (Jarah and Al Jarrah 2022). Although this method requires a lot of processes and procedures to facilitate IA operations, significant technological improvements have allowed banks to strategically use it. To do this, the bank’s management must be held accountable for enhancing employee performance, encouraging cooperation, and sharing information with the chain of command (Jarah et al. 2023b).
Therefore, the significance of this study is derived from the significance of its dependent, independent, and mediator factors. In order to improve the efficiency of the AIS in Jordanian banks. Thus, this study will focus on IA and the cycle of raising the efficiency of the AIS in Jordanian banks using OC as a mediator. Accordingly, it is necessary to inform the administration of the value of IA and its contribution to improving the effectiveness of AIS in Jordanian banking. The departments responsible for banks have paid close attention to IA because it is regarded as a crucial component of comprehensive banking control and because of how important it is in preventing, repelling, and limiting risks and errors that banks may be exposed to daily. Therefore, IA is based on a group among the controls for the conduct of banks’ business to ensure mathematical accuracy. This research will also highlight the significance of the Jordanian banking sector’s challenges in implementing AIS. The findings can therefore provide a clear picture of how much Jordanian banks are aware of the value of IA and how it contributes to improving the effectiveness of the AIS.
This paper is organized in five sections at the end of this introduction. Section 2 is the literature review of the study. The paper then proceeds to methodology in Section 3, which includes research questions, research design in the study, research instruments, statistical analysis, data collection procedures, and participants; Section 4 is the research results, Section 5 is discussion; and Section 6 includes the implications and limitations and future research and conclusions of this study.
2. Literature Review
IA has emerged as a critical aspect in helping effective controls and risk management. In times of economic crisis, internal audits are one of the most powerful and quickest strategies to minimize operational expenses and offer the firm competitive benefits in the global market (Jarah et al. 2022a). IA is a distinct activity that provides objective assurance and consulting services to improve and enhance an organization’s operations. IA helps banks achieve their objectives by utilizing a rigorous, disciplined approach to examine and enhance the efficacy of risk management and control (Mulyani et al. 2019). One of the most crucial elements in helping a company create high-quality financial reporting is OC; this shows that strong OC may lead to timely, accurate, comparable, and trustworthy information. In light of this, it is anticipated that the installation of IA, AIS, and OC to the quality of financial reporting will enhance the performance of the business (Setyaningsih et al. 2021). Additionally, IA activities assess the effectiveness of the practice, and the idea of IA frequently calls for management intervention reviews to handle situations that differ from those that were attained (Van Dung 2020). According to Rachman and Fitri (2023) study, operational auditing and AIS have a considerable impact on sales performance, internal control has no bearing on sales performance. The findings of the study by Wibowo et al. (2023) demonstrate that the IA and the AIS combined have an influential positive on organizational performance.
IA is defined as a corporate function that tests and assesses bank operations as a service supplied to the bank (Awuah et al. 2022). IA must thus guarantee that the AIS captures all crucial economic events and that summarizing and modifying financial data are error free. According to Sagala (2020), the AIS in the bank still faces a variety of risks during the course of operation. These risks are primarily from natural disasters, accidents, mistakes, dissatisfaction with the bank, or low quality of the staff, where these risk factors will affect the lack of accounting data tangibly, leading to data information errors, making it difficult to allocate resources reasonably, and causing irreparable losses to the bank (Jarah et al. 2023b; Liu 2023; Jarah et al. 2022a).
Furthermore, the implementation of AIS is essential for the success of an organization since it enhances the collection, administration, and management of large amounts of organizational data. However, such systems frequently have malfunctions that result in serious operational issues and monetary losses (Ayoub et al. 2020), while the inadequate implementation of IA was formerly the determining criterion for whether or not AIS qualified. Accordingly, AIS are necessary for effective business management and decision-making (Alawaqleh 2021; Jarah and Almatarneh 2021). IA is utilized to protect the bank against risk or lessen the consequences of risk incidents. In order to assure the accuracy of the bank’s financial statements, internal control must be built into the AIS (Van Dung 2020). As a result, the major goal of IA is to assist the entity in managing risks in order to meet the entity’s goals while it is being constructed and to uphold the bank’s work ethics. Internal controls may also be defined as rules or guidelines intended to ensure the accomplishment of a certain goal (Setyaningsih 2020). Moreover, the IA is a policy that protects assets from misappropriation, verifies bank information, ensures compliance with applicable rules and regulations, and prevents things from happening in the bank on purpose or by mistake (Sagala 2020).
Therefore, the financial components of bank events are captured, processed, and reported using AIS, where the AIS keeps track of and reports on financial activity inside the bank as well as commercial transactions (Mulyani et al. 2019). Therefore, the AIS has become more accessible to banks as technology has advanced. These systems are critical because they provide all levels of management with complete information that is used in the planning and control of operations inside banks (Faisal et al. 2023). Furthermore, AISs deliver high-quality information to internal and external users, with a focus on six key areas: people, processes, data, software, information technology, and internal controls (Ömer 2016). Moreover, with audits features in the accounting system, many frauds, irregularities, and mistakes may be avoided or monitored and addressed, where accounting information developments result in the development of information demands for interested parties as well as the necessity for quality procedures and performance in creating information (Wahyuni et al. 2022). In a study by Jarah et al. (2023a), it was proven that the IA has an effect on the relationship between the AIS and the performance of Jordanian banks. Wahyuni et al. (2022) findings revealed that the AIS and IA had a partially good and substantial influence on internal control.
IA, on the other hand, is based on the plans, strategies, and metrics selected by a bank activity to protect its assets, verify the correctness and dependability of the data, enhance operating effectiveness, and ensure adherence to specified management standards (Abed et al. 2022). It may be inferred that a bank’s subpar IA will have a significant impact on staff performance (Amira and Permatasari 2022). However, independence and impartiality in IA are essential for the profession (Lois et al. 2021). Similar to this, neutrality and presumptive doubt have evolved as the main perspectives of auditor professional skepticism, and IA should work to be fair in formulating its conclusions; there should be no prejudice on either side (Silva et al. 2023). IA must also set up appropriate controls in accordance with the control profession and exercise the requisite professional care in their work, taking into account the amount of labor necessary to complete the assignment’s objectives (Jarah et al. 2022b). According to Sandag et al. (2023), the effectiveness of the workforce, internal control systems, the quality of financial reports, and the function of AIS all have a positive and substantial impact on management performance.
Nevertheless, IA is a system that has access to organizational structure oversight as well as all mutually followed processes and ways to maintain the general stability of the bank’s assets from a variety of angles, where IA contributes significantly to the development of AIS (Alawaqleh 2021). When using an AIS, IA can aid in preventing fraud and errors. Assume that better IA is needed for the AIS. Because IA aims to offer accuracy, the information system will be less helpful in situations when there is a reasonably significant risk of fraud occurring and harming both internal and external parties (Putra 2023). IA also has a substantial influence on the comparability of AIS and the truthfulness of financial statement disclosure by limiting the extent, frequency, and proportion of related party transactions, particularly aberrant connected party dealings. IA, which can distinguish between different forms of related party transactions, is thus critical to the performance of corporate governance (Ningrum et al. 2022). The study by Irfan and Hamimi (2023) discovered that the AIS impacts the quality of financial reporting, and internal control influences financial reporting. OC strengthens the impact of AIS on the quality of financial reporting, and OC strengthens the influence of internal control on financial reporting. According to Amira and Permatasari (2022), AISs positively and insignificantly impact employee performance, and internal control positively and significantly impacts AISs.
In order to achieve bank goals, the bank must therefore enhance its IA and AIS (Hailat et al. 2023). Additionally, poor IA implementation will significantly lower the quality of the bank’s financial reports, as the financial data introduced must be of grade and be a base for evaluation. IA is also part of a framework used as a bank or organization-wide operational guideline approach to identify, assess, and share any corporate occurrences (Rachman 2021; Sastrawan et al. 2020). An AIS is a system that gathers and maintains data relevant to the bank’s activities, converts the data into meaningful information, shows plans, and delivers the required controls to protect the bank’s assets (Jarah et al. 2023a). The research by Wirdiansyah and Munandar (2022) revealed that the payroll AIS was functioning properly and was able to boost the efficacy of the bank’s IA. Syahputra (2022) research indicates that internal control has no influence on information quality. According to Li et al. (2022), internal control quality helps accounting information comparability. The stronger the constraining impact of aberrant related party transactions adversely connected to AIS comparability, the higher the quality of internal control.
As a consequence, the auditor’s performance is the result of the auditor’s labor or accomplishment based on the obligations or responsibilities he obtains in the form of auditing activities in an organization or corporation (Hazaea and Zhu 2022). Thus, auditor performance is determined by an improvement in auditor competence, the use of technology and an awareness of AIS, as well as OC (Pura 2017). According to the findings of Saputro (2022) study, the AIS and internal control have an effect on the quality of financial reports. The findings of the study by Dewi et al. (2021) show that there is an influence of IA on accounting information technology. According to the findings of Alawaqleh (2021), internal control has an influence on employee performance and AIS. According to the findings of this study, the AIS plays a crucial role in the link between internal control and performance. The study by Yusuf and Kanji (2020) found that IA and AIS have a positive effect on internal control. The study by Limpo and Junaidi (2023) found that ethical and empowered leaders had a positive impact on employee job satisfaction, which also connected the predictor variables to employee job performance and OC.
Internal auditors may therefore assist management in carrying out control operations of the bank activities since they can efficiently create information required by managers to fulfill defined bank goals (Wonoseto et al. 2022). Internal audit checks are performed by bank personnel who are not involved in the bank’s business activities and who record the bank’s financial statements. Internal auditors may help the bank achieve efficiency, effectiveness, and compliance when carrying out business activities (Yusuf and Kanji 2020). Napitupulu’s (2020) research showed that the efficacy of IA has little influence on the AIS in rural banks. Accountants’ and auditors’ experience may improve decision-making (Almaliki et al. 2019). According to Ayoub et al. (2020), the study’s findings show that organizational cultural qualities have a major effect on the internal control components of AIS, and hence such systems can be more prosperous in organizations that have supportive organizational cultural features. The findings of this study (Jarah and Almatarneh 2021) showed that the AIS offers financial information with a highly predictive capacity that benefits system users. Additionally, the findings showed that an accurate grasp of OC resulted in an improvement in work quality. Pura (2017) discovered that auditor competence, information technology, knowledge of AIS, and OC all had a substantial favorable influence on auditor performance. Almaliki et al.’s (2019) findings revealed that all of the AIS parameters studied had a substantial impact on IA effectiveness. Therefore, upon the illustration of the previous results and the gap in the studies, the researchers studied the results related to the role of IA in improving the AIS in Jordanian Banks by using OC as a mediator factor, where the banks can use financial statements to acquire a better understanding of their financial situation and operating performance.
Based on the above literature review, the researchers developed the conceptual framework as shown in Figure 1.
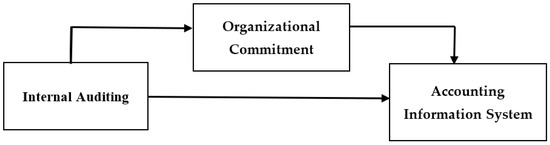
Figure 1.
Conceptual framework.
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Question
The importance of this study is derived from the relevance of the dependent, independent, and mediator variables of banking, which is considered to be one of the most important businesses for achieving growth and prosperity in bank sectors to increase the AIS’s effectiveness in Jordanian banks. The relevance of the difficulties that Jordanian banking has in implementing AIS will also be highlighted by this study.
Therefore, the purpose of this study is to investigate the relationship between IA and AIS in Jordanian banks, with a focus on the mediator role of OC. The study seeks to answer the following research questions:
- What is the direct effect of IA on AIS?
- What is the indirect effect of IA on AIS through the mediator variable of OC?
3.2. Research Design
This study employed a quantitative research design to collect and analyze data. A cross-sectional survey method was used to collect data from a sample of employees who work in banks, including those who work in the internal audit department. The survey questionnaire was divided into three sections: the first collected demographic information, the second collected data on IA and AIS, and the third collected information on OC.
3.3. Research Instruments
Three instruments were used in this study. The independent variable (IV) in this study is IA, which includes 9 items developed by (Al Matarneh 2011). The dependent variable (DV) is AIS, which includes 7 items developed by (Jarah and Iskandar 2019), and the mediator variable (MD) is OC, which includes 7 items developed by (Al-Fakeh et al. 2020)
3.4. Statistical Analysis
The collected data were analyzed using SPSS 26.0 and PROCESS V4.1. PROCESS V4.1 is used for evaluating direct and indirect effects in single and multiple mediator models (parallel and serial); it is frequently utilized in the social, business, and health sciences. Descriptive statistical methods, such as frequencies, percentages, means, and standard deviations, were employed to depict both the characteristics of the sample and the participants’ responses to the study items. Reliability analysis was conducted to ensure the internal consistency of the study instrument. The scale was corrected and adopted for a five-point Likert scale, where means below 2.33 were considered low, means between 2.34 and 3.66 were considered medium, and means between 3.67 and 5.00 were considered high.
The study utilized the PROCESS V4.1 macro for SPSS to test the mediator effect. Specifically, the nonparametric bootstrap method was used to test the significance level of the mediator effect.
3.5. Data Collection Procedures
In order to capture the opinions of the selected sample, the questionnaire was used as a technique of data collection. A self-administered questionnaire was selected as the survey instrument since it is a common method for gathering data for surveys and fits the nature of the current inquiry. In order to accomplish the goals of the study, the researchers employed the five-point Likert measures to create and enhance the questionnaire and gather data; the data were collected in the period between 2022 and 2023, and data collection took four months.
3.6. Participants
The study sample includes 214 employees who work in banks, including those who work in the internal audit department. A total of 193 questionnaires were completed and returned. A convenience sampling method was used to select the sample. A total of 193 individuals were surveyed, of whom 83 (43%) are male and 110 (57%) are female. In terms of age, the largest group was in the 18–34 age range, which makes up 57.5% of the sample. The 35–49 age group was the second largest group at 26.4%, followed by the 50–64 age group at 14%, and the 65 and over age group at 2.1%.
In terms of education, the most common level is a diploma, which is held by 44.6% of the sample. This is followed by a Bachelor’s degree at 34.2%, a Master’s degree at 11.9%, and a PhD at 9.3%. In terms of years of experience, the largest group has 10–15 years of experience, which accounts for 62.2% of the sample. The other three groups, less than 5 years, 5–10 years, and more than 15 years, make up 11.4%, 13%, and 13.5% of the sample, respectively.
Finally, Table 1 shows information on the distribution of respondents across six different banks. The Jordan Kuwait Bank is the most common bank among the sample, with 25.9% of respondents using this bank. The Cairo Amman Bank is the second most common at 20.7%, followed by the Capital Bank of Jordan at 18.7%. The other three banks, Jordan Ahli Bank JAB, Jordan Islamic Bank for Finance and Investment, and Arab Jordan Investment Bank, have 16.1%, 10.4%, and 8.3% of respondents, respectively.

Table 1.
Distribution of the sample according to personal information.
3.7. Validity
The questionnaire’s validity, including its content, was confirmed through peer review by the research supervisors’ members, who granted their approval. The questions were scrutinized to ensure their consistency with the content, and a sample of the questionnaire was used to test the definitions and eliminate any ambiguities for the research subjects.
3.8. Reliability Analysis
According to Table 2, Cronbach’s alpha coefficient is acceptable for the goals of the study; Cronbach’s alpha reliability coefficient is acceptable if it exceeds 0.60 (Sekaran and Bougie 2016).

Table 2.
The result of reliability (Cronbach’s alpha).
4. Results
4.1. Independent Variable: Internal Auditing (IA)
Table 3 shows that IA1 had the highest mean with a score of 3.67, indicating a high level of agreement. IA4 had the second-highest mean with a score of 3.65, indicating a medium level of agreement. The overall mean for all IA factor items was 3.06, with a standard deviation of 0.94, indicating a medium level of agreement overall.

Table 3.
Means and standard deviations for Internal Auditing (IA) factor items and overall mean.
4.2. Dependent Variable: Accounting Information System (AIS)
Table 4 shows that AIS1 and AIS4 have a high level of agreement, with means of 4.39 and 4.32, respectively. The other items have a medium level of agreement, with means ranging from 3.38 to 3.99. The overall mean for all items is 3.56, with a standard deviation of 0.67, indicating a medium level of agreement.

Table 4.
Means and standard deviations for Accounting Information System (AIS) factor items and overall mean.
4.3. Meditation Variable: Organizational Commitment (OC)
Table 5 shows that the highest mean is for OC4 (4.31), followed by OC2 (4.04) and OC7 (3.96). The lowest mean is for OC1 (3.04). The standard deviations range from 0.66 to 1.25. The total mean for the factor is 3.57, and the agreement degree is medium.

Table 5.
Means and standard deviations for Organizational Commitment (OC) factor items and overall mean.
Table 6 shows that the skewness and kurtosis values for all variables fall within acceptable ranges, with skewness values ranging from −1.199 to −0.142 and kurtosis values ranging from 0.727 to −0.553. Causal modeling assumes that variables are normally distributed, which means that their skewness and kurtosis should not exceed an absolute value of 2 (West et al. 2012).

Table 6.
Kurtosis, skewness, and correlation of all variables.
The correlation matrix shows that there is a significant positive correlation between “Internal Auditing (IA)” and “Accounting Information System (AIS)” (r = 0.645, p < 0.01), as well as between “Internal Auditing (IA)” and “Organizational Commitment (OC)” (r = 0.561, p < 0.01), and between “Accounting Information System (AIS)” and “Organizational Commitment (OC)” (r = 0.660, p < 0.01). These results indicate that as scores on one variable increase, scores on the other variables also tend to increase.
4.4. The mediator role of OC between IA and AIS in Jordanian Banks
A mediator variable is a component that clarifies the relationship between an independent and dependent variable. This link can be partially or totally mediated by the mediator variable. When the mediator variable accounts for the complete link between the independent and dependent variables, full mediation occurs. Partial mediation, on the other hand, happens when the mediator variable is only responsible for a portion of the link between the independent and dependent variables. If the mediator variable is eliminated, the link between the independent and dependent variables remains, but it is weaker.
The mediation model in this investigation was built with PROCESS v4.2 for SPSS, a regression software designed by Hayes (2017). Following the processes indicated by Baron and Kenny (1986), the mediational hypothesis can be found. These phases entail establishing that the independent variable is correlated with the mediator variable, that the dependent variable and mediator variable are likewise correlated, and that the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable when the mediator variable is controlled for is zero. If the findings do not equal zero, partial mediation has occurred (James and Brett 1984; Judd and Kenny 1981). As shown in Figure 2.
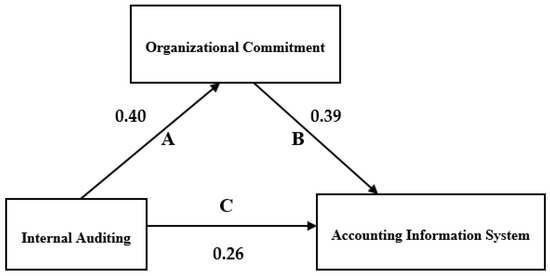
Figure 2.
Mediator effect analysis.
Table 7 shows that the following.

Table 7.
The regression model.
Path A: IV (Internal Auditing) has a positive relationship with MD (Organizational Commitment) with a beta coefficient (β) of 0.396, a t-value of 9.3551, and a p-value of 0.0000. The R-squared value (R2) for this path is 0.314, which indicates that 31.4% of the variance in the MD can be explained by the IV.
Path B: MD (Organizational Commitment) has a positive relationship with DV (Accounting Information System) with a beta coefficient (β) of 0.391, a t-value of 7.3653, and a p-value of 0.0000. The R-squared value (R2) for this path is 0.435, which shows that 43.5% of the variance in the DV can be explained by the MD.
Path C: The total effect of IV (Internal Auditing) on DV (Accounting Information System) is 0.410 with a t-value of 11.6795 and a p-value of 0.0000. The R-squared value (R2) for this path is 0.417, which shows that 41.7% of the variance in the DV can be explained by the IV and the MD together.
Path C’: The direct effect of IV (Internal Auditing) on DV (Accounting Information System) is 0.256 with a t-value of 6.8087 and a p-value of 0.0000. The R-squared value (R2) for this path is 0.546, which shows that 54.6% of the variance in the DV can be explained by the IV alone.
Path AB: The indirect effect of IV (Internal Auditing) on DV (Accounting Information System) through the MD is 0.155 with a standard error (SE) of 0.155. The bootstrap confidence interval for this indirect effect ranges from 0.0948 to 0.2184.
Overall, the results indicate that OC partially mediates the relationship between IA and AIS in Jordanian banks.
5. Discussion
Internal audits of bank performance are one of the most effective and speedy ways to reduce operational costs and give the bank a competitive edge in the global market during economic downturns (Jarah et al. 2022a). IA has emerged as a crucial component in aiding adequate controls and management (Setyaningsih 2020). Additionally, insufficient adoption of IA was previously the deciding factor for whether or not AIS qualified. The management and decision-making of businesses must thus be done effectively in order to use AISs (Alawaqleh 2021; Jarah and Almatarneh 2021). As a result, banks now have more access to AISs thanks to technological advancements (Faisal et al. 2023). Additionally, AISs provide both internal and external users with high-quality information (Ömer 2016). Therefore, accounting information developments lead to the development of information demands for interested parties as well as the necessity of quality procedures and performance in information creation (Wahyuni et al. 2022). Since internal auditors may effectively provide the information managers need to achieve specified bank goals, they may thus help management in carrying out control operations of the bank’s activities (Wonoseto et al. 2022). The bank must consequently improve its IA and AIS in order to meet its objectives (Hailat et al. 2023).
6. Implications and Limitations and Future Research and Conclusions
6.1. Implications
This study covers a wide range of IA-related subjects in this research as well as how it might help banks employ AIS more effectively. The goal of the research is to create fresh data that will expand the theoretical understanding of the many factors and the function that IA will play in enhancing AIS. Practically speaking, the researchers anticipate that the results will aid bank departments by offering recommendations on the AIS and the importance of IA in enhancing AIS.
6.2. Limitations
This work has several important contributions, but it also has some substantial limitations. By acknowledging these limitations, the findings of the present research are given more legitimacy. The current study concentrated on just 193 employees in order to retain a balanced perspective on the diagnostic and interactive use of the model in Jordanian banks. As a result, if there are more bank answers, the results could be more accurate.
6.3. Conclusions
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between IA and AISs in Jordanian banks, with a focus on the mediator role of OC. To gather and evaluate data for this study, a quantitative research design was used. Data were collected from a sample of bank workers, including those in the internal audit department, using a cross-sectional survey approach. The results indicate that IA has a positive correlation with AIS. Furthermore, the results indicated that OC partially mediates the relationship between IA and AIS in Jordanian banks. This result agreed with the results of the results of Jarah et al. 2023a; Putra 2023; Irfan and Hamimi 2023; Amira and Permatasari 2022; Wahyuni et al. 2022; Alawaqleh 2021; Yusuf and Kanji 2020; Mulyani et al. 2019; Pura 2017; and Ömer 2016, whose results indicated that AIS and IA had a significant influence on internal control, and the findings also revealed that the AIS and IA had a favorable and substantial influence on internal control at the same time. As the results of Rachman and Fitri (2023) indicated, operational auditing and AIS have a considerable impact on sales performance, and internal control has no bearing on sales performance. The findings of the study by Wibowo et al. (2023) demonstrate that internal control has no effect on performance, and the AIS has an effect on performance. For Jordanian banks, management should improve the present methods used to carry out internal audits in order to increase their efficacy. The board of directors must also pay close attention to confirming the efficacy of the AIS.
6.4. Future Research
In the future, further research on the impacts of IA on the AIS of Jordanian banks should be conducted. We were able to develop a linear regression model, which had some innovative implications for the government and other sectors, along with other mediator variables such as organizational performance and other variables and the use of statistical techniques. The current study further advises banks to concentrate on internal auditing system activation because of its favorable effects on AIS improvement, OC, and delivering value for target achievement. As a result, future research that broadens the field of knowledge could build on the existing study. As previously indicated, the most recent study supported certain findings from past research while contradicting others. However, in-depth research can address the inadequacies of the current study on banks around the world.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.A.F.J.; Data curation, M.K.A.Z.; Methodology, M.K.A.Z.; Project administration, B.A.F.J.; Resources, B.A.F.J.; Software, M.K.A.Z.; Validation, M.K.A.Z.; Visualization, M.K.A.Z.; Writing—original draft, B.A.F.J.; Writing—review and editing, B.A.F.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The accompanying authors are willing to provide the information that backs up the study’s conclusions upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Abed, Ibtihal A., Nazimah Hussin, Hossam Haddad, Tareq Hammad Almubaydeen, and Mostafa A. Ali. 2022. Creative accounting determination and financial reporting quality: The integration of transparency and disclosure. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 8: 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Matarneh, Ghassan F. 2011. Factors Determining the Internal Audit Quality in Banks: Empirical Evidence from Jordan. International Research Journal of Finance and Economics 73: 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Alawaqleh, Qasim Ahmad. 2021. Impact of accounting information system on internal audit quality: Mediating role of organizational culture. International Journal of Financial Research 12: 205–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldegis, Ahmad Mohammad. 2018. Impact of accounting information systems’ quality on the relationship between organizational culture and accounting information in Jordanian industrial public shareholding companies. International Journal of Academic Research in Accounting, Finance and Management Sciences 8: 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fakeh, Fuad Abdallah, Siti Falindah Padlee, Khatijah Omar, and Hayatul Safrah Salleh. 2020. The moderating effects of organizational commitment on the relationship between employee satisfaction and employee performance in Jordanian Islamic banks. Management Science Letters 10: 3347–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaliki, Oday Jasim, Nor Hanani Ahamad Rapani, Azam Abdelhakeem Khalid, and Rasool Majid Sahaib. 2019. Structural equation model for the relationship between accounting information system and internal audit effectiveness with moderating effect of experience. International Business Education Journal 12: 62–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqudah, Omar Mohammad Ali, Baker Akram Falah Jarah, Abdul Razzak Alshehadeh, Zeyad Almatarneh, Mohammed Zakaria Soda, and Haneen A. Al-Khawaja. 2023. Data processing related to the impact of performance expectation, effort expectation, and perceived usefulness on the use of electronic banking services for customers of Jordanian banks. International Journal of Data and Network Science 7: 657–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Taee, Salowan Hafadh Hamed, and Hakeem Hammood Flayyih. 2023. Impact of the electronic internal auditing based on IT governance to reduce auditing risk. Corporate Governance and Organizational Behavior Review 7: 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amira, Amira, and Ditya Permatasari. 2022. Internal control, organizational culture on employee performance with accounting information system as intervening. EL MUHASABA: Jurnal Akuntansi (e-Journal) 13: 148–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awuah, Benjamin, Joseph Mensah Onumah, and King Carl Tornam Duho. 2022. Determinants of adoption of computer-assisted audit tools and techniques among internal audit units in Ghana. The Electronic Journal of Information Systems in Developing Countries 88: e12203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, A., Vidyasagar Potdar, Amit Rudra, and Hoa Luong. 2020. The Impact of Organizational Culture on the Internal Controls Components of Accounting Information Systems in the City of Beirut, Lebanon. Paper presented at Big Data and Security: First International Conference, ICBDS 2019, Nanjing, China, December 20–22; Revised Selected Papers 1. pp. 157–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, Reuben M., and David A Kenny. 1986. The moderator--mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 51: 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewi, Yenty Astari, Nasfi Nasfi, and Mai Yuliza. 2021. Internal Control System, Utilization of Accounting Information Technology, on Village Fund Management Accountability. International Journal of Economics, Business and Accounting Research (IJEBAR) 5: 384–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, Yusuf, Annisa Rahayu Yulivianti, and Suci Dwi Rindiani. 2023. The Effect of Internal Control Systems and Accounting Information Systems on the Quality of Financial Statements PT. Gudang Garam, Tbk and PT. Wilmar Group. Jurnal Ilmiah Akuntansi dan Finansial Indonesia 6: 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, Indie, Puji Mesti Rahayu, and Veronica Christina. 2023. The Effect of Organizational Commitment on The Characteristics of Management Accounting Information Systems Case Study at PT. Indo-Rama Synthetics Tbk. Greenation International Journal of Economics and Accounting (GIJEA) 1: 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailat, Khaled Qassem, Baker Akram Falah Jarah, Mefleh Faisal Mefleh Al-Jarrah, and Zeyad Almatarneh. 2023. The impact of electronic banking services on the use of technology by customers of conventional and Islamic banks in Jordan. International Journal of Data and Network Science 7: 737–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, Andrew F. 2017. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach. New York: Guilford Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Hazaea, Saddam A., and Jinyu Zhu. 2022. Internal audit system and financial corruption in public institutions: Case study of Yemeni public telecommunication corporation. International Journal of Business Excellence 27: 360–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, Irfan, and Syahmina Hamimi. 2023. The Moderating Effect of Organizational Commitment on the Relationship Between Accounting Information Systems and Internal Control Systems on the Quality of Financial Reporting. Paper presented at Medan International Conference on Economic and Business, Medan, Indonesia, January 26; Volume 1, pp. 2212–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, Lawrence R., and Jeanne M Brett. 1984. Mediators, moderators, and tests for mediation. Journal of Applied Psychology 69: 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarah, Baker Akram Falah, and Mufleh Amin Al Jarrah. 2022. The role of accounting information systems (AIS) in increasing performance efficiency (IPE) in Jordanian companies. Academy of Strategic Management Journal 21: 111. [Google Scholar]
- Jarah, Baker Akram Falah, and Takiah Binti Mohd Iskandar. 2019. The role of characteristics of accounting information systems in the improve the financial performance of Jordanian companies. International Journal of All Research Writings 1: 32–45. [Google Scholar]
- Jarah, Baker Akram Falah, and Zeyad Almatarneh. 2021. The effect of the elements of accounting information system (AIS) on organizational culture (OC)-A field study. Academy of Strategic Management Journal 20: 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Jarah, Baker Akram Falah, Mufleh Amin Al Jarrah, and Murad Ali Ahmad Al-Zaqeba. 2022a. The role of internal audit in improving supply chain management in shipping companies. Uncertain Supply Chain Management 10: 1023–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarah, Baker Akram Falah, Mufleh Amin Al Jarrah, Murad Ali Ahmad Al-Zaqeba, and Mefleh Faisal Mefleh Al-Jarrah. 2022b. The Role of Internal Audit to Reduce the Effects of Creative Accounting on the Reliability of Financial Statements in the Jordanian Islamic Banks. International Journal of Financial Studies 10: 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarah, Baker Akram Falah, Mufleh Amin Al Jarrah, Salam Nawaf Almomani, Emran AlJarrah, and Maen Al-Rashdan. 2023a. The effect of reliable data transfer and efficient computer network features in Jordanian banks accounting information systems performance based on hardware and software, database and number of hosts. International Journal of Data and Network Science 7: 357–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarah, Baker Akram Falah, Nidal Zaqeeba, Mefleh Faisal Mefleh Al-Jarrah, Abdalla Mohammad Al Badarin, and Zeyad Almatarneh. 2023b. The Mediating Effect of the Internal Control System on the Relationship between the Accounting Information System and Employee Performance in Jordan Islamic Banks. Economies 11: 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, Charles M., and David A. Kenny. 1981. Process analysis: Estimating mediation in treatment evaluations. Evaluation Review 5: 602–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J., T. Xia, D. Wu, Jing Li, Tongshui Xia, and Dengsheng Wu. 2022. Internal control quality, related party transactions and accounting information comparability. Procedia Computer Science 199: 1252–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limpo, Lita, and Junaidi Junaidi. 2023. Influence of Empowering and Ethical Leadership on Employees’ Job Satisfaction, Performance, and Organization Commitment. Humanities and Social Sciences Letters 11: 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Zheyuan. 2023. The internal control method of modern management accounting information system. International Journal of Business and Management 1: 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lois, Petros, George Drogalas, Michail Nerantzidis, Ifigenia Georgiou, and Eleni Gkampeta. 2021. Risk-based internal audit: Factors related to its implementation. Corporate Governance: The International Journal of Business in Society 21: 645–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyani, Sri, Erlynda Kasim, Winwin Yadiati, and Haryono Umar. 2019. Influence of accounting information systems and internal audit on fraudulent financial reporting. Opción: Revista de Ciencias Humanas y Sociales 21: 323–38. [Google Scholar]
- Napitupulu, Ilham Hidayah. 2020. Internal Control, Manager’s Competency, Management Accounting Information Systems and Good Corporate Governance: Evidence from Rural Banks in Indonesia. Global Business Review 24: 563–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningrum, Endah Prawesti, Resista Vikaliana, Susan Rachmawati, Nurzalinar Joesah, Arman Syah Putra, and Nurul Aisyah. 2022. Internal Control System Applied To Online Based Company Accounting Information Systems. IJISTECH (International Journal of Information System and Technology) 5: 754–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ömer, T. A. N. 2016. Impact of accounting information systems on internal auditors in Turkey. Öneri Dergisi 12: 245–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pura, Rahman. 2017. Effects of Auditor Competence, Information Technology, Accounting Information Systems and Organizational Commitment on Auditors’ Performance at the State Audit Agency, in South Sulawesi. Scientific Research Journal (SCIRJ) 5: 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Putra, Vicky Dzaky Cahaya. 2023. The influences of user capability, internal control, and information technology on the quality of accounting information systems in conventional commercial banks. Enrichment: Journal of Management 12: 5105–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachman, Ibnu. 2021. The Effect Of Internal Control And Organizational Commitment To Fraud prevention in hospital x in the city of bandung indonesia. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education (TURCOMAT) 12: 1038–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachman, Purie Ayu Istiningdyah, and Hadiati Fitri. 2023. The Effect of Operational Audit, Internal Control, Implementation of Marketing Strategy and Sales Accounting Information System on Sales Effectiveness. Research of Accounting and Governance 1: 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagala, Friska Zagita. 2020. The Effect of Accounting Information Systems and Internal Control of Employee Performance. Jurnal Akuntansi, Audit dan Sistem Informasi Akuntansi 4: 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandag, Eltie Christi, Ribka Sari Butar-butar, Ibnu Sutomo, and Arifia Nurriqli. 2023. Financial report quality, accounting information systems, internal control systems, and labour efficiency’s effect on managerial performance at pt. karate. International Journal of Economics and Management Research 2: 240–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputro, Muhammad Deni. 2022. The Influence of Accounting Information Systems and Internal Control on the Quality Of Regional Financial Statements in the Government of Bondowoso District. Journal of Contemporary Information Technology, Management, and Accounting 3: 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Sastrawan, Hendrik, Fajar Gustiawaty Dewi, and Yuliansyah Yuliansyah. 2020. The effect of budgetary participation on managerial performance: Internal control and organizational commitments as intervening variables. Journal of Social, Humanity, and Education 1: 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekaran, Uma, and Roger Bougie. 2016. Research Methods for Business: A Skill Building Approach, 7th ed. Hoboken and Chichester: John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Setyaningsih, Puji Rahayu. 2020. Internal Control, Organizational Culture, and Quality of Information Accounting to Prevent Fraud: Case Study Fro. International Journal of Financial Research 11: 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyaningsih, S. D., S. Mulyani, B. Akbar, and Ida Farida. 2021. Implementation and performance of accounting information systems, internal control and organizational culture in the quality of financial information. Utopía y Praxis Latinoamericana: Revista Internacional de Filosofía Iberoamericana y Teoría Social 1: 222–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Tiago, Rui Pedro Marques, and Graça Azevedo. 2023. The Impact of ERP Systems in Internal Auditing: The Portuguese Case. Procedia Computer Science 219: 963–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumardjo, Mahendro, and Yudi Nur Supriadi. 2023. Perceived Organizational Commitment Mediates the Effect of Perceived Organizational Support and Organizational Culture on Organizational Citizenship Behavior. Calitatea 24: 376–84. [Google Scholar]
- Syahputra, Oky. 2022. The Effect of Internal Control and Quality of Accounting Information Systems on Quality Information on Pt. Pandu Siwi Sentosa (Pandu Logistics). Enrichment: Journal of Management 12: 1712–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dung, H. A. 2020. Impact of organizational culture on the accounting information system and operational performance of small and medium sized enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business 7: 301–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyuni, Putri, Muammar Rinaldi, and Anton Eka Saputra. 2022. The Effect of Accounting Information Systems And Internal Audits on Internal Control at PT. Sierra Mandiri Distribusindo. Enrichment: Journal of Management 12: 1673–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, Stephen G., Aaron B. Taylor, and Wei Wu. 2012. Model fit and model selection in structural equation modeling. In Handbook of Structural Equation Modeling. Edited by Rick. H. Hoyle. New York: The Guilford Press, Indianapolis: Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis, pp. 209–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wibowo, Teguh Setiawan, Taryana Taryana, Yayuk Suprihartini, Daniel Tulasi, Didik Supriyanto, and Amin Harahap. 2023. The Effect of Accountability, Internal Control System, and Accounting Information System on The Performance of the Organization in the Financial and Asset Management Agency. Settings International Journal of Economic Research and Financial Accounting (IJERFA) 1: 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Wirdiansyah, R. Dian, and Agus Munandar. 2022. The Effect of Application of Payroll Accounting Information System in Increasing the Effectiveness of Company’s Internal Control (Literature Study). Budapest International Research and Critics Institute-Journal (BIRCI-Journal) 5: 151–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonoseto, Muhammad Galih, Dinik Fitri Rahajeng Pangestuti, Mahfud Asyari, and A. Muh Fakhry Mubarak. 2022. Internal Audit Information System Design in the University:(Case Study at Islamic State University Sunan Kalijaga Yogyakarta). Paper presented at 2022 10th International Conference on Information and Education Technology (ICIET), Matsue, Japan, April 9–11; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Zhenying, and Jingjian Hu. 2020. Internal control of enterprise computer accounting information system in the age of big data. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, Cyber Security Intelligence and Analytics: Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Cyber Security Intelligence and Analytics (CSIA 2020). Cham: Springer International Publishing, vol. 2, pp. 315–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf, Marwah, and Lusiana Kanji. 2020. Effect of internal audit and accounting information system on the effectiveness of internal control. ATESTASI: Jurnal Ilmiah Akuntansi 3: 120–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).