The Determinant of Sukuk Rating: Agency Theory and Asymmetry Theory Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
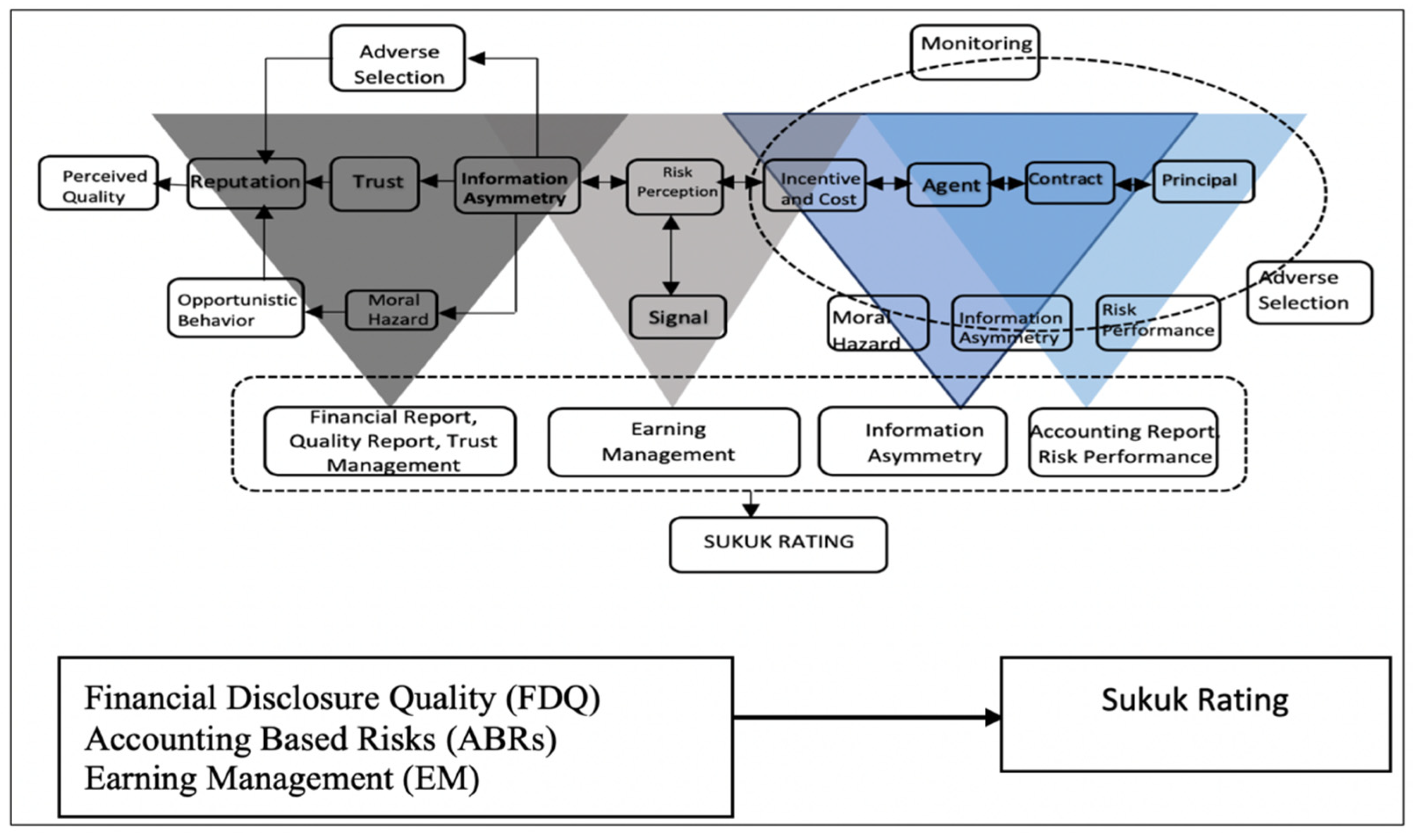
2.1. Agency, Asymmetry, and Signaling Theories and Highlight Perspective
2.2. Asymmetry Theory
2.3. Signaling Theory
2.4. Agency Theory
2.5. Sukuk Rating
2.6. Studies Related to Sukuk
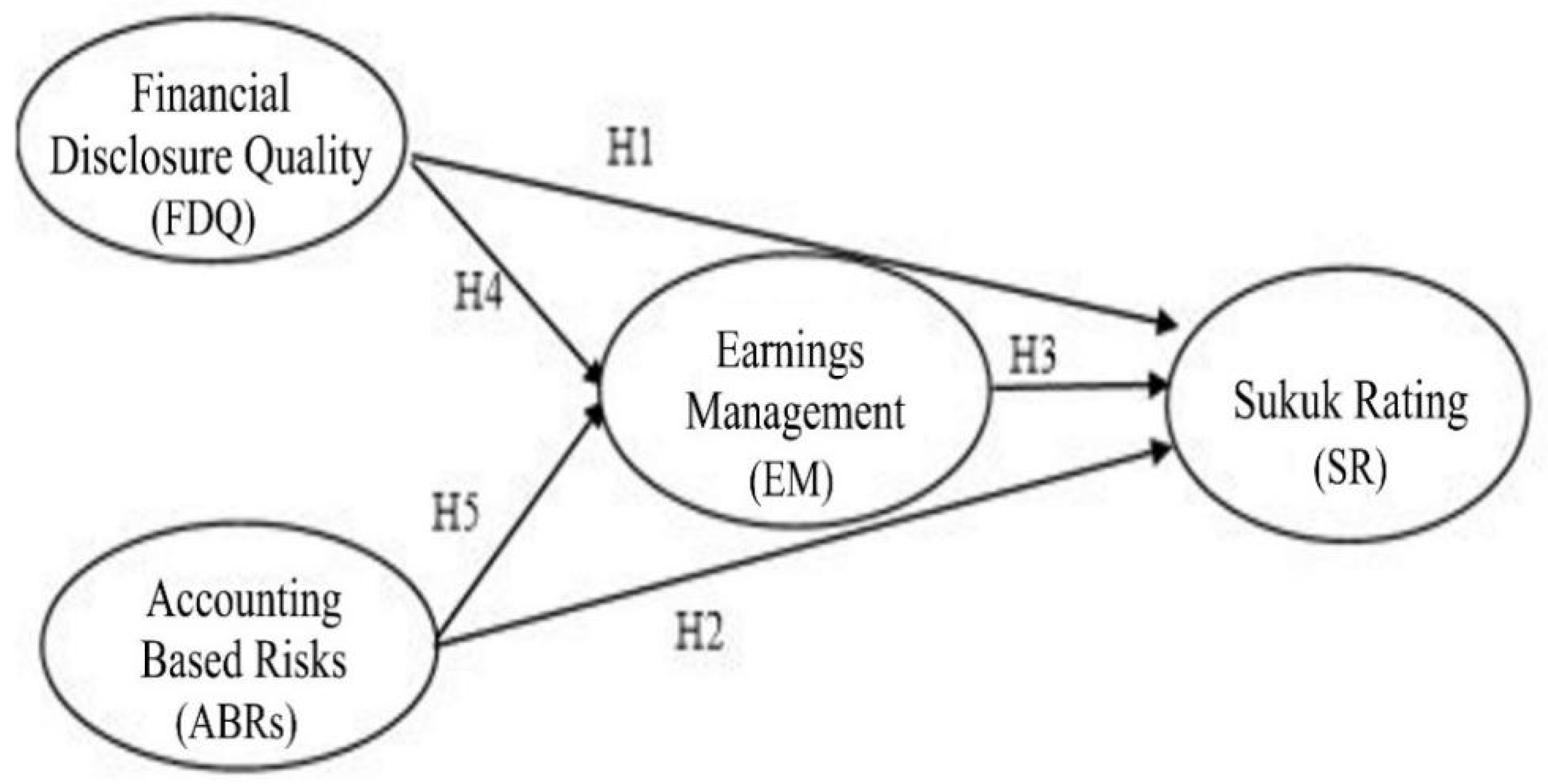
2.7. Theoretical Model
2.7.1. The Effect of Financial Disclosure Quality (FDQ) on Sukuk Rating
2.7.2. The Effect of Accounting-Based Risks (ABRs) on Sukuk Rating
2.7.3. The Effect of Earnings Management on Sukuk Rating
2.7.4. The Effect of Financial Disclosure Quality (FDQ) on Earnings Management
2.7.5. The Effect of Accounting-Based Risks (ABRs) on Earnings Management
3. Research Methods
Sukuk
4. Results
4.1. SEM Analysis—Partial Least Square
4.2. Internal Consistency or Construct Reliability
4.3. Average Variance Extracted (AVE)
4.4. Discriminant Validity Test
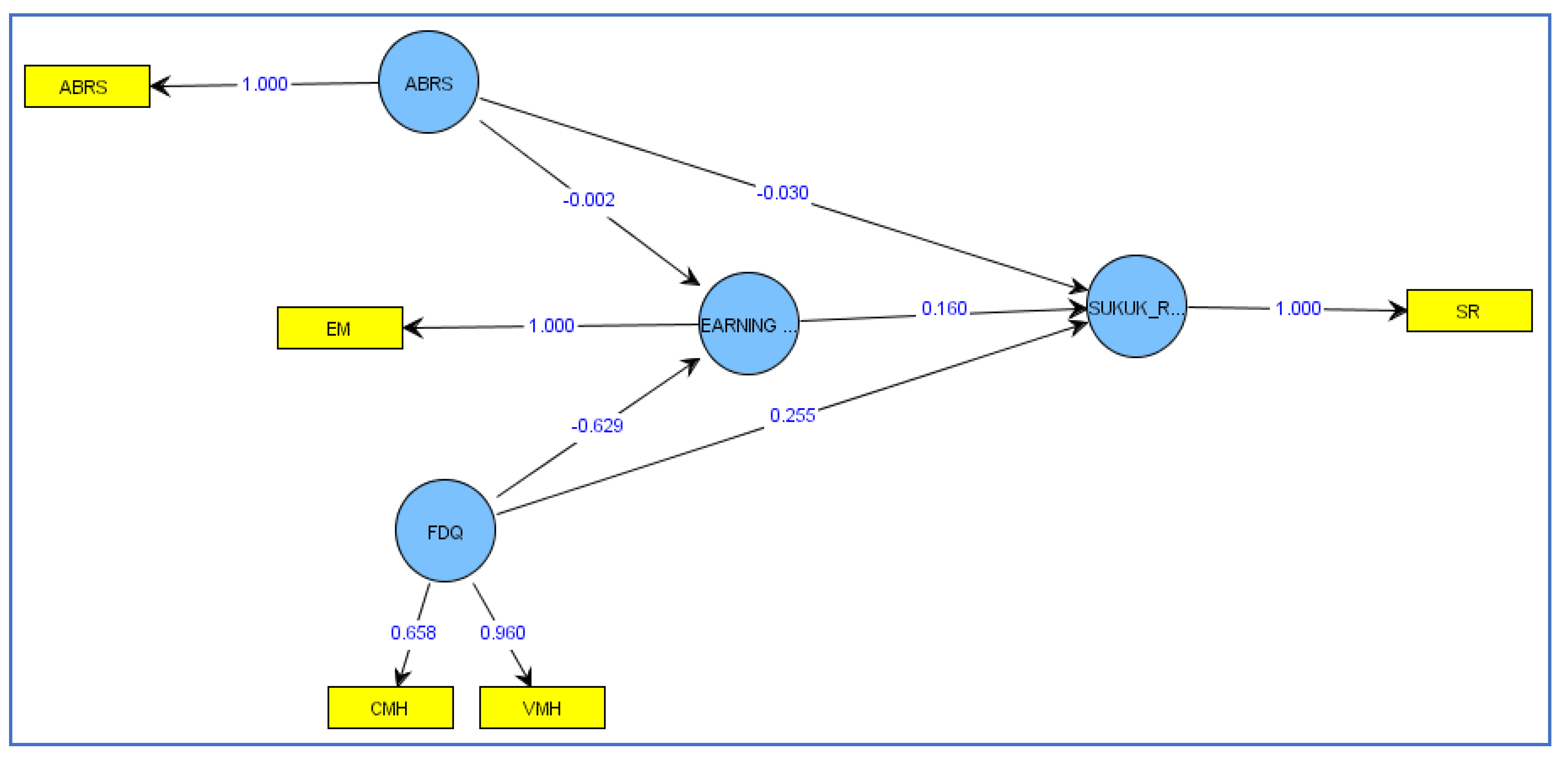
4.5. Results of the Inner Model (Structural Model)
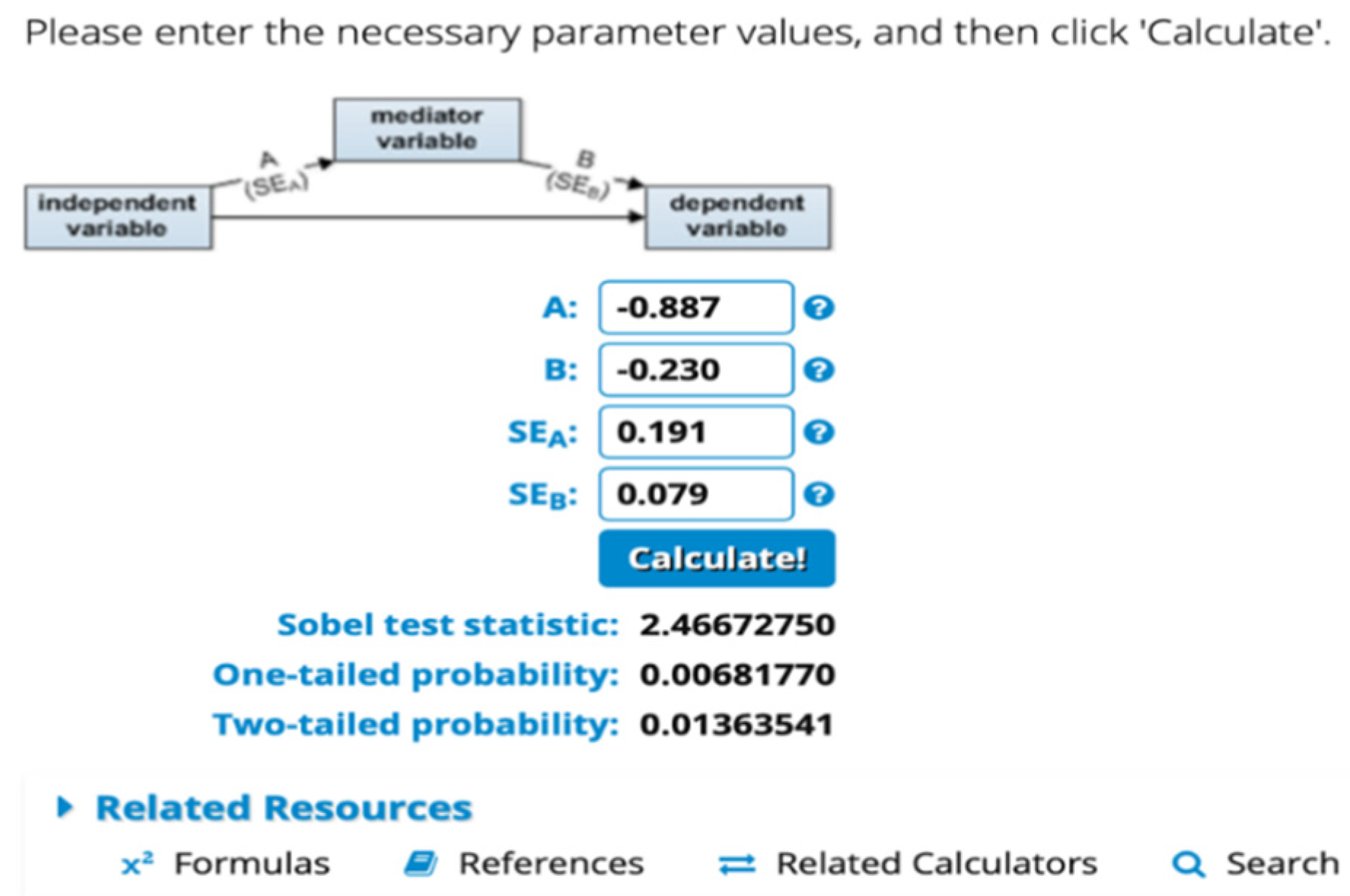
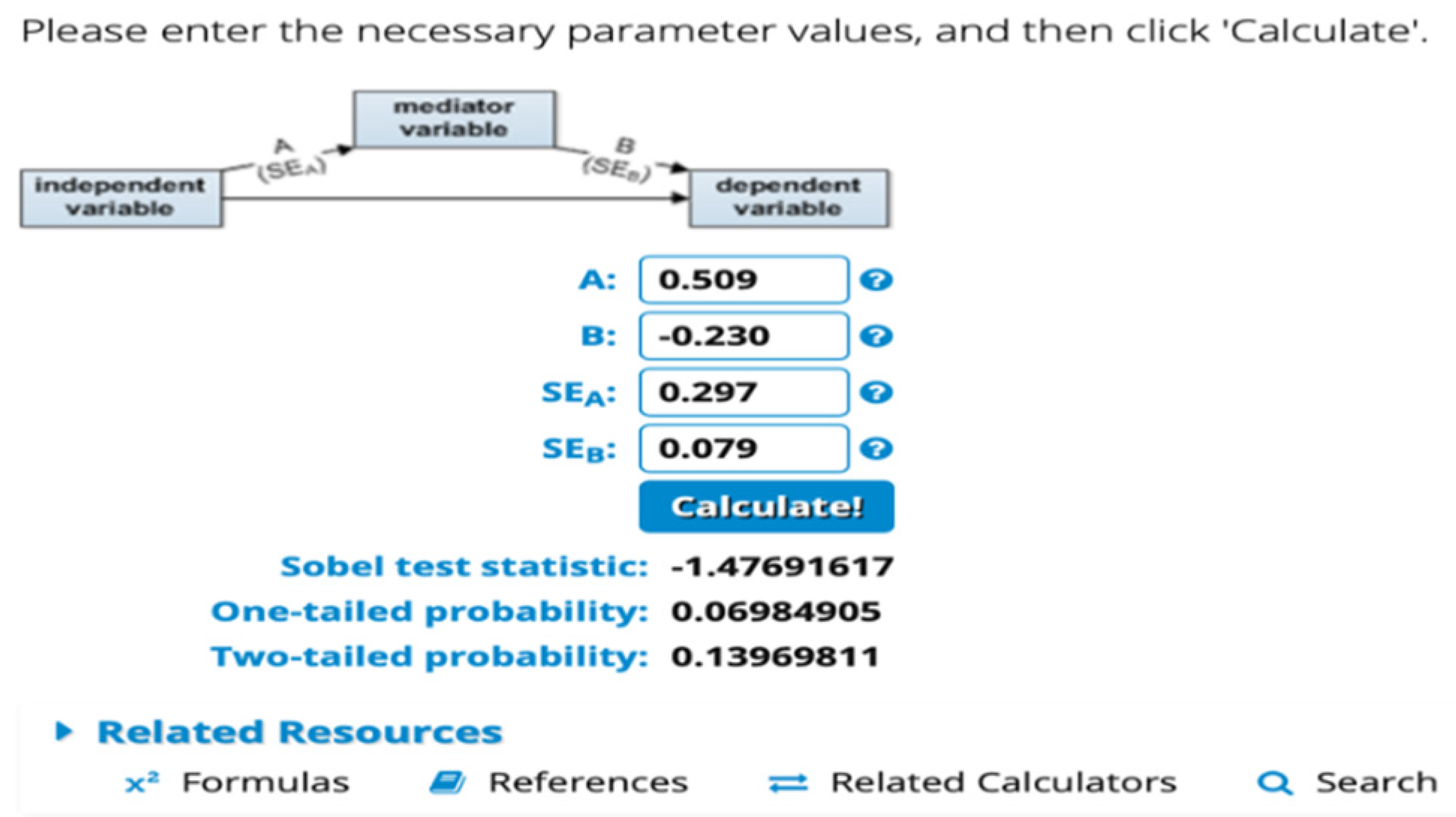
4.6. Mediating Test Results (Intervening)
5. Discussion
5.1. The Effect of Financial Disclosure Quality (FDQ) on Sukuk Rating
5.2. The Effect of Accounting-Based Risks (ABRs) on Sukuk Rating
5.3. The Effect of Earnings Management on Sukuk Rating
5.4. The Effect of Financial Disclosure Quality (FDQ) on Earnings Management Sukuk
5.5. Theoretical Implications
5.6. Managerial Implications
6. Conclusions
6.1. Research Limitations
6.2. Suggestions for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agustia, Yofi Prima, and Elly Suryani. 2018. Pengaruh Ukuran Perusahaan, Umur Perusahaan, Leverage, Dan Profitabilitas Terhadap Manajemen Laba (Studi Pada Perusahaan Pertambangan yang Terdaftar di Bursa Efek Indonesia Periode 2014–2016). Jurnal ASET (Akuntansi Riset) 10: 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haraqi, M. Siddiq, and Surasetyo Ningsih Endang. 2017. Pengaruh Return on Asset, Secure Dan Maturity Terhadap Rating Sukuk. Jurnal Ilmiah Mahasiswa Ekonomi Akuntansi 2: 116–24. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Homsi, Mahmoud, Zulkarnain M. Sori, and Shamser Mohamad. 2017. The Determinants of Sukuk Credit Ratings: The Malaysia Case. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320559454_Determinants_of_Sukuk_Credit_Ratings_the_Malaysia_Case (accessed on 9 December 2021).
- Alzoubi, Ebraheem Saleem Salem. 2016. Disclosure Quality and Earnings Management: Evidence from Jordan. Accounting Research Journal 29: 429–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arundina, Tika, Mira Kartiwi, and Mohammad Azmi Omar. 2016. Artificial intelligence for Islamic Sukuk Rating Predictions. In Artificial Intelligence in Financial Markets. London: Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 211–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, Retno Puji. 2020. The Influence Corporate Governance on Sukuk Rating. Journal of Islamic Economic and Social Science 1: 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaja, Lukas Setia. 2008. Structure and the Corporate Governance Role of Dividends. Jurnal Keuangan dan Perbankan 12: 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Borhan, Nur Amirah, and Noryati Ahmad. 2018. Identifying the determinants of Malaysian corporate Sukuk rating. International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management 11: 432–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botosan, C. Alice, and Marlene Plumlee. 2013. Are Information Attributes are Priced? Journal of Business Finance and Accounting 40: 1045–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouheraoua, Said, Shamsiah Mohamad, Noor Suhaida Kasri, and Syahida Abdullah. 2014. Sharia Issues in Intangible Assets. Available online: http://ajba.um.edu.my/index.php/JS/article/view/6926/4589 (accessed on 12 February 2022).
- Chandra, Prasanna. 2011. Financial Management: Theory and Practice. New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill Education. [Google Scholar]
- Covitz, Daniel, and Paul Harrison. 2003. Testing Conflicts of Interest at Bond Rating Agencies with Market Anticipation: Evidence That Reputation Incentives Dominate. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=512402 (accessed on 12 February 2022).
- Czaja-Cieszyńska, Hanna, Dominika Kordela, and Beata Zyznarska-Dworczak. 2021. How to Make Corporate Social Disclosures Comparable? Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues 9: 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Van Dan, and Japan Huynh. 2020. Holdings of Sovereign Bonds by Commercial Banks in Vietnam. Cogent Economics and Finance 8: 1818409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechow, M. Patricia, Amy P. Hutton, Jung Hoon Kim, and Richard G. Sloan. 2011. Detecting Earnings Management: A New Approach. Journal of Accounting Research 50: 275–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, M. Kathleen. 1989. Agency Theory; an Assessment and Review. Academy of Management Review 14: 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhaj, Mohamed Abulgasem, Nurul Aini Muhamed, and Nathasa Mazna Ramli. 2015. The Influence of Corporate Governance, Financial Ratios, and Sukuk Structure on Sukuk Rating. Procedia Economics and Finance 31: 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhaj, Mohamed Abulgasem, Nurul Aini Muhamed, and Nathasa Mazna Ramli. 2017. The Effects of Board Attributes on Sukuk Rating. International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management 11: 312–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdoğan, Seyfettin, Sema Yılmaz Genç, and Ayfer Gedikli. 2018. A Politico-Economic Evaluation on International Credit Rating Agencies, Cambridge International Academics 2018. Cambridge: Open Monographs. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329718235 (accessed on 19 November 2021).
- Fadah, I., A. Ayuningtyas, N. Puspitasari, and I. B. Yuswanto. 2020. Analysis of financial and non-financial factors affecting bond ratings. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 485: 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faozi, Imam, and Nunung Ghoniyah. 2019. Model of Corporate Value Improvement Through Investment Opportunity in Manufacturing Company Sector. International Research Journal of Business Studies 12: 185–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, Omar, and Allaa Abdel Bari. 2015. Earnings Management Behavior of Sharia-Compliant Firms and non-Shariah-Compliant Firm. Journal of Islamic Accounting and Business Research 6: 173–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, Claes, and David Larcker. 1981. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. Journal of Marketing Research 18: 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghozali, Imam. 2014. Structural Equation Modeling Metode Alternatif Dengan Partial Least Square (PLS). Semarang: Universitas Diponegoro. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, Omaima, and Claire Marston. 2019. Corporate Financial Disclosure Measurement in the Empirical Accounting Literature: A Review Article. The International Journal of Accounting 54: 1950006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemraj, Mohammed. 2015. Credit Rating Agencies: Self-Regulation, Statutory Regulation and Case Law Regulation in the United States and European Union. Cham: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Hermawan, Atang, and Ardi Gunardi. 2019. Motivation for Disclosure of Corporate Social Responsibility: Evidence from Banking Industry in Indonesia. Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues 6: 1297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Accounting Standards Board. 2016. IFRS Standards. Available online: https://www.ifrs.org/groups/international-accounting-standards-board/ (accessed on 9 December 2021).
- Jensen, C. Michael, and William H. Meckling. 1976. Theory of the Firm: Managerial Behavior, Agency Costs and Ownership Structure. Journal of Financial Economics 3: 305–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, Jasper. 2022. Global Sovereign Default Risk to Increase as Credit Rating Downgrades to Outnumber Upgrades in 2017. Available online: https://www.cityam.com/global-sovereign-default-risk-increase-credit-rating/ (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Jorion, Philippe, and Gaiyan Zhang. 2007. Information Effects of Bond Rating Changes: The Role of the Rating Prior to the Announcement. Journal of Fixed Income 16: 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. Young, Yura Kim, and Kyojik Roy Song. 2013. Credit Rating Changes and Earnings Management. Asia-Pacific Journal of Financial Studies 42: 109–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Chin-Shien, Ruei-Yuan Chang, and Van Thac Dang. 2015. An Integrated Model to Explain How Corporate Social Responsibility Affects Corporate Financial Performance. Sustainability 7: 8292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariana, M. 2016. Pengaruh Mekanisme Corporate Governance Terhadap Peringkat Obligasi Yang Tercatat di Bursa Efek Indonesia Periode Tahun 2008–2010. AKRUAL Jurnal Akuntansi 7: 91–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Melzatiaa, Shinta, Radin Firdaus, Radin Badaruddinb, and Zahri Hammatc. 2019. Sukuk Rating, the Involvement of Agency Theory. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Chang 6: 139–55. [Google Scholar]
- Nabila, Ismail, and Tika Arundina. 2019. Sukuk Rating Prediction: The Case of Corporate Sukuk in Indonesia. PERTANIKA Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities 27: 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ningrum, Nurani Puspa, Amirul Fatikhin, and Darsin. 2019. Identification of the Determinant Factors of Company Sukuk Rating in Indonesia: Using Profit Management as an Intervening Variable. Paper presented at 1st International Conference on Science, Health, Economics, Education and Technology (ICoSHEET 2019), Semarang, Indonesia, December 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoritas Jasa Keuangan (OJK). 2021. Statistik Sukuk Syariah Desember 2021. Available online: https://www.ojk.go.id/id/kanal/syariah/data-dan-statistik/data-produk-obligasi-syariah/Documents/Pages/Statistik-Sukuk-Syariah---Desember-2021/Statistik%20Sukuk%20Desember%202021.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- Oktaviyani, Rizka Dewi. 2021. Effect of Profit Management, Financial Ratio and Corporate Governance Mechanism on Bond Rating. Jurnal Ekonomi 10: 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pefindo. 2018. Rating Definitions. Available online: https://pefindo.com/fileman/file?file=95/ (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Pranoto, Galih Estu, Ratna Anggraini, and Erika Takidah. 2017. The influence of profitability, firm size, productivity and reputation of the auditor on the rating of Sukuk. Jurnal Wahana Akuntansi (Universitas Negeri Jakarta) 12: 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prastiani, Siti Chaerunisa. 2018. Pengaruh Kinerja Keuangan Terhadap Peringkat Obligasi dengan Manajemen Laba sebagai Variabel Intervening pada Perusahaan Manufaktur yang Terdaftar di Bei. JABI (Jurnal Akuntansi Berkelanjutan Indonesia) 1: 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qizam, Ibnu. 2011. The Economic Value of Financial Statement Information Risk and the Risk Relevance of Fundamentals: Nilai Ekonomik Informasi Laporan Keuangan dan Relevansi Risiko Fundamental. Unpublished Ph.D. dissertation, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia. [Google Scholar]
- Qizam, Ibnu, and Michelle Fong. 2019. Developing Financial Disclosure Quality in Sukuk and Bond Market: Evidence from Indonesia, Malaysia, and Australia. Borsa Istanbul Review 19: 228–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuters, Thompson. 2017. Opportunities in the Changing Sukuk Market. Available online: https://ceif.iba.edu.pk/pdf/ThomsonReuters-SukukPerceptionsForecastStudy2017.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Ross, A. Stephen. 1997. The Determination of Financial Structure: The Incentive-Signaling Approach. The Bell Journal of Economics 8: 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, Cinthia Valle. 2016. Literature Review of Earnings Management: Who, Why, When, How and What For. Finnish Business Review 11: 1–13. Available online: https://verkkolehdet.jamk.fi/finnish-business-review/files/2016/03/FBR-2015-5.pdf/ (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Scott, William R. 2006. Financial Accounting Theory, 4th ed. Ontario: Prentice Hall. [Google Scholar]
- Siswoyo, Haryono. 2016. Metode SEM Untuk Penelitian Manajemen Dengan AMOS 22.00, LISREL 8.80 dan Smart PLS 3.0. Jakarta: Badan Penerbit PT Intermedia Personalia Utama. [Google Scholar]
- Situmorang, Bornok. 2017. Pengaruh Peringkat Obligasi, Debt to Equity Ratio dan Ukuran Perusahaan terhadap Yield to Maturity Obligasi Korporasi dengan Bunga SBI sebagai Variabel Moderating. Jurnal Terapan Manajemen dan Bisnis 3: 42–58. [Google Scholar]
- Sudaryanti, Neneng, Akhmad Affandi Mahfud, and Ries Wulandari. 2011. Analisis Determinan Peringkat Sukuk dan Peringkat Obligasi di Indonesia. Tazkia Islamic Finance and Business Review 6: 105–37. [Google Scholar]
- Tamara, Antania Ghea, Muhammad Muslih, and Deannes Isynuwardhana. 2020. The Influence of Profitability, Assets Structure and Firm Size on Capital Structure (Study on Food and Beverage Manufacturing Sub Sector Companies Listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange period 2013–2017). e-Proceeding of Management 7: 2355–57. [Google Scholar]
- Toumeh, Ahmad A., Sofri Yahya, and Azlan Amran. 2020. Surplus Free Cash Flow, Stock Market Segmentations and Earnings Management: The Moderating Role of Independent Audit Committee. Global Business Review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulfa, Fitria. 2019. Pengaruh Rasio Keuangan dan Faktor Non Keuangan Terhadap Peringkat Obligasi dengan Manajemen Laba Sebagai Variabel Intervening. Jurnal Ekonomi dan Manajemen 20: 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Veganzones, David, Eric Séverin, and Souhir Chlibi. 2021. Influence of Earnings Management on Forecasting Corporate Failure. International Journal of Forecasting. International Journal of Forecasting. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, Ross, and Jerold L. Zimmerman. 1986. Positive Accounting Theory. Upper Saddle River: Prentice-Hall. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=928677 (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- West, Richard R. 1970. An Alternative Approach to Predicting Corporate Bond Ratings. Journal of Accounting Research 8: 118–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, Svante, Nouna Kettaneh, and Kjell Tjessem. 1996. Hierarchical Multiblock PLS and PC Models for Easier Model Interpretation and as an Alternative to Variable Selection. Journal of Chemometrics 10: 463–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Economic Forum. 2019. Annual Report 2019–2020. Available online: https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Annual_Report_2019_2020.pdf (accessed on 19 January 2022).
- Yamin, Sofyan, and Heri Kurniawan. 2011. Generasi Baru Mengolah Data Penelitian Dengan Partial Least Square Path Modeling. Jakarta: Salemba Infotek. [Google Scholar]
- Yofrizal, Ryan Hakam. 2013. Pengaruh Manajemen Laba Terhadap Peringkat Obligasi (Studi Pada Perusahaan yang Terdaftar di Bursa Efek Indonesia Periode 2008–2011). Unpublished Paper. Undergraduate thesis, Universitas Muhammadiyah Gresik, Indonesia. [Google Scholar]
- Yuwono, Wisnu, and Dita Aurelia. 2021. The Effect Of Profitability, Leverage, Institutional Ownership, Managerial Ownership, And Dividend Policy on Firm Value. Journal of Global Business and Management Review 3: 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeibote, Zane, Tatjana Volkova, and Kiril Todorov. 2019. The impact of globalization on Regional Development and Competitiveness: Cases of Selected Regions. Insights into Regional Development 1: 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Sheunesu. 2021. Macroeconomic Determinants of Long-Term Sovereign Bond Yields in South Africa. Cogent Economics and Finance 9: 1929678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Criteria | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The number of corporate Sukuk that were still listed until 2020. | 274 |
| 2 | The number of Corporate Sukuk which were not rated by PT. PEFINDO (Indonesian Rating Sukuk Agency) for three consecutive years. | 63 |
| 3 | The number of companies that published incomplete financial statements for three consecutive years. | 21 |
| 4 | The amount of data that can be used. | 190 |
| No. | Variables | Indicators | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sukuk Rating | Scale 1–18 | (Elhaj et al. 2017; Arundina et al. 2016) |
| 2 | FDQ | The relevance ratio (represented CMH) reflects the covariance of intrinsic value and market value divided by intrinsic and book values. The reliability of the ratio (represented VMH) reflects the market value variance divided by the book value variance. | (Qizam and Fong 2019) |
| 3 | ABRs | Proxy by leverage * Total debt ratio (total debt/total equity) | (Elhaj et al. 2017; Arundina et al. 2016; Qizam and Fong 2019; Faozi and Ghoniyah 2019) |
| 4 | Earnings Management | Modified Jones model ** | (Ningrum et al. 2019; Veganzones et al. 2021) |
| Delimiter: | Encoding: | U1 | |||||
| Value Quote Character: | None | Sample Size: | 570 | ||||
| Number Format: | Europe (example: 1.000, 23) | Indicators: | 5 | ||||
| Missing Value Marker: | None | Missing Values: | 0 | ||||
| Indicators | Indicator Correlations | Raw File | |||||
| No. | Missing | Mean | Median | Min. | Max. | Standard Deviation | |
| RAT | 1 | 0 | 14.482 | 14.000 | 1.000 | 18.000 | 5.668 |
| LEV | 2 | 0 | 1.815 | 1.319 | −2.128 | 7.341 | 2.360 |
| EM | 3 | 0 | 0.019 | −0.041 | −0.177 | 0.636 | 0.009 |
| CMH | 4 | 0 | 0.956 | 0.970 | −0.673 | 1.968 | 0.469 |
| VMH | 5 | 0 | 0.826 | 0.911 | −1.927 | 2.541 | 0.877 |
| Cronbach’s Alpha | rho_A | Composite Reliability | Average Variance Extracted | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABRs | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| FDQ | 0.587 | 0.969 | 0.832 | 0.687 |
| Earnings Management | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Sukuk Rating | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| ABRs | FDQ | Earnings Management | Sukuk Rating | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABRs | 1.000 | |||
| FDQ | 0.290 | 0.831 | ||
| Earnings Management | −0.109 | −0.639 | 1.000 | |
| Sukuk Rating | 0.553 | 0.828 | −0.491 | 1.000 |
| Original Sample | Sample Mean | Standard Deviation | t-Statistics | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
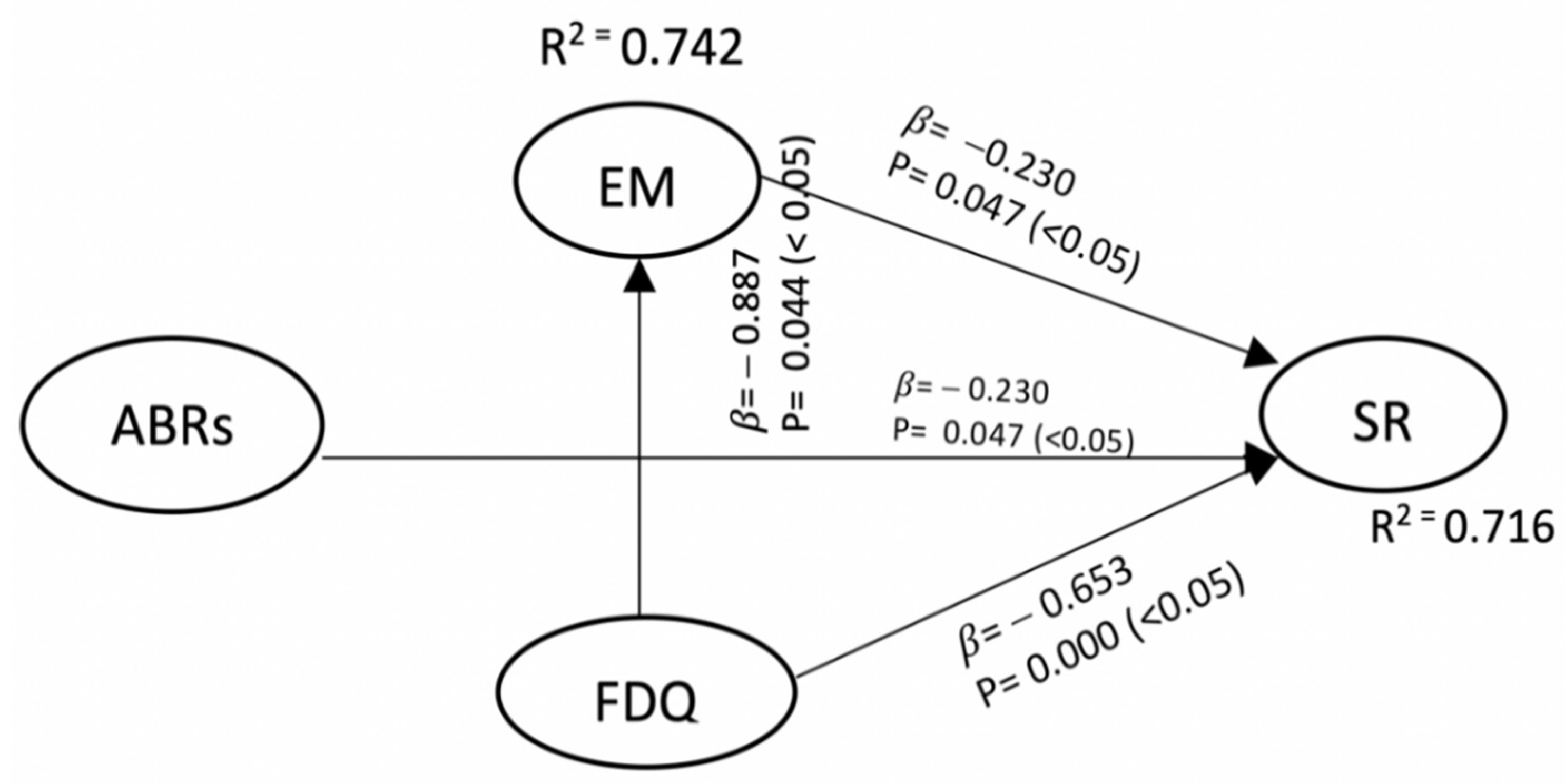
| ABRs → Earnings Management | 0.509 | 0.205 | 0.297 | 2.812 | 0.038 |
| ABRs → Sukuk Rating | −0.344 | 0.311 | 0.125 | 2.819 | 0.027 |
| FDQ → Earnings Management | −0.887 | 0.629 | 0.191 | 2.961 | 0.044 |
| FDQ → Sukuk Rating | 0.653 | 0.722 | 0.188 | 3.880 | 0.000 |
| Earnings Management → Sukuk Rating | −0.230 | 0.008 | 0.079 | 3.102 | 0.047 |
| R Square (R2) | |
|---|---|
| Sukuk Rating | 0.716 |
| Earnings Management | 0.742 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santoso, B.; Widodo, W.; Akbar, M.T.; Ahmad, K.; Setianto, R.H. The Determinant of Sukuk Rating: Agency Theory and Asymmetry Theory Perspectives. Risks 2022, 10, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks10080150
Santoso B, Widodo W, Akbar MT, Ahmad K, Setianto RH. The Determinant of Sukuk Rating: Agency Theory and Asymmetry Theory Perspectives. Risks. 2022; 10(8):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks10080150
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantoso, Bedjo, Widodo Widodo, Muhammad Taufiq Akbar, Khaliq Ahmad, and Rahmat Heru Setianto. 2022. "The Determinant of Sukuk Rating: Agency Theory and Asymmetry Theory Perspectives" Risks 10, no. 8: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks10080150
APA StyleSantoso, B., Widodo, W., Akbar, M. T., Ahmad, K., & Setianto, R. H. (2022). The Determinant of Sukuk Rating: Agency Theory and Asymmetry Theory Perspectives. Risks, 10(8), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks10080150







