A Proposed Methodology for Literature Review on Operational Risk Management in Banks
Abstract
1. Introduction
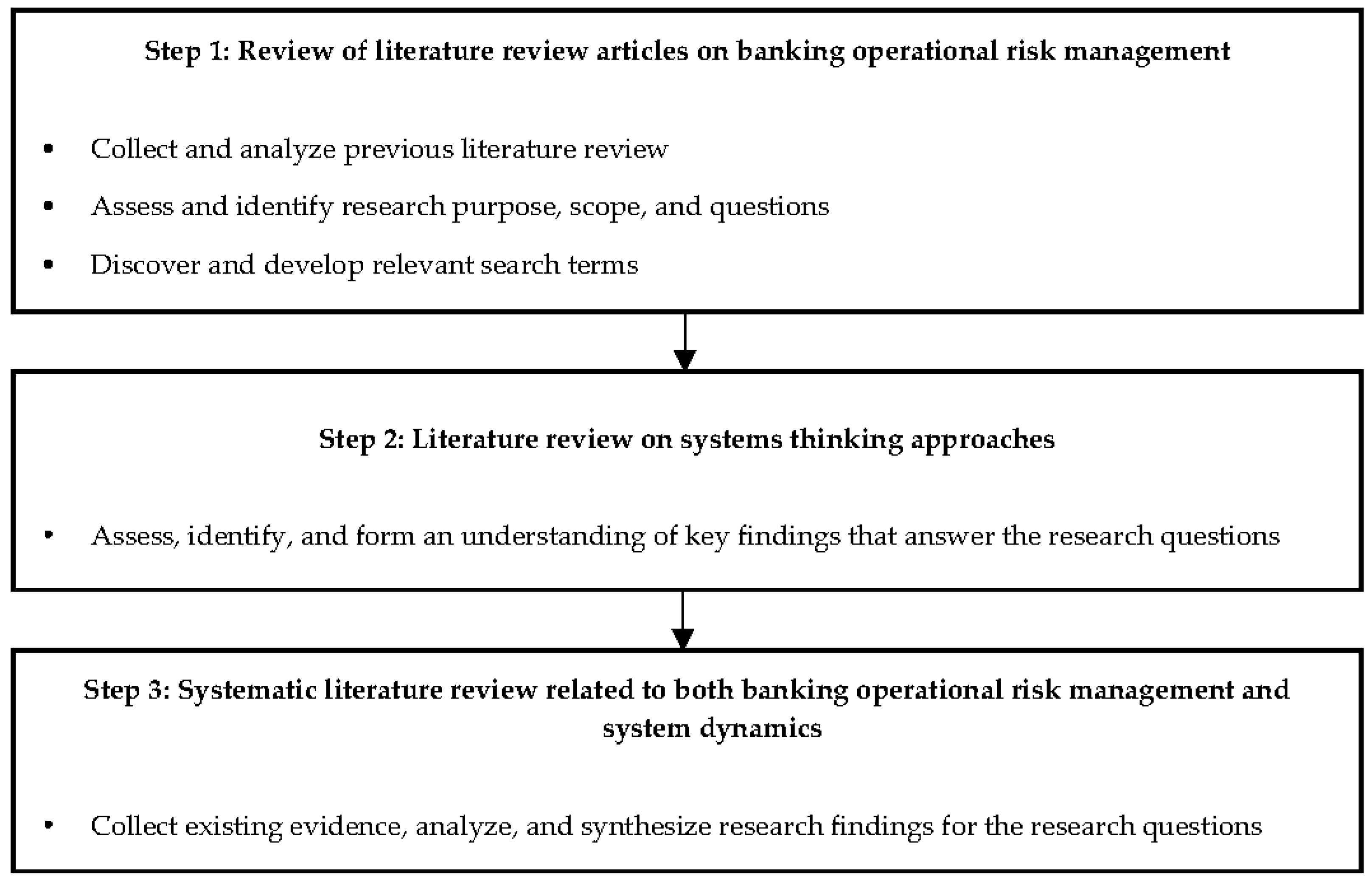
2. A Proposed Literature Review Methodology
3. Validating the Proposed Literature Review Methodology in Banking Operational Risk Management Literature
3.1. Step 1—Review of Literature Review Articles on Operational Risk Management in the Banking Industry
3.2. Step 2—Literature Review of Systems Thinking Approaches in Banking Operational Risk Management Studies
3.3. Step 3—A Systematic Literature Review on the Use of System Dynamics in Banking Operational Risk Management
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
5.1. Contributions
5.2. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ackoff, Russell L. 1994. Systems thinking and thinking systems. System Dynamics Review 10: 175–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, Anukrati, Michelle Boese, and Saonee Sarker. 2010. A review of the HCI literature in IS: The missing links of computer-mediated communication, culture, and interaction. Paper presented at the Americas Conference on Information Systems (AMCIS 2010) Proceedings, Lima, Peru, August 12–15. Paper 523. [Google Scholar]
- Aldasoro, Iñaki, Jon Frost, Leonardo Gambacorta, and David Whyte. 2021. COVID-19 and Cyber Risk in the Financial Sector. BIS Bulletin No. 37. Basel: Bank for International Settlements. Available online: https://www.bis.org/publ/bisbull37.pdf (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Aldasoro, Iñaki, Leonardo Gambacorta, Paolo Giudici, and Thomas Leach. 2020. Operational and Cyber Risks in the Financial Sector. BIS Working Paper No. 840. Basel: Bank for International Settlements. Available online: https://www.bis.org/publ/work840.pdf (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Aldasoro, Inaki, Leonardo Gambacorta, Paolo Giudici, and Thomas Leach. 2022. The drivers of cyber risk. Journal of Financial Stability 60: 100989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, David F., and George P. Richardson. 1997. Scripts for group model building. System Dynamics Review: The Journal of the System Dynamics Society 13: 107–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, Massimo, and Corrado Cuccurullo. 2017. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics 11: 959–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, Simon. 2022. Fundamentals of Operational Risk Management: Understanding and Implementing Effective Tools, Policies and Frameworks. New York: Kogan Page. [Google Scholar]
- Banomyong, Ruth, Paitoon Varadejsatitwong, and Richard Oloruntoba. 2019. A systematic review of humanitarian operations, humanitarian logistics and humanitarian supply chain performance literature 2005 to 2016. Annals of Operations Research 283: 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barki, Henri, Suzanne Rivard, and Jean Talbot. 1988. An information systems keyword classification scheme. MIS Quarterly 12: 299–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basel Committee on Banking Supervision. 2003. Sound Practices for the Management and Supervision of Operational Risk. Basel: Bank for International Settlements. Available online: https://www.bis.org/publ/bcbs96.pdf (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Basel Committee on Banking Supervision. 2011a. Principles for the Sound Management of Operational Risk. Basel: Bank for International Settlements. Available online: http://www.bis.org/publ/bcbs195.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2022).
- Basel Committee on Banking Supervision. 2011b. Operational Risk—Supervisory Guidelines for the Advanced Measurement Approaches. Basel: Bank for International Settlements. Available online: https://www.bis.org/publ/bcbs196.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2022).
- Basel Committee on Banking Supervision. 2017. Basel III: Finalising Post-Crisis Reforms. Basel: Bank for International Settlements. Available online: https://www.bis.org/bcbs/publ/d424.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2022).
- Basel Committee on Banking Supervision. 2019. The Basel Framework. Basel: Bank for International Settlements. Available online: https://www.bis.org/basel_framework/ (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Basel Committee on Banking Supervision. 2021a. Revisions to the Principles for the Sound Management of Operational Risk. Basel: Bank for International Settlements. Available online: https://www.bis.org/bcbs/publ/d515.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2022).
- Basel Committee on Banking Supervision. 2021b. Climate-Related Risk Drivers and Their Transmission Channels. Basel: Bank for International Settlements. Available online: https://www.bis.org/bcbs/publ/d517.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2022).
- Besiou, Maria, and Luk N. Van Wassenhove. 2021. System dynamics for humanitarian operations revisited. Journal of Humanitarian Logistics and Supply Chain Management 11: 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, A. S. 1995. Collapse of Barings Bank: Case of Market Failure. Economic and Political Weekly 30: 658–62. [Google Scholar]
- Biener, Christian, Martin Eling, and Jan Hendrik Wirfs. 2015. Insurability of cyber risk: An empirical analysis. The Geneva Papers on Risk and Insurance-Issues and Practice 40: 131–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boell, Sebastian K., and Dubravka Cecez-Kecmanovic. 2015. On being ‘systematic’ in literature reviews in IS. Journal of Information Technology 30: 161–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brailsford, Sally C., and Nicola A. Hilton. 2001. A comparison of discrete event simulation and system dynamics for modelling health care systems. In Planning for the Future: Health Service Quality and Emergency Accessibility. Operational Research Applied to Health Services (ORAHS). Glasgow: Glasgow Caledonian University, pp. 18–39. [Google Scholar]
- Brechmann, Eike, Claudia Czado, and Sandra Paterlini. 2014. Flexible dependence modeling of operational risk losses and its impact on total capital requirements. Journal of Banking and Finance 40: 271–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carfora, Maria, Fabio Martinelli, Franceso Mercaldo, and Albina Orlando. 2019. Cyber risk management: An actuarial point of view. Journal of Operational Risk 14: 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetorelli, Nicola, James McAndrews, and James Traina. 2014. Evolution in bank complexity. Federal Reserve Bank of New York Economic Policy Review 20: 85–106. [Google Scholar]
- Chabrow, Eric. 2012. 10 Concerns When Buying Cyber Insurance. Information Security Media Group. June 14. Available online: https://www.bankinfosecurity.com/10-concerns-when-buying-cyber-insurance-a-4859 (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Chapelle, Ariane, Yves Crama, Georges Hübner, and Jean-Philippe Peters. 2008. Practical methods for measuring and managing operational risk in the financial sector: A clinical study. Journal of Banking and Finance 32: 1049–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernobai, Anna, and Yildiray Yildirim. 2008. The dynamics of operational loss clustering. Journal of Banking and Finance 32: 2655–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowell, Robert G., Richard J. Verrall, and Yoon Khuen Yoon. 2007. Modeling operational risk with Bayesian networks. Journal of Risk and Insurance 74: 795–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, Geoff. 2000. Qualitative and quantitative modelling in system dynamics: Some research questions. System Dynamics Review 16: 225–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, Geoff. 2001. Rejoinder to Homer and Oliva. System Dynamics Review 17: 357–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, J. David, Christopher M. Lewis, and Ran Wei. 2006. The market value impact of operational loss events for US banks and insurers. Journal of Banking & Finance 30: 2605–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Valle, Luciana, and Paolo Giudici. 2008. A Bayesian approach to estimate the marginal loss distributions in operational risk management. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis 52: 3107–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fontnouvelle, Patrick, Virginia Dejesus-Rueff, John S. Jordan, and Eric S. Rosengren. 2006. Capital and risk: New evidence on implications of large operational losses. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 38: 1819–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloitte Development LLC. 2018. How Technology Is Shaping the Future of Operational Risk Management. The Wall Street Journal. June 5. Available online: https://deloitte.wsj.com/articles/how-technology-is-shaping-the-future-of-operational-risk-management-1528171333 (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Donthu, Naveen, Satish Kumar, Debmalya Mukherjee, Nitesh Pandey, and Weng Marc Lim. 2021. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research 133: 285–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durach, Christian F., Andreas Wieland, and Jose A. D. Machuca. 2015. Antecedents and dimensions of supply chain robustness: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management 45: 118–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eceiza, Joseba, Ida Kristensen, Dmitry Krivin, Hamid Samandari, and Olivia White. 2020. The Future of Operational-Risk Management in Financial Services. Brussels: McKinsey & Company. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/risk-and-resilience/our-insights/the-future-of-operational-risk-management-in-financial-services (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Eling, Martin, and Werner Schnell. 2016. What do we know about cyber risk and cyber risk insurance? The Journal of Risk Finance 17: 474–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsevier. n.d. Content Coverage. Scopus. Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/solutions/scopus/how-scopus-works/content?dgcid=RN_AGCM_Sourced_300005030 (accessed on 14 March 2022).
- Fantazzini, Dean, Luciana Dalla Valle, and Paolo Giudici. 2008. Copulae and operational risks. International Journal of Risk Assessment and Management 9: 238–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, Muhammad, and Hassan Mobeen Alam. 2019. Operational Risk Management in Islamic Banking: A System Thinking Approach. Paradigms 13: 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, Robert Louis. 2010. The relationship of ‘systems thinking’ to action research. Systemic Practice and Action Research 23: 269–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frachot, Antoine, and Thierry Roncalli. 2007. Mixing Internal and External Data for Managing Operational Risk. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=1032525 (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Galvan, Jose L., and Melisa C. Galvan. 2017. Writing Literature Reviews: A Guide for Students of the Social and Behavioral Sciences, 7th ed. New York: Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, Philip, and Gert Jan Sikking. 2010. Risks in running the business. In Risk Management in Financial Institutions: Formulating Value Propositions. Edited by Jürgen Hendrikus Marinus Grinsven. Amsterdam: IOS Press BV, pp. 81–133. [Google Scholar]
- Girling, Philippa X. 2022. Operational Risk Management: A Complete Guide for Banking and Fintech. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Giudici, Paolo, and Annalisa Bilotta. 2004. Modelling operational losses: A Bayesian approach. Quality and Reliability Engineering International 20: 407–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodhart, Charles. 2001. Operational Risk. No. sp131. Financial Markets Group. London: London School of Economics. [Google Scholar]
- Green, Bo. 2000. Cross the Borders. In Risk Behavior and Risk Management in Business Life. Edited by Bo Green. Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimwade, Michael. 2022. Ten Laws of Operational Risk. West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, Hossein, Stephan Unger, and Christina Beneki. 2020. Big Data and Actuarial Science. Big Data and Cognitive Computing 4: 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, Richard J. 2002. The basel 2 approach to bank operational risk: Regulation on the wrong track. Journal of Risk Finance 4: 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Homer, Jack, and Rogelio Oliva. 2001. Maps and models in system dynamics: A response to Coyle. System Dynamics Review 17: 347–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homolya, Dániel. 2009. The impact of the capital requirements for operational risk in the Hungarian banking system. MNB Bulletin (Discontinued) 4: 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, Jan-Alexander, and Daniele Funaro. 2018. How Banks Can Manage Operational Risk. Boston: Bain & Company. Available online: https://www.bain.com/insights/how-banks-can-manage-operational-risk/%20accessed%20October%2028,%202021 (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Jorion, Philippe. 2007. Value-at-Risk: The New Benchmark for Managing Financial Risk, 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, Gurpreet, and Renuka Sharma. 2017. Financial Risk Assessment and Management by Banks: Evidences from Past Research. International Journal of Applied Business and Economic Research 15: 265–82. [Google Scholar]
- Kopp, Emanuel, Lincoln Kaffenberger, and Christopher Wilson. 2017. Cyber Risk, Market Failures, and Financial Stability. IMF Working Paper No. WP/17/185. Washington, DC: International Monetary Fund. Available online: https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WP/Issues/2017/08/07/Cyber-Risk-Market-Failures-and-Financial-Stability-45104 (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Laot, Maxime. 2017. Managing operational risk in the banking business—An internal auditor point of view. In Extreme Events in Finance: A Handbook of Extreme Value Theory and Its Applications. Edited by François Longin. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, pp. 555–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, Martin, Suneel Sharma, and Koilakuntla Maddulety. 2019. Machine learning in banking risk management: A literature review. Risks 7: 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, Yair, and Timothy J. Ellis. 2006. A systems approach to conduct an effective literature review in support of information systems research. Informing Science 9: 181–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Jianping, Xiaoqian Zhu, Yongjia Xie, Jianming Chen, Lijun Gao, Jichuang Feng, and Wujiang Shi. 2014. The mutual-information-based variance-covariance approach: An application to operational risk aggregation in Chinese banking. Journal of Operational Risk 9: 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, Donella H. 2008. Thinking in Systems: A Primer. London: Earthscan,. [Google Scholar]
- Mizgier, Kamil J., Manpreet Hora, Stephan M. Wagner, and Matthias P. Jüttner. 2015. Managing operational disruptions through capital adequacy and process improvement. European Journal of Operational Research 245: 320–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosa, Imad A. 2007. Operational risk: A survey. Financial Markets, Institutions and Instruments 16: 167–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Operational Riskdata eXchange Association (ORX). 2019. Operational Risk Reporting Standards (ORSS). Available online: https://managingrisktogether.orx.org/standards (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Operational Riskdata eXchange Association (ORX). 2021. Annual Banking Loss Report Executive Summary. August 9. Available online: https://managingrisktogether.orx.org/loss-data/annual-banking-loss-report (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Pakhchanyan, Suren. 2016. Operational Risk Management in Financial Institutions: A Literature Review. International Journal of Financial Studies 4: 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, Michael. 2005. The invention of operational risk. Review of International Political Economy 12: 577–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ProQuest LLC. n.d. ProQuest: A Global Leader in EdTech. Proquest. Available online: https://about.proquest.com/en/ (accessed on 14 March 2022).
- Ramanujam, Rangaraj, and Paul S. Goodman. 2003. Latent errors and adverse organizational consequences: A conceptualization. Journal of Organizational Behavior 24: 815–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, Justus. 2009. A guide to writing the dissertation literature review. Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation 14: 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, Martin, and Sue Holwell. 2010. Introducing Systems Approaches. In Systems Approaches to Making Change: A Practical Guide. Edited by Martin Reynolds and Sue Holwell. London: Springer, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Rowley, Jennifer, and Frances Slack. 2004. Conducting a literature review. Management Research News 27: 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, Peter, Gordon Liao, and Yueran Ma. 2018. Rethinking operational risk capital requirements. Journal of Financial Regulation 4: 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute Inc. 2015. SAS® OpRisk Global Data. A Comprehensive Database of Operational Loss Information. Available online: https://www.sas.com/content/dam/SAS/en_us/doc/productbrief/sas-oprisk-global-data-101187.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2022).
- Senge, Peter M. 1990. The Fifth Discipline: The Art and Practice of the Learning Organization. New York: Doubleday. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi, Sifatullah, and Aditi Sharan. 2015. Keyword and keyphrase extraction techniques: A literature review. International Journal of Computer Applications 109: 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, Hannah. 2019. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research 104: 333–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterman, John. 2000. Business Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World. Boston: McGraw Hill. [Google Scholar]
- Tranfield, David, David Denyer, and Palminder Smart. 2003. Towards a Methodology for Developing Evidence-Informed Management Knowledge by Means of Systematic Review. British Journal of Management 14: 207–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, Diane. 2005. Organizational rituals of risk and error. In Organizational Encounters with Risk. Edited by Bridget Hutter and Michael Power. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 33–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vennix, Jac A. M. 1996. Group Model Building: Facilitating Team Learning Using System Dynamics. West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons Ltd. [Google Scholar]
- von Bertalanffy, Ludwig. 1968. General System Theory: Foundations, Development, Applications. New York: George Braziller, pp. 30–53. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, Jane, and Richard T. Watson. 2002. Analyzing the Past to Prepare for the Future: Writing a Literature Review. MIS Quarterly 26: Xiii–XXiii. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/4132319 (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Wei, Lu, Jianping Li, and Xiaoqian Zhu. 2018. Operational Loss Data Collection: A Literature Review. Annals of Data Science 5: 313–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, Josephine. 2014. Models for cybersecurity incident information sharing and reporting policies. TPRC 43: The 43rd Research Conference on Communication, Information and Internet Policy Paper. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2587398 (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Wolstenholme, Eric F. 1999. Qualitative vs. quantitative modelling: The evolving balance. Journal of the Operational Research Society 50: 422–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Yu, and Maria Watson. 2019. Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. Journal of Planning Education and Research 39: 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Huan, and Richard Wood. 2017. A structural model for estimating losses associated with the mis-selling of retail banking products. Journal of Operational Risk 12: 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author (Year) | Title | Scope | Number of Reviewed Papers | Database | Identified Gaps |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pakhchanyan (2016) | Operational Risk Management in Financial Institutions: A Literature Review | Academic papers from all peer-reviewed scientific journals, irrespective of their rankings, on operational risk in financial institutions, covering the period from 1998 to 2014 | 279 | Electronic databases, such as EBSCO and Google Scholar, and own collection specified as “articles referred to in previously identified studies and separately screen for relevance all the selected articles” | A lack of research on the effect of operational loss events on the firm’s rivals and large shareholders Concern over a reliability in the findings of empirical studies using internal database identified as scarce, inaccessible, and biased towards high-frequency and low-severity events |
| Kaur and Sharma (2017) | Financial Risk Assessment and Management by Banks: Evidences from Past Research | Published and unpublished articles related to risk and distress in banks, covering the period from 2000 to 2016 | 50 | Not mentioned | Requiring both the analysis of all parameters, including micro and macro factors, and alternative techniques for risk management scores |
| Wei et al. (2018) | Operational Loss Data Collection: A Literature Review | Academic papers on the topic of operational risk in banks, covering the period from 2002 to 2017 | 301 | Web of Science Core Collection platform and own collection specified as “relevant articles referred to in previously identified studies” | Concern over a reliability in the estimation of operational risk from the Standardized Approach that accounts only the internal database identified as insufficient and biased towards high-frequency and low-severity events Business environment and internal control factors (BEICFs), which provide “forward-looking assessments” of key business environment and internal control factors, such as Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) from Risk Control Self Assessments (RCSAs), not used as a primary source of data for operational risk capital calculation |
| Leo et al. (2019) | Machine Learning in Banking Risk Management: A Literature Review | Papers, including conference papers, journal articles, and selected theses (postgraduate or doctoral), that study the application of machine-learning in bank risk management, after 2007 | 50 | Google Scholar, SSRN, and ProQuest databases | Limited application of vast amounts of operational data internally available to a bank by existing researches |
| Combined Keywords | Number of Articles from Scopus | Combined Keywords | Number of Articles from Scopus |
|---|---|---|---|
| “operational risk”, “viable systems model”, and “bank” | - | “operational risk”, “viable systems model”, and “financial institution” | - |
| “operational risk”, “system dynamics”, and “bank” | 1 | “operational risk”, “system dynamics”, and “financial institution” | - |
| “operational risk”, “strategic options development and analysis”, and “bank” | - | “operational risk”, “strategic options development and analysis”, and “financial institution” | - |
| “operational risk”, “soft systems methodology”, and “bank” | - | “operational risk”, “soft systems methodology”, and “financial institution” | - |
| “operational risk”, “critical systems heuristics”, and “bank” | - | “operational risk”, “critical systems heuristics”, and “financial institution” | - |
| Keywords and Equivalent Keywords | Number of Articles | |
|---|---|---|
| Scopus | ProQuest | |
| Operational risk | 4037 | 6270 |
| Bank or financial institution | 7 | 135 |
| System dynamics | 1 | 55 |
| Author (Year) | Title | Objectives and Scope of SD Application | Source | Assessed Gaps |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ramanujam and Goodman (2003) | Latent errors and adverse organizational consequences: A conceptualization | The study developed the concept of latent errors and used SD conceptual model to:
| ProQuest | The effects of different types of latent errors that are execution, monitoring, and infrastructure need to be quantified in order to gain important insight into the dynamics of the system. |
| Yan and Wood (2017) | A structural model for estimating losses associated with the mis-selling of retail banking products | The study developed a structural model based on risk drivers and key dynamics, including resourcing cost and penalty, to estimate operational losses associated with the mis-selling of retail banking products. The frequency distribution is constructed using a Bayesian network. The severity distribution is developed using SD. Operational loss data, specifically to the mis-selling scenario category on the retail banking business line from Western Europe and North America, were collected from Operational Risk eXchange database, covering period from H2 2010 to H2 2014. | Scopus | SD is not appropriate for this study for two main reasons.
|
| Farhan and Alam (2019) | Operational Risk Management in Islamic Banking; a System Thinking Approach | The study developed a causal loop diagram to understand the interrelationships between various characteristics of operational risk and its management. The qualitative model was developed from the researchers’ knowledge and understanding through literature review and refined based on the semi-structured interviews with risk managers of sampling Islamic and conventional banks. | ProQuest | The model needs to be tested in order to uncover the flaws in the model. Impacts of variables and their interactions in the model also need to be quantified. |
| Author (Year) | Conceptual Model | Causal Loop Diagram | Simulation Model | Real Data | Hypothetical Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ramanujam and Goodman (2003) | X | X | X | ||
| Yan and Wood (2017) | X | X | X | X | |
| Farhan and Alam (2019) | X | X | X |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiravichai, A.; Banomyong, R. A Proposed Methodology for Literature Review on Operational Risk Management in Banks. Risks 2022, 10, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks10050108
Jiravichai A, Banomyong R. A Proposed Methodology for Literature Review on Operational Risk Management in Banks. Risks. 2022; 10(5):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks10050108
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiravichai, Ajjima, and Ruth Banomyong. 2022. "A Proposed Methodology for Literature Review on Operational Risk Management in Banks" Risks 10, no. 5: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks10050108
APA StyleJiravichai, A., & Banomyong, R. (2022). A Proposed Methodology for Literature Review on Operational Risk Management in Banks. Risks, 10(5), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks10050108






