Postoperative Urinary Retention after Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baldini, G.; Bagry, H.; Aprikian, A.; Carli, F.; Warner, D.S.; Warner, M.A. Postoperative urinary retention: Anesthetic and perioperative considerations. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 2009, 110, 1139–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooton, T.M.; Bradley, S.F.; Cardenas, D.D.; Colgan, R.; Geerlings, S.E.; Rice, J.C.; Saint, S.; Schaeffer, A.J.; Tambayh, P.A.; Tenke, P.; et al. Diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of catheter-aassociated urinary tract infection in adults: 2009 international clinical practice guidelines from the infectious diseases society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 625–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulis, N.M.; Mian, F.S.; Rodriguez, D.; Cho, E.; Hoff, J.T. Urinary retention following routine neurosurgical spine procedures. Surg. Neurol. 2001, 55, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carsi, B.; Gould, A.; Clarke, N.M.P. Bladder control increases the incidence of urinary retention after epidural analgesia after paediatric orthopaedic surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 109, 294–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.K.; Auerbach, A.D.; Aaronson, D.S. National incidence and outcomes of postoperative urinary retention in the Surgical Care Improvement Project. Am. J. Surg. 2012, 204, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Awad, I. Maintaining micturition in the perioperative period: Strategies to avoid urinary retention. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2013, 26, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, C.V.; Umscheid, C.A.; Agarwal, R.K.; Kuntz, G.; Pegues, D.A.; Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Guideline for Prevention of Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections 2009. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2010, 31, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Muhsin, H.M.; Jakob, N.; Cha, S.; Zhang, N.; Schwartz, A.; Navaratnam, A.; Khan, A.; Humphreys, M. Incidence, Outcomes, and Prediction of Postoperative Urinary Retention after a Nonurologic Procedure. JAAOS Glob. Res. Rev. 2020, 4, e19.00149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrah, D.M.; Griebling, T.L.; Silverstein, J.H. Postoperative Urinary Retention. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2009, 27, 465–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balderi, T.; Mistraletti, G.; D’Angelo, E.; Carli, F. Incidence of postoperative urinary retention (POUR) after joint arthroplasty and management using ultrasound-guided bladder catheterization. Minerva Anestesiol. 2011, 77, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Hollman, F.; Wolterbeek, N.; Veen, R. Risk factors for postoperative urinary retention in men undergoing total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics 2015, 38, e507–e511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrie, C.M.; Ong, A.C.; Hernandez, V.H.; Rosas, S.; Post, Z.D.; Orozco, F.R. Incidence and Risk Factors for Postoperative Urinary Retention in Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Under Spinal Anesthesia. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 3748–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, K.H.; Lee, K.M.; Chung, C.Y.; Kwon, S.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Ban, Y.S.; Park, M.S. What are the risk factors associated with urinary retention after orthopaedic surgery? Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 613216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjerregaard, L.S.; Bogø, S.; Raaschou, S.; Troldborg, C.; Hornum, U.; Poulsen, A.M.; Bagi, P.; Kehlet, H. Incidence of and risk factors for postoperative urinary retention in fast-track hip and knee arthroplasty: A prospective, observational study. Acta Orthop. 2015, 86, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.; Karthikeyan, S.; Wyse, M.; Foguet, P. The incidence of postoperative urinary retention in patients undergoing elective hip and knee arthroplasty. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2014, 96, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kort, N.P.; Bemelmans, Y.; Vos, R.; Schotanus, M.G.M. Low incidence of postoperative urinary retention with the use of a nurse-led bladder scan protocol after hip and knee arthroplasty: A retrospective cohort study. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2018, 28, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherburne, E.; Sawin, K. Investigating time to void after lower-extremity orthopedic surgery in a pediatric population. J. Spéc. Pediatr. Nurs. 2008, 13, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskinen, H.; Helenius, L.; Pajulo, O.; Helenius, I.J. Postoperative urinary retention or difficulties to empty the bladder in young patients undergoing posterior spinal fusion for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 53, 1542–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenn, B.R.; Brislin, R.P.; Rose, J.B. Epidural analgesia in children with cerebral palsy. Can. J. Anaesth. 1998, 45, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, E.K.; Reilly, A.F.; Fisher, B.T.; Fitzgerald, J.; Li, Y.; Seif, A.E.; Huang, Y.-S.; Bagatell, R.; Aplenc, R. Association of weekend admission with hospital length of stay, time to chemotherapy, and risk for respiratory failure in pediatric patients with newly diagnosed leukemia at freestanding US children’s hospitals. JAMA Pediatr. 2014, 168, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Children’s Hospital Association. PHIS. Available online: https://www.childrenshospitals.org/phis (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Children’s Hospital Association. Flag Code Lists-FY 2013. Available online: https://www.childrenshospitals.org/~/media/Files/Groups/PHIS/Reference%20Resources/Data%20Content/Other%20Materials/FlagsInfection%20Med%20Comp%20Surg%20Comp%20Current%20List.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Murphy, K.P.; Boutin, S.A.; Ide, K.R. Cerebral palsy, neurogenic bladder, and outcomes of lifetime care. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2012, 54, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, N.; Akkoç, Y.; Ersöz, M.; Gündüz, B.; Erhan, B.; Yesil, H.; Bardak, A.N.; Ozdolap, S.; Tunç, H.; Koklu, K.; et al. Cross-sectional study of urinary problems in adults with cerebral palsy: Awareness and impact on the quality of life. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciniak, C.; O’Shea, S.A.; Lee, J.; Jesselson, M.; Sheehan, D.; Beltran, E.; Gaebler-Spira, D. Urinary Incontinence in Adults with Cerebral Palsy: Prevalence, Type, and Effects on Participation. PM R 2014, 6, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaman, M.I.; Kaya, C.; Caskurlu, T.; Guney, S.; Ergenekon, E. Urodynamic findings in children with cerebral palsy. Int. J. Urol. 2005, 12, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamienski, M.C. Pediatric Femur Fractures. Orthop. Nurs. 2020, 39, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagala, N.N.; Marasigan, J.A.M.; Mian, H.M.; Schwend, R.M. Operative time in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis surgery: A need for a standard definition. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2020, 30, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, T.A.; van Roon, E.N.; Rosier, P.F.W.M.; Kalkman, C.J.; Veeger, N. Postoperative urinary retention: Risk factors, bladder filling rate and time to catheterization: An observational study as part of a randomized controlled trial. Perioper. Med. 2021, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, D.C.; Landrigan, C.P.; Toomey, S.L.; Westfall, M.Y.; Liu, S.; Parry, G.; Coopersmith, A.S.; Schuster, M.A.; for the GAPPS Study Group. Racial, Ethnic, and Socioeconomic Disparities in Patient Safety Events for Hospitalized Children. Hosp. Pediatr. 2019, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KFF. Hospital Adjusted Expenses per Inpatient Day by Ownership. Available online: https://www.kff.org/health-costs/state-indicator/expenses-per-inpatient-day-by-ownership/ (accessed on 15 September 2020).

| Risk Factor | Postoperative Urinary Retention | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No (n = 231,659) | Yes (n = 892) | ||
| Male | 0.22031 | ||
| No | 102,891 (44.4%) | 378 (42.4%) | |
| Yes | 128,742 (55.6%) | 514 (57.6%) | |
| Race | <0.0001 | ||
| Asian | 5550 (2.4%) | 17 (1.9%) | |
| Black | 33,246 (14.4%) | 108 (12.1%) | |
| Native American | 1365 (0.6%) | 12 (1.3%) | |
| White | 144,809 (62.5%) | 617 (69.2%) | |
| Other | 46,689 (20.2%) | 138 (15.5%) | |
| White | <0.0001 | ||
| No | 86,850 (37.5%) | 275 (30.8%) | |
| Yes | 144,809 (62.5%) | 617 (69.2%) | |
| Ethnicity | 0.0001 | ||
| Hispanic or Latino | 45,307 (19.6%) | 133 (14.9%) | |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 167,053 (72.1%) | 700 (78.5%) | |
| Unknown | 19,299 (8.3%) | 59 (6.6%) | |
| Age at Admission (years) | <0.0001 | ||
| N | 23,1659 | 892 | |
| Mean (SD) | 9.2 (5.0) | 11.9 (4.3) | |
| Range | (1.0–18.0) | (1.0–18.0) | |
| Primary Source of Insurance | 0.2510 | ||
| Government | 158,404 (68.4%) | 590 (66.1%) | |
| Private | 69,325 (29.9%) | 289 (32.4%) | |
| Other | 3930 (1.7%) | 13 (1.5%) | |
| Median Household Income ($) | 0.0003 | ||
| N | 231,659 | 892 | |
| Mean (SD) | 47,766.8 (18,851.9) | 49,864.4 (19,366.6) | |
| Range | (6320.0–196,032.0) | (6320.0–139,915.0) | |
| Surgical Location | <0.0001 | ||
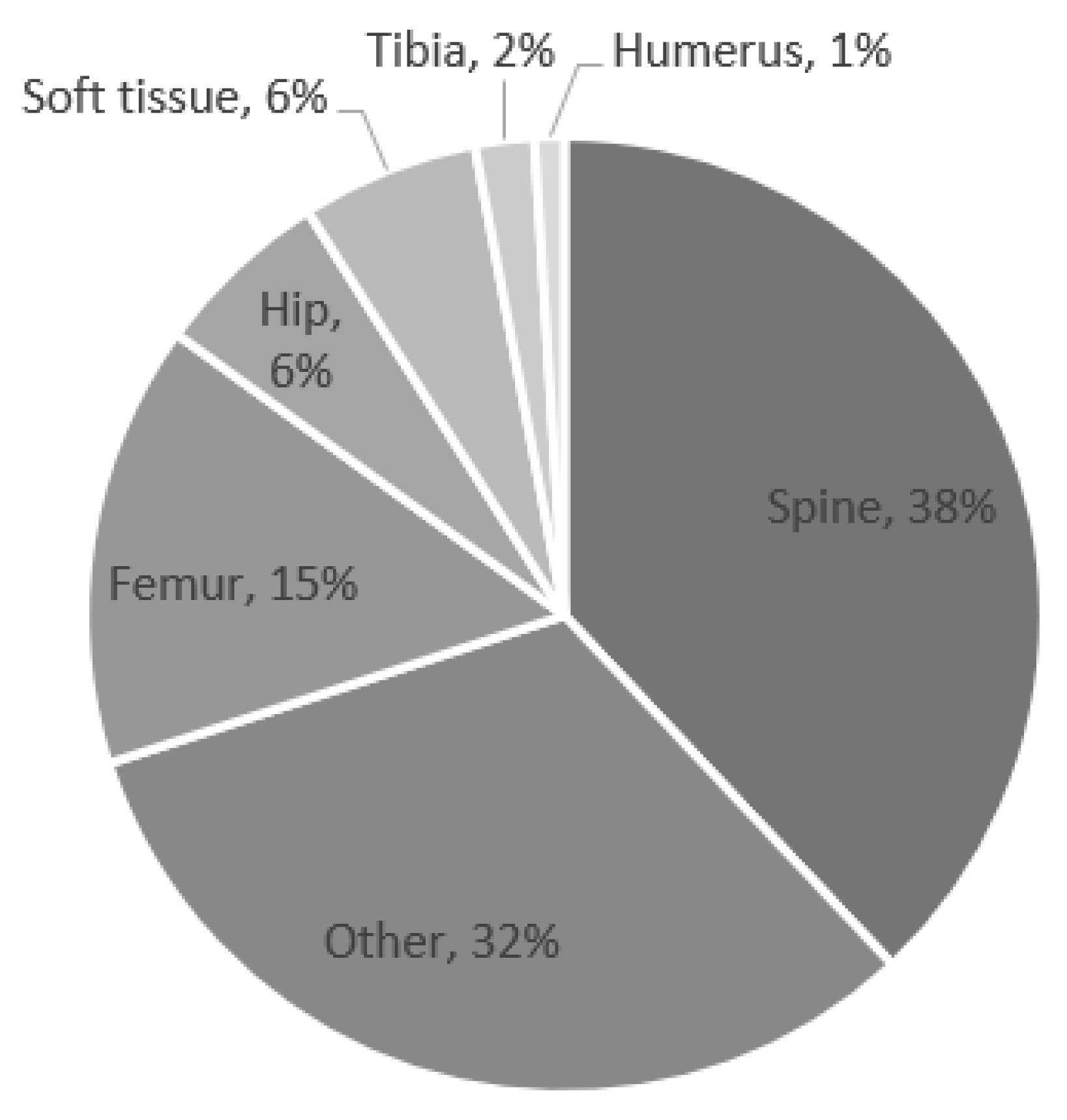
| Spine | 11,601 (5.0%) | 340 (38.1%) | |
| Femur | 13,316 (5.7%) | 137 (15.4%) | |
| Hip | 3363 (1.5%) | 58 (6.5%) | |
| Tibia | 5834 (2.5%) | 16 (1.8%) | |
| Humerus | 6781 (2.9%) | 9 (1.0%) | |
| Soft tissue | 12,035 (5.2%) | 50 (5.6%) | |
| Other | 178,729 (77.2%) | 282 (31.6%) | |
| Medical Complication Flag | <0.0001 | ||
| No | 231,490 (99.9%) | 884 (99.1%) | |
| Yes | 169 (0.1%) | 8 (0.9%) | |
| Surgical Complication Flag | <0.0001 | ||
| No | 226,091 (97.6%) | 601 (67.4%) | |
| Yes | 5568 (2.4%) | 291 (32.6%) | |
| Infection Flag | <0.0001 | ||
| No | 222,328 (96.0%) | 751 (84.2%) | |
| Yes | 9331 (4.0%) | 141 (15.8%) | |
| Complex Chronic Condition (CCC) | <0.0001 | ||
| Neuromuscular CCC | 13,618 (5.9%) | 333 (37.3%) | |
| Non-neuromuscular CCC | 23,033 (9.9%) | 325 (36.4%) | |
| No CCC | 195,008 (84.2%) | 234 (26.2%) | |
| Cerebral Palsy | <0.0001 | ||
| No | 223,022 (96.3%) | 671 (75.2%) | |
| Yes | 8637 (3.7%) | 221 (24.8%) | |
| Length of Stay (days) | <0.0001 | ||
| N | 231,659 | 892 | |
| Mean (SD) | 1.7 (2.6) | 7.8 (10.4) | |
| Range | (1.0–259.0) | (1.0–128.0) | |
| Risk Factor | Neurological and Muscular | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | ||
| Cerebral Palsy | |||
| Yes | 66.6% | 0.0% | 24.8% |
| No | 33.4% | 100.0% | 75.2% |
| Spina Bifida | |||
| Yes | 5.5% | 0.2% | 2.1% |
| No | 94.6% | 99.8% | 97.9% |
| Muscular Dystrophy | |||
| Yes | 7.2% | 0.0% | 2.7% |
| No | 92.8% | 100.0% | 97.3% |
| Risk Factor | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Male vs. Female | 1.09 (0.95–1.24) | 0.2204 |
| Race | ||
| Asian vs. White | 0.72 (0.44–1.16) | 0.1801 |
| Black vs. White | 0.76 (0.62–0.94) | 0.0094 |
| Native American vs. White | 2.06 (1.16–3.66) | 0.0134 |
| Other vs. White | 0.69 (0.58–0.83) | 0.0001 |
| White vs. Not | 1.35 (1.17–1.55) | <0.0001 |
| Age at Admission (years) | 1.12 (1.11–1.14) | <0.0001 |
| Primary Insurance | ||
| Government vs. Other | 1.13 (0.65–1.95) | 0.6728 |
| Private vs. Other | 1.26 (0.72–2.2) | 0.4155 |
| Cerebral Palsy vs. Not | 8.5 (7.29–9.91) | <0.0001 |
| Surgical Complication Flag vs. Not | 19.66 (17.05–22.67) | <0.0001 |
| Medical Complication Flag vs. Not | 12.4 (6.08–25.27) | <0.0001 |
| Infection Flag vs. Not | 4.47 (3.73–5.36) | <0.0001 |
| Complex Chronic Condition (CCC) | ||
| Neuromuscular CCC vs. No CCC | 20.38 (17.23–24.11) | <0.0001 |
| Non-Neuromuscular CCC vs. No CCC | 11.76 (9.93–13.92) | <0.0001 |
| Risk Factor | OR (95% CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Male vs. Female | 1.46 (1.27–1.68) | <0.0001 |
| White vs. Not | 1.26 (1.09–1.45) | 0.0018 |
| Neuromuscular CCC vs. NO CCC | 11.54 (9.6–13.88) | <0.0001 |
| Non-Neuromuscular CCC vs. NO CCC | 5.07 (4.11–6.25) | <0.0001 |
| Spine vs. other location | 3.98 (3.28–4.82) | <0.0001 |
| Femur/Hip vs. other location | 3.63 (3.03–4.36) | <0.0001 |
| Admit Age (years) | 1.06 (1.04–1.08) | <0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belthur, M.V.; Singleton, I.M.; Burns, J.D.; Temkit, M.H.; Sitzman, T.J. Postoperative Urinary Retention after Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery. Children 2022, 9, 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9101488
Belthur MV, Singleton IM, Burns JD, Temkit MH, Sitzman TJ. Postoperative Urinary Retention after Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery. Children. 2022; 9(10):1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9101488
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelthur, Mohan V., Ian M. Singleton, Jessica D. Burns, M’hamed H. Temkit, and Thomas J. Sitzman. 2022. "Postoperative Urinary Retention after Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery" Children 9, no. 10: 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9101488
APA StyleBelthur, M. V., Singleton, I. M., Burns, J. D., Temkit, M. H., & Sitzman, T. J. (2022). Postoperative Urinary Retention after Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery. Children, 9(10), 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9101488




