Delivery Room ST Segment Analysis to Predict Short Term Outcomes in Near-Term and Term Newborns
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Equipment and Data Collection
2.3. Processing and Interpretation of the ECG
2.4. Outcome Variables
2.5. Statistical Analyses
2.6. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
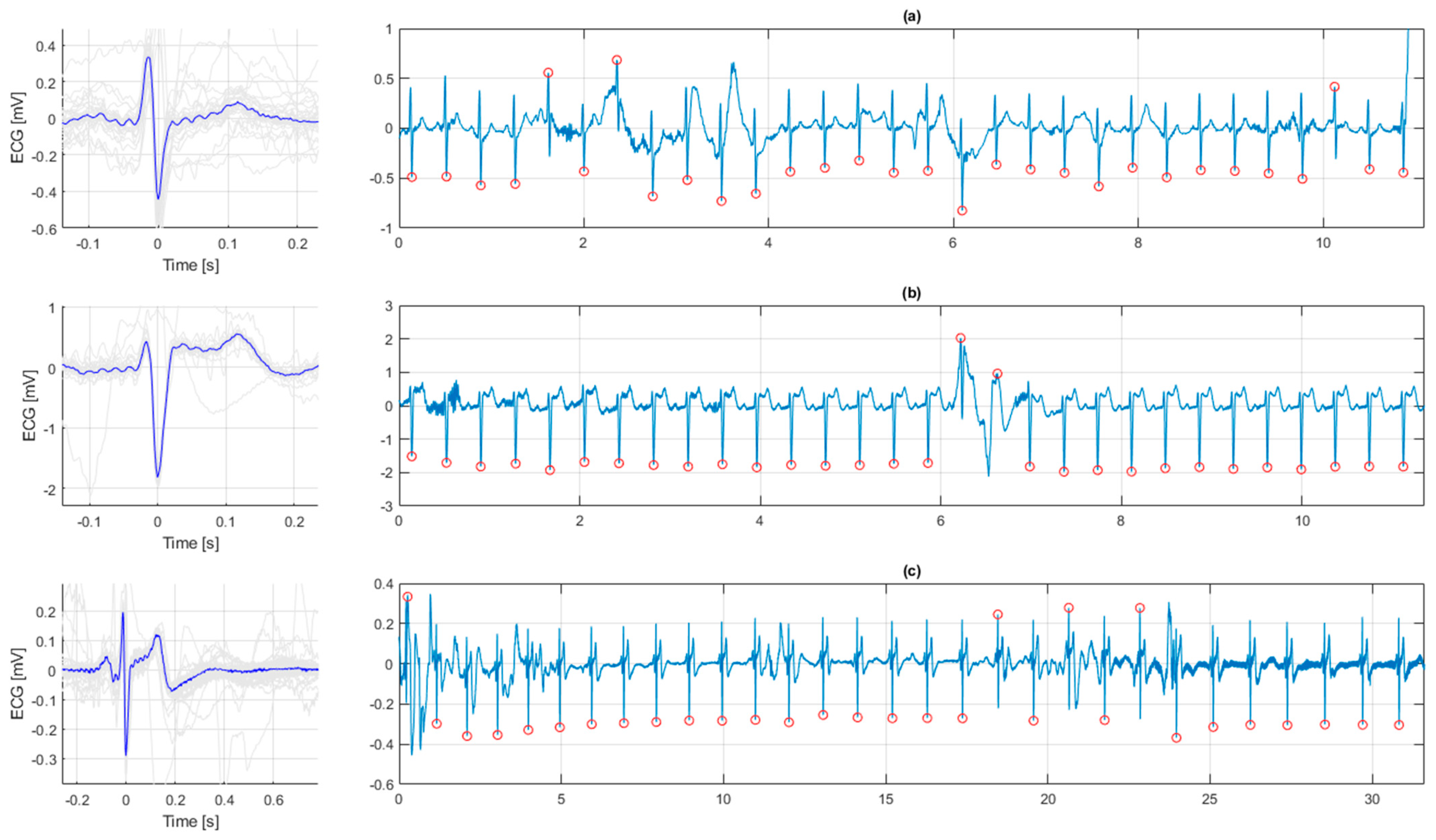
3.1. ECG in Healthy Newborn Infants
3.2. ECG in Resuscitated Newborn Infants
3.3. Association between ECG Morphology and Perinatal Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madar, J.; Roehr, C.C.; Ainsworth, S.; Ersdal, H.; Morley, C.; Rudiger, M.; Skare, C.; Szczapa, T.; Te Pas, A.; Trevisanuto, D.; et al. European Resuscitation Council Guidelines 2021: Newborn resuscitation and support of transition of infants at birth. Resuscitation 2021, 161, 291–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Ancel, A.; Garcia-Alix, A.; Gaya, F.; Cabanas, F.; Burgueros, M.; Quero, J. Multiple organ involvement in perinatal asphyxia. J. Pediatr. 1995, 127, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestaas, E.; Skranes, J.H.; Stoylen, A.; Brunvand, L.; Fugelseth, D. The myocardial function during and after whole-body therapeutic hypothermia for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, a cohort study. Early Hum. Dev. 2014, 90, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amer-Wahlin, I.; Marsal, K. ST analysis of fetal electrocardiography in labor. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011, 16, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neilson, J.P. Fetal electrocardiogram (ECG) for fetal monitoring during labour. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 21, CD000116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.R.; Panaitescu, A.M.; Pavel, B.; Zagrean, L.; Peltecu, G.; Zagrean, A.M. Getting an Early Start in Understanding Perinatal Asphyxia Impact on the Cardiovascular System. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, S.J.; Newland, P.; Yoxall, C.W.; Subhedar, N.V. Cardiac troponin T in cord blood. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2001, 84, F34–F37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Chakkarapani, E.; Stone, J.; Thoresen, M. Effect of cardiac compressions and hypothermia treatment on cardiac troponin I in newborns with perinatal asphyxia. Resuscitation 2013, 84, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katheria, A.; Rich, W.; Finer, N. Electrocardiogram provides a continuous heart rate faster than oximetry during neonatal resuscitation. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e1177–e1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Vonderen, J.J.; Hooper, S.B.; Kroese, J.K.; Roest, A.A.; Narayen, I.C.; van Zwet, E.W.; te Pas, A.B. Pulse oximetry measures a lower heart rate at birth compared with electrocardiography. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linde, J.E.; Schulz, J.; Perlman, J.M.; Øymar, K.; Francis, F.; Eilevstjønn, J.; Ersdal, H.L. Normal Newborn Heart Rate in the First Five Minutes of Life Assessed by Dry-Electrode Electrocardiography. Neonatology 2016, 110, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, J.E.; Eilevstjonn, J.; Oymar, K.; Ersdal, H.L. Feasibility of a prototype newborn resuscitation monitor to study transition at birth, measuring heart rate and ventilator parameters, an animal experimental study. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eilevstjonn, J.; Linde, J.E.; Blacy, L.; Kidanto, H.; Ersdal, H.L. Distribution of heart rate and responses to resuscitation among 1237 apnoeic newborns at birth. Resuscitation 2020, 152, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neoventa. Service Manual STAN S31 Fetal Heart Monitor. Mölndal, Sweden. Available online: https://www.neoventa.com/wp-content//uploads/filebase/Documents/10_PRD101004_44_R4B.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2021).
- Buendia-Fuentes, F.; Arnau-Vives, M.A.; Arnau-Vives, A.; Jimenez-Jimenez, Y.; Rueda-Soriano, J.; Zorio-Grima, E.; Osa-Saez, A.; Martinez-Dolz, L.V.; Almenar-Bonet, L.; Palencia-Perez, M.A. High-Bandpass Filters in Electrocardiography: Source of Error in the Interpretation of the ST Segment. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2012, 2012, 706217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linde, J.E.; Perlman, J.M.; Oymar, K.; Schulz, J.; Eilevstjonn, J.; Thallinger, M.; Kusulla, S.; Kidanto, H.L.; Ersdal, H.L. Predictors of 24-h outcome in newborns in need of positive pressure ventilation at birth. Resuscitation 2018, 129, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stordal, K.; Eilevstjonn, J.; Mduma, E.; Holte, K.; Thallinger, M.; Linde, J.; Mdoe, P.; Kidanto, H.; Ersdal, H.L. Increased perinatal survival and improved ventilation skills over a five-year period: An observational study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Guide for Implementation of Helping Babies Breathe (HBB). Healthy Newborn Network 2011. Available online: https://www.healthynewbornnetwork.org/resource/guide-for-implementation-of-helping-babies-breathe-hbb/ (accessed on 11 November 2021).
- Moshiro, R.; Perlman, J.; Kidanto, H.; Kvaløy, J.; Mdoe, P.; Ersdal, H. Predictors of death including quality of positive pressure ventilation during newborn resuscitation and the relationship to outcome at seven days in a rural Tanzanian hospital. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202641. [Google Scholar]
- Barberi, I.; Calabro, M.P.; Cordaro, S.; Gitto, E.; Sottile, A.; Prudente, D.; Bertuccio, G.; Consolo, S. Myocardial ischaemia in neonates with perinatal asphyxia. Electrocardiographic, echocardiographic and enzymatic correlations. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1999, 158, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedeikin, R.; Primhak, A.; Shennan, A.T.; Swyer, P.R.; Rowe, R.D. Serial electrocardiographic changes in healthy and stressed neonates. Arch. Dis. Child. 1983, 58, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinek, R.; Kahankova, R.; Martin, B.; Nedoma, J.; Fajkus, M. A novel modular fetal ECG STAN and HRV analysis: Towards robust hypoxia detection. Technol. Health Care. 2019, 27, 257–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, P.J.; Engelberts, D.; Finelli, M.; Adeli, K.; Kavanagh, B.P. Vasopressin improves survival compared with epinephrine in a neonatal piglet model of asphyxial cardiac arrest. Pediatr. Res. 2014, 75, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lelovas, P.P.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.G.; Xanthos, T.T. A comparative anatomic and physiologic overview of the porcine heart. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2014, 53, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Normal ECG (n = 142) | ST Elevation (n = 320) | Other ST-Segment Abnormalities (n = 32) | p-Value 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANTENATAL CHARACTERISTICS | ||||
| Obstructed labor * | 19 (13) | 34 (11) | 3 (9) | 0.65 |
| Vaginal head delivery | 73 (51) | 186 (58) | 11 (34) | 0.02 |
| Caesarean section | 63 (44) | 119 (37) | 20 (63) | 0.01 |
| Vaginal breech delivery | 4 (3) | 11 (3) | 1 (3) | 0.94 |
| Vacuum | 2 (1) | 4 (1) | 0 (0) | 0.80 |
| NEONATAL CHARACTERISTICS | ||||
| Gender (male) | 70 (49) | 207 (65) | 14 (44) | 0.002 |
| Birth weight (g) | 3155 (2750, 3500) | 3290 (2990, 3600) | 3110 (2943, 3415) | 0.06 |
| Apgar 1 min | 7 (5, 7) | 7 (5, 7) | 5 (3, 7) | 0.01 |
| Apgar 5 min | 10 (8, 10) | 10 (8, 10) | 9 (7, 10) | 0.09 |
| First heart rate [bpm] | 128 (76, 165) | 129 (74, 163) | 66 (53, 134) | <0.001 |
| Time from birth to ST analysis [s] | 120 (95, 151) | 116 (91, 142) | 107 (89, 135) | 0.21 |
| Heart rate during ST analysis [bpm] | 160 (139, 173) | 157 (137, 172) | 96 (56, 162) | <0.001 |
| Resuscitation and outcomes | ||||
| BMV duration (s) | 126 (68, 269) | 143 (63, 281) | 305 (117, 857) | 0.002 |
| Normal outcome | 83 (58) | 187 (58) | 11 (34) | 0.03 |
| Admitted neonatal unit | 44 (31) | 97 (30) | 13 (41) | 0.49 |
| Death-total | 15 (11) | 36 (11) | 8 (25) | 0.06 |
| Classified as fresh stillbirth | 1 (1) | 4 (1) | 1 (3) | 0.53 |
| Death within 24 h | 9 (6) | 21 (7) | 5 (16) | 0.15 |
| Death from 1–7 days | 5 (4) | 11 (3) | 2 (6) | 0.72 |
| Feature | Normal (n = 281) | Admitted (n = 154) | Death(n = 59) | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FHR < 120 bpm or > 160 bpm | 26 (9) | 28 (18) | 10 (17) | 0.02 |
| Caesarean section | 96 (34) | 71 (46) | 35 (59) | <0.001 |
| ST elevation | 187 (67) | 97 (63) | 36 (61) | 0.62 |
| Other ST abnormalities | 11 (4) | 13 (8) | 8 (14) | 0.01 |
| First HR < 60 bpm | 24 (9) | 25 (16) | 20 (34) | <0.001 |
| First HR 60–100 bpm | 49 (17) | 57 (37) | 25 (42) | <0.001 |
| First HR ≥ 100 bpm | 208 (74) | 72 (47) | 14 (24) | <0.001 |
| Apgar 1 min | 7 (7, 8) | 6 (4, 7) | 4 (2, 6) | 0.01 |
| Apgar 5 min | 10 (10, 10) | 8 (6, 10) | 6 (3, 10) | 0.09 |
| Duration of BMV [s] | 95 (53, 172) | 234 (96, 425) | 479 (211, 1297) | 0.002 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Linde, J.; Solevåg, A.L.; Eilevstjønn, J.; Blacy, L.; Kidanto, H.; Ersdal, H.; Klingenberg, C. Delivery Room ST Segment Analysis to Predict Short Term Outcomes in Near-Term and Term Newborns. Children 2022, 9, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010054
Linde J, Solevåg AL, Eilevstjønn J, Blacy L, Kidanto H, Ersdal H, Klingenberg C. Delivery Room ST Segment Analysis to Predict Short Term Outcomes in Near-Term and Term Newborns. Children. 2022; 9(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleLinde, Jørgen, Anne Lee Solevåg, Joar Eilevstjønn, Ladislaus Blacy, Hussein Kidanto, Hege Ersdal, and Claus Klingenberg. 2022. "Delivery Room ST Segment Analysis to Predict Short Term Outcomes in Near-Term and Term Newborns" Children 9, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010054
APA StyleLinde, J., Solevåg, A. L., Eilevstjønn, J., Blacy, L., Kidanto, H., Ersdal, H., & Klingenberg, C. (2022). Delivery Room ST Segment Analysis to Predict Short Term Outcomes in Near-Term and Term Newborns. Children, 9(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010054







