The Safety and Effectiveness of Laparoscopic Pyloromyotomy Using 3-mm Electrocautery Hook versus Open Surgery for Treatment of Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis in Infants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Outcomes of the Study
2.3. Study Design
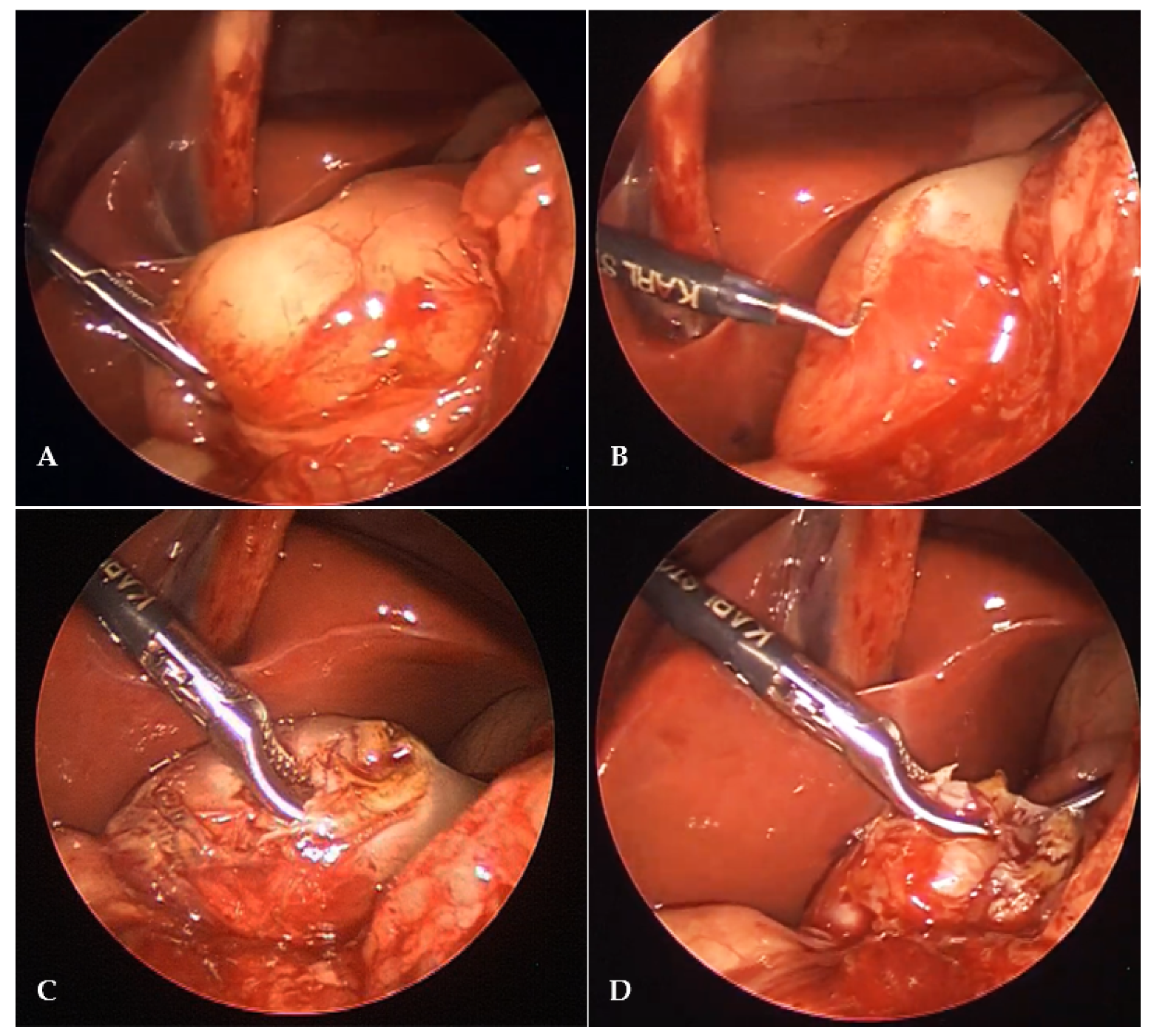
2.4. Surgical Technique
2.4.1. Open Pyloromyotomy
2.4.2. Laparoscopic Pyloromyotomy
2.5. Postoperative Protocol and Follow-Up
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galea, R.; Said, E. Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: An epidemiological review. Neonatal. Netw. 2018, 37, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Abdellatif, M.; Ghozy, S.; Kamel, M.G.; Elawady, S.S.; Ghorab, M.M.E.; Attia, A.W.; Le Huyen, T.T.; Duy, D.T.V.; Hirayama, K.; Huy, N.T. Association between exposure to macrolides and the development of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 178, 301–314. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, T.; Lin, Z.; Qu, Y.; Mu, D. Perinatal risk factors for infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: A meta-analysis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 52, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bunder, F.A.I.M.; Allema, J.H.; Benninga, M.A.; de Blaauw, I.; van de Brug, T.; den Dulk, M.; Hulscher, J.B.F.; Keyzer-Dekker, C.M.G.; Witvliet, M.J.; van Heurn, E.L.W.; et al. The Dutch incidence of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis and the influence of seasons. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelić, Z.; Čagalj, I.Č.; Žitko, V.; Nevešćanin, A.; Krželj, V. Late-onset hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in a 14-weeks-old full term male infant. Acta Med. 2019, 62, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zampieri, N.; Corato, V.; Scirè, G.; Camoglio, F.S. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: 10 years’ experience with standard open and laparoscopic approach. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2021, 24, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, B.G.; Gonzalez, K.W.; Boda, S.R.; Thomas, P.G.; Sherman, A.K.; Peter, S.D.S. Optimizing fluid resuscitation in hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2016, 51, 1279–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutay, G.J.; Capraro, G.; Spirko, B.; Garb, J.; Smithline, H. Electrolyte profile of pediatric patients with hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2013, 29, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M. Sonographic diagnosis of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis- use of simultaneous grey-scale & coour doppler examination. Int. J. Health Sci. 2008, 2, 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Calle-Toro, J.S.; Kaplan, S.L.; Andronikou, S. Are we performing ultrasound measurements of the wall thickness in hypertrophic pyloric stenosis studies the same way? Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2020, 36, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gohary, Y.; Abdelhafeez, A.; Paton, E.; Gosain, A.; Murphy, A.J. Pyloric stenosis: An enigma more than a century after the first successful treatment. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2018, 34, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Takenouchi, A.; Terui, K.; Yoshida, H.; Terui, E. Risk factors for unsuccessful atropine therapy in hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Pediatr. Int. 2019, 61, 1151–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, H.; Takama, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Nakai, H.; Okuyama, H.; Kubota, A.; Yoshimura, N.; Ida, S.; Okada, A. Medical treatment of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: Should we always slice the “olive”? J. Pediatr. Surg. 2005, 40, 1848–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, M.; Yasunaga, H.; Horiguchi, H.; Hashimoto, H.; Matsuda, S. Pyloromyotomy versus i.v. atropine therapy for the treatment of infantile pyloric stenosis: Nationwide hospital discharge database analysis. Pediatr. Int. 2013, 55, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.H.; Zhang, Q.L.; Chen, L.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhou, C.M. The safety and effectiveness of laparoscopic versus open surgery for congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, C.; Wayne, C.; Gotsch, A.; Vincent, J.; Sullivan, K.J.; Nasr, A. Laparoscopic versus open pyloromyotomy in infants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2017, 33, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, C.M.; Vinocur, C.; Berman, L. Postoperative outcomes of open versus laparoscopic pyloromyotomy for hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. J. Surg. Res. 2018, 224, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oomen, M.W.; Hoekstra, L.T.; Bakx, R.; Ubbink, D.T.; Heij, H.A. Open versus laparoscopic pyloromyotomy for hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis focusing on major complications. Surg. Endosc. 2012, 26, 2104–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Shah, A.V. Laparoscopic pyloromyotomy using an indigenous endoknife. J. Indian Assoc. Pediatr. Surg. 2004, 9, 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ramji, J.; Joshi, R.S. Laparoscopic pyloromyotomy for congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: Our experience with twenty cases. Afr. J. Paediatr. Surg. 2021, 18, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Kishk, I.; Stolero, S.; Klin, B.; Lotan, G. Myringotomy knife for pyloromyotomy. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. Percutan. Tech. 2010, 20, e47–e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Choudhury, S.R.; Chadha, R.; Puri, A.; Naga, A.S. Laparoscopic pyloromyotomy: Is a knife really necessary? World J. Pediatr. 2012, 8, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauriti, G.; Cascini, V.; Chiesa, P.L.; Pierro, A.; Zani, A. Atropine treatment for hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 28, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramstedt, C. Zur operation der angeborenen pylorus stenose. Med. Klin. 1912, 8, 1702–1705. [Google Scholar]
- Pogorelić, Z.; Huskić, D.; Čohadžić, T.; Jukić, M.; Šušnjar, T. Learning curve for laparoscopic repair of pediatric inguinal hernia using percutaneous internal ring suturing. Children 2021, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukic, M.; Todoric, M.; Todoric, J.; Susnjar, T.; Pogorelic, Z. Laparoscopic versus open high ligation for adolescent varicocele: A 6-year single center study. Indian Pediatr. 2019, 56, 653–658. [Google Scholar]
- Mihanović, J.; Šikić, N.L.; Mrklić, I.; Katušić, Z.; Karlo, R.; Jukić, M.; Jerončić, A.; Pogorelić, Z. Comparison of new versus reused Harmonic scalpel performance in laparoscopic appendectomy in patients with acute appendicitis-a randomized clinical trial. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2021, 406, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelić, Z.; Aralica, M.; Jukić, M.; Žitko, V.; Despot, R.; Jurić, I. Gallbladder disease in children: A 20-year single-center experience. Indian Pediatr. 2019, 56, 384–386. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, I.; Elsherbini, R.; Elsaied, A.; Aly, K.; Sheir, H. Laparoscopic vs. open pyloromyotomy in treatment of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, S.D.S.; Holcomb, G.W., 3rd; Calkins, C.M.; Murphy, J.P.; Andrews, W.S.; Sharp, R.J.; Snyder, C.L.; Ostlie, D.J. Open versus laparoscopic pyloromyotomy for pyloric stenosis: A prospective, randomized trial. Ann. Surg. 2006, 244, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Lau, S.T.; Lee, S.L.; Schaller, R., Jr.; Healey, P.J.; Ledbetter, D.J.; Sawin, R.S.; Waldhausen, J.H. Pyloromyotomy: A comparison of laparoscopic, circumumbilical, and right upper quadrant operative techniques. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2005, 201, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Mahida, J.B.; Asti, L.; Deans, K.J.; Minneci, P.C.; Groner, J.I. Laparoscopic pyloromyotomy decreases postoperative length of stay in children with hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2016, 51, 1436–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staerkle, R.F.; Lunger, F.; Fink, L.; Sasse, T.; Lacher, M.; von Elm, E.; Marwan, A.I.; Holland-Cunz, S.; Vuille-Dit-Bille, R.N. Open versus laparoscopic pyloromyotomy for pyloric stenosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 3, CD012827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.; Saha, D.K.; Rahman, M.A.; Aziz, M.A.; Islam, M.K. Laparoscopic versus open pyloromyotomy for infantile hypertropic pyloric stenosis: An early experience. Mymensingh. Med. J. 2012, 21, 430–434. [Google Scholar]
- Kethman, W.C.; Harris, A.H.S.; Hawn, M.T.; Wall, J.K. Trends and surgical outcomes of laparoscopic versus open pyloromyotomy. Surg. Endosc. 2018, 32, 3380–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelić, Z.; Perko, Z.; Druzijanić, N.; Tomić, S.; Mrklić, I. How to prevent lateral thermal damage to tissue using the harmonic scalpel: Experimental study on pig small intestine and abdominal wall. Eur. Surg. Res. 2009, 43, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Družijanić, N.; Pogorelić, Z.; Perko, Z.; Mrklić, I.; Tomić, S. Comparison of lateral thermal damage of the human peritoneum using monopolar diathermy, Harmonic scalpel and LigaSure. Can. J. Surg. 2012, 55, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perko, Z.; Pogorelić, Z.; Bilan, K.; Tomić, S.; Vilović, K.; Krnić, D.; Druzijanić, N.; Kraljević, D.; Juricić, J. Lateral thermal damage to rat abdominal wall after harmonic scalpel application. Surg. Endosc. 2006, 20, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelić, Z.; Katić, J.; Mrklić, I.; Jerončić, A.; Šušnjar, T.; Jukić, M.; Vilović, K.; Perko, Z. Lateral thermal damage of mesoappendix and appendiceal base during laparoscopic appendectomy in children: Comparison of the harmonic scalpel (Ultracision), bipolar coagulation (LigaSure), and thermal fusion technology (MiSeal). J. Surg. Res. 2017, 212, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulat, C.; Pešutić-Pisac, V.; Capkun, V.; Marović, Z.; Pogorelić, Z.; Družijanić, N. Comparison of thermal damage of the internal thoracic artery using ultra high radiofrequency and monopolar diathermy. Surgeon 2014, 12, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group I Open Pyloromyotomy (n = 61) | Group II Laparoscopic Pyloromyotomy (n = 64) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic characteristics of patients | |||
| Age (days) | 34 | 31 | 0.453 * |
| median (IQR) | (23.5, 46) | (24, 38) | |
| Gender, n (%) | 0.570 † | ||
| Male | 50 (82) | 54 (85.7) | |
| Female | 11 (18) | 9 (14.3) | |
| Weight (g) | 3 700 | 3 800 | 0.226 * |
| median (IQR) | (3525, 4240) | (3030, 4025) | |
| Malnutrition, n (%) | 16 (26.2) | 11 (17.8) | 0.255 † |
| Associated anomalies, n (%) | 5 (8.9) | 6 (10.3) | 1.000 ‡ |
| Laboratory data of patients | |||
| Hypokalemia, n (%) | 13 (21.6) | 18 (29) | 0.350 † |
| Hypochloremia, n (%) | 24 (39.3) | 24 (37.5) | 0.316 † |
| Metabolic alkalosis, n (%) | 54 (88.5) | 55 (85.9) | 0.974 † |
| Ultrasound findings of patients | |||
| Ultrasound—wall thickness (mm) median (IQR) | 5.5 (5, 5.8) | 5.2 (4.8, 6) | 0.260 * |
| Ultrasound—length of pyloric canal (mm); median (IQR) | 19 (18, 21.5) | 19 (18, 21) | 0.857 * |
| Ultrasound—diameter of pylorus (mm); median (IQR) | 17 (15, 18) | 18 (16, 18.5) | 0.441 * |
| Group I Open Pyloromyotomy | Group II Laparoscopic Pyloromyotomy | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 61) | (n = 64) | ||
| Surgical time (min) | 45 | 35 | 0.00008 * |
| median (IQR) | (40, 57.5) | (30, 45) | |
| Time to oral intake (min) | 22 | 6 | <0.00001 * |
| median (IQR) | (13.5, 24) | (4, 8) | |
| Postoperative vomiting, n (%) | 19 (31.1) | 10 (15.6) | 0.039 † |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | 6 | 3 | <0.00001 * |
| median (IQR) | (4.5, 8) | (2, 3) | |
| Complications, n (%) | 6 (9.8) | 2 (3.1) | 0.157 ‡ |
| Perforation of mucosa | 3 (4.9) | 2 (3.1) | |
| Wound infection | 3 (4.9) | 0 (0) | |
| Reoperations, n (%) | 3 (4.9) | 0 (0) | 0.113 ‡ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pogorelić, Z.; Zelić, A.; Jukić, M.; Llorente Muñoz, C.M. The Safety and Effectiveness of Laparoscopic Pyloromyotomy Using 3-mm Electrocautery Hook versus Open Surgery for Treatment of Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis in Infants. Children 2021, 8, 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080701
Pogorelić Z, Zelić A, Jukić M, Llorente Muñoz CM. The Safety and Effectiveness of Laparoscopic Pyloromyotomy Using 3-mm Electrocautery Hook versus Open Surgery for Treatment of Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis in Infants. Children. 2021; 8(8):701. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080701
Chicago/Turabian StylePogorelić, Zenon, Ana Zelić, Miro Jukić, and Carlos Martin Llorente Muñoz. 2021. "The Safety and Effectiveness of Laparoscopic Pyloromyotomy Using 3-mm Electrocautery Hook versus Open Surgery for Treatment of Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis in Infants" Children 8, no. 8: 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080701
APA StylePogorelić, Z., Zelić, A., Jukić, M., & Llorente Muñoz, C. M. (2021). The Safety and Effectiveness of Laparoscopic Pyloromyotomy Using 3-mm Electrocautery Hook versus Open Surgery for Treatment of Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis in Infants. Children, 8(8), 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080701








