Epidermal Nevus Syndrome Associated with Dwarfism and Atopic Dermatitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
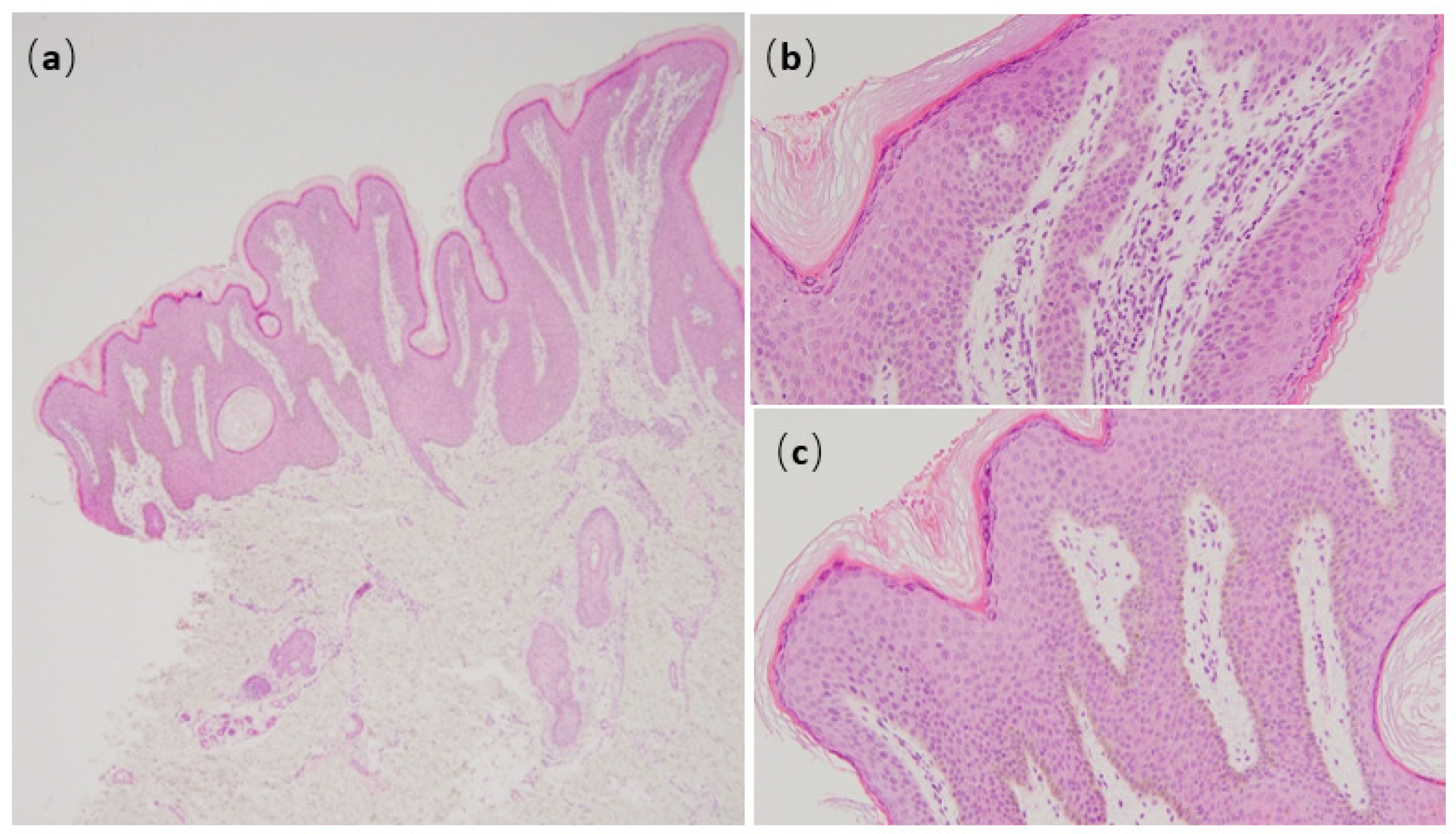
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Happle, R. The group of epidermal nevus syndromes Part I. Well defined phenotypes. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 63, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Wynshaw, B.A.; Zhou, F.; Kuo, A.; Leder, P. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 genes is a negative regulator of bone growth. Cell 1996, 84, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blomberg, M.; Jeppesen, E.M.; Skovby, F.; Benfeldt, E. FGFR3 mutations and the skin: Report of a patient with a FGFR3 gene mutation, acanthosis nigricans, hypochondroplasia and hyperinsulinemia and review of the literature. Dermatology 2010, 220, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafner, C.; Oers, M.M.J.; Vogt, T.; Landthaler, M.; Stoehr, R.; Blaszyk, H.; Hofstaedter, F.; Zwarthoff, C.E.; Hartmann, A. Mosaicism of activating FGFR3 mutations in human skin causes epidermal nevi. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2201–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Vargas, A.; Hafner, C.; Pérez-Rodríguez, G.A.; Rodríguez-Rojas, X.L.; González-Esqueda, P.; Stoehr, R.; Hernández-Torres, M.; Happle, R. An epidermal nevus syndrome with cerebral involvement caused by a mosaic FGFR3 mutation. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2008, 146, 2275–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bygum, A.; Fagerberg, C.R.; Clemmensen, O.J.; Fiebig, B.; Hafner, C. Systemic epidermal nevus with involvement of the oral mucosa due to FGFR3 mutation. BMC Med. Genet. 2011, 5, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, S.D.; Vora, R.; Bharani, S. Garcia-Hafner-Happle syndrome: A case report and review of a rare sub-type of epidermal nevus syndrome. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2014, 9, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, T.; Honda, T.; Kabashima, K. Multipolarity of cytokine axes in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis in terms of age, race, species, disease stage and biomarkers. Int. Immunol. 2018, 30, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yazd, N.K.K.; Patel, R.R.; Dellavalle, R.P.; Dunnick, C.A. Genetic risk factors for development of atopic dermatitis: A systematic review. Curr. Derm. Rep. 2017, 6, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smieszek, S.P.; Welsh, S.; Xiao, C.; Wang, J.; Polymeropoulos, C.; Birznieks, G.; Polymeropoulos, M.H. Correlation of age-of-onset of Atopic Dermatitis with Filaggrin loss-of-function variant status. Sci. Rep. 2020, 17, 2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mizutani, Y.; Nagai, M.; Iwata, H.; Matsunami, K.; Seishima, M. Epidermal Nevus Syndrome Associated with Dwarfism and Atopic Dermatitis. Children 2021, 8, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080697
Mizutani Y, Nagai M, Iwata H, Matsunami K, Seishima M. Epidermal Nevus Syndrome Associated with Dwarfism and Atopic Dermatitis. Children. 2021; 8(8):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080697
Chicago/Turabian StyleMizutani, Yuki, Miki Nagai, Hitoshi Iwata, Kunihiro Matsunami, and Mariko Seishima. 2021. "Epidermal Nevus Syndrome Associated with Dwarfism and Atopic Dermatitis" Children 8, no. 8: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080697
APA StyleMizutani, Y., Nagai, M., Iwata, H., Matsunami, K., & Seishima, M. (2021). Epidermal Nevus Syndrome Associated with Dwarfism and Atopic Dermatitis. Children, 8(8), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080697




