Children with Heiner Syndrome: A Single-Center Experience
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Reports
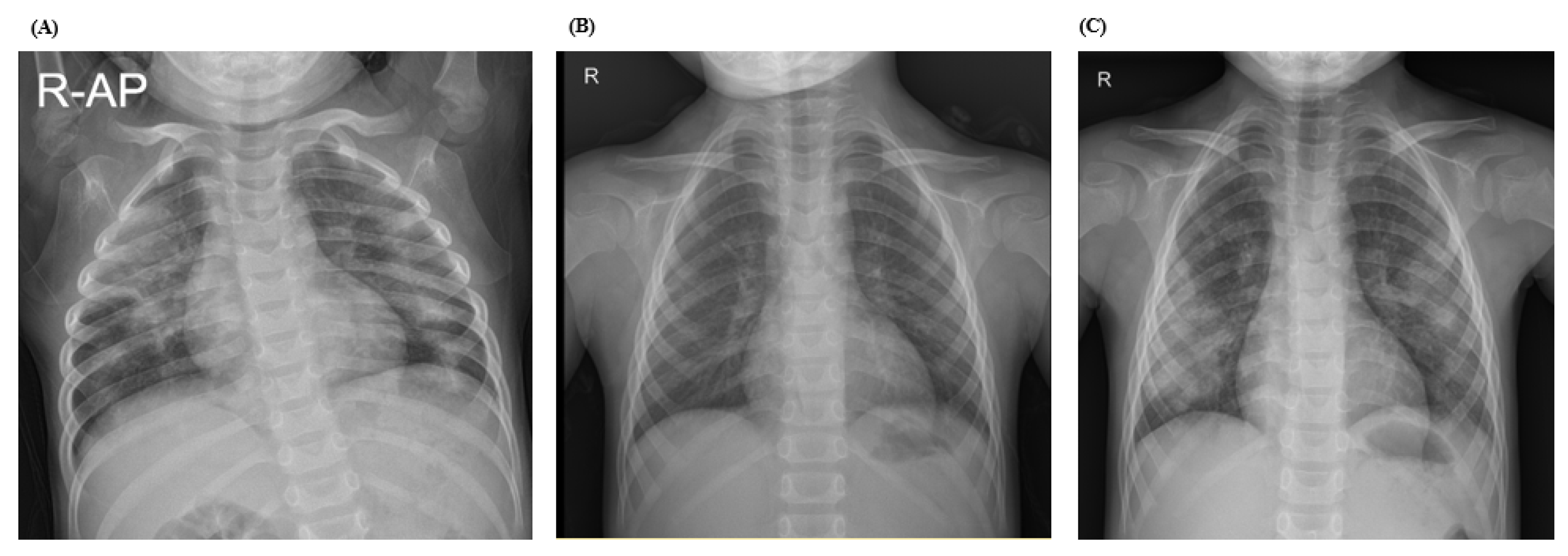
2.1. Case 1
2.2. Case 2
2.3. Case 3
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ioachimescu, O.C.; Sieber, S.; Kotch, A. Idiopathic pulmonary haemosiderosis revisited. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 24, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heiner, D.C.; Sears, J.W.; Kniker, W.T. Multiple precipitins to cow’s milk in chronic respiratory disease. A syndrome including poor growth, gastrointestinal symptoms, evidence of allergy, iron deficiency anemia, and pulmonary hemosiderosis. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1962, 103, 634–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moissidis, I.; Chaidaroon, D.; Vichyanond, P.; Bahna, S.L. Milk-induced pulmonary disease in infants (Heiner syndrome). Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 16, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, N.H.; Hong, R.; Davis, N.C.; West, C.D. Significance of precipitating antibodies to milk proteins in the serum of infants and children. J. Pediatr. 1962, 61, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzel, R.A.; Montana, E.; Sorenson, W.G.; Kullman, G.J.; Allan, T.M.; Dearborn, D.G. Acute pulmonary hemorrhage in infants associated with exposure to Stachybotrys atra and other fungi. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 1998, 152, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elidemir, O.; Colasurdo, G.N.; Rossmann, S.N.; Fan, L.L. Isolation of Stachybotrys from the lung of a child with pulmonary hemosiderosis. Pediatrics 1999, 104, 964–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasi, S.; Mastrorilli, C.; Pecoraro, L.; Giovannini, M.; Mori, F.; Barni, S.; Caminiti, L.; Castagnoli, R.; Liotti, L.; Saretta, F.; et al. Heiner Syndrome and Milk Hypersensitivity: An Updated Overview on the Current Evidence. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.C.; Hung, I.J.; Jaing, T.H.; Yang, C.P. Pitfalls in the diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary haemosiderosis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2002, 86, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chryssanthopoulos, C.; Cassimos, C.; Panagiotidou, C. Prognostic criteria in idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis in children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1983, 140, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Clainche, L.; Le Bourgeois, M.; Fauroux, B.; Forenza, N.; Dommergues, J.P.; Desbois, J.C.; Bellon, G.; Derelle, J.; Dutau, G.; Marguet, C.; et al. Long-Term Outcome of Idiopathic Pulmonary Hemosiderosis in Children. Medicine 2000, 79, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex/Age (years) | M/2.3 | F/1.0 | M/2.4 |
| Clinical presentation | Pallor | Hematemesis | Hemoptysis |
| Duration of symptoms | 3 days | 3 months (3 times) | Recurrent (2018, 2020) |
| Past History | None | Allergy to milk and egg, atopic dermatitis | Croup, pneumonia |
| Imaging Studies | |||
| Chest radiograph | Multifocal patchy consolidation | ||
| Chest CT | Bilateral, multifocal, and patchy ground glass opacities and consolidations | ||
| Anemia/Hematologic | |||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 3.1 | 7.0 | 11.4 |
| PT/INR (sec) | 11.9/1.04 | 13.1/1.14 | 12.0/1.05 |
| Serum iron (ug/dL)/TIBC | 6/410 | 30/363 | 46/355 |
| Transferrin saturation (%) | 1 | 8 | 15 |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | 29.3 | 65.6 | 90 |
| Microbiology | |||
| Blood/urine/sputum culture | No growth | No growth | No growth |
| Respiratory virus/PCP PCR | Negative | Rhinovirus, Coronavirus 229E | Negative |
| Mycoplasma Ab | 1:320 | Negative | 1:160 |
| EBV/CMV PCR | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Aspergillus/Candida Ag | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Immunology | |||
| ANA/anti-DNA titration | Negative | Negative | 1:320/Negative |
| MPO/PR3(P-ANCA/C-ANCA) | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Anti-GBM Ab | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| C3/C4 (mg/dL) | 155/41 | 95/7 | 100/11 |
| Allergy Total IgE (kU/L)Milk-specific IgE (kU/L) | 48.5 0.12 | 95.5 6.0 | 8.3 0.03 |
| Milk-specific IgG4 (kU/L) | 2.03 | 1.05 | Not tested |
| NGS | Non-pathognomic | ||
| Echocardiography | Nonspecific findings | ||
| Progress | |||
| Milk avoidance /provocation test | After first recurrence—until now/not done | At the time of diagnosis—until now/done | At the time of diagnosis—until now/done |
| Duration of follow-up | 2 years and 10 months | 2 years and 1 month | 2 years and 10 months |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.Y.; Park, M.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Hahn, S.M.; Kim, S.; Lee, M.-J.; Shim, H.S.; Sohn, M.H.; et al. Children with Heiner Syndrome: A Single-Center Experience. Children 2021, 8, 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121110
Lee JY, Park M, Jung JH, Kim SY, Kim YH, Hahn SM, Kim S, Lee M-J, Shim HS, Sohn MH, et al. Children with Heiner Syndrome: A Single-Center Experience. Children. 2021; 8(12):1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121110
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ji Young, Mireu Park, Jae Hwa Jung, Soo Yeon Kim, Yoon Hee Kim, Seung Min Hahn, Seung Kim, Mi-Jung Lee, Hyo Sup Shim, Myung Hyun Sohn, and et al. 2021. "Children with Heiner Syndrome: A Single-Center Experience" Children 8, no. 12: 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121110
APA StyleLee, J. Y., Park, M., Jung, J. H., Kim, S. Y., Kim, Y. H., Hahn, S. M., Kim, S., Lee, M.-J., Shim, H. S., Sohn, M. H., Kim, K. W., & Kim, M. J. (2021). Children with Heiner Syndrome: A Single-Center Experience. Children, 8(12), 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121110






