Upper Extremity Fractures in Children—Comparison between Worldwide, Romanian and Western Romanian Region Incidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
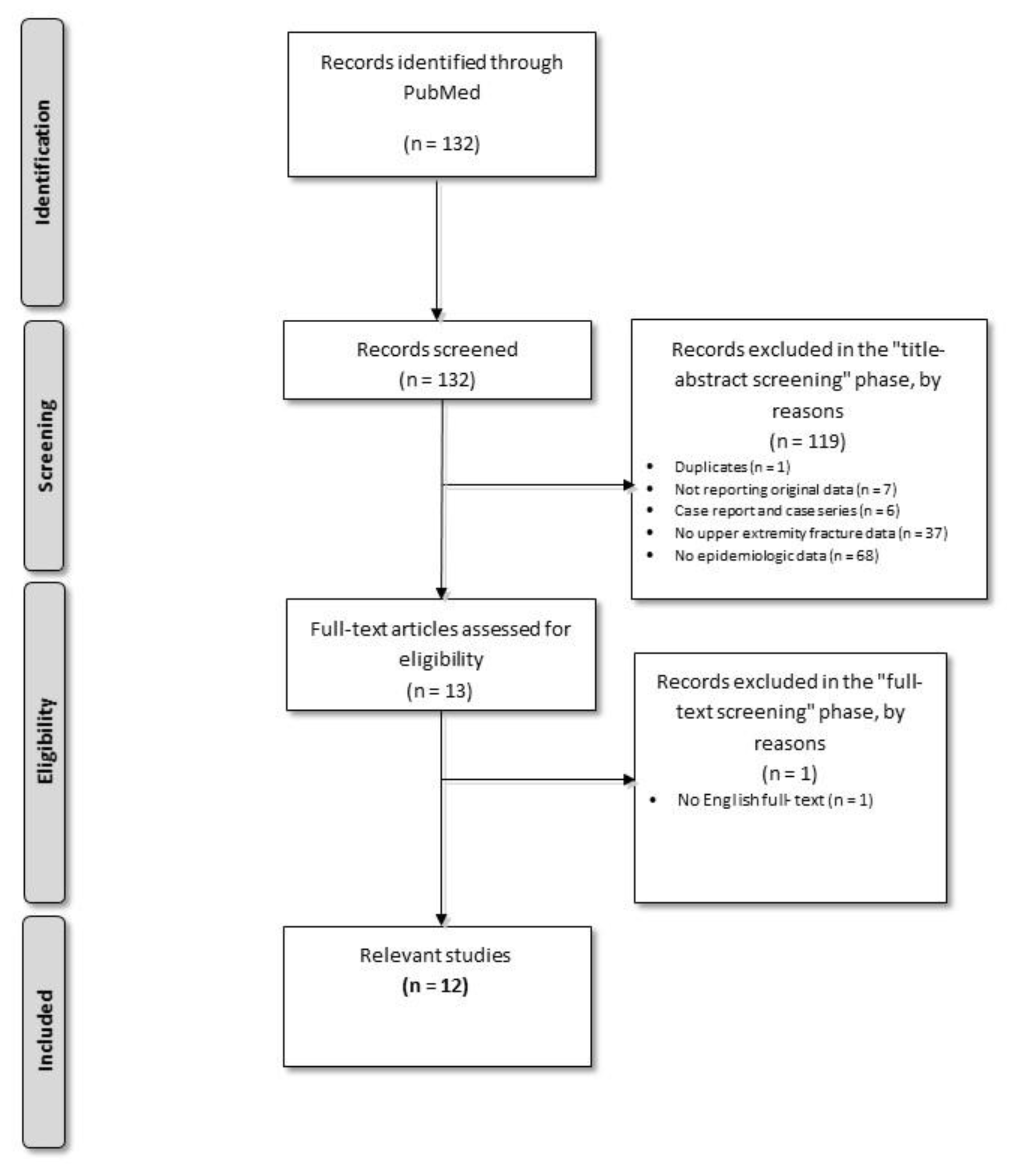
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Extraction from the Scientific Literature
2.2. Calculation of Nationwide and Regional Level Incidence Data
3. Results
3.1. Upper Arm Fractures
3.2. Forearm Fractures
3.3. Upper Extremity Fractures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Landin, L.A. Fracture patterns in children: Analysis of 8,682 fractures with special reference to incidence, etiology and secular changes in a Swedish urban population 1950–1979. Acta. Orthop. Scand. 1983, 54, 3–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, V.; Parkkari, J.; Kannus, P.; Rimpelä, A. Occurrence and risk factors of unintentional injuries among 12- to 18-year-old Finns—Asurvey of 8219 adolescents. Eur. J. Epidemiol 2004, 19, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.; Cooley, H.M. Symptomatic fracture incidence in those under 50 years of age in southern Tasmania. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2002, 38, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibert, J.R.; Maddocks, G.B.; Brown, B.M. Childhood accidents—An endemic of epidemic proportion. Arch. Dis. Child 1981, 56, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lempesis, V.; Jerrhag, D.; Rosengren, B.E.; Landin, L.; Tiderius, C.J.; Karlsson, M.K. Pediatric Distal Forearm Fracture Epidemiology in Malmö, Sweden—Time Trends During Six Decades. Wrist Surg. 2019, 8, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.; Dennison, E.M.; Leufkens, H.G.; Bishop, N.; Van Staa, T.P. Epidemiology of Childhood Fractures in Britain: A study using the general practice research database. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2004, 19, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedström, E.M.; Svensson, O.; Bergström, U.; Michno, P. Epidemiology of fractures in children and adolescents. Increased incidence over the past decade: A population-based study from northern Sweden. Acta. Orthop. 2010, 81, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/ (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Mei-Dan, O.; Carmont, M.R. Adventure and Extreme Sports Injuries: Epidemiology, Treatment, Rehabilitation and Prevention; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 315–316. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/documents/3859598/5916917/KS-RA-11-011-EN.PDF (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Naranje, S.M.; Erali, R.A.; Warner, W.C.; Sawyer, J.R.; Kelly, D.M. Epidemiology of Pediatric Fractures Presenting to Emergency Departments in the United States. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2016, 36, e45–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holloway, K.L.; Bucki-Smith, G.; Morse, A.G.; Brennan-Olsen, S.L.; Kotowicz, M.A.; Moloney, D.J.; Sanders, K.M.; Korn, S.; Timney, E.N.; Dobbins, A.G.; et al. Humeral Fractures in South-Eastern Australia: Epidemiology and Risk Factors. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 97, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, J.A.; Wolfe, H.; Banaag, A.; Tintle, S.; Koehlmoos, T.P. Early Pediatric Fractures in a Universally Insured Population within the United States. BMC Pediatrics 2019, 19, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasco, J.A.; Lane, S.E.; Brennan-Olsen, S.E.; Holloway, K.L.; Timney, E.N.; Bucki-Smith, G.; Morse, A.G.; Dobbins, A.G.; Williams, L.J.; Hyde, N.K.; et al. The Epidemiology of Incident Fracture from Cradle to Senescence. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 97, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, D.; Gonser, C.E.; Bahrs, C.; Hemmann, P. Change in paediatric upper extremity fracture incidences in German hospitals from 2002 to 2017: An epidemiological study. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2020, 140, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannonen, J.; Hyvönen, H.; Korhonen, L.; Serlo, W.; Sinikumpu, J.J. The incidence and treatment trends of pediatric proximal humerus fractures. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamoowala, N.; Johnson, N.A.; Dias, J.J. Trends in paediatric distal radius fractures: An eight-year review from a large UK trauma unit. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2019, 101, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, S.; Noda, T.; Kubo, S.; Myojin, T.; Nishioka, Y.; Higashino, T.; Imamura, T. Variation in fracture risk by season and weather: A comprehensive analysis across age and fracture site using a National Database of Health Insurance Claims in Japan. Bone 2019, 120, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoffersen, T.; Ahmed, L.A.; Winther, A.; Nilsen, O.A.; Furberg, A.S.; Grimnes, G.; Dennison, E.; Center, J.R.; Eisman, J.A.; Emaus, N. Fracture incidence rates in Norwegian children, The Tromsø Study, Fit Futures. Arch. Osteoporos 2016, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lyman, A.; Wenger, D.; Landin, L. Pediatric diaphyseal forearm fractures: Epidemiology and treatment in an urban population during a 10-year period, with special attention to titanium elastic nailing and its complications. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2016, 25, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Cao, C.; Lu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, G.; Li, C.; Zhou, Y.; Ou, L.; Liu, J.; et al. Incidence patterns of traumatic upper limb fractures in children and adolescents. Data from medical university-affiliated hospitals in Chongqing, China. Medicine 2019, 98, e17299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Fracture Location | First Author/Title | Study Country | Age (Years)/Age Interval | Gender | Incidence * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Humerus | Holloway K.L., Humeral Fractures in South-Eastern Australia: Epidemiology and Risk Factors [12] | Australia | 0–9 | Overall | 317.5 |
| Wolfe J. A., Early Pediatric Fractures in a Universally Insured Population within the United States [13] | USA | <1 | N/A | 38 ** | |
| 1 | N/A | 112 ** | |||
| 2 | N/A | 140 ** | |||
| 3 | N/A | 164 ** | |||
| 4 | N/A | 488 ** | |||
| Pasco J.A., The Epidemiology of Incident Fracture from Cradle to Senescence [14] | Australia | <20 | Male | 232† | |
| Female | 183† | ||||
| Humerus shaft | Holloway K.L., Humeral Fractures in South-Eastern Australia: Epidemiology and Risk Factors [12] | Australia | 0–9 | Overall | 294 |
| Female | 298.8 | ||||
| Körner D., Change in paediatric upper extremity fracture incidences in German hospitals from 2002 to 2017: an epidemiological study [15] | Germany | 0–4 | Overall | 2002: 4 2017: 4 | |
| 5–9 | Overall | 2002: 8 2017: 5 | |||
| 10–14 | Overall | 2002: 10 2017: 8 | |||
| 15–19 | Overall | 2002: 9 2017: 6 | |||
| Proximal humerus | Holloway K.L., Humeral Fractures in South-Eastern Australia: Epidemiology and Risk Factors [12] | Australia | 10–19 | Male | 58.5 |
| Hannonen J., The incidence and treatment trends of pediatric proximal humerus fractures [16] | Finland | <16 | N/A | 31.4 | |
| Körner D., Change in paediatric upper extremity fracture incidences in German hospitals from 2002 to 2017: an epidemiological study [15] | Germany | 0–4 | Overall | 2002: 3 2017: 1 | |
| 5–9 | Overall | 2002: 10 2017: 6 | |||
| 10–14 | Overall | 2002: 23 2017: 14 | |||
| 15–19 | Overall | 2002: 11 2017: 7 | |||
| Distal humerus | Körner D., Change in paediatric upper extremity fracture incidences in German hospitals from 2002 to 2017: an epidemiological study [15] | Germany | 0–4 | Overall | 2002: 48 2017: 39 |
| 5–9 | Overall | 2002: 110 2017: 102 | |||
| 10–14 | Overall | 2002: 43 2017: 36 | |||
| 15–19 | Overall | 2002: 14 2017: 9 | |||
| Upper arm | Naranje S.M., Epidemiology of Pediatric Fractures Presenting to Emergency Departments in the United States [11] | USA | 0–19 | Overall | 30 *** |
| <5 | 30 *** | ||||
| 5–9 | 50 *** | ||||
| 10–14 | 31 *** | ||||
| 15–19 | 10 *** |
| Humerus Fractures | Total (Nationwide) | Western Region |
|---|---|---|
| Number of cases | 2012 | 201 |
| Population | 3,669,563 | 310,254 |
| Incidence | 54.83 | 64.79 |
| Fracture Location | First Author/Title | Study Country | Age (Years)/Age Interval | Gender | Incidence * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ulna shaft | Körner D., Change in paediatric upper extremity fracture incidences in German hospitals from 2002 to 2017: an epidemiological study [15] | Germany | 0–4 | Overall | 2002: 4 2017: 5 |
| 5–9 | Overall | 2002: 10 2017: 13 | |||
| 10–14 | Overall | 2002: 5 2017: 4 | |||
| 15–19 | Overall | 2002: 3 2017: 2 | |||
| Radius shaft | Körner D., Change in paediatric upper extremity fracture incidences in German hospitals from 2002 to 2017: an epidemiological study [15] | Germany | 0–4 | Overall | 2002: 4 2017: 4 |
| 5–9 | Overall | 2002: 13 2017: 13 | |||
| 10–14 | Overall | 2002: 19 2017: 15 | |||
| 15–19 | Overall | 2002: 9 2017: 7 | |||
| Distal radius | Mamoowala N., Trends in paediatric distal radius fractures: an eight-year review from a large UK trauma unit [17] | UK | 0–16 | Overall | 337 *** |
| 0–2 | Overall | 82 *** | |||
| 2–5 | Overall | 160 *** | |||
| 5–10 | Overall | 384 *** | |||
| Male | 381 *** | ||||
| Female | 387 *** | ||||
| 10–16 | Overall | 509 *** | |||
| Hayashi S., Variation in fracture risk by season and weather: A comprehensive analysis across age and fracture site using a National Database of Health Insurance Claims in Japan [18] | Japan | 0–19 | Overall | 82.8 | |
| 10–19 | Overall | 212.4 | |||
| 0–9 | Overall | 47.4 | |||
| Körner D., Change in paediatric upper extremity fracture incidences in German hospitals from 2002 to 2017: an epidemiological study [15] | Germany | 0–4 | Overall | 2002: 5 2017: 4 | |
| 5–9 | Overall | 2002: 45 2017: 47 | |||
| 10–14 | Overall | 2002: 98 2017: 92 | |||
| 15–19 | Overall | 2002: 45 2017: 47 | |||
| Radius/ulna diaphyseal | Christoffersen T., Fracture incidence rates in Norwegian children, The Tromsø Study, Fit Futures [19] | Norway | <18 | Overall | 19 |
| Female | 26 | ||||
| Male | 13 | ||||
| Radius/ulna distal | Overall | 439 | |||
| Female | 423 | ||||
| Male | 456 | ||||
| Radius/ulna proximal | Overall | 32 | |||
| Female | 40 | ||||
| Male | 25 | ||||
| Radius/ulna total | Overall | 491 | |||
| Female | 489 | ||||
| Male | 494 | ||||
| Forearm | Wolfe J. A., Early Pediatric Fractures in a Universally Insured Population within the United States [13] | USA | <1 | N/A | 56 ** |
| 1 | N/A | 244 ** | |||
| 2 | N/A | 245 ** | |||
| 3 | N/A | 287 ** | |||
| 4 | N/A | 856 ** | |||
| Naranje S.M., Epidemiology of Pediatric Fractures Presenting to Emergency Departments in the United States [11] | USA | 0–19 | Overall | 169 | |
| <5 | Overall | 100 | |||
| 5–9 | Overall | 252 | |||
| 10–14 | Overall | 251 | |||
| 15–19 | Overall | 78 | |||
| Pasco J.A., The Epidemiology of Incident Fracture from Cradle to Senescence [14] | Australia | <20 | Male | 170 | |
| Female | 125 | ||||
| Forearm shaft | Körner D., Change in paediatric upper extremity fracture incidences in German hospitals from 2002 to 2017: an epidemiological study [15] | Germany | 0–4 | Overall | 2002: 17 2017: 31 |
| 5–9 | Overall | 2002: 57 2017: 103 | |||
| 10–14 | Overall | 2002: 50 2017: 72 | |||
| 15–19 | Overall | 2002: 13 2017: 12 | |||
| Distal forearm | Lempesis V., Pediatric Distal Forearm Fracture Epidemiology in Malmö [5] | Sweden | N/A | Overall | 564 |
| Male | 719 | ||||
| female | 401 | ||||
| Pasco J.A., The Epidemiology of Incident Fracture from Cradle to Senescence [14] | Australia | <20 | Male | 948 | |
| female | 645 | ||||
| Körner D., Change in paediatric upper extremity fracture incidences in German hospitals from 2002 to 2017: an epidemiological study [15] | Germany | 0–4 | Overall | 2002: 12 2017: 9 | |
| 5–9 | Overall | 2002: 65 2017: 59 | |||
| 10–14 | Overall | 2002: 60 2017: 53 | |||
| 15–19 | Overall | 2002: 11 2017: 9 | |||
| Diaphyseal forearm | Lyman A., Pediatric diaphyseal forearm fractures: epidemiology and treatment in an urban population during a 10-year period, with special attention to titanium elastic nailing and its complications [20] | Sweden | 0–16 | Overall | 70 ** |
| Forearm Fractures | Total (Nationwide) | Western Region |
|---|---|---|
| Number of cases | 5129 | 433 |
| Population | 3,669,563 | 310,254 |
| Incidence | 139.77 | 139.56 |
| Fracture Location | First Author/Title | Study Country | Age (Years)/Age Interval | Gender | Incidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper extremity | Yang H., Incidence patterns of traumatic upper limb fractures in children and adolescents Data from medical university-affiliated hospitals in Chongqing, China [21] | China | N/A | N/A | 101.6 (± 47.5) * |
| Upper Limb Fractures (Not Otherwise Specified) | Total (Nationwide) | Western Region |
|---|---|---|
| Number of cases | 419 | 49 |
| Population | 3,669,563 | 310,254 |
| Incidence | 11.42 | 15.79 |
| Upper Extremity Fractures | Total (Nationwide) | Western Region |
|---|---|---|
| Number of cases | 7560 | 683 |
| Population | 3,669,563 | 310,254 |
| Incidence | 206.02 | 220.14 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adam, O.; Horhat, F.G.; Amaricai, E.; David, V.-L.; Derzsi, Z.; Boia, E.S. Upper Extremity Fractures in Children—Comparison between Worldwide, Romanian and Western Romanian Region Incidence. Children 2020, 7, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7080084
Adam O, Horhat FG, Amaricai E, David V-L, Derzsi Z, Boia ES. Upper Extremity Fractures in Children—Comparison between Worldwide, Romanian and Western Romanian Region Incidence. Children. 2020; 7(8):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7080084
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdam, Ovidiu, Florin George Horhat, Elena Amaricai, Vlad-Laurentiu David, Zoltán Derzsi, and Eugen Sorin Boia. 2020. "Upper Extremity Fractures in Children—Comparison between Worldwide, Romanian and Western Romanian Region Incidence" Children 7, no. 8: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7080084
APA StyleAdam, O., Horhat, F. G., Amaricai, E., David, V.-L., Derzsi, Z., & Boia, E. S. (2020). Upper Extremity Fractures in Children—Comparison between Worldwide, Romanian and Western Romanian Region Incidence. Children, 7(8), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7080084







