Interpretation of Cerebral Oxygenation Changes in the Preterm Infant
Abstract
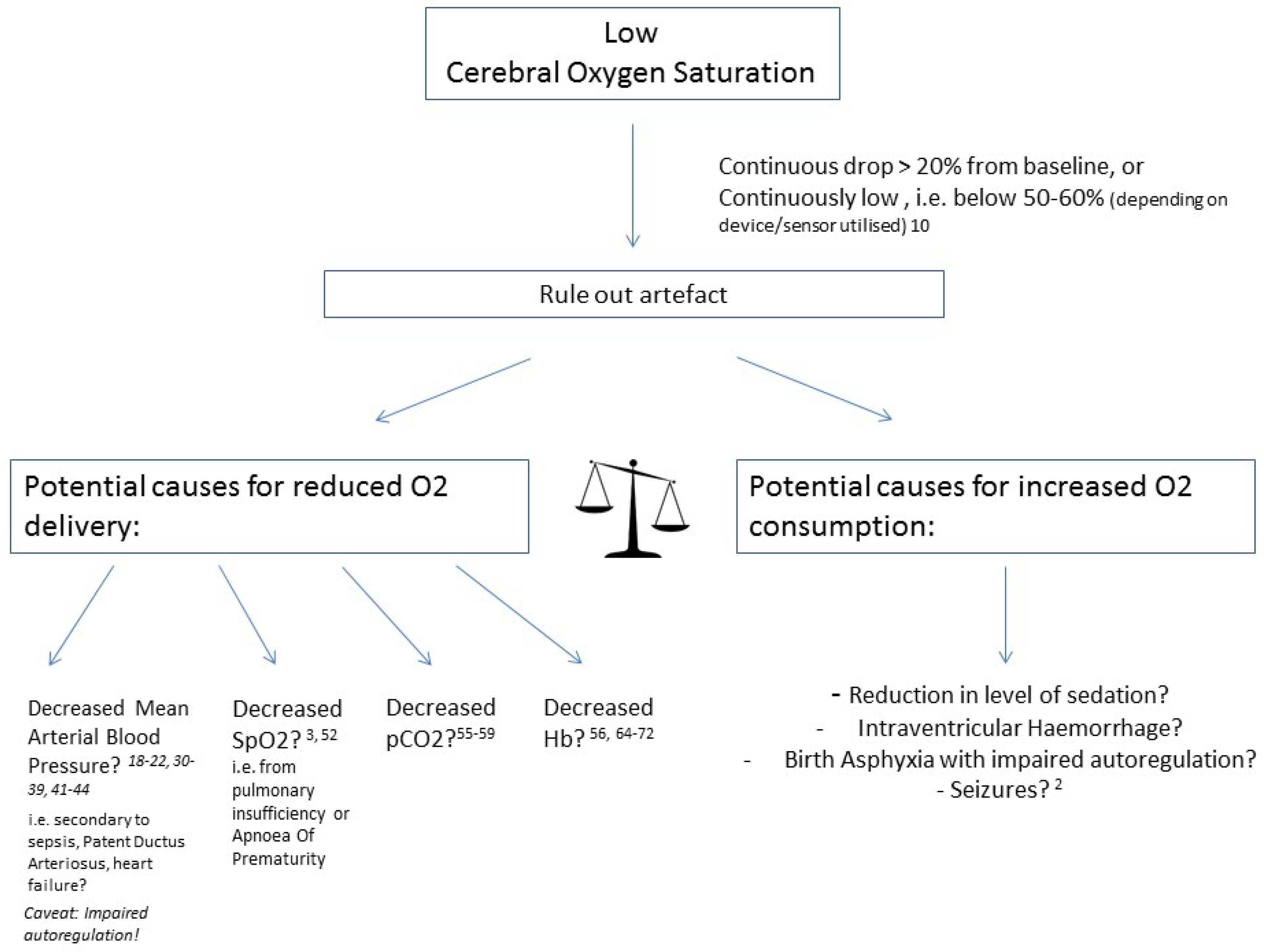
1. Introduction
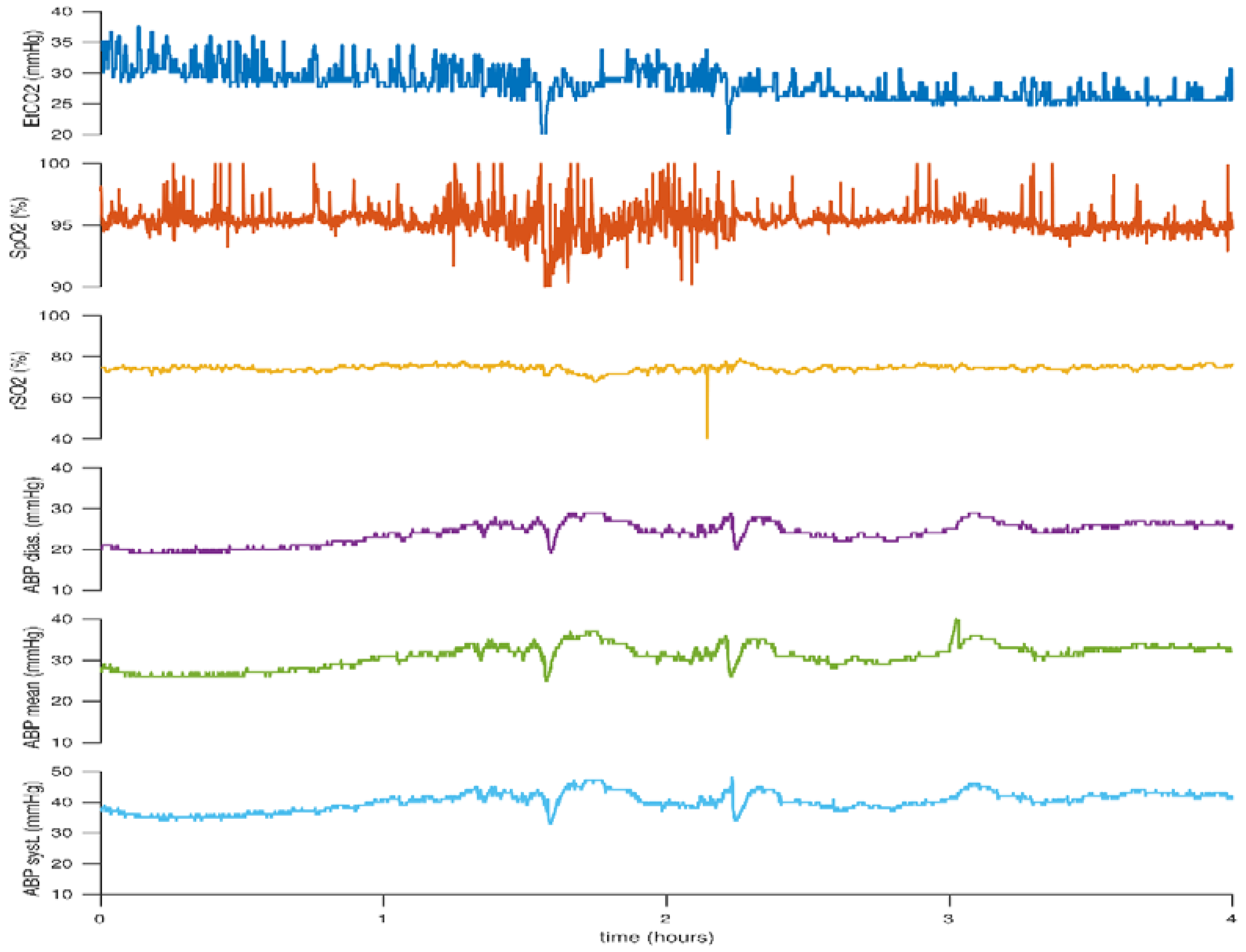
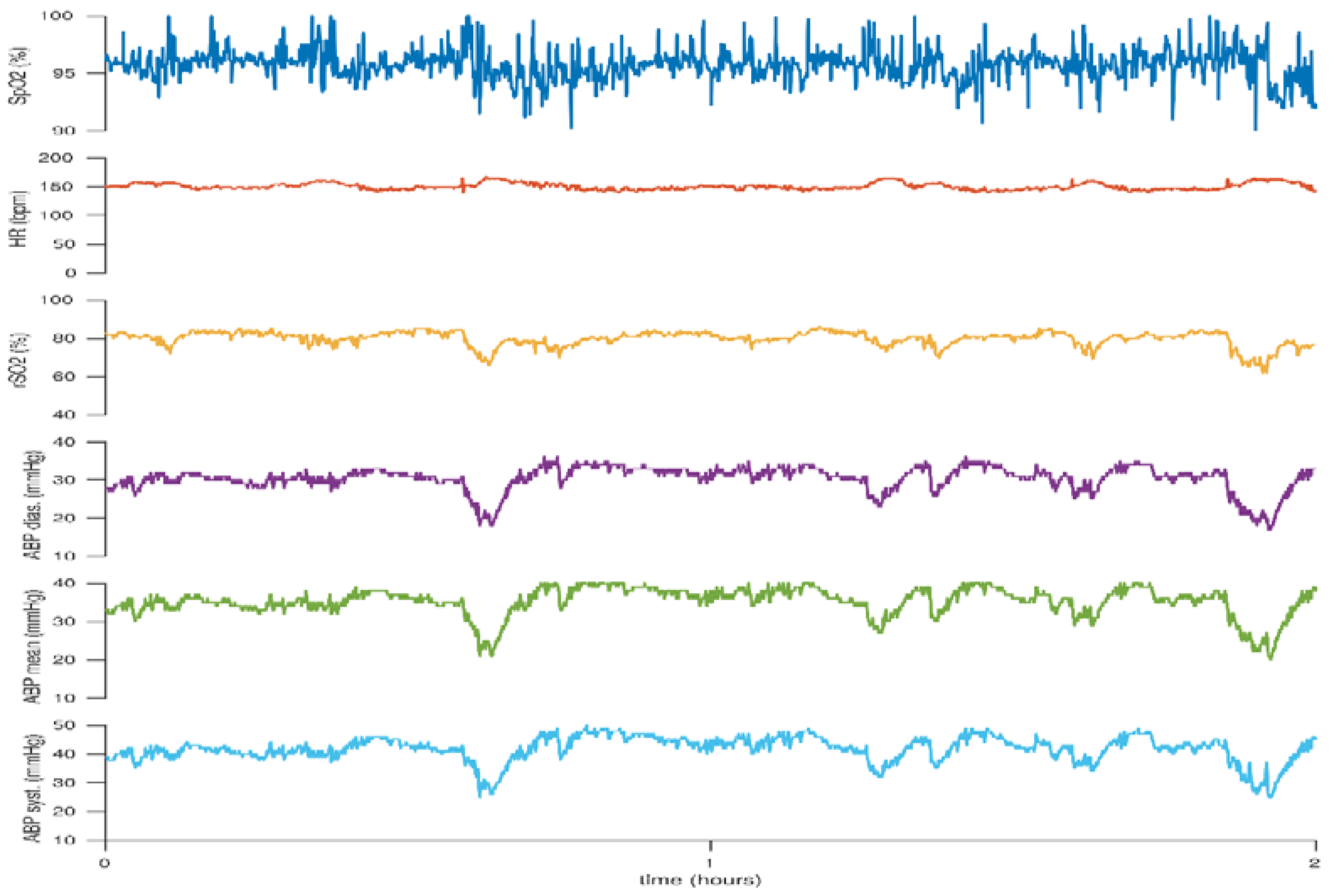
2. Hypotension
3. Patent Ductus Arteriosus: Significant or Not?
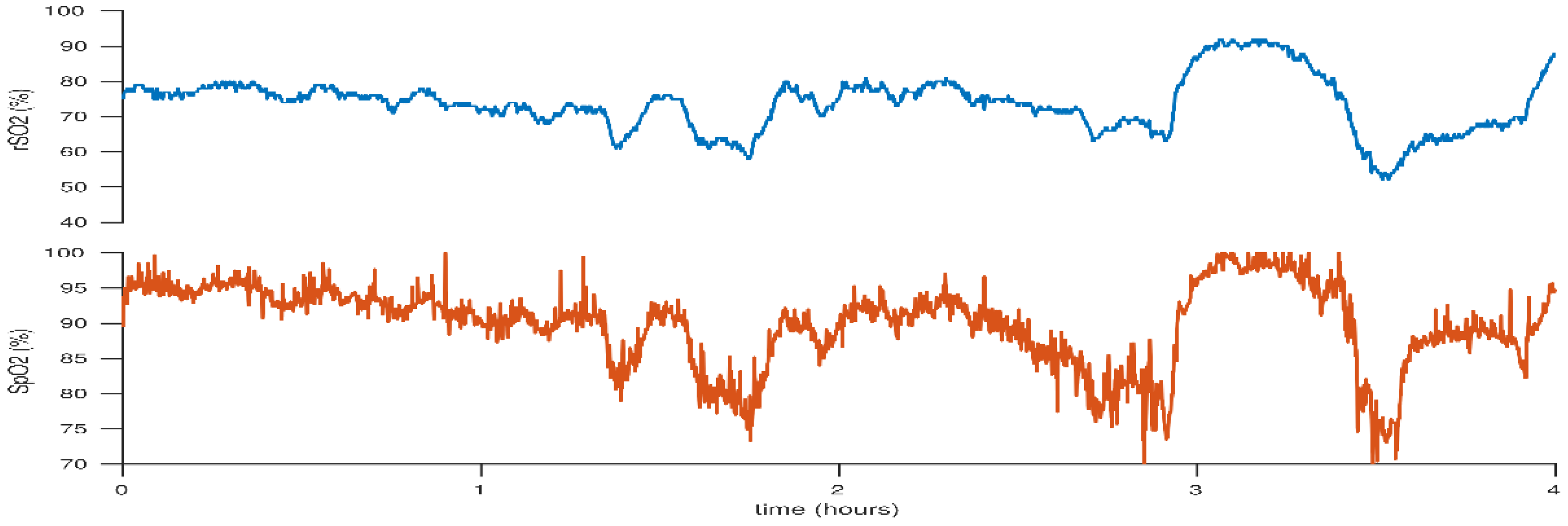
4. Peripheral Arterial Oxygen Saturation
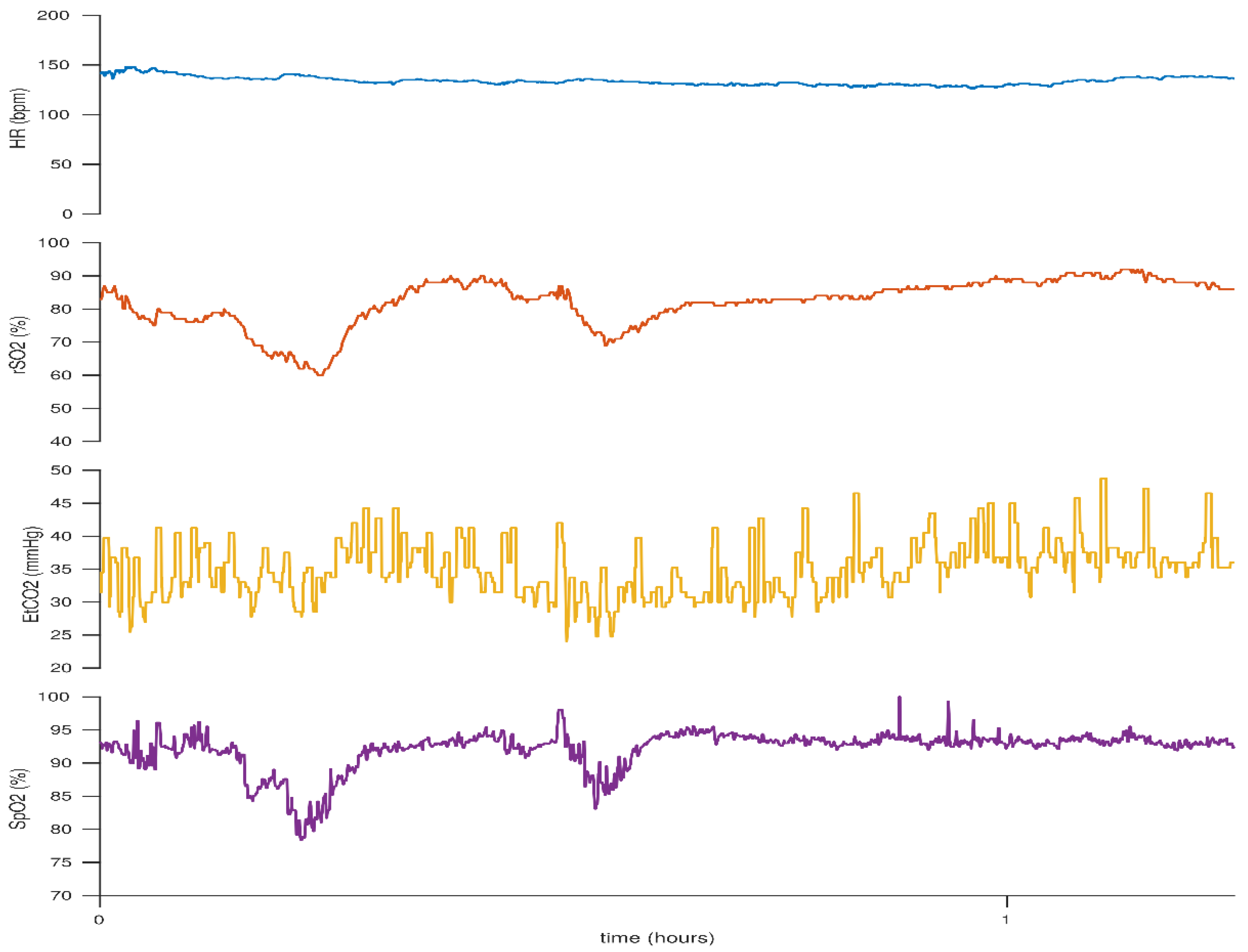
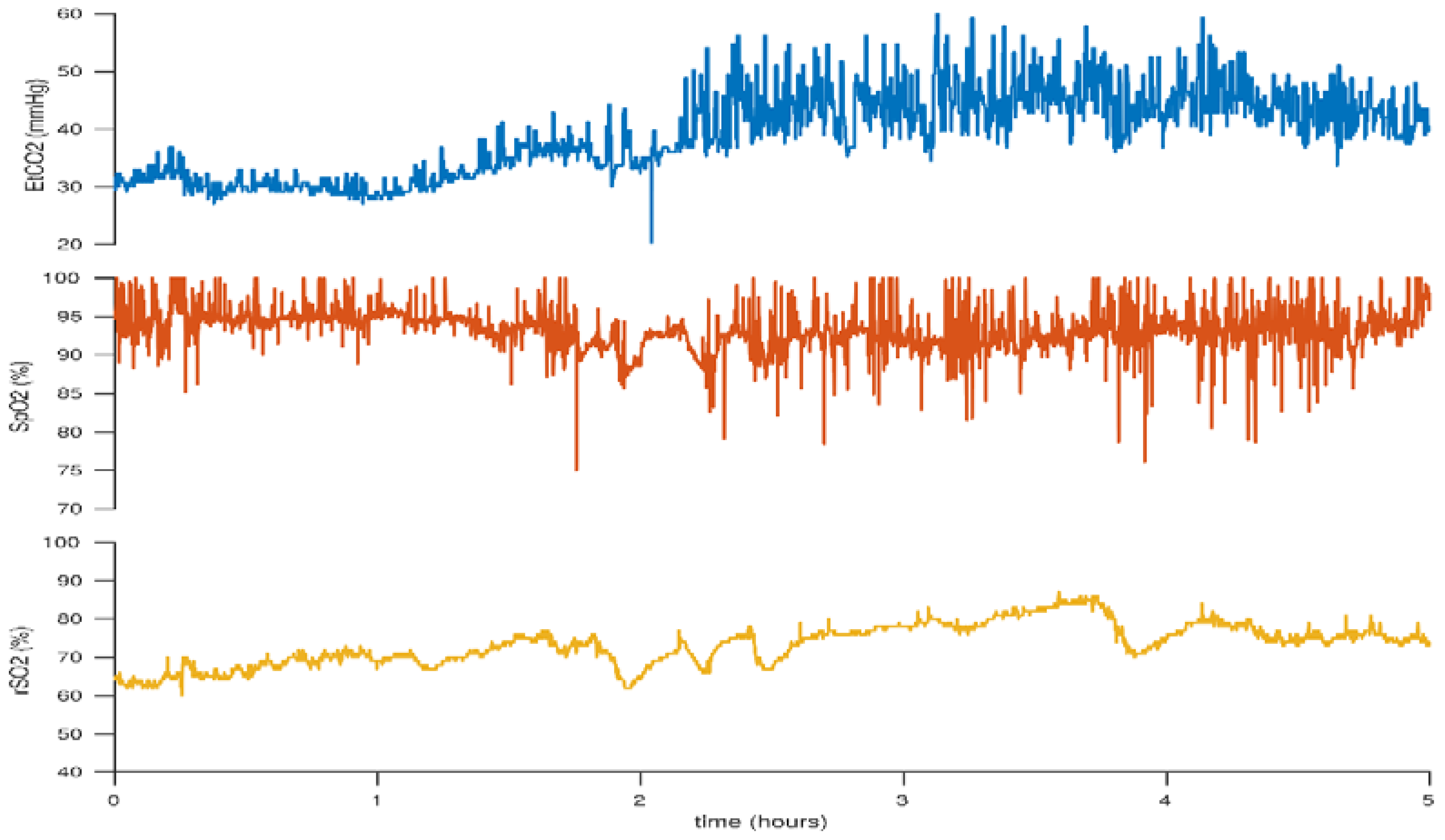
5. Carbon Dioxide: Hypocarbia versus Hypercarbia
6. Anaemia: Anaemia versus Polycythaemia
7. Blood Glucose Level: Hypoglycaemia
8. Discussion
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sood, B.G.; McLaughlin, K.; Cortez, J. Near-infrared spectroscopy: Applications in neonates. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 20, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, A.A.; Dempsey, E.M. Applications of near infrared spectroscopy in the neonate. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2018, 30, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plomgaard, A.M.; van Oeveren, W.; Petersen, T.H.; Alderliesten, T.; Austin, T.; van Bel, F.; Benders, M.; Claris, O.; Dempsey, E.; Franz, A.; et al. The SafeBoosC II randomized trial: Treatment guided by near-infrared spectroscopy reduces cerebral hypoxia without changing early biomarkers of brain injury. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 79, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bel, F.; Lemmers, P.; Naulaers, G. Monitoring neonatal regional cerebral oxygen saturation in clinical practice: Value and pitfalls. Neonatology 2008, 94, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhagen, E.A.; Van Braeckel, K.N.; van derVeere, C.N.; Groen, H.; Dijk, P.H.; Hulzebos, C.V.; Bos, A.F. Cerebral oxygenation is associated with neurodevelopmental outcome of preterm children at age 2 to 3 years. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2015, 57, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderliesten, T.; Dix, L.; Baerts, W.; Caicedo, A.; van Huffel, S.; Naulaers, G.; Groenendaal, F.; van Bel, F.; Lemmers, P. Reference values of regional cerebral oxygen saturation during the first 3 days of life in preterm neonates. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 79, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiser, S.; Nasseri, N.; Andresen, B.; Greisen, G.; Wolf, M. Comparison of tissue oximeters on a liquid phantom with adjustable optical properties. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 2973–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greisen, G. Is near-infrared spectroscopy living up to its promises? Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2006, 11, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dix, L.M.; van Bel, F.; Baerts, W.; Lemmers, P.M. Comparing near-infrared spectroscopy devices and their sensors for monitoring regional cerebral oxygen saturation in the neonate. Pediatr. Res. 2013, 74, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, F.Y.; Barfield, C.P.; Campbell, L.; Brodecky, V.A.; Walker, A.M. Validation of cerebral venous oxygenation measured using near-infrared spectroscopy and partial jugular venous occlusion in the newborn lamb. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2008, 28, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, J.M.; Kenosi, M.; Finn, D.; Boylan, G.B.; Dempsey, E.M. Features of cerebral oxygenation detects brain injury in premature infants. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 3614–3617. [Google Scholar]
- Naulaers, G.; Meyns, B.; Miserez, M.; Leunens, V.; Van Huffel, S.; Casaer, P.; Weindling, M.; Devlieger, H. Use of tissue oxygenation index and fractional tissue oxygen extraction as non-invasive parameters for cerebral oxygenation. A validation study in piglets. Neonatology 2007, 92, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mebius, M.J.; van der Laan, M.E.; Verhagen, E.A.; Roofthooft, M.T.; Bos, A.F.; Kooi, E.M. Cerebral oxygen saturation during the first 72h after birth in infants diagnosed prenatally with congenital heart disease. Early Hum. Dev. 2016, 103, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesoulis, Z.A.; Liao, S.M.; Mathur, A.M. Gestational age-dependent relationship between cerebral oxygen extraction and blood pressure. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 82, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giesinger, R.E.; McNamara, P.J. Hemodynamic instability in the critically ill neonate: An approach to cardiovascular support based on disease pathophysiology. Semin. Perinatol. 2016, 40, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stranak, Z.; Semberova, J.; Barrington, K.; O’Donnell, C.; Marlow, N.; Naulaers, G.; Dempsey, E. HIP Consortium. International survey on diagnosis and management of hypotension in extremely preterm babies. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2014, 173, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miall-Allen, V.M.; de Vries, L.S.; Whitelaw, A.G. Mean arterial blood pressure and neonatal cerebral lesions. Arch. Dis. Child. 1987, 62, 1068–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bada, H.S.; Korones, S.B.; Perry, E.H.; Arheart, K.L.; Ray, J.D.; Pourcyrous, M.; Magill, H.L.; Runyan, W.; Somes, G.W.; Clark, F.C.; et al. Mean arterial blood pressure changes in premature infants and those at risk for intraventricular hemorrhage. J. Pediatr. 1990, 117, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, A.M.; West, C.R.; Cooke, R.W. Blood pressure and cerebral haemorrhage and ischaemia in very low birthweight infants. Early Hum. Dev. 1989, 19, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammann, O.; Allred, E.N.; Kuban, K.C.; Van Marter, L.J.; Pagano, M.; Sanocka, U.; Leviton, A. Systemic hypotension and white-matter damage in preterm infants. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2002, 44, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicer, A.; Valverde, E.; Elorza, M.D.; Madero, R.; Gayá, F.; Quero, J.; Cabanas, F. Cardiovascular support for low birth weight infants and cerebral hemodynamics: A. randomized, blinded, clinical trial. Pediatrics 2005, 115, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, M.C.; López-Ortego, P.; Sánchez, L.; Riera, J.; Madero, R.; Cabañas, F.; Pellicer, A. Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Dobutamine for Low Superior Vena Cava Flow in Infants. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde, E.; Pellicer, A.; Madero, R.; Elorza, D.; Quero, J.; Cabanas, F. Dopamine versus epinephrine for cardiovascular support in low birth weight infants: Analysis of systemic effects and neonatal clinical outcomes. Pediatrics 2006, 117, e1213–e1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooi, E.M.; Verhagen, E.A.; Elting, J.W.; Czosnyka, M.; Austin, T.; Wong, F.Y.; Aries, M.J.H. Measuring cerebrovascular autoregulation in preterm infants using near-infrared spectroscopy: An overview of the literature. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2017, 17, 801–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruda, F.D. The structure of blood vessels in the germinal matrix and the autoregulation of cerebral blood flow in premature infants. Pediatrics 2001, 108, 1050–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, F.Y.; Leung, T.S.; Austin, T.; Wilkinson, M.; Meek, J.H.; Wyatt, J.S.; Walker, A.M. Impaired autoregulation in preterm infants identified by using spatially resolved spectroscopy. Pediatrics 2008, 121, e604–e611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa, C.S.; Greisen, G.; Austin, T. Is near-infrared spectroscopy clinically useful in the preterm infant? Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2015, 100, F558–F561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Laan, M.E.; Roofthooft, M.T.; Fries, M.W.; Schat, T.E.; Bos, A.F.; Berger, R.M.; Kooi, E.M. Multisite Tissue Oxygenation Monitoring Indicates Organ-Specific Flow Distribution and Oxygen Delivery Related to Low Cardiac Output in Preterm Infants with Clinical Sepsis. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 17, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Laan, M.E.; Schat, T.E.; Olthuis, A.J.; Boezen, H.M.; Bos, A.F.; Kooi, E.M. The Association between Multisite Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Routine Hemodynamic Measurements in Relation to Short-Term Outcome in Preterms with Clinical Sepsis. Neonatology 2015, 108, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Overmeire, B.; Chemtob, S. The pharmacologic closure of the patent ductus arteriosus. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2005, 10, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, N. Preterm patent ductus arteriosus: A continuing conundrum for the neonatologist? Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 20, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonnenberg, I.; de Waal, K. The definition of a haemodynamic significant duct in randomized controlled trials: A systematic literature review. Acta Paediatr. 2012, 101, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, P.J.; Sehgal, A. Towards rational management of the patent ductus arteriosus: The need for disease staging. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2007, 92, F424–F427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagarsamy, S.; Chhabra, M.; Gudavalli, M.; Nadroo, A.M.; Sutija, V.G.; Yugrakh, D. Comparison of clinical criteria with echocardiographic findings in diagnosing PDA in preterm infants. J. Perinat. Med. 2005, 33, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmers, P.M.; Toet, M.C.; van Bel, F. Impact of patent ductus arteriosus and subsequent therapy with indomethacin on cerebral oxygenation in preterm infants. Pediatrics 2008, 121, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dix, L.; Molenschot, M.; Breur, J.; de Vries, W.; Vijlbrief, D.; Groenendaal, F.; van Bel, F.; Lemmers, P. Cerebral oxygenation and echocardiographic parameters in preterm neonates with a patent ductus arteriosus: An observational study. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2016, 101, F520–F526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderhaegen, J.; De Smet, D.; Meyns, B.; Van De Velde, M.; Van Huffel, S.; Naulaers, G. Surgical closure of the patent ductus arteriosus and its effect on the cerebral tissue oxygenation. Acta Paediatr. 2008, 97, 1640–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.; Dix, L.; Baerts, W.; Alderliesten, T.; Lemmers, P.; van Bel, F. Reduction in Cerebral Oxygenation due to Patent Ductus Arteriosus Is Pronounced in Small-for-Gestational-Age Neonates. Neonatology 2017, 111, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Laan, M.E.; Roofthooft, M.T.; Fries, M.W.; Berger, R.M.; Schat, T.E.; van Zoonen, A.G.; Tanis, J.C.; Bos, A.F.; Kooi, E.M. A Hemodynamically Significant Patent Ductus Arteriosus Does Not Affect Cerebral or Renal Tissue Oxygenation in Preterm Infants. Neonatology 2016, 110, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, A.; Bhatt, M.; Mehta, R. Regional tissue oxygenation in preterm born infants in association with echocardiographically significant patent ductus arteriosus. J. Perinatol. 2011, 31, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, C.E.; Preusche, A.; Wolf, M.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Prospective observational study on assessing the hemodynamic relevance of patent ductus arteriosus with frequency domain near-infrared spectroscopy. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naulaers, G.; Delanghe, G.; Allegaert, K.; Debeer, A.; Cossey, V.; Vanhole, C.; Casaer, P.; Devlieger, H.; Van Overmeire, B. Ibuprofen and cerebral oxygenation and circulation. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2005, 90, F75–F76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chock, V.Y.; Rose, L.A.; Mante, J.V.; Punn, R. Near-infrared spectroscopy for detection of a significant patent ductus arteriosus. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 80, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.; Roberts, I.; Azzopardi, D.; Hamilton, P.; Edwards, A.D. Randomized double-blind controlled trial comparing the effects of ibuprofen with indomethacin on cerebral hemodynamics in preterm infants with patent ductus arteriosus. Pediatr. Res. 2000, 47, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dani, C.; Poggi, C.; Cianchi, I.; Corsini, I.; Vangi, V.; Pratesi, S. Effect on cerebral oxygenation of paracetamol for patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2018, 177, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huning, B.M.; Asfour, B.; Konig, S.; Hess, N.; Roll, C. Cerebral blood volume changes during closure by surgery of patent ductus arteriosus. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2008, 93, F261–F264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaramella, P.; Freato, F.; Quaresima, V.; Ferrari, M.; Bartocci, M.; Rubino, M.; Falcon, E.; Chiandetti, L. Surgical closure of patent ductus arteriosus reduces the cerebral tissue oxygenation index in preterm infants: A near-infrared spectroscopy and Doppler study. Pediatr. Int. Off. J. Jpn. Pediatr. Soc. 2006, 48, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmers, P.M.; Molenschot, M.C.; Evens, J.; Toet, M.C.; van Bel, F. Is cerebral oxygen supply compromised in preterm infants undergoing surgical closure for patent ductus arteriosus? Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2010, 95, F429–F434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chock, V.Y.; Ramamoorthy, C.; Van Meurs, K.P. Cerebral oxygenation during different treatment strategies for a patent ductus arteriosus. Neonatology 2011, 100, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmers, P.M.; Benders, M.J.; D’Ascenzo, R.; Zethof, J.; Alderliesten, T.; Kersbergen, K.J.; Isgum, I.; de Vries, L.S.; Groenendaal, F.; van Bel, F. Patent Ductus Arteriosus and Brain Volume. Pediatrics 2016, 137, 20153090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenson, B.; Brocklehurst, P.; Tarnow-Mordi, W. Increased 36-Week Survival with High Oxygen Saturation Target in Extremely Preterm Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1680–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlo, W.A.; Finer, N.N.; Walsh, M.C.; Rich, W.; Gantz, M.G.; Laptook, A.R.; Yoder, B.A.; Faix, R.G.; Das, A.; Poole, W.K.; et al. Target ranges of oxygen saturation in extremely preterm infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.G.; Benitz, W.E.; Madan, A. Retinopathy of prematurity and pulse oximetry: A national survey of recent practices. J. Perinatol. 2004, 24, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- STOP-ROP Multicenter Study Group. Supplemental Therapeutic Oxygen for Prethreshold Retinopathy of Prematurity (STOP-ROP), a randomized, controlled trial. I: Primary outcomes. Pediatrics 2000, 105, 295–310. [Google Scholar]
- Askie, L.M.; Henderson-Smart, D.J.; Irwig, L.; Simpson, J.M. Oxygen-saturation targets and outcomes in extremely preterm infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, B.; Whyte, R.K.; Asztalos, E.V.; Moddemann, D.; Poets, C.; Rabi, Y.; Solimano, A.; Roberts, R.S. Effects of targeting higher vs. lower arterial oxygen saturations on death or disability in extremely preterm infants: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013, 309, 2111–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baerts, W.; Lemmers, P.M.; van Bel, F. Cerebral oxygenation and oxygen extraction in the preterm infant during desaturation: Effects of increasing FiO(2) to assist recovery. Neonatology 2011, 99, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, M.B.; Hopfner, R.J.; Lenhof, S.; Hummler, H.D.; Fuchs, H. Cerebral oxygenation during intermittent hypoxemia and bradycardia in preterm infants. Neonatology 2015, 107, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, A.; Mehta, R. Regional tissue oxygenation in association with duration of hypoxaemia and haemodynamic variability in preterm neonates. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2010, 95, F213–F219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, H.; Takami, T.; Fujioka, T.; Mizukaki, N.; Kondo, A.; Sunohara, D.; Hoshika, A.; Akutagawa, O.; Isaka, K. Comparison of changes in cerebral and systemic perfusion between appropriate- and small-for-gestational-age infants during the first three days after birth. Brain Dev. 2014, 36, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanis, J.C.; Boelen, M.R.; Schmitz, D.M.; Casarella, L.; van derLaan, M.E.; Bos, A.F.; Bilardo, C.M. Correlation between Doppler flow patterns in growth-restricted fetuses and neonatal circulation. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 48, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.; Baerts, W.; Alderliesten, T.; Derks, J.; Lemmers, P.; van Bel, F. Growth restriction and gender influence cerebral oxygenation in preterm neonates. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2016, 101, F156–F161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greisen, G.; Vannucci, R.C. Is periventricular leucomalacia a result of hypoxic-ischaemic injury? Hypocapnia and the preterm brain. Biol. Neonate 2001, 79, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wardle, S.P.; Yoxall, C.W.; Weindling, A.M. Determinants of cerebral fractional oxygen extraction using near infrared spectroscopy in preterm neonates. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2000, 20, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pryds, O.; Greisen, G.; Skov, L.L.; Friis-Hansen, B. Carbon dioxide-related changes in cerebral blood volume and cerebral blood flow in mechanically ventilated preterm neonates: Comparison of near infrared spectrophotometry and 133Xenon clearance. Pediatr. Res. 1990, 27, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietz, V.; Wolf, M.; Keel, M.; v Siebenthal, K.; Baenziger, O.; Bucher, H. CO2 reactivity of the cerebral hemoglobin concentration in healthy term newborns measured by near infrared spectrophotometry. Biol. Neonate 1999, 75, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderhaegen, J.; Naulaers, G.; Vanhole, C.; De Smet, D.; Van Huffel, S.; Vanhaesebrouck, S.; Devlieger, H. The effect of changes in tPCO2 on the fractional tissue oxygen extraction—As measured by near-infrared spectroscopy—In neonates during the first days of life. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. EJPN Off. J. Eur. Paediatr. Neurol. Soc. 2009, 13, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dix, L.M.L.; Weeke, L.C.; de Vries, L.S.; Groenendaal, F.; Baerts, W.; van Bel, F.; Lemmers, P.M.A. Carbon Dioxide Fluctuations Are Associated with Changes in Cerebral Oxygenation and Electrical Activity in Infants Born Preterm. J. Pediatr. 2017, 187, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pryds, A.; Tonnesen, J.; Pryds, O.; Knudsen, G.M.; Greisen, G. Cerebral pressure autoregulation and vasoreactivity in the newborn rat. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 57, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, J.R.; Gauss, C.H.; Williams, D.K. The effects of hypercapnia on cerebral autoregulation in ventilated very low birth weight infants. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 58, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuik, S.J.; van der Laan, M.E.; Brouwer-Bergsma, M.T.; Hulscher, J.B.F.; Absalom, A.R.; Bos, A.F.; Kooi, E.M.W. Preterm infants undergoing laparotomy for necrotizing enterocolitis or spontaneous intestinal perforation display evidence of impaired cerebrovascular autoregulation. Early Hum. Dev. 2018, 118, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, H.V.; Vesoulis, Z.A.; Maheshwari, A.; Rao, R.; Mathur, A.M. Anemia of prematurity and cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy: Should transfusion thresholds in preterm infants be revised? J. Perinatol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dani, C.; Pratesi, S.; Fontanelli, G.; Barp, J.; Bertini, G. Blood transfusions increase cerebral, splanchnic, and renal oxygenation in anemic preterm infants. Transfusion 2010, 50, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dani, C.; Pezzati, M.; Martelli, E.; Prussi, C.; Bertini, G.; Rubaltelli, F.F. Effect of blood transfusions on cerebral haemodynamics in preterm infants. Acta Paediatr. 2002, 91, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baenziger, O.; Stolkin, F.; Keel, M.; von Siebenthal, K.; Fauchere, J.C.; Das Kundu, S.; Dietz, V.; Bucher, H.U.; Wolf, M. The influence of the timing of cord clamping on postnatal cerebral oxygenation in preterm neonates: A randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 2007, 119, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hoften, J.C.; Verhagen, E.A.; Keating, P.; ter Horst, H.J.; Bos, A.F. Cerebral tissue oxygen saturation and extraction in preterm infants before and after blood transfusion. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2010, 95, F352–F358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalteren, W.S.; Kuik, S.J.; Van Braeckel, K.; Hulscher, J.B.F.; Bos, A.F.; Kooi, E.M.W.; van der Laan, M.E. Red Blood Cell Transfusions Affect Intestinal and Cerebral Oxygenation Differently in Preterm Infants with and without Subsequent Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Am. J. Perinatol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkrantz, T.S.; Oh, W. Cerebral blood flow velocity in infants with polycythemia and hyperviscosity: Effects of partial exchange transfusion with Plasmanate. J. Pediatr. 1982, 101, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maertzdorf, W.J.; Tangelder, G.J.; Slaaf, D.W.; Blanco, C.E. Effects of partial plasma exchange transfusion on cerebral blood flow velocity in polycythaemic preterm, term and small for date newborn infants. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1989, 148, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bada, H.S.; Korones, S.B.; Kolni, H.W.; Fitch, C.W.; Ford, D.L.; Magill, H.L.; Anderson, G.D.; Wong, S.P. Partial plasma exchange transfusion improves cerebral hemodynamics in symptomatic neonatal polycythemia. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1986, 291, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergenekon, E.; Hirfanoglu, I.M.; Turan, O.; Beken, S.; Gucuyener, K.; Atalay, Y. Partial exchange transfusion results in increased cerebral oxygenation and faster peripheral microcirculation in newborns with polycythemia. Acta Paediatr. 2011, 100, 1432–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, T.H.; Aynsley-Green, A.; Tarbit, M.; Eyre, J.A. Neural dysfunction during hypoglycaemia. Arch. Dis. Child. 1988, 63, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Davis, A.; Shekhawat, P.S. Hypoglycemia in the preterm neonate: Etiopathogenesis, diagnosis, management and long-term outcomes. Transl.Pediatr. 2017, 6, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerstjens, J.M.; Bocca-Tjeertes, I.F.; de Winter, A.F.; Reijneveld, S.A.; Bos, A.F. Neonatal morbidities and developmental delay in moderately preterm-born children. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e265–e272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, A.; Morley, R.; Cole, T.J. Adverse neurodevelopmental outcome of moderate neonatal hypoglycaemia. BMJ 1988, 297, 1304–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderhaegen, J.; Vanhaesebrouck, S.; Vanhole, C.; Casaer, P.; Naulaers, G. The effect of glycaemia on the cerebral oxygenation in very low birthweight infants as measured by near-infrared spectroscopy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 662, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skov, L.; Pryds, O. Capillary recruitment for preservation of cerebral glucose influx in hypoglycemic, preterm newborns: Evidence for a glucose sensor? Pediatrics 1992, 90, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pryds, O.; Christensen, N.J.; Friis-Hansen, B. Increased cerebral blood flow and plasma epinephrine in hypoglycemic, preterm neonates. Pediatrics 1990, 85, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pellicer, A.; Greisen, G.; Benders, M.; Claris, O.; Dempsey, E.; Fumagalli, M.; Gluud, C.; Hagmann, C.; Hellstrom-Westas, L.; Hyttel-Sorensen, S.; et al. The SafeBoosC phase II randomised clinical trial: A treatment guideline for targeted near-infrared-derived cerebral tissue oxygenation versus standard treatment in extremely preterm infants. Neonatology 2013, 104, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyttel-Sorensen, S.; Austin, T.; van Bel, F.; Benders, M.; Claris, O.; Dempsey, E.; Fumagalli, M.; Greisen, G.; Grevstad, B.; Hagmann, C.; et al. A phase II randomized clinical trial on cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy plus a treatment guideline versus treatment as usual for extremely preterm infants during the first three days of life (SafeBoosC): Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2013, 14, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plomgaard, A.M.; Hagmann, C.; Alderliesten, T.; Austin, T.; van Bel, F.; Claris, O.; Dempsey, E.; Franz, A.; Fumagalli, M.; Gluud, C.; et al. Brain injury in the international multicenter randomized SafeBoosC phase II feasibility trial: Cranial ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging assessments. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 79, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plomgaard, A.M.; Alderliesten, T.; Austin, T.; van Bel, F.; Benders, M.; Claris, O.; Dempsey, E.; Franz, A.; Fumagalli, M.; Gluud, C.; et al. Early biomarkers of brain injury and cerebral hypo- and hyperoxia in the SafeBoosC II trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigshospitalet. Available online: https://www.rigshospitalet.dk/english/departments/juliane-marie-centre/department-of-neonatology/research/SafeBoosC-III/Sider/default.aspx (accessed on 8 July 2018).



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garvey, A.A.; Kooi, E.M.W.; Smith, A.; Dempsey, E.M. Interpretation of Cerebral Oxygenation Changes in the Preterm Infant. Children 2018, 5, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/children5070094
Garvey AA, Kooi EMW, Smith A, Dempsey EM. Interpretation of Cerebral Oxygenation Changes in the Preterm Infant. Children. 2018; 5(7):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/children5070094
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarvey, Aisling A., Elisabeth M. W. Kooi, Aisling Smith, and Eugene M. Dempsey. 2018. "Interpretation of Cerebral Oxygenation Changes in the Preterm Infant" Children 5, no. 7: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/children5070094
APA StyleGarvey, A. A., Kooi, E. M. W., Smith, A., & Dempsey, E. M. (2018). Interpretation of Cerebral Oxygenation Changes in the Preterm Infant. Children, 5(7), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/children5070094



