Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Children: A Retrospective Study of 419 Cases and Polysomnographic Findings with Implications for Rapid Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Mild form of SRBD; AHI from 1 to 5.
- Moderate form of SRBD; AHI from 5 to 10.
- Severe form of SRBD; AHI above 10.
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
- Very strong positive correlation between the AHI and ODI variables (r = 0.829; p = 0.000).
- Strong negative correlation between the AHI and minimum saturation variables (r = −0.594; p = 0.000).
- Strong positive correlation between the AHI and time below 89% (r = 0.536; p = 0.000).
- Strong negative correlation between the AHI and average saturation variables (r = −0.324; p = 0.000).
- Moderate negative correlation between the AHI and rem% variables (r = −0.129; p = 0.009).
- This study demonstrated that there were 334 children with tonsillar hyperplasia. In order to determine the scale of this condition, the total number of surgeries performed for tonsillar hyperplasia at our hospital clinic was checked from 2017 to 2024 and found to be 5640. Children with suspected sleep apnea (n = 334) thus constituted 5.92% of this group.
| AHI Correlations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Variable | r | p |
| Age | −0.003 | 0.957 |
| BMI | 0.008 | 0.939 |
| Apnea | 0.911 | 0.000 |
| AH | 0.985 | 0.000 |
| Snoring (%) | 0.040 | 0.672 |
| ODI | 0.829 | 0.000 |
| Av. Saturation | −0.324 | 0.000 |
| Min. Saturation | −0.594 | 0.000 |
| Time below 89% | 0.536 | 0.000 |
| REM% | −0.129 | 0.009 |
| n1% | 0.040 | 0.421 |
| n2% | 0.072 | 0.149 |
| n3% | −0.074 | 0.136 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHI | Apnea–Hypopnea Index |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| EOG | Electrooculogram |
| EMG | Electromyogram |
| RDI | Respiratory Disturbance Index |
| ODI | Oxygen Desaturation Index |
| SRBD | Sleep-related breathing disorder |
References
- White, D.P. Pathogenesis of obstructive and central sleep apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaleel, Z.; Schaeffer, T.; Trinh, C.; Cohen, M.B.; Levi, J.R. Prematurity: A Prognostic Factor for Increased Severity of Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, L.M.; Tamanyan, K.; Weichard, A.J.; Davey, M.J.; Nixon, G.M.; Horne, R.S.C. Sleep Disordered Breathing in Children Disrupts the Maturation of Autonomic Control of Heart Rate and Its Association with Cerebral Oxygenation. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez Cuevas, E.; Muñoz Peláez, C.; Ordax Carbajo, E.; Navazo Eguia, A.I.; Martín Viñe, L.; Prieto Jimeno, A.; Alonso-Álvarez, M.L. Sleep Apnoea-Hypopnoea Syndrome in the Obese and Non-Obese: Clinical, Polysomnographical and Clinical Characteristics. An. Pediatr. 2021, 95, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Harmon, H.; Slaven, J.E.; Daftary, A.S. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes at Two Years of Age for Premature Infants Diagnosed with Neonatal Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilleminault, C.; Huang, Y.-S.; Kirisoglu, C.; Chan, A. Is Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome a Neurological Disorder? A Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Follow-up Study. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 58, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.L.; Goldberg, A.N.; Alt, J.A.; Mohammed, A.; Ashbrook, L.; Auckley, D.; Ayappa, I.; Bakhtiar, H.; Barrera, J.E.; Bartley, B.L.; et al. International Consensus Statement on Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2023, 13, 1061–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medical Advisory Secretariat. Polysomnography in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An Evidence-Based Analysis. Ont. Health Technol. Assess. Ser. 2006, 6, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb, D.J.; Punjabi, N.M. Diagnosis and Management of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Review: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukwa, W.; Guilleminault, C.; Tomaszewska, M.; Kukwa, A.; Krzeski, A.; Migacz, E. Prevalence of Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Habitually Snoring and Mouth Breathing Children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 107, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izu, S.C.; Itamoto, C.H.; Pradella-Hallinan, M.; Pizarro, G.U.; Tufik, S.; Pignatari, S.; Fujita, R.R. Ocorrência Da Síndrome Da Apneia Obstrutiva Do Sono (SAOS) Em Crianças Respiradoras Orais. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 76, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Ríos, J.A.; Ramírez-Hernández, E.; Vázquez-Rodríguez, E.M.; Vázquez-Nava, F. Asthma-associated oral and dental health repercussions in children aged 6 to 12 years. Rev. Alerg. Mex. 2017, 64, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Celestin, J.; Lockey, R.F. Pediatric Sleep Apnea Syndrome: An Update. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2016, 4, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, T.M. The Great Leap Forward: The Anatomic Basis for the Acquisition of Speech and Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Sleep Med. 2003, 4, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Tai, J.; Feng, G.; Ge, W.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, Z.; Ni, X. Risk Factors of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Children. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 49, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, S.N.; Nixon, G.M.; Horne, R.S.C. The Conundrum of Primary Snoring in Children: What Are We Missing in Regards to Cognitive and Behavioural Morbidity? Sleep Med. Rev. 2014, 18, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhao, T.; Qin, D.; Hua, F.; He, H. The Impact of Mouth Breathing on Dentofacial Development: A Concise Review. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 929165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Ou, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, S. Sleep Disordered Breathing and Neurobehavioral Deficits in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Pediatr. 2024, 24, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.B.; Archer, S.M.; Ishman, S.L.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Coles, S.; Finestone, S.A.; Friedman, N.R.; Giordano, T.; Hildrew, D.M.; Kim, T.W.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Tonsillectomy in Children (Update)-Executive Summary. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 160, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshuroon-Koffler, K.; Shemer-Avni, Y.; Keren-Naus, A.; Goldbart, A.D. Detection of Common Respiratory Viruses in Tonsillar Tissue of Children with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Viruses and Hypertrophic Tonsils in Children with OSA. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2015, 50, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannella, G.; Magliulo, G.; Greco, A.; de Vincentiis, M.; Ralli, M.; Maniaci, A.; Pace, A.; Vicini, C. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: From Symptoms to Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaoussoglou, M.; Hatzinikolaou, S.; Baltatzis, G.E.; Lianou, L.; Maragozidis, P.; Balatsos, N.A.A.; Chrousos, G.; Kaditis, A.G. Expression of Leukotriene Biosynthetic Enzymes in Tonsillar Tissue of Children with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Prospective Nonrandomized Study: A Prospective Nonrandomized Study. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 140, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson, E.; Lundeborg, I.; Hultcrantz, E. Child Behavior and Quality of Life before and after Tonsillotomy versus Tonsillectomy. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 73, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, R.A., Jr.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Rao, M. First Place–Resident Clinical Science Award 1999. Quality of Life for Children with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2000, 123, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, K.A.; Lindberg, E. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Is a Common Disorder in the Population-a Review on the Epidemiology of Sleep Apnea. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, E.V.; Kadhiravan, T.; Mishra, H.K.; Sreenivas, V.; Handa, K.K.; Sinha, S.; Sharma, S.K. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Obstructive Sleep Apnea among Middle-Aged Urban Indians: A Community-Based Study. Sleep Med. 2009, 10, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosten, K.F.; van den Berg, S. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in children. Ned. Tijdschr. Geneeskd. 1998, 142, 2665–2669. [Google Scholar]
- Varghese, L.; Rebekah, G.; Priya, N.; Oliver, A.; Kurien, R. Oxygen desaturation index as alternative parameter in screening patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Sci. 2022, 15, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuźmińska, M.; Walicka, M.; Sawicka, A.; Kukwa, W.; Marcinowska-Suchowierska, E. Average and minimum oxygen saturation in patients with suspected OSA as a disease severity index in polysomnographic evaluation. Postępy Nauk. Med. 2016, XXIX, 64–70. Available online: http://www.pnmedycznych.pl/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/pnm_2016_064-070.pdf (accessed on 26 January 2025).
- Simmonds, M.; Burch, J.; Llewellyn, A.; Griffiths, C.; Yang, H.; Owen, C.; Duffy, S.; Woolacott, N. The use of measures of obesity in childhood for predicting obesity and the development of obesity-related diseases in adulthood: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Technol. Assess. 2015, 19, 1–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abel, F.; Tan, H.L.; Negro, V.; Bridges, N.; Carlisle, T.; Chan, E.; Laverty, A.; Miligkos, M.; Samuels, M.; Kaditis, A.G. Hypoventilation disproportionate to OSAS severity in children with Prader-Willi syndrome. Arch. Dis. Child. 2019, 104, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliendo, C.; Femiano, R.; Umano, G.R.; Martina, S.; Nucci, L.; Perillo, L.; Grassia, V. Effect of Obesity on the Respiratory Parameters in Children with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Children 2023, 10, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglia, L.; Friuli, S.; Colombo, S.; Paglia, M. The effect of added sugars on children’s health outcomes: Obesity, Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (OSAS), Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Chronic Diseases. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2019, 20, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passali, D.; Passali, F.M.; Cambi, J.; Bellussi, L. Role of adenotonsillectomy in OSAS children and behavioural disturbance. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2013, 67, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, E.T.W.; Au, C.T.; Chan, R.N.C.; Chan, J.W.Y.; Chan, N.Y.; Wing, Y.K.; Li, A.M.; Lam, E.; Chan, K.C. Ferritin Is a Potential Marker of Cardiometabolic Risk in Adolescents and Young Adults with Sleep-Disordered Breathing. Sleep Adv. 2024, 5, zpae048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.M.; Au, C.T.; Ho, C.; Fok, T.F.; Wing, Y.K. Blood Pressure Is Elevated in Children with Primary Snoring. J. Pediatr. 2009, 155, 362–368.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xing, Y.; Wan, W. Meta-Analysis: Characteristics of Retinal Vasculature in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome Humans. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 2024, 4600428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

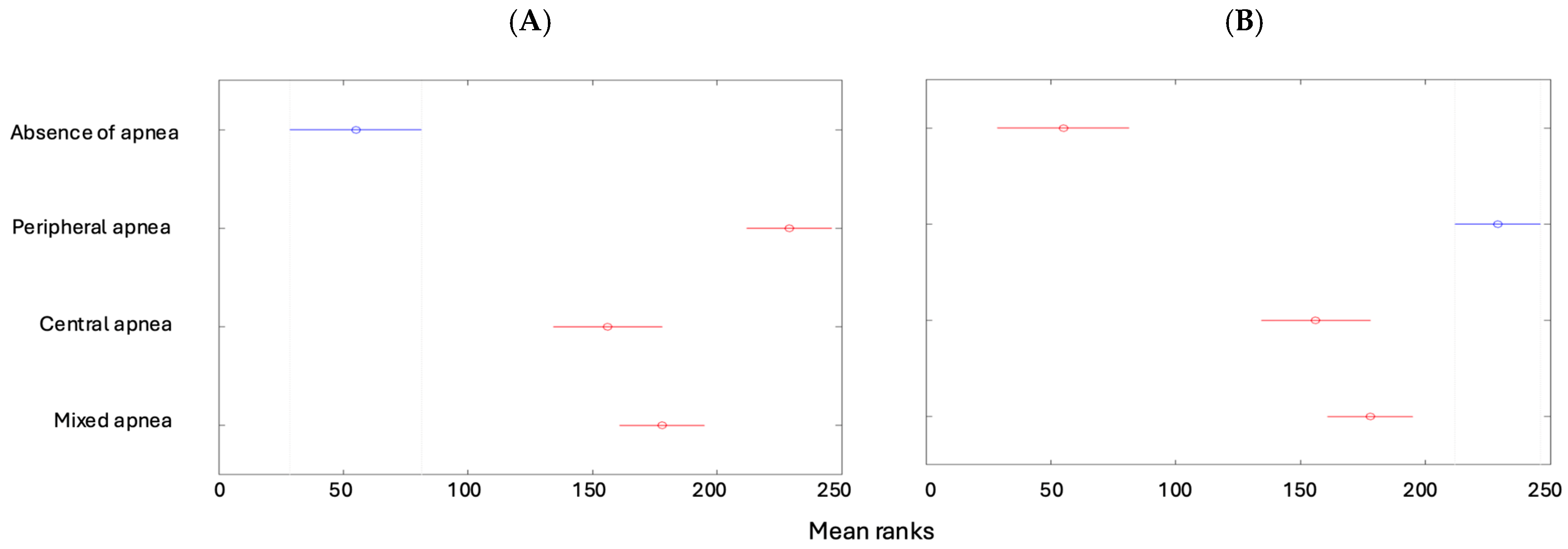
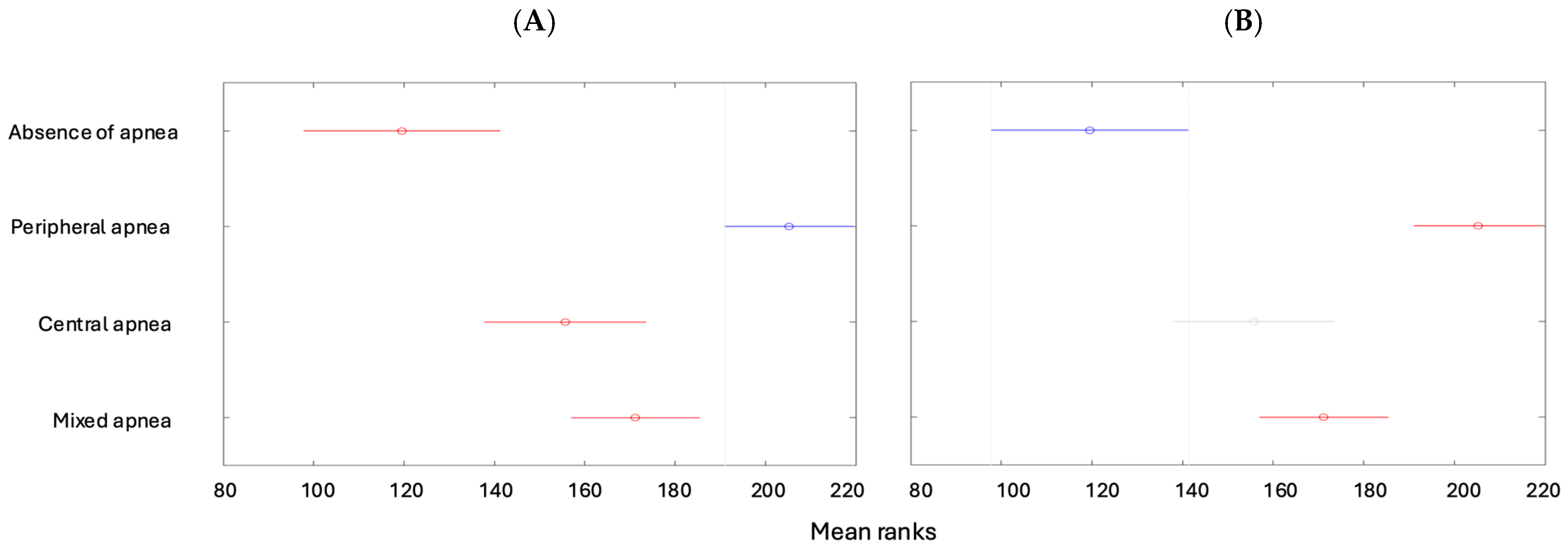
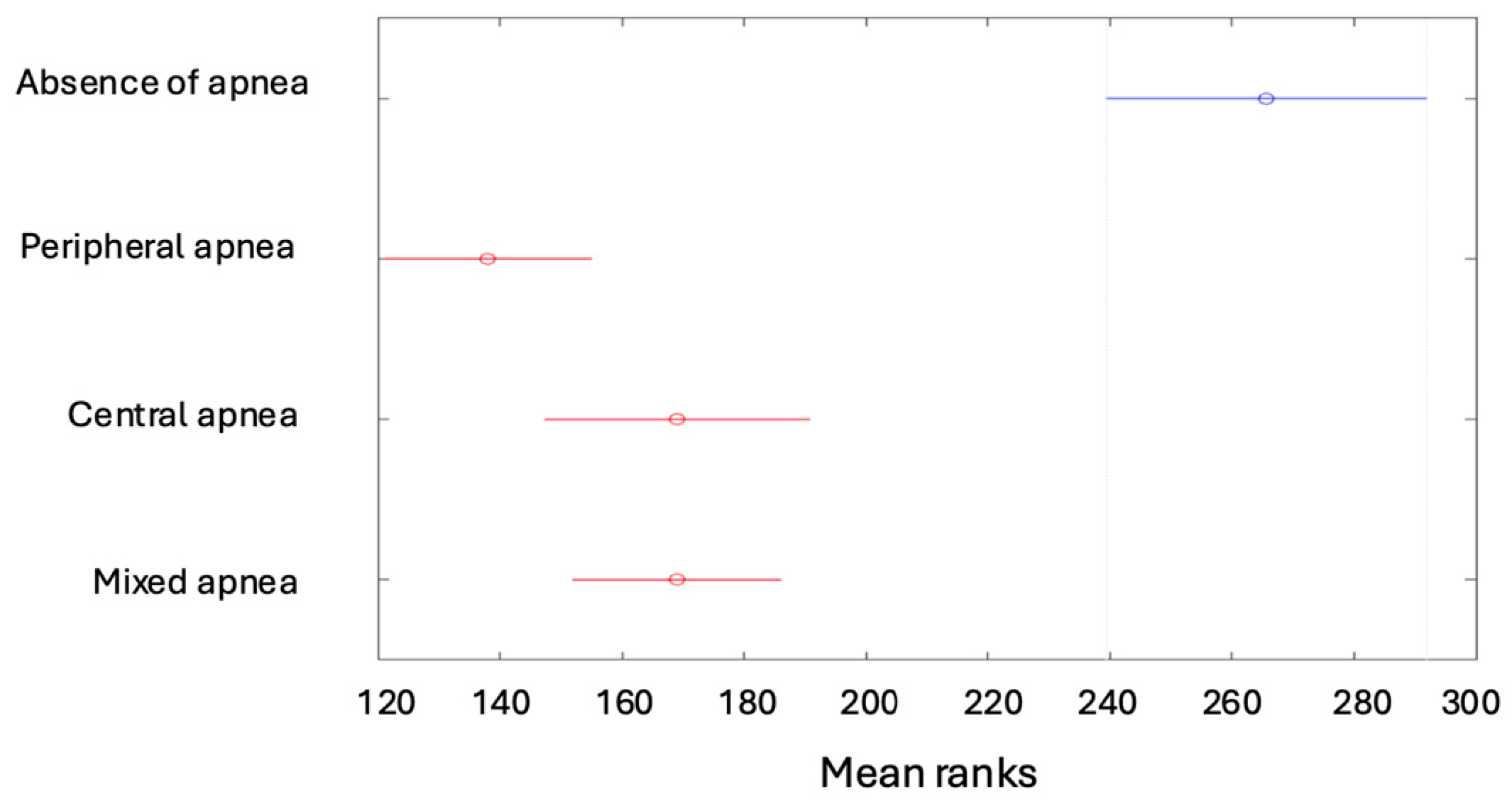

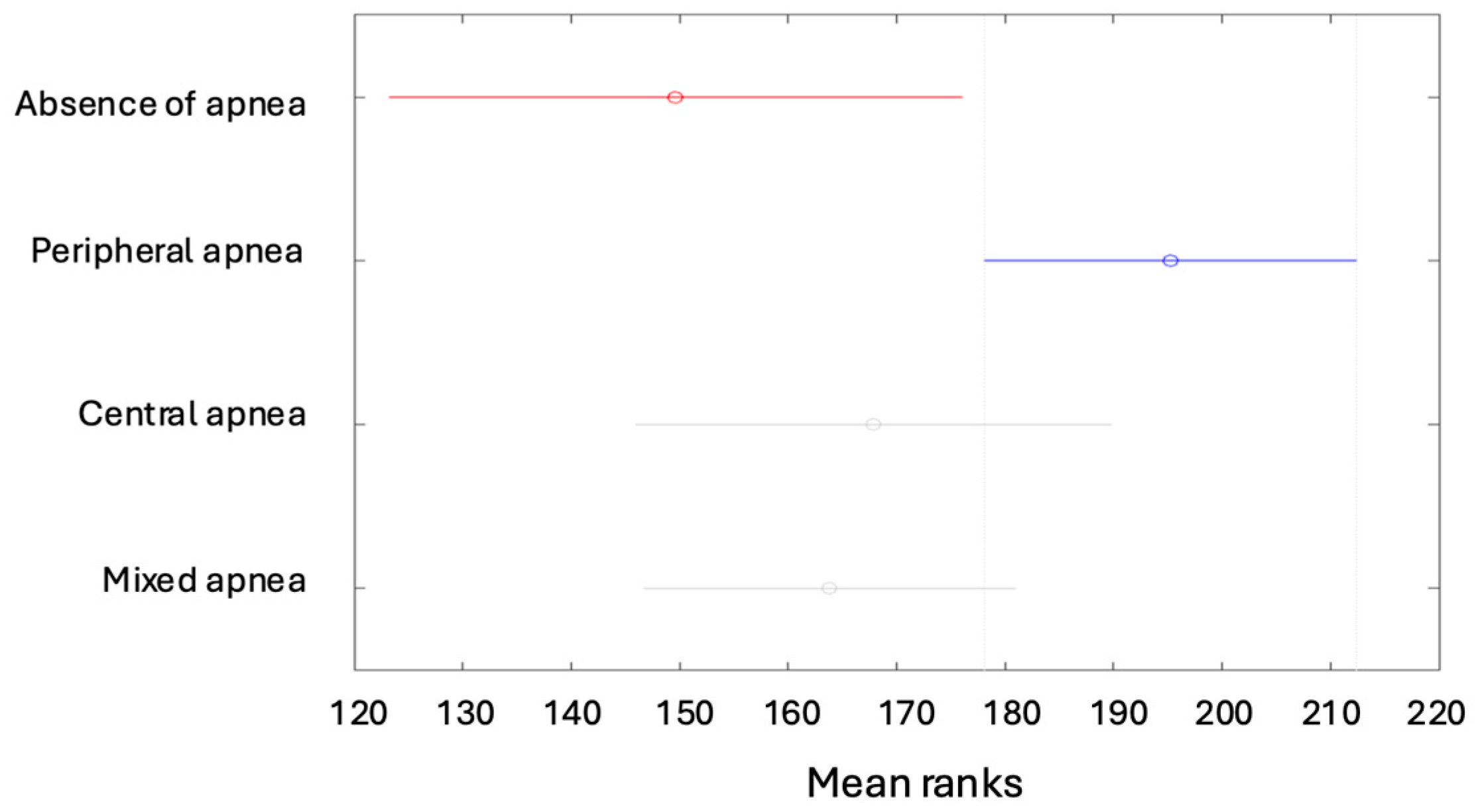
| Min | Max | Median | Average | Standard Deviation | Kurtosis | Skewness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.00 | 17.00 | 4.00 | 4.98 | 2.91 | 6.25 | 1.57 |
| BMI | 8.90 | 33.50 | 15.90 | 17.34 | 4.69 | 5.68 | 1.65 |
| AH (index) | 1.00 | 808.00 | 28.00 | 56.22 | 94.94 | 27.78 | 4.48 |
| Snoring (%) | 0.00 | 23.60 | 0.60 | 2.12 | 4.32 | 16.93 | 3.66 |
| AHI | 0.20 | 103.50 | 3.60 | 7.27 | 12.12 | 26.73 | 4.35 |
| ODI | 0.00 | 92.10 | 1.20 | 3.76 | 9.25 | 42.29 | 5.65 |
| Average saturation | 0.95 | 98.90 | 97.80 | 97.19 | 4.95 | 345.88 | −17.92 |
| Minimum saturation | 51.00 | 98.00 | 91.00 | 89.42 | 5.60 | 10.91 | −2.31 |
| Time below 89% (min) | 0.00 | 385.10 | 0.00 | 2.47 | 20.50 | 295.17 | 16.15 |
| rem% | 0.00 | 25.10 | 6.70 | 7.81 | 4.79 | 3.30 | 0.83 |
| n1% | 3.10 | 63.50 | 19.40 | 19.15 | 7.25 | 9.66 | 1.51 |
| n2% | 4.40 | 91.10 | 56.75 | 56.54 | 8.31 | 8.93 | −0.72 |
| n3% | 0.40 | 40.60 | 16.35 | 16.49 | 5.26 | 5.88 | 0.85 |
| Absent [1] | Mild Form [2] | Moderate Form [3] | Severe Form [4] | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
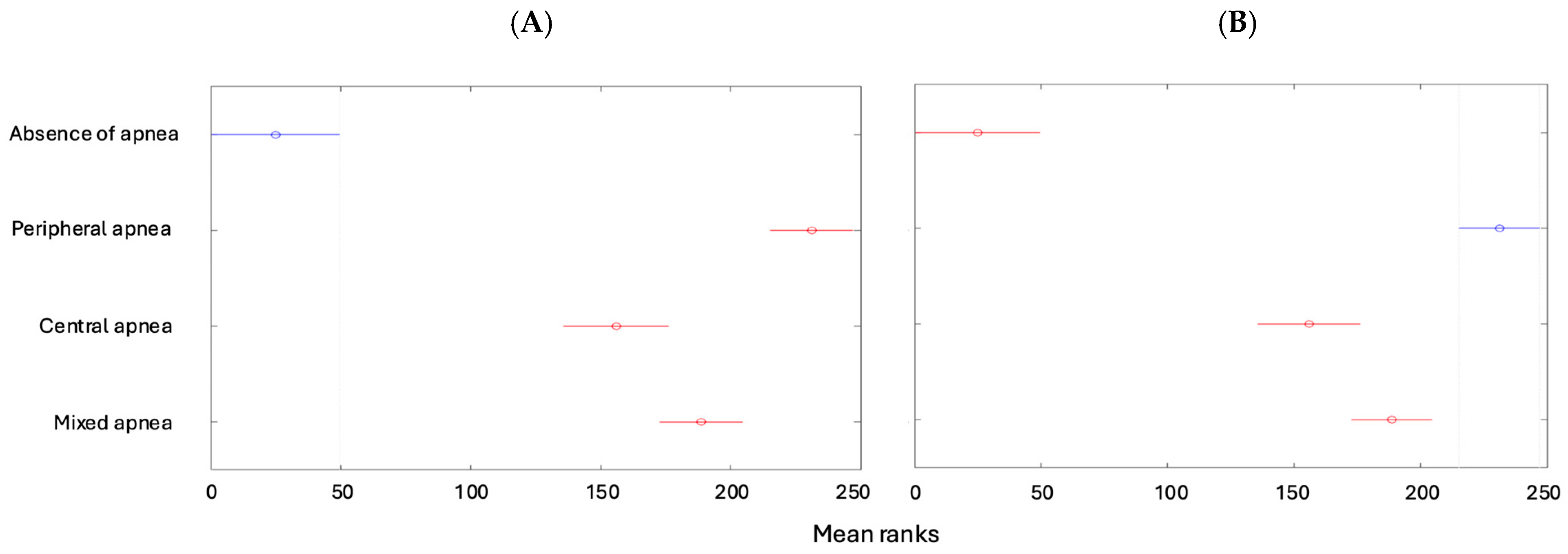
| Absence of apnea | 50 (11.93%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 (11.93%) |
| Peripheral apnea | 0 | 43 (10.26%) | 40 (9.55%) | 33 (7.88%) | 116 (27.68%) |
| Central apnea | 0 | 107 (25.54%) | 22 (5.25%) | 4 (0.95%) | 133 (31.74%) |
| Mixed apnea | 0 | 73 (17.42%) | 40 (9.55%) | 7 (1.67%) | 120 (28.64%) |
| Total | 50 (11.93%) | 223 (53.22%) | 102 (24.34%) | 44 (10.50%) | 419 (100%) |
| Absence | Mild Form | Moderate Form | Severe Form | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
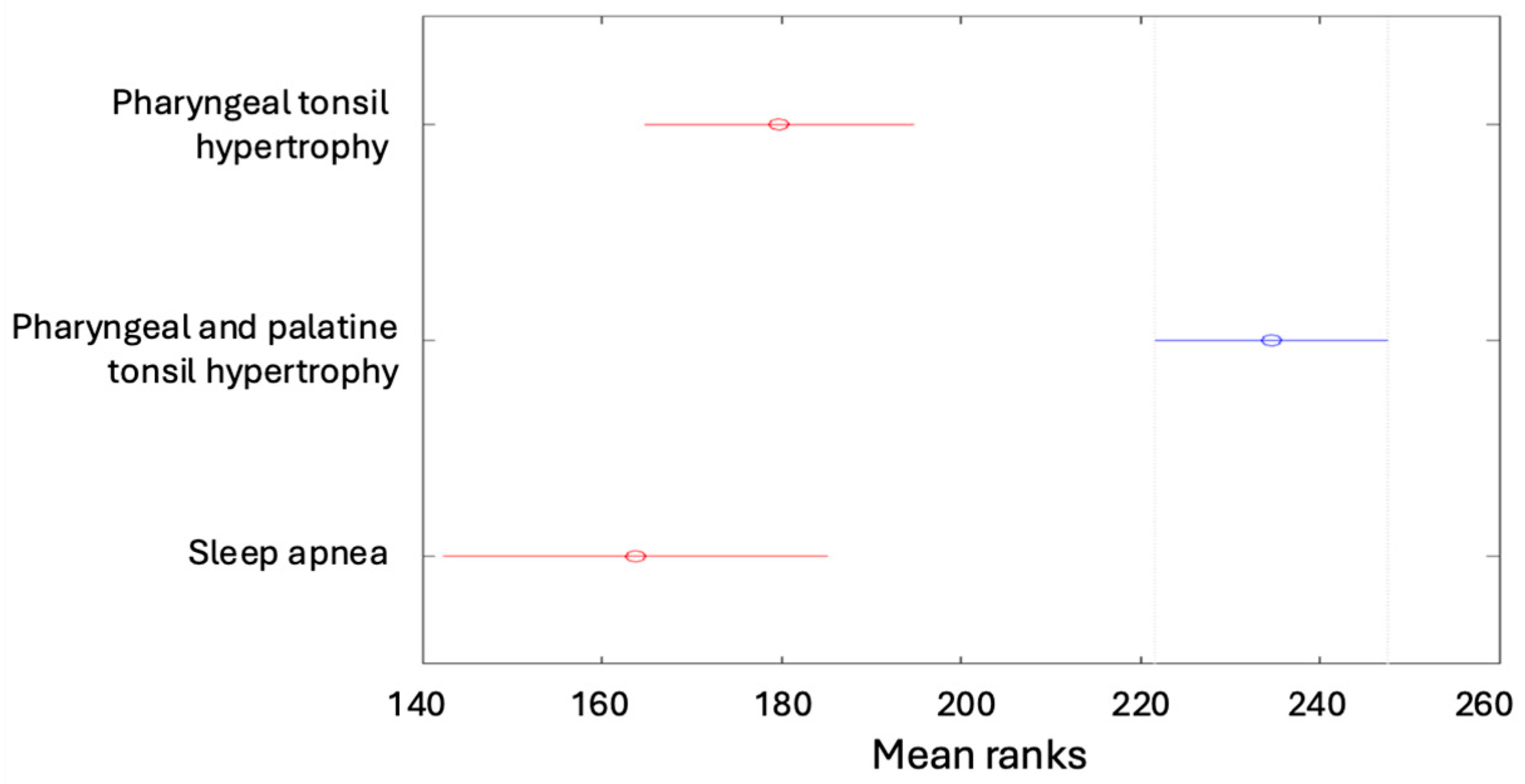
| Pharyngeal tonsil hypertrophy | 19 (4.53%) | 19 (4.53%) | 26 (6.21%) | 7 (1.67%) | 136 (32.46%) |
| Pharyngeal and palatine tonsil hypertrophy | 13 (3.10%) | 82 (19.57%) | 58 (13.84%) | 31 (7.4%) | 184 (43.91%) |
| Palatine tonsil hypertrophy | 1 (0.24%) | 6 (1.43%) | 4 (0.95%) | 2 (0.48%) | 13 (3.10%) |
| Developmental defects | 1 (0.24%) | 2 (0.48%) | 0 | 0 | 3 (0.72%) |
| Sleep apnea | 16 (3.82%) | 42 (10.02%) | 11 (2.63%) | 4 (0.95%) | 73 (17.42%) |
| Chronic sinusitis | 0 | 5 (1.19%) | 0 | 0 | 5 (1.19%) |
| Deviated nasal septum | 0 | 2 (0.48%) | 1 (0.24%) | 0 | 3 (0.72%) |
| Nasal turbinate hypertrophy | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.24%) | 0 | 1 (0.24%) |
| Pharyngeal and palatine tonsil hypertrophy and developmental defects | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.24%) | 0 | 1 (0.24%) |
| Total | 50 (11.93%) | 223 (53.22%) | 102 (24.34%) | 44 (10.50%) | 419 (100%) |
| Absence | Peripheral Apnea | Central Apnea | Mixed Apnea | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
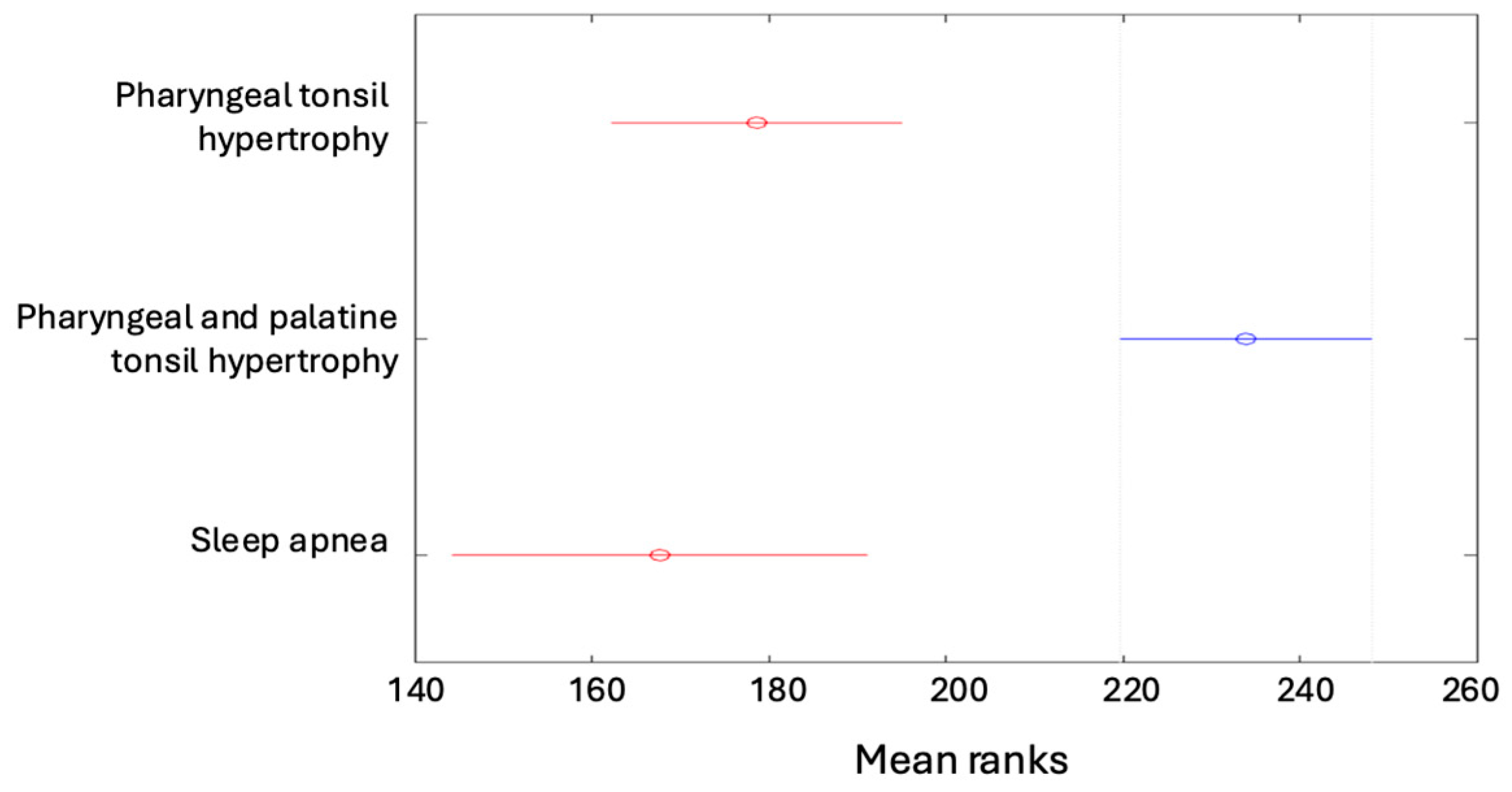
| Pharyngeal tonsil hypertrophy | 19 (4.53%) | 26 (6.21%) | 47 (11.22%) | 44 (10.5%) | 136 (32.46%) |
| Pharyngeal and palatine tonsil hypertrophy | 13 (3.1%) | 82 (19.57%) | 35 (8.35%) | 54 (12.89%) | 184 (43.91%) |
| Palatine tonsil hypertrophy | 1 (0.24%) | 3 (0.72%) | 2 (0.48%) | 7 (1.67%) | 13 (3.10%) |
| Developmental defects | 1 (0.24%) | 0 | 1 (0.24%) | 1 (0.24%) | 3 (0.72%) |
| Sleep apnea | 16 (3.82%) | 3 (0.72%) | 45 (10.74%) | 9 (2.15%) | 73 (17.42%) |
| Chronic sinusitis | 0 | 0 | 2 (0.48%) | 3 (0.72%) | 5 (1.19%) |
| Deviated nasal septum | 0 | 1 (0.24%) | 1 (0.24%) | 1 (0.24%) | 3 (0.72%) |
| Nasal turbinate hypertrophy | 0 | 1 (0.24%) | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.24%) |
| Pharyngeal and palatine tonsil hypertrophy and developmental defects | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.24%) | 1 (0.24%) |
| Total | 50 (11.93%) | 116 (27.68%) | 133 (31.74%) | 120 (28.64%) | 419 (100%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chmielik, L.P.; Kasprzyk, A.; Sala, Z.; Chmielik, T.; Hatliński, G.J.; Mielnik-Niedzielska, G.; Niedzielski, A. Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Children: A Retrospective Study of 419 Cases and Polysomnographic Findings with Implications for Rapid Treatment. Children 2025, 12, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12020222
Chmielik LP, Kasprzyk A, Sala Z, Chmielik T, Hatliński GJ, Mielnik-Niedzielska G, Niedzielski A. Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Children: A Retrospective Study of 419 Cases and Polysomnographic Findings with Implications for Rapid Treatment. Children. 2025; 12(2):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12020222
Chicago/Turabian StyleChmielik, Lechosław Paweł, Anna Kasprzyk, Zuzanna Sala, Tadeusz Chmielik, Grzegorz Jacek Hatliński, Grażyna Mielnik-Niedzielska, and Artur Niedzielski. 2025. "Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Children: A Retrospective Study of 419 Cases and Polysomnographic Findings with Implications for Rapid Treatment" Children 12, no. 2: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12020222
APA StyleChmielik, L. P., Kasprzyk, A., Sala, Z., Chmielik, T., Hatliński, G. J., Mielnik-Niedzielska, G., & Niedzielski, A. (2025). Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Children: A Retrospective Study of 419 Cases and Polysomnographic Findings with Implications for Rapid Treatment. Children, 12(2), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12020222







