Sensory Processing of Time and Space in Autistic Children
Abstract
Highlights
- Autistic children showed slower reaction times across visual temporal, auditory temporal, and visuospatial tasks, reflecting a speed processing deficit
- Despite slower responses, autistic children demonstrated higher accuracy in visual and auditory temporal tasks, indicating a strength in temporal integration
- Autism reflects a preference for accuracy over speed, underscoring the need for interventions that alleviate time pressure and promote structured, slower-paced environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Sensory Processing in Autism
1.2. Spatial and Temporal Perception Modalities Challenges
1.3. Sensory Processing Through Spatial-Temporal Modalities
1.4. Importance of Early Identification and Intervention
1.5. Research Objectives and Hypothesis
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.2.1. Processing Tasks
2.2.2. Visual Temporal Processing Task
2.2.3. Auditory Temporal Processing Task
2.2.4. Visuospatial Processing Task
2.3. Data Recording and Analysis and Community Involvement
3. Results
Summary of Hypotheses and Findings
4. Discussion
4.1. Practical Implications for Interventions, Education, and Daily Life
4.2. Future Research Implications Regarding the Digital Life
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrowski, J.; Religioni, U.; Gellert, B.; Sytnik-Czetwertyński, J.; Pinkas, J. Autism Spectrum Disorders: Etiology, Epidemiology, and Challenges for Public Health. Med. Sci. Monit. 2024, 30, e944161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchin, M.E.B. El Vínculo Afecto-Lenguaje-Invariabilidad en el Autismo Infantil Precoz: Aporte para una Redescripción y Ajuste del Fenómeno Autístico. Ph.D. Dissertation, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba (UNC), Córdoba, Argentina, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Happé, F.; Frith, U. Annual Research Review: Looking Back to Look Forward—Changes in the Concept of Autism and Implications for Future Research. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2020, 61, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5TM, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-89042-554-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, J.K.; Geier, D.A.; Sykes, L.K.; Geier, M.R. Evidence of Neurodegeneration in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Transl. Neurodegener. 2013, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvão, M.C.B.; Ricarte, I.L.M. A Classificação Internacional de Doenças e Problemas Relacionados à Saúde (CID-11): Características, inovações e desafios para implementação. Asklep. Informação Saúde 2021, 1, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.M.; Monteiro, P. Autism Spectrum Disorder and Auditory Sensory Alterations: A Systematic Review on the Integrity of Cognitive and Neuronal Functions Related to Auditory Processing. J. Neural Transm. 2023, 130, 325–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. ICD-11: International Classification of Diseases, 11th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Camarata, S.; Miller, L.J.; Wallace, M.T. Evaluating Sensory Integration/Sensory Processing Treatment: Issues and Analysis. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 556660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigh, S.M. Variable Sensory Perception in Autism. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 47, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemann, J.K.; Veenstra-VanderWeele, J.; Wallace, M.T. Approaches to Understanding Multisensory Dysfunction in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. 2020, 13, 1430–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeld, J.; Hagström, A.; Van’t Westeinde, A.; Lundin, K.; Cauvet, É.; Willfors, C.; Isaksson, J.; Lichtenstein, P.; Bölte, S. Global and Local Visual Processing in Autism—A Co-Twin-Control Study. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2020, 61, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, C.; Seernani, D.; Stefanou, M.E.; Biscaldi-Schaefer, M.; Tebartz Van Elst, L.; Fleischhaker, C.; Boccignone, G.; Klein, C. Social Visual Perception Under the Eye of Bayesian Theories in Autism Spectrum Disorder Using Advanced Modeling of Spatial and Temporal Parameters. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 585149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, L.; Van Den Bos, N.; Houwen, S.; Schoemaker, M.M.; Rosenblum, S. Motor Skills, Visual Perception, and Visual-Motor Integration in Children and Youth with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2022, 96, 101998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farashi, S.; Jenabi, E.; Bashirian, S.; Fayyazi, A.; Rezaei, M.; Razjouyan, K. Differences Between Autism Spectrum Disorder and Typically Developing Individuals During Visual Information Processing—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Focusing on Visual Event-Related Potentials. Rev. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2025, 12, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, M.; Constantin, L.; Thorne, P.R.; Montgomery, J.M.; Scott, E.K.; Cheyne, J.E. Auditory Processing in Rodent Models of Autism: A Systematic Review. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2022, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.; Son, J.-W. Visual Perception in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Review of Neuroimaging Studies. J. Korean Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2020, 31, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gignac, G.E.; Palermo, R.; Bothe, E.; Walker, D.L.; Wilmer, J.B. Face Perception and Facial Emotional Expression Recognition Ability: Both Unique Predictors of the Broader Autism Phenotype. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2024, 77, 1140–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tola, G.; Talu, V.; Congiu, T.; Bain, P.; Lindert, J. Built Environment Design and People with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.; Abreu, A.M. Sensory Processing and Occupational Participation. J. Occup. Ther. Sch. Early Interv. 2023, 16, 480–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, A.M. Relação Entre Anomalias No Processamento Visual e o Comportamento Social Em Crianças Com Perturbações Do Espectro Do Autismo e Síndrome de Williams. Rev. Educ. Espec. Reabil. 2009, 16, 19–38. [Google Scholar]
- Abreu, A.M.; Soares, J.; De Schonen, S.; Happé, F. Motion Perception and Social Cognition in Autism: Speed Selective Impairments in Socio-Conceptual Processing? J. Adv. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 3, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, A.M.; Schonen, S.D. Heterogeneity in Motion Perception Deficits in Developmental Disorders: Evidence from Autism and Williams Syndrome. Cad. Saúde 2009, 2, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroor, G.; Mokhtari, S.; Pouretemad, H. Priming Global Processing Strategy Improves the Perceptual Performance of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2022, 52, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuno-Fujita, A.; Iwabuchi, T.; Wakusawa, K.; Ito, H.; Suzuki, K.; Shigetomi, A.; Hirotaka, K.; Tsujii, M.; Tsuchiya, K.J. Sensory Processing Patterns and Fusiform Activity During Face Processing in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. 2020, 13, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åkerlund, S.; Håkansson, A.; Claesdotter-Knutsson, E. An Auditory Processing Advantage Enables Communication in Less Complex Social Settings: Signs of an Extreme Female Brain in Children and Adolescents Being Assessed for Autism Spectrum Disorders. Front. Psychol. 2023, 13, 1068001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.K.; Kraus, N.; Bonacina, S.; Nicol, T.; Otto-Meyer, S.; Roberts, M.Y. Auditory Processing Differences in Toddlers with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2020, 63, 1608–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotschafer, S.E. Auditory Discrimination in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 651209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, E.C.; Mathews, L.; Gopal, K.; Canale, E.; Creech, A.; Manning, J.; Kaiser, K. Behavioral Auditory Processing in Children and Young Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2020, 31, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Stocker, A.A. Sensory Perception Is a Holistic Inference Process. Psychol. Rev. 2024, 131, 858–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorquera-Cabrera, S.; Romero-Ayuso, D.; Rodriguez-Gil, G.; Triviño-Juárez, J.-M. Assessment of Sensory Processing Characteristics in Children between 3 and 11 Years Old: A Systematic Review. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaciai, M. Sensory Mechanisms for the Processing of Spatial, Temporal and Numerical Information. Ph.D. Thesis, Università degli Studi di Firenze, Firenze, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- He, T.; Richter, D.; Wang, Z.; De Lange, F.P. Spatial and Temporal Context Jointly Modulate the Sensory Response within the Ventral Visual Stream. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2022, 34, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C.E.; Baron-Cohen, S. Sensory Perception in Autism. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoni, N.; Ricciardelli, P.; Actis-Grosso, R.; Venuti, P. Difficulties in Recognising Dynamic but Not Static Emotional Body Movements in Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2022, 52, 1092–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hus, Y. Detecting Time Concept Competence in Children with Autism Spectrum and Attention Disorders. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2022, 18, 2323–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaughnessy, N. Learning with Labyrinths: Neurodivergent Journeying towards New Concepts of Care and Creative Pedagogy through Participatory Community Autism Research. Crit. Stud. Teach. Learn. 2022, 10, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agron, A.M.; Martin, A.; Gilmore, A.W. Scene Construction and Autobiographical Memory Retrieval in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. 2024, 17, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meilleur, A.; Foster, N.E.V.; Coll, S.-M.; Brambati, S.M.; Hyde, K.L. Unisensory and Multisensory Temporal Processing in Autism and Dyslexia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 116, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanglakh Ghoochan Atigh, A.; Joghataei, M.T.; Moradkhani, S.; Alizadeh Zarei, M.; Nazari, M.A. Early Auditory Temporal Processing Deficit in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: The Research Domain Criteria Framework. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Ghafar, M.A.; Abdelraouf, O.R.; Abdelgalil, A.A.; Seyam, M.K.; Radwan, R.E.; El-Bagalaty, A.E. Quantitative Assessment of Sensory Integration and Balance in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: Cross-Sectional Study. Children 2022, 9, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svancara, A.M.; Kana, R.; Bednarz, H.; Sherrod, G.; Visscher, K.; McManus, B.; Stavrinos, D. Time-to-Collision Estimations in Young Drivers with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2022, 52, 3933–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freschl, J.; Melcher, D.; Carter, A.; Kaldy, Z.; Blaser, E. Seeing a Page in a Flipbook: Shorter Visual Temporal Integration Windows in 2-Year-Old Toddlers with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. 2021, 14, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, A.P.; D’Ambrose Slaboch, K. Speech Processing in Autism Spectrum Disorder: An Integrative Review of Auditory Neurophysiology Findings. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2021, 64, 4192–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.A.L.; Petrulla, V.; Zampella, C.J.; Waller, R.; Schultz, R.T. Gross Motor Impairment and Its Relation to Social Skills in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Two Meta-Analyses. Psychol. Bull. 2022, 148, 273–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, M.; Skrimpa, V. Theory of Mind Deficits and Neurophysiological Operations in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Review. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.S.; Ding, Z.; Lee, T.; Sze, S.L.; Cheung, M.-C. Temporal Processing Deficit in Children and Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder: An Online Assessment. Digit. Health 2023, 9, 20552076231171500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, S.; Otsuka, S. Multisensory Processing in Autism Spectrum Disorders. In Autism Spectrum Disorders; Grabrucker, A.M., Ed.; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2021; ISBN 978-0-6450017-8-5. [Google Scholar]
- Mathews, L.; Schafer, E.C.; Gopal, K.V.; Lam, B.; Miller, S. Speech-in-Noise and Dichotic Auditory Training Students With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2024, 55, 1054–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brucato, M. Investigating the Neural and Behavioral Association of Spatial, Cognitive, and Affective Perspective Taking. Ph.D. Dissertation, Temple University, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Godoi, G.A.D.; Oliveira, F.N.D.; Amado, A.C.D.S.; Reis, L.A.D. The notions of space and time and their relationship with the construction of geographic knowledge. Braz. J. Dev. 2021, 7, 28556–28571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasundaram, P.; Avulakunta, I.D. Human Growth and Development. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, F.; Shi, X.; Zhang, A.; Gu, C. Development of Young Children’s Time Perception: Effect of Age and Emotional Localization. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 688165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespi, B. Pattern Unifies Autism. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 621659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franich, K.; Wong, H.Y.; Yu, A.C.L.; To, C.K.S. Temporal Coordination and Prosodic Structure in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Timing Across Speech and Non-Speech Motor Domains. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 2929–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallory, C.; Keehn, B. Implications of Sensory Processing and Attentional Differences Associated With Autism in Academic Settings: An Integrative Review. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 695825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.; Sheppard, E.; Cassidy, S. Autism and the Double Empathy Problem: Implications for Development and Mental Health. Br. J. Dev. Psychol. 2021, 39, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beker, S.; Foxe, J.J.; Molholm, S. Oscillatory Entrainment Mechanisms and Anticipatory Predictive Processes in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Neurophysiol. 2021, 126, 1783–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosos, K.; Papanicolaou, A.; Voniati, L.; Panayidou, K.; Thodi, C. Auditory Processing and Speech-Sound Disorders. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullagh, E.A.; Rotschafer, S.E.; Auerbach, B.D.; Klug, A.; Kaczmarek, L.K.; Cramer, K.S.; Kulesza, R.J., Jr.; Razak, K.A.; Lovelace, J.W.; Lu, Y.; et al. Mechanisms Underlying Auditory Processing Deficits in Fragile X Syndrome. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 3501–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Font-Alaminos, M.; Cornella, M.; Costa-Faidella, J.; Hervás, A.; Leung, S.; Rueda, I.; Escera, C. Increased Subcortical Neural Responses to Repeating Auditory Stimulation in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Biol. Psychol. 2020, 149, 107807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, H.J.; Jones, T.; Valenzuela, K.A.; Haegele, J.A. Inter and Intra-Limb Coordination Variability during Walking in Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Clin. Biomech. 2021, 89, 105474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadad, B.-S.; Yashar, A. Sensory Perception in Autism: What Can We Learn? Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci. 2022, 8, 239–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoen, S.A.; Lane, S.J.; Mailloux, Z.; May-Benson, T.; Parham, L.D.; Smith Roley, S.; Schaaf, R.C. A Systematic Review of Ayres Sensory Integration Intervention for Children with Autism. Autism Res. 2019, 12, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vives-Vilarroig, J.; Ruiz-Bernardo, P.; García-Gómez, A. Sensory Integration and Its Importance in Learning for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Cad. Bras. Ter. Ocup. 2022, 30, e2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, D.; Yuill, N. Social Motor Synchrony in Autism Spectrum Conditions: A Systematic Review. Autism 2024, 28, 1638–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Gong, X.; Luo, X.; Yin, T.; Liu, J.; Yi, L. Social Synchronization during Joint Attention in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. 2021, 14, 2120–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posar, A.; Visconti, P. Early Motor Signs in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Children 2022, 9, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones-Camacho, L.E.; Fishburn, F.A.; Belardi, K.; Williams, D.L.; Huppert, T.J.; Perlman, S.B. Dysfunction in Interpersonal Neural Synchronization as a Mechanism for Social Impairment in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. 2021, 14, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerullo, S.; Fulceri, F.; Muratori, F.; Contaldo, A. Acting with Shared Intentions: A Systematic Review on Joint Action Coordination in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Brain Cogn. 2021, 149, 105693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuang, Y.-P.; Huang, C.-L.; Tsai, H.-Y. Sensory Integration and Perceptual-Motor Profiles in School-Aged Children with Autistic Spectrum Disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 1661–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasco, L.; Provenzano, G.; Bozzi, Y. Sensory Abnormalities in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Focus on the Tactile Domain, From Genetic Mouse Models to the Clinic. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portnova, G.V.; Skorokhodov, I.V.; Mayorova, L.A. The Levels of Auditory Processing during Emotional Perception in Children with Autism. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2023, 22, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choueiri, R.; Garrison, W.T.; Tokatli, V. Early Identification of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Strategies for Use in Local Communities. Indian J. Pediatr. 2023, 90, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.F.; Barreto, J.B.M.; Sousa-Gomes, V. Early Intervention in Autism Spectrum Disorder: An Integrative Literature Review. Eur. Psychol. 2022, 27, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ozonoff, S.; Miller, M. Assessment of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Assessment 2024, 31, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodak, T.; Bergmann, S. Autism Spectrum Disorder: Characteristics, Associated Behaviors, and Early Intervention. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 67, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfanti, L.; Charvet, C.J. Brain Plasticity in Humans and Model Systems: Advances, Challenges, and Future Directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.-M.; Chung, E.; Lee, H. Behavioral Interventions for Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Brief Review and Guidelines with a Specific Focus on Applied Behavior Analysis. J. Korean Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2024, 35, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mualem, R.; Morales-Quezada, L.; Farraj, R.H.; Shance, S.; Bernshtein, D.H.; Cohen, S.; Mualem, L.; Salem, N.; Yehuda, R.R.; Zbedat, Y.; et al. Econeurobiology and Brain Development in Children: Key Factors Affecting Development, Behavioral Outcomes, and School Interventions. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1376075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, T.; Devine, S.L.; Walker, S.C. Affective Touch and Regulation of Stress Responses. Health Psychol. Rev. 2023, 17, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, M.M.; Kiverstein, J. Play in Cognitive Development: From Rational Constructivism to Predictive Processing. Top. Cogn. Sci. 2024, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.E.; Carlson, S.M. Pretending with Realistic and Fantastical Stories Facilitates Executive Function in 3-Year-Old Children. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2021, 207, 105090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ávila-Álvarez, A.; Alonso-Bidegain, M.; De-Rosende-Celeiro, I.; Vizcaíno-Cela, M.; Larrañeta-Alcalde, L.; Torres-Tobío, G. Improving Social Participation of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Pilot Testing of an Early Animal-Assisted Intervention in Spain. Health Soc. Care Community 2020, 28, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, C.; Obialo-Ibeawuchi, C.M.; Obajeun, O.A.; Sarwar, S.; Tawfik, C.; Waleed, M.S.; Wasim, A.U.; Mohamoud, I.; Afolayan, A.Y.; Mbaezue, R.N. Early Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Review and Analysis of the Risks and Benefits. Cureus 2023, 15, e43226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, T.; King, B.H. Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Review. JAMA 2023, 329, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandy, W. Six Ideas about How to Address the Autism Mental Health Crisis. Autism 2022, 26, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, J.F.; Grattão, C.C.; Gomes, R.M.R. The Challenges for Early Intervention and Its Effects on the Prognosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2024, 18, e20230034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murat Baldwin, M.; Xiao, Z.; Murray, A. Temporal Synchrony in Autism: A Systematic Review. Rev. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2022, 9, 596–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardillo, R.; Lanfranchi, S.; Mammarella, I.C. A Cross-Task Comparison on Visuospatial Processing in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Autism 2020, 24, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaaf, R.C.; Mailloux, Z.; Ridgway, E.; Berruti, A.S.; Dumont, R.L.; Jones, E.A.; Leiby, B.E.; Sancimino, C.; Yi, M.; Molholm, S. Sensory Phenotypes in Autism: Making a Case for the Inclusion of Sensory Integration Functions. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2023, 53, 4759–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norcia, A.M.; Lee, A.; Meredith, W.J.; Kohler, P.J.; Pei, F.; Ghassan, S.A.; Libove, R.A.; Phillips, J.M.; Hardan, A.Y. A Case–Control Study of Visual, Auditory and Audio–Visual Sensory Interactions in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Vis. 2021, 21, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, Y.; Burchell, A.; Kulesza, R.J. Central Auditory and Vestibular Dysfunction Are Key Features of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 743561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, E.B.; Caballero, C.; Mistry, S. Aging with Autism Departs Greatly from Typical Aging. Sensors 2020, 20, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hearn, K.; Lynn, A. Age Differences and Brain Maturation Provide Insight into Heterogeneous Results in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 957375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, L.R.; Simpson, A.; Roberson, D. Brief Report: Is Impaired Classification of Subtle Facial Expressions in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders Related to Atypical Emotion Category Boundaries? J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 2628–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.H.; Loyal, S.; Lond, B. Metacognitive Awareness Scale, Domain Specific (MCAS-DS): Assessing Metacognitive Awareness During Raven’s Progressive Matrices. Front. Psychol. 2021, 11, 607577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, M.; Gomes, C.M.A.; Pasian, S.R. Factor Structure of Raven’s Coloured Progressive Matrices. Psico-USF 2016, 21, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.A.; Raman, V.; Thomas, T.; Ashok, M.V. IQ in Autism: Is There an Alternative Global Cognitive Index? Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2015, 37, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chepure, A.H.; Jog, P.P.; Ungratwar, A.K.; Subramanyam, A.A.; Kamath, R.K. Comparison of Intelligence in Children with Autism and Controls: Raven’s Progressive Matrices and Wechsler Intelligence Scale-III. Ann. Indian Psychiatry 2023, 7, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz-Garcia, I.; Espirito-Santo, H.; Pires, C. Psychometric Properties of the Raven’s Standard Progressive Matrices in a Portuguese Sample. Rev. Port. Investig. Comport. Soc. 2021, 7, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nader, A.-M.; Courchesne, V.; Dawson, M.; Soulières, I. Does WISC-IV Underestimate the Intelligence of Autistic Children? J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2016, 46, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, F.J.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Bolton, P.; Brayne, C. The CAST (Childhood Asperger Syndrome Test): Preliminary Development of a UK Screen for Mainstream Primary-School-Age Children. Autism 2002, 6, 9–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Hidalgo, P.; Roigé-Castellví, J.; Vigil-Colet, A.; Canals Sans, J. The Childhood Autism Spectrum Test (CAST): Spanish Adaptation and Validation. Autism Res. 2017, 10, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takesaki, N.; Kikuchi, M.; Yoshimura, Y.; Hiraishi, H.; Hasegawa, C.; Kaneda, R.; Nakatani, H.; Takahashi, T.; Mottron, L.; Minabe, Y. The Contribution of Increased Gamma Band Connectivity to Visual Non-Verbal Reasoning in Autistic Children: A MEG Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turbett, K.; Jeffery, L.; Bell, J.; Burton, J.; Palermo, R. Autistic Traits Are Associated with Less Precise Perceptual Integration of Face Identity. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2022, 52, 2168–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeth, M.; Morgan, E.J. I See You, You See Me: The Impact of Social Presence on Social Interaction Processes in Autistic and Non-Autistic People. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2023, 378, 20210479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Tang, H.; Zhang, X.; Qu, X.; Hu, X.; Lu, J. Classification of Children With Autism and Typical Development Using Eye-Tracking Data From Face-to-Face Conversations: Machine Learning Model Development and Performance Evaluation. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e29328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, D.; Bhavnani, S.; Lockwood Estrin, G.; Rao, V.; Dasgupta, J.; Irfan, H.; Chakrabarti, B.; Patel, V.; Belmonte, M.K. Digital Tools for Direct Assessment of Autism Risk during Early Childhood: A Systematic Review. Autism 2024, 28, 6–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, G.; Sapiro, G. Potential for Digital Behavioral Measurement Tools to Transform the Detection and Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnia, R. Importance of Reliability and Validity in Research. Psychol. Behav. Sci. 2024, 13, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conson, M.; Mazzarella, E.; Frolli, A.; Esposito, D.; Marino, N.; Trojano, L.; Massagli, A.; Gison, G.; Aprea, N.; Grossi, D. Motor Imagery in Asperger Syndrome: Testing Action Simulation by the Hand Laterality Task. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, M.J.; Kochhar, P.; Hamilton, A.; Liddle, E.B.; Simeou, M.; Hollis, C. Atypical Processing of Gaze Cues and Faces Explains Comorbidity between Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 1496–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thérien, V.D.; Degré-Pelletier, J.; Barbeau, E.B.; Samson, F.; Soulières, I. Different Levels of Visuospatial Abilities Linked to Differential Brain Correlates Underlying Visual Mental Segmentation Processes in Autism. Cereb. Cortex 2023, 33, 9186–9211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, H.H.S.; Lai, C.H.-Y.; Wong, S.W.L.; Tsui, J.K.Y.; Li, R.C.; Lau, K.S.-Y.; Chan, D.F.Y. Visuospatial Attention in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Comparison between 2-D and 3-D Environments. Cogent Educ. 2017, 4, 1307709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; D’Agostini, A.R.; Pichini, F.D.S.; Pazini, E.; Rechia, I.C.; Biaggio, E.P.V. Auditory Training in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Case Report. CoDAS 2019, 31, e20180212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, A.; DuBois, M.; Biagianti, B.; Brumley, C.; Jacob, S. Auditory Domain Sensitivity and Neuroplasticity-Based Targeted Cognitive Training in Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, F.; Rando, B.; Salgado, M.; Abreu, A.M. Sensory Processing of Time and Space in Autistic Children. Open Sci. Framew. (OSF) 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marôco, J. Análise Estatística Com o SPSS Statistics, 8th ed.; ReportNumber: Pêro Pinheiro, Portugal, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tabachnick, B.; Fidell, L. Using Multivariate Statistics, 6th ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, B.H. Explaining Psychological Statistics, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-470-00718-1. [Google Scholar]
- DiCriscio, A.S.; Smith, J.; Troiani, V. Comprehensive Assessment of Visual Perceptual Skills in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 662808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Chen, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Yan, J.; Chen, G.; Luo, Q.; Cui, L.; Zong, Y.; Xie, Q.; Niu, C.M. Hemodynamic Activity Is Not Parsimoniously Tuned to Index-of-Difficulty in Movement with Dual Requirements on Speed-Accuracy. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1398601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelánek, R. Leveraging Response Times in Learning Environments: Opportunities and Challenges. User Model. User Adap. Inter. 2024, 34, 729–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, J.C.; Filipe, C.N. Disentangling Response Initiation Difficulties from Response Inhibition in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Sentence-Completion Task. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 964200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.; McGonigle-Chalmers, M. Exploring Perceptual Skills in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: From Target Detection to Dynamic Perceptual Discrimination. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2014, 44, 1144–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishne, G.; Jacoby, N.; Malinovitch, T.; Epstein, T.; Frenkel, O.; Ahissar, M. Slow Update of Internal Representations Impedes Synchronization in Autism. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosnan, M.; Ashwin, C. Thinking, Fast and Slow on the Autism Spectrum. Autism 2023, 27, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosn, F.; Perea, M.; Lizarán, M.; Labusch, M.; Moreno-Giménez, A.; Sahuquillo-Leal, R.; Almansa, B.; Buesa, J.; Campos, L.; Pérez, J.A.; et al. Understanding Decision-Making in Autistic Children and Adolescents: Insights from Deliberative Processes and Behavioral Economic Paradigms. Autism 2025, 29, 1597–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagmann, C.E.; Wyble, B.; Shea, N.; LeBlanc, M.; Kates, W.R.; Russo, N. Children with Autism Detect Targets at Very Rapid Presentation Rates with Similar Accuracy as Adults. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2016, 46, 1762–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, E.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Y. Auditory Pitch Perception in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2022, 65, 4866–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ong, J.H.; Ponsot, E.; Hou, Q.; Jiang, C.; Liu, F. Mental Representations of Speech and Musical Pitch Contours Reveal a Diversity of Profiles in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism 2023, 27, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapparrata, N.M.; Brooks, P.J.; Ober, T.M. Slower Processing Speed in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Meta-Analytic Investigation of Time-Based Tasks. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2023, 53, 4618–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strömberg, M.; Liman, L.; Bang, P.; Igelström, K. Experiences of Sensory Overload and Communication Barriers by Autistic Adults in Health Care Settings. Autism Adulthood 2022, 4, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jertberg, R.M.; Begeer, S.; Geurts, H.M.; Chakrabarti, B.; Van der Burg, E. Slow but Steady: Similarities and Differences in Executive Functioning Between Autistic and Non-Autistic Adults. Autism Res. 2025, 18, 802–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Hallen, R.; Evers, K.; Brewaeys, K.; Van den Noortgate, W.; Wagemans, J. Global Processing Takes Time: A Meta-Analysis on Local-Global Visual Processing in ASD. Psychol. Bull. 2015, 141, 549–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.-Y.; Booth, J.R.; Liu, M.; Chou, T.-L.; Gau, S.S.-F. Developmental Differences in Neural Connectivity for Semantic Processing in Youths with Autism. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2021, 62, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsetsos, K. Unlocking a New Dimension in the Speed–Accuracy Trade-Off. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2023, 27, 510–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, P.; Gutteling, T.; Melcher, D.; Hickey, C. Spatial Attention Tunes Temporal Processing in Early Visual Cortex by Speeding and Slowing Alpha Oscillations. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 7824–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otstavnov, N.; Riaz, A.; Moiseeva, V.; Fedele, T. Temporal and Spatial Information Elicit Different Power and Connectivity Profiles during Working Memory Maintenance. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2024, 36, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comstock, D.C.; Hove, M.J.; Balasubramaniam, R. Sensorimotor Synchronization with Auditory and Visual Modalities: Behavioral and Neural Differences. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Mohsenzadeh, Y. Neural Processing of Naturalistic Audiovisual Events in Space and Time. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, R.A.; Segers, M.; Ferber, S.; Barense, M.D.; Camarata, S.; Wallace, M.T. Keeping Time in the Brain: Autism Spectrum Disorder and Audiovisual Temporal Processing. Autism Res. 2016, 9, 720–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.M.; Gallo, S.; Cerliani, L.; Zhutovsky, P.; El-Gazzar, A.; van Wingen, G. Classifying Autism Spectrum Disorder Using the Temporal Statistics of Resting-State Functional MRI Data With 3D Convolutional Neural Networks. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Brillinger, M.; Karlinsky, A.; Poliakoff, E.; Welsh, T.N.; Gowen, E. Speed-Accuracy Trade-Offs in Action Perception, Motor Imagery, and Execution of Hand Movements in Autistic and Non-Autistic Adults. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leber, A.B.; Irons, J.L. A Methodological Toolbox for Investigating Attentional Strategy. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2019, 29, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C.J.; Lawson, R.P.; Hohwy, J. Bayesian Approaches to Autism: Towards Volatility, Action, and Behavior. Psychol. Bull. 2017, 143, 521–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, J. Tips for Treating Autistic Children. BDJ Pract. 2020, 33, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, M.; Baxter, J.; Grayson, Z.; Johnston, L.; O’Hare, A. Visual Supports at Home and in the Community for Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Scoping Review. Autism 2020, 24, 447–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, V.; Pennington, C.G. Tips for Including Individuals with Autism in Physical Education. J. Phys. Educ. Recreat. Danc. 2022, 93, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkett, L.; McGrath, L.; Tucker, I. Muting, Filtering and Transforming Space: Autistic Children’s Sensory ‘Tactics’ for Navigating Mainstream School Space Following Transition to Secondary School. Emot. Space Soc. 2022, 42, 100872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, R.E. A Personalized Multidisciplinary Approach to Evaluating and Treating Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Herrera, A.I.; Pérez-Jorge, D.; Díaz-Fuentes, Y.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, M.D.C.; Ariño-Mateo, E. Dealing with Stress and Intervention Models in Families with Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2021, 8, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, B.F.; Tillmann, J.; Ahmad, J.; Crawley, D.; San José Cáceres, A.; Holt, R.; Charman, T.; Banaschewski, T.; Buitelaar, J.; Simonoff, E.; et al. How Do Core Autism Traits and Associated Symptoms Relate to Quality of Life? Findings from the Longitudinal European Autism Project. Autism 2021, 25, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øzerk, K.; Øzerk, G.; Silveira-Zaldivar, T. Developing Social Skills and Social Competence in Children with Autism. Int. Electron. J. Elem. Educ. 2021, 13, 341–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigh, S.M.; Walsh, J.A.; Mazefsky, C.A.; Minshew, N.J.; Eack, S.M. Processing Speed Is Impaired in Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder, and Relates to Social Communication Abilities. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2018, 48, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, R.J.; Kalb, L.G. Long-Term Outcomes of Toddlers with Autism Spectrum Disorders Exposed to Short-Term Intervention. Pediatrics 2012, 130, S186–S190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, F.; Bloomfield, B.S. An Evaluation of a Developmental Individual Differences Relationship-Based (DIR®)-Creative Arts Therapies Program for Children with Autism. Arts Psychother. 2021, 73, 101752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raditha, C.; Handryastuti, S.; Pusponegoro, H.D.; Mangunatmadja, I. Positive Behavioral Effect of Sensory Integration Intervention in Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 93, 1667–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Ventola, P. Pivotal Response Treatment for Autism Spectrum Disorder: Current Perspectives. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 1613–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ona, H.N.; Larsen, K.; Nordheim, L.V.; Brurberg, K.G. Effects of Pivotal Response Treatment (PRT) for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD): A Systematic Review. Rev. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2020, 7, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.B.; Burdekin, E.D.; Jackson, N.J.; Hughart, L.; Anderson, J.; Dusing, S.C.; Gulsrud, A.; Kasari, C. Slower Pace in Early Walking Onset Is Related to Communication, Motor Skills, and Adaptive Function in Autistic Toddlers. Autism Res. 2024, 17, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yela-González, N.; Santamaría-Vázquez, M.; Ortiz-Huerta, J.H. Activities of Daily Living, Playfulness and Sensory Processing in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Spanish Study. Children 2021, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmawati, M.; Ruslan, A.; Bandarsyah, D. The Era of Society 5.0 as the Unification of Humans and Technology: A Literature Review on Materialism and Existentialism. J. Sosiol. Dialekt. 2021, 16, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, N.-K.; Shim, S.-H.; Cheon, H.-W. Digital Learning Designs in Occupational Therapy Education: A Scoping Review. BMC Med. Educ. 2023, 23, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odom, S.L.; Hall, L.J.; Morin, K.L.; Kraemer, B.R.; Hume, K.A.; McIntyre, N.S.; Nowell, S.W.; Steinbrenner, J.R.; Tomaszewski, B.; Sam, A.M.; et al. Educational Interventions for Children and Youth with Autism: A 40-Year Perspective. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 4354–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, L.-J. The Brain Digitalization: It’s All Happening so Fast! Front. Hum. Dyn. 2024, 6, 1475438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, B.A.; Tough, S.; Madigan, S. Screen Time and Developmental and Behavioral Outcomes for Preschool Children. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 91, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.-Y.; Feng, J.-Y.; Wang, B.; Shan, L.; Jia, F.-Y. Screen Time and Autism: Current Situation and Risk Factors for Screen Time Among Pre-School Children With ASD. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 675902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffler, K.F.; Oestreicher, L.M. Causation Model of Autism: Audiovisual Brain Specialization in Infancy Competes with Social Brain Networks. Med. Hypotheses 2016, 91, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, B.A.; Volkova, V.; Tomopoulos, S.; Madigan, S. Global Prevalence of Meeting Screen Time Guidelines Among Children 5 Years and Younger: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2022, 176, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Hinkley, T. Too Much Time on Screens? Screen Time Effects and Guidelines for Children and Young People; Australian Institute of Family Studies: Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2021.
- Dong, H.-Y.; Wang, B.; Li, H.-H.; Yue, X.-J.; Jia, F.-Y. Correlation Between Screen Time and Autistic Symptoms as Well as Development Quotients in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 619994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, F.; Abreu, A.M. Geração Digital: Como as Tecnologias Afetam o Potencial Humano? In Ciberpsicologia e Humanidades Digitais; De Almeida Santos, A., Donard, V., De Souza Torres, M., Eds.; Pimenta Cultural: São Paulo, Brazil, 2025; pp. 75–106. [Google Scholar]
- Heffler, K.F.; Frome, L.R.; Garvin, B.; Bungert, L.M.; Bennett, D.S. Screen Time Reduction and Focus on Social Engagement in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Pilot Study. Pediatr. Int. 2022, 64, e15343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degtiar, I.; Rose, S. A Review of Generalizability and Transportability. Annu. Rev. Stat. Its Appl. 2023, 10, 501–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganggayah, M.D.; Zhao, D.; Liew, E.J.Y.; Mohd Nor, N.A.; Paramasivam, T.; Lee, Y.Y.; Abu Hasan, N.I.; Shaharuddin, S. Accelerating Autism Spectrum Disorder Care: A Rapid Review of Data Science Applications in Diagnosis and Intervention. Asian J. Psychiatry 2025, 108, 104498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, K.A.; Gordillo, M.; Orsmond, G.I. Improving the Validity and Generalizability of Adult Autism Research Through Incorporating Family and Cultural Contexts. Autism Adulthood 2020, 2, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golson, M.E.; Ficklin, E.; Haverkamp, C.R.; McClain, M.B.; Harris, B. Cultural Differences in Social Communication and Interaction: A Gap in Autism Research. Autism Res. 2022, 15, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood-Downie, H.; Wong, B.; Kovshoff, H.; Mandy, W.; Hull, L.; Hadwin, J.A. Sex/Gender Differences in Camouflaging in Children and Adolescents with Autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood-Downie, H.; Wong, B.; Kovshoff, H.; Cortese, S.; Hadwin, J.A. Research Review: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Sex/Gender Differences in Social Interaction and Communication in Autistic and Nonautistic Children and Adolescents. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2021, 62, 922–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, E.E.; Bausback, K.; Beard, C.L.; Higinbotham, M.; Bunge, E.L.; Gengoux, G.W. Social Skills Training for Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Meta-Analysis of In-Person and Technological Interventions. J. Technol. Behav. Sci. 2021, 6, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacrey, L.-A.R.; Zwaigenbaum, L.; Elshamy, Y.; Smith, I.M.; Brian, J.A.; Wass, S. Comparative Strengths and Challenges on Face-to-Face and Computer-Based Attention Tasks in Autistic and Neurotypical Toddlers. Autism Res. 2023, 16, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherton, G.; Cross, L. The Use of Analog and Digital Games for Autism Interventions. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 669734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougeard, C.; Picarel-Blanchot, F.; Schmid, R.; Campbell, R.; Buitelaar, J. Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder and Co-Morbidities in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Literature Review. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 744709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khachadourian, V.; Mahjani, B.; Sandin, S.; Kolevzon, A.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Reichenberg, A.; Janecka, M. Comorbidities in Autism Spectrum Disorder and Their Etiologies. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, S.; Byrne, M.L.; De La Fuente, A.; Harrewijn, A.; Nugiel, T.; Rosen, M.; van Atteveldt, N.; Matusz, P.J. Assessing the Degree of Ecological Validity of Your Study: Introducing the Multidimensional Assessment of Research in Context (MARC) Tool. Mind Brain Educ. 2022, 16, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.O.; Dores, A.R.; Peixoto, B.; Barbosa, F. Ecological Validity in Neurocognitive Assessment: Systematized Review, Content Analysis, and Proposal of an Instrument. Appl. Neuropsychol. Adult 2025, 32, 577–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
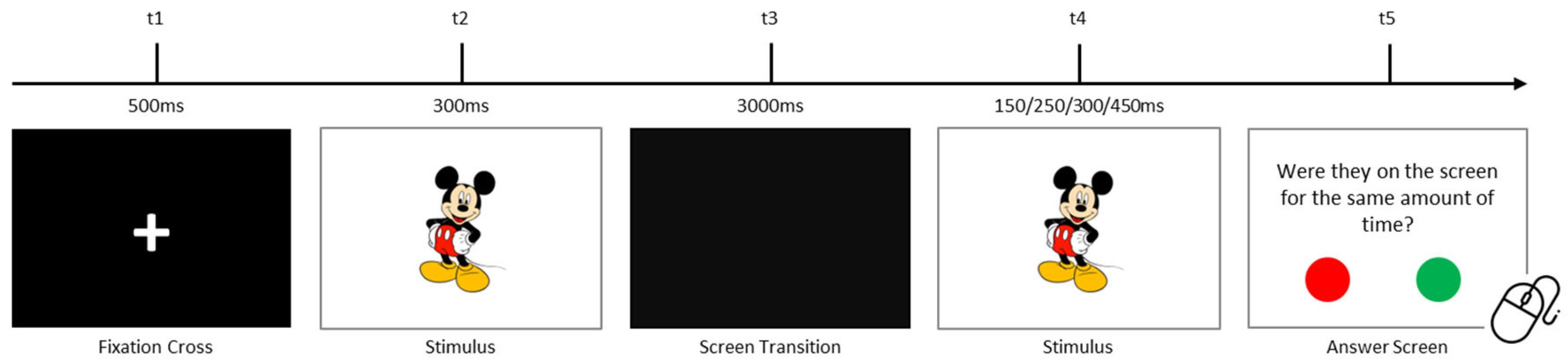
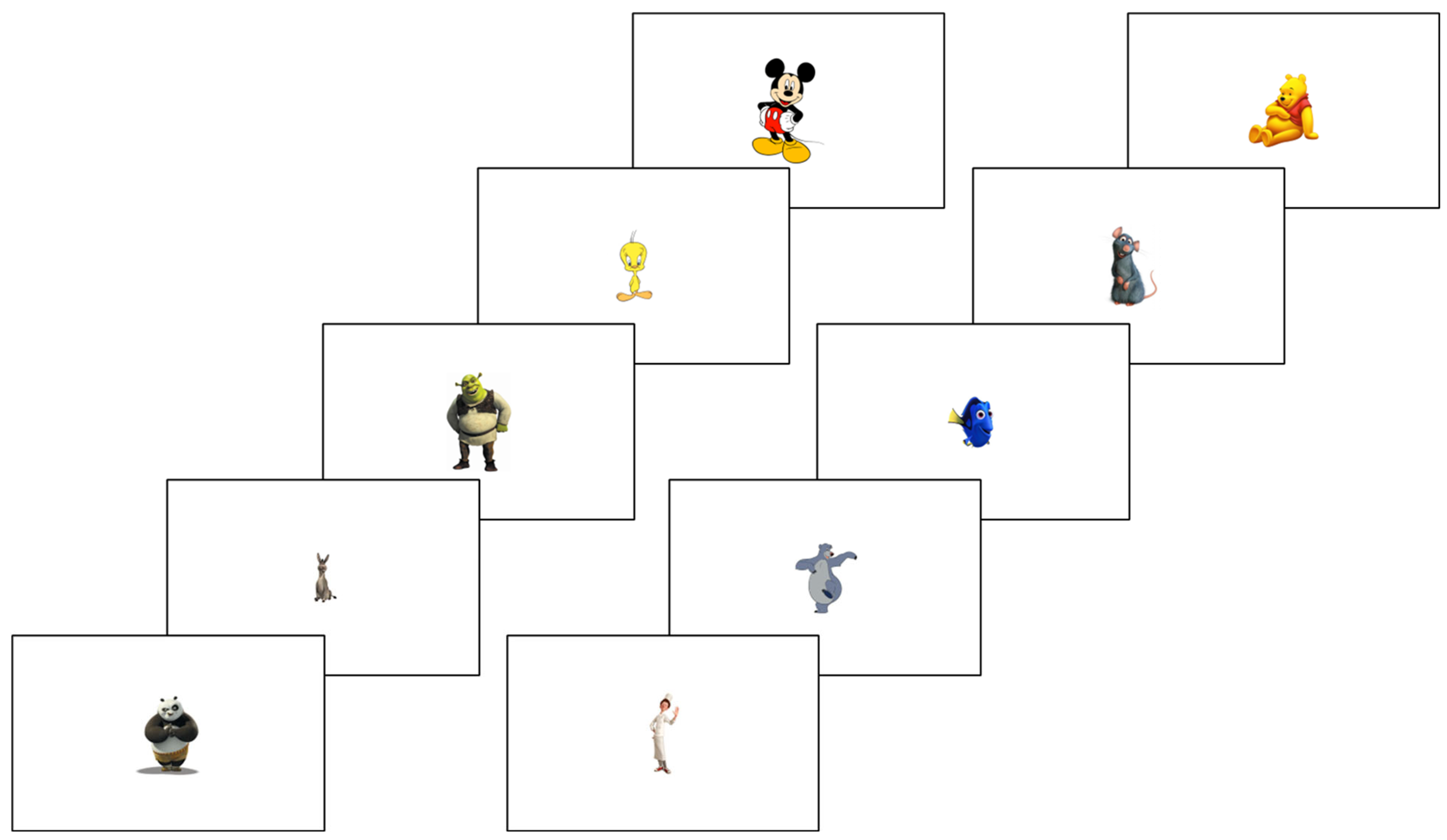
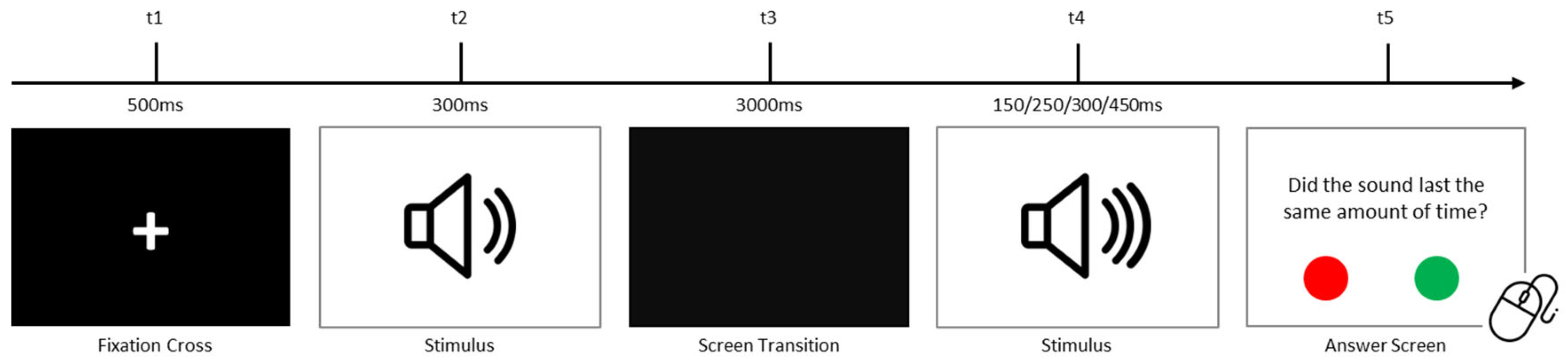
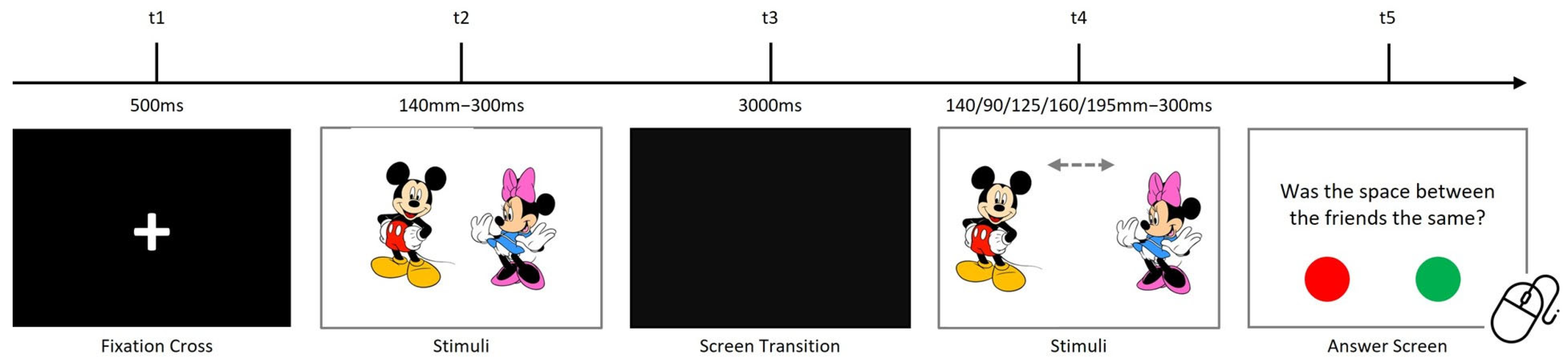

| Processing Modality | Hypotheses | Hypotheses Description |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Temporal Processing | H1a | Autistic individuals exhibit deficits in visual temporal processing compared to neurotypicals, regarding processing accuracy. |
| H1b | Autistic individuals exhibit deficits in visual temporal processing compared to neurotypicals, regarding processing speed. | |
| Auditory Temporal Processing | H2a | Autistic individuals exhibit deficits in auditory temporal processing compared to neurotypicals, regarding processing accuracy. |
| H2b | Autistic individuals exhibit deficits in auditory temporal processing compared to neurotypicals, regarding processing speed. | |
| Visuospatial Processing | H3a | Autistic individuals exhibit deficits in visuospatial processing compared to neurotypicals, regarding processing accuracy. |
| H3b | Autistic individuals exhibit deficits in visuospatial processing compared to neurotypicals, regarding processing speed. |
| Variable | Group | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | AG | 62.9 | 6.946 |
| (months) | Chronological | 67.29 | 5.861 |
| Developmental | 67.5 | 6.661 | |
| Raven’s | AG | 15.57 | 5.219 |
| Score | Chronological | 16.21 | 4.048 |
| Developmental | 15.57 | 5.043 | |
| Variable | Group | Percentage | |
| Gender | Girls | Boys | |
| AG | 18.76 | 81.25 | |
| Chronological | 53.57 | 46.43 | |
| Developmental | 40.63 | 59.38 | |
| Variable | Group | Mean | Standard Deviation | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion Correct (Visual) | AG Group | 0.61810 | 0.082347 | 29 |
| Chronological CG | 0.30583 | 0.087268 | 30 | |
| Developmental CG | 0.46250 | 0.151764 | 28 | |
| Total | 0.46034 | 0.169496 | 87 | |
| Proportion Correct (Visuospatial) | AG | 0.69304 | 0.079176 | 29 |
| Chronological CG | 0.69935 | 0.096655 | 30 | |
| Developmental CG | 0.67017 | 0.067725 | 28 | |
| Total | 0.68785 | 0.082391 | 87 | |
| Proportion Correct (Auditory) | AG | 0.57780 | 0.114975 | 29 |
| Chronological CG | 0.42114 | 0.094340 | 30 | |
| Developmental CG | 0.51742 | 0.125136 | 28 | |
| Total | 0.50435 | 0.128497 | 87 | |
| Mean Reaction Time (Correct, Visual) | AG | 5548.0194 | 2844.92692 | 29 |
| Chronological CG | 2341.1035 | 451.06680 | 30 | |
| Developmental CG | 2760.4483 | 929.84217 | 28 | |
| Total | 3545.0370 | 2243.67825 | 87 | |
| Mean Reaction Time (Correct, Visuospatial) | AG | 5588.7866 | 2126.07044 | 29 |
| Chronological CG | 3213.3321 | 295.97822 | 30 | |
| Developmental CG | 3563.2797 | 820.63016 | 28 | |
| Total | 4117.7771 | 1681.60370 | 87 | |
| Mean Reaction Time (Correct, Auditory) | AG | 6734.9140 | 2631.65505 | 29 |
| Chronological CG | 4329.3552 | 193.62329 | 30 | |
| Developmental CG | 4688.6469 | 722.15939 | 28 | |
| Total | 5246.8422 | 1890.24199 | 87 | |
| Mean Reaction Time (Incorrect, Visual) | AG | 5226.3212 | 2734.05984 | 29 |
| Chronological CG | 2230.2407 | 333.84586 | 30 | |
| Developmental CG | 2504.5807 | 737.81964 | 28 | |
| Total | 3317.2275 | 2120.94882 | 87 | |
| Mean Reaction Time (Incorrect, Visuospatial) | AG | 5525.9358 | 1794.49644 | 29 |
| Chronological CG | 3496.6668 | 715.97360 | 30 | |
| Developmental CG | 3671.2680 | 755.63844 | 28 | |
| Total | 4229.2833 | 1502.04175 | 87 | |
| Mean Reaction Time (Incorrect, Auditory) | AG | 6371.9631 | 2415.56475 | 29 |
| Chronological CG | 4243.5340 | 170.86549 | 30 | |
| Developmental CG | 4660.3571 | 780.77953 | 28 | |
| Total | 5087.1603 | 1721.97657 | 87 |
| Source | Variable | Sum of Squares (Type III) | df | Mean Squares | F | p | Partial η2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensory Modality | Proportion of Correct Responses | 2.487 | 2 | 1.243 | 181.303 | <0.001 | 0.683 |
| Mean Reaction Time (Correct) (1) | 130,278,892.78 | 2 | 65,139,446.39 | 102.872 | <0.001 | 0.550 | |
| Mean Reaction Time (Incorrect) | 136,451,420.15 | 2 | 68,225,710.08 | 118.123 | <0.001 | 0.584 | |
| Sensory Modality × Group | Proportion of Correct Responses | 0.769 | 4 | 0.192 | 28.016 | <0.001 | 0.400 |
| Mean Reaction Time (Correct) (1) | 7,993,158.408 | 3.688 | 2,167,492.208 | 3.156 | 0.019 | 0.070 | |
| Mean Reaction Time (Incorrect) | 11,521,246.651 | 4 | 2,880,311.663 | 4.987 | <0.001 | 0.106 | |
| Error | Proportion of Correct Responses | 1.152 | 168 | 0.007 | |||
| Mean Reaction Time (Correct) (1) | 106,379,444.80 | 154.885 | 686,827.308 | ||||
| Mean Reaction Time (Incorrect) | 97,034,014.544 | 168 | 577,583.420 |
| Variable | Type III Sum of Squares | Error Sum of Squares | Mean Square | Error Mean Square | F | p | Partial η2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion Correct | 1.052 | 1.502 | 0.526 | 0.018 | 29.421 | <0.001 | 0.412 |
| Mean Reaction Time (Correct) | 363,169,009.48 | 505,859,606.48 | 181,584,504.74 | 6,022,138.172 | 30.153 | <0.001 | 0.418 |
| Mean Reaction Time (Incorrect) | 296,011,427.00 | 431,332,379.79 | 148,005,713.50 | 5,134,909.283 | 28.823 | <0.001 | 0.407 |
| Measure | Group | Mean | Standard Error | 95% Confidence Interval [Inferior, Superior Limit] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion Correct | AG | 0.630 | 0.014 | [0.601, 0.658] |
| Chronological | 0.475 | 0.014 | [0.447, 0.503] | |
| Developmental | 0.550 | 0.015 | [0.521, 0.579] | |
| Mean Reaction Time (Correct) | AG | 5957.24 | 263.10 | [5434.04, 6480.44] |
| Chronological | 3294.60 | 258.67 | [2780.19, 3809.00] | |
| Developmental | 3670.79 | 267.75 | [3138.33, 4203.25] | |
| Mean Reaction Time (Incorrect) | AG | 5708.07 | 242.94 | [5224.95, 6191.20] |
| Chronological | 3323.48 | 238.86 | [2848.48, 3798.48] | |
| Developmental | 3612.07 | 247.24 | [3120.40, 4103.74] |
| Measure | Sensory Modality | Mean | Standard Error | 95% Confidence Interval [Inferior, Superior Limit] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion Correct | Visual | 0.462 | 0.012 | [0.438, 0.486] |
| Visuospatial | 0.688 | 0.009 | [0.670, 0.705] | |
| Auditory | 0.505 | 0.012 | [0.482, 0.529] | |
| Mean Reaction Time (Correct) | Visual | 3549.857 | 187.188 | [3177.612, 3922.102] |
| Visuospatial | 4121.799 | 142.022 | [3839.372, 4404.227] | |
| Auditory | 5250.972 | 169.213 | [4914.473, 5587.471] | |
| Mean Reaction Time (Incorrect) | Visual | 3320.381 | 176.404 | [2969.582, 3671.180] |
| Visuospatial | 4231.290 | 128.432 | [3975.889, 4486.692] | |
| Auditory | 5091.951 | 157.302 | [4779.139, 5404.764] |
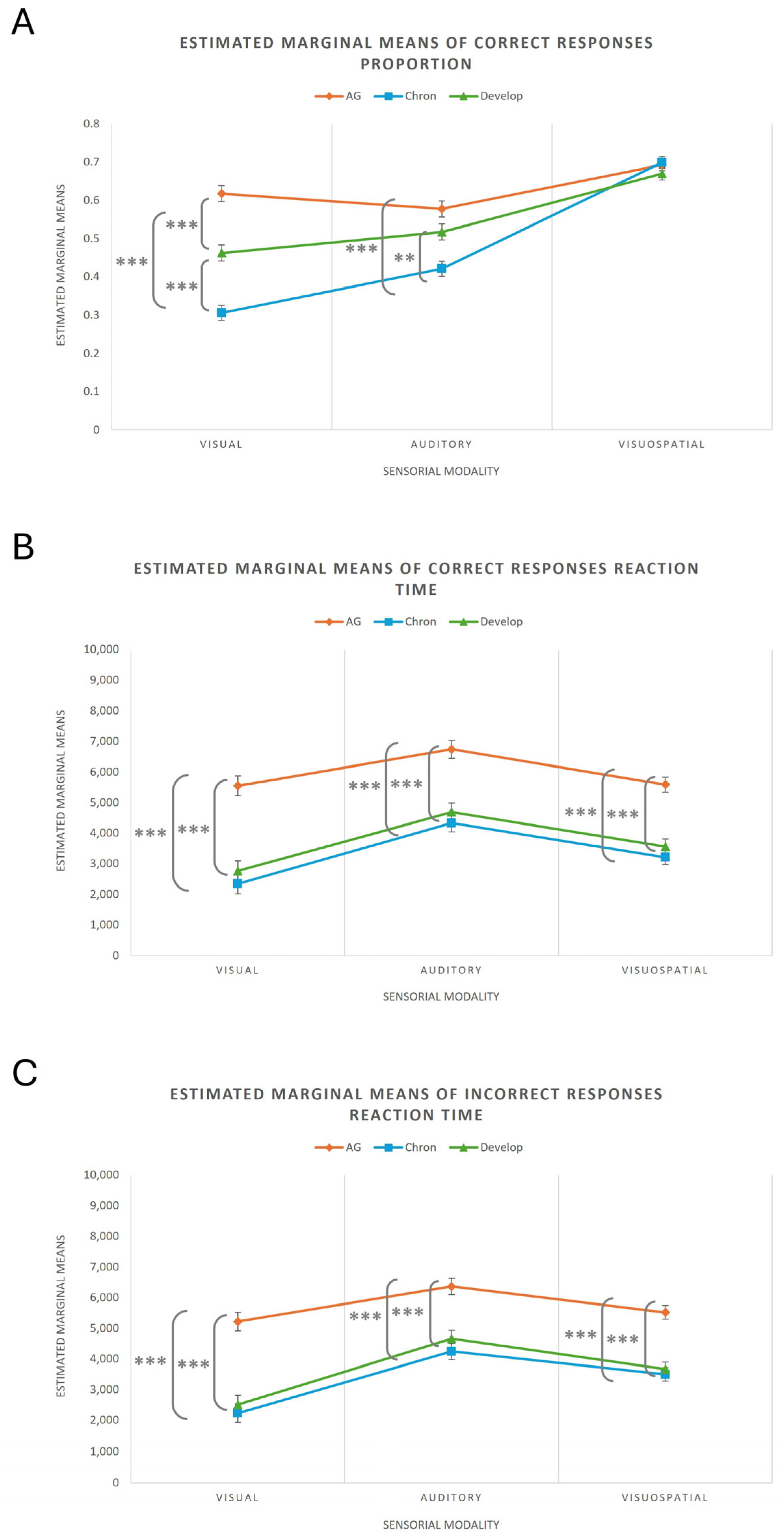
| Measure | Group | Sensory Modality | Mean | Standard Error | 95% Confidence Interval [Inferior, Superior Limit] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion Correct | AG | Visual | 0.618 | 0.021 | [0.577, 0.659] |
| Visuospatial | 0.693 | 0.015 | [0.663, 0.723] | ||
| Auditory | 0.578 | 0.021 | [0.536, 0.619] | ||
| Chronological | Visual | 0.306 | 0.020 | [0.266, 0.346] | |
| Visuospatial | 0.699 | 0.015 | [0.669, 0.729] | ||
| Auditory | 0.421 | 0.020 | [0.381, 0.462] | ||
| Developmental | Visual | 0.462 | 0.021 | [0.421, 0.504] | |
| Visuospatial | 0.670 | 0.016 | [0.639, 0.701] | ||
| Auditory | 0.517 | 0.021 | [0.475, 0.559] | ||
| Mean Reaction Time (Correct) | AG | Visual | 5548.019 | 324.091 | [4903.528, 6192.511] |
| Visuospatial | 5588.787 | 245.892 | [5099.802, 6077.771] | ||
| Auditory | 6734.914 | 292.970 | [6152.311, 7317.517] | ||
| Chronological | Visual | 2341.104 | 318.644 | [1707.445, 2974.762] | |
| Visuospatial | 3213.332 | 241.760 | [2732.567, 3694.097] | ||
| Auditory | 4329.355 | 288.046 | [3756.545, 4902.166] | ||
| Developmental | Visual | 2760.448 | 329.828 | [2104.549, 3416.347] | |
| Visuospatial | 3563.280 | 250.245 | [3065.640, 4060.919] | ||
| Auditory | 4688.647 | 298.156 | [4095.732, 5281.562] | ||
| Mean Reaction Time (Incorrect) | AG | Visual | 5226.321 | 305.419 | [4618.961, 5833.681] |
| Visuospatial | 5525.936 | 222.363 | [5083.743, 5968.129] | ||
| Auditory | 6371.963 | 272.347 | [5830.371, 6913.555] | ||
| Chronological | Visual | 2230.241 | 300.286 | [1633.089, 2827.392] | |
| Visuospatial | 3496.667 | 218.626 | [3061.906, 3931.428] | ||
| Auditory | 4243.534 | 267.769 | [3711.045, 4776.023] | ||
| Developmental | Visual | 2504.581 | 310.826 | [1886.470, 3122.691] | |
| Visuospatial | 3671.268 | 226.299 | [3221.248, 4121.288] | ||
| Auditory | 4660.357 | 277.168 | [4109.179, 5211.535] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coelho, F.; Rando, B.; Salgado, M.; Abreu, A.M. Sensory Processing of Time and Space in Autistic Children. Children 2025, 12, 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101366
Coelho F, Rando B, Salgado M, Abreu AM. Sensory Processing of Time and Space in Autistic Children. Children. 2025; 12(10):1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101366
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoelho, Franz, Belén Rando, Mariana Salgado, and Ana Maria Abreu. 2025. "Sensory Processing of Time and Space in Autistic Children" Children 12, no. 10: 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101366
APA StyleCoelho, F., Rando, B., Salgado, M., & Abreu, A. M. (2025). Sensory Processing of Time and Space in Autistic Children. Children, 12(10), 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101366







