Risk Factors Associated with Endoscopic Intervention in Pediatric Patients Presenting with Foreign Body Ingestion to the Emergency Department
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Eligibility Criteria and Definitions
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Follow-Up and Ethics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| High-Risk Foreign Body Criteria |
|---|
| sharp or wide/elongated objects (≥2.5 cm in width or ≥6 cm in length) |
| multiple FBs |
| button batteries |
| evidence of perforation |
| a coin at the cricopharyngeus muscle level |
| airway compromise |
| presence ≥ 24 h |
References
- Sink, J.R.; Kitsko, D.J.; Mehta, D.K.; Georg, M.W.; Simons, J.P. Diagnosis of pediatric foreign body ingestion: Clinical presentation, physical examination, and radiologic findings. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2016, 125, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-H.; Chen, A.-C.; Tsai, J.-D.; Wei, S.-H.; Hsueh, K.-C.; Lin, W.-C. Endoscopic removal of foreign bodies in children. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2007, 23, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, B.M.; Sweetser, S.; Song, L.M.W.K.; Tabibian, J.H. Foreign object ingestion and esophageal food impaction: An update and review on endoscopic management. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevik, M.; Gokdemir, M.T.; Boleken, M.E.; Sogut, O.; Kurkcuoglu, C. The characteristics and outcomes of foreign body ingestion and aspiration in children due to lodged foreign body in the aerodigestive tract. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2013, 29, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navia-López, L.; Cadena-León, J.; Ignorosa-Arellano, K.; Toro-Monjaraz, E.; Zárate-Mondragón, F.; Loredo-Mayer, A.; Cervantes-Bustamante, R.; Ramírez-Mayans, J. Foreign body ingestion and associated factors in pediatric patients at a tertiary care center. Rev. Gastroenterol. México 2022, 87, 20–28. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conners, G.P. Pediatric foreign body ingestion: Complications and patient and foreign body factors. Sci 2022, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguin, J.; Kwan, C. Novel uses of point-of-care ultrasound for pediatric foreign bodies: An emergency department case series. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 55, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, D.C.; Shah, S.R.; St Peter, S.D.; Calkins, C.M.; Morrow, S.E.; Murphy, J.P.; Sharp, R.J.; Andrews, W.S.; Holcomb, G.W., III; Ostlie, D.J. Esophageal foreign bodies in the pediatric population: Our first 500 cases. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2006, 41, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowski, J.A.; Kay, M. Caustic ingestions and foreign bodies ingestions in pediatric patients. Pediatr. Clin. 2017, 64, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skae, C.C. Esophageal Foreign Bodies. Pediatr. Rev. 2005, 26, 34–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyemura, M.C. Foreign body ingestion in children. Am. Fam. Physician 2005, 72, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dereci, S.; Koca, T.; Serdaroğlu, F.; Akçam, M. Foreign body ingestion in children. Turk. Arch. Pediatr./Türk Pediatri Arşivi 2015, 50, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, R.I.; Christoffel, K.K.; Binns, H.J.; Jaffe, D.M.; The Pediatric Practice Research Group. Foreign body ingestions in children: Risk of complication varies with site of initial health care contact. Pediatrics 1993, 91, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J. Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal foreign bodies in children. Indian J. Pediatr. 1999, 66, S75–S80. [Google Scholar]
- Ayantunde, A.; Oke, T. A review of gastrointestinal foreign bodies. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2006, 60, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Yang, Y.; Cho, S.; Lee, B.; Han, N.; Han, S.; Chung, I. Management of foreign bodies in the gastrointestinal tract: An analysis of 104 cases in children. Endoscopy 1999, 31, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyllie, R. Foreign bodies in the gastrointestinal tract. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2006, 18, 563–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louie, J.P.; Alpern, E.R.; Windreich, R.M. Witnessed and unwitnessed esophageal foreign bodies in children. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2005, 21, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crysdale, W.S.; Sendi, K.S.; Yoo, J. Esophageal foreign bodies in children, 15-year review of 484 cases. Ann. Otal. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1991, 100, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, P.; Law, B.; Young, L. Down’s syndrome, duodenal stenosis/annular pancreas, and a stack of coins. Am. J. Dis. Child. (1960) 1988, 142, 459–460. [Google Scholar]
- Shakir, A.K.; Ramji, F.; El Halabi, I. Penny for Your Thoughts; A Coin in the Stomach: Why Did It Get Stuck? Hosp. Pediatr. 2017, 7, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringer, M.; Kiely, E.; Drake, D. Gastric retention of swallowed coins after pyloromyotomy. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 1991, 45, 66–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, L.O.; Towbin, A.J. Causes of esophageal food bolus impaction in the pediatric population. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybojad, B.; Niedzielska, G.; Niedzielski, A.; Rudnicka-Drozak, E.; Rybojad, P. Esophageal foreign bodies in pediatric patients: A thirteen-year retrospective study. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 102642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denney, W.; Ahmad, N.; Dillard, B.; Nowicki, M.J. Children will eat the strangest things: A 10-year retrospective analysis of foreign body and caustic ingestions from a single academic center. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2012, 28, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikenberry, S.O.; Jue, T.L.; Anderson, M.A.; Appalaneni, V.; Banerjee, S.; Ben-Menachem, T.; Decker, G.A.; Fanelli, R.D.; Fisher, L.R.; Fukami, N. Management of ingested foreign bodies and food impactions. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 73, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahshan, A.H.; Donovan, G.K. Bougienage versus endoscopy for esophageal coin removal in children. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 41, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conners, G.P.; Chamberlain, J.M.; Ochsenschlager, D.W. Symptoms and spontaneous passage of esophageal coins. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 1995, 149, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçin, Ş.; Karnak, I.; Ciftci, A.O.; Şenocak, M.E.; Tanyel, F.C.; Büyükpamukçu, N. Foreign body ingestion in children: An analysis of pediatric surgical practice. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2007, 23, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, M.A.; Navia, L.A.; González, C. Caracterización de los pacientes pediátricos con ingestión de cuerpo extraño que ingresaron al servicio de urgencias de una institución de cuarto nivel. Pediatría 2015, 48, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorana, J.; Tantivit, Y.; Phiuphong, C.; Pattapong, S.; Siripan, S. Foreign body ingestion in pediatrics: Distribution, management and complications. Medicina 2019, 55, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Rodríguez, G.; Teyssier-Morales, G.; Penchyna-Grub, J.; Madriñan-Rivas, J.E.; Rivas-Rivera, I.A.; de León, A.T.-P.; Domingo-Porras, J.; Jaramillo-Alvarado, J.G.; Cruz-Romero, E.V.; Zurita-Cruz, J.N. Characteristics and outcomes of foreign body ingestion in children. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2018, 116, 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Laya, B.F.; Restrepo, R.; Lee, E.Y. Practical imaging evaluation of foreign bodies in children: An update. Radiol. Clin. 2017, 55, 845–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.W.; Park, M.H.; Do, H.J.; Yeom, J.-S.; Park, J.S.; Park, E.S.; Seo, J.H.; Park, J.J.; Lim, J.Y.; Park, C.H. Factors associated with removal of impactted fishbone in children, suspected ingestion. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2016, 19, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, R.E.; Lerner, D.G.; Lin, T.; Manfredi, M.; Shah, M.; Stephen, T.C.; Gibbons, T.E.; Pall, H.; Sahn, B.; McOmber, M. Management of ingested foreign bodies in children: A clinical report of the NASPGHAN Endoscopy Committee. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velitchkov, N.G.; Grigorov, G.I.; Losanoff, J.E.; Kjossev, K.T. Ingested foreign bodies of the gastrointestinal tract: Retrospective analysis of 542 cases. World J. Surg. 1996, 20, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
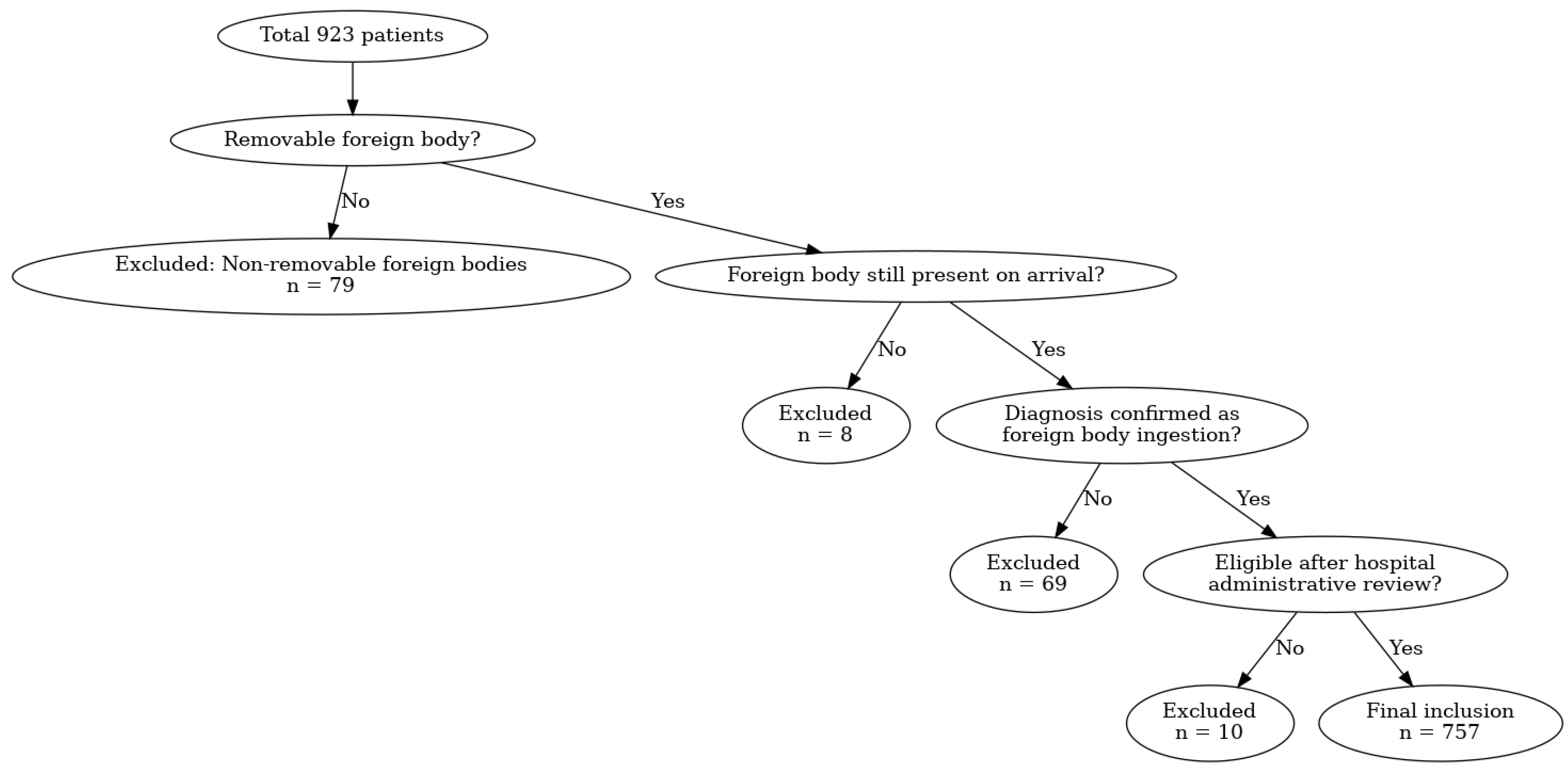

| Gender | 1 |
| Male | 409 (54.0) |
| Female | 348 (46.0) |
| Age, months | |
| Mean, SD | 27.2 ± 24.3 |
| Median IQR | 17.0 [10.0–38.0] |
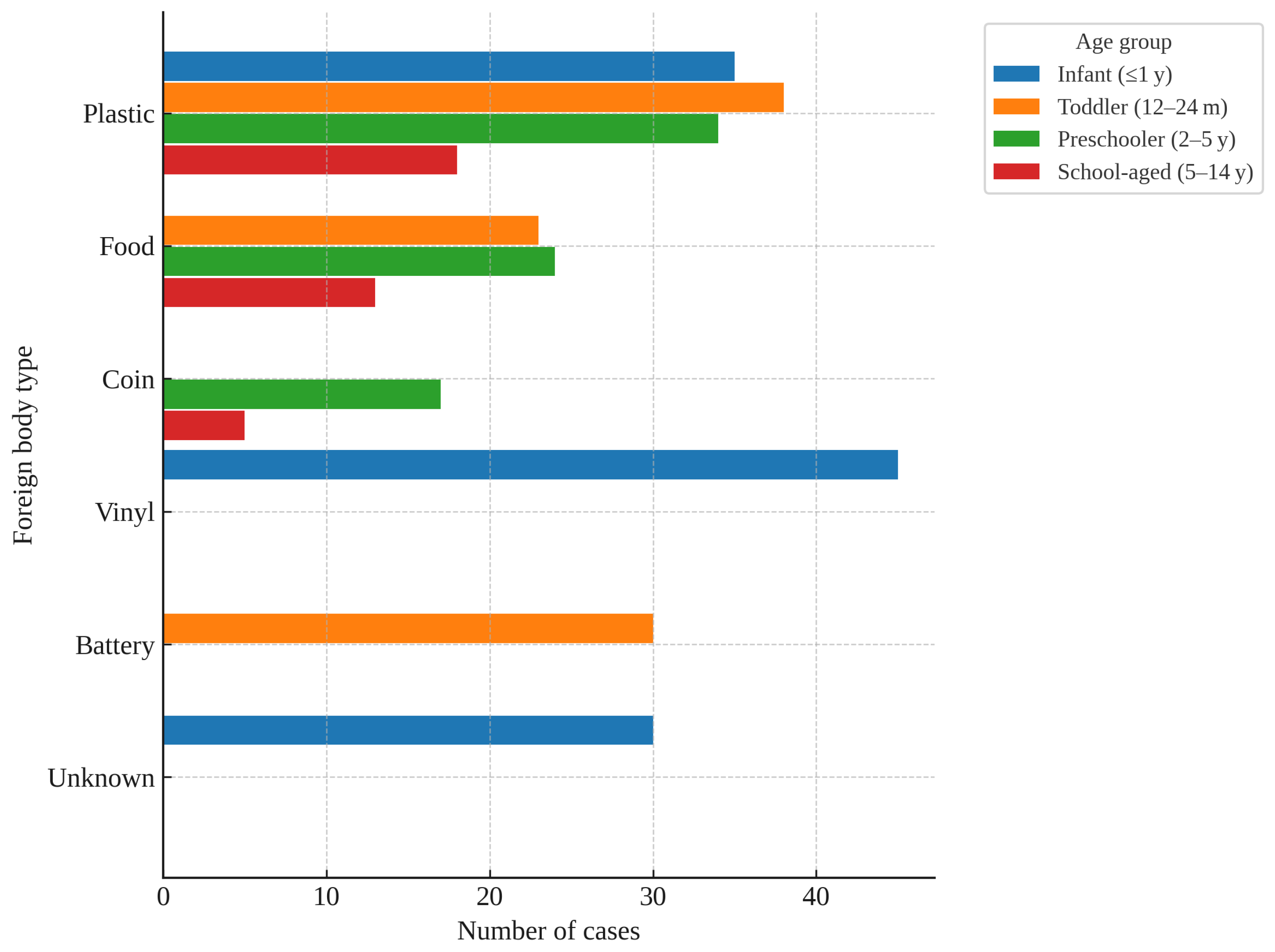
| Age group | |
| Infant (<12 months) | 235 (31.0) |
| Toddler (12–23 months) | 241 (31.8) |
| Preschooler (2–5 years) | 230 (30.4) |
| School-aged (6–14 years) | 51 (6.7) |
| Symptoms | |
| Gastrointestinal | 186 (24.6) |
| (abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, oral bleeding) | |
| Respiratory | 217 (28.7) |
| (sore throat, cough, drooling, cyanosis, wheezing, chest pain) | |
| Neurologic | 8 (1.1) |
| (seizure, irritability) | |
| None | 418 (55.2) |
| Foreign body type | |
| Plastic | 126 (16.6) |
| Metal | 92 (12.2) |
| Vinyl/Sticker | 91 (12.0) |
| Food | 73 (9.6) |
| Battery | 62 (8.2) |
| Coin | 61 (8.1) |
| Magnetic | 59 (7.8) |
| Soft synthetic materials | 37 (4.9) |
| Others | 97 (12.8) |
| Unknown | 59 (7.8) |
| EDLOS, minutes | |
| Median, IQR | 40.0 [27.0–64.0] |
| Gender | 1 |
| Male | 31 (66.0) |
| Female | 16 (34.0) |
| Age, months | |
| Mean, SD | 36.8 ± 32.2 |
| Median IQR | 20.0 [13.0–47.5] |
| Age group | |
| Infant (<12 months) | 7 (14.9) |
| Toddler (12–23 months) | 17 (36.2) |
| Preschooler (2–5 years) | 15 (31.9) |
| School-aged (6–14 years) | 8 (17.0) |
| Symptoms | |
| Present | 19 (40.4) |
| None | 28 (59.6) |
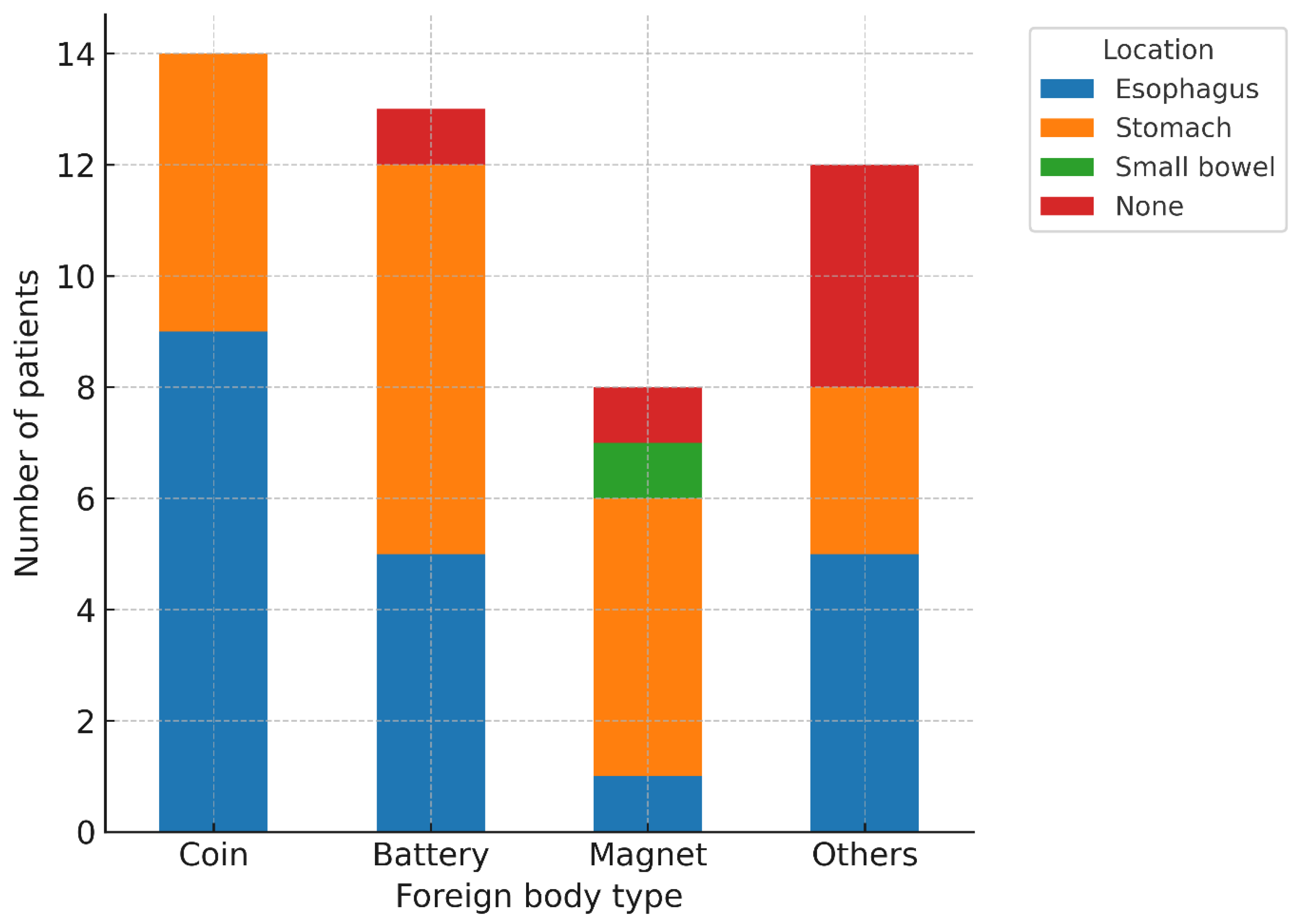
| Foreign body type | |
| Coin | 14 (29.8) |
| Battery | 13 (27.7) |
| Magnetic | 8 (17.0) |
| Metal | 3 (6.4) |
| Plastic | 2 (4.3) |
| Soft synthetic materials | 3 (6.4) |
| Others | 3 (6.4) |
| Food | 1 (2.1) |
| Foreign body location | |
| Esophagus | 20 (42.6) |
| Stomach | 20 (42.6) |
| Small bowel | 1 (2.1) |
| None | 6 (12.8) |
| Foreign body size, mm | |
| Mean, SD | 21.2 ± 7.3 |
| Median, IQR | 22.0 [17.5–26.0] |
| Successful removal | 35 (74.5) |
| High-risk ingestion | 34 (72.3) |
| * | Non High-Risk | High-Risk | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Male | 346 (52.0) | 63 (68.5) | |
| Female | 319 (48.0) | 29 (31.5) | 0.004 |
| Age, months | |||
| Mean, SD | 25.2 ± 22.2 | 41.6 ± 32.4 | <0.001 |
| Median, IQR | 16.0 [10.0–35.0] | 35.5 [13.8–57.0] | <0.001 |
| Age group | |||
| Infant (<12 months) | 225 (33.8) | 10 (10.9) | |
| Toddler (12–23 months) | 212 (31.9) | 29 (31.5) | |
| Preschooler (2–5 years) | 173 (26.0) | 32 (34.8) | |
| School-aged (6–14 years) | 55 (8.3) | 21 (22.8) | <0.001 |
| Symptom | |||
| Gastrointestinal | 149 (22.4) | 23 (25.0) | 0.672 |
| Respiratory | 164 (24.7) | 14 (15.2) | 0.061 |
| Neurologic | 8 (1.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0.607 |
| None | 406 (61.1) | 61 (66.3) | |
| Foreign body type | |||
| Plastic | 123 (18.5) | 3 (3.3) | |
| Vinyl/Sticker | 91 (13.7) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Metal | 78 (11.7) | 14 (15.2) | |
| Food | 71 (10.7) | 2 (2.2) | |
| Magnetic | 46 (6.9) | 13 (14.1) | |
| Soft synthetic materials | 39 (5.9) | 2 (2.2) | |
| Battery | 36 (5.4) | 26 (28.3) | |
| Coin | 34 (5.1) | 27 (29.3) | |
| Others | 88 (13.2) | 5 (5.4) | |
| Unknown | 59 (8.9) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 |
| EGDS performed | 13 (2.0) | 34 (37.0) | <0.001 |
| EDLOS, minutes | |||
| Median, IQR | 37.0 [26.0–58.0] | 74.0 [37.0–184.5] | <0.001 |
| * | Adjusted Odd Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age group | |||
| Infant (Reference) | |||
| Toddler | 1.85 | 0.22–15.35 | 0.571 |
| Preschooler | 0.96 | 0.10–8.91 | 0.971 |
| School—aged | 0.17 | 0.01–2.85 | 0.221 |
| Male | 0.78 | 0.19–3.15 | 0.722 |
| Foreign body type | |||
| Battery (Reference) | |||
| Coin | 7.26 | 1.07–49.31 | 0.042 |
| Magnetic | 1.44 | 0.19–11.03 | 0.723 |
| Symptom present | 1.34 | 0.31–5.81 | 0.700 |
| High risk | 179.36 | 29.90–1075.78 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Byun, Y.-h.; Kim, J.E.; Paek, S.H.; Kim, M.-J.; Park, S.H.; Song, H.-Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.-H.; Kwon, J.H. Risk Factors Associated with Endoscopic Intervention in Pediatric Patients Presenting with Foreign Body Ingestion to the Emergency Department. Children 2025, 12, 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101344
Byun Y-h, Kim JE, Paek SH, Kim M-J, Park SH, Song H-Y, Kim JH, Kim S-H, Kwon JH. Risk Factors Associated with Endoscopic Intervention in Pediatric Patients Presenting with Foreign Body Ingestion to the Emergency Department. Children. 2025; 12(10):1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101344
Chicago/Turabian StyleByun, Young-hoon, Ji Eun Kim, So Hyun Paek, Min-Jung Kim, Soo Hyun Park, Ho-Young Song, Jin Hee Kim, Sung-Ha Kim, and Jae Hyun Kwon. 2025. "Risk Factors Associated with Endoscopic Intervention in Pediatric Patients Presenting with Foreign Body Ingestion to the Emergency Department" Children 12, no. 10: 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101344
APA StyleByun, Y.-h., Kim, J. E., Paek, S. H., Kim, M.-J., Park, S. H., Song, H.-Y., Kim, J. H., Kim, S.-H., & Kwon, J. H. (2025). Risk Factors Associated with Endoscopic Intervention in Pediatric Patients Presenting with Foreign Body Ingestion to the Emergency Department. Children, 12(10), 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101344







