Children with Genetically Confirmed Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia: A Single-Center Experience
Abstract
Highlights
- We identified a new inheritance pattern, a novel variants and a different clinical phenotype in some forms of hereditary spastic paraplegia.
- The new inheritance patterns, new variants and phenotypes identified will contribute to the clinical and genetic diagnosis and monitoring of HSP.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- DNA Sequencing
- Variant Analysis and Classification
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Salinas, S.; Proukakis, C.; Crosby, A.; Warner, T.T. Hereditary spastic paraplegia: Clinical features and pathogenetic mechanisms. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lallemant-Dudek, P.; Darios, F.; Durr, A. Recent advances in understanding hereditary spastic paraplegias and emerging therapies. Fac. Rev. 2021, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyyazhagan, A.; Orlacchio, A. Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, R.A.; Grimmel, M.; Wagner, M.; Hennings, J.C.; Marx, C.; Feichtinger, R.G.; Saadi, A.; Rostásy, K.; Radelfahr, F.; Bevot, A.; et al. Bi-allelic HPDL variants cause a neurodegenerative disease ranging from neonatal encephalopathy to adolescent-onset spastic paraplegia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 107, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiessner, M.; Maroofian, R.; Ni, M.Y.; Pedroni, A.; Müller, J.S.; Stucka, R.; Beetz, C.; Efthymiou, S.; Santorelli, F.M.; Alfares, A.A.; et al. Biallelic variants in HPDL cause pure and complicated hereditary spastic paraplegia. Brain 2021, 144, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marelli, C.; Lamari, F.; Rainteau, D.; Lafourcade, A.; Banneau, G.; Humbert, L.; Monin, M.-L.; Petit, E.; Debs, R.; Castelnovo, G.; et al. Plasma oxysterols: Biomarkers for diagnosis and treatment in spastic paraplegia type 5. Brain 2018, 141, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcel, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Auwera, G.A.; Carneiro, M.O.; Hartl, C.; Poplin, R.; Del Angel, G.; Levy-Moonshine, A.; Jordan, T.; Shakir, K.; Roazen, D.; Thibault, J.; et al. From FastQ data to high confidence variant calls: The Genome Analysis Toolkit best practices pipeline. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2013, 43, 11.10.1–11.10.33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaren, W.; Gil, L.; Hunt, S.E.; Riat, H.S.; Ritchie, G.R.; Thormann, A.; Flicek, P.; Cunningham, F. The Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.T.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Winckler, W.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.Y.; Do, H.J.; Lee, S.; Jang, J.H.; Cho, E.H.; Jang, D.H. Identification of a Heterozygous SPG11 Mutation by Clinical Exome Sequencing in a Patient With Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia: A Case Report. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 40, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utz, K.S.; Kohl, Z.; Marterstock, D.C.; Doerfler, A.; Winkler, J.; Schmidt, M.; Regensburger, M. Neuropsychology and MRI correlates of neurodegeneration in SPG11 hereditary spastic paraplegia. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, B.; de Bot, S.T.; Daniels, M.R.; França, M.C.; Toro, C., Jr.; Riverol, M.; Hedera, P.; Bassi, M.T.; Bresolin, N.; van de Warrenburg, B.P.; et al. “Ears of the Lynx” MRI Sign Is Associated with SPG11 and SPG15 Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, E.; Meyyazhagan, A.; Orlacchio, A. Hereditary spastic paraplegia: Genetic heterogeneity and common pathways. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 357, 114203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, M.; Magri, S.; Di Bella, D.; Sarto, E.; Taroni, F.; Mariotti, C.; Nanetti, L. Spastic paraplegia type 46: Novel and recurrent GBA2 gene variants in a compound heterozygous Italian patient with spastic ataxia phenotype. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 4741–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchia, S.D.; Tessa, A.; Dosi, C.; Baldacci, J.; Pasquariello, R.; Antenora, A.; Astrea, G.; Bassi, M.T.; Battini, R.; Casali, C.; et al. Monoallelic KIF1A-related disorders: A multicenter cross sectional study and systematic literature review. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicita, F.; Ginevrino, M.; Travaglini, L.; D’Arrigo, S.; Zorzi, G.; Borgatti, R.; Terrone, G.; Catteruccia, M.; Vasco, G.; Brankovic, V.; et al. Heterozygous KIF1A variants underlie a wide spectrum of neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 58, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remiche, G.; Vandernoot, I.; Sadeghi-Meibodi, N.; Desmyter, L. SPG43 and ALS-like syndrome in the same family due to compound heterozygous mutations of the C19orf12 gene: A case description and brief review. Neurogenetics 2021, 22, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilleur, K.G.; Traoré, M.; Sangaré, M.; Britton, A.; Landouré, G.; Coulibaly, S.; Niaré, B.; Mochel, F.; La Pean, A.; Rafferty, I.; et al. Hereditary spastic paraplegia and amyotrophy associated with a novel locus on chromosome 19. Neurogenetics 2010, 11, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landouré, G.; Zhu, P.P.; Lourenço, C.M.; Johnson, J.O.; Toro, C.; Bricceno, K.V.; Rinaldi, C.; Meilleur, K.G.; Sangaré, M.; Diallo, O.; et al. Hereditary spastic paraplegia type 43 (SPG43) is caused by mutation in C19orf12. Hum. Mutat. 2013, 34, 1357–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçakaya, N.H.; Haryanyan, G.; Mercan, S.; Sozer, N.; Ali, A.; Tombul, T.; Ozbek, U.; İşEri, S.A.U.; Yapıcı, Z. Clinical and genetic spectrum of an orphan disease MPAN: A series with new variants and a novel phenotype. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2019, 53, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, C.; Schmidt, T.; Situ, A.J.; Johnson, J.O.; Lee, P.R.; Chen, K.L.; Bott, L.C.; Fadó, R.; Harmison, G.H.; Parodi, S.; et al. Mutation in CPT1C Associated With Pure Autosomal Dominant Spastic Paraplegia. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.; Cong, L.; Zhong, S.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J. A novel CPT1C variant causes pure hereditary spastic paraplegia with benign clinical course. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorrami, M.; Tabatabaiefar, M.A.; Khorram, E.; Yaghini, O.; Rezaei, M.; Hejazifar, A.; Riahinezhad, M.; Kheirollahi, M. Homozygous TFG gene variants expanding the mutational and clinical spectrum of hereditary spastic paraplegia 57 and a review of literature. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 66, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harlalka, G.V.; McEntagart, M.E.; Gupta, N.; Skrzypiec, A.E.; Mucha, M.W.; Chioza, B.A.; Simpson, M.A.; Sreekantan-Nair, A.; Pereira, A.; Günther, S.; et al. Novel Genetic, Clinical, and Pathomechanistic Insights into TFG-Associated Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, D.; Yun, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, C.; Lin, P. Novel TFG mutation causes autosomal-dominant spastic paraplegia and defects in autophagy. J. Med. Genet. 2024, 61, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, A.; Saffari, A.; Kellner, M.; Döbler-Neumann, M.; Jordan, C.; Srivastava, S.; Zhang, B.; Sahin, M.; Fink, J.K.; Smith, L.; et al. Early-Onset and Severe Complex Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Caused by De Novo Variants in SPAST. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 2440–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSheikh, R.H.; Aravindhan, A.; Boysen, S.; Veerapandiyan, A. Infantile-Onset Complex Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Due to a Novel Mutation in SPAST Gene. Pediatr. Neurol. 2022, 134, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josifova, D.J.; Monroe, G.R.; Tessadori, F.; de Graaff, E.; van der Zwaag, B.; Mehta, S.G.; The DDD Study; Harakalova, M.; Duran, K.J.; Savelberg, S.M.; et al. Heterozygous KIDINS220/ARMS nonsense variants cause spastic paraplegia, intellectual disability, nystagmus, and obesity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 2158–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Dessouky, S.H.; Issa, M.Y.; Aboulghar, M.M.; Gaafar, H.M.; Elarab, A.E.; Ateya, M.I.; Omar, H.H.; Beetz, C.; Zaki, M.S. Prenatal delineation of a distinct lethal fetal syndrome caused by a homozygous truncating KIDINS220 variant. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2020, 182, 2867–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Chen, Y.J.; Wang, M.W.; Lin, X.H.; Dong, E.L.; Chen, W.; Wang, N.; Lin, X. Genetic and Clinical Profile of Chinese Patients with Autosomal Dominant Spastic Paraplegia. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2019, 23, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Hussein, H.S.; Guerra, L.M.; Raza, S.A.; Javalkar, V.; Raza, M. Pure Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia in a Patient With a Novel Heterozygous KIDINS220 Gene Mutation. Cureus 2024, 16, e64023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micule, I.; Lace, B.; Wright, N.T.; Chrestian, N.; Strautmanis, J.; Diriks, M.; Stavusis, J.; Kidere, D.; Kleina, E.; Zdanovica, A.; et al. Case Report: Two Families With HPDL Related Neurodegeneration. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 780764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.; Miller, C.; Kuno, S.; Rey Hipolito, A.G.; El Nagar, S.; Riboldi, G.M.; Korn, M.; Tran, W.C.; Wang, Z.; Ficaro, L.; et al. Coenzyme Q headgroup intermediates can ameliorate a mitochondrial encephalopathy. Nature 2025, 645, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöls, L.; Rattay, T.W.; Martus, P.; Meisner, C.; Baets, J.; Fischer, I.; Jägle, C.; Fraidakis, M.J.; Martinuzzi, A.; Saute, J.A.; et al. Hereditary spastic paraplegia type 5: Natural history, biomarkers and a randomized controlled trial. Brain 2017, 140, 3112–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goizet, C.; Boukhris, A.; Durr, A.; Beetz, C.; Truchetto, J.; Tesson, C.; Tsaousidou, M.; Forlani, S.; Guyant-Maréchal, L.; Fontaine, B.; et al. CYP7B1 mutations in pure and complex forms of hereditary spastic paraplegia type 5. Brain 2009, 132, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignarri, A.; Malandrini, A.; Del Puppo, M.; Magni, A.; Monti, L.; Ginanneschi, F.; Tessa, A.; Santorelli, F.M.; Federico, A.; Dotti, M.T. Hereditary spastic paraplegia type 5: A potentially treatable disorder of cholesterol metabolism. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

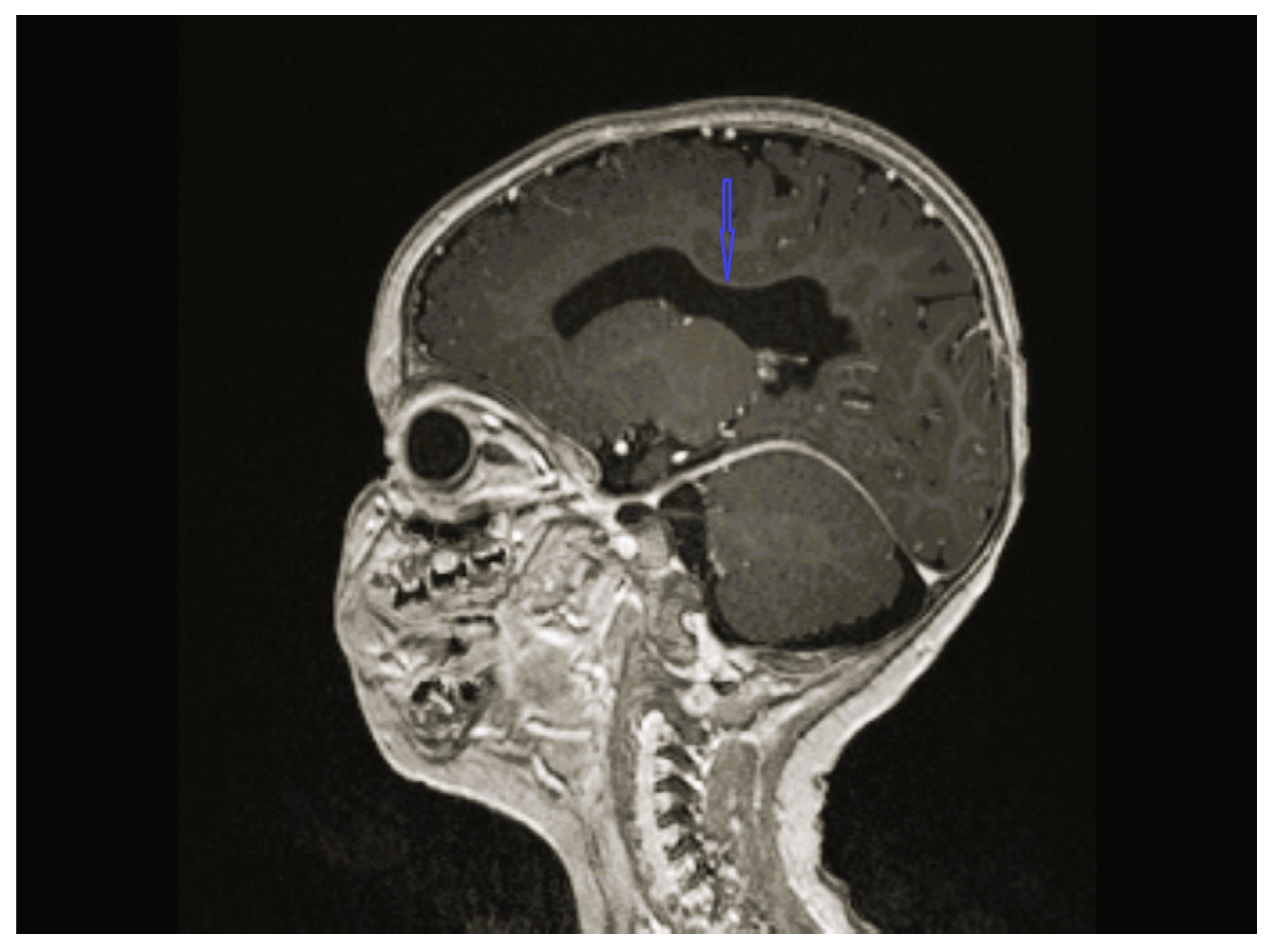
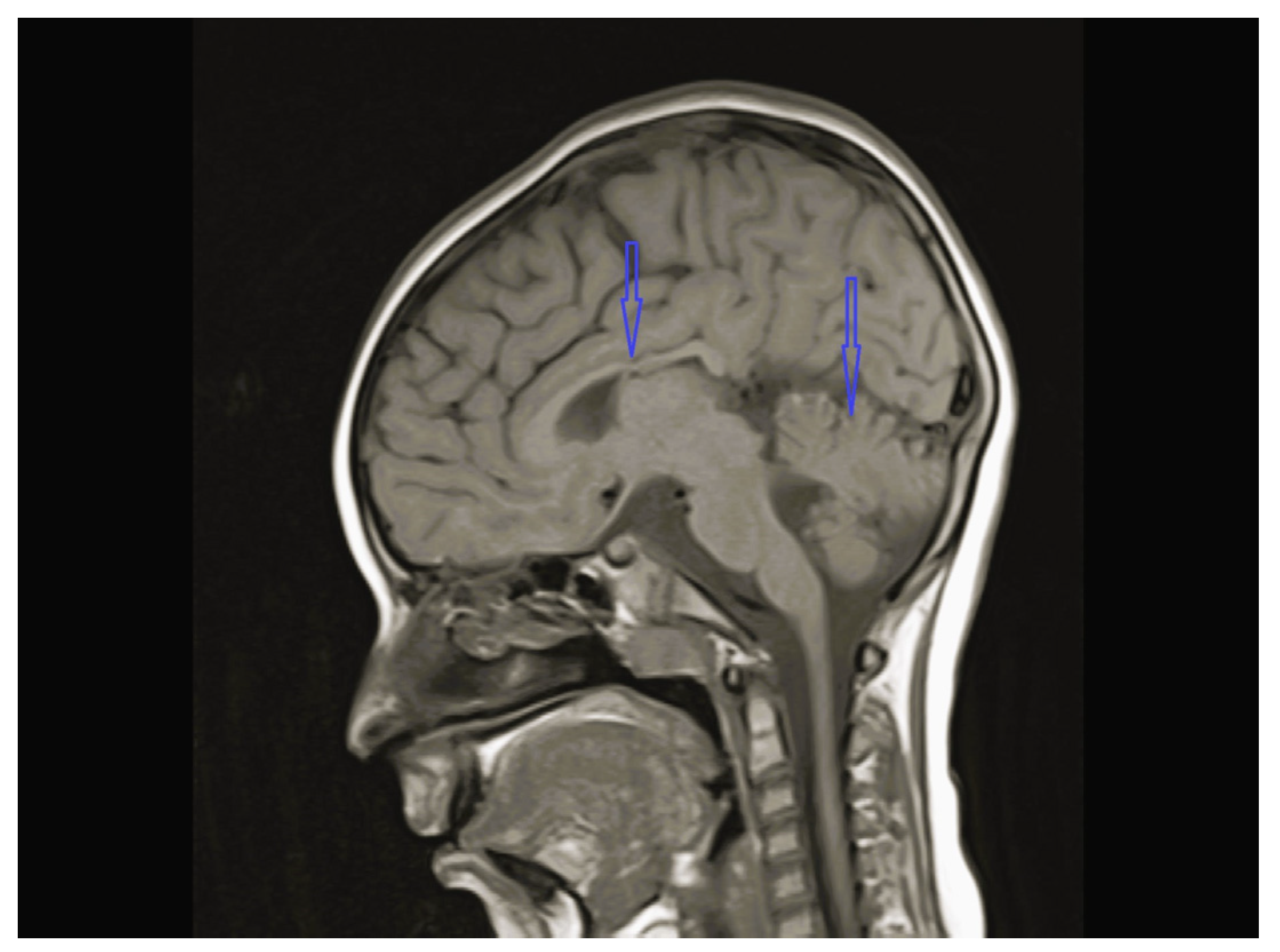
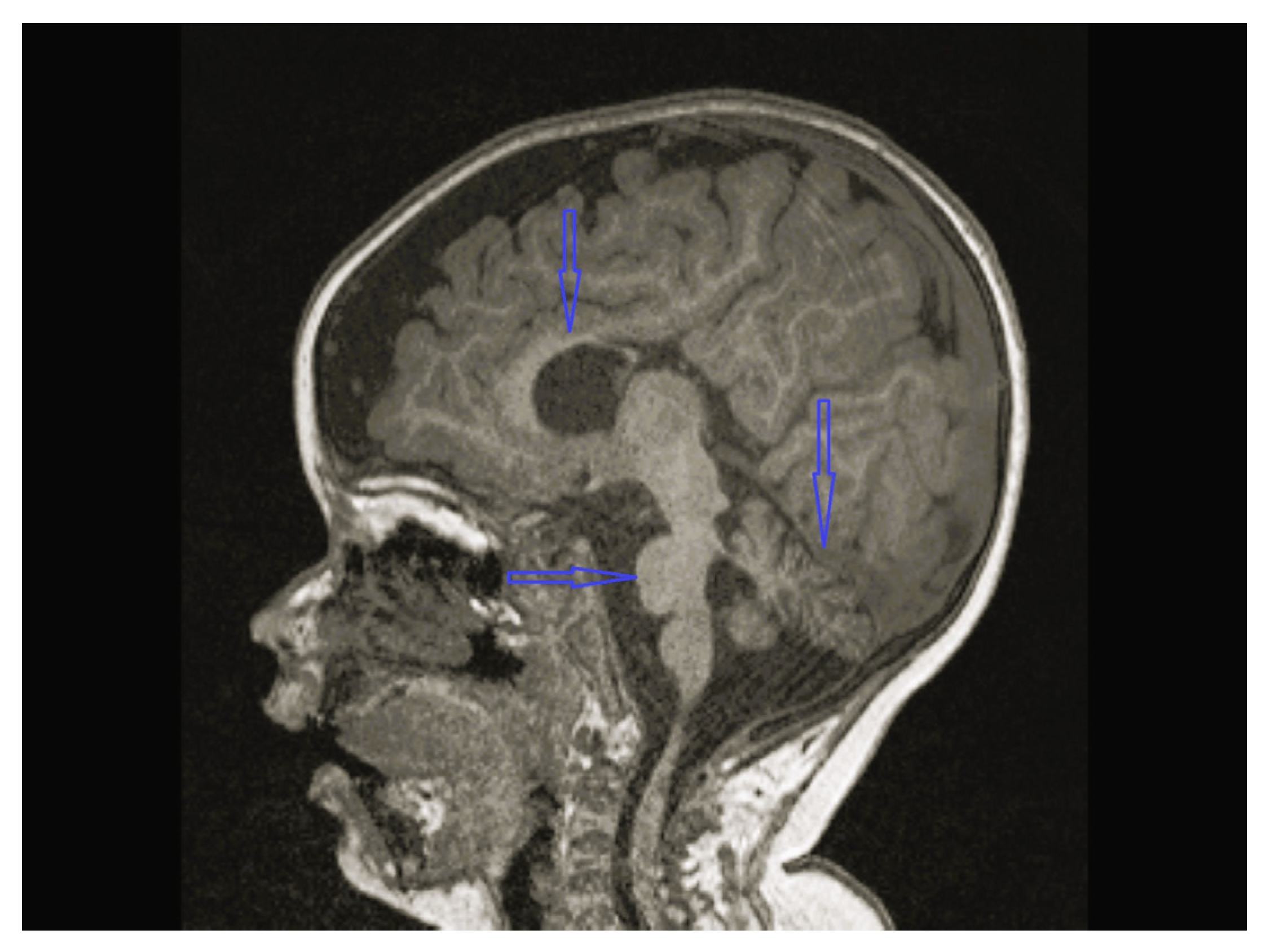
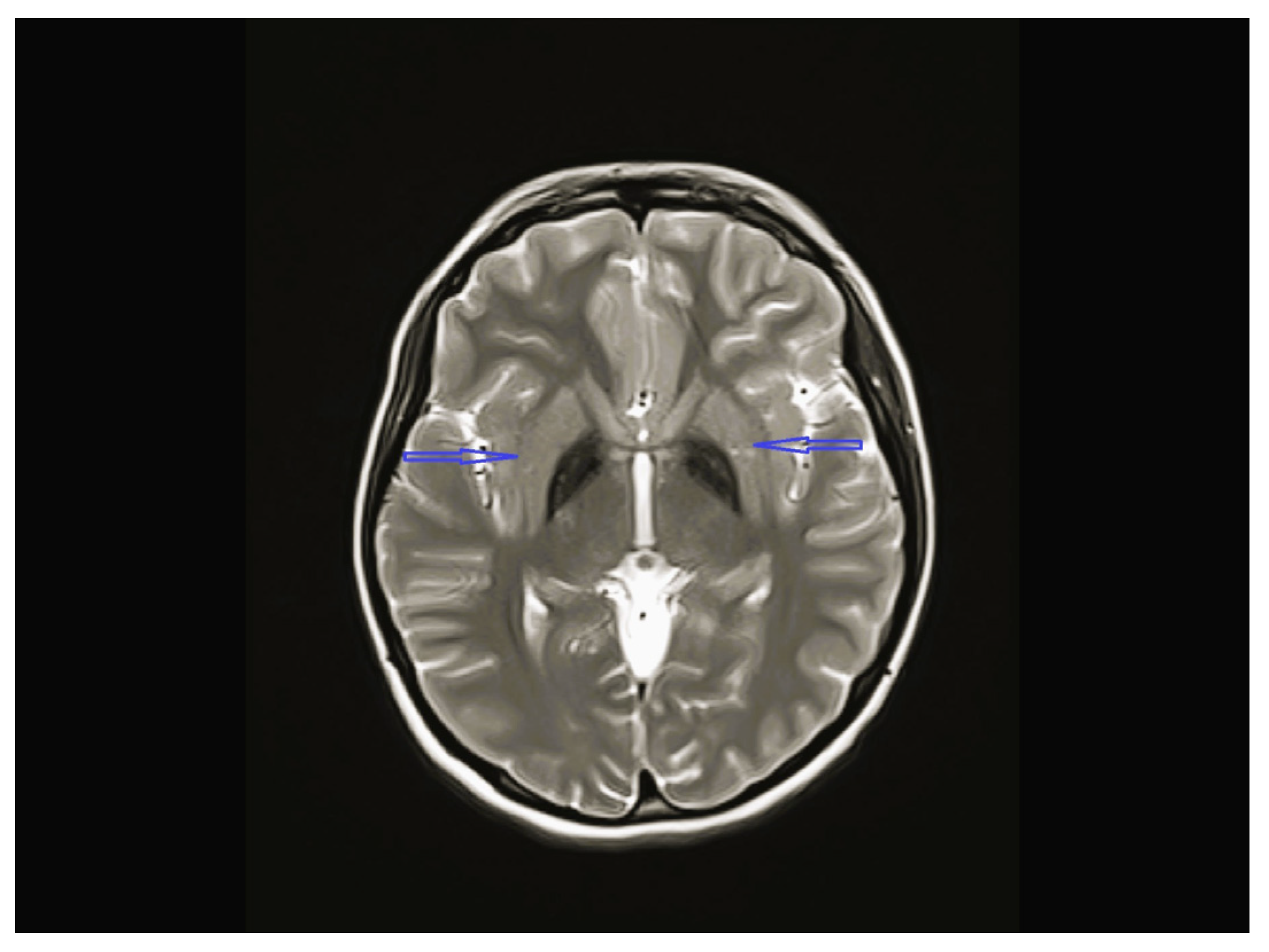
| Patient No/ Sex | Clinical Follow-Up Ages | Family Medical History/ Consanguinity | Physical and Neurological Findings | Diagnosis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y/m) | Presentation Age | Time of Progression of Symptoms | Follow Up Time | Age at Time of Diagnosis | Presentation Symptoms | Early Motor Development | Neurologic Findings | Initial | Final | ||
| 1/F | 7 y 6 m | 2y | 5 y | 5 y 6 m | 6 y 1 m | No/No | Gait disturbance and urine, stool incontinence | Able to walk at the age of 2 | Spastic gait, brisk reflexes | HSP | SPG 11 P-HSP |
| 2/M | 4 y 7 m | 6 m | 2 y 3 m | 4 y 1 m | 2 y | No/Yes | Motor delay | No gain of ability to walk | Spastic gait, brisk reflexes, intellectual disability | DD | SPG46 C-HSP |
| 3/F | 9 y 10 m | 1y | Stable disease | 8 y 10 m | 7 y | Yes/No | Gait disturbance | Able to walk at the age of 18 m | Spastic gait and brisk reflexes | HSP | SPG30 P-HSP |
| 4/F | 16 y 11 m | 7y | 7 y | 9 y 11 m | 14 y 2 m | Yes/Yes | Generalized weakness, falling frequently, and urine incontinence | No delayed motor milestones | Spastic gait, brisk reflexes, ataxia, ID, weakness in lower limbs | ID | SPG43 C-HSP |
| 5/M | 5 y 6 m | 2 y 6 m | 2 y 6 m | 3 y | 3 y | Yes/No | Gait disturbance and pain in lower limbs | No delayed motor milestones | Brisk reflexes, lower limb weakness | Spinal cord injury | SPG73 P- HSP |
| 6/F | 5 y 8 m | 2 y 6 m | 2 y 6 m | 3 y 2 m | 4 y 1 m | Yes/Yes | Tiptoe walking | No delayed motor milestones | Lower limb weakness, brisk reflexes, spasticity | HSP | SPG57 P-HSP |
| 7/F | 7 y 2 m | 1 y | Stable disease | 2 y 8 m | 7 y | Yes/No | Delayed gait, Falling frequently | Able to walk at the age of 4, 5 | Lower limb weakness, spasticity, Delayed speech, ID | CP | SPG4 P-HSP |
| 8/F | 6 y 3 m | Birth | Stable disease | 4 y 3 m | 5 y 5 m | Yes/No | Seizures, gait disturbance | No gain of ability to walk | Mild dysmorphic features, Spastic gait, brisk reflexes | Epilepsy, ID | SİNO syndrome C-HSP |
| 9/F | 12 y 9 m | 12 y | 12 y | 8 m | 12 y 1 m | Yes/No | Gait disturbance, falling frequently | No delayed motor milestones | Lower limb weakness, brisk reflexes, spasticity | HSP | SPG83 P-HSP |
| 10/F | 12 y 3 m | 1 y 6 m | 10 y | 1 y 4 m | 12 y 3 m | Yes/No | Gait disturbance, ID | Able to walk at the age of 2 | Failure to thrive, mild dysmorphic features, lower limb weakness, spasticity | MD | SPG5 C-HSP |
| Patient No | Neurologic Diagnostic Tests | Neuroimaging Tests | Genetic Findings | Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic Screening Tests | ENMG | EEG | Brain MRG | Spinal MRG | |||
| 1 | - | - | - | Cerebellar hypoplasia, vermis dysplasia and corpus callosum (CC) hypoplasia | Normal | SPG11 c.6730C>T heterozygote (p.L2244F) | Physical therapy |
| 2 | Normal | Normal | Centrotemporal spike and waves on the left side with normal background | CC hypoplasia | Normal | GBA2 NM_020944.3 c.1688-2A>C heterozygote | Physical therapy, baclofen, diazepam, orthopedic braces, levetiracetam |
| 3 | Normal | - | Normal | Vermis and CC hypoplasia | Normal | KIF1A c.773C>T heterozygote (p.V391M) | Physical therapy, baclofen |
| 4 | Normal | Normal | Normal | Bilateral globus pallidus T2 hypointensity and iron accumulation | - | C19orf12c.385C>T (p.Q1239*)(p.Gln129Ter) Homozygote | Physical therapy, carbidopa/levodopa, baclofen, |
| 5 | - | - | - | Normal | Normal | CPT1C c.109C>T (p.R37C) heterozygote | Physical therapy |
| 6 | Normal | - | - | Normal | Normal | TFG NM_001195478.1 c.269-8_269-4dup Homozygote TFG NM_001195478.1 c.288_297 delCCTTGAATCAinsTGACTTG Homozygote | Physical therapy, baclofen, orthopedic braces |
| 7 | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | SPAST NM_014946.4 c.1496G>A heterozygote p.R499H | Physical therapy, baclofen orthopedic braces |
| 8 | Normal | - | Multifocal spike and waves pattern | Vermian, CC and brainstem hypoplasia | Normal | KIDINS220 NM_020738.4 c.4388C>A heterozygote p.S1463* | Physical therapy, clonazepam, sodium valproate |
| 9 | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | HPDL NM_032756.4 c.149G>A (p.Gly50Asp) Homozygote | Physical therapy, carbidopa/levodopa, baclofen, CoQ10, vitamin B1, B2 and biotin |
| 10 | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | CYP7B1 NM_004820.5 c.1346G>A Homozygotep.C449y | Physical therapy, ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), orthopedic braces |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Besen, S.; Özkale, Y.; Özkale, M.; Bozdoğan, S.T.; Alkan, Ö.; Ceylaner, S.; Erol, İ. Children with Genetically Confirmed Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia: A Single-Center Experience. Children 2025, 12, 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101332
Besen S, Özkale Y, Özkale M, Bozdoğan ST, Alkan Ö, Ceylaner S, Erol İ. Children with Genetically Confirmed Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia: A Single-Center Experience. Children. 2025; 12(10):1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101332
Chicago/Turabian StyleBesen, Seyda, Yasemin Özkale, Murat Özkale, Sevcan Tuğ Bozdoğan, Özlem Alkan, Serdar Ceylaner, and İlknur Erol. 2025. "Children with Genetically Confirmed Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia: A Single-Center Experience" Children 12, no. 10: 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101332
APA StyleBesen, S., Özkale, Y., Özkale, M., Bozdoğan, S. T., Alkan, Ö., Ceylaner, S., & Erol, İ. (2025). Children with Genetically Confirmed Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia: A Single-Center Experience. Children, 12(10), 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101332




