Current Trends in the Treatment of Pediatric Hydrocephalus: A Narrative Review Centered on the Indications, Safety, Efficacy, and Long-Term Outcomes of Available Treatment Modalities
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Overview, Definition, and Classification
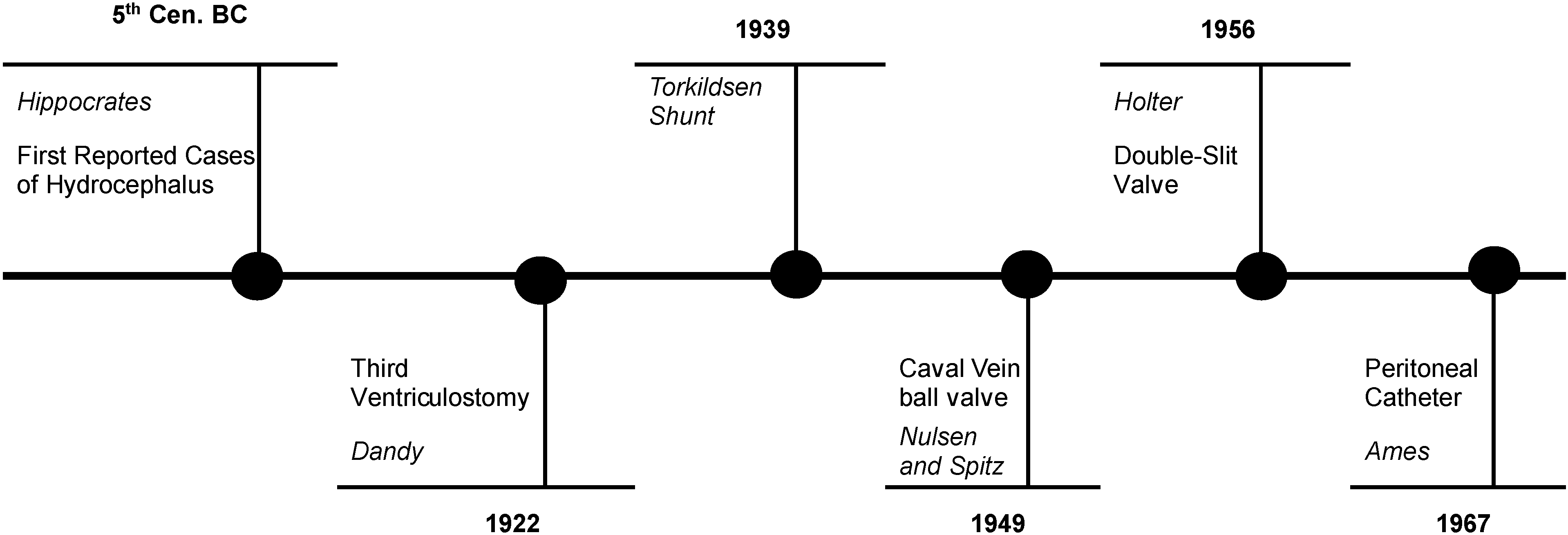
1.2. Hydrocephalus Treatment: The Evolution of Shunt Technology and the Development of Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy
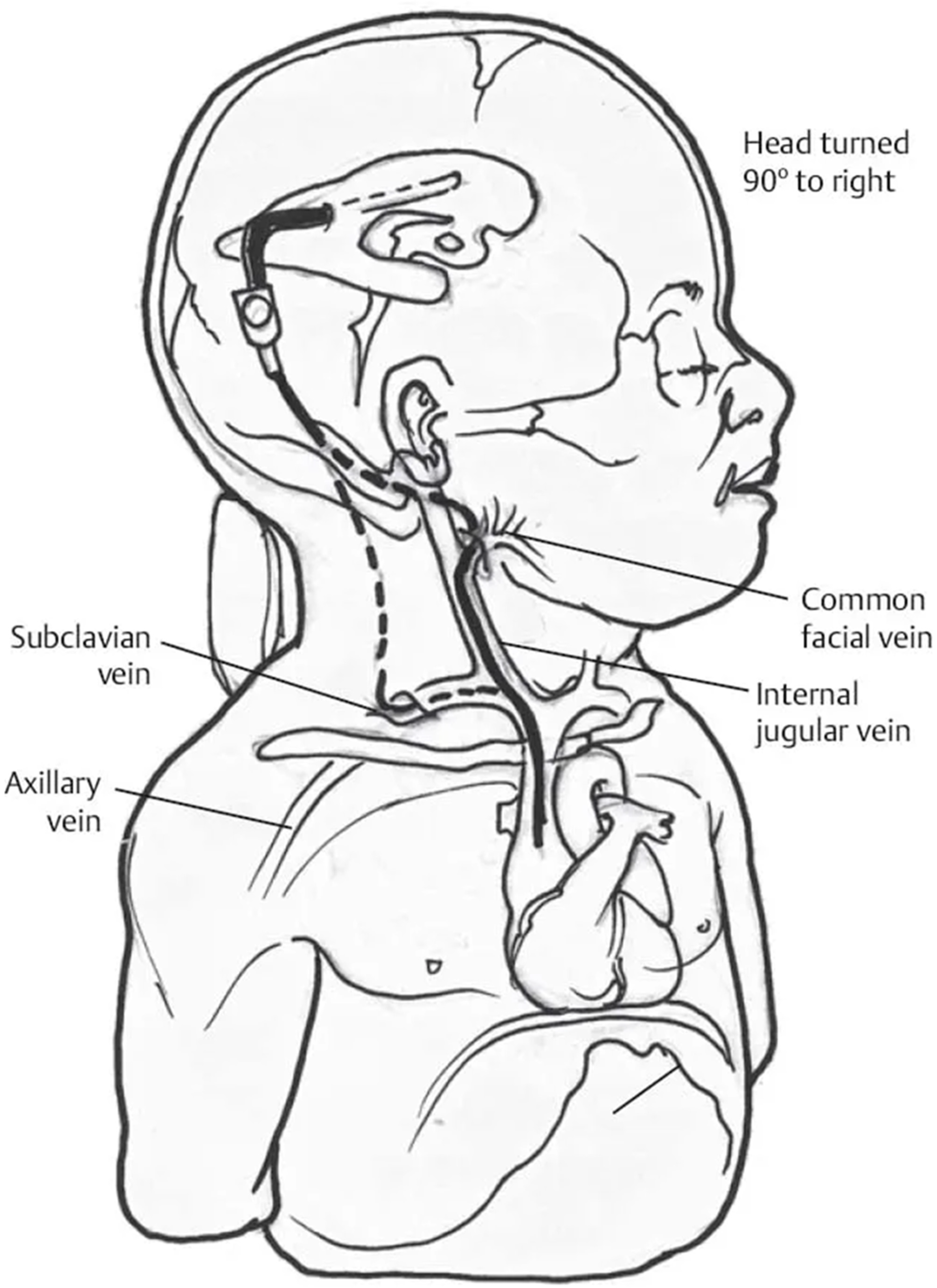
- As the child grows, the peripheral catheter is gradually getting shorter and eventually needs to be elongated. Sometimes this is quite technically demanding due to clot formation around the tube in the lumen of the jugular vein;
- If bacterial infection complicates our case and this involves the shunt system, the risk of development of septicemia is significantly increased.
- Fixed differential pressure (DP) valves;
- Over-drainage control devices (OCDs);
- Adjustable DP valves;
- Fixed DP valves with OCDs;
- Adjustable DP valves with OCDs.
1.3. Lumboperitoneal Shunts
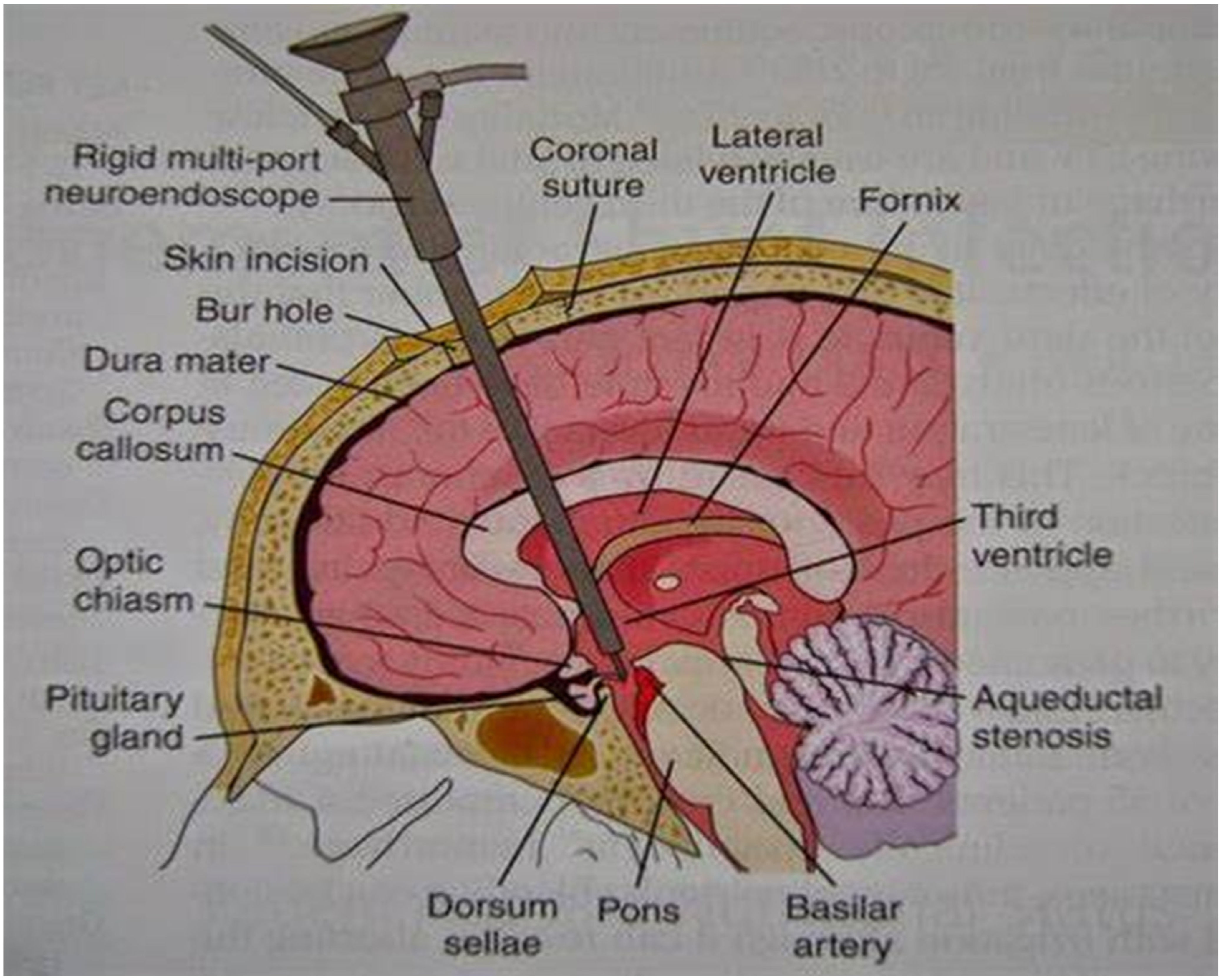
1.4. Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy
2. Materials and Methods
3. Discussion
3.1. Treatment Paradigm Standards of Surgical Intervention
3.2. Comparison of Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy and Shunt Placement in the Pediatric Population
3.3. Comparison of Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy and Ventriculo-Peritoneal Shunt Placement in Infants and Children in Terms of Safety and Efficacy
3.4. Shunt Independence and the Role of Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy
3.5. Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy and Infant Patient Population
3.6. The Role of Neuroendoscopy in the Management of Post-Infection Hydrocephalus
3.7. Posthemorrhagic Hydrocephalus in Premature Infants and Available Treatment Modalities
3.8. The Entity of the Isolated Fourth Ventricle and Available Treatment Options: Relative Advantages and Disadvantages
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ETV | endoscopic third ventriculostomy |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| PHH | post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus |
| CPC | choroid plexus cauterization |
| RCT | randomized controlled trials |
| PHH | post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus |
| IVH | intraventricular hemorrhage |
| PIH | post-infectious hydrocephalus |
| ICP | intra-cranial pressure |
| TFV | Trapped or isolated fourth ventricle |
| VA | shunt: ventriculo-atrial shunt |
| VPlS | ventriculo-pleural shunt |
| VSGS | ventriculo-subgaleal shunt |
| NEL | neuroendoscopic lavage |
| LPs | Lumboperitoneal shunts |
| SVS | slit ventricle syndrome |
| VPS | Ventriculo-peritoneal shunts |
| VPlS | Ventriculo-pleural shunts |
| EVD | external ventricular drain |
| ETVSS | ETV success score |
References
- Hochstetler, A.; Raskin, J.; Blazer-Yost, B.L. Hydrocephalus: Historical analysis and considerations for treatment. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokri, B. The Monro–Kellie hypothesis: Applications in CSF volume depletion. Neurology 2001, 56, 1746–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fact Sheet: Hydrocephalus Fact Sheet [Internet]. National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA. Available online: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Hydrocephalus-Fact-Sheet (accessed on 7 January 2022).
- Robinson, S. Neonatal posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus from prematurity: Pathophysiology and current treatment concepts. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2012, 9, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torkildsen, A. A new palliative procedure in cases of inoperable occlusion of the Sylvian duct. Acta Chir. Scand. 1939, 82, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, C.H.; Ritter, A.M.; Bruce, D.A. Development of shunt valves used for treating hydrocephalus: Comparison with endoscopy treatment. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2023, 39, 2709–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nulsen, F.E.; Spitz, E.B. Treatment of hydrocephalus by a direct shunt from ventricle to jugular vein. In Surgical Forum; American College of Surgeons: Chicago, IL, USA, 1952; pp. 399–402. [Google Scholar]
- Pudenz, R.H.; Russell, F.E.; Hurd, A.H.; Shelden, C.H. Ventriculo-auriculostomy; a technique for shunting cerebrospinal fluid into the right auricle; preliminary report. J. Neurosurg. 1957, 14, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Cornejo, V.J.; Elbabaa, S.K. Shunt technology for infants and lifetime. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2021, 37, 3475–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomei, K.L. The evolution of cerebrospinal fluid shunts: Advances in technology and technique. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2017, 52, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boockvar, J.A.; Loudon, W.; Sutton, L.N. Development of the Spitz—Holter valve in Philadelphia. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 95, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, R.H. Ventriculo-peritoneal shunts in the management of hydrocephalus. J. Neurosurg. 1967, 27, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, L.; Frykberg, T. Complications in the treatment of hydrocephalus in children. A comparison of ventriculoatrial and ventriculoperitoneal shunts in a 20-year material. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1983, 72, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kast, J.; Duong, D.; Nowzari, F.; Chadduck, W.M.; Schiff, S.J. Time-related patterns of ventricular shunt failure. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 1994, 10, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualin, A.; Mazza, C.; Da Pian, R. Results of treatment with ventriculoatrial and ventriculoperitoneal shunt in infantile nontumoral hydrocephalus. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1980, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainte-Rose, C. Shunt obstruction: A preventable complication? Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1993, 19, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EL Foltz, B.J. Symptomatic low intracranial pressure in shunted huydrocephalus. J. Neurosurg. 1988, 68, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, S.H.; Prein, T.H.; Ammar, A.; Grotenhuis, A.; Hamilton, M.G.; Hansen, T.S.; Kehler, U.; Rekate, H.; Thomale, U.-W.; Juhler, M. How to define CSF overdrainage: A systematic literature review. Acta Neurochir. 2023, 165, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudenz, R.H.; Foltz, E.L. Hydrocephalus: Overdrainage by ventricular shunts. A review and recommendations. Surg. Neurol. 1991, 35, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekate, H.L. Classification of slit-ventricle syndromes using intracranial pressure monitoring. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1993, 19, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, K.T.; Alghamdi, M.D.; Neazy, S.; Algamdi, M.M.; Alzahrani, A.; Khan, M.A.; Algahtani, A. Incidental and clinical significance of slit ventricles in fixed pressure valves. Cureus 2022, 14, e30902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudenz, R.H.; Constantini, S. Pudenz antisiphon device tear as a cause of shunt malfunction. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 1990, 6, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koueik, J.; Kraemer, M.R.; Hsu, D.; Rizk, E.; Zea, R.; Haldeman, C.; Iskandar, B.J. A 12-year single-center retrospective analysis of antisiphon devices to prevent proximal ventricular shunt obstruction for hydrocephalus. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2019, 24, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierbrauer, K.S.; Storrs, B.B.; McLone, D.G.; Tomita, T.; Dauser, R. A prospective, randomized study of shunt function and infections as a function of shunt placement. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1990, 16, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, J.M.; Kestle, J.R.W.; Tuli, S. CSF shunts 50 years on –past, present and future. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2000, 16, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, N. Lumboperitoneal shunt: Clinical applications, complications, and comparison with ventriculoperitoneal shunt. Neurosurgery 1990, 26, 998–1003; discussion 1003–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, V.Y.; Barbaro, N.M.; Lawton, M.T.; Pitts, L.; Kunwar, S.; Parsa, A.T.; Gupta, N.; McDermott, M.W. Complications of lumboperitoneal shunts. Neurosurgery 2007, 60, 1045–1048; discussion 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzayan, M.J.; Klinge, P.M.; Samii, M.; Goetz, F.; Krauss, J.K. MRI safety of a programmable shunt assistant at 3 and 7 Tesla. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 26, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumas, P.D.; Armstrong, D.C.; Drake, J.M.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Hoffman, H.J.; Humphreys, R.P.; Rutka, J.T.; Hendrick, E.B. Tonsillar herniation: The rule rather than the exception after lumboperitoneal shunting in the pediatric population. J. Neurosurg. 1993, 78, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgirt, M.J.; Woodworth, G.; Thomas, G.; Miller, N.; Williams, M.; Rigamonti, D. Cerebrospinal fluid shunt placement for pseudotumor cerebri—Associated intractable headache: Predictors of treatment response and an analysis of long-term outcomes. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 101, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menger, R.P.; Connor, D.E., Jr.; Thakur, J.D.; Sonig, A.; Smith, E.; Guthikonda, B.; Nanda, A. A comparison of lumboperitoneal and ventriculoperitoneal shunting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: An analysis of economic impact and complications using the Nationwide Inpatient Sample. Neurosurg. Focus 2014, 37, E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, T.D.; Zhang, Y.; Varshneya, K.; Veeravagu, A.; Ratliff, J.K.; Li, G. Lumboperitoneal and ventriculoperitoneal shunting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension demonstrate comparable failure and complication rates. Neurosurgery 2020, 86, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, H.J.; Harwood-Nash, D.; Gilday, D.L. Percutaneous third ventriculostomy in the management of noncommunicating hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 1980, 7, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinalli, G.; Salazar, C.; Mallucci, C.; Yada, J.Z.; Zerah, M.; Sainte-Rose, C. The role of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the management of shunt malfunction. Neurosurgery 1998, 43, 1323–1327; discussion 1327–1329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warf, B.C. Comparison of 1-year outcomes for the Chhabra and Codman-Hakim Micro Precision shunt systems in Uganda: A prospective study in 195 children. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2005, 102, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Canadian Pediatric Neurosurgery Study Group; Kulkarni, A.V.; Warf, B.C.; Drake, J.M.; Mallucci, C.L.; Sgouros, S.; Constantini, S. Surgery for hydrocephalus in sub-Saharan Africa versus developed nations: A risk-adjusted comparison of outcome. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2010, 26, 1711–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ribaupierre, S.; Rilliet, B.; Vernet, O.; Regli, L.; Villemure, J.-G. Third ventriculostomy vs ventriculoperitoneal shunt in pediatric obstructive hydrocephalus: Results from a Swiss series and literature review. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2007, 23, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.; Bo, X.; Beni-Adani, L.; Elran, H.; Constantini, S. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy—A physiological alternative to shunts as treatment for obstructive hydrocephalus in children. Harefuah 2007, 146, 660–665, 735. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, S.; Harris, D.; Rocque, B.G.; Ham, S.A. Pediatric endoscopic third ventriculostomy: A population-based study. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2014, 14, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, M.C.; Lim, J.; Shannon, C.N.; Wellons, J.C., 3rd. The durability of endoscopic third ventriculostomy and ventriculoperitoneal shunts in children with hydrocephalus following posterior fossa tumor resection: A systematic review and time-to-failure analysis. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2017, 19, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.V.; Drake, J.M.; Kestle, J.R.; Mallucci, C.L.; Sgouros, S.; Constantini, S. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy vs cerebrospinal fluid shunt in the treatment of hydrocephalus in children: A propensity score-adjusted analysis. Neurosurgery 2010, 67, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.V.; Riva-Cambrin, J.; Holubkov, R.; Browd, S.R.; Cochrane, D.D.; Drake, J.M.; Limbrick, D.D.; Rozzelle, C.J.; Simon, T.D.; Tamber, M.S.; et al. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in children: Prospective, multicenter results from the Hydrocephalus Clinical Research Network. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2016, 18, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovell, M.; Zakaria, R.; Ellenbogen, J.R.; Gallagher, M.J.; Jenkinson, M.D.; Hayhurst, C.; Malucci, C.L. Long-term follow-up of endoscopic third ventriculostomy performed in the pediatric population. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2016, 17, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.V.; Drake, J.M.; Kestle, J.R.W.; Mallucci, C.L.; Sgouros, S.; Constantini, S. Predicting who will benefit from endoscopic third ventriculostomy compared with shunt insertion in childhood hydrocephalus using the ETV success score. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2010, 6, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado, L.M.F.; da Costa Val Filho, J.A.; Dos Santos Júnior, E.C. External validation of the ETV success score in 313 pediatric patients: A Brazilian single-center study. Neurosurg. Rev. 2021, 44, 2727–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.V.; Riva-Cambrin, J.; Browd, S.R. Use of the ETV success score to explain the variation in reported endoscopic third ventriculostomy success rates among published case series of childhood hydrocephalus. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2011, 7, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yordanov, S.; Garnett, M.R.; Santarius, T.; Holland, K.; Jalloh, I.; Naushahi, M.J. An audit of endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) in a regional paediatric neurosurgical centre assessing the accuracy and feasibility of the ETV success score. Acta Neurochir. 2022, 164, 1453–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Israel, D.; Mann, J.A.; Yang, M.M.H.; Isaacs, A.M.; Cadieux, M.; Sader, N.; Muram, S.; Albakr, A.; Manoranjan, B.; Yu, R.W.; et al. Clinical outcomes in pediatric hydrocephalus patients treated with endoscopic third ventriculostomy and choroid plexus cauterization: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2022, 30, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellenbogen, Y.; Brar, K.; Yang, K.; Lee, Y.; Ajani, O. Comparison of endoscopic third ventriculostomy with or without choroid plexus cauterization in pediatric hydrocephalus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2020, 26, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, S.; Warf, B.C. Combined endoscopic third ventriculostomy and choroid plexus cauterization as primary treatment for infantshydrocephalus: A prospective North American series. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2014, 14, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warf, B.C. The impact of combined endoscopic third ventriculostomy and choroid plexus cauterization on the management of pediatric hydrocephalus in developing countries. World Neurosurg. 2013, 79, S23.e13–S23.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fame, R.M.; Cortés-Campos, C.; Sive, H.L. Brain ventricular system and cerebrospinal fluid development and function: Light at the end of the tube: A primer with latest insights. BioEssays. 2020, 42, e1900186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fame, R.M.; Lehtinen, M.K. Emergence and developmental roles of the cerebrospinal fluid system. Dev. Cell 2020, 52, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimy, J.K.; Reeves, B.C.; Damisah, E.; Duy, P.Q.; Antwi, P.; David, W.; Wang, K.; Schiff, S.J.; Limbrick, D.D., Jr.; Alper, S.L.; et al. Inflammation in acquired hydrocephalus: Pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, J.P., 2nd. Pathophysiology of congenital and neonatal hydrocephalus. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012, 17, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahle, K.T.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Limbrick, D.D.; Warf, B.C. Hydrocephalus in children. Lancet 2016, 387, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Yu, C.; Yang, J. Molecular mechanisms and risk factors for the pathogenesis of hydrocephalus. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 777926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, E.J.; Yamada, S. Cerebrospinal fluid flow studies and recent advancements. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2016, 37, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, B.C.; Karimy, J.K.; Kundishora, A.J.; Mestre, H.; Cerci, H.M.; Matouk, C.; Alper, S.L.; Lundgaard, I.; Nedergaard, M.; Kahle, K.T. G-lymphatic System impairment in Alzheimer’s disease and idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Trends Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.A.; Malm, J. Diagnosis and Treatment of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2016, 22, 579–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, F.; Ding, J.; Wang, X. Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2020, 26, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.C.; Dong, W.; Kundishora, A.J.; Panchagnula, S.; Moreno-De-Luca, A.; Furey, C.G.; Allocco, A.A.; Walker, R.L.; Nelson-Williams, C.; Smith, H.; et al. Exome sequencing implicates genetic disruption of prenatal neuro-gliogenesis in sporadic congenital hydrocephalus. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1754–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomale, U.W.; Ginalli, G.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Al-Hakin, S.; Roth, J.; Schaumann, A.; Buhrer, C.; Cavalheiro, S.; Sgouros, S.; Constanini, S.; et al. TROPHY registry study design: A prospective, international multicenter study for the surgical treatment of post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus in neonates. Child. Nerv. Syst. 2019, 35, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blitz, A.M.; Ahmed, A.K.; Rigamonti, D. Founder of modern hydrocephalus diagnosis and therapy: Walter Dandy at the Johns Hopkins Hospital. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 131, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagno, V.; Navarrete, E.A.; Mirone, G.; Esposito, F. Management of Hydrocephalus Around the World. World Neurosurg. 2013, 79, S23.e17–S23.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warf, B.C. Comparison of endoscopic third ventriculostomy alone and combined with choroid plexus cauterization in infants younger than 1 year of age: A prospective study in 550 African children. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2005, 103, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, J.M.; Kestle, J. Rational and methodology of the multicenter pediatric cerebrospinal fluid shunt design trial. Pediatric hydrocephalus treatment evaluation group. Childs Nerv. Syst. 1996, 12, 434–447. [Google Scholar]
- Kestle, J.; Milner, R.; Drake, J. The shunt design trial: Variation in surgical experience did not influence shunt survival. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1999, 30, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestle, J.; Drake, J.; Milner, R.; Sainte-Rose, C.; Cinalli, G.; Boop, F.; Piatt, J.; Haines, S.; Schiff, S.; Cochrane, D.; et al. Long-term follow-up data from the Shunt Design Trial. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2000, 33, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.N.; Carr, K.R.; Tomycz, L.; Wellons, J.C.; Tulipan, N. Time to first shunt failure in pediatric patients over 1 year old: A 10-year retrospective study. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2013, 49, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texakalidis, P.; Tora, M.S.; Wetzel, J.S.; Chern, J.J. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy versus shunt for pediatric hydrocephalus: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2019, 35, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuriat, P.-A.; Puget, S.; Cinalli, G.; Blauwblomme, T.; Beccaria, K.; Zerah, M.; Sainte-Rose, C. Hydrocephalus treatment in children: Long-term outcome in 975 consecutive patients. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2017, 20, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pople, I.K. Hydrocephalus and shunts: What the neurologist should know. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 73 (Suppl. 1), i17–i22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jernigan, S.C.; Berry, J.G.; Graham, D.A.; Goumnerova, L. The comparative effectiveness of ventricular shunt placement versus endoscopic third ventriculostomy for initial treatment of hydrocephalus in infants. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2014, 13, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uche, E.; Onyia, E.; Mezue, U.; Okorie, E.; Ozor, I.; Chikani, M. Determinants and outcomes of ventriculoperitoneal shunt infections in Enugu, Nigeria. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2013, 49, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, S.C.; Guo, W. Have we made progress in preventing shunt failure? A critical analysis. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2008, 1, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.V.; Riva-Cambrin, J.; Butler, J.; Browd, S.R.; Drake, J.M.; Holubkov, R.; Kestle, J.R.W.; Limbrick, D.D.; Simon, T.D.; Tamber, M.S.; et al. Outcomes of CSF shunting in children: Comparison of hydrocephalus clinical research network cohort with historical controls. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2013, 12, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greitz, D. Paradigm shift in hydrocephalus research in legacy of Dandy’s pioneering work: Rationale for third ventriculostomy in communicating hydrocephalus. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2007, 23, 487–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch-Wiewrodt, D.; Wagner, W. Success and failure of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in young infants: Are there different age distributions? Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2006, 22, 1537–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warf, B.C.; Tracy, S.; Mugamba, J. Long-term outcome for endoscopic third ventriculostomy alone or in combination with choroid plexus cauterization for congenital aqueductal stenosis in African infants. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2012, 10, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, I.-W.; Harris, D.A.; Luerssen, T.G.; Lam, S.K. Comparative Effectiveness of surgical treatments for pediatric hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 2017, 83, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.V.; Schiff, S.J.; Mbabazi-Kabachelor, E.; Mugamba, J.; Ssenyonga, P.; Donnelly, R.; Levenbach, J.; Monga, V.; Peterson, M.; MacDonald, M.; et al. Endoscopic treatment versus shunting for infant hydrocephalus in Uganda. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2456–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uche, E.O.; Okorie, C.; Iloabachie, I.; Amuta, D.S.; Uche, N.J. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) and ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VPS) in non-communicating hydrocephalus (NCH): Comparison of outcome profiles in Nigerian children. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2018, 34, 1683–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kestle, J.R.W.; Holubkov, R.; Cochrane, D.D.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Limbrick, D.D., Jr.; Luerssen, T.G.; Oakes, W.J.; Riva-Cambrin, J.; Rozzelle, C.; Simon, T.D.; et al. A new hydrocephalus clinical research network protocol to reduce cerebrospinal fluid shunt infection. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2016, 17, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gui, S.; Zhang, Y. Compare the safety and efficacy of endoscopic third ventriculostomy and ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement in infants and children with hydrocephalus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Neurosci. 2023, 134, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.F.C.; Kwok, B.C.T.; Stening, W.A.; Vonau, M. The current status of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the management of non-communicating hydrocephalus. min-Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 1994, 37, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, F.T.; Marcus, H.J.; Toma, A.K.; Thorne, L.; Watkins, L.D. Is endoscopic third ventriculostomy superior to shunts in patients with non-communicating hydrocephalus? A systematic review and meta-analysis of the evidence. Acta Neurochir. 2013, 155, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, O.A.; Bankole, O.B.; Kanu, O.O.; Okubadejo, N.U. Efficacy of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the management of hydrocephalus in children under 2 years of age: Experience from a tertiary institution in Nigeria. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2015, 18, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouras, T.; Sgouros, S. Complications of endoscopic third ventriculostomy. World Neurosurg. 2013, 79, S22.e9–S22.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warf, B.C. Hydrocephalus in Uganda: The predominance of infectious origin and primary management with endoscopic third ventriculostomy. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 102, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogiwara, H.; Dipatri, A.J., Jr.; Alden, T.D.; Bowman, R.M.; Tomita, T. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy for obstructive hydrocephalus in children younger than 6 months of age. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2010, 26, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rocco, C.; Marchese, E.; Velardi, F. A survey of the first complication of newly implanted CSF shunt devices for the treatment of nontumoral hydrocephalus. Cooperative survey of the 1991-1992 Education Committee of the ISPN. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 1994, 10, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, S.; Ros, B.; Ibáñez, G.; Delgado, A.; Ros, A.; Arráez, M.A. Shunt independence in paediatric hydrocephalus: Our 16-year experience and review. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2019, 35, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskin, J.J.; Manwaring, K.H.; Rekate, H.L. Ventricular shunt removal: The ultimate treatment of the slit ventricle syndrome. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 88, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernov, M.F.; Kamikawa, S.; Yamane, F.; Ishihara, S.; Hori, T. Neurofiberscope-guided management of slit-ventricle syndrome due to shunt placement. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2005, 102, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, F.J.; Hochwald, G.M.; Wald, A.; Ransohoff, J. Avoidance of shunt dependency in hydrocephalus. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 1975, 17, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannelli, A.; Rea, G.; Di Rocco, C. CSF shunt removal in children with hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir. 2005, 147, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, S.; Ros, B.; Martín, Á.; Carrasco, A.; Segura, M.; Delgado, A.; Rius, F.; Arráez, M. Surgical outcome of the shunt: 15-year experience in a single institution. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2016, 32, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinchon, M.; Rekate, H.; Kulkarni, A.V. Pediatric hydrocephalus outcomes: A review. Fluids Barriers CNS 2012, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqar, M.; Ellenbogen, J.R.; Mallucci, C. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy for shunt malfunction in children: A review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 51, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.V.; Drake, J.M.; Mallucci, C.L.; Sgouros, S.; Roth, J.; Constantini, S. Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in the Treatment of Childhood Hydrocephalus. J. Pediatr. 2009, 155, 254–259.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavarda, D.; Bednarek, N.; Litre, F.; Koch, C.; Lena, G.; Morville, P.; Rousseaux, P. Acquired aqueductal stenosis in preterm infants: An indication for neuroendoscopic third ventriculostomy. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2003, 19, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaben, M.; Manivannan, S.; Sharouf, F.; Hammad, A.; Patel, C.; Bhatti, I.; Leach, P. The efficacy of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in children 1 year of age or younger: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2020, 26, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadrian, D.; van Gelder, J.; Florida, D.; Jones, R.; Vonau, M.; Teo, C.; Stening, W.; Kwok, B. Long-term reliability of endoscopic third ventriculostomy. Neurosurgery 2005, 56, 1271–1278; discussion 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Beltagy, M.A.; Kamal, H.M.; Taha, H.; Awad, M.; El Khateeb, N. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy before tumor surgery in children with posterior fossa tumors, CCHE experience. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2010, 26, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, Y.R.; Jaiswal, S.; Adam, N.; Basoor, A.; Jain, G. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in infants. Neurol. India 2006, 54, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Wang, K.C.; Cho, B.K. Surgical outcome of pediatric hydrocephalus treated by endoscopic III ventriculostomy: Prognostic factors and interpretation of postoperative neuroimaging. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2000, 16, 161–168; discussion 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, P.; Szathmari, A.; De Biasi, S.; Mottolese, C. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in obstructive infantile hydrocephalus: Remarks about the so-called ‘Unsuccessful Cases’. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2010, 46, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewuerbati, S.; Maimaitili, M.; Zhu, G.; Du, G.; Liu, B.; Sailike, D.; Fan, Y.; Dangmurenjiafu, G. Timing of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in pediatric patients with congenital obstructive hydrocephalus: Assessment of neurodevelopmental outcome and short-term operative success rate. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, D.; Wagner, W. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in infants of less than1 year of age: Which factors influence the outcome? Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2004, 20, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadpour, M.; Mallucci, C.; Brodbelt, A.; Golash, A.; May, P. The impact of endoscopic third ventriculostomy on the management of newly diagnosed hydrocephalus in infants. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2001, 35, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorayeb, R.P.; Cavalheiro, S.; Zymberg, S.T. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in children younger than 1 year of age. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2004, 100, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldauf, J.; Oertel, J.; Gaab, M.R.; Schroeder, H.W.S. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in children younger than 2 years of age. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2007, 23, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Chari, A.; Gillespie, C.S.; Ekert, J.O.; Saffari, S.E.; James, G.; Aquilina, K. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy for shunt malfunction in the pediatric population: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression analysis. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2023, 31, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deopujari, C.E.; Padayachy, L.; Azmi, A.; Figaji, A.; Samantray, S.K. Neuroendoscopy for post-infective hydrocephalus in children. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2018, 34, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.H.; Holekamp, T.F.; Murphy, T.M.; Mercer, D.; Leonard, J.R.; Smyth, M.D.; Park, T.S.; Limbrick, D.D., Jr. Surgical management of complex multiloculated hydrocephalus in infants and children. Child. Nerv. Syst. 2015, 31, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andresen, M.; Juhler, M. Multiloculated hydrocephalus: A review of current problems in classification and treatment. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2012, 28, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsch, M.J.; Mehdorn, M. Endoscopic intraventricular surgery for treatment of hydrocephalus and loculated csf space in children less than one year of age. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2002, 36, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhoke, G.S.; Frassanito, P.; Chandra, N.; Ojha, B.K.; Singh, A. Role of magnetic resonance ventriculography in multiloculated hydrocephalus. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2013, 11, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.I.; Keiper, G.L., Jr.; Crone, K.R. Endoscopic treatment of loculated hydrocephalus. J. Neurosurg. 1995, 82, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spennato, P.; Cinalli, G.; Ruggiero, C.; Aliberti, F.; Trischitta, V.; Cianciulli, E.; Maggi, G. Neuroendoscopic treatment of multiloculated hydrocephalus in children. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2007, 106, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccaro, G.; Ramos, J.G. Multiloculated hydrocephalus. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2011, 27, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowoslawska, E.; Polis, L.; Kaniewska, D.; Mikolajczyk, W.; Krawczyk, J.; Szymanski, W.; Zakrzewski, K.; Podciechowska, J. Effectiveness of neuroendoscopic procedures in the treatment of complex compartmentalized hydrocephalus in children. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2003, 19, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandberg, D.I.; McComb, J.G.; Krieger, M.D. Craniotomy for fenestration of multiloculated hydrocephalus in pediatric patients. Neurosurg. 2005, 57, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, M.; Bohner, G.; Knaus, H.; Haberl, H.; Thomale, U.-W. Navigated endoscopic surgery for multiloculated hydrocephalus in children. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2010, 5, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzola, C.A.; Choudhri, A.F.; Auguste, K.I.; Limbrick, D.D., Jr.; Rogido, M.; Mitchell, L. Pediatric hydrocephalus: Systematic literature review and evidence-based guidelines. Part 2: Management of posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus in premature infants. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2014, 14 (Suppl. 1), 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadigh, Y.; van Surksum, C.; Schröder, P.H.D.; Cozar, A.; Khandour, D.; Talbi, L.; Spoor, J.K.H.; Rooda, O.H.J.E.; Volovici, V.; van Veelen, M.-L.C. Trapped fourth ventricle: To stent, shunt, or fenestrate—A systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis. Neurosurg. Rev. 2023, 46, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, J.C., 3rd; Hoffman, H.J.; Humphreys, R.P. Isolated fourth ventricle as a complication of ventricular shunting: Report of three cases. J. Neurosurg. 1978, 49, 910–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foltz, E.L.; Shurtleff, D.B. Conversion of communicating hydrocephalus to stenosis or occlusion of the aqueduct during ventricular shunt. J. Neurosurg. 1966, 24, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, D.H. Management strategies for treatment of the trapped fourth ventricle. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2004, 20, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Leahu, D.; Weiner, H.L.; Abbott, R.; Wisoff, J.H.; Epstein, F.J. Complications of fourth-ventricular shunts. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1995, 22, 309–313; discussion 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, M.J.; Kienke, S.; Manwaring, K.H.; Mehdorn, H.M. Endoscopic aqueductoplasty and interventriculostomy for the treatment of isolated fourth ventricle in children. Neurosurgery 2004, 55, 372–377; discussion 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalheiro, S.; Moron, A.F.; Zymberg, S.T.; Dastoli, P. Fetal hydrocephalus—Prenatal treatment. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2003, 19, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalheiro, S.; Moron, A.F.; Almodin, C.G.; Suriano, I.C.; Hisaba, V.; Dastoli, P.; Barbosa, M.M. Fetal hydrocephalus. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2011, 27, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán-Ojeda, A.; Campos-Fajardo, S.; Suárez-Monsalve, S.; Lindado-Pacheco, C.A.; Becerra-Ospina, J.E. Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy for the Management of Obstructive Hydrocephalus in Pregnancy: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. J. Neurol. Surg. Rep. 2024, 85, e59–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panagopoulos, D.; Stranjalis, G.; Gavra, M.; Boviatsis, E.; Korfias, S.; Karydakis, P. Current Trends in the Treatment of Pediatric Hydrocephalus: A Narrative Review Centered on the Indications, Safety, Efficacy, and Long-Term Outcomes of Available Treatment Modalities. Children 2024, 11, 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11111334
Panagopoulos D, Stranjalis G, Gavra M, Boviatsis E, Korfias S, Karydakis P. Current Trends in the Treatment of Pediatric Hydrocephalus: A Narrative Review Centered on the Indications, Safety, Efficacy, and Long-Term Outcomes of Available Treatment Modalities. Children. 2024; 11(11):1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11111334
Chicago/Turabian StylePanagopoulos, Dimitrios, Georgios Stranjalis, Maro Gavra, Efstathios Boviatsis, Stefanos Korfias, and Ploutarchos Karydakis. 2024. "Current Trends in the Treatment of Pediatric Hydrocephalus: A Narrative Review Centered on the Indications, Safety, Efficacy, and Long-Term Outcomes of Available Treatment Modalities" Children 11, no. 11: 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11111334
APA StylePanagopoulos, D., Stranjalis, G., Gavra, M., Boviatsis, E., Korfias, S., & Karydakis, P. (2024). Current Trends in the Treatment of Pediatric Hydrocephalus: A Narrative Review Centered on the Indications, Safety, Efficacy, and Long-Term Outcomes of Available Treatment Modalities. Children, 11(11), 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11111334






