Transcatheter Management of Pulmonary Sequestrations in Children—A Single-Center Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Study Outcomes
2.4. Catheterization Procedure
2.5. Statistical Analysis
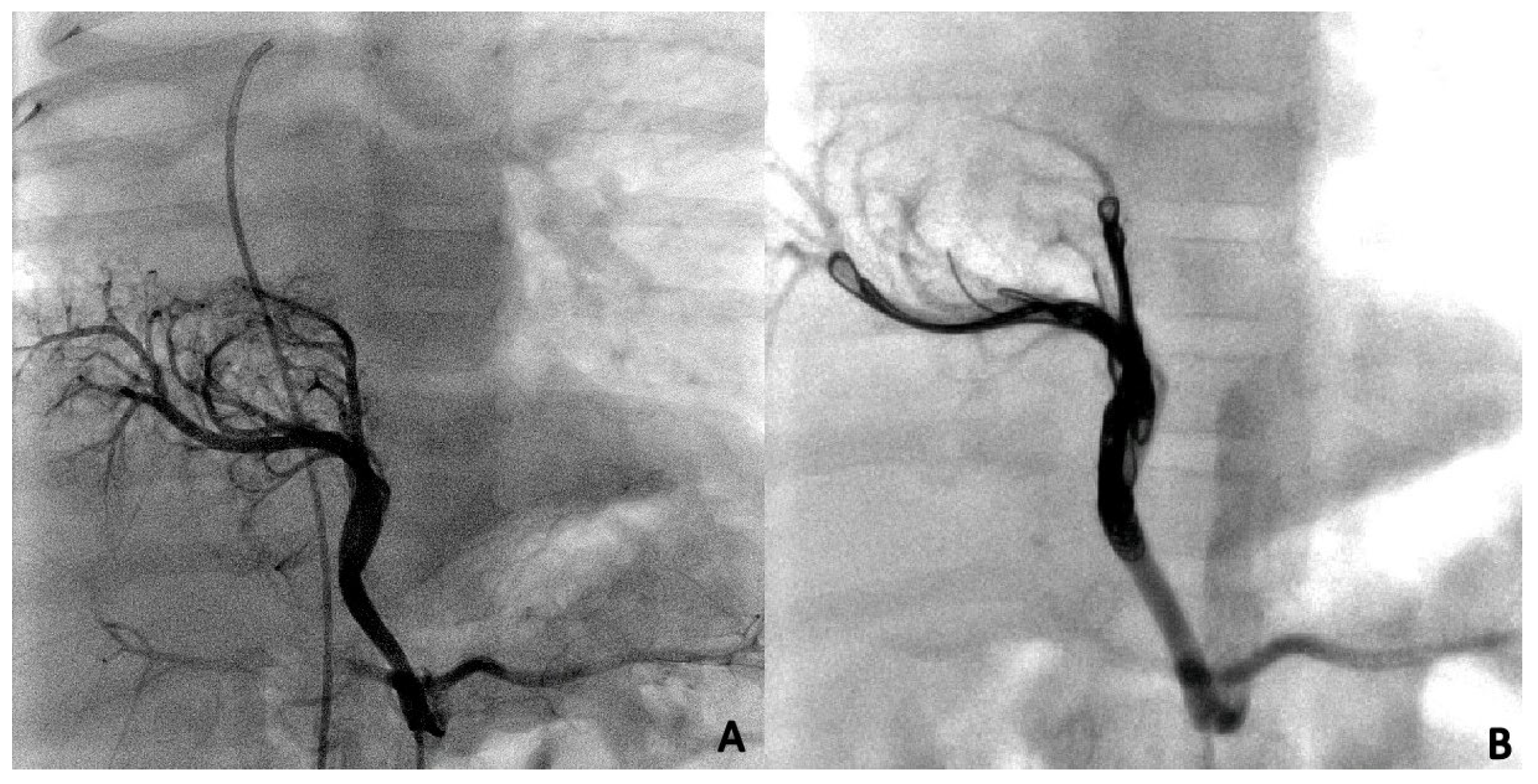
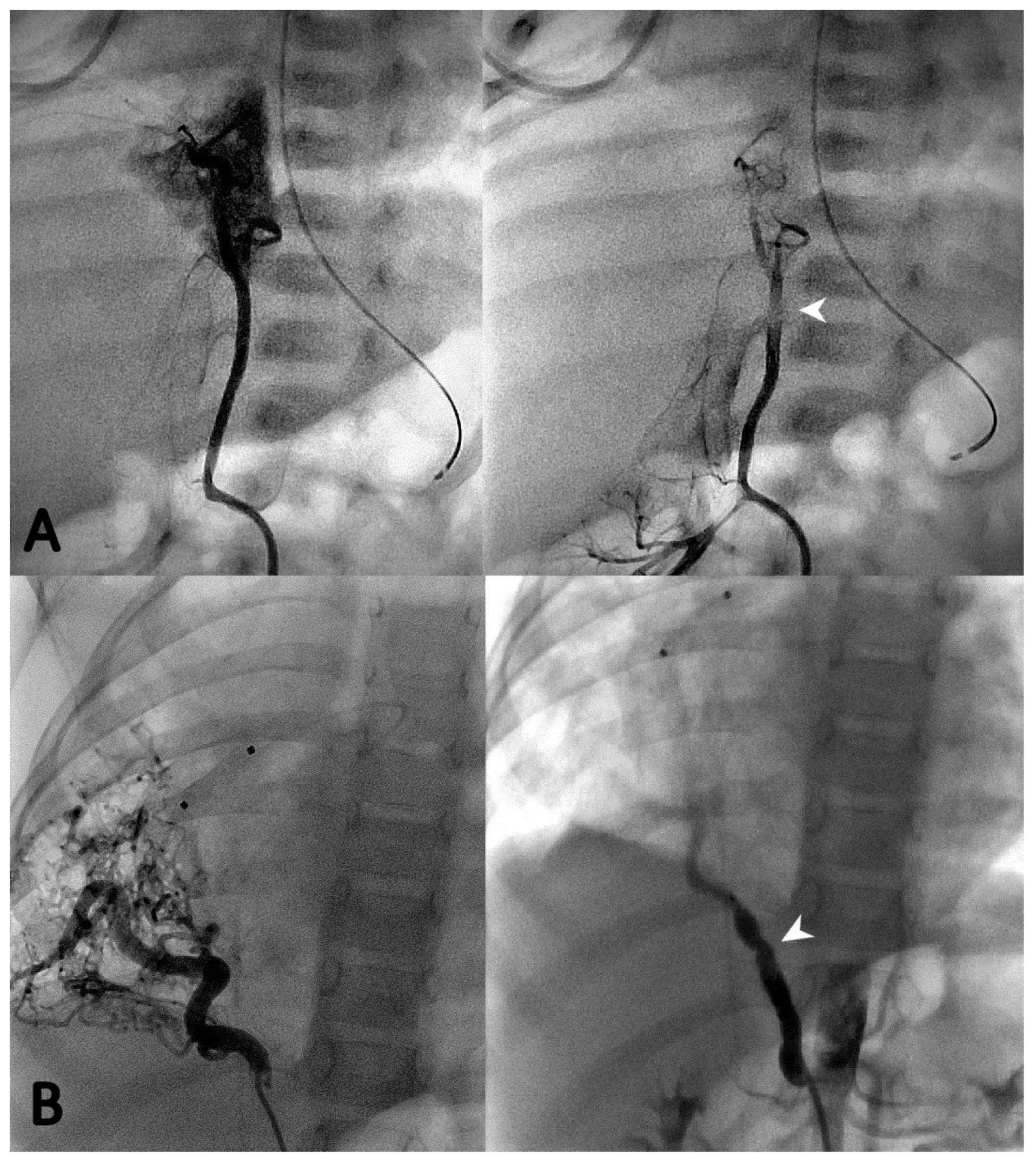
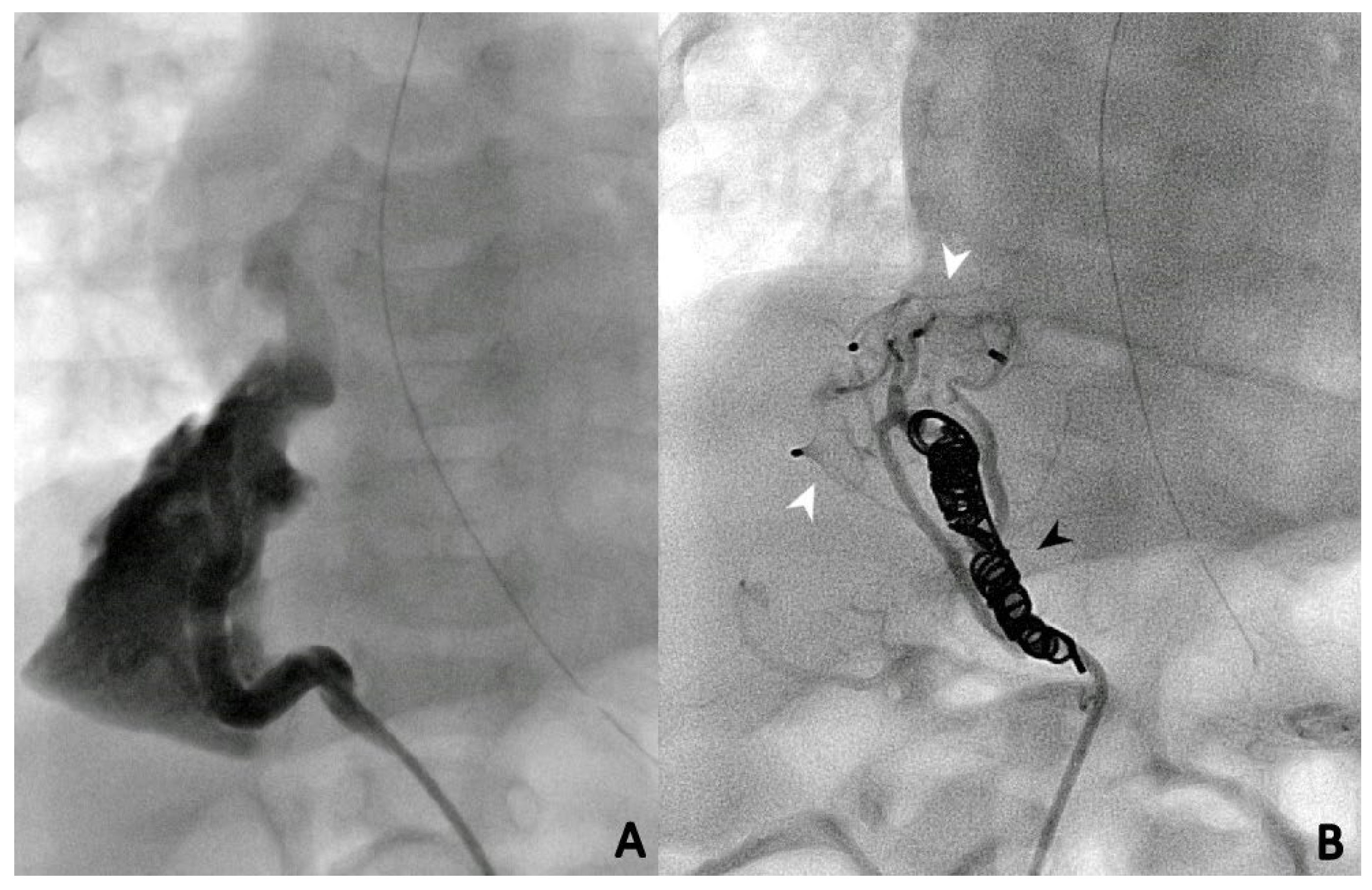
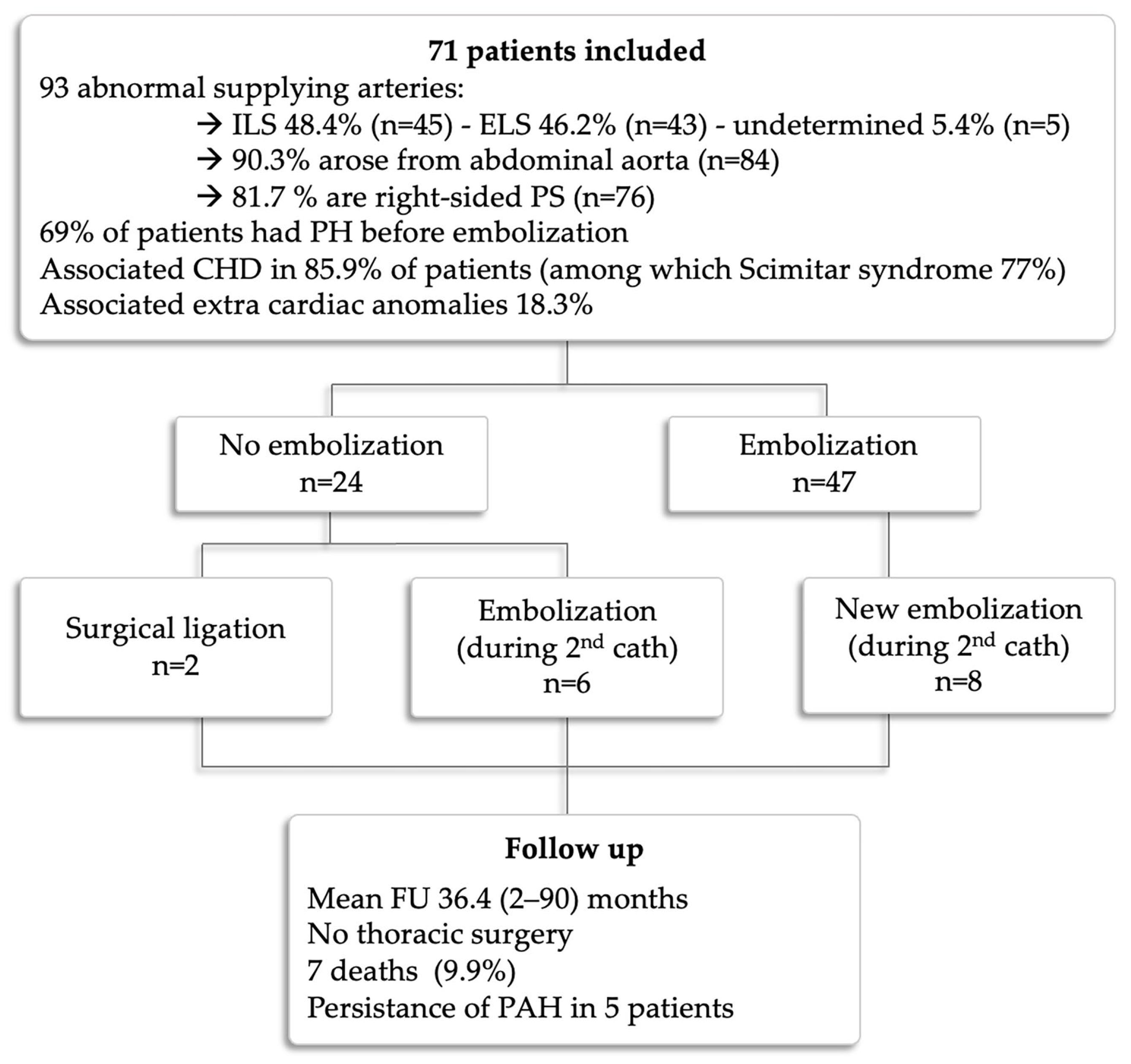
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Catheterization Procedure
3.3. Endovascular Embolization
3.4. Follow-Up and Outcomes
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pryce, D.M. Lower accessory pulmonary artery with intralobar sequestration of lung; a report of seven cases. J. Pathol. Bacteriol. 1946, 58, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Corbett, H.J.; Humphrey, G.M. Pulmonary sequestration. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2004, 5, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazier, A.A.; Rosado de Christenson, M.L.; Stocker, J.T.; Templeton, P.A. Intralobar sequestration: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. RadioGraphics 1997, 17, 725–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deparedes, C.G.; Pierce, W.S.; Johnson, D.G.; Waldhausen, J.A. Pulmonary sequestration in infants and children: A 20-year experience and review of the literature. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1970, 5, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, R.K.; Modi, P.; Sharma, S. Pulmonary Sequestration. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, C.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X. Distribution, diagnosis, and treatment of pulmonary sequestration: Report of 208 cases. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2019, 54, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, M.; Conner, P.; Ehren, H.; Bitkover, C.; Burgos, C.M. The natural history of prenatally diagnosed congenital pulmonary airway malformations and bronchopulmonary sequestrations. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2022, 57, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruano, R.; Da Silva, M.M.; Salustiano, E.; Kilby, M.D.; Tannuri, U.; Zugaib, M. Percutaneous laser ablation under ultrasound guidance for fetal hyperechogenic microcystic lung lesions with hydrops: A single center cohort and a literature review. Prenat. Diagn. 2012, 32, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, D.; Windrim, R.; Kachura, J.R.; Jefferies, A.; Pantazi, S.; Shah, P.; Langer, J.C.; Forsey, J.; Chaturvedi, R.R.; Jaeggi, E.; et al. Minimally invasive fetal therapy for hydropic lung masses: Three different approaches and review of the literature. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 42, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabra, R.; Gheorghe, C.P.; Monson, M.A.; Masri, J.; Chmait, R.H. In utero Treatment of Congenital High Airway Obstruction Syndrome via Fetal Laryngoscopy and EXIT Procedure. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2022, 49, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, M.; Njere, I.; Ade-Ajayi, N.; Patel, S.; Davenport, M. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the postnatal management of congenital cystic lung lesions. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2009, 44, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khen-Dunlop, N.; Farmakis, K.; Berteloot, L.; Gobbo, F.; Stirnemann, J.; De Blic, J.; Brunelle, F.; Delacourt, C.; Revillon, Y. Bronchopulmonary sequestrations in a paediatric centre: Ongoing practices and debated management. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2018, 54, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijagal, A.; Jelin, E.; Feldstein, V.A.; Courtier, J.; Urisman, A.; Jones, K.D.; Lee, H.; Hirose, S.; MacKenzie, T.C. The diagnosis and management of intradiaphragmatic extralobar pulmonary sequestrations: A report of 4 cases. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2012, 47, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-W.; Hsu, W.-M.; Lu, F.L.; Chen, P.-C.; Jeng, S.-F.; Peng, S.S.-F.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chou, H.-C.; Tsao, P.-N.; Hsieh, W.-S. Management of congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation and bronchopulmonary sequestration in newborns. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2010, 51, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokel, K.; Boyvat, F.; Varan, B. Coil Embolization of Pulmonary Sequestration in Two Infants. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 175, 993–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, K.-J.; Huang, T.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Lee, C.-L.; Hsieh, K.-S.; Weng, K.-P. Early and late outcomes of coil embolization of pulmonary sequestration in children. Circ. J. 2009, 73, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.C.; Dch, F.; De Laat, M.; Proesmans, M.; De Boeck, K.; Van Raemdonck, D.; Louw, J.; Heying, R.; Cools, B.; Eyskens, B.; et al. Treatment strategies for pulmonary sequestration in childhood: Resection, embolization, observation? Acta Cardiol. 2012, 67, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudhan, K.; Das, C.J.; Dutta, R.; Kumar, A.; Bhalla, A.S. Endovascular Embolization of Pulmonary Sequestration in an Adult. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 20, 1640–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzelli, A.; Paladini, A.; Giurazza, F.; Tecame, S.; Giordano, F.; Cavaglià, E.; Amodio, F.; Corvino, F.; Zobel, D.B.; Frauenfelder, G.; et al. Successful endovascular embolization of an intralobar pulmonary sequestration. Radiol. Case Rep. 2017, 13, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Balasubramanian, S.; Jackson, R.; Agrawal, D. Combined endovascular and surgical approaches to treat intralobar pulmonary sequestration: A case report. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2021, 103, e35–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Sun, M.-S.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, J.-B.; Nie, Q.-Q.; Zheng, X.; Fan, X.-Q.; Liu, P. Hybrid and Endovascular Treatment of Pulmonary Sequestration: Two Case Reports and Literature Review. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 69, 447.e1–447.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Tang, S.; Fu, Q.; Yu, L.; Liu, L. Hybrid surgery in treatment of pulmonary sequestration with abdominal aorta feeding vessel: A case report. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2018, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-H.; Sung, K.-B.; Yoon, H.-K.; Ko, G.-Y.; Yoon, C.H.; Goo, H.W.; Kim, E.A.-R.; Kim, K.S.; Pi, S.Y. Transcatheter arterial embolization of pulmonary sequestration in neonates: Long-term follow-up results. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2003, 14, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.T.; Yoon, C.H.; Sung, K.-B.; Yoon, H.-K.; Goo, D.E.; Kim, K.S.; Pi, S.Y.; Auh, Y.H. Pulmonary sequestration in a newborn infant: Treatment with arterial embolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 1998, 9, 648–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curros, F.; Chigot, V.; Emond, S.; Sayegh, N.; Revillon, Y.; Scheinmann, P.; Lebourgeois, M.; Brunelle, F. Role of embolisation in the treatment of bronchopulmonary sequestration. Pediatr. Radiol. 2000, 30, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.M.; Kim, E.A.-R.; Chung, S.-H.; Kim, S.-O.; Jung, A.Y.; Cho, Y.A.; Yoon, C.H.; Lee, J.S. Extralobar pulmonary sequestration in neonates: The natural course and predictive factors associated with spontaneous regression. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 2489–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, R.N.; Bonnet, D.; Malekzadeh-Milani, S. Embolization of vascular abnormalities in children with congenital heart diseases using medtronic micro vascular plugs. Hear. Vessel. 2022, 37, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vida, V.L.; Padalino, M.A.; Boccuzzo, G.; Tarja, E.; Berggren, H.; Carrel, T.; Çiçek, S.; Crupi, G.; Di Carlo, D.; Di Donato, R.; et al. Scimitar Syndrome: A European Congenital Heart Surgeons Association (ECHSA) multicentric study. Circulation 2010, 122, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusenbery, S.M.; Geva, T.; Seale, A.; Valente, A.M.; Zhou, J.; Sena, L.; Geggel, R.L. Outcome predictors and implications for management of scimitar syndrome. Am. Hear. J. 2013, 165, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zener, R.; Bottoni, D.; Zaleski, A.; Fortin, D.; Malthaner, R.A.; Inculet, R.I.; Mujoomdar, A. Transarterial embolization of intralobar pulmonary sequestration in a young adult with hemoptysis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, E188–E193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.E.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, J.S. Transcatheter embolization for massive hemoptysis from an intralobar pulmonary sequestration: A case report. Clin. Imaging 2014, 38, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, D.; Szezepanski, I.; Delacourt, C.; Malkezadeh-Milani, S.; Lévy, M. Multifactorial pulmonary hypertension in infantile scimitar syndrome. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 115, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Total | Non-Embolized | Embolized † | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 71 | N = 18 | N = 53 | ||
| Male, N (%) | 37 (52.1) | 10 (55.6) | 27 (50.9) | 0.79 a |
| Age (months), median (IQR) | 4.9 (2.1–26.6) | 16.1 (2.9–50.5) | 4.3 (1.9–11.6) | 0.07 b |
| Age groups, N (%) | 0.928 c | |||
| Neonates (0–30 days) | 10 (14.1) | 2 (11.1) | 8 (15.1) | |
| Infants (1–12 months) | 33 (46.5) | 8 (24.3) | 25 (75.7) | |
| Young children (1–6 years) | 17 (23.9) | 5 (29.4) | 12 (70.6) | |
| Children (6–12 years) | 6 (8.5) | 2 (11.1) | 4 (7.5) | |
| Adolescents (12–18 years) | 5 (7) | 1 (5.6) | 4 (7.5) | |
| Weight (kg), median (IQR) | 4.2 (3.9–12.1) | 9 (4.9–19) | 4.2 (3.2–8.8) | 0.007 c |
| Body surface area (m2), median (IQR) | 0.25 (0.24–0.54) | 0.43 (0.28–0.76) | 0.25 (0.21–0.43) | 0.007 c |
| Prenatal diagnosis of pulmonary sequestration, N (%) | 7 (9.9) | 1 (5.6) | 6 (11.3) | 0.67 c |
| Prenatal diagnosis of associated heart defects, N (%) | 13 (18.3) | 4 (22.2) | 9 (17) | 0.726 c |
| Associated congenital heart diseases, N (%) | 61 (85.9) | 15 (83.3) | 46 (86.8) | 0.706 c |
| Associated non-cardiac anomalies/malformations, N (%) | 13 (18.3) | 6 (33.3) | 7 (13.2) | 0.079 c |
| Heart position on chest X-ray, N (%) | 0.749 c | |||
| Levocardia | 30 (42.2) | 8 (44.4) | 22 (41.5) | |
| Dextrocardia | 32 (40.1) | 7 (38.9) | 25 (47.2) | |
| Mesocardia | 9 (12.7) | 3 (16.7) | 6 (11.3) | |
| Clinical presentation/symptoms *, N (%) | ||||
| Asymptomatic/incidental diagnosis/persistent dry cough | 13 (18.3) | 5 (27.8) | 8 (15.1) | 0.292 c |
| Cyanosis | 12 (16.9) | 1 (5.6) | 11 (20.8) | 0.273 c |
| Heart murmur | 32 (45.1) | 6 (33.3) | 26 (49.1) | 0.284 a |
| Failure to thrive | 16 (22.5) | 2 (11.1) | 14 (26.4) | 0.327 c |
| Mild-to-moderate respiratory distress | 21 (26.9) | 1 (5.6) | 20 (37.7) | 0.014 a |
| Chronic or recurrent chest infection | 27 (38) | 5 (27.8) | 22 (41.5) | 0.403 a |
| Mild-to-moderate symptoms of heart failure | 11 (15.5) | 1 (5.6) | 10 (18.9) | 0.269 c |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 42 (59.1) | 8 (44.4) | 34 (64.2) | 0.171 a |
| Respiratory failure | 9 (12.7) | 1 (5.6) | 8 (15.1) | 0.432 c |
| Intubation, N (%) | 9 (12.7) | 1 (5.6) | 8 (15.1) | 0.432 c |
| Nitrite oxide therapy, N (%) | 2 (2.8) | -- | 2 (3.8) | -- |
| Baseline ultrasound findings *, N (%) | ||||
| Normal pulmonary artery pressure | 29 (40.8) | 10 (55.6) | 19 (35.8) | |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 42 (59.2) | 8 (44.4) | 34 (64.2) | |
| Infra-systemic | 18 (25.4) | 7 (38.9) | 11 (20.8) | |
| Iso-systemic | 9 (12.7) | -- | 9 (17) | 0.025 c |
| Supra-systemic | 15 (21.1) | 1 (5.6) | 14 (26.4) | |
| Dilated right ventricle | 39 (54.9) | 7 (38.9) | 32 (60.4) | 0.17 a |
| Right ventricular dysfunction | 6 (8.5) | 1 (5.6) | 5 (9.4) | 1 c |
| Dilated left ventricle | 10 (14.1) | 1 (5.6) | 9 (17) | 0.434 a |
| Pulmonary artery anatomy/anomaly, N (%), n = 71 | |
| Normal anatomy | 34 (47.9) |
| RPA agenesis | 2 (2.8) |
| RPA hypoplasia | 32 (45.1) |
| LPA hypoplasia | 3 (4.2) |
| Number of individual supply arteries per patient, N (%), n = 71 | |
| 1 | 55 (77.5) |
| 2 | 13 (18.3) |
| 4 | 3 (4.2) |
| Arterial blood supply origin, N (%), n = 93 | |
| Abdominal aorta | 84 (90.3) |
| Thoracic aorta | 9 (9.7) |
| Side of pulmonary sequestration, N (%), n = 93 | |
| Left lung | 9 (9.7) |
| Right lung | 76 (81.7) |
| Both lungs | 8 (8.6) |
| Distribution of pulmonary sequestration, N (%), n = 93 | |
| Lower left lobe | 14 (15.1) |
| Right lower lobe | 71 (76.3) |
| Right upper lobe | 3 (3.2) |
| Right middle lobe | 5 (5.4) |
| Type of pulmonary sequestration, N (%), n = 93 | |
| Intra-lobar | 45 (48.4) |
| Extra-lobar | 43 (46.2) |
| Mixed | 5 (5.4) |
| Associated anomalous pulmonary vein into the systemic venous system, N (%), n = 71 | 47 (66.2) |
| Non-obstructed | 37 (78.7) |
| Occluded | 4 (8.5) |
| Stenotic | 4 (8.5) |
| Atypical | 2 (4.3) |
| Pulmonary artery pressure, N (%), n = 71 | |
| Normal | 22 (31) |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 49 (69) |
| Infra-systemic | 29 |
| Iso-systemic | 9 |
| Supra-systemic | 11 |
| Planned embolization post-corrective surgery, N (%), n = 71 | 5 (7) |
| Embolization, N (%), n = 71 | 47 (66.2) |
| Vascular plugs/occluder devices | 14 (29.8) |
| Coils/microcoils | 16 (34) |
| Combination of embolization material | 17 (36.2) |
| Number of vascular plugs/occluder devices per setting, median (IQR), n = 47 | 1 (1–2) |
| Number of coils/microcoils per setting, median (IQR), n = 47 | 2 (1–3) |
| Number of embolized supply vessels during the same procedure, N (%), n = 47 | |
| 1 | 33 (70.2) |
| 2 | 11 (23.4) |
| 3 | 3 (6.4) |
| Reason for non-embolization or delayed embolization *, N (%), n = 24 | |
| Small supply vessel/hemodynamical insignificance | 16 (66.7) |
| Supply vessel too large | 2 (8.3) |
| Underestimation/re-evaluation of hemodynamical significance | 5 (20.8) |
| Patient instability/anesthesia problems | 1 (4.2) |
| Re-embolization during second/third catheterization, N (%), n = 71 | 14 (19.7) |
| Previously non/delayed embolized vessel supply, N (%), n = 24 | 6 (25) |
| Previously embolized vessel supply (residual shunt), N (%), n = 47 | 2 (4.3) |
| Previously embolized site (recanalization), N (%), n = 47 | 6 (12.8) |
| Procedure time (min) ‡, median (IQR), n = 57 ⫲ | 60 (40–90) |
| Fluoroscopy time (min) ‡, median (IQR), n = 61 ⫲ | 16.9 (9.5–24.8) |
| Total dose area product (µGy.m2) ‡, median (IQR), n = 50 ⫲ | 264.8 (147.5–663.7) |
| Kar (mGy) ‡, median (IQR), n = 58 ⫲ | 64 (31.5–127.2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu Zahira, I.; Haddad, R.N.; Meot, M.; Bonnet, D.; Malekzadeh-Milani, S. Transcatheter Management of Pulmonary Sequestrations in Children—A Single-Center Experience. Children 2023, 10, 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10071197
Abu Zahira I, Haddad RN, Meot M, Bonnet D, Malekzadeh-Milani S. Transcatheter Management of Pulmonary Sequestrations in Children—A Single-Center Experience. Children. 2023; 10(7):1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10071197
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu Zahira, Ibrahim, Raymond N. Haddad, Mathilde Meot, Damien Bonnet, and Sophie Malekzadeh-Milani. 2023. "Transcatheter Management of Pulmonary Sequestrations in Children—A Single-Center Experience" Children 10, no. 7: 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10071197
APA StyleAbu Zahira, I., Haddad, R. N., Meot, M., Bonnet, D., & Malekzadeh-Milani, S. (2023). Transcatheter Management of Pulmonary Sequestrations in Children—A Single-Center Experience. Children, 10(7), 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10071197







