Assessment of the Impact of Increased Physical Activity on Body Mass and Adipose Tissue Reduction in Overweight and Obese Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Applied Research Methods
- Sit-and-reach flexibility test—reaching forward when sitting. The participant made two attempts and a better score was recorded.
- Standing broad jump test—long jump from the take-off line. Out of two attempts, the longer jump was recorded to the nearest centimetre.
- Handgrip strength test—handgrip dynamometry. The participant made two attempts with their stronger had. The better score was recorded to the nearest kilogramme.
- Sit-up test—trunk strength attempt. The participant made one attempt. The test result was the number of correctly performed sit-ups from lying down in 30 s.
- Bent-arm hang test—the functional strength test on horizontal bar. The participant performed the test only once with bare feet. The time of hang was measured to the nearest second.
- Agility shuttle run—10 × 5 m shuttle run. The participant performed the test once. The total time taken to complete five full repetitions (50 m in total) was measured to the nearest 0.1 s.
- Cooper test—endurance test. The participant performed the test once. Test participants covered as much a distance as they could in a continuous 12-min run. The score was recorded in metres.
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results
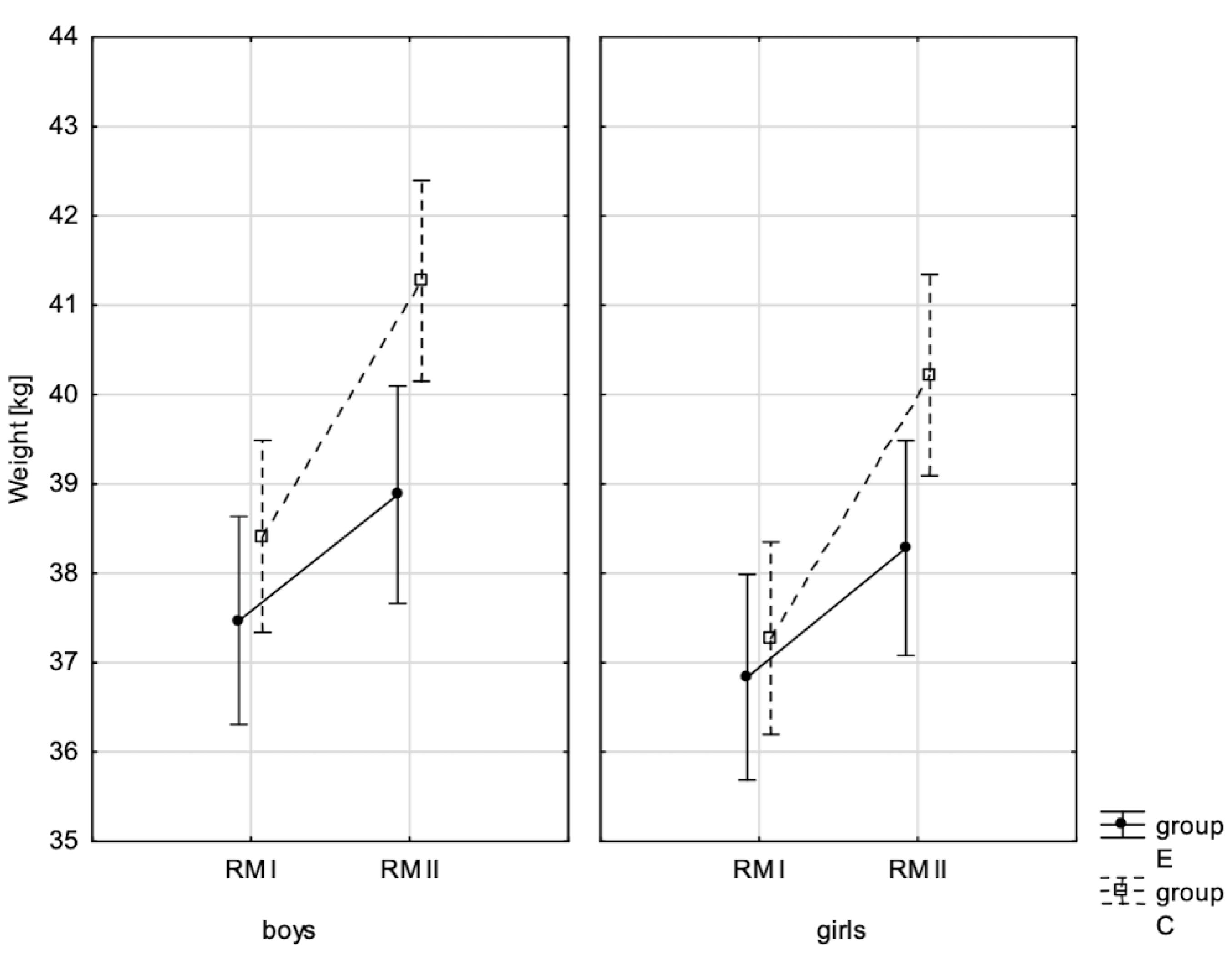
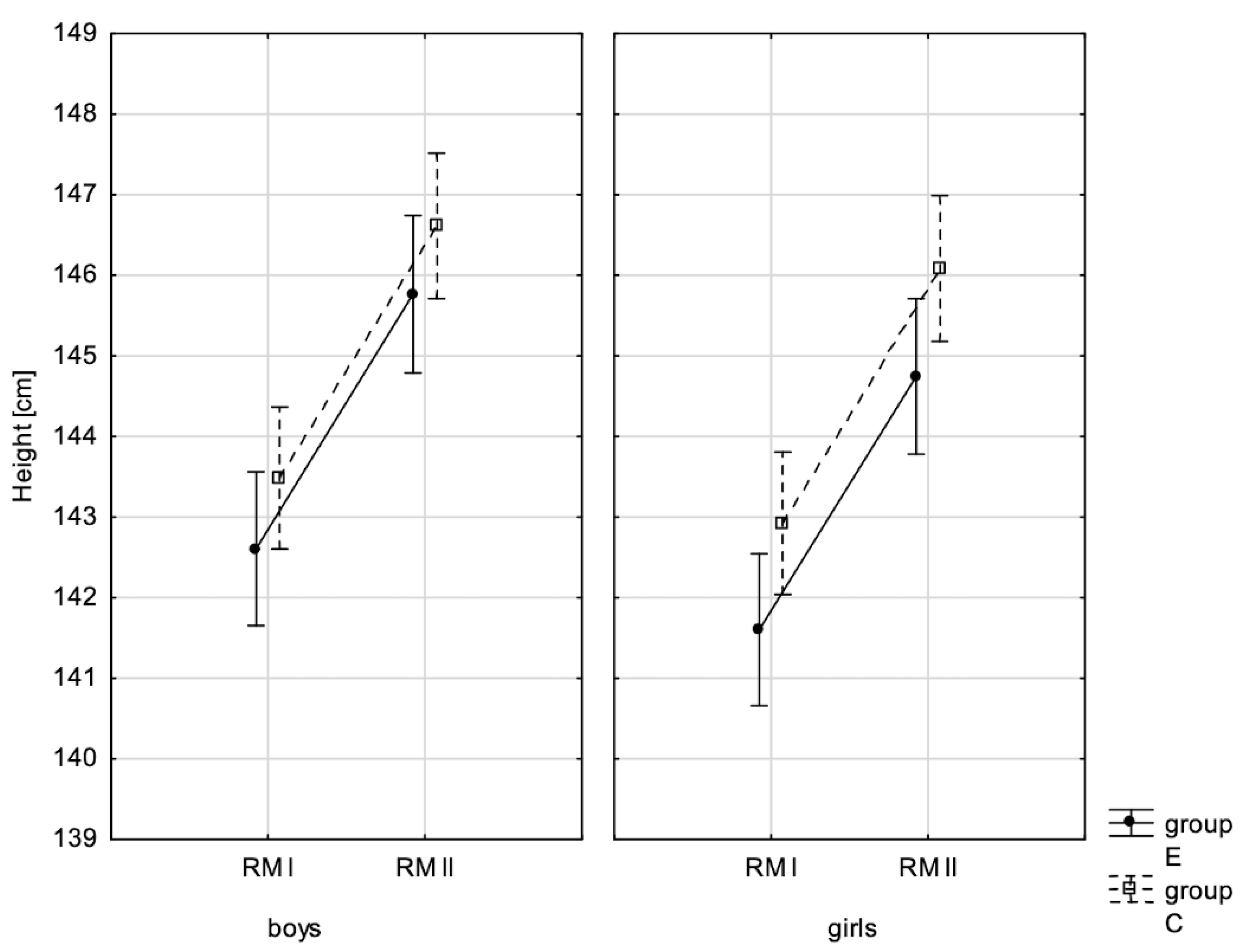
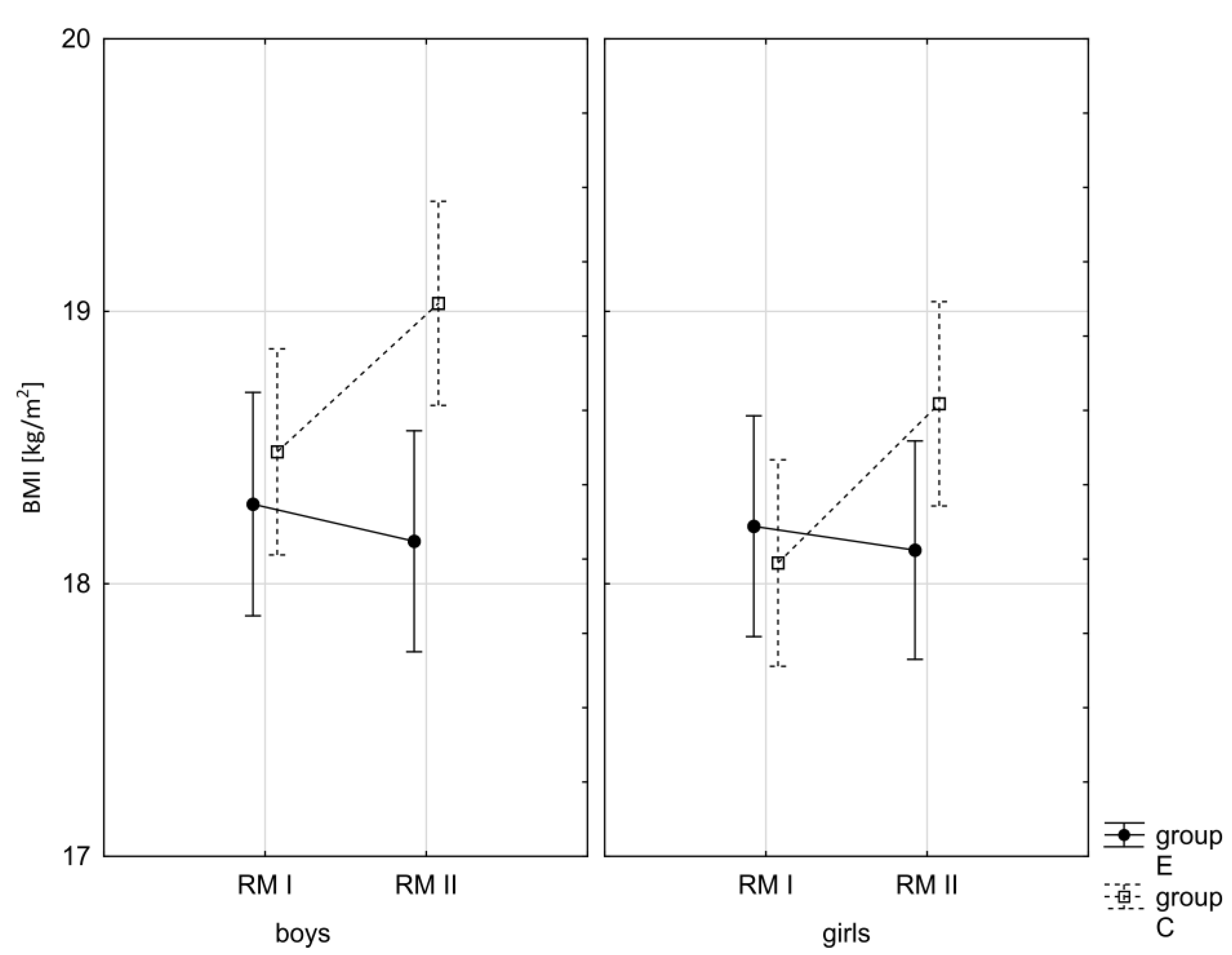
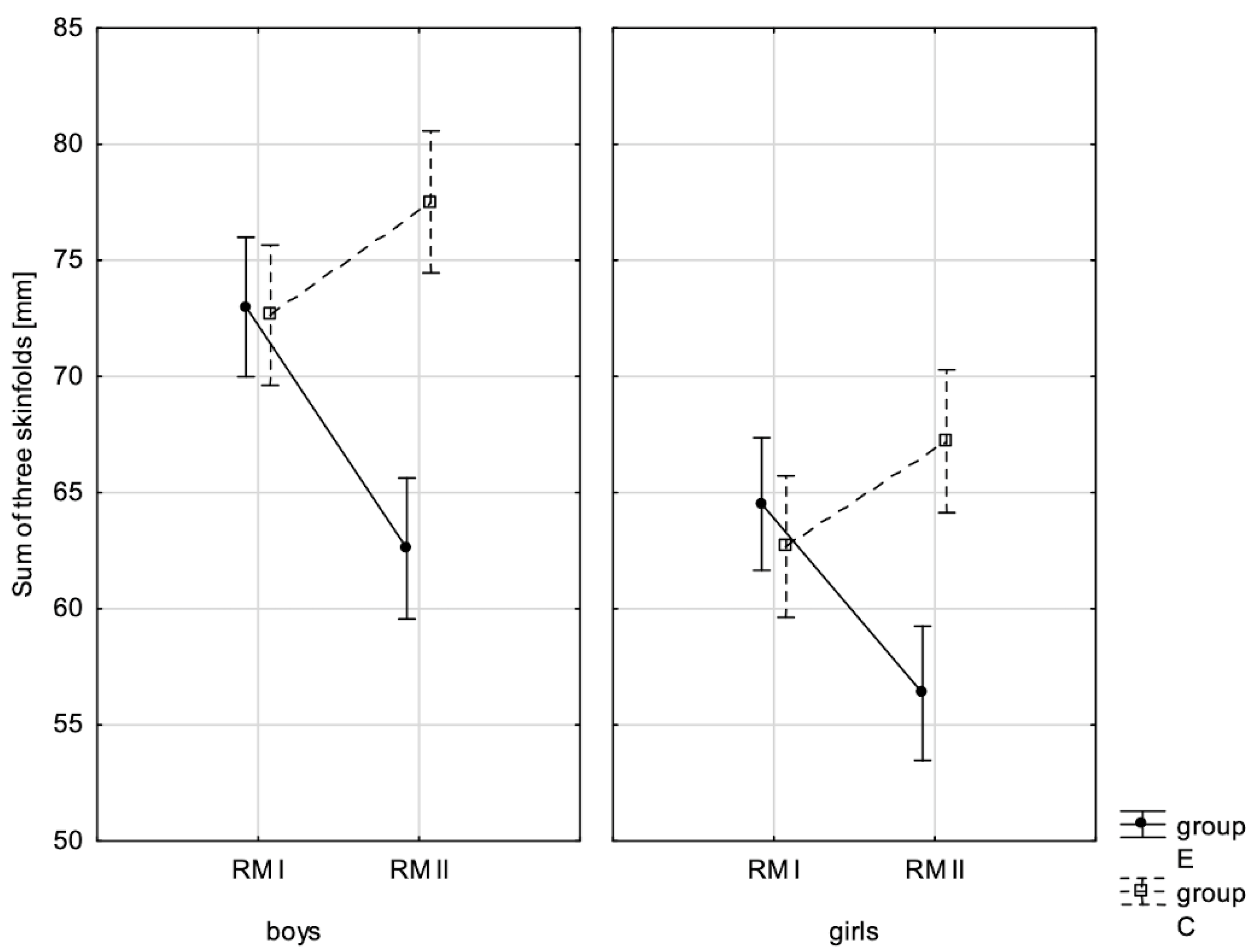
3.1. Effect of Increased Physical Activity on Somatic Characteristics Value and Body Composition
3.2. Influence of Increased Physical Activity on Fitness Components
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eurostat. Eurostat Regional Yearbook, 2017 ed.; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2017; pp. 52–70.
- World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2018: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Drygas, W.; Gajewska, M.; Zdrojewski, T. Insufficient Level of Physical Activity in Poland as a Threat and Challenge to Public Health; The Report of the Committee on Public Health of the Polish Academy of Sciences; the Committee on Public Health of the Polish Academy of Sciences: Warszawa, Poland, 2021. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Pyrżak, B.; Czerwonogrodzka-Senczyna, A.; Majcher, A.; Janczarska, D. Risk of metabolic syndrome in children 1–7 years with simple obesity. Endokrynol. Ped. 2012, 1, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Przybylska, D.; Kurowska, M.; Przybylski, P. Obesity and overweight in the adolescent. Hygeia Public Health 2012, 47, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Gawlik, A.; Zachurzok-Buczyńska, A.; Małecka-Tendera, E. Complications of obesity in children and adolescents. Endokrynol. Zab. Przem. Mat. 2009, 5, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- van Vliet-Ostaptchouk, J.; Nuotio, M.L.; Slagter, S.N.; Doiron, D.; Fisher, K.; Foco, L.; Gaye, A.; Gogele, M.; Heier, M.; Hiekkalinna, T.; et al. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome and metabolically healthy obesity in Europe: A collaborative analysis of ten large cohort studies. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2014, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Health Topics. Obesity. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Reilly, J.J.; Kelly, L.; Montgomery, C.; Williamson, A.; Fisher, A.; McColl, J.H.; Lo Conte, R.; Paton, J.Y.; Grant, S. Physical activity to prevent obesity in young children: Cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2006, 333, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, A.; Buoncristiano, M.; Kovacs, V.A.; Yngve, A.; Spiroski, I.; Obreja, G.; Starc, G.; Pérez, N.; Rito, A.I.; Kunešová, M.; et al. Prevalence of Severe Obesity among Primary School Children in 21 European Countries. Obes. Facts 2019, 12, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijałkowska, A.; Dzielska, A.; Mazur, J.; Korzycka, M.; Breda, J.; Obłacińska, A. Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative (COSI) in Poland: Implementation of Two Rounds of the Study in the Context of International Methodological Assumptions. J. Mother Child 2020, 24, 2–12. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 9 June 2022).
- Benefit System. Do 2030 Otyłość Dotknie w Polsce Prawie Milion Dzieci. Available online: https://www.benefitsystems.pl/o-nas/biuro-prasowe/komunikat/do-2030-otylosc-dotknie-w-polsce-prawie-milion-dzieci/ (accessed on 5 June 2022).
- Finkelstein, E.A.; Khavjou, O.A.; Thompson, H.; Trogdon, J.G.; Pan, L.; Sherry, B.; Dietz, W. Obesity and severe obesity forecasts through 2030. Am. J. Prev. Medm. 2012, 42, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, M.; Kryst, Ł.; Woronkowicz, A.; Sobiecki, J. Long-term changes in body composition and prevalence of overweight and obesity in girls (aged 3–18) from Kraków (Poland) from 1983, 2000 and 2010. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2014, 41, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomula, A.; Nowak-Szczepańska, N.; Danel, D.P.; Koziel, S. Overweight trends among Polish schoolchildren before and after the transition from communism to capitalism. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2015, 19, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, J.; Małkowska-Szkutnik, A. Pupils’ Health in 2018 Against the New HBSC Research Model; Instytut Matki i Dziecka: Warszawa, Poland, 2018. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Pasquali, R.; Oriolo, C. Obesity and Androgens in Women. Front. Horm. Res. 2019, 53, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bauman, A.; Craig, C.L. The place of physical activity in the WHO Global Strategy on Diet and Physical Activity. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2005, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Męczekalski, B.; Czyżyk, A.; Warenik-Szymankiewicz, A. The role of genes in pathogenesis of obesity. Contemporary view, pathogenesis, clinical aspects. Endokrynol. Otył. Zab. Przem. Mat. 2008, 4, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Royo, M.M.; Ciscar, C.P.; Villaescusa, C.G.; Fabra, M.J.B.; Benito, C.A.; Rodriguez, A.L.A.; Silvestre, A.H.; Cataluna, J.J.S. Physical Activity and its Relationship With the State of Health of Stable COPD. Patients Arch. Bronconeumol. 2011, 47, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lwow, F.; Dunajska, K.; Milewicz, A.; Laczmanski, L.; Jedrzejuk, D.; Trzmiel-Bira, A.; Szmigiero, L. ADRB3 and PPARƔ2 gene polymorphisms and their association with cardiovascular disease risk in postmenopausal women. Climacteric 2013, 16, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lwow, F.; Jedrzejuk, D.; Dunajska, K.; Milewicz, A.; Szmigiero, L. Cardiovascular disease risk factors associated with low level of physical activity in postmenopausal Polish women. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2013, 29, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woynarowska, B.; Oblacińska, A. Stan zdrowia dzieci i młodzieży w Polsce. Najważniejsze problemy. Studia BAS 2014, 2, 41–64. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Chagarna, N.S.; Andreeva, T.I. Lifestyle correlates of overweight and obesity among the population of Ukraine. Tob. Control Public Health East. Eur. 2014, 4, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wiklund, P. The role of physical activity and exercise in obesity and weight management: Time for critical appraisal. J. Sport Health Sci. 2016, 5, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Wadden, T.A. Mechanisms, pathophysiology, and management of obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, C.; Tokarski, W.; Predel, H.G.; Koch, B.; Dordel, S. Overweight and obesity in childhood—How can physical activity help? J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2006, 50, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Prevalence of Insufficient Physical Activity. Global Health Observatory 2016. Available online: http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/risk_factors/physical_activity/en/ (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Westerterp, K. Control of energy expenditure in humans. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyszyńska, J.; Ring-Dimitriou, S.; Thivel, D.; Weghuber, D.; Hadjipanayis, A.; Grossman, Z.; Ross-Russell, R.; Dereń, K.; Mazur, A. Physical Activity in the Prevention of Childhood Obesity: The Position of the European Childhood Obesity Group and the European Academy of Pediatrics. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 535705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najwyższa Izba Kontroli. The Official Website of the Supreme Audit Office in Poland. Obesity and Overweight in Children—A Growing Problem, Less and Less Effective Actions. Available online: https://www.nik.gov.pl/aktualnosci/otylosc-i-nadwaga-u-dzieci-coraz-wiekszy-problem-coraz-mniej-skuteczne-dzialania.html (accessed on 23 July 2022). (In Polish)
- Zegan, M.; Michota-Katulska, E.; Lewandowska, M.; Boniecka, I. The role of physical activity in prevention and support for the treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Med. Rodz. 2017, 20, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Krzysztoszek, J.; Maciaszek, J.; Bronikowski, M.; Karasiewicz, M.; Laudańska Krzemińska, I. Comparison of Fitness and Physical Activity Levels of Obese People with Hypertension. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoey, H. Management of obesity in children differs from that of adults. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2014, 73, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Suárez, A. Burden of cancer attributable to obesity, type 2 diabetes and associated risk factors. Metabolism 2019, 92, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulis, W.D.; Silva, S.; Koes, B.W.; Middelkoop, M. Overweight and obesity are associated with musculoskeletal complaints as early as childhood: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twig, G.; Yaniv, G.; Levine, H.; Leiba, A.; Goldberger, N.; Derazne, E.; Ben-Ami Shor, D.; Tzur, D.; Afek, A.; Shamiss, A.; et al. Body-mass index in 2.3 million adolescents and cardiovascular death in adulthood. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2430–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortis, C.; Puggina, A.; Pesce, C.; Aleksovska, K.; Buck, C.; Burns, C.; Cardona, P.; Carlin, A.; Simon, C.; Ciarapica, D.; et al. Psychological determinants of physical activity across the life course: A “DEterminants of DIet and Physical ACtivity” (DEDIPAC) umbrella systematic literature review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samek, I.; Jańczyk, M.; Milanowska, J. Physical activity of the society. J. Educ. Health Sport 2021, 11, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, K.; Suszczewicz, N. Natural methods of supporting immunity in the fight against coronavirus. Wiedza Med. Wyd. Spec. 2020, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onder, G.; Rezza, G.; Brusaferro, S. Case-Fatality Rate and Chracteristics of Patient Dying in Relation to COVID-19 in Italy. JAMA 2020, 323, 1775–1776. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Guohui, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vancini, R.L.; Viana, R.B.; dos Santos Andrade, M.; de Lira, C.A.; Nikolaidis, P.T.; de Almeida, A.A.; Knechtle, B. YouTube as a Source of Information About Physical Exercise During COVID-19 Outbreak. Int. J. Sport Stud. Health 2021, 4, e123312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biskupek-Wanot, A.; Wanot, B.; Kasprowska-Nowak, K. Physical Activity and Stress-Related Issues; JDU Publishing House in Częstochowa: Częstochowa, Poland, 2020. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Tanha, T.; Wollmer, P.; Thorsson, O.; Karlsson, M.K.; Lindén, C.; Andersen, L.B.; Dencker, M. Lack of physical activity in young children is related to higher composite risk factor score for cardiovascular disease. Acta Paediatr. 2011, 100, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesa, C.C.; Sbruzzi, G.; Ribeiro, R.A.; Barbiero, S.M.; de Oliveira Petkowicz, R.; Eibel, B.; Bigolin, M.N.; das Virgens Marques, R.; Tortato, G.; dos Santos, T.J.; et al. Physical activity and cardiovascular risk factors in children: Meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Prev. Med. 2014, 69, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nga, V.T.; Dung, V.N.T.; Chu, D.-T.; Tien, N.L.B.; Van Thanh, V.; Ngoc, V.T.N.; Hoan, L.N.; Phuong, N.T.; Pham, V.-H.; Tao, Y.; et al. School education and childhood obesity: A systemic review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2019, 13, 2495–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khudairy, L.; Loveman, E.; Colquitt, J.L.; Mead, E.; Johnson, R.E.; Fraser, H.; Olajide, J.; Murphy, M.; Velho, R.M.; O’Malley, C.; et al. Diet, physical activity and behavioural interventions for the treatment of overweight or obese adolescents aged 12 to 17 years. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, CD012691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, E.; Brown, T.; Rees, K.; Azevedo, L.B.; Whittaker, V.; Jones, D.; Olajide, J.; Mainardi, G.M.; Corpeleijn, E.; O’Malley, C.; et al. Diet, physical activity and behavioural interventions for the treatment of overweight or obese children from the age of 6 to 11 years. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, CD012651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilińska, I.; Kryst, Ł. Effectiveness of a school-based intervention to reduce the prevalence of overweight and obesity in children aged 7–11 from Poznań (Poland). Anthropol. Anz. 2017, 74, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.; Moore, T.H.; Hooper, L.; Gao, Y.; Zayegh, A.; Ijaz, S.; Elwenspoek, M.; Foxen, S.C.; Magee, L.; O’Malley, C.; et al. Interventions for preventing obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 7, CD001871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Floody, P.; Latorre-Roman, P.; Jerez-Mayorga, D.; Caamano-Navarrete, F.; Garcia-Pinillos, F. Feasibility of incorporating high-intensity interval training into physical education programs to improve body composition and cardiorespiratory capacity of overweight and obese children: A systematic review. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2019, 17, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, T.J.; Bellizzi, M.C.; Flegel, K.M.; Dietz, W.H. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: International survey. Br. Med. J. 2000, 320, 1240–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R. Anthropologie; Gustav Fischer Verlag. Stuttgart: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, C.; Klissouras, V.; Ravassolo, M.; Renson, R.; Tuxworth, W. Eurofit: Handbook for the Eurofit Test of Physical Fitness, Communittee for The Development of Sport; Council of Europe: London, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, K.H. A means of assessing maximal oxygen intake: Correlation between field and treadmill testing. JAMA 1968, 203, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffrin, M.Y. 2009 Body composition determination by bioimpedance: An update. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2009, 12, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charzewska, J.; Pastuszak, A.; Lewandowska, J.; Piechaczek, H.; Kęsicka, E. Relationship between physical activity and obesity in adolescents. In Obesity as an Epidemic of the 21st Century; Charzewska, M., Bregman, P., Koczanowski, K., Piechaczek, H., Eds.; PAN: Warszawa, Polan, 2006; pp. 74–81. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Ługowska, K.; Kolanowski, W.; Trafialek, J. The Impact of Physical Activity at School on Children’s Body Mass during 2 Years of Observation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkowski, T.; Sobiech, K.A.; Chwałczyńska, A. The effect of karate training on changes in physical fitness in school-age children with normal and abnormal body weight. PQ 2019, 27, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, J. The Influence of Physical Activity and Selected Perinatal Risk Factors on the Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Children. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Rzeszów, Rzeszów, Poland, 2018. (In Polish). [Google Scholar]
- Januszek-Trzciąkowska, A.; Małecka-Tendera, E.; Klimek, K.; Matusik, P. Obesity risk factors in a representative group of Polish prepubertal children. Arch. Med. Sci. 2014, 10, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajka, K.; Kochan, K. BMI and selected health behaviors of primary and junior high school students. Probl. Hig. Epidemiol. 2012, 93, 551–557. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Basterfield, L.; Jones, A.R.; Parkinson, K.N.; Reilly, J.; Pearce, M.S.; Reilly, J.J.; Adamson, A.J. Physical activity, diet and BMI in children aged 6–8 years: A cross-sectional analysis. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e005001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, J.; Aldrich, H.; Callahan, T.J.; Matthews, E.E.; Gance-cleveland, B. Characterization of Childhood Obesity and Behavioral Factors. J. Pediatr. Health Care 2014, 30, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koca, T.; Akcam, M.; Serdaroglu, F.; Dereci, S. Breakfast habits, dairy product consumption, physical activity, and their associations with body mass index in children aged 6–18. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2017, 176, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, I.; LeBlanc, A.G. Systematic review of the health benefits of physical activity and fitness in schoolaged children and youth. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2010, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelishadi, R.; Azizi-Soleiman, F. Controlling childhood obesity: A systematic review on strategies and challenges. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2014, 19, 993–1008. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makaracı, Y.; Yücetaş, Z.; Devrilmez, E.; Soslu, R.; Devrilmez, M.; Akpınar, S.; Popovic, S. Physical Activity and Nutrition Education Programs Changes Body Mass Index and Eating Habits of 12th Grade Students: An Intervention during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Ann. Appl. Sport Sci. 2023, 11, e1105. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie, H.J.; Standage, M.; Gillison, F.B.; Cumming, S.P.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Multiple lifestyle behaviours and overweight and obesity among children aged 9–11 years: Results from the UK site of the International Study of Childhood Obesity, Lifestyle and the Environment. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman-Viñas, B.; Chaput, J.-P.H.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Fogelholm, M.; Lambert, E.V.; Maher, C.; Maia, J.; Olds, T.; Onywera, V.; Sarmiento, O.L.; et al. ISCOLE Research Group. Proportion of children meeting recommendations for 24-h movement guidelines and associations with adiposity in a 12-country study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dygrýn, J.; Medrano, M.; Molina-Garcia, P.; Rubín, L.; Jakubec, L.; Janda, D.; Gába, A. Associations of novel 24-h accelerometer-derived metrics with adiposity in children and adolescents. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2021, 26, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Fan, J.; Yuan, F.; Feng, G.; Gong, W.; Song, C.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, A. Association between Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviors, Sleep, Diet, and Adiposity among Children and Adolescents in China. Obes. Facts 2022, 15, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raczek, J. Human motor skills, views, controversial concepts. In Motor Skills of Children and Adolescents—Theoretical Aspects and Methodological Implications; AWF Katowice [University of Physical Education in Katowice]: Katowice, Poland, 1986; pp. 9–27. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Pluta, B.; Korcz, A.; Krzysztofa, J.; Bronikowski, M.; Bronikowska, M. Associations between adolescents’ physical activity behavior and their perceptions of parental, peer and teacher support. Arch. Public Health 2020, 78, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Experimental Group | Control Group | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boys (♂) | 207 | 243 | 450 |
| Girls (♀) | 212 | 242 | 454 |
| Total (♂♀) | 419 | 485 | 904 |
| Variable | Group (E, C) | RM (PRE, POST) | RM*Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | η2 | p | η2 | p | η2 | |
| Body weight ♂ | 0.049 * | 0.009 | 0.000 ** | 0.709 | 0.000 ** | 0.220 |
| Body weight ♀ | 0.137 | 0.005 | 0.000 ** | 0.704 | 0.000 ** | 0.217 |
| Body height ♂ | 0.170 | 0.004 | 0.000 ** | 0.799 | 0.827 | 0.000 |
| Body height ♀ | 0.057 | 0.008 | 0.000 ** | 0.821 | 0.894 | 0.000 |
| BMI ♂ | 0.072 | 0.007 | 0.000 ** | 0.071 | 0.000 ** | 0.175 |
| BMI ♀ | 0.447 | 0.001 | 0.000 ** | 0.135 | 0.000 ** | 0.222 |
| Sum 3-SF ♂ | 0.001 ** | 0.076 | 0.000 ** | 0.376 | 0.000 ** | 0.822 |
| Sum 3-SF ♀ | 0.029 * | 0.034 | 0.000 ** | 0.222 | 0.000 ** | 0.778 |
| Body Weight (kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-PRE | E-POST | C-PRE | C-POST | ||
| Body Height (cm) | E-PRE | 0.000 ** | 0.268 | 0.000 ** | |
| E-POST | 0.000 ** | 0.582 | 0.005 * | ||
| C-PRE | 0.165 | 0.0003 ** | 0.000 ** | ||
| C-POST | 0.000 ** | 0.182 | 0.000 ** | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-PRE | E-POST | C-PRE | C-POST | ||
| Sum of three skinfolds (mm) | E-PRE | 0.008 * | 0.518 | 0.013 | |
| E-POST | 0.000 ** | 0.269 | 0.003 * | ||
| C-PRE | 0.874 | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | ||
| C-POST | 0.046 | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | ||
| Body Weight (kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-PRE | E-POST | C-PRE | C-POST | ||
| Body Height (cm) | E-PRE | 0.000 ** | 0.585 | 0.000 ** | |
| E-POST | 0.000 ** | 0.207 | 0.016 | ||
| C-PRE | 0.06 | 0.010 ** | 0.000 ** | ||
| C-POST | 0.000 ** | 0.056 | 0.000 ** | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-PRE | E-POST | C-PRE | C-POST | ||
| Sum of three skinfolds (mm) | E-PRE | 0.044 | 0.614 | 0.092 | |
| E-POST | 0.000 ** | 0.86 | 0.044 | ||
| C-PRE | 0.375 | 0.003 * | 0.000 ** | ||
| C-POST | 0.193 | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | ||
| Group | N | Body Weight I–II | Body Height I–II | BMI I–II | Sum of Three Skinfolds I–II | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | SD | X | SD | X | SD | N | X | SD | |||
| E | ♂♀ | 419 | −1.43 | 1.34 | −3.15 | 1.65 | 0.11 | 0.78 | 141 | 9.22 | 4.29 |
| ♂ | 207 | −1.41 | 1.27 | −3.16 | 1.74 | 0.14 | 0.82 | 67 | 10.40 | 4.23 | |
| ♀ | 212 | −1.45 | 1.40 | −3.14 | 1.55 | 0.09 | 0.75 | 74 | 8.15 | 4.08 | |
| C | ♂♀ | 485 | −2.90 | 1.44 | −3.14 | 1.41 | −0.56 | 0.59 | 131 | −4.71 | 2.49 |
| ♂ | 243 | −2.86 | 1.44 | −3.13 | 1.42 | −0.54 | 0.66 | 66 | −4.88 | 2.77 | |
| ♀ | 242 | −2.95 | 1.44 | −3.16 | 1.40 | −0.58 | 0.50 | 65 | −4.54 | 2.40 | |
| Variable | ♂♀ | ♂ | ♀ |
|---|---|---|---|
| p | p | p | |
| Body weight | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** |
| Body height | 0.945 | 0.827 | 0.894 |
| BMI | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** |
| Sum of three skinfolds | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** |
| Body Fat Percentage | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total ♂♀ | Boys ♂ | Girls ♀ | |
| Study I (PRE) | 28.62 | 28.97 | 28.31 |
| Study II (POST) | 23.98 | 23.89 | 24.06 |
| p | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** |
| Variable | Boys ♂ | Girls ♀ | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental group (E) | |||
| Body weight I–II | −1.41 | −1.45 | 0.776 |
| Body height I–II | −3.16 | −3.14 | 0.923 |
| BMI I–II | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.524 |
| Sum 3-SF I–II | 10.40 | 8.15 | 0.002 ** |
| BFP I–II | 5.08 | 4.25 | 0.014 * |
| Control group (C) | |||
| Body weight I–II | −2.19 | −2.25 | 0.607 |
| Body height I–II | −3.14 | −3.15 | 0.906 |
| BMI I–II | −0.23 | −0.27 | 0.439 |
| Sum 3-SF I–II | 2.82 | 2.22 | 0.529 |
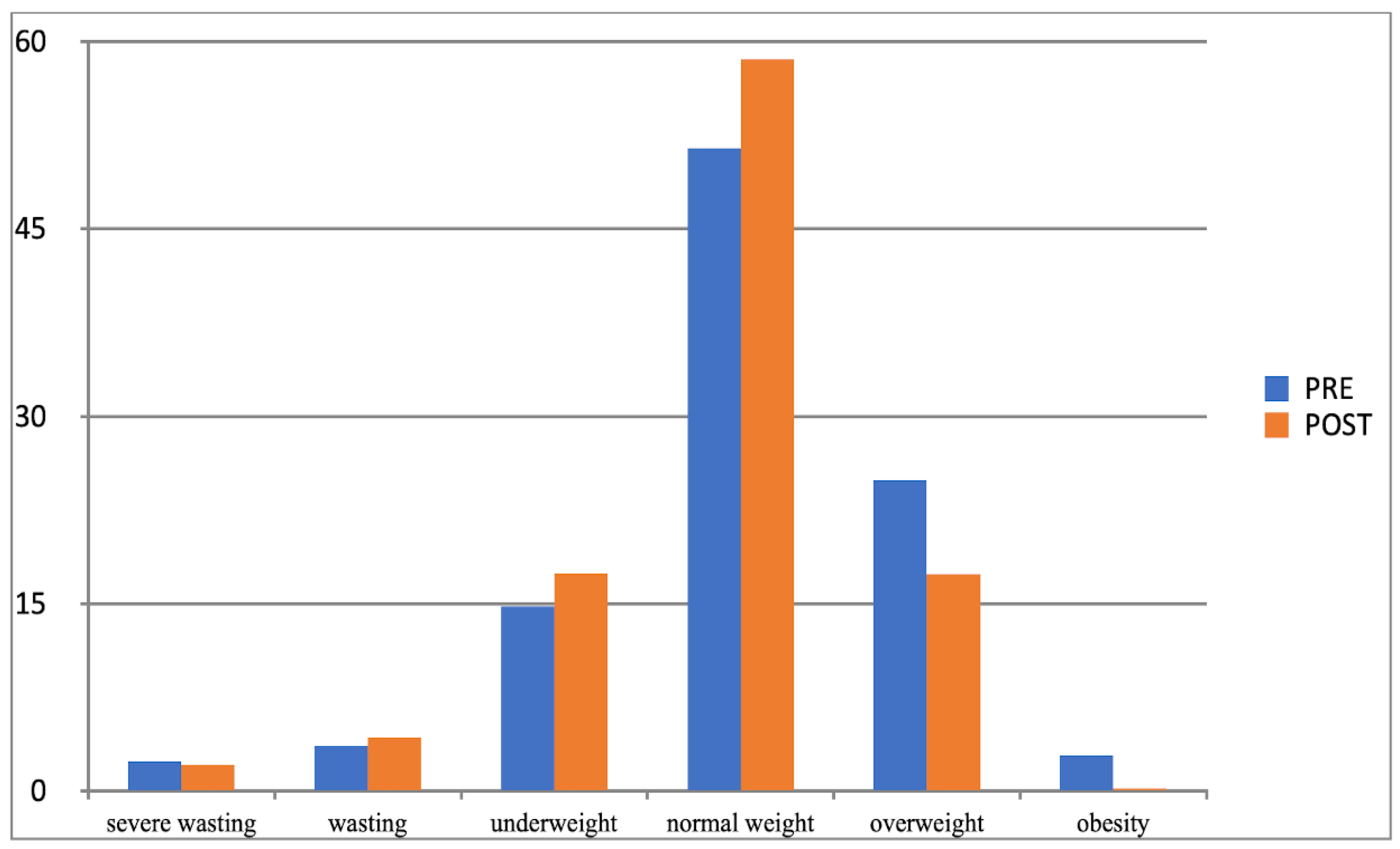
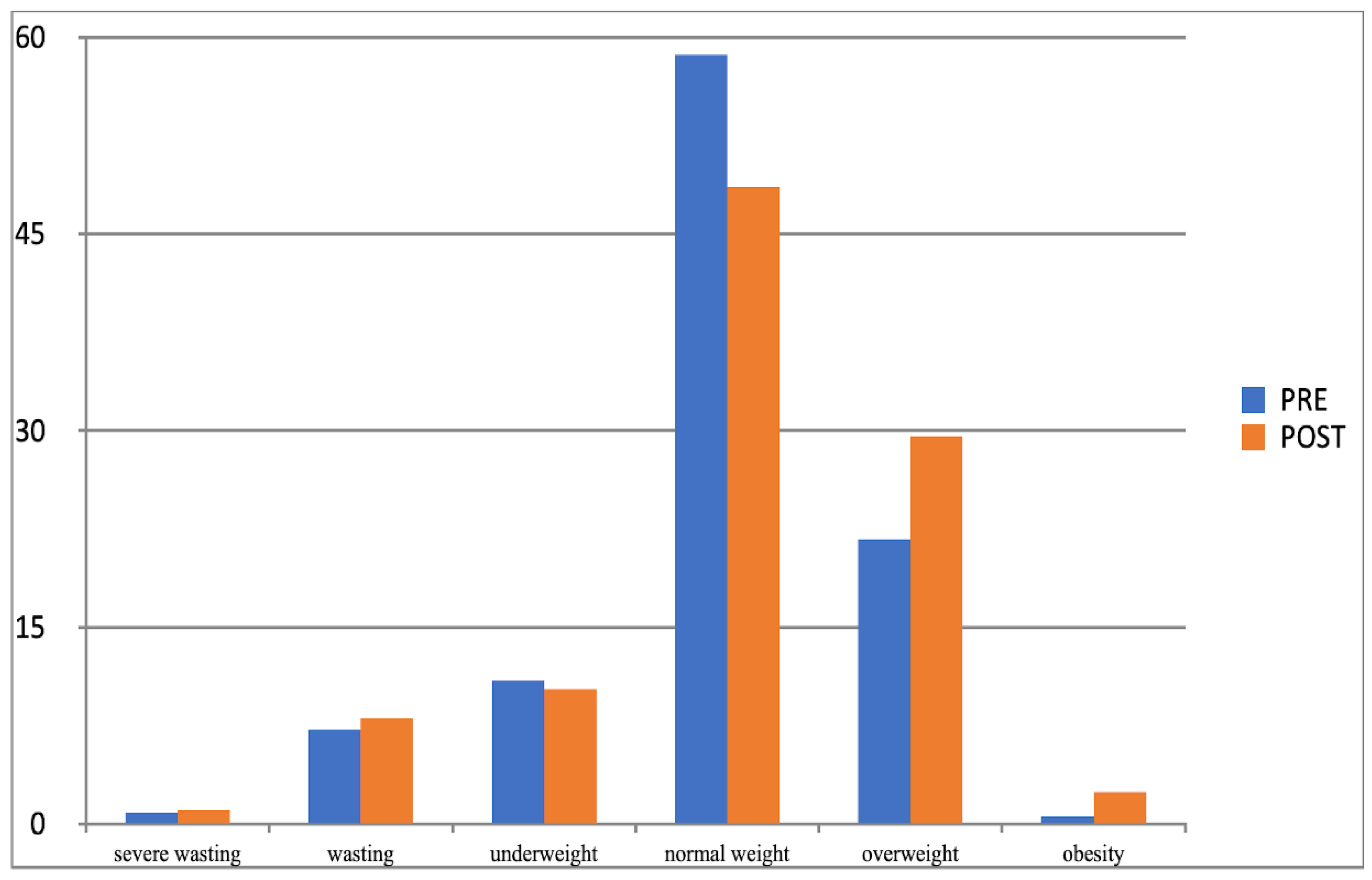
| Categories | Group E | Group C | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRE | POST | p | PRE | POST | p | ||
| % | % | % | % | ||||
| Severe wasting | ♂♀ | 2.39 | 2.15 | 0.816 | 0.82 | 1.03 | 0.733 |
| ♂ | 3.86 | 2.42 | 0.401 | 0.82 | 1.23 | 0.654 | |
| ♀ | 0.94 | 1.89 | 0.001 ** | 0.83 | 0.83 | 1.000 | |
| Wasting | ♂♀ | 3.58 | 4.30 | 0.592 | 7.22 | 8.04 | 0.631 |
| ♂ | 2.42 | 4.83 | 0.190 | 5.35 | 4.52 | 0.677 | |
| ♀ | 4.72 | 3.77 | 0.628 | 9.09 | 11.57 | 0.370 | |
| Underweight | ♂♀ | 14.80 | 17.42 | 0.303 | 10.93 | 10.31 | 0.754 |
| ♂ | 14.98 | 17.39 | 0.506 | 12.35 | 13.99 | 0.593 | |
| ♀ | 14.62 | 17.45 | 0.428 | 9.50 | 6.61 | 0.243 | |
| Normal weight | ♂♀ | 51.48 | 58.55 | 0.027 * | 58.70 | 48.58 | 0.001 ** |
| ♂ | 51.64 | 58.07 | 0.202 | 58.48 | 47.08 | 0.002 ** | |
| ♀ | 51.32 | 59.01 | 0.066 | 58.93 | 50.08 | 0.023 * | |
| Overweight | ♂♀ | 24.89 | 17.36 | 0.001 ** | 21.71 | 29.56 | 0.008 ** |
| ♂ | 24.69 | 16.81 | 0.004 ** | 22.59 | 30.29 | 0.016 * | |
| ♀ | 25.1 | 17.88 | 0.014 * | 20.83 | 28.84 | 0.017 * | |
| Obesity | ♂♀ | 2.86 | 0.24 | 0.002 ** | 0.61 | 2.42 | 0.020 * |
| ♂ | 2.42 | 0.48 | 0.100 | 0.41 | 2.88 | 0.032 * | |
| ♀ | 3.30 | 0.00 | 0.008 ** | 0.83 | 2.07 | 0.254 | |
| Variable | Group (E, C) | RM (PRE, POST) | RM*Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | η2 | p | η2 | p | η2 | |
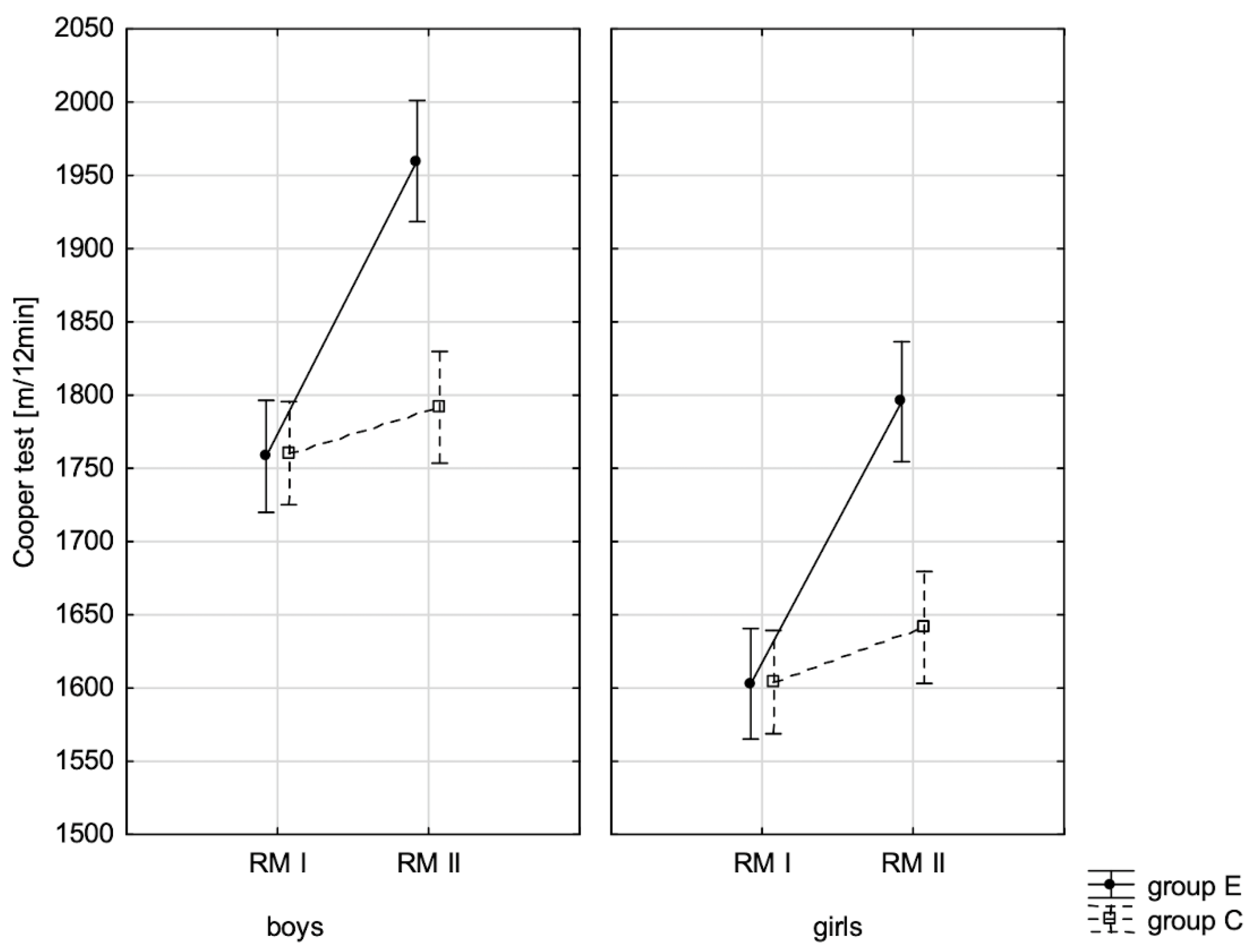
| Cooper test ♂ | 0.006 ** | 0.017 | 0.000 ** | 0.644 | 0.000 ** | 0.492 |
| Cooper test ♀ | 0.002 ** | 0.022 | 0.000 ** | 0.509 | 0.000 ** | 0.321 |
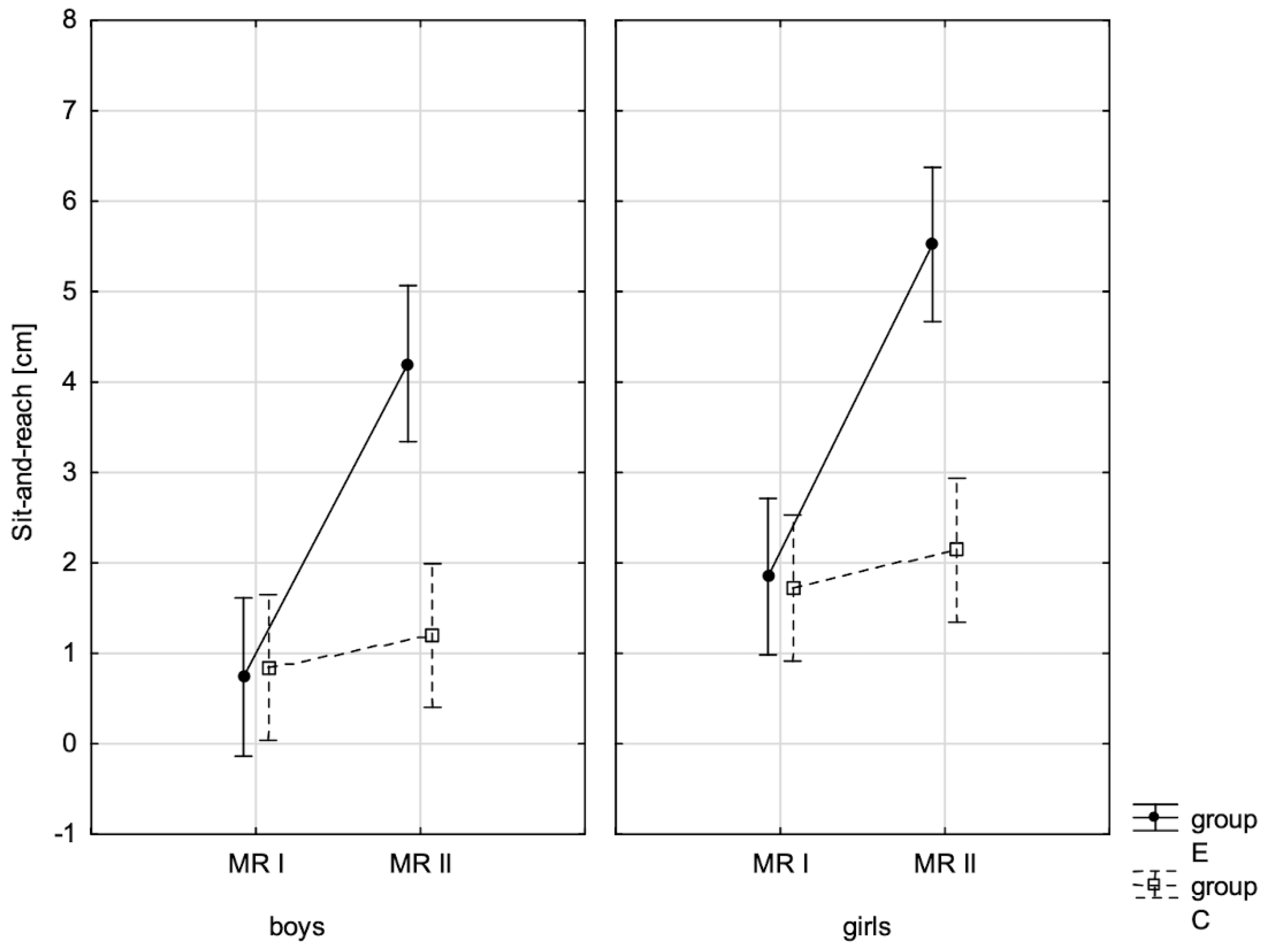
| Sit-and-reach ♂ | 0.014 * | 0.014 | 0.000 ** | 0.476 | 0.000 ** | 0.376 |
| Sit-and-reach ♀ | 0.004 ** | 0.019 | 0.000 ** | 0.541 | 0.000 ** | 0.427 |
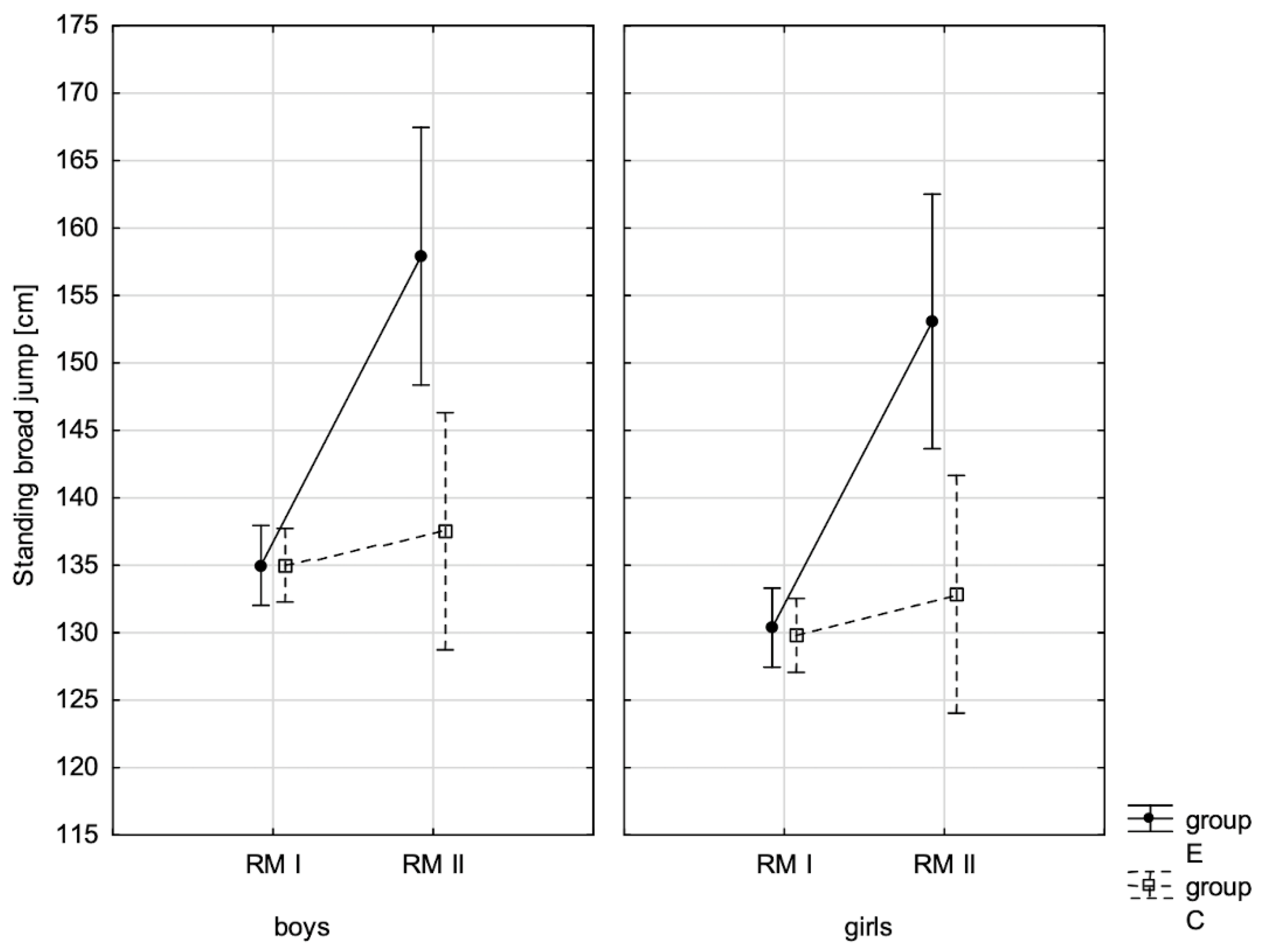
| Standing broad jump ♂ | 0.008 ** | 0.016 | 0.000 ** | 0.036 | 0.001 ** | 0.023 |
| Standing broad jump ♀ | 0.006 ** | 0.0167 | 0.000 ** | 0.037 | 0.002 ** | 0.022 |
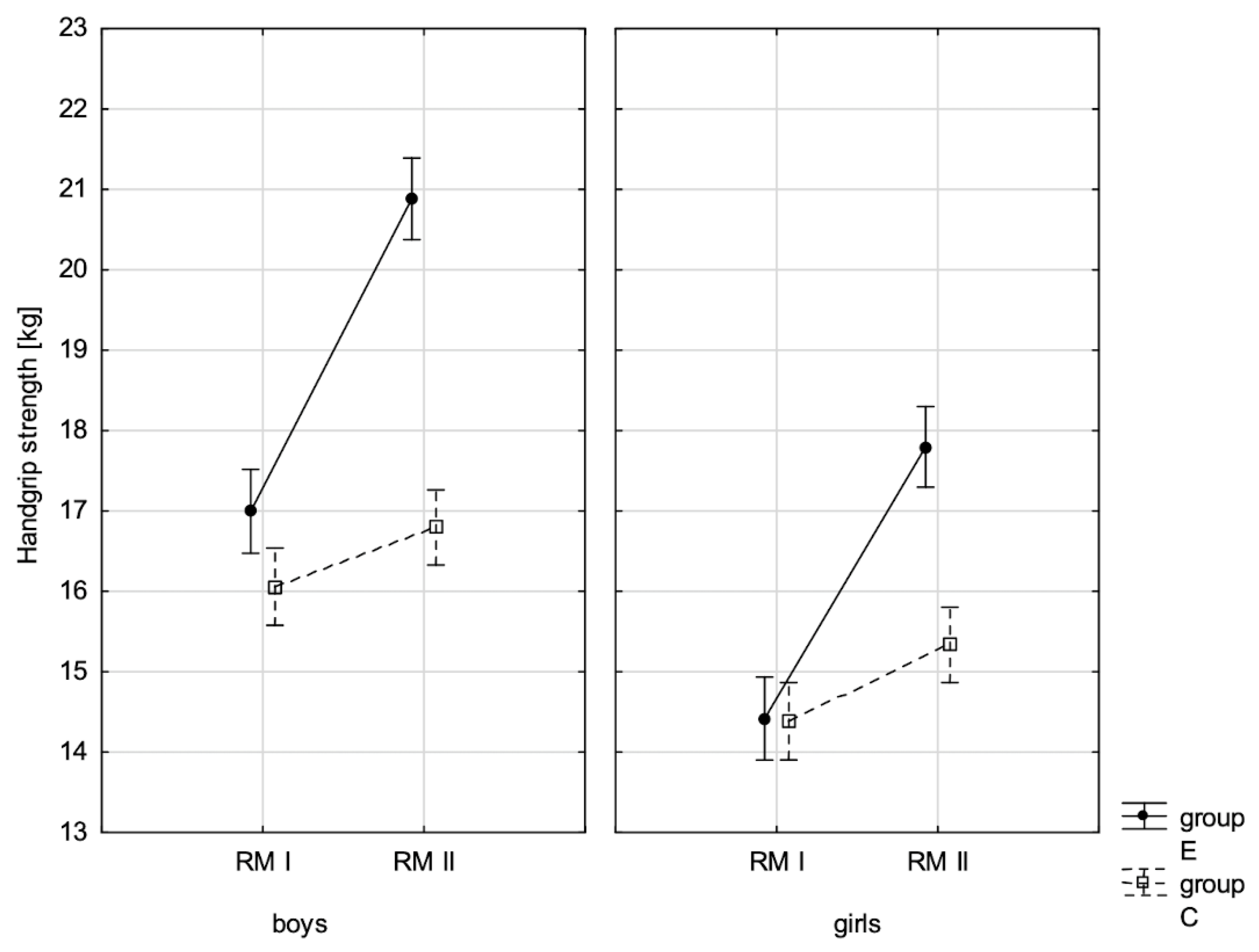
| Handgrip strength ♂ | 0.000 ** | 0.111 | 0.000 ** | 0.581 | 0.000 ** | 0.391 |
| Handgrip strength ♀ | 0.000 ** | 0.028 | 0.000 ** | 0.445 | 0.000 ** | 0.201 |
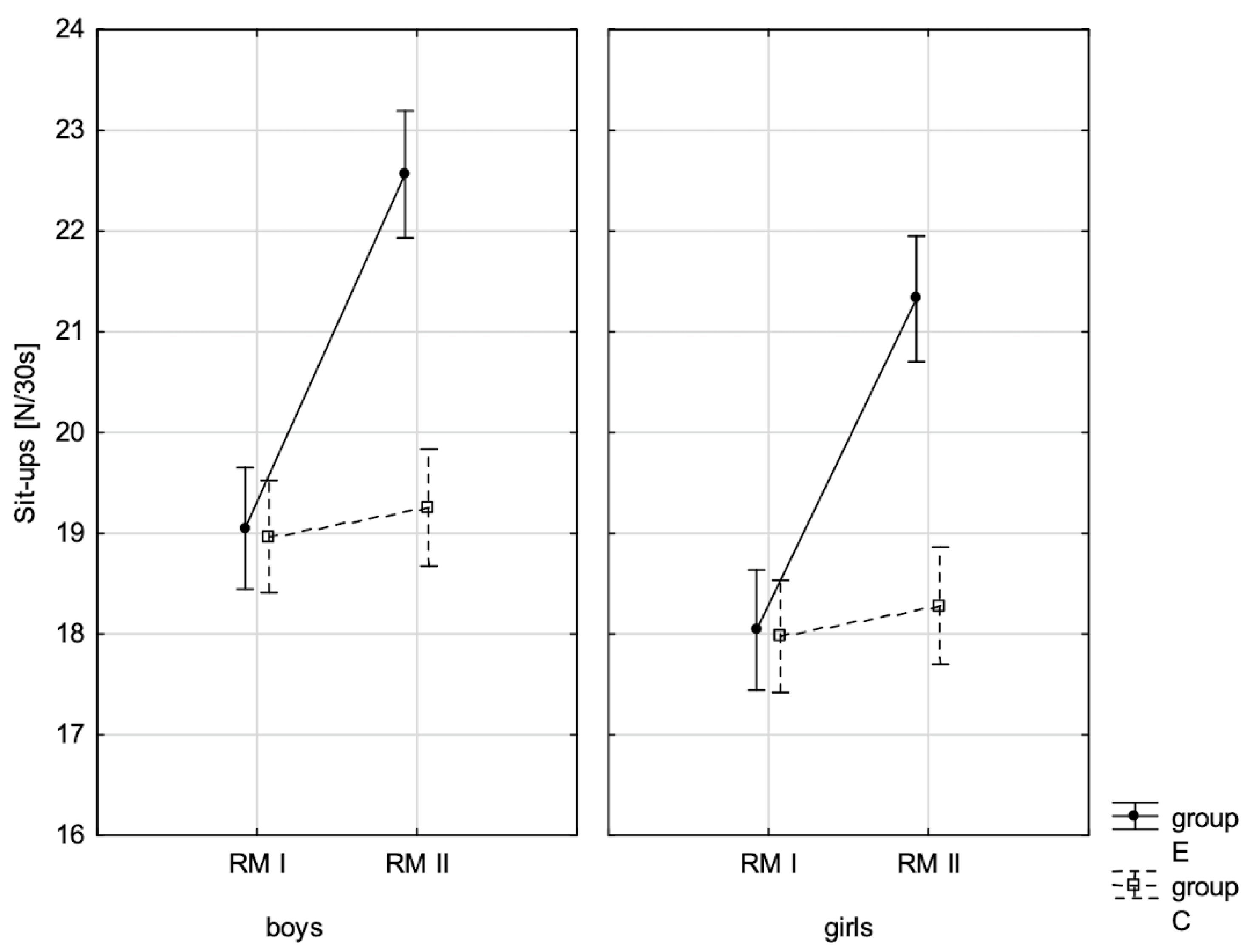
| Sit-ups ♂ | 0.000 ** | 0.034 | 0.000 ** | 0.520 | 0.000 ** | 0.438 |
| Sit-ups ♀ | 0.000 ** | 0.032 | 0.000 ** | 0.400 | 0.000 ** | 0.315 |
| Bent-arm hang ♂ | 0.000 ** | 0.048 | 0.000 ** | 0.276 | 0.000 ** | 0.213 |
| Bent-arm hang ♀ | 0.000 ** | 0.061 | 0.000 ** | 0.259 | 0.000 ** | 0.204 |
| Agility shuttle run ♂ | 0.001 ** | 0.027 | 0.000 ** | 0.233 | 0.000 ** | 0.151 |
| Agility shuttle run ♀ | 0.000 ** | 0.036 | 0.000 ** | 0.515 | 0.000 ** | 0.355 |
| Cooper Test I–II | Sit-and-Reach I–II | Standing Broad Jump I–II | Handgrip Strength I–II | Sit-Ups I–II | Bent-Arm Hang I–II | Agility Shuttle Run I–II | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| E | 207 | −201.626 | −3.466 | −22.922 | −3.888 | −3.514 | −9.812 | 2.314 |
| C | 243 | −31.255 | −0.354 | −2.523 | −0.737 | −0.288 | −0.847 | 0.254 |
| p | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.001 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | |
| Cooper Test I–II | Sit-and-Reach I–II | Standing Broad Jump I–II | Handgrip Strength I–II | Sit-Ups I–II | Bent-Arm Hang I–II | Agility Shuttle Run I–II | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| E | 212 | −192.559 | −3.673 | −22.701 | −3.289 | −3.289 | −6.993 | 2.144 |
| C | 242 | −37.293 | −0.417 | −3.050 | −0.950 | −0.306 | −0.547 | 0.350 |
| p | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.002 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nowaczyk, M.; Cieślik, K.; Waszak, M. Assessment of the Impact of Increased Physical Activity on Body Mass and Adipose Tissue Reduction in Overweight and Obese Children. Children 2023, 10, 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10050764
Nowaczyk M, Cieślik K, Waszak M. Assessment of the Impact of Increased Physical Activity on Body Mass and Adipose Tissue Reduction in Overweight and Obese Children. Children. 2023; 10(5):764. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10050764
Chicago/Turabian StyleNowaczyk, Marta, Krystyna Cieślik, and Małgorzata Waszak. 2023. "Assessment of the Impact of Increased Physical Activity on Body Mass and Adipose Tissue Reduction in Overweight and Obese Children" Children 10, no. 5: 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10050764
APA StyleNowaczyk, M., Cieślik, K., & Waszak, M. (2023). Assessment of the Impact of Increased Physical Activity on Body Mass and Adipose Tissue Reduction in Overweight and Obese Children. Children, 10(5), 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10050764





