WIN55,212-2 Attenuates Cognitive Impairments in AlCl3 + d-Galactose-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Rats by Enhancing Neurogenesis and Reversing Oxidative Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
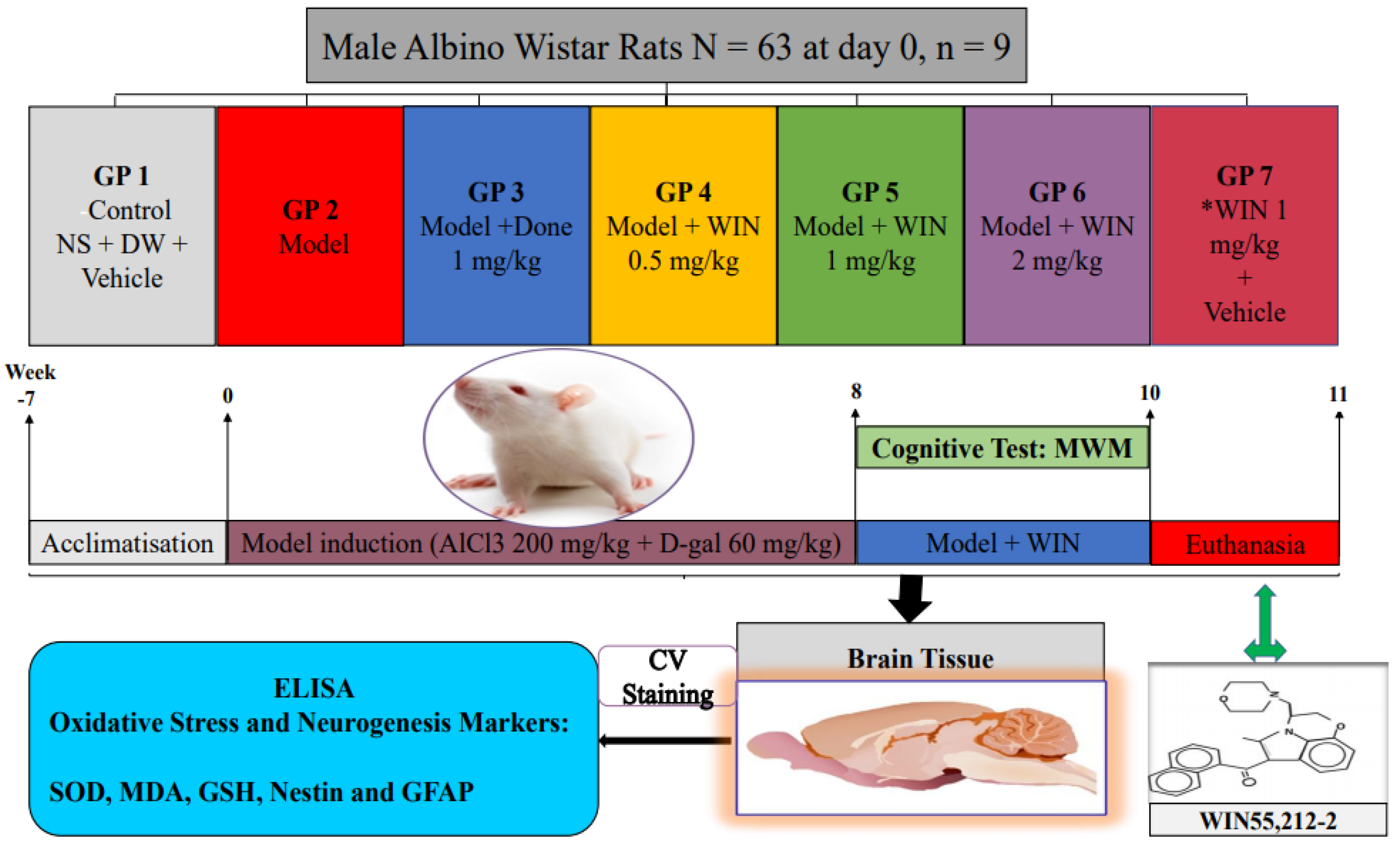
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design
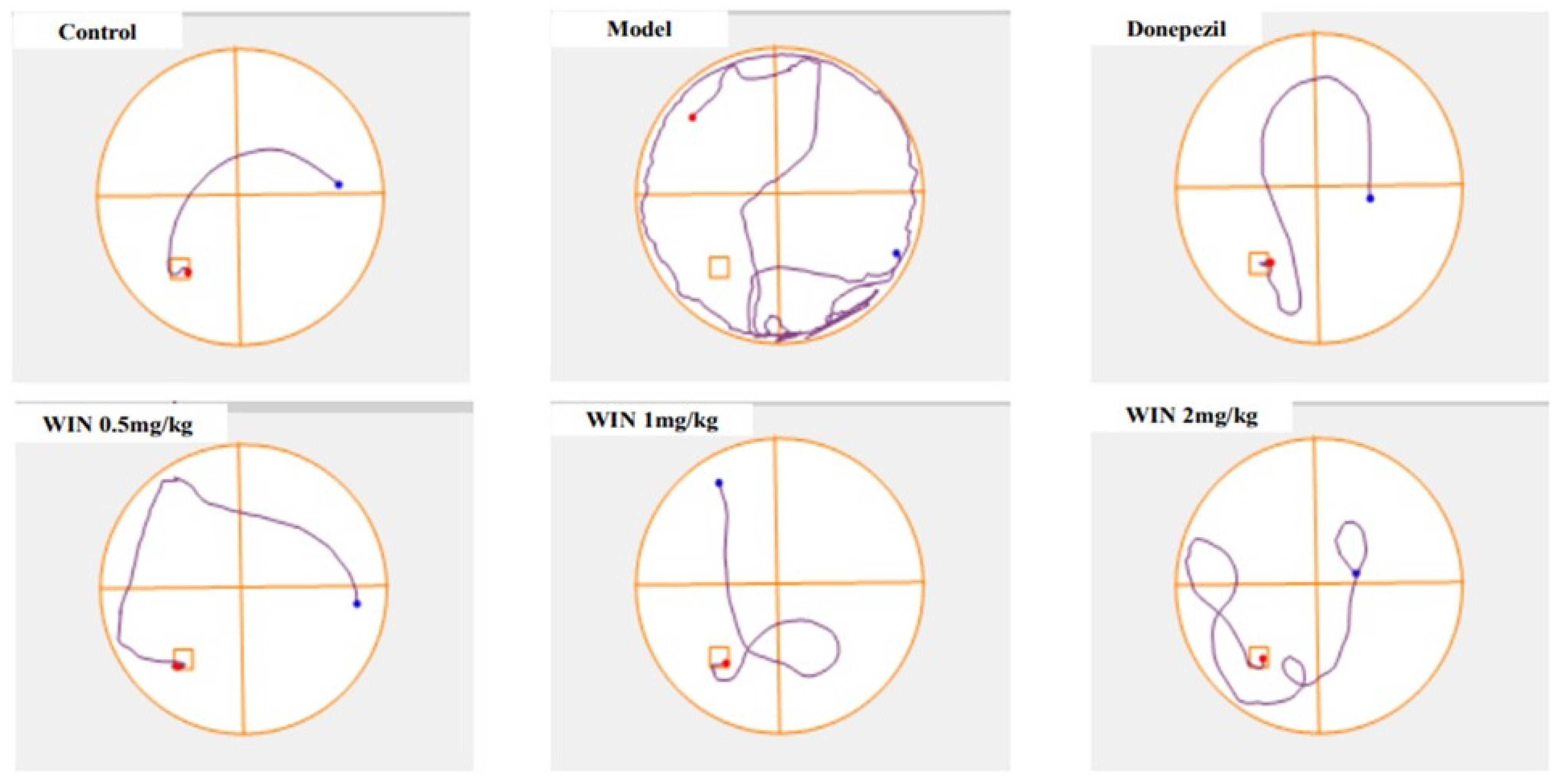
2.3. Morris Water Maze Test
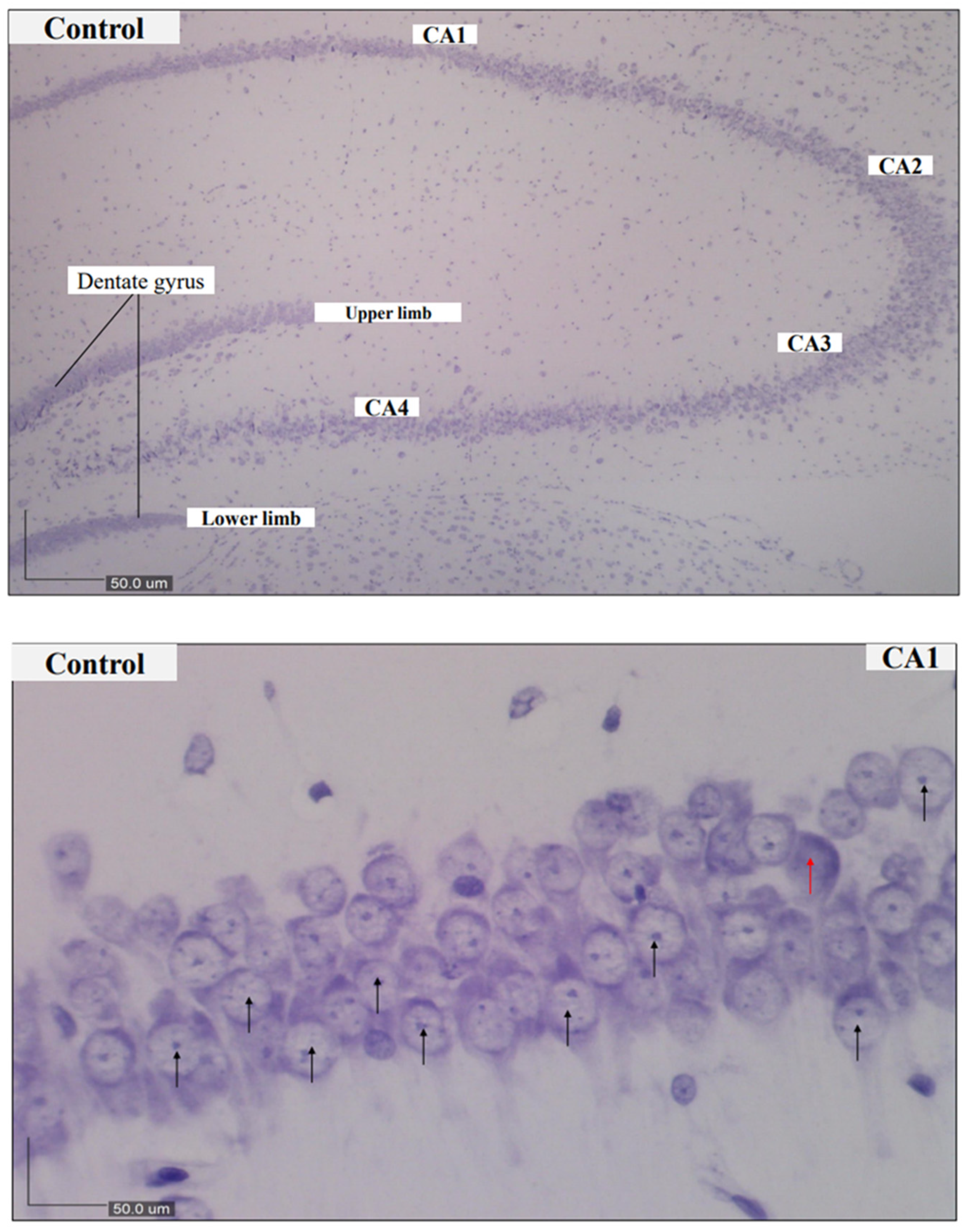
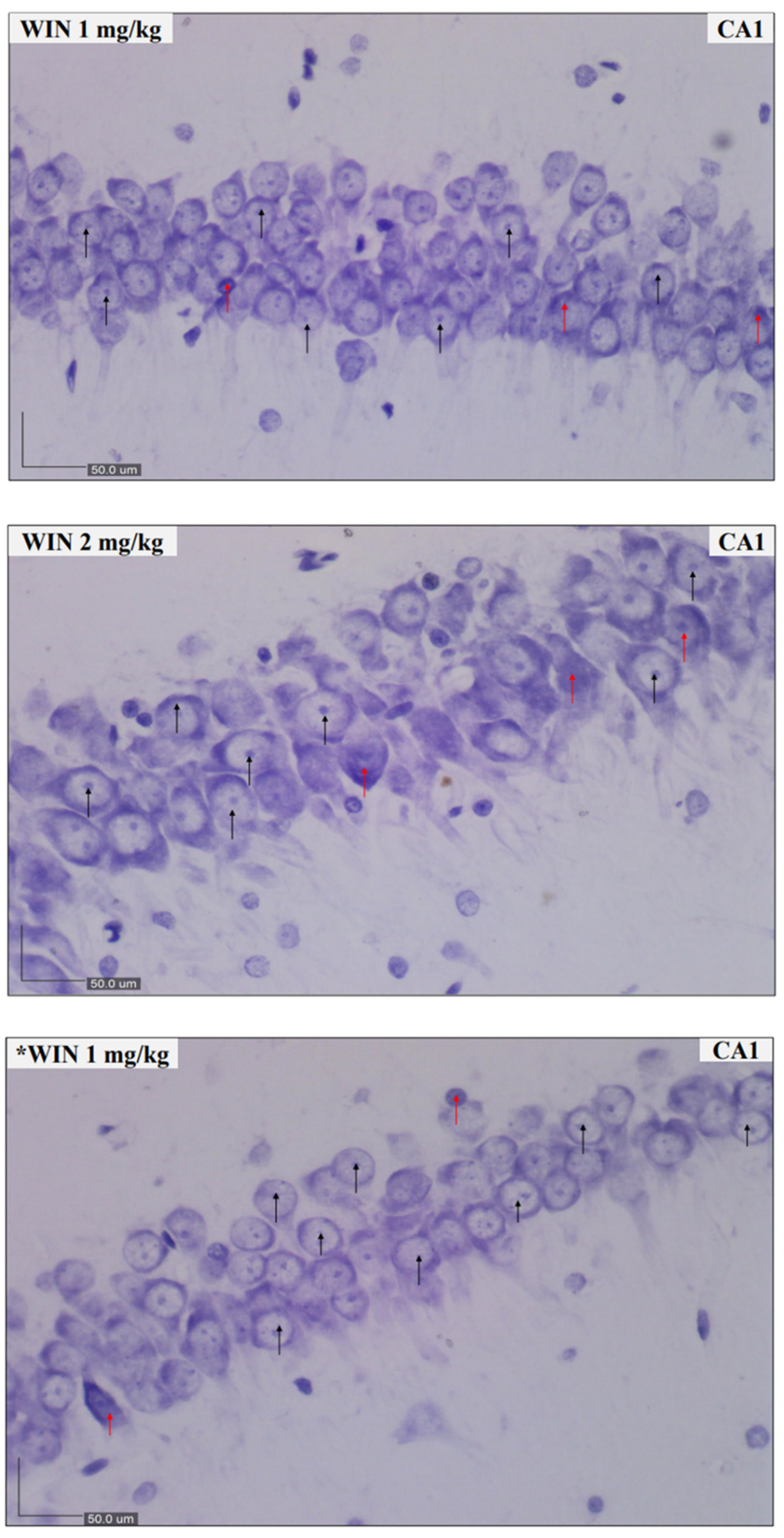
2.4. Nissl Staining and Scoring
2.5. Preparation of Brain Tissue Samples
2.6. Measurement of Protein
2.7. Measurements of Biochemical and Neurogenesis Parameters
3. Results
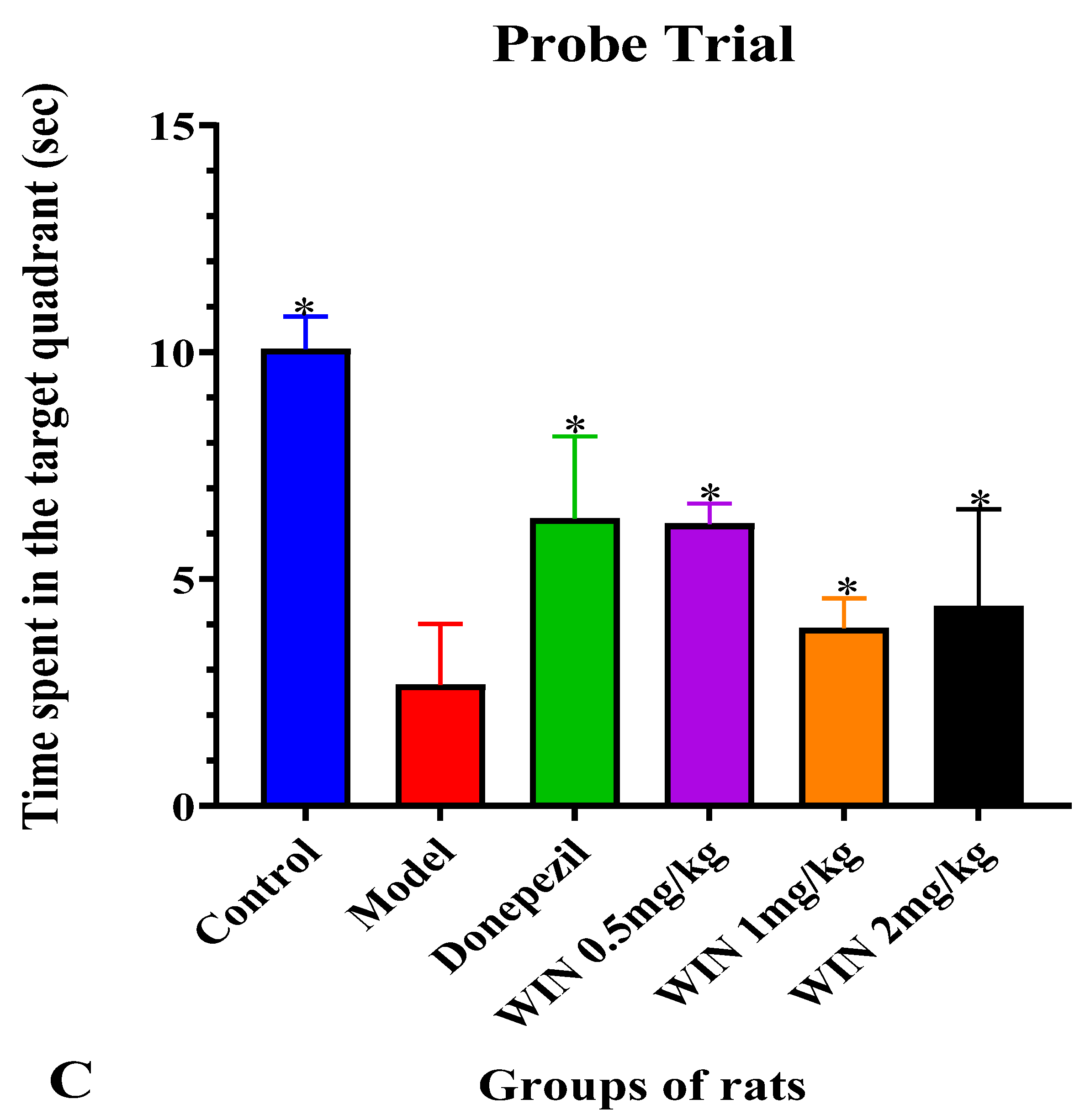
3.1. WIN Attenuated AlCl3− and d-gal-Induced Cognitive Impairments in Rats during MWM Test
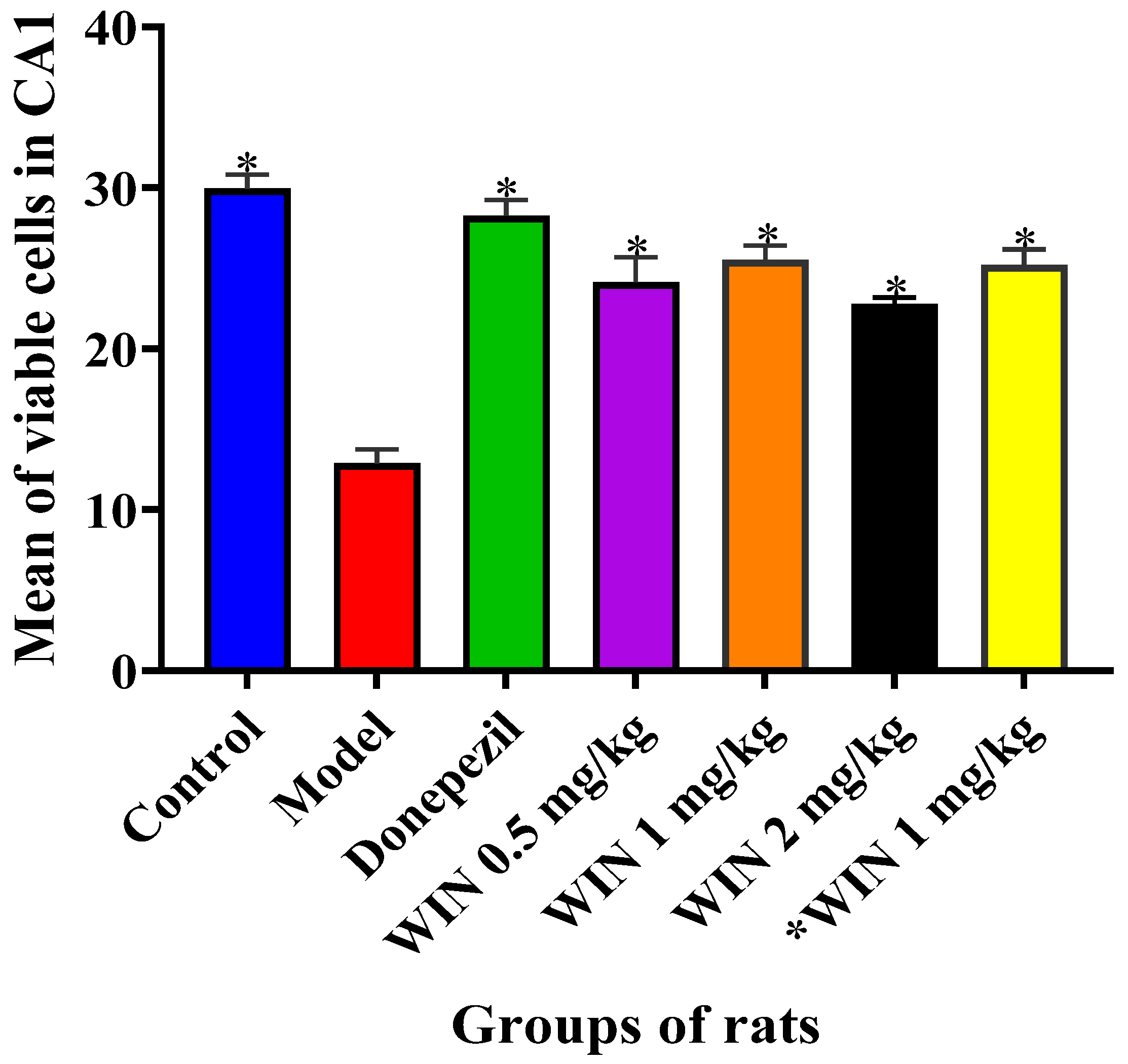
3.2. Histological Findings
3.3. Biochemical Findings
3.3.1. Effects of WIN on MDA Levels in the Brains of AlCl3 and d-gal-Induced Rats
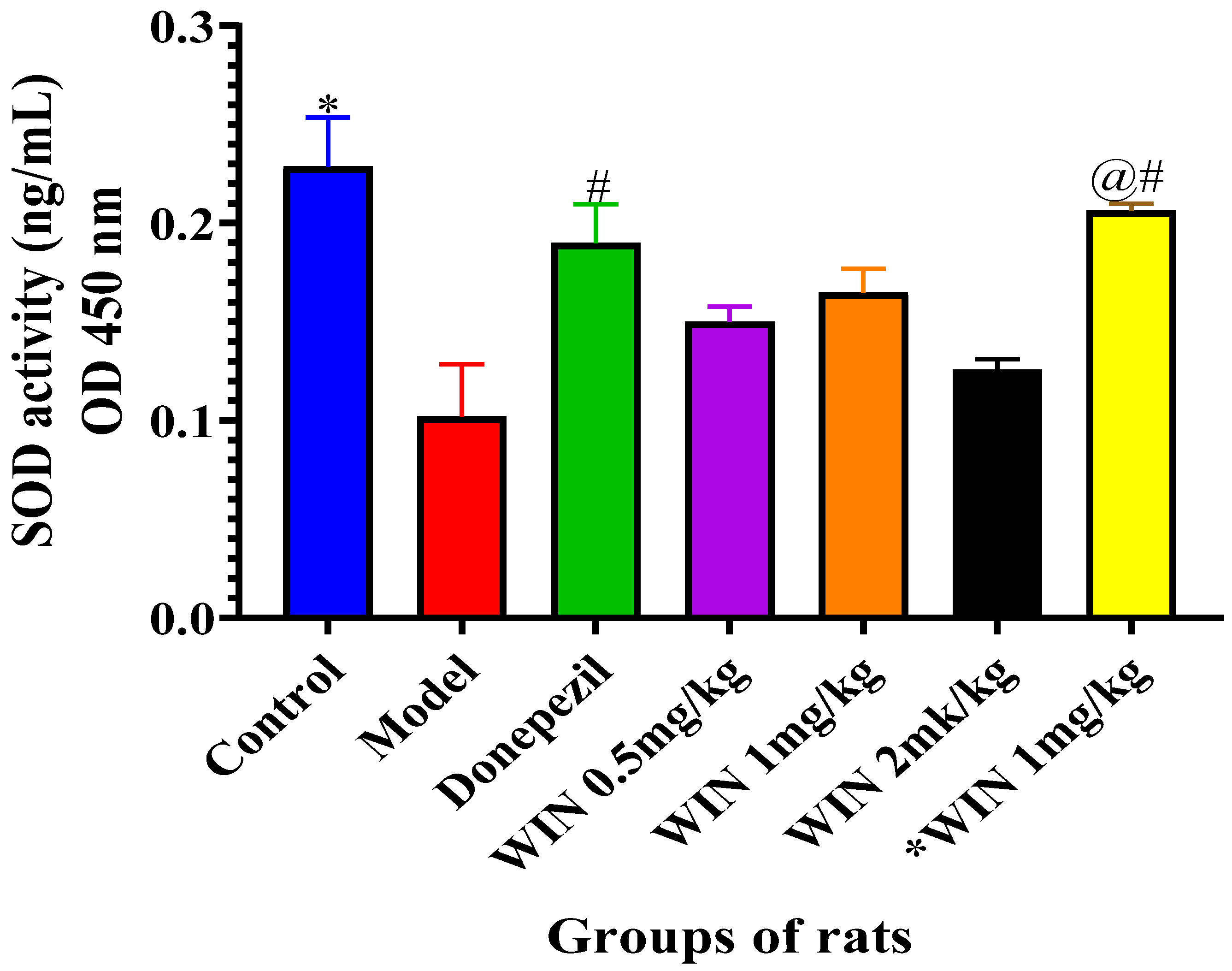
3.3.2. Effects of WIN on SOD Activities in the Brain of AlCl3 and d-gal and Induced Rats
3.3.3. WIN Potentially Enhances Reduced Glutathione (GSH) Concentrations in the Brain of AlCl3 and d-gal-Induced Rats
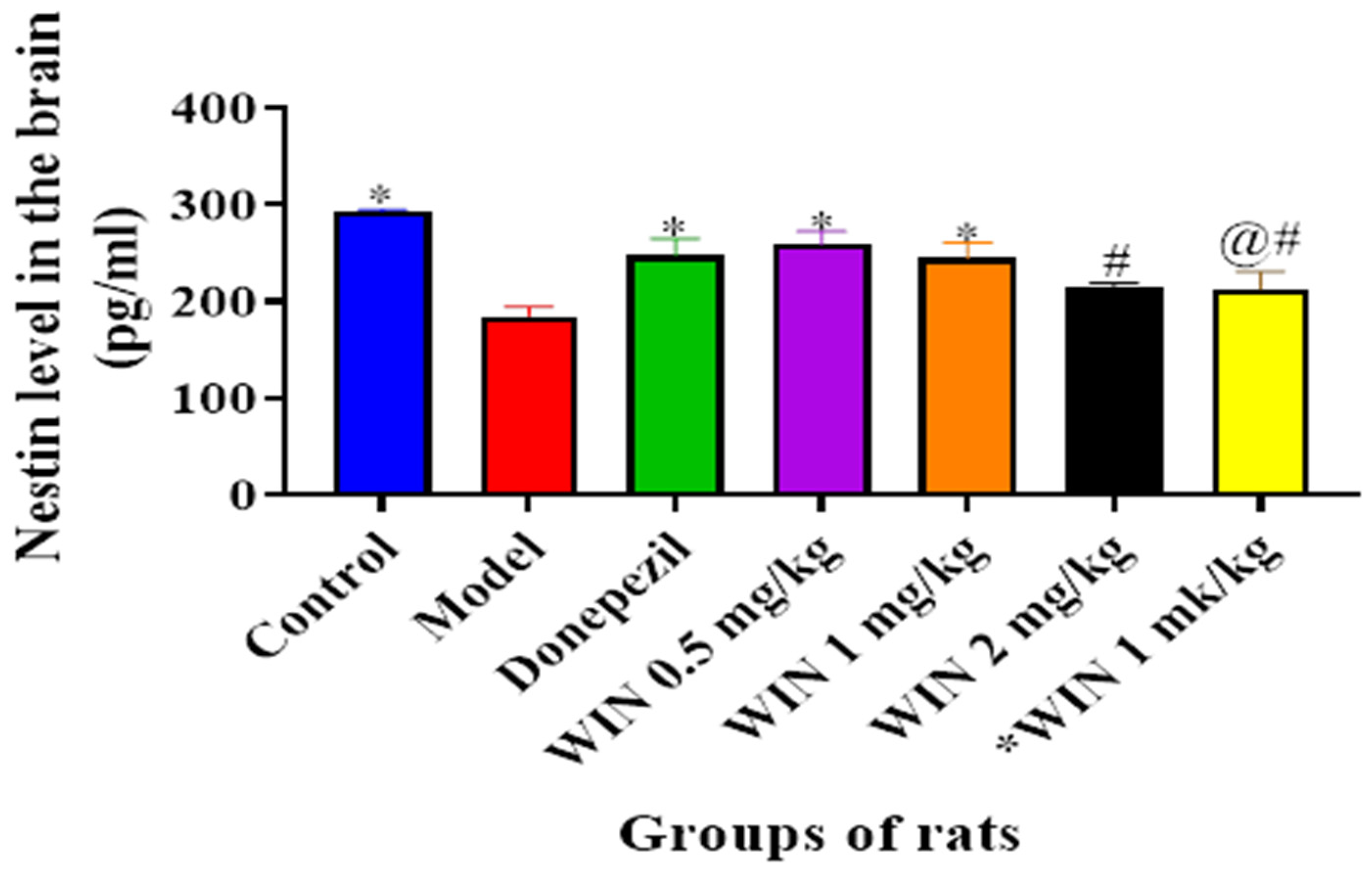
3.3.4. WIN Enhances Nestin Level, a Marker for Neurogenesis in the Brain of AlCl3− and d-gal-Induced Rats
3.3.5. WIN Enhances the Level of Neurogenesis Marker Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP) in the Brain of AlCl3− and d-gal-Induced Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACh | acetyl choline |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AGES | Advanced glycation end products |
| AlCl3 | Aluminium chloride |
| Aβ42 | Amyloid beta 42 |
| BCA | Bicinchoninic acid assay |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| CA1–4 | Connus ammonis 1–4 |
| ChEIs | Cholinesterase inhibitors |
| CV | Cresyl Violet Acetate |
| DG | Dentate gyrus |
| d-gal | d-galactose |
| DONE | Donepezil |
| DW | Distilled water |
| EC | Endocannabinoid system |
| GFAP | Glial Fibrillary Acid Protein |
| GP | Group |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| IACUC | Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee |
| MDA | Malonaldehyde |
| MWM | Morris Water Maze |
| n | Number of rats per group |
| NMDA | N-methyl-d-aspartate |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NS | Normal saline |
| OD | Optical density |
| OH | Hydroxyl radical |
| ONOO– | Peroxynitrite |
| RIPA | Radioimmunoprecipitatation assay |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SEM | Standard error of mean |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| USFDA | United States Food and Drugs Administration |
| T-GSH | Total glutathione |
| THC | Tetrahydrocannabinol |
| WIN | WIN55,212-2 |
References
- Selkoe, D.J. Alzheimer’s Disease Is a Synaptic Failure. Science 2002, 298, 789–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Querfurth, H.W.; LaFerla, F.M. Alzherimer’s Disease: The many paths to brain failure supplementary appendix. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zilka, N.; Filipcik, P.; Koson, P.; Fialova, L.; Skrabana, R.; Zilkova, M.; Rolkova, G.; Kontsekova, E.; Novak, M. Truncated tau from sporadic Alzheimer’s disease suffices to drive neurofibrillary degeneration in vivo. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 3582–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doody, R.; Pavlik, V.; Massman, P.; Kenan, M.; Yeh, S.; Powell, S.; Cooke, N.; Dyer, C.; Demirovic, J.; Waring, S.; et al. Changing patient characteristics and survival experience in an Alzheimer’s center patient cohort. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2005, 20, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafii, M.S.; Aisen, P.S. Advances in alzheimer’s disease drug development. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaugler, J.; James, B.; Johnson, T.; Scholz, K.; Weuve, J. 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2016, 12, 459–509. [Google Scholar]
- Brookmeyer, R.; Johnson, E.; Ziegler-Graham, K.; Arrighi, H.M. Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2007, 3, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.L.; Tsai, W.H.; Chen, C.J.; Pan, T.M. Centella asiatica extract protects against amyloid β1–40-induced neurotoxicity in neuronal cells by activating the antioxidative defence system. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2016, 6, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farina, M.; Lara, F.S.; Brandão, R.; Jacques, R.; Rocha, J.B.T. Effects of aluminum sulfate on erythropoiesis in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 132, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, M.; Kato-Negishi, M. Link between aluminum and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: The integration of the aluminum and amyloid cascade hypotheses. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 2011, 276393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, C.A.; Tomljenovic, L. Aluminum in the central nervous system (CNS): Toxicity in humans and animals, vaccine adjuvants, and autoimmunity. Immunol. Res. 2013, 56, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.H.; Chen, S.C.; Lin, Y.F.; Lee, Y.C.; Huang, M.Y.; Chen, K.C.; Wu, H.Y.; Lin, P.C.; Gozes, I.; Tyan, Y.C. Reduction of aluminum ion neurotoxicity through a small peptide application—NAP treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed Umesalma, S.A. Protective Effect of Centella asiatica against Aluminium-Induced Neurotoxicity in Cerebral Cortex, Striatum, Hypothalamus and Hippocampus of Rat Brain- Histopathological, and Biochemical Approach. J. Mol. Biomark. Diagn. 2015, 6, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.A.; Ahmed, H.I.; Abu-Elfotuh, K. Modeling Stages Mimic Alzheimer’s Disease Induced by Different Doses of Aluminum in Rats: Focus on Progression of the Disease in Response to Time. J. Alzheimer’s Park. Dement. 2016, 11, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mattson, M.P. Pathways towards and away from AD. Nature 2011, 430, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahdi, O.; Baharuldin, M.T.H.; Nor, N.H.M.; Chiroma, S.M.; Jagadeesan, S.; Moklas, M.A.M. Chemicals used for the induction of Alzheimer’s disease-like cognitive dysfunctions in rodents. Biomed. Res. Ther. 2019, 6, 3460–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumont, M. Behavioral phenotyping of mouse models of neurodegeneration. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 793, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bucala, R.; Cerami, A. Advanced Glycosylation: Chemistry, Biology, and Implications for Diabetes and Aging. Adv. Pharmacol. 1992, 23, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vlassara, H.; Bucala, R.; Striker, L. Pathogenic effects of advanced glycosylation: Biochemical, biologic, and clinical implications for diabetes and aging. Lab. Investig. 1994, 70, 138–151. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, S.C.; Liu, J.H.; Wu, R.Y. Establishment of the mimetic aging effect in mice caused by D-galactose. Biogerontology 2003, 4, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Li, L.; Song, Q.; Ai, H.; Chu, J.; Li, W. Behavioural study of the D-galactose induced aging model in C57BL/6J mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2005, 157, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Wang, B.; Li, W.P.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, A.W.; Chen, M.Z. Anti-aging effect of astragalosides and its mechanism of action. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2003, 24, 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Ishibashi, K.; Ishibashi, K.; Reiser, K.; Grebe, R.; Biswal, S.; Gehlbach, P.; Handa, J.T. Advanced glycation endproduct-induced aging of the retinal pigment epithelium and choroid: A comprehensive transcriptional response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11846–11851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; He, H.; Jiang, W.; Chang, X.; Zhu, L.; Luo, F.; Zhou, R.; Ma, C.; Yan, T. Salidroside ameliorates cognitive impairment in a d-galactose-induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 293, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Mu, X.; Zeng, J.; Xu, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Chen, J.; Li, T.; Wang, Y. Ginsenoside Rg1 prevents cognitive impairment and hippocampus senescence in a rat model of D-galactose-induced aging. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xian, Y.F.; Lin, Z.X.; Zhao, M.; Mao, Q.Q.; Ip, S.P.; Che, C.T. Uncaria rhynchophylla Ameliorates Cognitive Deficits Induced by D-galactose in Mice. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauckner, J.E.; Hille, B.; Mackie, K. The cannabinoid agonist WIN55,212-2 increases intracellular calcium via CB1 receptor coupling to Gq/11 G proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 19144–19149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, H.C.; MacKie, K. An introduction to the endogenous cannabinoid system. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulep, M.G.; Saraon, S.K.; McLea, S. Alzheimer Disease. J. Nurse Pract. 2018, 14, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bao, X.; Wang, R. Experimental models of Alzheimer’s disease for deciphering the pathogenesis and therapeutic screening (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yiannopoulou, K.G.; Papageorgiou, S.G. Current and future treatments for Alzheimer’s disease. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2013, 6, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, W.; Hooli, B.; Mullin, K.; Jin, S.C.; Cella, M.; Ulland, T.K.; Wang, Y.; Tanzi, R.E.; Colonna, M. Alzheimer’s disease-associated TREM2 variants exhibit either decreased or increased ligand-dependent activation. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchalant, Y. Cannabinoid agonist WIN-55,212–2 partially restores neurogenesis in the aged rat brain. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 1068–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchalant, Y.; Brothers, H.M.; Norman, G.J.; Karelina, K.; DeVries, A.C.; Wenk, G.L. Cannabinoids attenuate the effects of aging upon neuroinflammation and neurogenesis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 34, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, P.; Suwalsky, M.; Jemiola-Rzeminska, M.; Strzalka, K.; Sepúlveda, B.; Gallardo, M.J. The acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor and anti-Alzheimer drug donepezil interacts with human erythrocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisman, H.; McIntyre, D.C. Conceptual, spatial, and cue learning in the morris water maze in fast or slow kindling rats: Attention deficit comorbidity. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 7809–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnhart, C.D.; Yang, D.; Lein, P.J. Using the Morris water maze to assess spatial learning and memory in weanling mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorhees, C.V.; Williams, M.T. Morris water maze: Procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McNamara, R.K.; Skelton, R.W. The neuropharmacological and neurochemical basis of place learning in the Morris water maze. Brain Res. Rev. 1993, 18, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1984, 11, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, P.A.; Bland, R.J.; Das, P.; Price, R.W.; Holloway, V.; Smithson, L.; Dicker, B.L.; During, M.J.; Young, D.; Golde, T.E. Novel rat Alzheimer’s disease models based on AAV-mediated gene transfer to selectively increase hippocampal Aβ levels. Mol. Neurodegener. 2007, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Kang, T.; Qi, B.; Kong, L.; Jiao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J. Neuroprotective effects of ginseng protein on PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the hippocampus of D-galactose/AlCl3 inducing rats model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 179, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pi, Z.; Song, F.; Liu, Z. Ginsenosides attenuate D-galactose- and AlCl3-inducedspatial memory impairment by restoring the dysfunction of the neurotransmitter systems in the rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riljak, V.; Milotová, M.; Jandová, K.; Pokorný, J.; Langmeier, M. Morphological changes in the hippocampus following nicotine and kainic acid administration. Physiol. Res. 2007, 56, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adeli, S.; Zahmatkesh, M.; Tavoosidana, G.; Karimian, M.; Hassanzadeh, G. Simvastatin enhances the hippocampal klotho in a rat model of streptozotocin-induced cognitive decline. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 72, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiroma, S.M.; Hidayat Baharuldin, M.T.; Mat Taib, C.N.; Amom, Z.; Jagadeesan, S.; Adenan, M.I.; Mohd Moklas, M.A. Protective effect of Centella asiatica against D -galactose and aluminium chloride induced rats: Behavioral and ultrastructural approaches. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asle-Rousta, M.; Kolahdooz, Z.; Oryan, S.; Ahmadiani, A.; Dargahi, L. FTY720 (fingolimod) attenuates beta-amyloid peptide (Aβ42)-induced impairment of spatial learning and memory in rats. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 50, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Prakash, A.; Dogra, S. Neuroprotective effect of carvedilol against aluminium induced toxicity: Possible behavioral and biochemical alterations in rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2011, 63, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Jin, G.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y. Polysaccharides from Pleurotus ostreatus alleviate cognitive impairment in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Ahmed, M.; Surapaneni, K.M.; Veeraraghavan, V.P.; Arulselvan, P. Neuroprotective effects of ononin against the aluminium chloride-induced Alzheimer’s disease in rats. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4232–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, H.M.; Georgy, G.S.; Hamad, S.R.; Badr, W.K.; El Raey, M.A.; Abdelfattah, M.A.O.; Wink, M.; Sobeh, M. A leaf extract of harrisonia abyssinica ameliorates neurobehavioral, histological and biochemical changes in the hippocampus of rats with aluminum chloride-induced alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Zuo, P.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Long, J.; Packer, L.; Liu, J. Chronic systemic D-galactose exposure induces memory loss, neurodegeneration, and oxidative damage in mice: Protective effects of R-??-lipoic acid. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 84, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Prakash, A.; Pahwa, D. Galantamine potentiates the protective effect of rofecoxib and caffeic acid against intrahippocampal Kainic acid-induced cognitive dysfunction in rat. Brain Res. Bull. 2011, 85, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Hua, X.; Xiao, M.; Ding, J.; Han, Q.; Hu, G. Impairments of astrocytes are involved in the d-galactose-induced brain aging. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 369, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiroma, S.M.; Mohd Moklas, M.A.; Mat Taib, C.N.; Baharuldin, M.T.H.; Amon, Z. D-galactose and aluminium chloride induced rat model with cognitive impairments. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.P.; Yin, H.; Kang, K.; Lin, Q.; Su, S.H.; Hai, J. The potential protective effects of cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN55,212-2 on cognitive dysfunction is associated with the suppression of autophagy and inflammation in an experimental model of vascular dementia. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 267, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; Qin, Y.; Guan, E.; He, D.; Wei, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, Q. Propofol inhibits proliferation and induces neuroapoptosis of hippocampal neurons in vitro via downregulation of NF-κB p65 and Bcl-2 and upregulation of caspase-3. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2014, 32, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.M.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, L.; Qian, L.B.; Ma, L.L.; Yu, J.; Zhu, M.H.; Wen, C.Y.; Yu, L.N.; Yan, M. Both PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 pathways participate in the protection by dexmedetomidine against transient focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Brain Res. 2013, 1494, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya-López, M.; Colín-González, A.L.; Aguilera, G.; de Lima, M.E.; Colpo-Ceolin, A.; Rangel-López, E.; Villeda-Hernández, J.; Rembao-Bojórquez, D.; Túnez, I.; Luna-López, A.; et al. Neuroprotective effect of WIN55,212-2 against 3-nitropropionic acid-induced toxicity in the rat brain: Involvement of CB1 and NMDA receptors. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.H.; Kim, J.E.; Rhie, S.J.; Yoon, S. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Exp. Neurobiol. 2015, 24, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Jiang, Z.; Liao, Y.; Song, Z.; Nan, X. Lycopene Prevents Amyloid [Beta]-Induced Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress and Dysfunctions in Cultured Rat Cortical Neurons. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilgun-Sherki, Y.; Melamed, E.; Offen, D. Antioxidant treatment in Alzheimer’s disease: Current state. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2003, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, H.; Khan, M.M.; Khan, A.; Vaibhav, K.; Ahmad, A.; Khuwaja, G.; Ahmed, M.E.; Raza, S.S.; Ashafaq, M.; Tabassum, R.; et al. S-allyl cysteine attenuates oxidative stress associated cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration in mouse model of streptozotocin-induced experimental dementia of Alzheimer’s type. Brain Res. 2011, 1389, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, R.; Perkins, G. Dynamics of mitochondrial structure during apoptosis and the enigma of Opa1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg. 2009, 1787, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miranda, S.; Opazo, C.; Larrondo, L.F.; Muñoz, F.J.; Ruiz, F.; Leighton, F.; Inestrosa, N.C. The role of oxidative stress in the toxicity induced by amyloid β-peptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2000, 62, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P.; Duan, W. “Apoptotic” biochemical cascades in synaptic compartments: Roles in adaptive plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. J. Neurosci. Res. 1999, 58, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swomley, A.M.; Butterfield, D.A. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment: Evidence from human data provided by redox proteomics. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, M.A.; Ehmann, W.D.; Butler, S.M.; Markesbery, W.R. Elevated thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances and antioxidant enzyme activity in the brain in alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 1995, 45, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Liaquat, L.; Ahmad, S.; Batool, Z.; Siddiqui, R.A.; Tabassum, S.; Shahzad, S.; Rafiq, S.; Naz, N. Naringenin protects AlCl3/D-galactose induced neurotoxicity in rat model of AD via attenuation of acetylcholinesterase levels and inhibition of oxidative stress. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, R.A.; Eissa, T.F.; Abdallah, D.M.; Saad, M.A.; El-Abhar, H.S. Peganum harmala enhanced GLP-1 and restored insulin signaling to alleviate AlCl3-induced Alzheimer-like pathology model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bernal, A.; Arranz, L. Nestin-expressing progenitor cells: Function, identity and therapeutic implications. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 2177–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



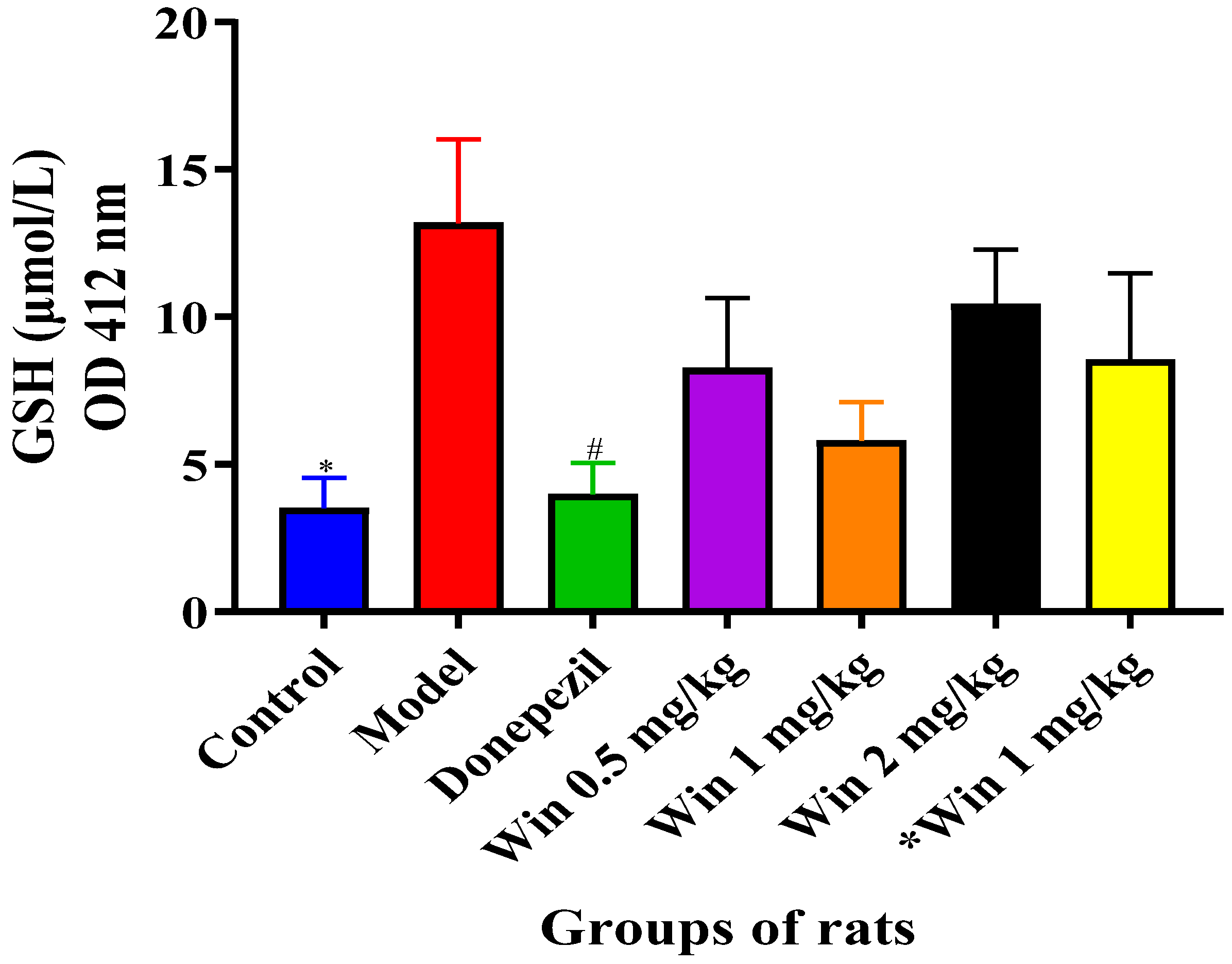

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahdi, O.; Chiroma, S.M.; Hidayat Baharuldin, M.T.; Mohd Nor, N.H.; Mat Taib, C.N.; Jagadeesan, S.; Devi, S.; Mohd Moklas, M.A. WIN55,212-2 Attenuates Cognitive Impairments in AlCl3 + d-Galactose-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Rats by Enhancing Neurogenesis and Reversing Oxidative Stress. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091270
Mahdi O, Chiroma SM, Hidayat Baharuldin MT, Mohd Nor NH, Mat Taib CN, Jagadeesan S, Devi S, Mohd Moklas MA. WIN55,212-2 Attenuates Cognitive Impairments in AlCl3 + d-Galactose-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Rats by Enhancing Neurogenesis and Reversing Oxidative Stress. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(9):1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091270
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahdi, Onesimus, Samaila Musa Chiroma, Mohamad Taufik Hidayat Baharuldin, Nurul Huda Mohd Nor, Che Norma Mat Taib, Saravanan Jagadeesan, Shamala Devi, and Mohamad Aris Mohd Moklas. 2021. "WIN55,212-2 Attenuates Cognitive Impairments in AlCl3 + d-Galactose-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Rats by Enhancing Neurogenesis and Reversing Oxidative Stress" Biomedicines 9, no. 9: 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091270
APA StyleMahdi, O., Chiroma, S. M., Hidayat Baharuldin, M. T., Mohd Nor, N. H., Mat Taib, C. N., Jagadeesan, S., Devi, S., & Mohd Moklas, M. A. (2021). WIN55,212-2 Attenuates Cognitive Impairments in AlCl3 + d-Galactose-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Rats by Enhancing Neurogenesis and Reversing Oxidative Stress. Biomedicines, 9(9), 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091270





