Enisamium Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 RNA Synthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
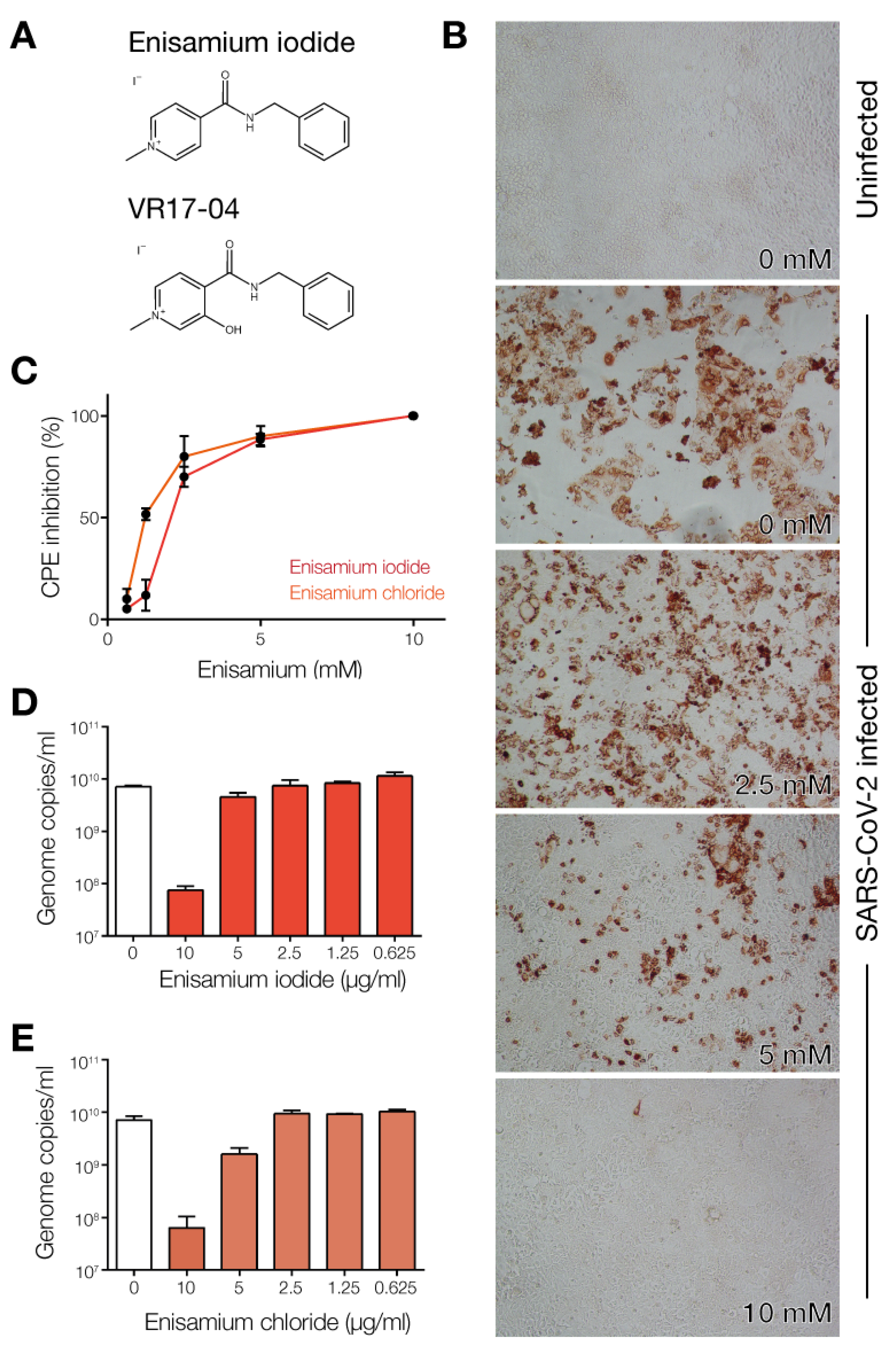
2.1. SARS-CoV-2 Infections
2.2. HCoV-NL63 NHBE Infections
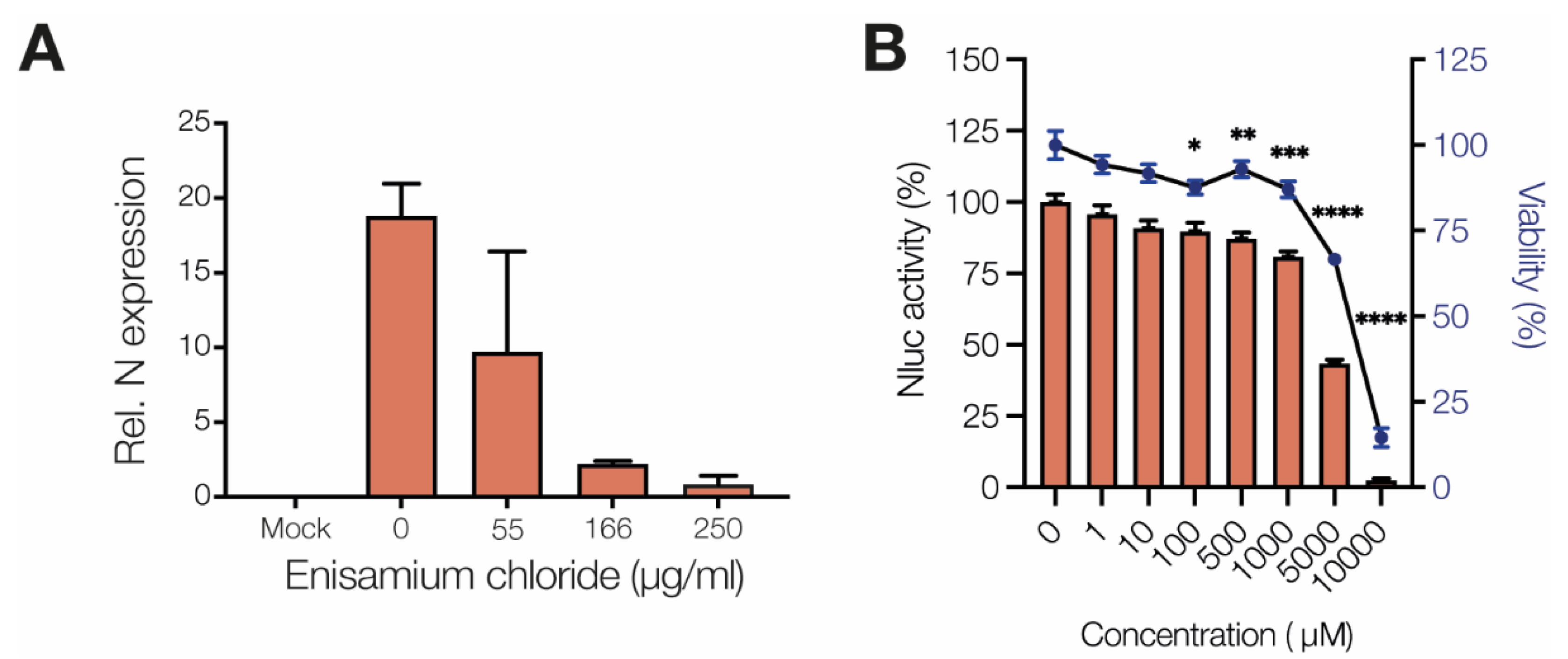
2.3. SARS-CoV-2 Minigenome Assay
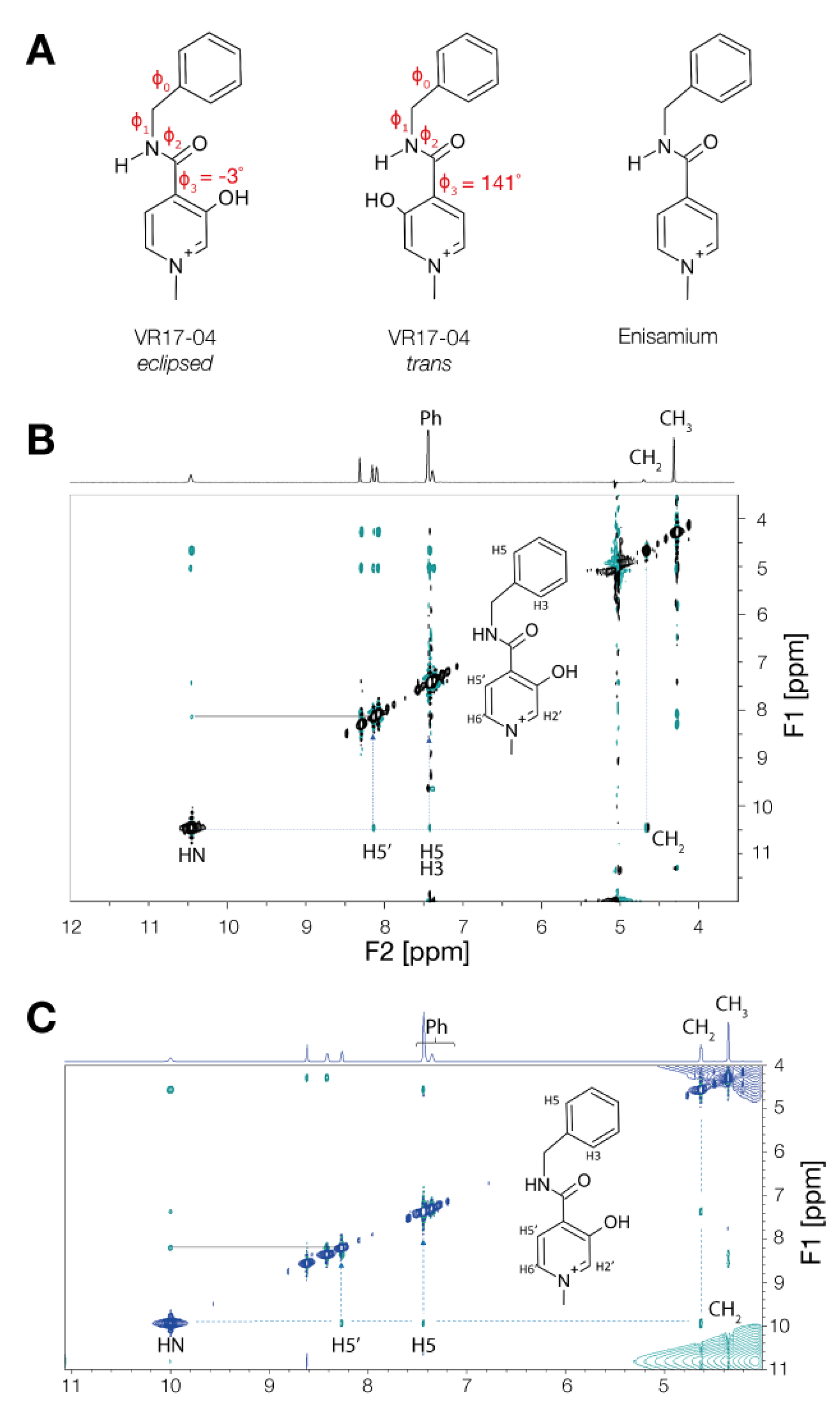
2.4. NOE NMR Spectra Measurement
2.5. Conformational Characterization and Geometry Optimization
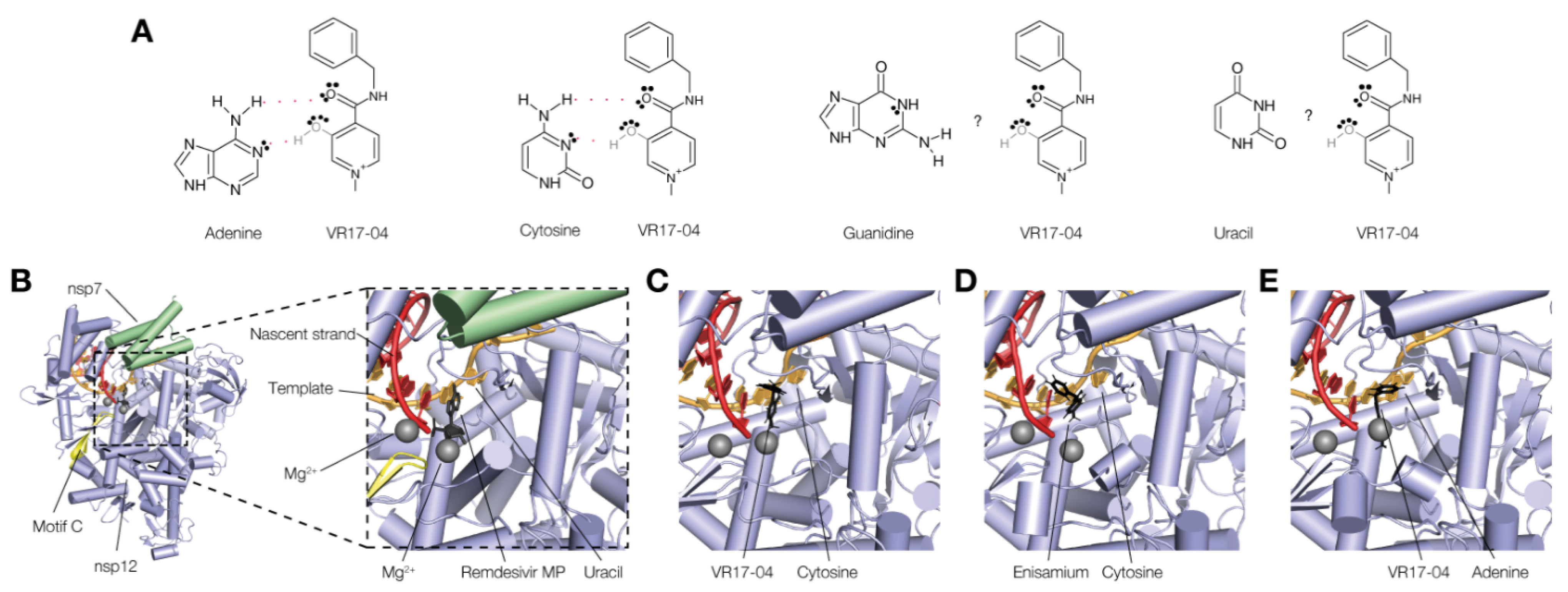
2.6. Molecular Docking
2.7. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
2.8. Estimation of Poisson-Boltzmann Free Energy of Binding
3. Results
3.1. Enisamium Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Cell Culture
3.2. Enisamium Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 nsp12/7/8 Activity
3.3. Enisamium Adopts a Conformation in Solution That Would Be Compatible with Hydrogen Bond Formation
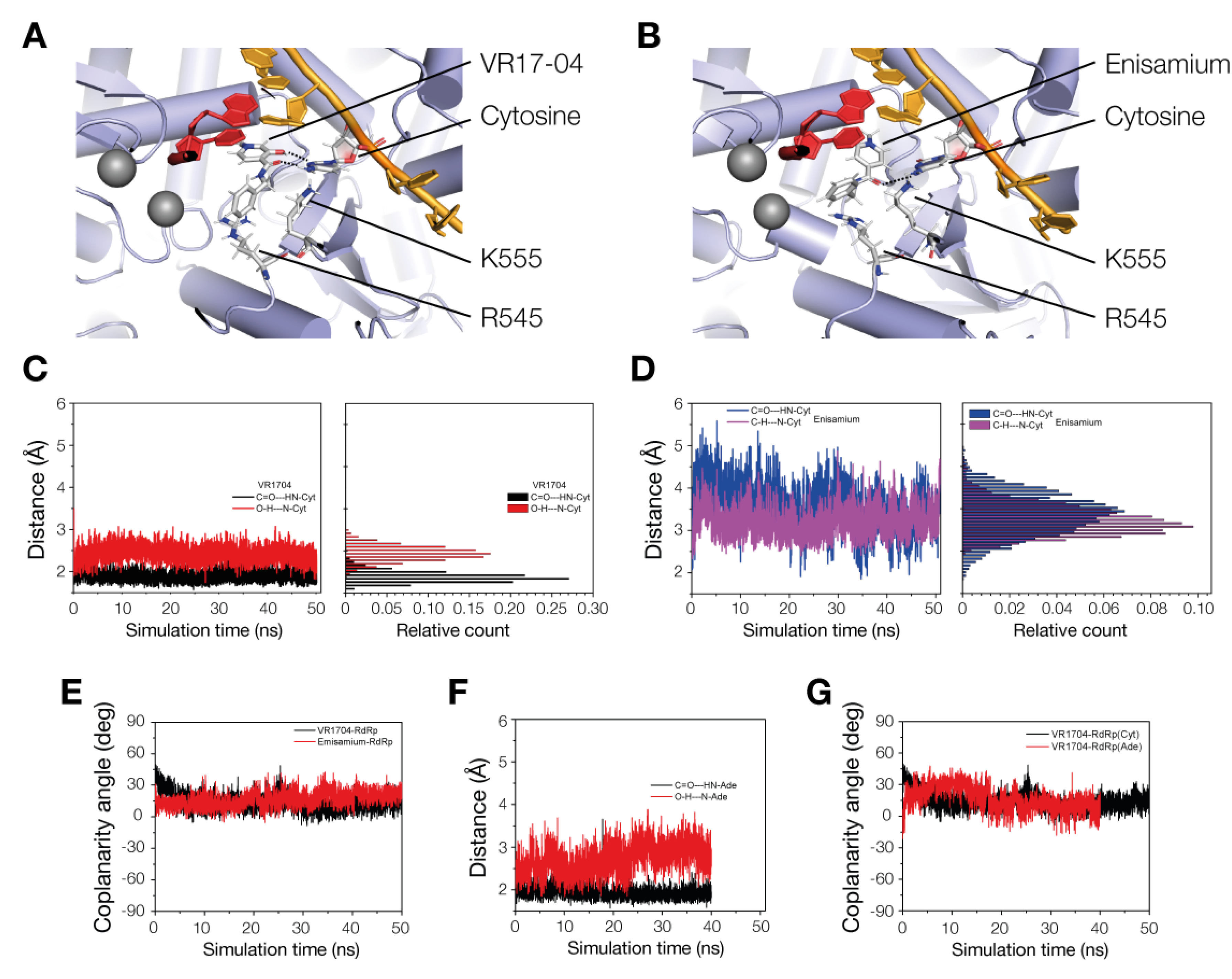
3.4. VR17-04 Forms Hydrogen Bonds with Cytosine and Adenosine in MD Simulations
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheahan, T.P.; Sims, A.C.; Zhou, S.; Graham, R.L.; Pruijssers, A.J.; Agostini, M.L.; Leist, S.R.; Schafer, A.; Dinnon, K.H., 3rd; Stevens, L.J.; et al. An orally bioavailable broad-spectrum antiviral inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human airway epithelial cell cultures and multiple coronaviruses in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cox, R.M.; Wolf, J.D.; Plemper, R.K. Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, A.; Selisko, B.; Le, N.T.; Huchting, J.; Touret, F.; Piorkowski, G.; Fattorini, V.; Ferron, F.; Decroly, E.; Meier, C.; et al. Rapid incorporation of Favipiravir by the fast and permissive viral RNA polymerase complex results in SARS-CoV-2 lethal mutagenesis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhill, D.H.; Te Velthuis, A.J.W.; Fletcher, R.A.; Langat, P.; Zambon, M.; Lackenby, A.; Barclay, W.S. The mechanism of resistance to favipiravir in influenza. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 11613–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartenian, E.; Nandakumar, D.; Lari, A.; Ly, M.; Tucker, J.M.; Glaunsinger, B.A. The molecular virology of coronaviruses. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 12910–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of V. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subissi, L.; Imbert, I.; Ferron, F.; Collet, A.; Coutard, B.; Decroly, E.; Canard, B. SARS-CoV ORF1b-encoded nonstructural proteins 12-16: Replicative enzymes as antiviral targets. Antivir. Res. 2014, 101, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Velthuis, A.J.; Arnold, J.J.; Cameron, C.E.; van den Worm, S.H.; Snijder, E.J. The RNA polymerase activity of SARS-coronavirus nsp12 is primer dependent. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subissi, L.; Posthuma, C.C.; Collet, A.; Zevenhoven-Dobbe, J.C.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Decroly, E.; Snijder, E.J.; Canard, B.; Imbert, I. One severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus protein complex integrates processive RNA polymerase and exonuclease activities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3900–E3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, J.; Zheng, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, T.; Jia, Z.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, M.; et al. Architecture of a SARS-CoV-2 mini replication and transcription complex. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillen, H.S.; Kokic, G.; Farnung, L.; Dienemann, C.; Tegunov, D.; Cramer, P. Structure of replicating SARS-CoV-2 polymerase. Nature 2020, 584, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Malone, B.; Llewellyn, E.; Grasso, M.; Shelton, P.M.M.; Olinares, P.D.B.; Maruthi, K.; Eng, E.T.; Vatandaslar, H.; Chait, B.T.; et al. Structural Basis for Helicase-Polymerase Coupling in the SARS-CoV-2 Replication-Transcription Complex. Cell 2020, 182, 1560–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Te Velthuis, A.J.W.; Zubkova, T.G.; Shaw, M.; Mehle, A.; Boltz, D.; Gmeinwieser, N.; Stammer, H.; Milde, J.; Muller, L.; Margitich, V. Enisamium Reduces Influenza Virus Shedding and Improves Patient Recovery by Inhibiting Viral RNA Polymerase Activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2021, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vial, T.; Oade, M.S.; Russell, C.A.; Eggink, D.; te Velthuis, A.J.W. A SARS-CoV-2 mini-genome assay based on negative-sense RNA to study replication inhibitors and emerging mutations. BioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.P.; Fan, H.; Keown, J.R.; Margitich, V.; Grimes, J.M.; Fodor, E.; Te Velthuis, A.J.W. Enisamium is a small molecule inhibitor of the influenza A virus and SARS-CoV-2 RNA polymerases. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E.; Mehta, A.K.; Zingman, B.S.; Kalil, A.C.; Hohmann, E.; Chu, H.Y.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Kline, S.; et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19—Final Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltz, D.; Peng, X.; Muzzio, M.; Dash, P.; Thomas, P.G.; Margitich, V. Activity of enisamium, an isonicotinic acid derivative, against influenza viruses in differentiated normal human bronchial epithelial cells. Antivir Chem. Chemother. 2018, 26, 2040206618811416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurbaev, V.V.; Slita, A.V.; Sinegubova, E.O.; Muryleva, A.A.; Lavrentieva, I.N. Anti-viral activity of enisamium iodide against viruses of influenza and ARVI’s on different cell lines. Ther. Arch. 2020, 92, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojkova, D.; Klann, K.; Koch, B.; Widera, M.; Krause, D.; Ciesek, S.; Cinatl, J.; Munch, C. Proteomics of SARS-CoV-2-infected host cells reveals therapy targets. Nature 2020, 583, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojkova, D.; Bechtel, M.; McLaughlin, K.M.; McGreig, J.E.; Klann, K.; Bellinghausen, C.; Rohde, G.; Jonigk, D.; Braubach, P.; Ciesek, S.; et al. Aprotinin Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Replication. Cells 2020, 9, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toptan, T.; Hoehl, S.; Westhaus, S.; Bojkova, D.; Berger, A.; Rotter, B.; Hoffmeier, K.; Cinatl, J., Jr.; Ciesek, S.; Widera, M. Optimized qRT-PCR Approach for the Detection of Intra- and Extra-Cellular SARS-CoV-2 RNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Revision C.01; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, W.; Mao, C.; Luan, X.; Shen, D.D.; Shen, Q.; Su, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, W.; Gao, M.; et al. Structural basis for inhibition of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from SARS-CoV-2 by remdesivir. Science 2020, 368, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesteiger, J.; Marsili, M. Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity a rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 1980, 36, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Braun, R.; Wang, W.; Gumbart, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Villa, E.; Chipot, C.; Skeel, R.D.; Kale, L.; Schulten, K. Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Case, D.A.; Cheatham, T.E., 3rd; Darden, T.; Gohlke, H.; Luo, R.; Merz, K.M., Jr.; Onufriev, A.; Simmerling, C.; Wang, B.; Woods, R.J. The Amber biomolecular simulation programs. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1668–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, A.; Katebzadeh, K.; Söderhjelm, P.; Nilsson, I.; Ryde, U. Ligand affinities predicted with the MM/PBSA method: Dependence on the simulation method and the force field. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6596–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, J.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Cieplak, T.E.; Kollman, P.; Case, D.A. Continuum solvent studies of the stability of DNA, RNA, and phosphoramidate–DNA helices. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 9401–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | φ0 | φ1 | φ2 | φ3 | Conf. | EB3LYP (Hartree) | EZPE (Hartree) | EB3LYP+ EZPE (Hartree) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VR17-04 | 80 | 44 | 148 | 141 | trans | −802.2589 | 0.2720 | −801.9869 |
| VR17-04 | 83 | 9 | 177 | −3 | eclipsed | −802.2713 | 0.2715 | −801.9998 |
| Enisamium | 77 | 27 | 170 | −21 | − | −727.0392 | 0.2672 | −726.7720 |
| 1H Resonance. | HN | H2′ | H6′ | H5′ | Ph | CH2 | CH3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ ppm | 10.45 | 8.29 | 8.08 | 8.13 | 7.42/7.36 | 4.66 | 4.28 |
| Complex | D | 〈d〉 (Å) | χ | 〈χ〉 (°) | Avg Interval (ns) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VR17-04-RdRp(C) | CO---H2N-Cyt, OH---:N-Cyt | 1.9, 2.4 | CO-HN-N:-HO | 13 | 30–50 |
| Enisamium-RdRp(C) | CO---H2N-Cyt | 3.3 | CO-HN-N:-HC | 20 | 30–50 |
| VR17-04-RdRp(A) | CO---H2N-Ade, OH---:N-Ade | 1.9, 2.9 | CO-HN-N:-HO | 11 | 20–40 |
| Inhibitor | Complex | Average MD Interval (ns) | 〈ΔGPBBind〉 (kcal mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| VR17-04 | VR17-04-RdRp(Cyt) | [46, 50] | −19.8(4) |
| Enisamium | Enisamium-RdRp(Cyt) | [46, 50] | 43.6(5) |
| VR17-04 | VR17-04-RdRp(Ade) | [28, 32] | −14.8(5) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elli, S.; Bojkova, D.; Bechtel, M.; Vial, T.; Boltz, D.; Muzzio, M.; Peng, X.; Sala, F.; Cosentino, C.; Goy, A.; et al. Enisamium Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 RNA Synthesis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091254
Elli S, Bojkova D, Bechtel M, Vial T, Boltz D, Muzzio M, Peng X, Sala F, Cosentino C, Goy A, et al. Enisamium Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 RNA Synthesis. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(9):1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091254
Chicago/Turabian StyleElli, Stefano, Denisa Bojkova, Marco Bechtel, Thomas Vial, David Boltz, Miguel Muzzio, Xinjian Peng, Federico Sala, Cesare Cosentino, Andrew Goy, and et al. 2021. "Enisamium Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 RNA Synthesis" Biomedicines 9, no. 9: 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091254
APA StyleElli, S., Bojkova, D., Bechtel, M., Vial, T., Boltz, D., Muzzio, M., Peng, X., Sala, F., Cosentino, C., Goy, A., Guerrini, M., Müller, L., Cinatl, J., Margitich, V., & te Velthuis, A. J. W. (2021). Enisamium Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 RNA Synthesis. Biomedicines, 9(9), 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091254






