Biosensors Designed for Clinical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Important Optimization Issues
3. Microfluidic Detection of Oral Cancer
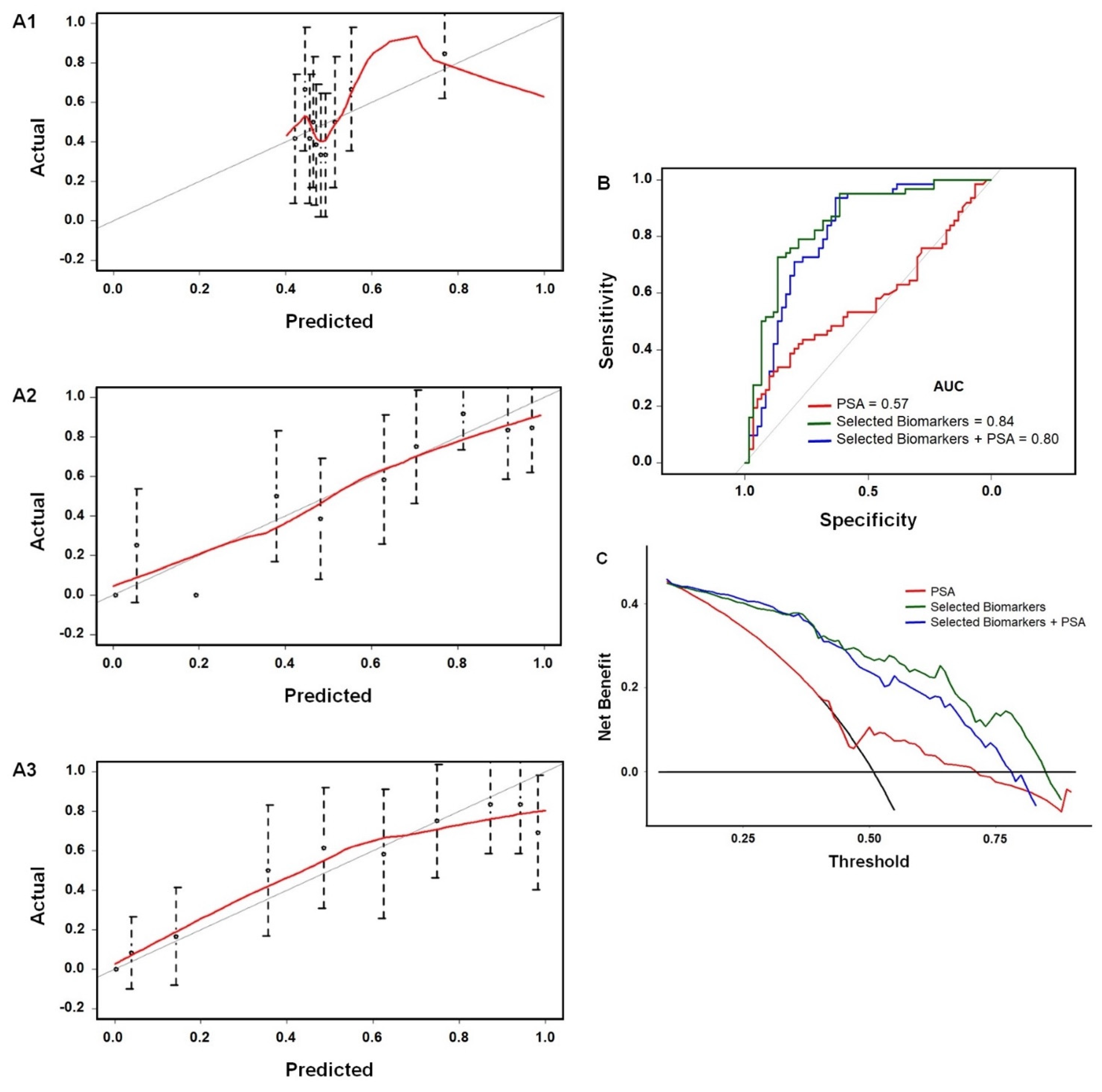
4. Predicting the Need for Prostate Cancer Biopsy
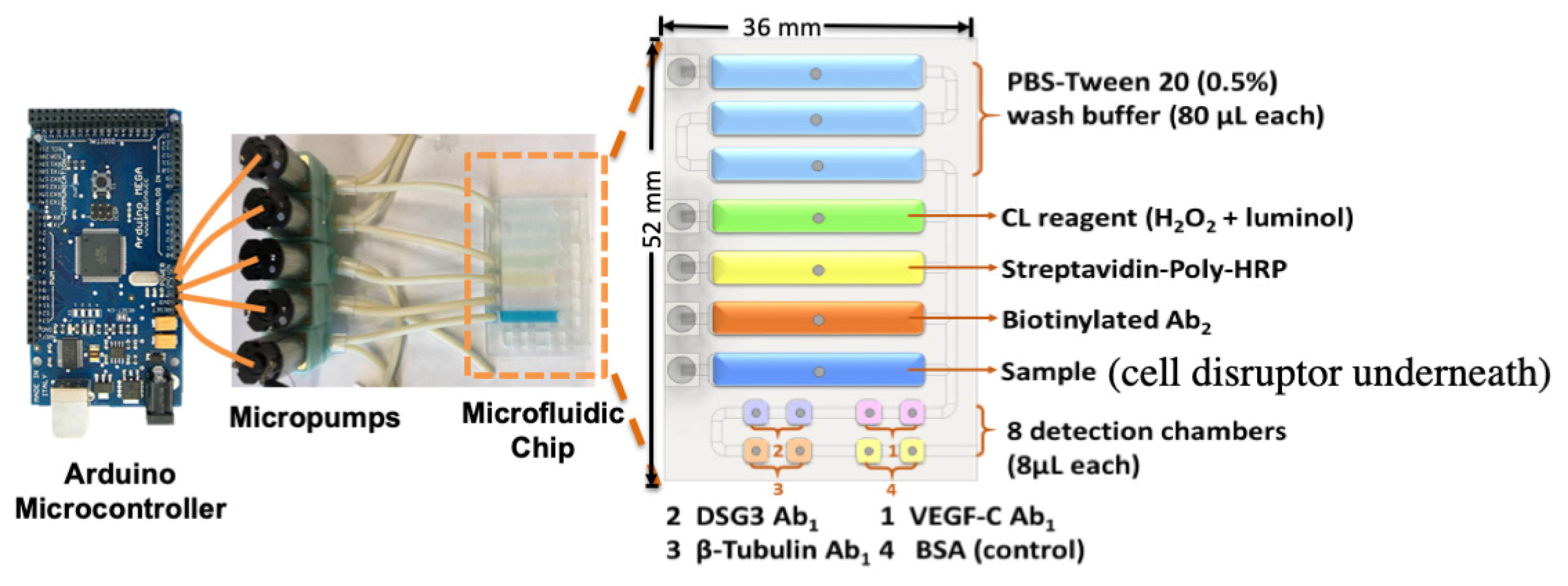
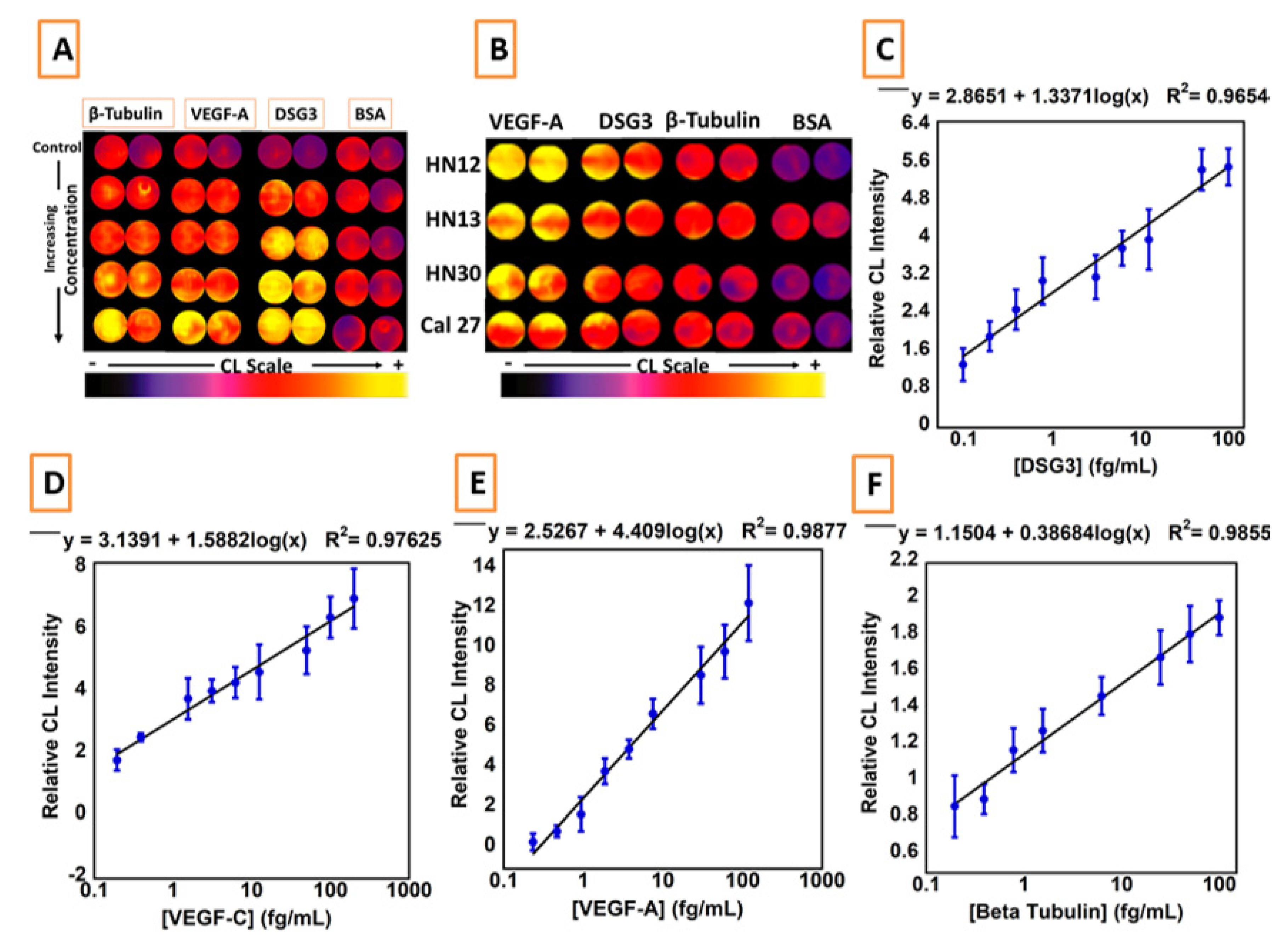
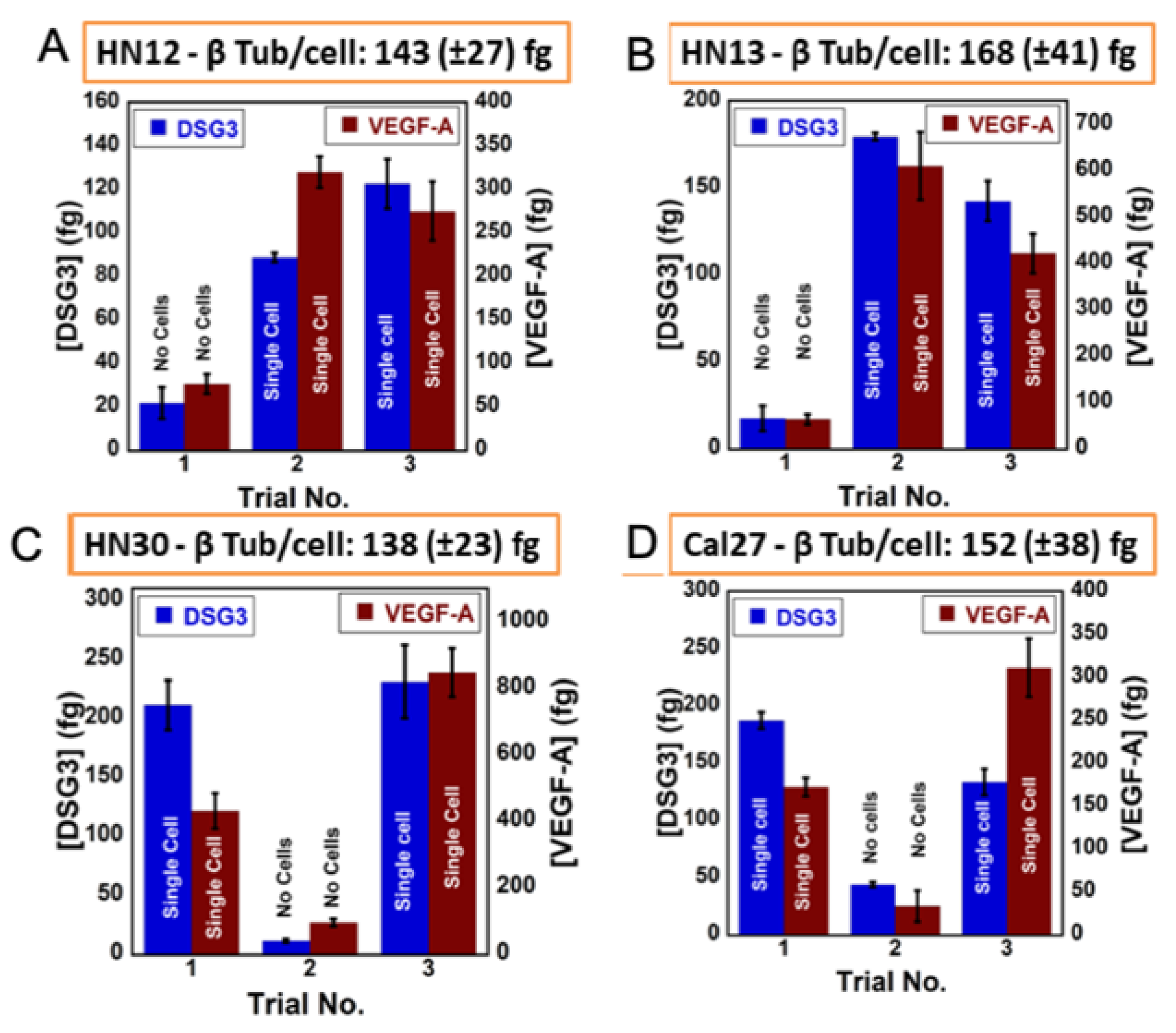
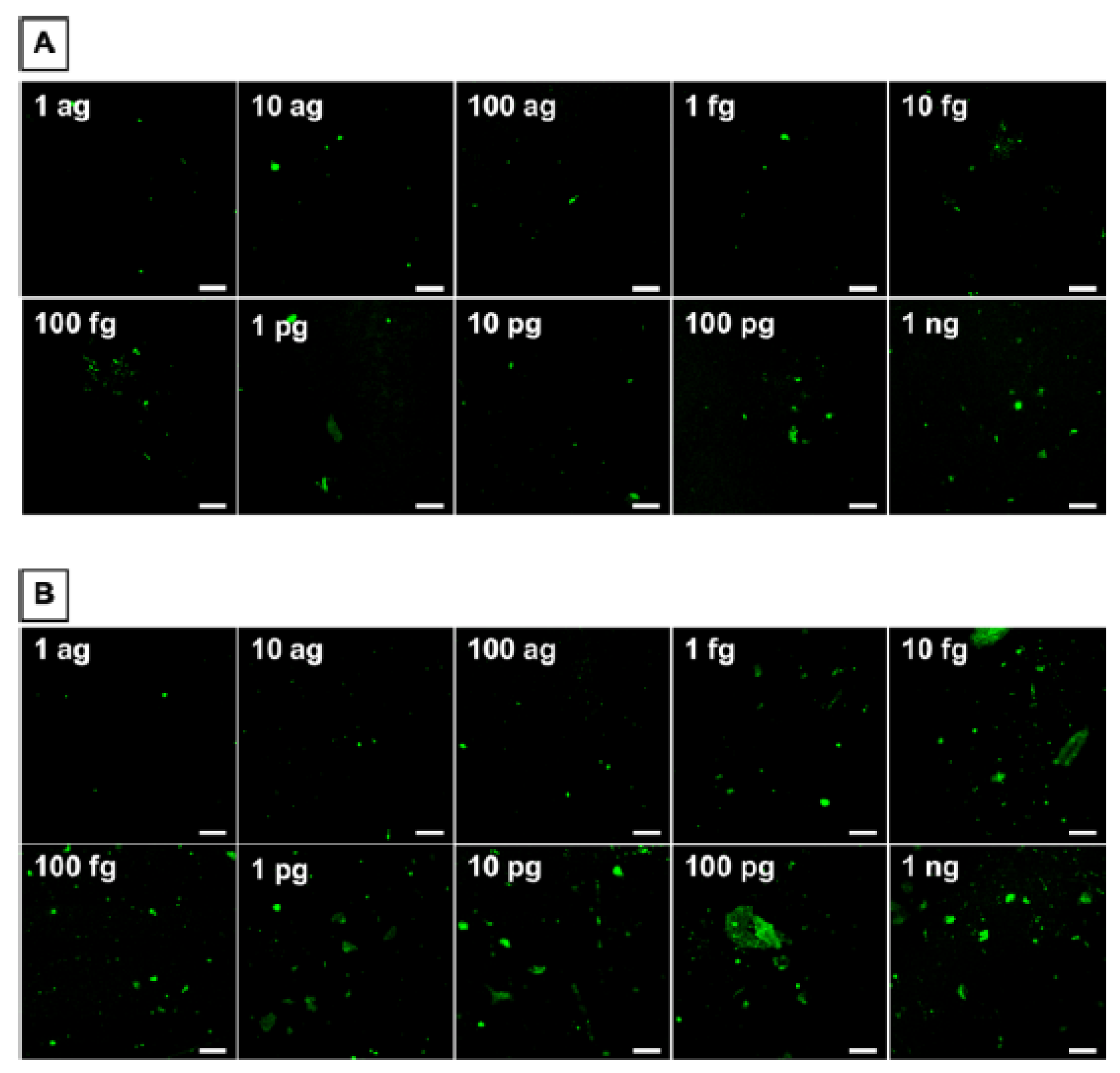
5. Detecting a Cell-Bound Metastatic Biomarker
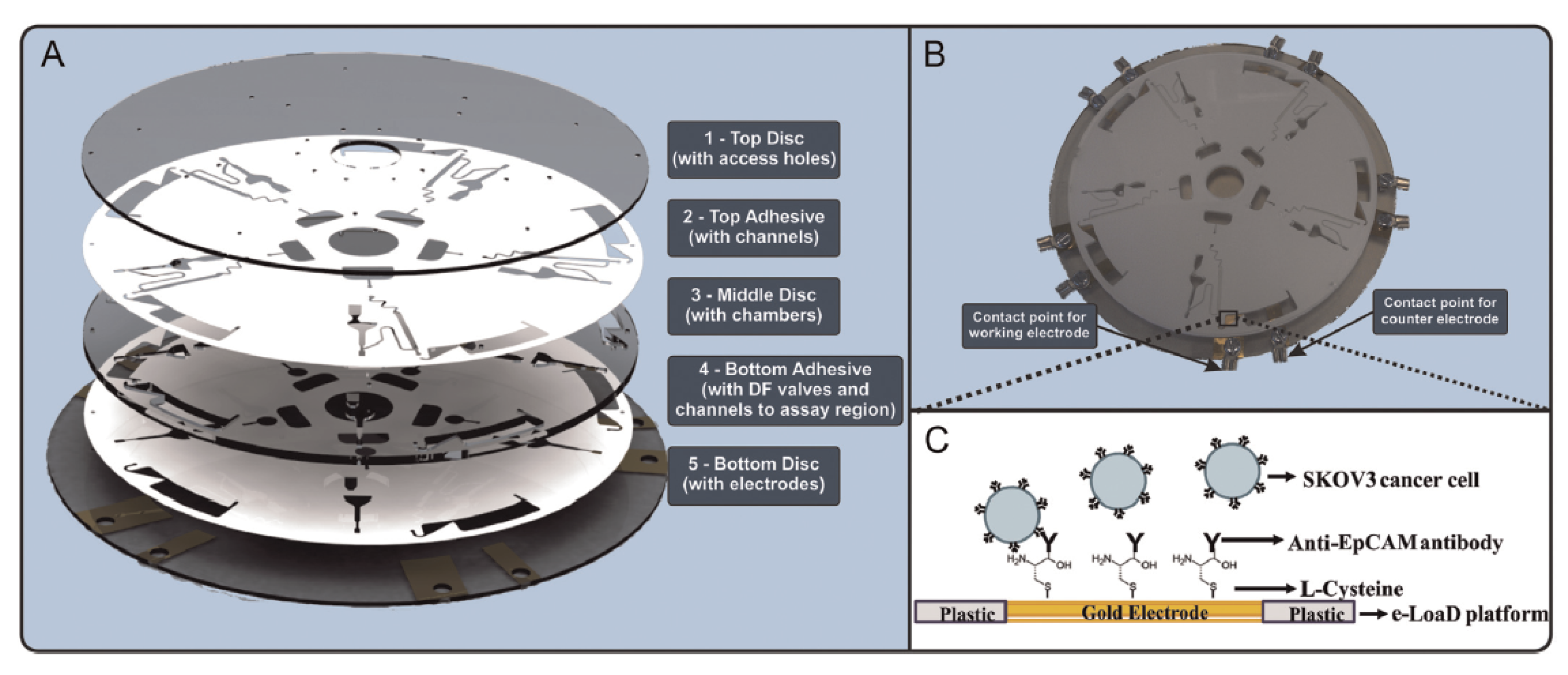
6. Label Free Electrochemical Detection of Cancer Cells
7. Sample to Answer Microfluidic Device for Neurological Disease
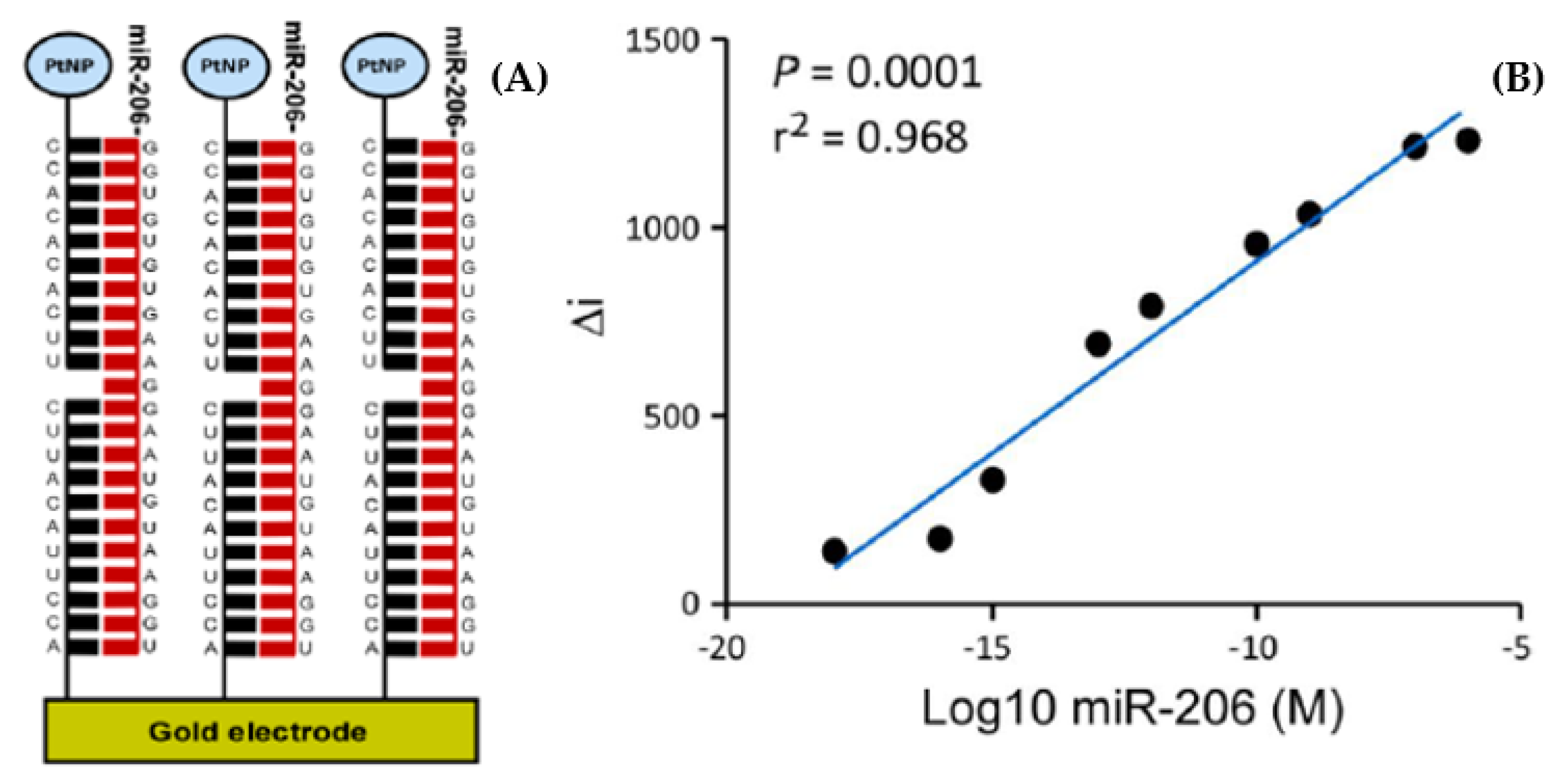
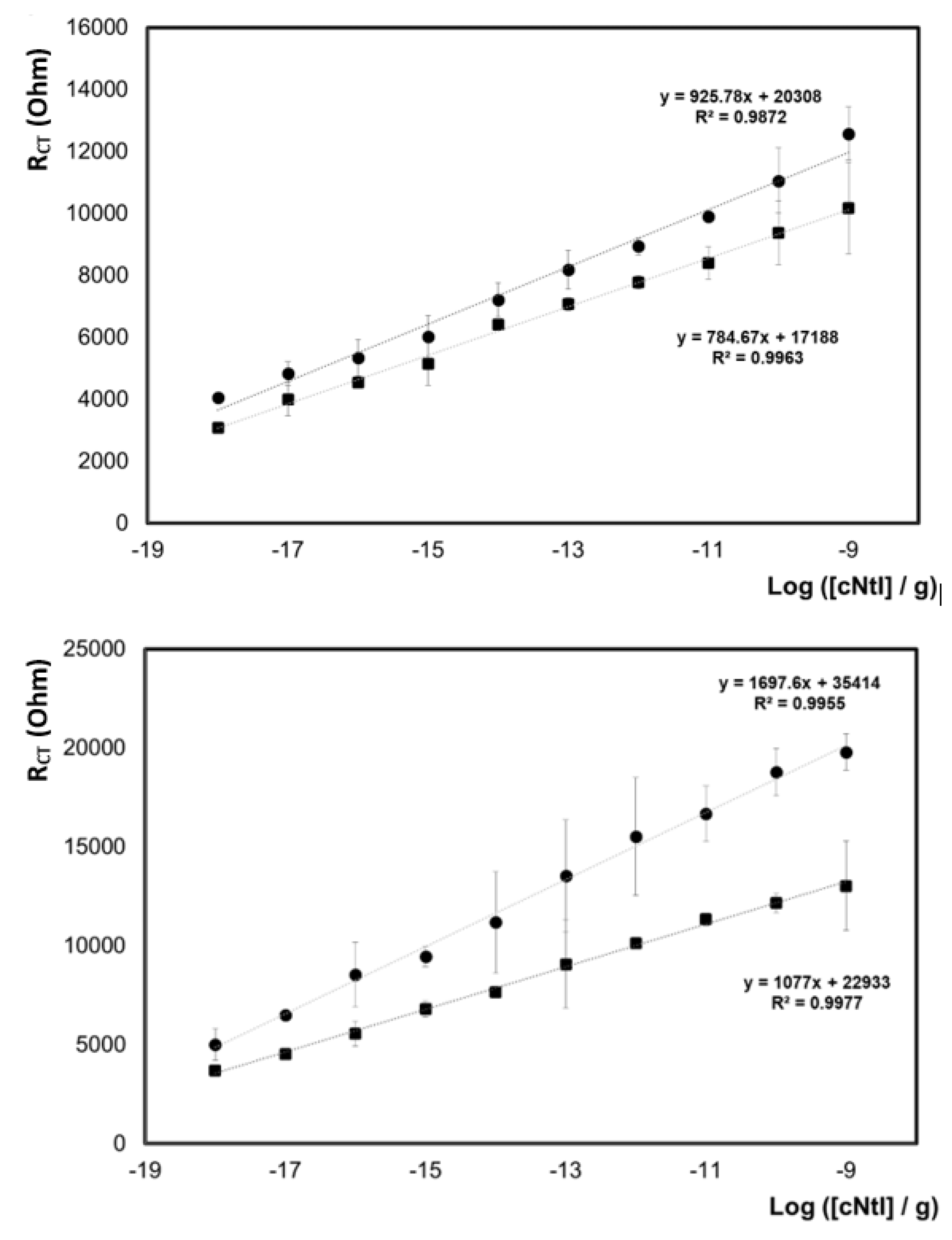
7.1. Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
7.2. Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease
8. Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Disease
9. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: https://jamaicahospital.org/newsletter/history-of-thermometers/ (accessed on 19 March 2021).
- Wang, J. Glucose Biosensors: 40 Years of Advances and Challenges. Electroanalysis 2001, 12, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, T.P.; Cunningham, D.D. Biosensors for Personal Diabetes Management. In Commercial Biosensors: Applications to Clinical, Bioprocess, and Environmental Samples; Ramsey, G., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 3–46. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, R.J.; Cumba, L.R. Optimizing Glucose Sensing for Diabetes Monitoring. In Bioelectronics and Medical Devices; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 765–778. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.; Dhanapala, L.; Kankanamage, R.N.T.; Kumar, C.V.; Rusling, J.F. Multiplexed Immunosensors and Immunoarrays. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biomarkers Definitions Working Group. Biomarkers and Surrogate Endpoints: Preferred Definitions and Conceptual Framework. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 69, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Spaine, E.; Keyes, T.E.; Forster, R.J. DNA sensor based on vapour polymerised pedot films functionalised with gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, T.; Liu, Z.; Han, Z.; Ge, Q. MicroRNA Detection Specificity: Recent Advances and Future Perspective. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3179–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forster, R.J.; Bertoncello, P.; Keyes, T.E. Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2009, 2, 359–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertoncello, P.; Forster, R.J. Nanostructured materials for electrochemiluminescence (ECL)-based detection methods: Recent advances and future perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusling, J.F.; Kumar, C.V.; Gutkind, J.S.; Patel, V. Measurement of Biomarker Proteins for Point-Of-Care Early Detection and Monitoring of Cancer. Analyst 2010, 135, 2496–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forster, R.J. ECL of Nanomaterials: Novel Materials, Detection Strategies and Applications. In Analytical Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence: From Fundamentals to Bioassays; Sojic, N., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2019; pp. 247–273. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Zang, X.; Lv, Y. Detection of circulating tumor cells: Advances and critical concerns. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.C.P. Circulating tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarioglu, A.F.; Aceto, N.; Kojic, N.; Donaldson, M.C.; Zeinali, M.; Hamza, B.; Engstrom, A.; Zhu, H.; Sundaresan, T.K.; Miyamoto, D.T.; et al. A microfluidic device for label-free, physical capture of circulating tumor cell clusters. Nat. Methods. 2015, 12, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manne, U.; Srivastava, R.G.; Srivastava, S. Recent Advances in Biomarkers for Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment. Drug. Discov. Today 2005, 10, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, J.A.; Weinstein, J.N. Biomarkers in Cancer Staging, Prognosis and Treatment Selection. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanapala, L.; Krause, C.E.; Jones, A.L.; Rusling, J.F. Printed Electrodes in Microfluidic Arrays for Cancer Biomarker Protein Detection. Biosensors 2020, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, S. PSA and Beyond: Alternative Prostate Cancer Biomarkers. Cell Oncol. 2016, 39, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spain, E.; Gilgunn, S.; Sharma, S.; Adamson, K.; Carthy, E.; O’Kennedy, R.; Forster, R.J. Detection of prostate specific antigen based on electrocatalytic platinum nanoparticles conjugated to a recombinant scFv antibody. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsmore, S.F. Multiplexed Protein Measurement: Technologies and Applications of Protein and Antibody Arrays. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chin, C.D.; Laksanasopin, T.; Cheung, Y.K.; Steinmiller, D.; Linder, V.; Parsa, H.; Wang, J.; Moore, H.; Rouse, R.; Umviligihozo, G. Microfluidics-Based Diagnostics of Infectious Diseases in The Developing World. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivnak, A.J.; Rissin, D.M.; Kan, C.W.; Song, L.; Fishburn, M.W.; Piech, T.; Campbell, T.G.; DuPont, D.R.; Gardel, M.; Sullivan, S.; et al. A Fully-Automated, Six-Plex Single Molecule Immunoassay for Measuring Cytokines in Blood. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 424, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, C.E.; Otieno, B.A.; Latus, A.; Faria, R.C.; Patel, V.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Rapid Microfluidic Immunoassays of Cancer Biomarker Proteins using Disposable Inkjet-printed Gold Nanoparticle Arrays. ChemistryOpen 2013, 2, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Munge, B.; Patel, V.; Jensen, G.; Bhirde, A.; Gong, J.D.; Kim, S.-N.; Gillespie, J.; Gutkind, J.S.; Papadimitrakopoulos, F.; et al. Carbon Nanotube Amplification Strategies for Highly Sensitive Immunodetection of Cancer Biomarkers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 11199–11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malhotra, R.; Patel, V.; Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Munge, B.S.; Cheong, S.C.; Zain, R.B.; Abraham, M.T.; Dey, D.K.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Oral Cancer Detection in the Clinic Using an Ultrasensitive Microfluidic Array for a Panel of Biomarker Proteins. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6249–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MedCalc Software. Available online: http://www.medcalc.org/index.php (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Prostate Cancer. 2019. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/prost.html (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Pal, R.P.; Maitra, N.U.; Mellon, J.K.; Khan, M.A. Defining Prostate Cancer Risk before Prostate Biopsy. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2013, 31, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariat, S.F.; Scardino, P.T.; Lilja, H. Screening for Prostate Cancer: An Update. Can. J. Urol. 2009, 15, 4363–4674. [Google Scholar]
- Prostate Conditions Education Council. Gleason Score: Prostate Cancer Grading & Prognostic Scoring. 2019. Available online: https://www.prostateconditions.org/about-pcec/media/10-about-prostate-conditions/prostate-cancer (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Fanning, D.M.; Kay, E.; Fan, Y.; Fitzpatrick, J.M.; Watson, R.W.G. Prostate Cancer Grading: The Effect of Stratification of Needle Biopsy Gleason Score 4 + 3 as High or Intermediate Grade. BJU Int. 2010, 105, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, J.C.; Downes, M.R.; O’Donoghue, N.; O’Keane, C.; O’Neill, A.; Fan, Y.; Fitzpatrick, J.M.; Dunn, M.J.; Watson, R.W.G. 2D-DIGE as a Strategy to Identify Serum Markers for the Progression of Prostate Cancer. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 942–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.; Dhanapala, L.; Baldo, T.A.; Sharafeldin, M.; Krause, C.; Shen, M.; Faria, R.C.; Dey, D.; Moghaddam, S.; Watson, R.W.; et al. Detection of Aggressive Prostate Cancer in the Clinic using an 8-Protein Biomarker Panel. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, V.; Mukunyadzi, P.; Dennis, R.A.; Siegel, E.R.; Johnson, D.E.; Kohil, M. Stage-Specific Characterization of the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Axis in Prostate Cancer: Expression of Lymphangiogenic Markers Is Associated with Advancer-Stage Disease. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 11, 584–593. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Yu, J.; Mani, R.S.; Cao, Q.; Brenner, C.J.; Cao, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; Hu, M.; et al. An Integrated Network of Androgen Receptor, Polycomb, and TMPRSS2-ERG Gene Fusions in Prostate Cancer Progression. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varambally, S.; Laxman, B.; Mehra, R.; Cao, Q.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Tomlins, S.A.; Granger, J.; Vellaichamy, A.; Sreekumar, A.; Yu, J.; et al. Golgi Protein GOLM1 Is a Tissue and Urine Biomarker of Prostate Cancer. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mantzoros, C.S.; Tzonou, A.; Signorello, L.B.; Stampfer, M.; Trichopoulos, D.; Adami, H.O. Insulin like Growth Factor 1 in Relation to Prostate Cancer and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 76, 1115–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shariat, S.F.; Lamb, D.J.; Kattan, M.W.; Nguyen, C.; Kim, J.; Beck, J.; Wheeler, T.M.; Slawin, K.M. Association of Preoperative Plasma Levels of Insulin-Like Growth Factor I and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Proteins-2 and -3 With Prostate Cancer Invasion, Progression, and Metastasis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-Related Inflammation. Nature 2008, 456, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, S.; Fan, Y.; Watson, R.W.; Murphy, T.B. Evaluation of Prediction Models for the Staging of Prostate Cancer. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2013, 13, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleveland, W.S.; Grosse, E.; Shyu, W.M. Local regression models. In Statistical Models in S; Chambers, J.M., Hastie, T.J., Eds.; Wadsworth & Brooks/Cole Advanced Books & Software: Monterey, CA, USA, 1992; Chapter 8. [Google Scholar]
- Sharafeldin, M.; Chen, T.; Ozkaya, G.U.; Choudhary, D.; Molinolo, A.A.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Detecting Cancer Metastasis and Accompanying Protein Biomarkers at Single Cell Levels using a 3D-Printed Microfluidic Immunoarray. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spano, D.; Heck, C.; Antonellis, P.D.; Christofori, G.; Zollo, M. Molecular Networks that Regulate Cancer Metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2012, 22, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Martin, D.; Malhotra, R.; Marsh, C.A.; Doçi, C.L.; Veenstra, T.D.; Nathan, C.-A.O.; Sinha, U.K.; Singh, B.; Molinolo, A.A.; et al. DSG3 as a Biomarker for the Ultrasensitive Detection of Occult Lymph Node Metastasis in Oral Cancer Using Nanostructured Immunoarrays. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, C.; Ho, B.; Ng, S.H.; Ho, K.; Li, H.; Yoon, Y.-J. 3D Printed Microfluidics for Biological Applications. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3627–3637. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Wu, Y.; Fu, J.; Gao, Q.; Qiu, J. Developments of 3D printing Microfluidics and Applications in Chemistry and Biology. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1658–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusling, J.F. Developing Microfluidic Sensing Devices using 3-D Printing. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharafeldin, M.; Jones, A.; Rusling, J.F. 3D Printed Biosensor Arrays for Medical Diagnostics. Micromachines 2018, 9, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharafeldin, M.; Kadimisetty, K.; Bhalero, K.R.; Chen, T.; Rusling, J.F. 3D-Printed Immunosensor Arrays for Cancer Diagnostics. Sensors 2020, 20, 4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiati, S.; Küpcü, S.; Peacock, M.; Eilenberger, C.; Zamzami, M.; Qadri, I.; Choudhry, H.; Sleytr, U.B.; Schuster, B. Acoustic And Hybrid 3D-Printed Electrochemical Biosensors for the Real-Time Immunodetection of Liver Cancer Cells (HepG2). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiati, S.; Peacock, M.; Leonhardt, S.; Damiati, L.; Baghdadi, M.A.; Becker, H.; Kodzius, R.; Schuster, B. Embedded Disposable Functionalized Electrochemical Biosensor with a 3D-Printed Flow Cell for Detection of Hepatic Oval Cells (HOCs). Genes 2018, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, A.C.; Yao, C.; Venkatesh, A.G.; Hall, D.A. An Efficient Power Harvesting Mobile Phone-Based Electrochemical Biosensor For Point-Of-Care Health Monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 235, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, Z.; Shu, J.; Liu, J.; Tang, D. Dual-Channel Photoelectrochemical Ratiometric Aptasensor with up-Converting Nanocrystals Using Spatial-Resolved Technique on Homemade 3D Printed Device. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadimisetty, K.; Mosa, I.M.; Malla, S.; Satterwhite-Warden, J.E.; Kuhns, T.M.; Faria, R.C.; Lee, N.H.; Rusling, J.F. 3D-Printed Supercapacitor-Powered Electrochemiluminescent Protein Immunoarray. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadimisetty, K.; Malla, S.; Bhalerao, K.S.; Mosa, I.M.; Bhakta, S.; Lee, N.H.; Rusling, J.F. Automated 3D-Printed Microfluidic Array for Rapid Nanomaterial-enhanced Detection of Multiple Proteins. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7569–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, A.; Mirasoli, M.; Dolci, L.S.; Buragina, A.; Bonvicini, F.; Simoni, P.; Guardigli, M. Portable Device Based on Chemiluminescence Lensless Imaging for Personalized Diagnostics through Multiplex Bioanalysis. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3178–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.K.; Vaze, A.; Rusling, J.F. Automated 3D-Printed Unibody Immunoarray for Chemiluminescence Detection of Cancer Biomarker Proteins. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafeldin, M.; Kadimisetty, K.; Bhalerao, K.R.; Bist, I.; Jones, A.; Chen, T.; Lee, N.H.; Rusling, J.F. Accessible Telemedicine Diagnostics with ELISA in a 3D Printed Pipette Tip. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7394–7402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Mohammed, S.I.; Wereley, S.; Irudayaraj, J. Magnetic Focus Lateral Flow Sensor for Detection of Cervical Cancer Biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 2876–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiadò, A.; Palmara, G.; Chiappone, A.; Tanzanu, C.; Pirri, C.F.; Roppolo, I.; Frascella, F. A Modular 3D Printed Lab-On-A-Chip for Early Cancer Detection. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz de Eguilaz, M.; Cumba, L.R.; Forster, R.J. Electrochemical Detection of Viruses and Antibodies: A Mini Review. Electrochem. Commun. 2020, 116, 106762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorin, M.A.; Verdone, J.E.; van der Toom, E.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; Allaf, M.E.; Pienta, K.J. Circulating Tumour Cells as Biomarkers of Prostate, Bladder, and Kidney Cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2017, 14, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Pantel, K. Circulating Tumor Cells: Liquid Biopsy of Cancer. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuske, A.; Gorges, T.M.; Tennstedt, P.; Tiebel, A.-K.; Pompe, R.; Preißer, F.; Prues, S.; Mazel, M.; Markou, A.; Lianidou, E.; et al. Improved Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells in Non-Metastatic High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Tian, T.; Shi, Y.; Liu, W.; Zou, Y.; Khajvand, T.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C. Enrichment and Single-Cell Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 1736–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drancourt, M.; Michel-Lepage, A.; Boyer, S.; Raoult, D. The Point-Of-Care Laboratory in Clinical Microbiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zarei, M. Portable Biosensing Devices for Point-Of-Care Diagnostics: Recent Developments and Applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 91, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lifson, M.A.; Inci, F.; Liang, L.-G.; Sheng, Y.-F.; Demirci, U. Advances in Addressing Technical Challenges of Point-Of-Care Diagnostics in Resource-Limited Settings. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 16, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capaldo, P.; Alfarano, S.R.; Laneselli, L.; Dal Zilio, S.; Bosco, A.; Parisse, P.; Casalis, L. Circulating Disease Biomarker Detection in Complex Matrices: Real-Time, In Situ Measurements of DNA/miRNA Hybridization via Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ll, J.; Sánchez, A.; Joda, H.; Henry, O.Y.F.; Solnestam, B.W.; Kvastad, L.; Akan, P.S.; Lundeberg, J.; Laddach, N.; Ramakrishnan, D.; et al. Electrochemical Genetic Profiling of Single Cancer Cells. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 3378–3385. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasaraghavan, V. Bioimpedance Spectroscopy of Breast Cancer Cells: A Microsystems Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Waylen, L.N.; Nim, H.T.; Martelotto., L.G.; Ramialison, M. From whole-mount to single-cell spatial assessment of gene expression in 3D. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanghelini, F.; Frías, I.A.M.; Rêgo, M.J.B.; Pitta, M.G.R.; Sacilloti, M.; Oliveira, M.D.L.; Andrade, C.A.S. Biosensing Breast Cancer Cells Based on a Three-Dimensional TIO2 Nanomembrane Transducer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, C.; Gao, R.; Niu, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; He, J. An Impedimetric Biosensor for the Diagnosis of Renal Cell Carcinoma Based on the Interaction Between 3-Aminophenyl Boronic Acid and Sialic Acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatanarayanan, A.; Keyes, T.E.; Forster, R.J. Label-free Impedance Detection of Cancer Cells. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2216–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwankire, C.E.; Venkatanarayanan, A.; Glennon, T.; Keyes, T.E.; Forster, R.J.; Ducree, J. Label-Free Impedance Detection of Cancer Cells from Whole Blood on an Integrated Centrifugal Microfluidic Platform. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, A.; McArdle, H.; Calero, M.; Rabano, A.; Madden, S.F.; Adamson, K.; Forster, R.J.; Spaine, E.; Prehn, J.H.M.; Henshall, D.C.; et al. Elevated Plasma microRNA-206 Levels Predict Cognitive Decline and Progression to Dementia from Mild Cognitive Impairment. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raoof, R.; Bauer, S.; El Naggar, H.; Connolly, N.M.C.; Brennan, G.P.; Brindley, E.; Hill, T.; McArdle, H.; Spain, E.; Forster, R.J.; et al. Dual-Center, Dual-Platform MicroRNA Profiling Identifies Potential Plasma Biomarkers of Adult Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. EBioMedicine 2018, 38, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kinahan, D.J.; Kearney, S.M.; Dimov, N.; Glynn, M.T.; Ducree, J. Event-Triggered Logical Flow Control for Comprehensive Process Integration of Multi-Step Assays on Centrifugal Microfluidic Platforms. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horak, J.; Dincer, C.; Qelibari, E.; Bakirci, H.; Urban, G. Polymer-Modified Microfluidic Immunochip for Enhanced Electrochemical Detection of Troponin I. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, V.S.; Jarolim, P. How to interpret elevated cardiac troponin levels. Circulation 2011, 124, 2350–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spaine, E.; Carrara, S.; Adamson, K.; Ma, H.; O’Kennedy, R.; De Cola, L.; Forster, R.J. Cardiac Troponin I: Ultra-sensitive Detection Using Faradaic Electrochemical Impedance. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 17116–17124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, R.J.; Keyes, T.E. Redox Properties of Ground and Electronically Excited States: [Ru(bpy)2Qbpy]2+ Mono-layers. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 10004–10012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devadoss, A.; Spehar-Déleze, A.-M.; Bertoncello, P.; Marthi, R.; Keyes, T.E.; Forster, R.J. Enhanced Electrochemiluminescence and Charge Transport Through Films of Metallopolymer-Gold Nanoparticle Composites. Langmuir 2010, 26, 2130–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dennany, L.; Forster, R.J.; Rusling, J.F. Simultaneous Direct Electrochemiluminescence and Catalytic Voltammetry Detection of DNA in Ultrathin Films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 5213–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennany, L.; Forster, R.J.; White, B.; Smyth, M.; Rusling, J.F. Direct electrochemiluminescence detection of oxidized DNA in ultrathin films containing [Os(bpy)2(PVP)10]2+. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8835–8841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennany, L.; O’Reilly, E.; Forster, R.J. Electrochemiluminescent Monolayers on Metal Oxide Electrodes: Detection of Amino Acids. Electrochem. Commun. 2006, 8, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanut, A.; Fiorani, A.; Canola, S.; Saito, T.; Ziebart, N.; Rapino, S.; Rebeccani, S.; Barbon, A.; Irie, T.; Josel, H.-P.; et al. Insights into the Mechanism of Co-reactant Electrochemiluminescence Facilitating Enhanced Bioanalytical Performance. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
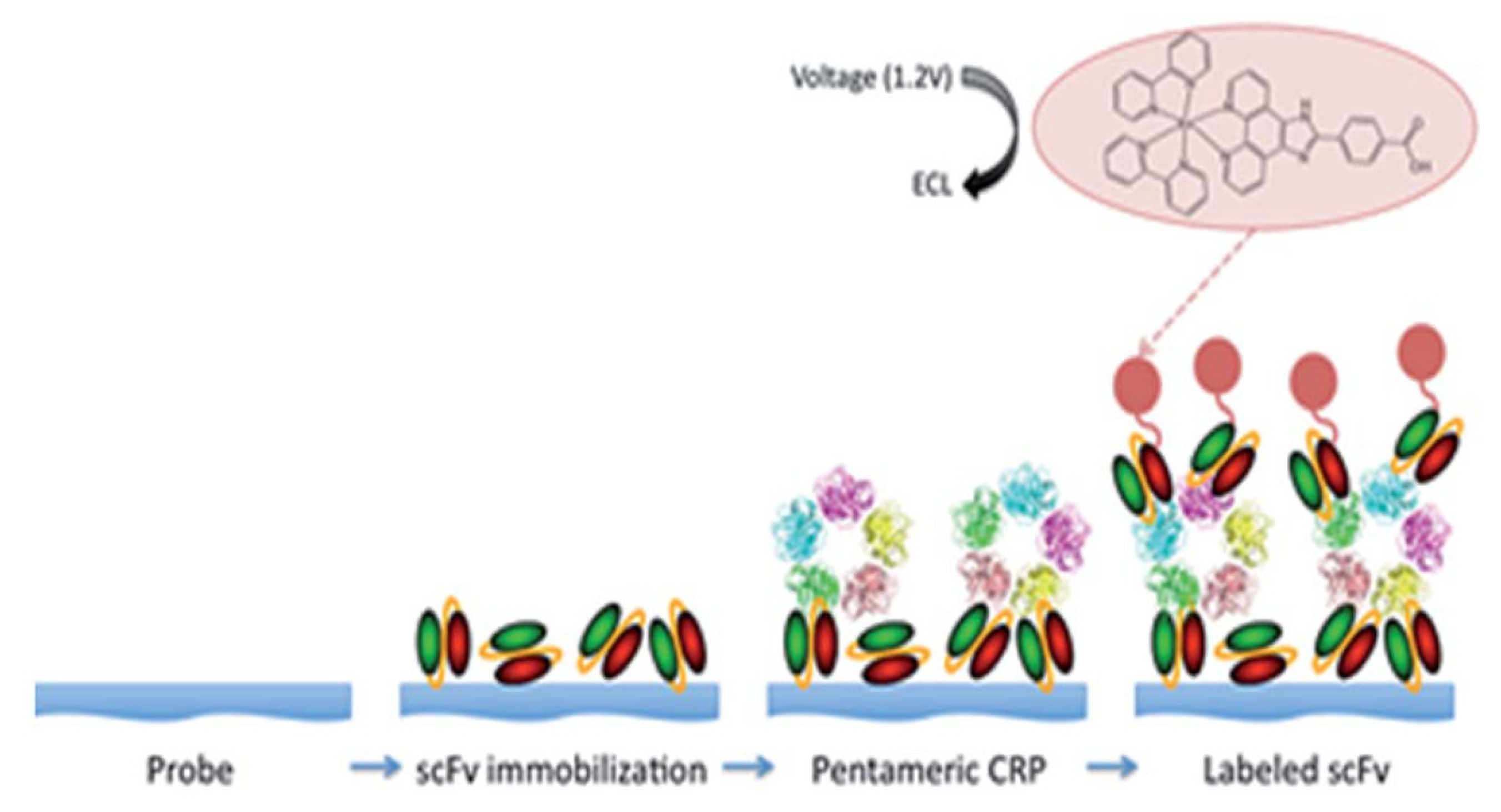
- O’Reilly, E.J.; Conroy, P.J.; Hearty, S.; Keyes, T.E.; O’Kennedy, R.; Forster, R.J. Electrochemiluminescence Platform for the Detection of C-Reactive Proteins: Application of Recombinant Antibody Technology to Cardiac Biomarker Detection. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 67874–67877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conroy, P.J.; Hearty, S.; Leonard, P.; O’Kennedy, R.J. Antibody Production, Design and Use for Biosensor-Based Applications. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009, 20, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakanya, W.M.; Tothill, I.E. Detection of the Inflammation Biomarker C-Reactive Protein in Serum Samples: Towards an Optimal Biosensor Formula. Biosensors 2014, 4, 340–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryan, T.; Luo, X.; Bueno, P.R.; Davis, J.J. An optimised electrochemical biosensor for the label-free detection of C-reactive protein in blood. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 39, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
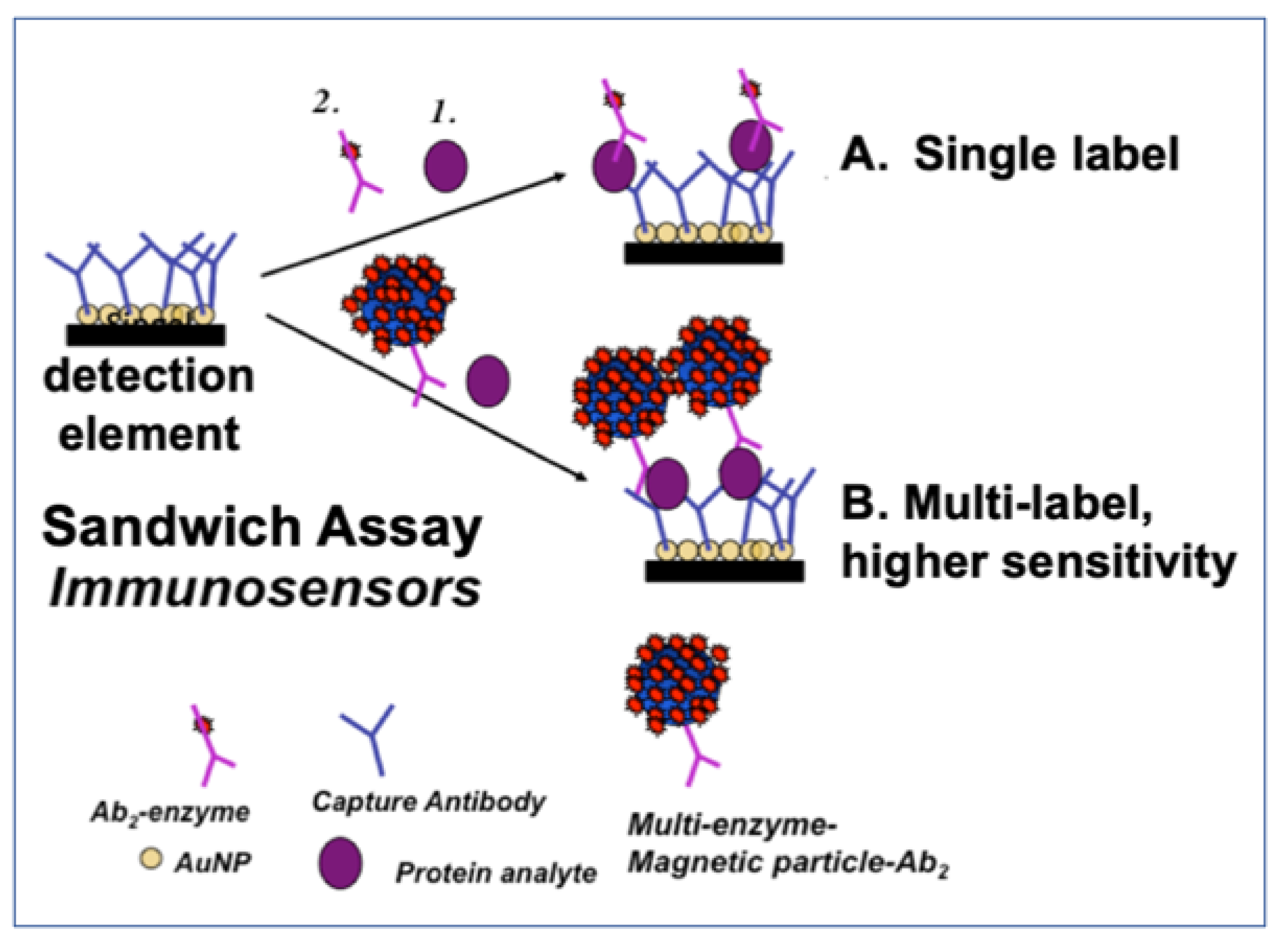
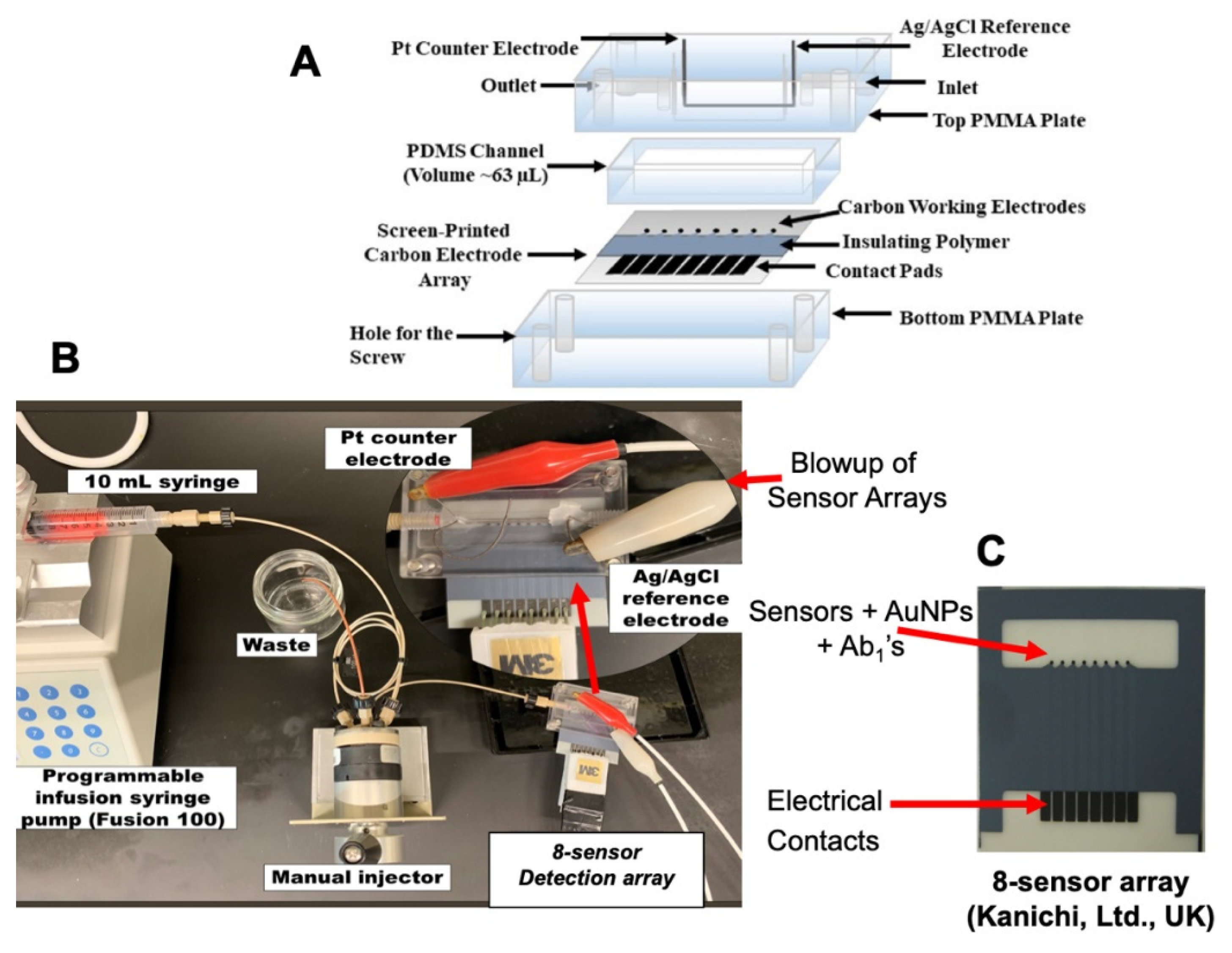
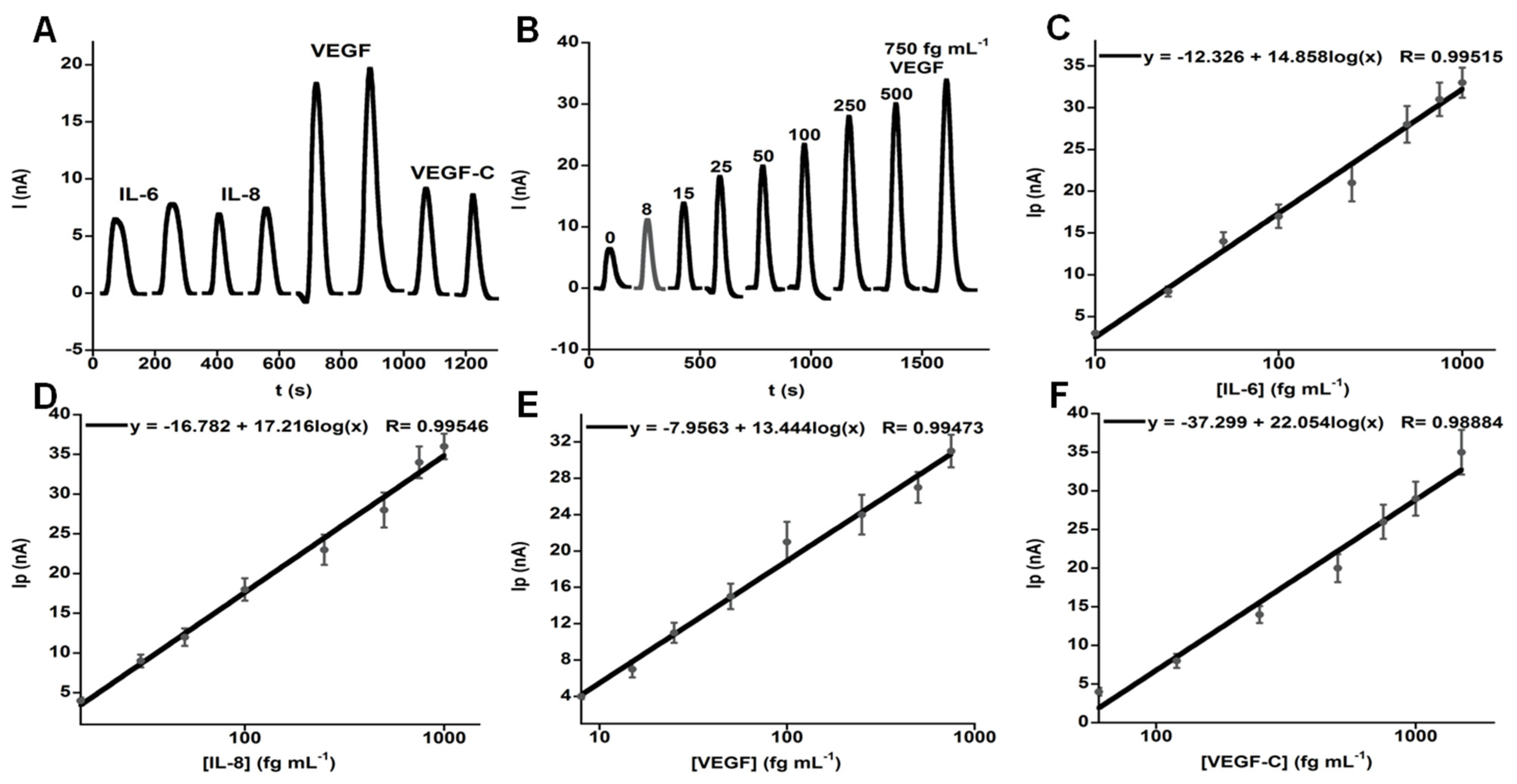
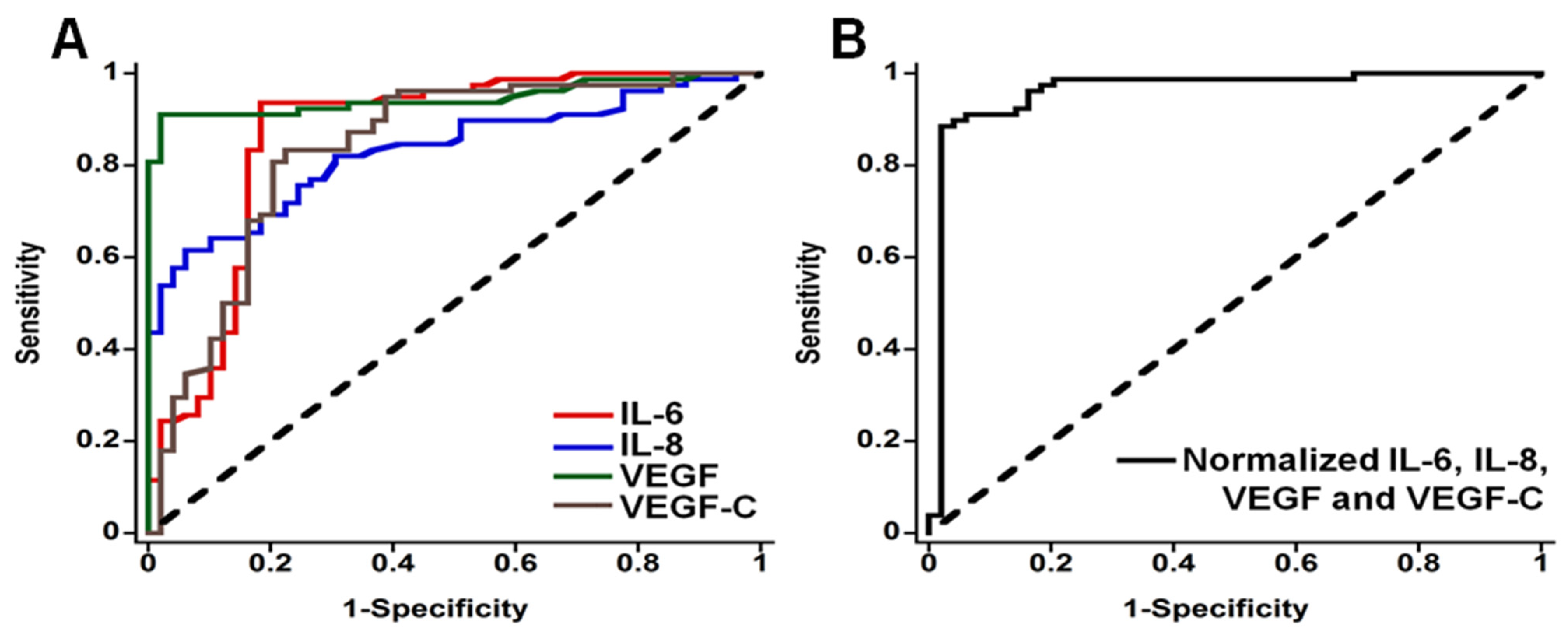


| Biomarker | Sample | Cancer | Clinical Use | Assay | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbrev. | Name | ||||
| Free PSA/fPSa | Free PSA | Serum | Prostate | S, M | Immunoassay |
| tPSA | Total PSA | Serum | Prostate | S, M | Immunoassay |
| cPSA | Complex PSA | Serum | Prostate | S, M | Immunoassay |
| p63 | Transformation-related protein 63 | FFPE tissue † | Prostate | S, M | Immunohistochemistry |
| TG | Thyroglobulin | Serum | Thyroid | S, M | Immunoassay |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor | Colon tissue | Colon | Pre | Immunoassay |
| CEA | Carcinoembryonic antigen | Serum | Colon | M | Immunoassay |
| MW CEA | High molecular weight CEA | Urine | Bladder | M | Immunofluorescence |
| FDP (AMDL-ELISA DR-70) | Fibrin/fibrinogen degradation products | Urine/Serum | Bladder | M | Immunoassay |
| NMP/22 | Nuclear matrix protein 22 | Urine | Bladder | S, M | Immunoassay |
| BTA | Bladder tumor antigen | Urine | Bladder | M | Immunoassay |
| HER2 | Human EGF receptor | Serum | Breast | M | Immunohistochemistry |
| CA15-3 * | Carbohydrate antigen 15-3 | Serum, plasma | Breast | M | Immunoassay |
| CA27-29 * | Carbohydrate antigen 27–29 | Serum | Breast | M | Immunoassay |
| HER/NEU | Human EGF receptor 2 | FFPE tissue † | Breast | P, Pre | Immunohistochemistry |
| ER | Estrogen factor | FFPE tissue † | Breast | P, Pre | Immunohistochemistry |
| PR | Progesterone factor | FFPE tissue † | Breast | P, Pre | Immunohistochemistry |
| AFP * | α-fetoprotein | Ser., plasma, amniotic fluid | Testicular | St | Immunoassay |
| β-hGC * | Human chorionic gonadotropin-β | Serum | Testicular | St | Immunoassay |
| AFP-L3% | α-fetoprotein L3% isoform | Serum | Hepatocellular | P | HPLC, microfluidic capillary electrophoresis |
| KIT | Receptor Tyrosine Kinase | FFPE tissue † | Gastrointestinal stromal tumors | Pre | Immunohistochemistry |
| CA 19-9 * | Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 | Serum | Pancreatic | M | Immunoassay |
| CA 125 * | Carbohydrate antigen 125 | Serum | Ovarian | M | Immunoassay |
| HE4 | Human epididymis protein 4 | Serum | Ovarian | M | Immunoassay |
| OVA1 (Multiprotein test | CA125, Apolipoprotein A1, β -2 microglobulin, Transferrin, Pre-albumin | Ovarian | Serum | P | Immunoassay |
| Benign | Gleason Score 6 | Gleason Score 7 | Gleason Score ≥ 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | n = 64 (49%) | n = 3 2 (25%) | n = 22 (17%) | n = 12 (9%) |
| Age (average, years) | 63 | 67 | 65 | 65 |
| Patients with [PSA] ≤ 4.0 ng/mL | 50 (78%) | 21 (66%) | 12 (55%) | 4 (33%) |
| Patients with [PSA] > 4.0 ng/mL | 14 (22%) | 11 (34%) | 10 (45%) | 8 (67%) |
| Cancer | Biomarker | Sensor | Range or LOD a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | CD133 | Screen-printed gold electrode integrated into a 3D printed chamber | 1 × 105 to 3 × 106 HepG2 liver cancer cells/mL [51] |
| Hepatocellular | Oval cell marker antibody (OV6) | Multiwall carbon nanotube (MWCNT) functionalized electrode integrated into a 3D printed flow cell | 1 × 102–5 × 105 hepatic oval cells (HOCs)/mL [52] |
| Cystic fibrosis | Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI) | Printed circuit board with built-in screen-printed electrode integrated into a 3D printed case and connected to a smart phone for control | Limit of 1 nM [53] |
| Pancreatic, breast cancer and gastric | Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) | Self-designed and printed photoelectrode integrated into a 3D printed platform | 10.0 pg/mL–5.0 ng/mL with limit of 4.8 pg/mL [54] |
| Prostate | Prostate-specific antigen (PSA), prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) | 3D printed multiplexed ECL immunoarray with programmable syringe pump | Limits of 150 fg/mL for PSA, and 230 fg/mL for PSMA [55] |
| Prostate | PSA, cluster of differentiation 14 (CD-14), Golgi membrane protein 1 (GOLM-1), insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGFBP-3), insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), platelet factor 4 (PF-4), vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGF-D), PSMA | 3D printed multiplexed ECL immunoarray with lab-built electronic control system | Limits of 78−110 fg/mL [56] |
| Breast | Nucleolin | Functionalized bipolar electrode (BPE) mounted in a 3D printed microchannel for ECL detection | LOD of 10 MCF-7 breast cancer cells [57] |
| Prostate | PSA, PS-4 | Unibody 3D printed multiplexed CL immunoarray | LOD 0.5 pg/mL [58] |
| Prostate | PSA, VEGF, IGF-1, CD-14 | ELISA based 3D printed multiplexed pipette tip for CL and colorimetric detection | Limits of 5 pg/mL for PSA, 25 pg/mL for VEGF, 2.5 pg/mL for IGF-1, and 0.5 pg/mL for CD-14 [59] |
| Cervical | Valosin-containing protein (VCP) | Magnetic focus lateral flow immunosensor (mLFS) integrated into a 3D printed frame for colorimetric detection | Limit of 25 fg/mL [60] |
| Ovarian, breast | VEGF, angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2) | 3D-printed immunoarray using lab-formulated carboxyl group rich resin for colorimetric detection | Limit of 11 ng/mL for VEGF, and 0.8 ng/mL for Ang-2 [61] |
| Oral cancer metastasis | DSG3, VEGF-A, VEGF-C | 3D-printed array with cell disruption device to detect metastasis biomarker DSG3 at single cell level | LODs 0.10 fg/mL for DSG3, and 0.20 fg/mL for VEGF-A, VEGF-C and β-Tub [43] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rusling, J.F.; Forster, R.J. Biosensors Designed for Clinical Applications. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070702
Rusling JF, Forster RJ. Biosensors Designed for Clinical Applications. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(7):702. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070702
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusling, James F., and Robert J. Forster. 2021. "Biosensors Designed for Clinical Applications" Biomedicines 9, no. 7: 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070702
APA StyleRusling, J. F., & Forster, R. J. (2021). Biosensors Designed for Clinical Applications. Biomedicines, 9(7), 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070702







