Involvement of microRNA in Solid Cancer: Role and Regulatory Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MiRNA and Solid Cancer
2.1. Colorectal Cancer
2.2. Tumor-Suppressive miRNA in CRC
2.2.1. Clusters miR-1/133a and miR-206/133b
2.2.2. Clusters miR-15a/16-1 and miR-15b/16-2
2.2.3. Clusters miR-100/let-7a/miR-125 and miR-99/let-7c
2.3. Lung Cancer
2.3.1. Oncogenic miRNAs in LC Cells
2.3.2. Tumor-Suppressive miRNAs in LC
2.4. Breast Cancer
2.4.1. Oncogenic miRNAs in BC
2.4.2. Tumor-Suppressive miRNAs in BC
2.4.3. Oncogenic and Tumor-Suppressive of miR-23/27/24 Cluster
2.5. Liver Cancer
2.5.1. Oncogenic miRNAs in HCC
2.5.2. Tumor-Suppressive miRNAs in HCC
2.6. Ovarian and Cervical Cancer
2.6.1. Oncogenic miRNA in Ovarian Cancer and Cervical Cancer
2.6.2. Tumor-Suppressive miRNA in Ovarian Cancer and Cervical Cancer
3. Role of Exosomal miRNA and Its Application
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akgül, B.; Erdoğan, I. Intracytoplasmic Re-localization of miRISC Complexes. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leva, G.; Garofalo, M.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2014, 9, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, A.; Jacks, T. MicroRNAs and Cancer: Short RNAs Go a Long Way. Cell 2009, 136, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menigatti, M.; Staiano, T.; Manser, C.N.; Bauerfeind, P.; Komljenovic, A.; Robinson, M.; Jiricny, J.; Buoli, F.; Marra, G. Epige-netic silencing of monoallelically methylated miRNA loci in precancerous colorectal lesions. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Wang, H.; Yao, X.; Zhang, D.; Xie, Y.; Cui, R.; Zhang, X. Circulating MicroRNAs in Cancer: Potential and Challenge. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.Y.M.; Walsh, W.R.; Yu, Y.; Yang, J.-L. microRNA-34 family and treatment of cancers with mutant or wild-type p53 (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 38, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, W.; Hu, C.; Zhang, H.; Qu, Z.; Cen, J.; Qiu, Z.; Li, C.; Ren, H.; Li, Y.; He, X.; et al. miR-27b synergizes with anticancer drugs via p53 activation and CYP1B1 suppression. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Q.; Zhao, L.; Gao, J.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, X. Mutant p53 increases exosome-mediated transfer of miR-21-3p and miR-769-3p to promote pulmonary metastasis. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 31, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarczyk, M.; Fatyga, E.; Dzięgielewska-Gęsiak, S.; Waniczek, D.; Grabarek, B.; Zmarzły, N.J.; Anikowska, G.; Muc-Wierzgoń, M. The Expression Paterns of BECN1, LAMP2, and PINK1 Genes in Colorectal Cancer Are Potentially Regu-lated by Micrornas and CpG Islands: An in Silico Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Liang, G.; Egger, G.; Friedman, J.M.; Chuang, J.C.; Coetzee, G.A.; Jones, P.A. Specific activation of microRNA-127 with downregulation of the proto-oncogene BCL6 by chromatin-modifying drugs in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-J.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Zhou, C.-X.; Yin, Q.-Q.; He, M.; Yu, X.-T.; Cao, D.-X.; Chen, G.-Q.; He, J.-R.; Zhao, Q. MiR-124 targets Slug to regulate epithelial–mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 2012, 34, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.-W.; Wu, C.-W.; Hu, L.-Y.; Li, S.-C.; Liao, Y.-L.; Lai, C.-H.; Kao, H.-W.; Fang, W.-L.; Huang, K.-H.; Chan, W.-C.; et al. Epigenetic regulation of miR-34b and miR-129 expression in gastric cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 2600–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegert, J.; Ishaque, N.; Vardapour, R.; Georg, C.; Gu, Z.; Bieg, M.; Ziegler, B.; Bausenwein, S.; Nourkami, N.; Ludwig, N.; et al. Mutations in the SIX1/2 pathway and the DROSHA/DGCR8 miRNA microprocessor complex underlie high-Risk blastemal typeWilms tumors. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, A.; Kashima, R. Dysregulation of microRNA biogenesis machinery in cancer. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 51, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kock, L.; Rivera, B.; Revil, T.; Thorner, P.; Goudie, C.; Soglio, D.B.-D.; Choong, C.S.; Priest, J.R.; Van Diest, P.J.; Tanboon, J.; et al. Sequencing of DICER1 in sarcomas identifies biallelic somatic DICER1 mutations in an adult-onset embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.J.; Bailey, S.M.; Raby, K.L.; Saini, H.K.; De Kock, L.A.A.; Burke, G.; Foulkes, W.D.; Enright, A.J.; Coleman, N.; Tischkowitz, M. Serum levels of mature microRNAs in DICER1-mutated pleuropulmonary blastoma. Oncog. 2014, 3, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, S.A.; Terzic, A. A study of microRNAs in silico and in vivo: Diagnostic and therapeutic applications in cancer. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Dutta, A. MicroRNAs in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2009, 4, 199–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, V.P.; Ngo, T.A.; Pernestig, A.-K.; Tilevik, D.; Kant, K.; Nguyen, T.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D. MicroRNA amplification and detection technologies: Opportunities and challenges for point of care diagnostics. Lab. Investig. 2018, 99, 452–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Geng, L.; Dai, B.; Zheng, T.; Fuv, J.; Qiao, L.; Cai, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J. Repression of let-7a cluster prevents ad-hesion of colorectal cancer cells by enforcing a mesenchymal phenotype in presence of liver inflammation. Cell Death. Dis. 2018, 9, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-F.; Mandel, E.M.; Thomson, J.M.; Wu, Q.E.; Callis, T.; Hammond, S.M.; Conlon, F.L.; Wang, D.-Z. The Role of MicroRNA-1 and MicroRNA-133 in Skeletal Muscle Proliferation and Differentiation. Nat. Genet. 2005, 38, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-S.; Leung, C.-M.; Pan, H.-W.; Hu, L.-Y.; Li, S.-C.; Ho, M.-R.; Tsai, K.-W. Silencing of miR-1-1 and miR-133a-2 cluster expression by DNA hypermethylation in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Li, L.; Duan, X. Long non-coding RNA ABHD11-AS1 promotes colorectal cancer development through regulation of miR-133a/SOX4 axis. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, 20181386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Miao, R.; Xu, X.; Qu, X. CXCL12/CXCR4 promotes inflamma-tion-driven colorectal cancer progression through activation of RhoA signaling by sponging miR-133a-3p. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Huang, L.; Tao, J.; Shen, R.; Wang, T. Ferritin Light Chain (FTL) competes with long noncoding RNA Linc00467 for miR-133b binding site to regulate chemoresistance and metastasis of colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2019, 41, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, D.; Dong, M.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J. miR‑1 inhibits the progression of colon cancer by regulating the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Kawasaki, Y.; Miyamoto, M.; Hiyoshi, M.; Kitayama, J.; Akiyama, T. The miR-1-NOTCH3-Asef Pathway Is Important for Colorectal Tumor Cell Migration. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, K.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, M.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, P.; He, L.; et al. MiR-1 suppresses tumor cell proliferation in colorectal cancer by inhibition of Smad3-mediated tumor glycolysis. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.-Q.; Han, F.; Shi, Z.-L.; Yu, L.; Li, X.-F.; Yu, C.; Shen, C.-L.; Wan, D.-W.; Zhu, X.-G.; Li, R.; et al. miR-133a-3p Targets SUMO-Specific Protease 1 to Inhibit Cell Proliferation and Cell Cycle Progress in Colorectal Cancer. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2018, 26, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Fu, R. miR-206 regulates 5-FU resistance by targeting Bcl-2 in colon cancer cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, ume 11, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.N.; Zhi, Z.; Chen, L.Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.M.; Gan, W.J.; Chen, S.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Shen, T.; et al. SIRT1 suppresses col-orectal cancer metastasis by transcriptional repression of miR-15b-5p. Cancer. Lett. 2017, 409, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, L.; Qiu, C.; Luo, R. LINC00473 promotes the Taxol resistance via miR-15a in colorectal cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, 20180790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, S.; Song, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ren, F. Long non‑coding RNA SNHG12 promotes proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by acting as a molecular sponge of microRNA‑16. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, R.; Dai, L.; Cheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Y.Q.; Deng, H.X. Vector-based miR-15a/16-1 plasmid inhibits colon cancer growth in vivo. Cell Biol. Int. 2012, 36, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, V.; Ebrahimi, F.; Islam, F.; Vider, J.; Qallandar, O.B.; Pillai, S.; Lu, C.-T.; Lam, A.K.-Y. Tumour suppressor properties of miR-15a and its regulatory effects on BCL2 and SOX2 proteins in colorectal carcinomas. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 370, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Jackstadt, R.; Siemens, H.; Li, H.; Kirchner, T.; Hermeking, H. p53-induced miR-15a/16-1 and AP4 form a dou-ble-negative feedback loop to regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesler, A.; Liu, H.; Ju, J. Modified miR-15a has therapeutic potential for improving treatment of advanced stage colorectal cancer through inhibition of BCL2, BMI1, YAP1 and DCLK. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 2367–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Liang, H.; Sun, W.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yue, X.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; et al. Deregulation of the miR-16-KRAS axis promotes colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I.-P.; Tsai, H.-L.; Huang, C.-W.; Lu, C.-Y.; Miao, Z.-F.; Chang, S.-F.; Juo, S.-H.H.; Wang, J.-Y. High blood sugar levels significantly impact the prognosis of colorectal cancer patients through down-regulation of microRNA-16 by targeting Myb and VEGFR. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18837–18850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Feng, L.; Liu, P.; Duan, W. ANRIL promotes chemoresistance via disturbing expression of ABCC1 by regulating the expression of Let-7a in colorectal cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, 20180620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Xu, Z. Hypermethylation-Associated Silencing of miR-125a and miR-125b: A Potential Marker in Colorectal Cancer. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, D.; Ye, F.; Lin, J.; Wang, W. The lncRNA HOXA11-AS functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate PADI2 expression by sponging miR-125a-5p in liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 70642–70652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Tang, X.; Lu, L. Elevated MIR100HG promotes colorectal cancer metastasis and is as-sociated with poor prognosis. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 6483–6490. [Google Scholar]
- Sureban, S.M.; May, R.; Ramalingam, S.; Subramaniam, D.; Natarajan, G.; Wyche, J.H.; Anant, S.; Houchen, C.W. S1942 Selective Blockade of DCAMKL-1 Results in Tumor Growth Arrest by a Let-7a MicroRNA Dependent Mechanism. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, A–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, P.; Ma, Y.; Yang, J.; Moyer, M.P.; Shi, C.; Peng, J.; Qin, H. NIRF is frequently upregulated in colorectal cancer and its oncogenicity can be suppressed by let-7a microRNA. Cancer Lett. 2012, 314, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, P.; Chang, Y.; Qi, J.; Fu, H.; Guo, H. Let-7a inhibits tumor cell growth and metastasis by directly targeting RTKN in human colon cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.B.; Gu, J.; Zuo, H.J.; Chen, Z.G.; Zhao, W.; Li, M.; Ji, D.B.; Lu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.Q. Let-7c functions as a metastasis sup-pressor by targeting MMP11 and PBX3 in colorectal cancer. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlan, A.K.; Saidijam, M.; Amini, R.; Samadi, P.; Najafi, R. Induction of let-7e gene expression attenuates oncogenic phenotype in HCT-116 colorectal cancer cells through targeting of DCLK1 regulation. Life Sci. 2019, 228, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Pan, W.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Q.; Ying, X. IGF1/IGF1R and microRNA let-7e down-regulate each other and modulate proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Liu, J.; Lu, M.; Wu, G.; Lin, X.; Cai, L.; Zhang, X. Influence and mechanism of miR-99a suppressing development of colorectal cancer (CRC) with diabetes mellitus (DM). OncoTargets Ther. 2019, ume 12, 10311–10321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Liu, N.; Lin, L.; Guo, X.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Q. miR-125a-5p inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in colon cancer via targeting BCL2, BCL2L12 and MCL. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 75, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Qiu, J.; Kang, H.; Wang, Y.; Qian, J. miR-125a-5p suppresses colorectal cancer progression by targeting VEGFA. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, ume 10, 5839–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, X.; Miao, J.; Cai, J. MicroRNA-125a inhibits tumorigenesis by targeting Smurf1 in colorectal carcinoma. FEBS Open Bio 2019, 9, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, J.A.; Powell, C.A.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Global Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.-W.; Mendell, J.T. MicroRNAs in cell proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, F.; Lieberman, J. miR-34 and p53: New Insights into a Complex Functional Relationship. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banzhaf-Strathmann, J.; Edbauer, D. Good guy or bad guy: The opposing roles of microRNA 125b in cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2014, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bublik, D.R.; Bursa´c, S.; Sheffer, M.; Oršoli´c, I.; Shalit, T.; Tarcic, O.; Kotler, E.; Mouhadeb, O.; Hoffman, Y.; Fuchs, G.; et al. Regulatory module involving FGF13, miR-504, and p53 regulates ribosomal biogenesis and supports cancer cell survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E496–E505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffer, C.L.; Weinberg, R.A. A Perspective on Cancer Cell Metastasis. Science 2011, 331, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-G.; Chang, T.-H.; Liu, Y.-N.; Shih, J.-Y. MicroRNA in Lung Cancer Metastasis. Cancers 2019, 11, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claperon, A.; Mergey, M.; Ho-Bouldoires, T.H.N.; Vignjevic, D.; Wendum, D.; Chretien, Y.; Merabtene, F.; Frazao, A.; Paradis, V.; Housset, C.; et al. EGF/EGFR axis contributes to the progression of cholangiocarcinoma through the induction of an epi-thelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Development and Disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 449, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Fan, Y.; Li, X.; Dong, M.; Liu, H.; Chen, J. Expression levels of microRNA-145 and microRNA-10b are associated with metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, W.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhong, G.; Chen, D.; Shen, J.; Bao, C.; Xu, L.; Pan, J.; Cheng, J.; et al. MicroRNAs in cancer metastasis and angiogenesis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 115787–115802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.; Liu, Y.; Fang, X.; Liu, Y.; Fang, L.; Lin, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, N. Tumor-derived microRNA-494 promotes angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Angiogenesis 2015, 18, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, Z.; Pan, Y.; Liu, G.; Fu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, K.; Feng, Y. microRNA-128 plays a critical role in human non-small cell lung cancer tumourigenesis, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis by directly targeting vascular endothelial growth factor-C. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2336–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Dai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, L.; Shen, J.; Ju, H.; Li, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-206 attenuates the growth and angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by blocking the 14-3-3ζ/STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 79805–79813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Wang, D.; Li, Q. Effect of microRNA-135a on Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, Apoptosis and Tumor Angiogenesis Through the IGF-1/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 1431–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, Z.-M.; Yu, J.-L.; Zhou, S.; Song, J. MiR-126-3p suppresses the growth, migration and invasion of NSCLC via targeting CCR. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Meng, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, W.; Hu, J.; Xue, F.; Wang, X.; Cai, L. TRIM44 promotes proliferation and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer via mTOR signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 30479–30491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H. MiR-7-5p suppresses tumor metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting NOVA. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2019, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Peng, L. MiR-206 may suppress non-small lung cancer metastasis by targeting CORO1C. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2020, 25, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Tang, H.; Lei, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.-A. miR-335-5p inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer via ROCK. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Yu, Q.; Chu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lu, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Q. MicroRNA-98-5p inhibits proliferation and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting TGFBR. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 54, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, L. MicroRNA‑126: A new and promising player in lung cancer (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2020, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, D.; Gu, C.; Liu, X.; Pei, W.; Li, J.; Cao, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Tong, J.; Nie, J. Down-regulation of let-7 microRNA increased K-ras expression in lung damage induced by radon. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Li, D.; Gu, Y.; Wen, Z.-M.; Jie, J.; Zhao, D.; Peng, L.-P. MicroRNA-126 Targeting PIK3R2 Inhibits NSCLC A549 Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion by Regulation of PTEN/PI3K/AKT Pathway. Clin. Lung Cancer 2016, 17, e65–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Globocan, Estimated Cancer Incidence, Mortality et Prevalence Worldwide. Available online: http://globocan.iarc.fr/Default.aspx (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Kasiappan, R.; Rajarajan, D. Role of MicroRNA Regulation in Obesity-Associated Breast Cancer: Nutritional Perspectives. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 868–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantini, L.; Bertoli, G.; Cava, C.; Dubois, T.; Zinovyev, A.; Caselle, M.; Castiglioni, I.; Barillot, E.; Martignetti, L. Identification of microRNA clusters cooperatively acting on epithelial to mesenchymal transition in triple negative breast cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Sheng, C.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Zhu, Q. MiR-183/-96/-182 cluster is up-regulated in most breast cancers and increases cell proliferation and migration. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambal, S.; Shah, M.; Mihelich, B.L.; Nonn, L. The microRNA-183 cluster: The family that plays together stays together. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 7173–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liang, A.-J.; Fan, Y.-P.; Huang, Y.-R.; Zhao, X.-M.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.-F. Dysregulation and functional roles of miR-183-96-182 cluster in cancer cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42805–42825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Di, M.; Liang, J.; Shi, S.; Tan, Q.; Wang, Z. MicroRNA-183 in Cancer Progression. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xiang, G.; Meng, Y.; Dong, R. MiRNA-183-5p promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in human breast cancer by targeting the PDCD. Reprod. Biol. 2016, 16, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Liang, H.; Rehman, U.-U.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, S.; Yu, M.; Cui, S.; Liu, M.; et al. miR-96 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting PTPN9 in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttilla, I.K.; White, B.A. Coordinate Regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in Breast Cancer Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 23204–23216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Che, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.; Fan, C.; Yuan, W. Potential value of miR-221/222 as diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic biomarkers for diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leva, G.; Gasparini, P.; Piovan, C.; Ngankeu, A.; Garofalo, M.; Taccioli, C.; Iorio, M.V.; Li, M.; Volinia, S.; Alder, H.; et al. MicroRNA Cluster 221-222 and Estrogen Receptor α Interactions in Breast Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 706–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; Han, X.; Mao, J.; Li, J.; Yu, L.; Wang, B.; Fan, S.; Yu, X.; et al. MiR-221/222 enhance the tumorigenicity of human breast cancer stem cells via modulation of PTEN/Akt pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 79, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimirah, F.; Peng, X.; Gupta, A.; Yuan, L.; Welsh, J.E.; Cleary, M.; Mehta, R.G. Crosstalk between the vitamin D receptor (VDR) and miR-214 in regulating SuFu, a hedgehog pathway inhibitor in breast cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 349, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derfoul, A.; Juan, A.H.; Difilippantonio, M.J.; Palanisamy, N.; Ried, T.; Sartorelli, V. Decreased microRNA-214 levels in breast cancer cells coincides with increased cell proliferation, invasion and accumulation of the Polycomb Ezh2 methyltransferase. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.-J.; Li, L.-L.; Tu, W.-B. MiR-214 negatively regulates proliferation and WNT/β-catenin signaling in breast cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 5148–5154. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Tian, Y.; Like, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhai, C.; Han, X.; Zhang, L. Tumor-suppressing roles of miR-214 and miR-218 in breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 3178–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhou, G.; Hu, X.; Liu, Z.; Jin, F.; Yu, M.; Sang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, Z.; et al. HIC1 and miR-23~27~24 clusters form a double-negative feedback loop in breast cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannafon, B.N.; Cai, A.; Calloway, C.L.; Xu, Y.-F.; Zhang, R.; Fung, K.-M.; Ding, W.-Q. miR-23b and miR-27b are oncogenic microRNAs in breast cancer: Evidence from a CRISPR/Cas9 deletion study. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ell, B.; Qiu, Q.; Wei, Y.; Mercatali, L.; Ibrahim, T.; Amadori, D.; Kang, Y. The MicroRNA-23b/27b/24 Cluster Promotes Breast Cancer Lung Metastasis by Targeting Metastasis-suppressive Gene Prosaposin. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 21888–21895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Han, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Lin, C.; Zhang, E.; Chi, X.; Hu, J.; Xu, H. Transmembrane protein 170B is a novel breast tu-morigenesis suppressor gene that inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, L.; Stebbing, J.; Braga, V.M.; Frampton, A.E.; Jacob, J.; Buluwela, L.; Jiao, L.R.; Periyasamy, M.; Madsen, C.D.; Caley, M.P.; et al. miR-23b regulates cytoskeletal remodeling, motility and metastasis by directly targeting multiple transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 5400–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiels, M.S.; O’Brien, T.R. Recent Decline in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Rates in the United States. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1503–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandan, K.; Sarwat, M. Role of microRNA and Long Non-Coding RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Leidinger, P.; Becker, K.; Backes, C.; Fehlmann, T.; Pallasch, C.; Rheinheimer, S.; Meder, B.; Stähler, C.; Meese, E.; et al. Distribution of miRNA expression across human tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 3865–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Henson, R.; Wehbe-Janek, H.; Ghoshal, K.; Jacob, S.T.; Patel, T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, J.; Yu, S.; Lavker, R.M.; Cai, L.; Liu, W.; Yang, K.; He, X.; Chen, S. MicroRNA-21 acts as an oncomir through multiple targets in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, L.; Gao, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, Z.; Wang, J.-F.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, S.; Huang, X.; et al. Plasma MicroRNA Panel to Diagnose Hepatitis B Virus–Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4781–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineau, P.; Volinia, S.; McJunkin, K.; Marchio, A.; Battiston, C.; Terris, B.; Mazzaferro, V.; Lowe, S.W.; Croce, C.M.; Dejean, A. miR-221 overexpression contributes to liver tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 107, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornari, F.; Gramantieri, L.; Ferracin, M.; Veronese, A.; Sabbioni, S.; Calin, G.A.; Grazi, G.L.; Giovannini, C.; Croce, C.M.; Bolondi, L.; et al. MiR-221 controls CDKN1C/p57 and CDKN1B/p27 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5651–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Gusev, Y.; Aderca, I.; Mettler, T.A.; Nagorney, D.M.; Brackett, D.J.; Roberts, L.R.; Schmittgen, T.D. Association of MicroRNA Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinomas with Hepatitis Infection, Cirrhosis, and Patient Survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-J.; Ju, Q.; Li, G.-C. Tumor markers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 1, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderburg, C.; Urban, G.-W.; Bettermann, K.; Vucur, M.; Zimmermann, H.W.; Schmidt, S.; Janssen, J.; Koppe, C.; Knolle, P.; Castoldi, M.; et al. Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2010, 53, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Fang, J.H.; Yun, J.P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, W.H.; Zhuang, S.M. Effects of microRNA-29 on apoptosis, tumor-igenicity, and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010, 51, 836–845. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; An, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Huang, C.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, X. miR-101 inhibits autophagy and enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 2019–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Zhang, J.-P.; Li, B.; Zeng, C.; You, K.; Chen, M.-X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuang, S.-M. MicroRNA-125b promotes apoptosis by regulating the expression of Mcl-1, Bcl-w and IL-6R. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3071–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, M.; Jacquemin, E.; Munnich, A.; Lyonnet, S.; Henrion-Caude, A. miR-122, a paradigm for the role of microRNAs in the liver. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; He, J.-H.; Xiao, Z.-D.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Chen, Y.-Q.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.-H. Liver-enriched transcription factors regulate MicroRNA-122 that targets CUTL1 during liver development. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, G.; Bala, S. MicroRNAs in liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCI. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Cancer Stat Facts: Ovarian Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/ovary.html (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehdaivand, S.; WHO. Classification of Ovarian Neoplasms. Available online: https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumorwhoclassif.html (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- Berman, T.A.; Schiller, J.T. Human papillomavirus in cervical cancer and oropharyngeal cancer: One cause, two diseases. Cancer 2017, 123, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardini, B.; De Maria, D.; Francavilla, A.; Di Gaetano, C.; Ronco, G.; Naccarati, A. MicroRNAs as markers of progression in cervical cancer: A systematic review. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, C.P.; García-Vázquez, R.; Rincón, D.G.; Ruiz-García, E.; De La Vega, H.A.; Marchat, L.A.; Vera, Y.M.S.; López-Camarillo, C. MicroRNAs driving invasion and metastasis in ovarian cancer: Opportunities for translational medicine (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 1461–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Xu, C.; Fu, Y. MicroRNA-17-5p induces drug resistance and invasion of ovarian carcinoma cells by targeting PTEN signaling. J. Biol. Res. 2015, 22, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Kong, W.; He, L.; Zhao, J.-J.; O’Donnell, J.D.; Wang, J.; Wenham, R.M.; Coppola, D.; Kruk, P.A.; Nicosia, S.V.; et al. MicroRNA Expression Profiling in Human Ovarian Cancer: miR-214 Induces Cell Survival and Cisplatin Resistance by Targeting PTEN. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishodia, G.; Shukla, S.; Srivastava, Y.; Masaldan, S.; Mehta, S.; Bhambhani, S.; Sharma, S.; Mehrotra, R.; Das, B.C.; Bharti, A.C. Alterations in microRNAs miR-21 and let-7a correlate with aberrant STAT3 signaling and downstream effects during cervical carcinogenesis. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumrungthai, S.; Ekalaksananan, T.; Evans, M.F.; Chopjitt, P.; Tangsiriwatthana, T.; Patarapadungkit, N.; Kleebkaow, P.; Luanratanakorn, S.; Kongyingyoes, B.; Worawichawong, S.; et al. Up-Regulation of miR-21 Is Associated with Cervicitis and Human Papillomavirus Infection in Cervical Tissues. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. MicroRNA-21 regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells via tumor ne-crosis factor-alpha. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 4659–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.-C.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Chen, F. MicroRNA-155 regulates cervical cancer via inducing Th17/Treg imbalance. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 3719–3726. [Google Scholar]
- Vang, S.; Wu, H.-T.; Fischer, A.; Miller, D.H.; MacLaughlan, S.; Douglass, E.; Steinhoff, M.; Collins, C.; Smith, P.J.S.; Brard, L.; et al. Identification of Ovarian Cancer Metastatic miRNAs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Yang, Z.; Ye, W.; Xu, H.; Hua, X. MicroRNA-150 Predicts a Favorable Prognosis in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer, and Inhibits Cell Invasion and Metastasis by Suppressing Transcriptional Repressor ZEB1. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, X.; Li, J.; Liang, S.; Jin, H.; Xu, C.; Ma, D. Tiam1, negatively regulated by miR-22, miR-183 and miR-31, is involved in migration, invasion and viability of ovarian cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1835–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, S.; Kandala, P.K.; Gupta, P.; Srivastava, S.K. Inhibition of EGFR-AKT Axis Results in the Suppression of Ovarian Tumors In Vitro and in Preclinical Mouse Model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Han, Y.; Song, C.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, K.; Li, S.; Ma, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. Systematic review and me-ta-analysis of the prognostic significance of microRNAs in cervical cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 17141–17148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.Y.; Fan, Y.J.; Wang, X.L.; Xie, H.; Gao, H.J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Tang, H. miR-429 is involved in regulation of NF-kB activity by targeting IKKbeta and suppresses oncogenic activity in cervical cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Lin, C.; Shi, Y.H.; Kuerban, G. MicroRNA-101 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion, and promotes apoptosis by reg-ulating cyclooxygenase-2 in Hela cervical carcinoma cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 5915–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, K.S.; Sathyanarayanan, A.; Karunagaran, D. Downregulation of HMGB1 by miR-34a is sufficient to suppress proliferation, migration and invasion of human cervical and colorectal cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 13155–13166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, G. MiR-1284 enhances sensitivity of cervical cancer cells to cisplatin via downregulating HMGB1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Cai, H. MiR-142 inhibits the development of cervical cancer by targeting HMGB1. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 4001–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, D.; Li, H.; She, H. Significance of high YKL-40 expression regulated by miR-24 in cervical cancer progression and prognosis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2016, 9, 5128–5137. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Ingvarsson, S.; Chen, H. MicroRNA-451 suppresses tumor cell growth by down-regulating IL6R gene expression. Cancer Epidemiol. 2014, 38, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Cui, H.; Xu, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Kang, L.; Han, B.; Meng, J.; Yan, Z.; Yan, X.; et al. MiR-125a suppresses tumor growth, invasion and metastasis in cervical cancer by targeting STAT3. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 25266–25280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hu, C.; Pan, P. Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNA Transfer in Lung Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, J.; Tyagi, N. Exosomes: Mediators of bone diseases, protection, and therapeutics potential. Oncoscience 2018, 5, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Li, X.; Gong, S.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, W.; Sun, X.; Dang, X. Serum exosomes contain ECRG4 mRNA that suppresses tumor growth via inhibition of genes involved in inflammation, cell proliferation, and angiogenesis. Cancer Gene Ther. 2018, 25, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhou, J.; Mei, S.; Wu, D.; Mu, Z.; Chen, B.; Xie, Y.; Ye, Y.; Liu, J. Circulating exosomal microRNA-96 promotes cell proliferation, migration and drug resistance by targeting LMO7. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 21, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-L.; Hung, J.-Y.; Chang, W.-A.; Lin, Y.-S.; Pan, Y.-C.; Tsai, P.-H.; Wu, C.-Y.; Kuo, P.-L. Hypoxic lung cancer-secreted exosomal miR-23a increased angiogenesis and vascular permeability by targeting prolyl hydroxylase and tight junction protein ZO-1. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4929–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Ma, C.; Zhou, T.; Dong, X.; Luo, Q.; Geng, L.; Ding, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, N.; et al. Exosomes derived from gemcitabine-resistant cells transfer malignant phenotypic traits via delivery of miRNA-222-3p. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Cao, H.; Qin, X.; Yu, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Ma, R.; Feng, J. Exosome‑mediated gefitinib resistance in lung cancer HCC827 cells via delivery of miR‑21. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9811–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aushev, V.N.; Zborovskaya, I.B.; Laktionov, K.K.; Girard, N.; Cros, M.-P.; Herceg, Z.; Krutovskikh, V. Comparisons of microRNA Patterns in Plasma before and after Tumor Removal Reveal New Biomarkers of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Fei, S.; Chen, D.; Cai, X.; Liu, L.; Lin, B.; Su, H.; Zhao, L.; et al. Evaluation of Tumor-Derived Exosomal miRNA as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Early-Stage Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Next-Generation Sequencing. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5311–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syn, N.L.; Wang, L.; Chow, E.K.-H.; Lim, C.T.; Goh, B.-C. Exosomes in Cancer Nanomedicine and Immunotherapy: Prospects and Challenges. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monfared, H.; Jahangard, Y.; Nikkhah, M.; Mirnajafi-Zadeh, S.J.; Mowla, S.J. Potential Therapeutic Effects of Exosomes Packed With a miR-21-Sponge Construct in a Rat Model of Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
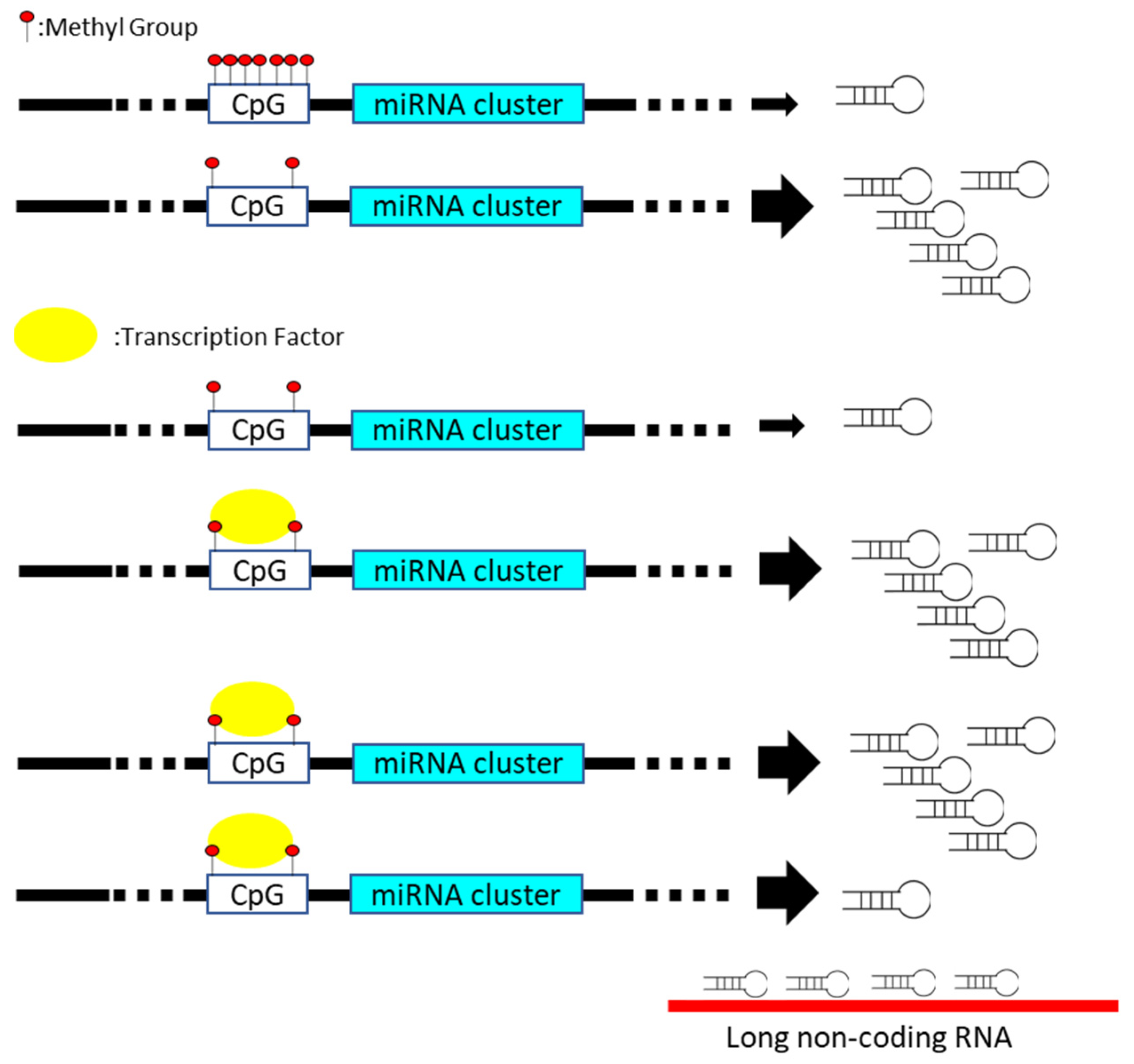
| miRNA | Disease | Manipulating Mechanism | Candidate | Physiological Influence | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-17 | LC; Ovarian cancer | CNVs; Transcriptional control (MYC) | E2F1, PTEN | Cell Growth, apoptosis, metastasis | [55,128] |
| miR-125b | LC | Epigenetic control | p53 | Apoptosis | [60] |
| miR-504 | LC | Transcriptional control (EGFR signaling) | p53 | Apoptosis | [61] |
| miR-10b | LC | Epigenetic control | Homeobox D10, | Metastasis | [71,72] |
| miR-183 | BC | Transcriptional control (ZEB1, HSF2) | PCD4, EGR1, p21, p27 | Apoptosis, DNA repair, metabolism, EMT | [84,85,86] |
| miR-96 | BC | miRNA sponge | FOXO1, PTPN9 | Proliferation, migration, metabolism | [87] |
| miR-182 | BC | miRNA sponge | FOXO1 | Metabolism | [88] |
| miR-221/222 | BC | Epigenetic control, miRNA sponge, transcriptional control (TGF-β) | Transcriptional Repressor GATA Binding 1, Adiponectin Receptor 1, Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1, Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1B, ERα, p27, and TIMP Metallopeptidase Inhibitor 3 | Proliferation, EMT process, metastasis | [89] |
| miR-23/27/24 | BC | Transcriptional control (HIC1) | Hypermethylated in Cancer 1 (HIC1), Sprouty RTK Signaling Antagonist 2, BCL2 Antagonist/Killer, PPARγ, Nischarin, Transmembrane Protein 170B, PAK2 | Cell growth, migration | [88,99,100] |
| miR-21 | HCC; Cervical Cancer | miRNA sponge | PTEN, MMP2, MMP9, PDCD4, PTEN, TIMP-3, TNF-α, ANXA1 | Metastasis and proliferation | [105,130,131,132] |
| miR-221 | HCC | Transcriptional control (NF-κB) | CDKN1B/p27, CDKN1C/p57 DNA damage-inducible transcript 4, BMF | Cell growth, apoptosis | [108,109] |
| miR-214 | Ovarian Cancer | Transcriptional control (hedgehog signaling) | PTEN | Metastasis, chemoresistance | [129] |
| miR-155 | Cervical Cancer | miRNA sponge, transcriptional control (c-MYB) | SOSC1 | Inflammation | [133] |
| miRNA | Disease | Manipulating Mechanism | Candidate | Physiological Influence | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-1 | CRC | Epigenetic control; miRNA sponge | VEGF, NOTCH3 | Proliferation, migration, motility and metabolism | [25,26,27] |
| miR-133 | CRC | Epigenetic control; miRNA sponge | FSCN1, SENP1 | Growth or motility of CRC cells | [28] |
| miR-206 | CRC, LC | Epigenetic control; miRNA sponge | FMNL2, NOTCH3, BCL2, STA3, HIF-1, Coronin 1C | Migration, proliferation, and immortality, metastasis | [29,65,76] |
| miR15/16 | CRC | Transcriptional control (SIRT1) | cyclin B1, TFAP-4, Bcl-2,K-Ras, MYB | Epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), apoptosis | [35,36,37,38] |
| let-7 family | CRC; Cervical cancer | miRNA sponge | PHD, ring finger domains 2, RTKN, IGF-1, MYC, MMP11, PBX3, DCLK1, STAT3 | Cell cycle arrest, metastasis | [43,44,45,46,47,145,146] |
| miR-125 | CRC Cervical Cancer | miRNA sponge | Bcl-2, Mcl-1, SMURF1, VEGFA, CREB5, STAT3, MMP-9, MMP-2, N-cadherin | Apoptosis, angiogenic or metastatic activity, inflammaation | [50,51,52,146] |
| let-7 family | LC | miRNA sponge | Ras | Proliferation | [57] |
| miR-126 | LC | miRNA sponge | PTEN, CX3CR1 | Proliferation, metastasis | [58,73] |
| miR-34 | LC; Cervical Cancer | Transcriptional control (p53) | Cyclin E2, HMGB1 | Cell cycle arrest | [59,141] |
| miR-128 | LC | miRNA sponge | VEGFA, VEGFR2, VEGFR3 | Angiogenesis | [64] |
| miR-135a | LC | miRNA sponge | IGF-1 | Angiogenesis | [66] |
| miR-192 | LC | Transcriptional control (p53) | TRIM44 | Metastasis | [74] |
| miR-7 | LC; Ovarian cancer | miRNA sponge | Nova2, EGFR | Angiogenesis, EMT | [75,137] |
| miR-335 | LC | miRNA sponge | ROCK1 | EMT | [77] |
| miR-98 | LC | miRNA sponge | TGFβR1 | Proliferation, migration, and invasion | [78] |
| miR-199 | BC | Transcriptional control (hedgehog signaling) | Ezh2, β-catenin, Ki-67 | Proliferation, migration, and invasion | [93,94,95] |
| miR-214 | BC | Transcriptional control (hedgehog signaling) | Ezh2, β-catenin, Ki-67 | Proliferation, migration, and invasion | [93,94,95] |
| miR-29 | HCC | Transcriptional control (NF-κB, TGF-β) | CDC42, PIK3R1, Bcl-2, Mcl-1 | Cell cycle, apoptosis | [112] |
| miR-101 | HCC; Cervical Cancer | miRNA sponge | Mcl-1, Cox-2 | Apoptosis, inflammation, proliferation, invasion | [115,140] |
| miR-125b | HCC | Epigenetic, transcriptional control; miRNA sponge | Mcl-1 | Apoptosis | [115] |
| miR-122 | HCC | Transcriptional control (C/EBP, HNF) | Cyclin G1, PKM2, and Wnt family member 1 | Cell cycle, apoptosis | [108] |
| miR-150 | Ovarian cancer | miRNA sponge | ZEB1 | Invasion, metastasis | [134,135] |
| miR-22, miR-183, miR-31 | Ovarian cancer | Transcriptional control (Snail) | TIAM1 | Invasion, migration | [136] |
| miR-429 | Cervical Cancer | miRNA sponge | IL-6,IFN-β | Chronic inflammation | [139] |
| miR-142 | Cervical Cancer | miRNA sponge | HMGB1 | Chronic inflammation, progressive tumorigenesis, active metastasis | [141,142,143] |
| miR-24 | Cervical Cancer | Uncertain | chitinase-3-like protein 1 | Proliferation, metastasis, inflammation | [144] |
| miR-451 | Cervical Cancer | Uncertain | IL-6 receptor | Inflammation, invasion, angiogenesis, proliferation | [144] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.-C.; Chen, T.-H.; Huang, Y.-M.; Wei, P.-L.; Lin, J.-C. Involvement of microRNA in Solid Cancer: Role and Regulatory Mechanisms. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040343
Lin Y-C, Chen T-H, Huang Y-M, Wei P-L, Lin J-C. Involvement of microRNA in Solid Cancer: Role and Regulatory Mechanisms. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(4):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040343
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Ying-Chin, Tso-Hsiao Chen, Yu-Min Huang, Po-Li Wei, and Jung-Chun Lin. 2021. "Involvement of microRNA in Solid Cancer: Role and Regulatory Mechanisms" Biomedicines 9, no. 4: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040343
APA StyleLin, Y.-C., Chen, T.-H., Huang, Y.-M., Wei, P.-L., & Lin, J.-C. (2021). Involvement of microRNA in Solid Cancer: Role and Regulatory Mechanisms. Biomedicines, 9(4), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040343






