Intestinal Intervention Strategy Targeting Myeloid Cells to Improve Hepatic Immunity during Hepatocarcinoma Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Protease Inhibitors (SETIs)
2.2. Induction of the Hepatocarcinoma (HCC)
2.3. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.4. Cytokine Production
2.5. Analysis of the Hepatic Phospholipid Profile
2.6. Immunohistochemistry for Hepatic F4/80+ Cells
2.7. Immunophenotyping of Hepatic Infiltrated Cells
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
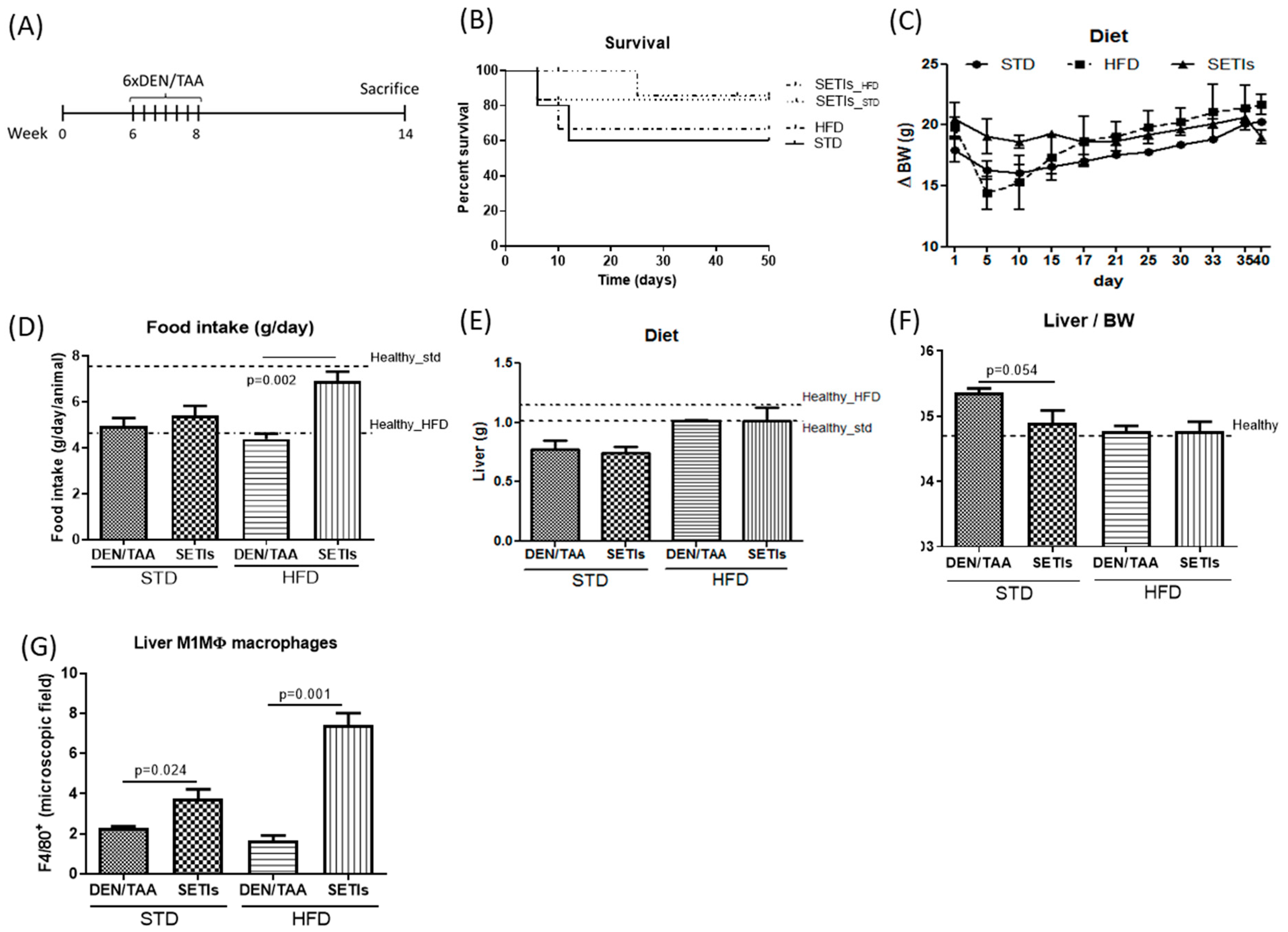
3.1. Amelioration of Tumor Burden in Hepatocarcinoma-Developing Mice
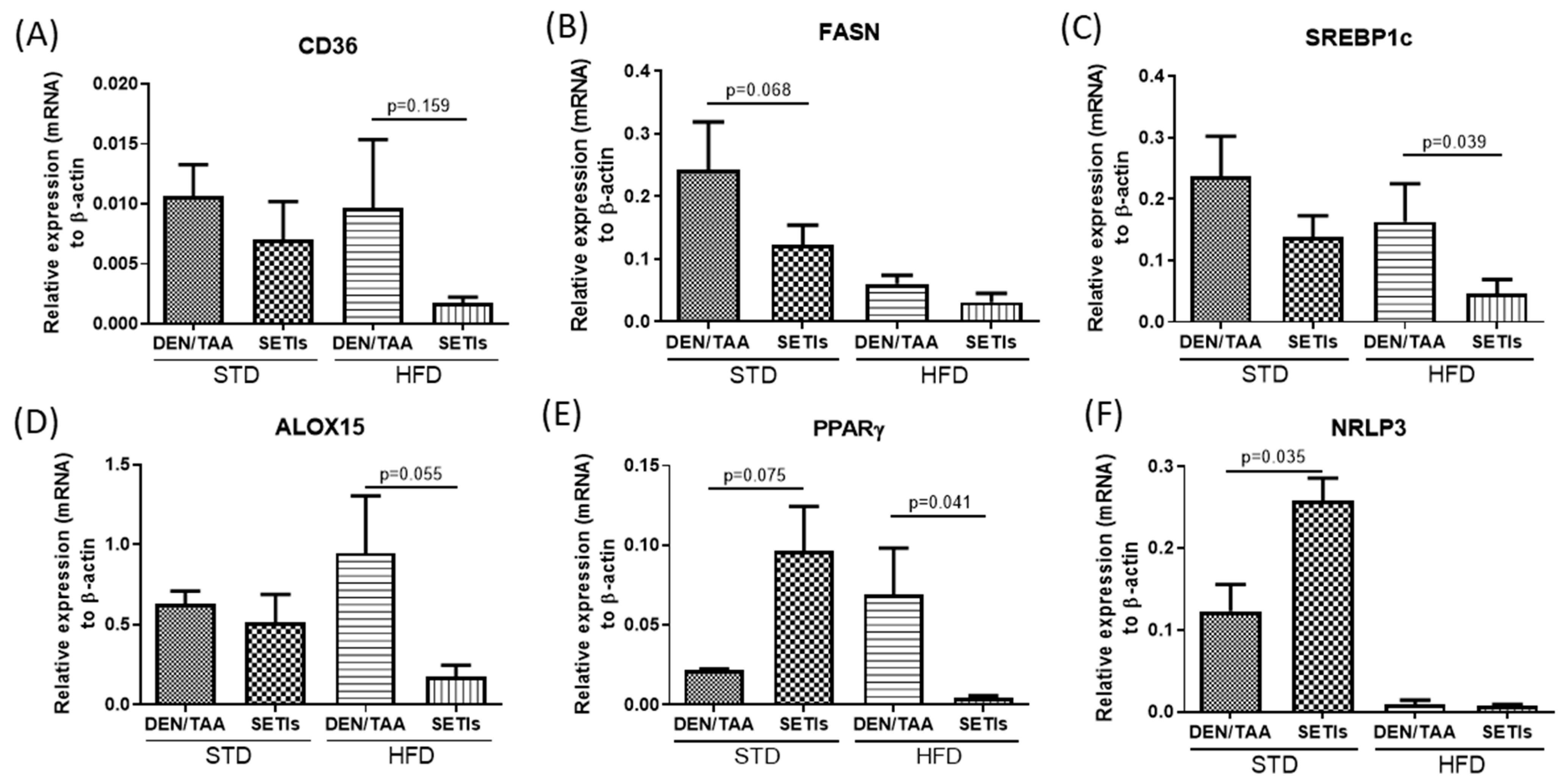
3.2. Modulation of Neoplastic Markers
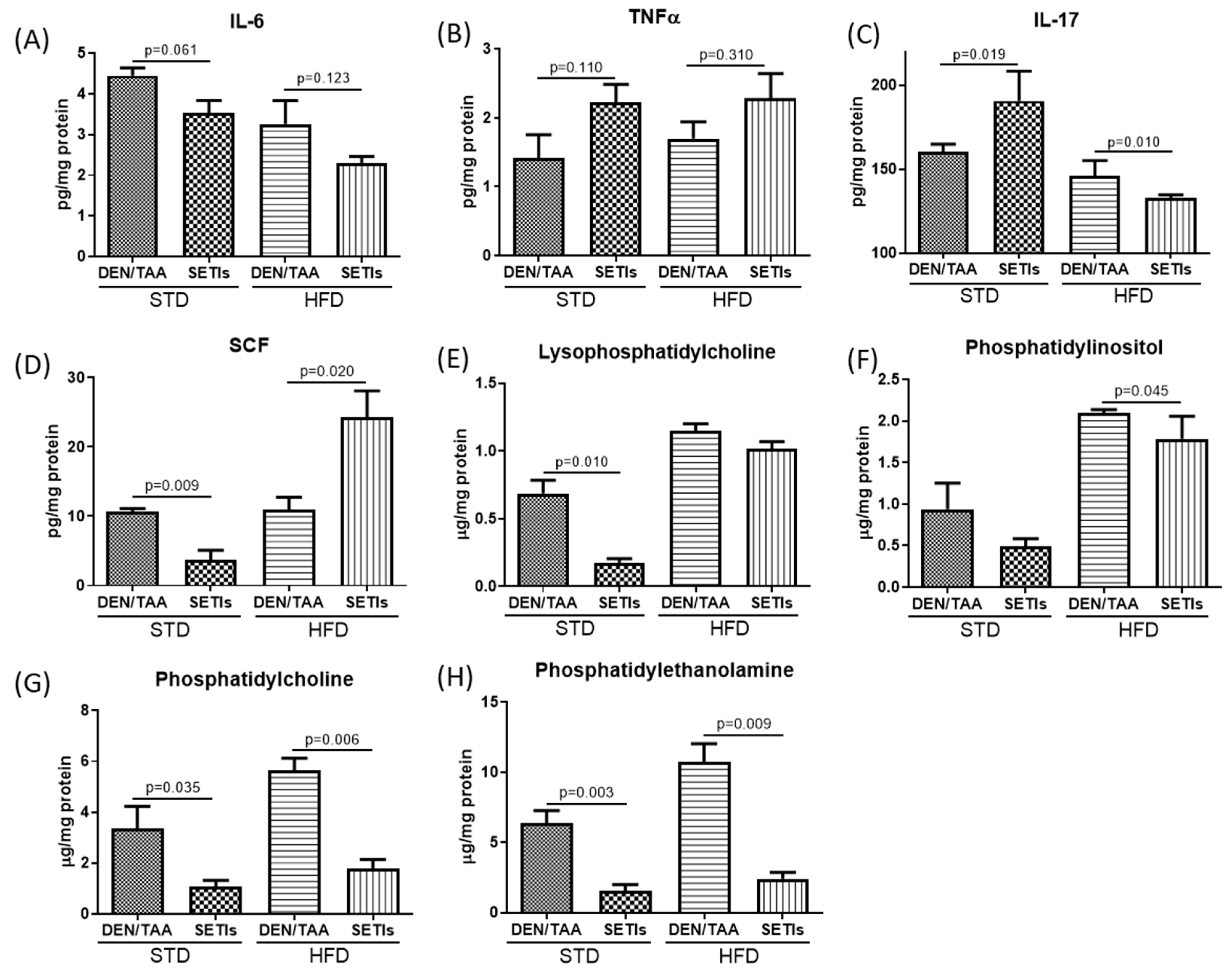
3.3. Modulation of Inflammatory Mediators and Cellular Pattern Recognition Agonists
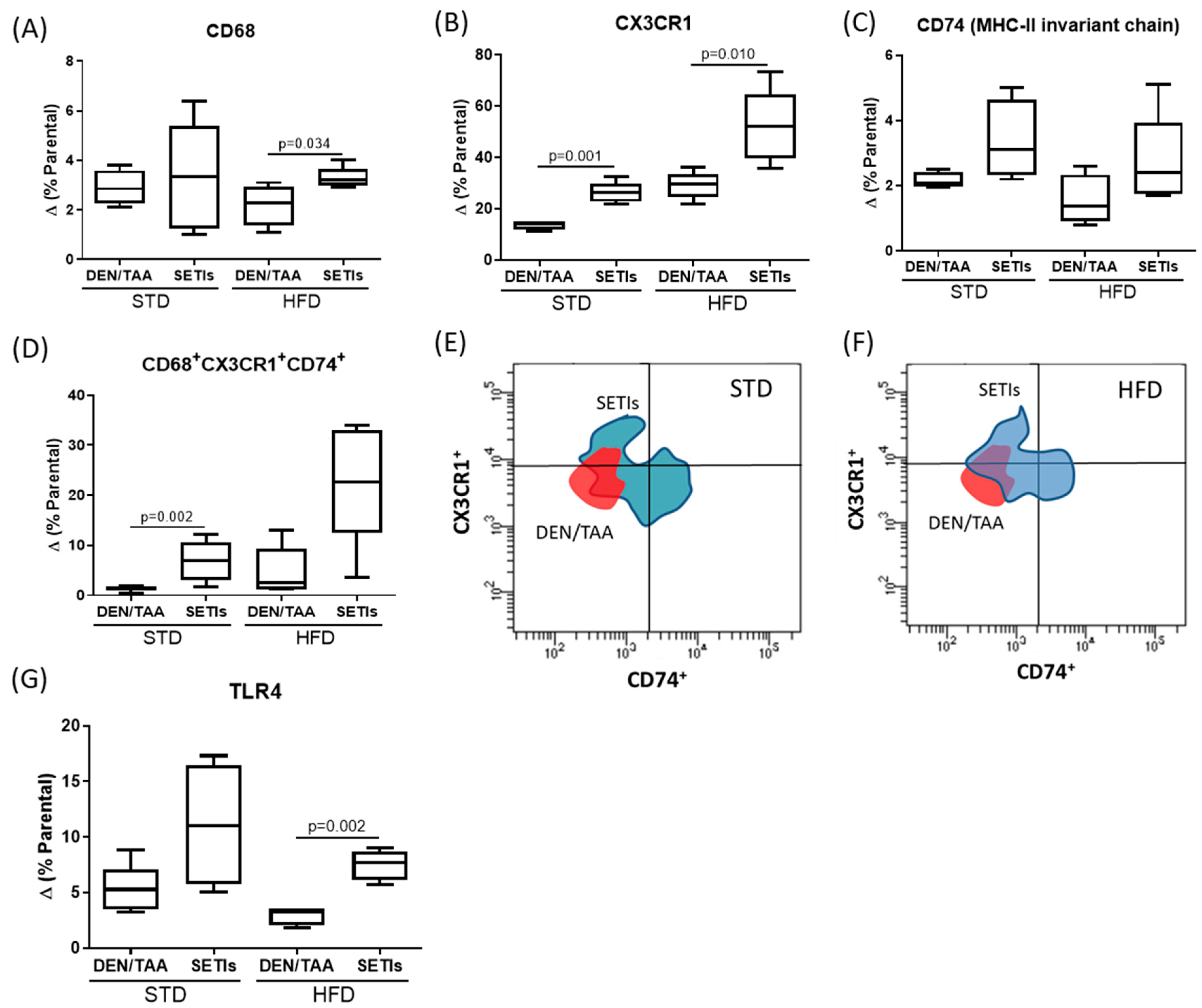
3.4. Promotion of Infiltrated Macrophages with Antitumoral Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.; He, Y.; Luo, N.; Patel, S.J.; Han, Y.; Gao, R.; Modak, M.; Carotta, S.; Haslinger, C.; Kind, D.; et al. Landscape and Dynamics of Single Immune Cells in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell 2019, 179, 829–845.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association For The Study Of The Liver. EASL–EORTC Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 908–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dapito, D.H.; Mencin, A.; Gwak, G.-Y.; Pradere, J.-P.; Jang, M.-K.; Mederacke, I.; Caviglia, J.M.; Khiabanian, H.; Adeyemi, A.; Bataller, R.; et al. Promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma by the intestinal microbiota and TLR4. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zucman-Rossi, J.; Villanueva, A.; Nault, J.-C.; Llovet, J.M. Genetic Landscape and Biomarkers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1226–1239.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llovet, J.M.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Pikarsky, E.; Sangro, B.; Schwartz, M.; Sherman, M.; Gores, G. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satriano, L.; Lewinska, M.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Banales, J.M.; Andersen, J.B. Metabolic rearrangements in primary liver cancers: Cause and consequences. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 748–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laparra, J.M.; Fotschki, B.; Haros, C. Immunonutritional consequences of different serine-type protease inhibitors in a C57BL/6 hepatocarcinoma model. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laparra, J.M.; Brown, D.; Saiz, B. Chenopodium Quinoa and Salvia Hispanica Provide Immunonutritional Agonists to Ameliorate Hepatocarcinoma Severity under a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laparra, J.M.; Haros, C.M. Plant seed protease inhibitors differentially affect innate immunity in a tumor microenvironment to control hepatocarcinoma. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4210–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srdić, M.; Ovčina, I.; Fotschki, B.; Haros, C.M.; Llopis, J.M.L. C. quinoa and S. hispanica L. Seeds Provide Immunonutritional Agonists to Selectively Polarize Macrophages. Cells 2020, 9, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butler, M.J.; Cole, R.M.; Deems, N.P.; Belury, M.A.; Barrientos, R.M. Fatty food, fatty acids, and microglial priming in the adult and aged hippocampus and amygdala. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yona, S.; Kim, K.-W.; Wolf, Y.; Mildner, A.; Varol, D.; Breker, M.; Strauss-Ayali, D.; Viukov, S.; Guilliams, M.; Misharin, A.; et al. Fate mapping reveals origins and dynamics of monocytes and tissue macrophages under homeostasis. Immunity 2013, 38, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlmark, K.R.; Zimmermann, H.W.; Roderburg, C.; Gassler, N.; Wasmuth, H.E.; Luedde, T.; Trautwein, C.; Tacke, F. The fractalkine receptor CX3CR1 protects against liver fibrosis by controlling differentiation and survival of infiltrating hepatic monocytes. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1769–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Meng, S.; Yan, B.; Yu, J.; Liu, J. Protectin D1 reduces concanavalin A-induced liver injury by inhibiting NF-κB-mediated CX3CL1/CX3CR1 axis and NLR family, pyrin domain containing 3 inflammasome activation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 3627–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, N.; Li, K.; Zhu, X.; Xu, B.; Liu, X.; Lei, M.; Sun, H.-C. CD74+ macrophages are associated with favorable prognosis and immune contexture in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Na, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y. The biological function and significance of CD74 in immune diseases. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 66, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrichs, D.; Knauel, M.; Offermanns, C.; Berres, M.-L.; Nellen, A.; Leng, L.; Schmitz, P.; Bucala, R.; Trautwein, C.; Weber, C.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) exerts antifibrotic effects in experimental liver fibrosis via CD74. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17444–17449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heinrichs, D.; Berres, M.-L.; Coeuru, M.; Knauel, M.; Nellen, A.; Fischer, P.; Philippeit, C.; Bucala, R.; Trautwein, C.; Wasmuth, H.E.; et al. Protective role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 5136–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamandl, D.; Bahrami, M.; Wessner, B.; Weigel, G.; Ploder, M.; Fürst, W.; Roth, E.; Boltz-Nitulescu, G.; Spittler, A. Modulation of Toll-Like Receptor 4 Expression on Human Monocytes by Tumor Necrosis Factor and Interleukin-6: Tumor Necrosis Factor Evokes Lipopolysaccharide Hyporesponsiveness, Whereas Interleukin-6 Enhances Lipopolysaccharide Activity. Shock 2003, 20, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.-X.; Ling, Y.; Wang, H.-Y. Role of nonresolving inflammation in hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raggi, F.; Pelassa, S.; Pierobon, D.; Penco, F.; Gattorno, M.; Novelli, F.; Eva, A.; Varesio, L.; Giovarelli, M.; Bosco, M.C. Regulation of Human Macrophage M1–M2 Polarization Balance by Hypoxia and the Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells-1. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheedy, F.J.; Grebe, A.; Rayner, K.J.; Kalantari, P.; Ramkhelawon, B.; Carpenter, S.B.; Becker, C.E.; Ediriweera, H.N.; Mullick, A.E.; Golenbock, D.T.; et al. CD36 coordinates NLRP3 inflammasome activation by facilitating intracellular nucleation of soluble ligands into particulate ligands in sterile inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll, R.G.; Zasłona, Z.; Galván-Peña, S.; Koppe, E.L.; Sévin, D.C.; Angiari, S.; Triantafilou, M.; Triantafilou, K.; Modis, L.K.; O’Neill, L.A. An unexpected link between fatty acid synthase and cholesterol synthesis in proinflammatory macrophage activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 5509–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, C.; Chi, Z.; Jiang, D.; Xu, T.; Yu, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Guo, X.; et al. Cholesterol Homeostatic Regulator SCAP-SREBP2 Integrates NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Cholesterol Biosynthetic Signaling in Macrophages. Immunity 2018, 49, 842–856.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ershaid, N.; Sharon, Y.; Doron, H.; Raz, Y.; Shani, O.; Cohen, N.; Monteran, L.; Leider-Trejo, L.; Ben-Shmuel, A.; Yassin, M.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome in fibroblasts links tissue damage with inflammation in breast cancer progression and metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pennathur, S.; Pasichnyk, K.; Bahrami, N.M.; Zeng, L.; Febbraio, M.; Yamaguchi, I.; Okamura, D.M. The macrophage phagocytic receptor CD36 promotes fibrogenic pathways on removal of apoptotic cells during chronic kidney injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 2232–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Prados, J.-C.; Través, P.G.; Cuenca, J.; Rico, D.; Aragonés, J.; Martín-Sanz, P.; Cascante, M.; Boscá, L. Substrate fate in activated macrophages: A comparison between innate, classic, and alternative activation. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porta, C.; De Amici, M.; Quaglini, S.; Paglino, C.; Tagliani, F.; Boncimino, A.; Moratti, R.; Corazza, G.R. Circulating interleukin-6 as a tumor marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2008, 19, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Q.; Li, P.-C.; Pan, N.; Gao, R.; Wen, Z.-F.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Huang, F.; Wu, F.-Y.; Ou, X.-L.; Zhang, J.-P.; et al. Tumor-released autophagosomes induces CD4+T cell-mediated immunosuppression via a TLR2–IL-6 cascade. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malaguarnera, M.; Di Fazio, I.; Laurino, A.; Romeo, M.A.; Giugno, I.; Trovato, B.A. Role of interleukin 6 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Bull. Cancer 1996, 83, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Yu, G.-Y.; He, G.; Ali, S.R.; Holzer, R.G.; Osterreicher, C.H.; Takahashi, H.; Karin, M. Dietary and genetic obesity promote liver inflammation and tumorigenesis by enhancing IL-6 and TNF expression. Cell 2010, 140, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, Y.; Sun, K.; Liu, W.; Sheng, D.; Zhao, S.; Gao, L.; Wei, L. Tumor necrosis factor-α promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis through the activation of hepatic progenitor cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 434, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Su, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. Activation of the TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway contributes to the development of human hepatocellular carcinoma via upregulation of IL-23 and IL-17A. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9647–9654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kader, M.; Alaoui-El-Azher, M.; Kode, B.; McArthur, M.; Shinde, A.; Wells, A.; Ismail, N. MyD88 suppresses IL-10 and IL-17 production in response to obligate intracellular Ehrlichia infection. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 206. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, F.; Ruddy, M.J.; Plamondon, P.; Gaffen, S.L. Cytokines link osteoblasts and inflammation: Microarray analysis of interleukin-17- and TNF-α-induced genes in bone cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 77, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.-P.; Yan, J.; Xu, J.; Pang, X.-H.; Chen, M.-S.; Li, L.; Wu, C.; Li, S.-P.; Zheng, L. Increased intratumoral IL-17-producing cells correlate with poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Fan, K.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, S.; Kong, C.; Zheng, L.; Wu, F.; Weng, Q.; et al. The ferroptosis and iron-metabolism signature robustly predicts clinical diagnosis, prognosis and immune microenvironment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-de-Gómez, L.; Astudillo, A.M.; Meana, C.; Rubio, J.M.; Guijas, C.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. A Phosphatidylinositol Species Acutely Generated by Activated Macrophages Regulates Innate Immune Responses. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 5169–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, X.; Qiu, C.; Zhao, L. Lysophosphatidylcholine perpetuates macrophage polarization toward classically activated phenotype in inflammation. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 289, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, C.M.V.; Bincoletto, C.; Barros, C.C.; Ferreira, A.T.; Paredes-Gamero, E.J. PLCγ2 and PKC Are Important to Myeloid Lineage Commitment Triggered by M-SCF and G-CSF. J. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 115, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.T.; Elfert, A.; Helal, M.; Salama, I.; El-Said, H.; Fiehn, O. Remodeling Lipids in the Transition from Chronic Liver Disease to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Ma, K.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, W. Choline Plasmalogens Isolated from Swine Liver Inhibit Hepatoma Cell Proliferation Associated with Caveolin-1/Akt Signaling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, M.-H.; Yi, H.-S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.-H.; Kim, J.H.; Yeon, J.E.; Byun, K.S.; Byun, J.-S.; Jeong, W.-I. CX3CR1 differentiates F4/80low monocytes into pro-inflammatory F4/80high macrophages in the liver. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.H.; Kim, I.; Lee, H.; Joo, H.; Lim, J.U.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Moon, H. Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces liver fibrosis in mice with diet-induced obesity via TLR4/MyD88/MAPK/NF-kB signaling pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 490, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bouzas Muñoz, A.; Giménez-Bastida, J.A.; Tejedor, A.G.; Haros, C.M.; Gómez de Cedrón, M.; Ramírez de Molina, A.; Laparra Llopis, J.M. Intestinal Intervention Strategy Targeting Myeloid Cells to Improve Hepatic Immunity during Hepatocarcinoma Development. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111633
Bouzas Muñoz A, Giménez-Bastida JA, Tejedor AG, Haros CM, Gómez de Cedrón M, Ramírez de Molina A, Laparra Llopis JM. Intestinal Intervention Strategy Targeting Myeloid Cells to Improve Hepatic Immunity during Hepatocarcinoma Development. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(11):1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111633
Chicago/Turabian StyleBouzas Muñoz, Adrián, Juan Antonio Giménez-Bastida, Aurora García Tejedor, Claudia Monika Haros, Marta Gómez de Cedrón, Ana Ramírez de Molina, and José Moisés Laparra Llopis. 2021. "Intestinal Intervention Strategy Targeting Myeloid Cells to Improve Hepatic Immunity during Hepatocarcinoma Development" Biomedicines 9, no. 11: 1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111633
APA StyleBouzas Muñoz, A., Giménez-Bastida, J. A., Tejedor, A. G., Haros, C. M., Gómez de Cedrón, M., Ramírez de Molina, A., & Laparra Llopis, J. M. (2021). Intestinal Intervention Strategy Targeting Myeloid Cells to Improve Hepatic Immunity during Hepatocarcinoma Development. Biomedicines, 9(11), 1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111633







